Fibrogastroscopy (hereinafter referred to as FGS) is today one of the most successful and widespread methods of endoscopic examination, which allows not only to assess the condition and health of the patient’s stomach, but also his duodenum. The essence of the procedure is that a flexible tube (endoscope) is inserted into a person through the oral cavity, equipped with a light conductor and a camera that allows you to visually assess the condition of the patient’s organs, as well as remove a fragment of the patient’s gastric mucosa for further examination for various pathologies.
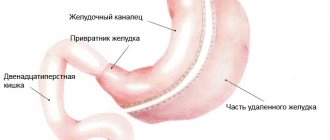
Fibrogastroscopy of the stomach
Unfortunately, not many patients fully understand the full benefits and mechanism of this study, as a result of which one can often hear a refusal to carry out the procedure, when fibrogastroscopy is an indispensable assistant in detecting a wide range of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
The study also allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis in the shortest possible time, namely:
- various types of gastritis and ulcers;
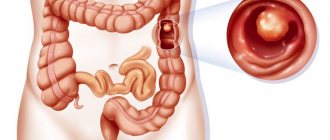
- erosions that occur in the mucous walls of the stomach;
Erosion and gastric ulcer
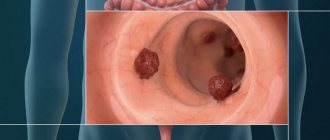
- polyps, tumors, hernias;
- any changes that occur both with the mucous walls of the stomach and with changes in its volume;
- other pathological processes that can lead to serious complications (hidden bleeding, wall perforation).
Perforation of the stomach walls
FGS capabilities
Modern high-tech equipment in endoscopy allows you to perform a visual examination of hollow organs. Fibrogastroscopy is an ideal way to see the following anatomical structures from the inside:
- pharynx;
- esophagus;
- all parts of the stomach;
- the initial segment of the duodenum.
The full name of the procedure (fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy) reflects the capabilities of the method, but it is easier and more convenient to use the abbreviation FGS. During a diagnostic study, the doctor may take suspicious tissue for histological examination, which is especially important if a malignant process is suspected.
Historical excursion
A modern gastroscope is a device designed to examine the mucous membranes of the digestive organs. The device is made in the form of a flexible and long tube, the end of which is equipped with a video camera and lighting. During the diagnostic process, a tube is inserted into the organ through the oral cavity. In relatively recent times, a biopsy gastroscope has been developed, which allows for multiple targeted biopsies. This model is distinguished by high quality, information content, and also a lower degree of pain.
Indications for use
The endoscopic technique is used in the following cases:
- against the background of difficulty swallowing food;
- with dyspepsia that is not amenable to conventional treatment methods (nausea, belching, vomiting, heartburn, lack of appetite);
- with unexplained weight loss;
- against the background of chronic anemia of unknown origin with no effect of therapy;
- when blood is detected in the vomit.
If there is a suspicion of a disease in the digestive system, it is necessary to perform an unpleasant but extremely necessary procedure: FGS will help to identify in time the initial signs of a life-threatening pathology.
Factors that increase the duration of gastroscopy
A routine examination, during which only an examination of the internal state of organs is carried out, is always short-lived, but FGS is carried out not only for diagnostic purposes.
The procedure can be done in the following cases:
- Removing a foreign object from the esophagus or stomach. The duration of FGDS is difficult to calculate: it will depend on the structure of the foreign body (smooth or too hard objects are more difficult to remove) and on its location. In some cases, the object that has gotten inside is first crushed, and then gradually removed from the digestive organs.
- Removal of polyps. This procedure is done after a detailed clarification of the location of the polyposis, and the doctor can almost always calculate how long the therapeutic gastroscopy will last.
- Irrigation of certain areas of the gastric wall with medicine. This type of FGS is performed quickly and takes 3-5 minutes more than diagnostic gastroscopy.
- Elimination of certain types of bleeding. Minor erosive bleeding or ulcer bleeding is not always a reason for surgical intervention. In some cases, bleeding can be stopped using more gentle methods during gastroscopy.
But even in therapeutic cases, FGDS lasts no more than half an hour.
The duration of gastroscopy is not very long; if the patient behaves correctly during the examination, it causes almost no discomfort. Then only a slight numbness in the throat after the anesthetic reminds of the examination completed. Probably, this information will help many people to have a positive attitude towards the research necessary for diagnosis and treatment, because every person can endure 10-20 minutes of unpleasant sensations.
Fibrogastroscopy – when not to do it
The main contraindications for the use of FGS in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases include:
- worsening hypertension with a high risk of heart attack or stroke;
- arrhythmia without treatment;
- congenital anomalies and acquired heart defects requiring surgical treatment;
- aneurysm of large arterial trunks;
- acute and purulent inflammation in the mouth, pharynx and esophagus;
- the presence of dysphagia (complete inability to swallow of anatomical or mental origin).
In most cases, fibrogastroscopy can be performed on adults and children without any particular difficulties - the main thing is to listen to the doctor and not try to resist: all problems during the procedure are associated with irritation of the pharyngeal receptors, which provoke the gag reflex.
Elimination of consequences
Although there are possible side effects, some of them can be managed:
Painful sensations in the organ occur due to air, which is pumped into the stomach in order to smooth out the mucous membrane. In most cases, pain and discomfort do not require special treatment, as they go away on their own after a couple of days.
They arise during the process of swallowing and can manifest as a feeling of numbness, which is accompanied by the appearance of hoarseness in the voice. This phenomenon is one of the most common consequences of gastroscopy, which may be a consequence of mechanical damage during the passage of the endoscope. In this case it is necessary:
- exclude panic moods, since there is a high probability of normalization of the condition within a couple of days;
- in order to alleviate the condition, use absorbable lozenges;
- gargle with warm water with the addition of a few drops of iodine and a pinch of soda;
- try to talk less;
- if signs of pain and dryness persist, take a teaspoon of sea buckthorn oil before meals;
- if you are not allergic to honey, consume it before going to bed at night;
- eat soft and warm foods.
Preparation for fibrogastroscopy
To obtain an optimal diagnostic result, the necessary preparatory measures should be strictly followed:
- on the eve of the study, you need to give up hard-to-digest foods (brown bread, meat and fish foods, legumes);
- do not have breakfast in the morning (6-8 hours should pass between the last meal and the study);
- do not smoke at least 1 hour before fibrogastroscopy of the stomach.
It is advisable to calm down: an optimal psychological attitude will help you survive the unpleasant procedure without any problems.
What not to do before undergoing the procedure
Gastroscopy is a rather specific procedure, and in order not to get even more sick after it, you need to take into account a lot of nuances. Most often, doctors introduce the following restrictions into a person’s daily life:
- he should not smoke at least 3-4 hours before the procedure;
- It is not recommended to drink alcohol the day before gastroscopy, as this can significantly increase the gag reflex;
- You should not eat 8–12 hours before the examination, since food residues in the esophagus and stomach may complicate the examination;
- It is not recommended to drink water 2-3 hours before your doctor’s appointment;
- Tablet medications also do not need to be taken before this procedure.
Doctors recommend strictly following these rules, since otherwise the risk of painful consequences of gastroscopy increases. Strict restrictions on food should be introduced, since a full stomach significantly increases the risk of obtaining uninformative results. Sometimes, due to non-compliance with the above requirements, doctors have to conduct the examination again.
It is also important to maintain the correct position and absolute calm during gastroscopy. If a person is active all the time, the pain from the procedure will be much more serious.
Endoscopy technique
The main stages of examination of the stomach using FGS include:
- Local anesthesia with an aerosol anesthetic (or general anesthesia - according to indications);
- Inserting a mouthpiece into the mouth (to prevent damage to teeth or the device);
- Passing the flexible tip of the fiberscope through the pharynx (the doctor will tell you when to make a swallowing movement);
- Inspection of all parts of the upper part of the digestive tube;
- Carrying out the necessary research.
An ulcerative defect on the gastric mucosa may be the site of a malignant tumor
After completion of gastroscopy, discomfort in the throat and upper abdomen may persist, but all problems will disappear in the coming hours after completion of the study.
What does the procedure look like from the outside?
Probably, having become familiar with the most likely sensations of gastroscopy of the stomach, many want to know how FGDS will occur:
- first, the patient is given a subcutaneous injection of Atropine to reduce hypersalivation and the pharynx is irrigated with an anesthetic solution;
- after the injection and irrigation with anesthetic, the person is placed on the table (on his left side) and allowed to clamp a mouth guard with his teeth, which prevents the reflex closure of the jaws;
- a gastroscopic probe lubricated with gel to improve sliding is inserted through the hole in the mouthguard, placed on the root of the tongue and pushed into the opening of the esophagus;
- After the esophagus is passed, the probe enters the stomach cavity. If necessary, the organ can be filled with air to straighten the folds of the mucous membrane and study the walls in more detail;
- after the stomach, the duodenum is examined in the same way;
- at the end of a detailed examination of all accessible digestive organs, the gastroscope is smoothly removed, the person is asked to remove the mouth guard from the mouth and spit out excess saliva into a special tray.
All data on the examination is displayed on a large monitor in the office, and if necessary, the gastroscopist can take photos and videos of individual moments of the examination for a more detailed study.
On average, a typical examination procedure along with patient preparation takes about 10 minutes, but in some cases, gastroscopy of the stomach can take longer.
Detectable diseases
Fibrogastroscopy is an effective diagnosis of the following main diseases and conditions:
- diseases of the esophagus of inflammatory or tumor origin;
- erosive or atrophic gastroduodenitis;
- peptic ulcer in any part of the stomach or at the junction with the duodenum;
- reflux esophagitis;
- gastroduodenal reflux;
- stomach cancer.
Using a biopsy taken during FGS, it is possible to detect the presence of the bacterial carcinogen Helicobacter pylori and determine the stage of the malignant tumor as accurately as possible. If there are indications for the study, one cannot refuse the diagnostic procedure: untimely detection of a dangerous disease can cause early death from an advanced form of stomach cancer.
Possible complications after FGDS
Despite the fact that complications after gastroscopy are considered a rare occurrence, you need to know about them in order to recognize alarming symptoms in time. Most often, patients are concerned about side effects after using a local anesthetic. These include prolonged numbness, which is accompanied by swelling of the larynx. Signs of this process include difficulty swallowing food. Such negative consequences of gastroscopy disappear after 1-2 hours. If they persist for longer, you should consult a doctor.
Approximately 3% of patients experience complications after FGDS associated with injury to the mucous membranes. In most cases, reactive sore throat develops, which is no different in symptoms from a cold. Local preparations containing an anesthetic and antiseptic will help to cope with it.
The least common complications after gastroscopy are changes in the soft tissues and skin of the face. About 1.5% of those examined who experience severe nausea during FGDS, in the following hours notice that their face is swollen. In isolated cases, it is noted that capillaries in the eyes, nose and cheeks have burst. Such signs are a consequence of excessive physical stress during vomiting. Cool lotions and ice compresses will help restore your appearance to normal after gastroscopy.
Important! The listed complications after FGDS are rarely life-threatening, but they should not be ignored.
Symptoms that require medical observation, evaluation and, possibly, special treatment include such consequences after gastroscopy as bleeding, fever, persistent bowel movements, or the appearance of increasing pain in the stomach and intestines.
Slight bleeding after FGDS is allowed if the procedure was carried out in conjunction with taking a biopsy. Also, the cause of small bloody or bloody discharge can be an injury to the throat and esophagus. If there are complaints of spitting blood when coughing, we are talking about damage to the mucous membranes of the larynx and pharynx. Normally, such symptoms last no more than 24 hours, and are not considered a pathology if the bleeding is insignificant.
The negative consequences of FGDS are excessive bleeding. It can be judged if blood is found in the stool (it turns black and acquires a tarry texture) or vomit. In these cases, you should go to the emergency department and inform the doctor who performed the gastroscopy.
Low-grade (up to 37.9 degrees) temperature after FGDS is considered normal, especially if the duration of its deviation from the norm does not exceed a day. If the temperature rises to febrile levels (more than 38 degrees) and persists for longer than 24 hours, we are talking about a complication. This symptom should be reported to your doctor.
Theoretically, gastroscopy cannot provoke diarrhea. But the wrong way out of short-term fasting, which is necessary for proper preparation, often leads to bowel problems. Taking special medications and adjusting your diet will help eliminate diarrhea. If diarrhea after FGDS is accompanied by acute abdominal pain and fever, there is a possibility of a gastrointestinal infection.
What can replace gastroscopy?
All alternative gastric methods eliminate the most unpleasant action: swallowing the tube. However, not every one of them allows you to obtain similar results, and some are carried out exclusively in paid clinics. What can replace gastroscopy?
Capsule endoscopy
The operating principle of capsule endoscopy is similar to gastroscopy. The difference is that instead of a probe, the patient swallows a small capsule (the size of which is only 10x25 mm), which is equipped with LEDs and a color video camera. The device moves along the esophagus independently. The patient wears a special vest in which a recording device is located.
The capsule is disposable and is removed from the body on its own. During the study, several thousand photographs of internal organs are taken. For a certain time, the doctor examines the images and organs.
Capsule endoscopy is not recommended for intestinal obstruction: in this case, it is difficult for the device to leave the body
Using capsule endoscopy, you can identify the causes of hidden bleeding in the stomach or intestines, identify lesions of the small intestine, and find polyps. The resulting image is magnified 8-10 times, which allows you to examine the gastric mucosa in detail.
The capsule is easy to swallow; there is no need for freezing or anesthesia. Harmful effects on the body are excluded, the device is completely sterile. There are also some contraindications: such a study is usually not performed on children under 10 years of age and pregnant women. You will also have to refuse endoscopy if there is obstruction of the respiratory tract and impaired swallowing function.
Virtual gastroscopy
A computed tomography scan of the intestines and stomach is also performed without invasive intervention. For examination, the patient's stomach must be filled with fluid - these are the areas that are most easily examined. Immediately before the procedure, you must drink a weak solution of contrast liquid or plain water.
The patient lies under a tomograph, the ring of which moves around the part of the body being examined. The examination does not cause discomfort and is absolutely painless. The doctor will interpret the results immediately after the CT scan is completed.
Barium X-ray
Another alternative to gastroscopy of the stomach is x-ray with contrast. Without barium, research is often impossible. The usual survey procedure will not show the intestines: it is filled with air and does not retain X-rays. Contrast is administered orally.
During the procedure, the patient receives significant radiation exposure
The examination is carried out in several positions: oblique, straight, lateral, standing, lying and with the pelvis raised at a slight angle. Using an X-ray machine, the specialist will take several photographs that will show the surface of the stomach and the condition of the esophagus. Afterwards a conclusion is issued.
The scanning lasts no longer than half an hour and does not cause any particularly unpleasant sensations in the patient. Barium contrast fluid can cause dehydration, so it is recommended to drink as much fluid and dairy products as possible after the examination.
Electrogastroenterography
During this test, skin electrodes are attached to the patient's abdomen to pick up electrical signals from the stomach. The data is processed on a computer, and after decoding, the specialist receives information about wave-like movements in the intestines and stomach. The information obtained also reflects the condition of the blood vessels.
Typically, electrogastroenterography plays the role of an auxiliary method to confirm the diagnosis. Frequencies are recorded twice: on an empty stomach and immediately after eating.
The research method is selected individually by a specialist, based on the symptoms or existing disease. One method may not be sufficient, while gastroscopy is in most cases the most effective procedure for making a diagnosis.
Reviews
Alexey, 45 years old, Volgograd. I went through this miracle procedure and identified a number of pros and cons. Capsule endoscopy is painless, I swallowed the “smart pill” and received the diagnosis the next day. The disadvantages are that the procedure is expensive, and preparation, restrictions and diets.
Maria, 29 years old, Samara. I recently heard about tubeless gastroscopy, I underwent an examination, everything was painless, because I had previously undergone a regular gastroscopy, and I always shuddered from these memories. But I think that the procedure is very expensive.
List of references: https://diagnostica.docdoc.ru/articles/gastroskopiya/gastroskopiya-bez-glotaniya-zonda/?pid=18324 https://primamed.msk.ru/index.php/stati/70-gastroskopiya-zheludka -bez-glotaniya-zonda.html https://www.kp.ru/guide/obsledovanie-zheludka.html https://womanadvice.ru/gastroskopiya-zheludka-bez-glotaniya-zonda https://medi-center. ru/statji/gastroskopiya-bez-glotaniya-zonda This material is exclusively subjective in nature and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
About the method
Capsule gastroscopy is a diagnostic method that allows you to check the stomach without swallowing a tube.
With its appearance in the arsenal of a practicing physician, the answer to the question of whether there is an alternative to FGDS has become positive. However, there are nuances - let's figure out what they are. Gastroscopy of the stomach without swallowing a probe (however, this formulation of the term is not entirely correct, since the esophagus and duodenum are also examined) was developed several decades ago. The test is carried out using a miniature video camera enclosed in a special capsule, the ingestion of which allows you to examine various areas of the gastrointestinal tract:
- Esophagus.
- Stomach.
- Sections of the intestine.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is a method based on manual control of the probe. If the stomach is examined with a camera, there is no way to control its movement; it depends on peristalsis.
The test lasts on average from 4 to 10 hours, the swallowed capsule comes out naturally - during bowel movements. The patient can carry out daily activities and does not require anesthesia or painkillers.