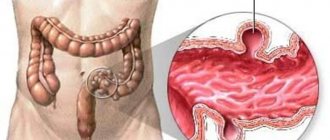
Reflux gastritis - what is this diagnosis, what types is it divided into, can it be cured forever, and how to do it? We will answer all these questions in our article. Let's start with the concept of reflux gastritis. This is a chronic inflammatory process in the walls of the distal stomach. It begins due to partial ingress of processed food into the stomach from the duodenum along with bile, causing the gastric mucosa to become irritated and inflamed. This condition soon becomes chronic.
In general, one of the most common types of gastritis is chronic reflux gastritis. As a rule, the disease proceeds painlessly for quite a long time, which is why a person consults a doctor with an already advanced form. It is not very treatable, so those diagnosed with it are advised to constantly follow a special diet. However, one thing that can be said in favor of this diet is that it is not too strict and fits into the framework of a healthy lifestyle.
Types of reflux gastritis
There are several main types of reflux gastritis, which radically differ in their cause and localization in the gastrointestinal tract. Pathology can occur differently in people, so a special typology and subtypes of the disease are distinguished:
- Superficial reflux gastritis . It differs from other types of the disease in that only the upper layer of intestinal epithelial cells is affected. Bile can flow from the duodenum directly into the stomach, causing destruction to the intestinal walls. If this developing process is not stopped in time, the digestion process can be seriously disrupted, and in some cases, a cancerous tumor may occur .
- Erosive reflux gastritis . A characteristic sign of erosive reflux gastritis is that it is accompanied by the appearance of ulcers and small erosions on the walls of the stomach. The patient experiences pronounced pain and unpleasant syndromes that can occur at different times of the day. To treat this type of gastritis, you will need a long course of complex procedures. If you do not choose the right direction of treatment, erosive reflux gastritis can later develop into a gastric ulcer.
- Atrophic reflux gastritis . The most dangerous and irreversible process occurring in the gastric mucosa. Rapid atrophy of the mucous membrane occurs, the restoration of which is almost impossible, or occurs very slowly. In some patients, atrophic reflux gastritis is a precancerous condition and often leads to the subsequent development of a malignant tumor.
Characteristics of reflux lesions of the gastrointestinal tract
In official medicine, the disease is called “bile reflux gastritis type C.” So, what is reflux inflammation of the digestive organ - and can reflux be cured?
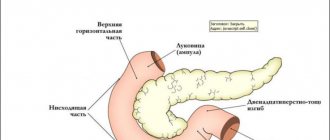
At the junction of the stomach and intestines, in the bile ducts there are special muscles in the form of a valve - sphincters that open or close the passage. When crushed food particles move from the digestive organ into the intestine, the valve opens and the contents from the epigastrium enter the duodenal intestine, then the muscle contracts, closing the cavity, and the digestion process continues in the intestine. Normally, the sphincters work synchronously to ensure proper digestive activity. When pyloric motility is impaired, undigested food remains, along with bile and enzymes, return to the antrum.
The aggressive intestinal mixture begins to corrode the walls of the organ mucosa.
In turn, hydrochloric acid from the gastric sections seeps into the duodenum with an alkaline environment, causing irritation and inflammation of the intestinal walls. The release of intestinal contents into the stomach and the reverse process is called reflux, and the resulting pathology is chronic reflux gastritis. This is due to the fact that, despite intensive treatment, the disease remains in the body forever, and the diet accompanying reflux gastritis must be followed by the patient for the rest of his life.
Forms of the disease
The forms of the disease differ from each other only in the location of the process, as well as its complexity for the patient:
- In most cases, when doctors diagnose patients with “focal gastritis,” this indicates the localization of the developing pathological process. The focus of the disease can absorb the entire surface of the mucous membrane, or can be observed only in its individual areas. If we are talking about local damage to the gastric mucosa, then this is “focal” gastritis . In its symptoms and characteristic manifestations it is very similar to reflux gastritis.
- The diffuse form of gastritis manifests itself in gradual inflammation of the entire surface of the mucous membrane.
- The acute form is characterized by rapid damage and spread throughout the mucous membrane and pronounced pain syndromes. It often occurs in people due to chemical poisoning. This form of the disease can also be caused by pathogenic bacteria that enter the stomach with low-quality and expired products.
- The chronic form of gastritis leads to the fact that irreversible changes occur on the human mucosa for a long time. Symptoms may not be pronounced.
Prevention
To prevent the development of biliary reflux gastritis with esophagitis, you should follow simple rules:
- Eat right, avoiding unhealthy foods and drinks.
- Diagnose and treat other pathological processes in a timely manner. Do not delay the preventive treatment of chronic pathologies.
- Regularly undergo preventive endoscopic examinations. With their help, relapses and other diseases are detected in the early stages, which allows them to be stopped in a timely manner.
- Increase the protective properties of the gastrointestinal mucosa by consuming complete vitamin complexes, fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Avoid stress and prevent depression.
- Avoid self-treatment, especially with non-steroidal anti-infective drugs, which reduce the secretion of protective mucus in the stomach, making its lining susceptible to the effects of acidic contents.
Causes
Until recently, the vast majority of doctors were confident that the cause of reflux gastritis and its typical forms was poor human nutrition.
However, thanks to the achievements of scientific medicine, it was possible to identify additional factors that may affect the development and further spread of the disease. Among them:
- chronic duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum);
- long-term use of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- gastric resection;
- pathological disturbances in the work of the gatekeeper;
- increased pressure in the duodenum.
Remember that the listed “provocateurs” of reflux gastritis are not the main ones. For many people, the disease can occur due to other reasons.
Symptoms of pathology and complications
Reflux gastritis, the symptoms of which are considered ambiguous, occurs with vague signs, so in most cases the patient is not aware of the presence of the disease. At this time, the acidity changes, causing the transformation of cells resembling those located in the intestines. There is a huge risk of complications.
The treatment is determined by the doctor, so if you suspect a disease, you must go for an examination and consultation. Main symptoms of the disease:
- lack of appetite;
- weight loss;
- belching;
- ulcers and seizures appear in the corner of the mouth;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- aching pain is concentrated in the epigastric region;
- the presence of an unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- heartburn;
- alternating diarrhea and constipation.
One of the complications of reflux gastritis is esophagitis. Esophagitis is an inflammatory lesion of the esophagus, namely its mucous membrane. This disease manifests itself as follows:
- increased salivation;
- heartburn;
- burning pain behind the sternum;
- swallowing function is impaired.
Esophagitis can provoke the following pathological conditions:
- stenosis;
- Barrett's disease;
- perforation of the esophagus;
- peptic ulcer.
To diagnose esophagitis, the following tests must be performed:
- X-ray of the esophagus;
- endoscopic biopsy;
- esophagoscopy.
Treatment is prescribed based on the etiology of esophagitis. It is carried out through diet, physiotherapy and medications. In case of urgent need, surgery may be necessary.
In some cases, a complication such as gastritis duodenitis may develop. When the duodenal mucosa becomes inflamed, the disease duodenitis occurs. If inflammation also affects the stomach, gastroduodenitis develops.
Symptoms of the disease:
- constant pain in the epigastrium is aching in nature;
- most often, hunger pain and night pain occur;
- spread of pain to the shoulder blade and left arm, back;
- irritability;
- lack of sleep;
- inflammation;
- gastrointestinal motility is impaired;
- belching;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- aversion to food;
- weight loss;
- constipation and diarrhea.
A number of examinations will help confirm the presence of reflux gastritis and possible complications. Most often, they do the following:
- gastric biopsy;
- FEGDS;
- Ultrasound;
- daily monitoring of the patient's stomach pH.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
How to determine reflux gastritis
In most patients, reflux gastritis manifests itself with pronounced symptoms. We strongly recommend that you carefully familiarize yourself with all the symptoms, the presence of which will allow you to quickly detect a developing disease and consult a doctor in time for treatment.
Among the main symptoms:
- stomach pain that increases after eating;
- heartburn, vomiting and diarrhea due to insufficient gastric cardia;
- vomiting can be with bile, and in complex forms – with blood;
- constipation;
- weight loss and appetite disorder;
- after eating, you feel heaviness and bloating in the abdomen;
- belching is accompanied by an acidic, unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- weakness and general malaise;
- dry mouth;
- periodically after eating, the temperature may rise slightly.
Agree that there are not so few symptoms, but others may be added to those listed above. If you begin to notice these symptoms in yourself, we advise you to immediately go to the doctor so that gastritis reflux does not become chronic .
Biliary reflux gastritis
In the lumen of the stomach, the level of acidity fluctuates in different parts of the stomach:
- at the bottom, where the food lies, there is more acid, which is necessary to break down the food bolus;
- in the antral zone, in front of the outlet into the intestine with a neutral environment, below.
If the functioning of the sphincter valves is not impaired, as is the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract, a stable digestive process is ensured with consistent breakdown of food.
Due to the influence of negative factors, the process is disrupted, and the acidic contents begin to pour into the intestines. The aggressive influence of a hostile environment irritates its walls, which begin to become inflamed in response. To get rid of the irritant, protective mechanisms are triggered, resulting in the return of intestinal contents into the lumen of the stomach. This phenomenon is called reflux.
With cyclical repetition of reverse food boluses, a severe inflammatory process develops - gastritis. Therefore, inflammation caused by reverse reflux is also called reflux gastritis, which can be duodenal or biliary.
Biliary reflux gastritis is provoked by:
- dysfunction of the biliary system;
- chronic stagnation of intestinal contents saturated with bile;
- motor dysfunction (dyskinesia);
- disordered functioning of both sphincters;
- weakness of the tone of the orbicularis muscle in the papilla of Vater of the duodenum;
- pathological anomalies of the pylorus, which affects its closure;
- inflammatory processes in the upper intestinal sections;
- the presence of systemic and endocrine pathologies;
- peptic ulcers.
When any of the disturbances occur with a failure in the sequence, the pressure in the biliary tract and intestines increases, and the compression of the stomach and channels in the pancreas changes reflexively. Against this background, the contents of the duodenum with lysolecithin, intestinal, pancreatic and bile enzymes penetrate the stomach, burning its walls and causing gastritis. At the site of the injuries received, erosive foci often form, which are characteristic of erosive reflux gastritis.
https://youtu.be/2ygBuP01akQ
Effective treatment of reflux gastritis
Treatment prescribed by a doctor will bring a positive effect and restore the dynamics of recovery only if it includes a complex of drugs. A mandatory requirement for all patients without exception with this form of the disease is an active lifestyle and taking medications .
Additional factors that positively influence the recovery of patients are:
- proper nutrition;
- frequent exposure to fresh air;
- active sports;
- good and sound sleep;
- minimum stressful situations;
- constantly comply with the doctor’s recommendations;
- undergoing routine examinations by a doctor.
Next, we’ll look at how to treat reflux gastritis with maximum effect.
Drug treatment of reflux gastritis
Drug therapy offered to patients has a positive effect in eliminating the main symptoms and causes that lead to the further progression of the disease to the chronic stage.
What is included in the complex of drug treatment?
- Mandatory use of medications that reduce the amount of gastric juice produced (ranitidine and omeprazole).
- Taking medications to protect the integrity of the gastric mucosa. Medicines include Denol and Venter.
- Prescribing antibacterial medications to treat an infection in the stomach (Amoxiclav).
- Taking Itomed and Motilium to improve the peristaltic state of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Taking enzyme-based medications (Festal, Mezim and Creon).
- For persistent diarrhea and constipation, patients are prescribed prebiotics.
- Vitamin complexes Vitrum and Alphabet also become an integral part of treatment.
Diagnosis of pathology
Diagnosis of reflux lesions of the gastrointestinal tract is carried out in several stages. Laboratory and instrumental procedures are prescribed after examining the patient, compiling a list of complaints and collecting an anamnesis. Additionally, a specialist may prescribe daily monitoring of gastric acidity. This procedure is in most cases carried out in a hospital setting. A gastroenterologist diagnoses the disease. If complications are suspected, the patient is scheduled for additional consultation with specialized doctors.
Diagnostic measures:
general blood and urine analysis;
- analysis of stool for occult blood;
- biochemical analysis of urine and blood;
- gastroscopy;
- antroduodenal manometry;
- Ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract;
- radiography of the gastrointestinal tract;
- histological examination;
- biopsy;
- electrogastrography;
- FGDS.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapeutic procedures are actively used as one of the complex methods of treating reflux gastritis. As a rule, procedures are carried out during remission of the disease or only after the complete disappearance of ulcers that appear on the gastric mucosa.
The ideal means of physiotherapy are electrophoresis and phonophoresis. The appointment of additional procedures is controlled only by the attending physician based on the general condition of the patient and the stage of the disease.
The duration of physiotherapeutic treatment is approximately 12 days. If necessary, the course of treatment is extended until positive dynamics of treatment are obtained.
How to treat?
To get rid of reflux gastritis, the patient will need to make a considerable amount of effort. Treatment consists of taking medications, following a special diet, and physiotherapeutic procedures. To enhance the therapeutic result, you can resort to traditional medicine recipes, if there are no contraindications.
Drug treatment
The basis of treatment for reflux gastritis is drug therapy. You will need to take several medications at once to eliminate symptoms and improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
What medications are prescribed:
- Enzymes (promote better digestion of food).
- Ursodeoxycholic acid (helps neutralize reflux).
- Antacids (help protect the gastric mucosa and relieve pain).
- Antispasmodics (relieve stomach pain).
- Antiemetics.
Other medications are prescribed in each individual clinical case. Sometimes taking vitamins and minerals is indicated, and in some situations antibiotics are used to eliminate bacteria from the stomach. The attending physician will be able to select the most appropriate medicinal complex after a survey, examination and other diagnostic measures.
Diet
An equally important step in treatment is following a diet for reflux gastritis. It helps to almost completely remove the load from the stomach, thereby reducing the negative impact on the organ.
Food should be light, not hot or cold, and enter the body in small portions to prevent stretching of the digestive tract. The patient will need to adhere to the list of permitted products, from which it is necessary to prepare as varied a variety of dishes as possible.
You will need to give up alcoholic beverages and smoking, fatty meats and fish, rough vegetables, and caffeine-based strong drinks.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are carried out after the main treatment, when the main symptoms of reflux gastritis have been eliminated. Electrophoresis or phonophoresis is often used for these purposes, which help improve digestive processes and help restore the body after illness.
This treatment lasts at least 2 weeks. Also, for prevention, it is recommended to take table mineral water, which is medicinal and is intended to eliminate stomach diseases.
Folk remedies in the treatment of reflux gastritis
Treatment with folk remedies allows you to achieve amazing results. Herbal infusions that are taken orally are excellent. Remember that herbal medicine at home will not completely get rid of the disease, but it will reduce the likelihood of it developing into a complex chronic form .
What folk remedies and methods should be used for treatment?
- During a relapse (acute form of reflux gastritis), dandelion syrup is good. The flowers are collected in a glass bowl and poured with boiling water, stirring with sugar. You can take 1 spoon per day. The course of complete treatment should last at least 1 week.
- The fruits of anise, fireweed and calendula are well suited for preparing gastrointestinal decoctions. They are prepared in a steam bath and taken half a glass once a day.
- Celery roots produce juice, which can be consumed 1 teaspoon before meals.
- An infusion of St. John's wort is well suited to reduce pain. Prepared in a steam bath.
Question answer
Is it possible to get rid of reflux gastritis forever?
This is possible if the origin of the disease is not related to gross morphological disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, operations, while the disease itself should not be diagnosed in an acute form, and so that the inflammatory process does not affect the mucous membrane deeper than the superficial layer, only the superficial layer of the mucous membrane.
List of references: https://www.obozrevatel.com/health/bolezni/biliarnyij-reflyuks-gastrit.htm www.noav.ru/?p=1796 https://www.gastroscan.ru/patient/disease/01/ 06/ https://gastronika.ru/school_of_patients/reflyuks_gastrit_lechenie_i_simptomy/ https://www.fesmu.ru/elib/Article.aspx?id=337302 https://medportal.ru/faq/Gastrit/kak_lechit_refluks_gastrit/ https:/ /www.lvrach.ru/2012/02/15435349/ Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Healthy eating and diet
According to GERD, during reflux gastritis a person must have a well-developed and balanced diet and follow a diet. This allows you to normalize intestinal function and motility.
Be sure to exclude from your diet: spicy, salty, fried foods. Sauces, semi-finished products and fermented milk products are also excluded, but on the recommendation of a doctor they can be consumed infrequently.
Make meals small and frequent, and food should only be taken warm. This will avoid possible injury to the already inflamed gastric mucosa.
Medicines to treat illness
The mucous membrane of the stomach suffers from acid, so it is necessary to prescribe remedies to protect it. Treatment should be based on proton pump inhibitors. Your doctor will tell you how to treat reflux gastritis using such drugs. He will prescribe medications according to the most appropriate regimen.
To reduce acid formation, you can drink products containing rabeprazole, pantoprazole and omeprazole. For the drug to work, it must be taken according to the correct regimen. Improvement usually begins by the end of the first week of use.
Treatment of a disease such as gastritis, duodenitis, reflux usually lasts from several weeks to 2 months. With long-term use, various side effects may occur, so if discomfort occurs, you should consult a specialist.
An important role should be given to stimulants of the motor function of the digestive tract. Domperidone-based products help stop the stomach and improve digestion. They eliminate heaviness and nausea. Superficial antral reflux gastritis necessarily requires the use of such a medicine.
To ensure that bile circulates normally and does not stagnate, you need to drink products containing ursodeoxycholic acid. They will dilute stagnant bile and improve the functioning of the hepatobiliary system. Drugs of this group are usually classified as: Ursohol, Ukrliv, Urosan. They are natural and safe.
You should definitely drink sorbents when you are sick. They will remove toxins and improve your well-being. The best representatives of this group are the following drugs: Atoxil, Enterosgel and other medications.
Primer is a modern remedy that improves the peristaltic function of the stomach. Treatment of reactive reflux gastritis without this drug is impossible. Thanks to the medication, food moves well through the gastrointestinal tract in the desired path and there is no stagnation, rotting, or fermentation. It tones the tone of the sphincters, the functioning of which is impaired, so the treatment of such an ailment should be accompanied by taking a similar medication.
The primer is well absorbed and does not have a negative effect on the body, so it can be taken for a long time. Drug treatment for reflux gastritis should last at least several weeks. The doctor will tell you how to treat the biliary type of disease, since before prescribing drugs you need to assess the condition of the bile ducts.