The prevalence of inflammatory pathology of the upper gastrointestinal tract in adults reaches up to 50% for certain nosological forms. Among them, gastroduodenitis occurs in most cases. Considering the high incidence rate among people of working age, experts pay special attention to this problem. In recent years, there has been a tendency towards chronicity of the process, which manifests itself with mild symptoms. Therefore, the doctor’s task is timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment, which includes medications and proper nutrition.
What it is
Catarrhal duodenitis is an acute inflammatory process that affects the mucous membrane of the duodenum. 12 – the duodenum is one of the main organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Food entering the duodenum is processed by digestive juice, and processing occurs by pancreatic juices. After the processing process, the food is absorbed into the body. In addition, the duodenum produces hormones that help normalize metabolism and regulate the functioning of the entire digestive system. Therefore, the inflammatory process in the duodenum is a big problem for the body. The disease is often referred to as superficial duodenitis, since with this type of duodenitis only the superficial layer of the mucous membrane of the duodenum 12 is affected, and the deeper layers do not have structural changes, hyperemia and edema. Catarrhal duodenitis is the most common form of the disease.
This type of duodenitis can develop in childhood, but does not persist for a long time. Under the influence of certain factors, the process is activated, and disease-specific symptoms are recorded.
When the disease worsens, the normal blood supply to the duodenum is disrupted, and the process of restoration of the intestinal mucosa slows down. The production of gastric juice increases under conditions of decreased protective function of the mucous membrane. As a result, the duodenum is exposed to aggressive factors, which leads to inflammation of the surface layer. Pathogenic pathogens can penetrate into the inflamed areas of the intestine, which leads to an exacerbation of the condition, as well as to the development of infectious pathologies.
The mechanism of development of inflammation of the duodenum
The gastrointestinal tract consists of several sections, the mucous membrane of which may be subject to adverse effects. The anatomy of the upper gastrointestinal tract looks like this: the esophagus tube passes into the stomach, followed by the duodenum. It got its name from the fact that its length corresponds to approximately 12 fingers of an adult and is about 20-25 centimeters.
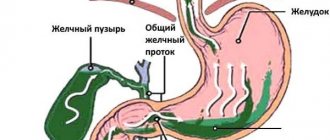
The main stage of digestion (the breakdown of food) occurs not in the stomach, but in the duodenum, where food enters in portions and the ducts of the gallbladder and pancreas open. That is why any disturbances in this part of the gastrointestinal tract, including motility disorders, and especially inflammation, negatively affect the digestion process and lead to numerous symptoms.
Symptoms
The symptoms and treatment regimen for this type of duodenitis differ little from the signs and treatment of other diseases of the digestive tract. When the upper layer of the duodenal mucosa is affected, the symptoms are very similar to those of a peptic ulcer.
Characteristic features are:
- Pain and discomfort in the epigastric zone. The pain intensifies about 2 hours after eating;
- Bitter taste in the mouth, heartburn may bother you;
- Weight loss. To prevent another attack of severe pain after eating, the patient refuses food, which leads to weight loss;
- Increased salivation, nausea, vomiting, followed by relief;
- Deterioration in health. Headaches, weakness, drowsiness, dizziness, hyperhidrosis appear;
- Increased work of intestinal loops, periodic bloating;
- Abnormal bowel habits. If the inflammatory process in the duodenum is quite pronounced, the patient experiences alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- Irritability, excessive nervousness, bad mood for no reason.
Currently reading: What is proximal duodenitis: stages, symptoms and proper treatment
https://youtu.be/u_OUdjohOTI
Causes
Catarrhal duodenitis manifests itself under the influence of certain etiological factors. The bacterium Heliobacter pylori is the most common cause of duodenitis. The bacterium damages the walls of the organ, poisoning it with the products of its vital activity. Toxic substances are absorbed into the sensitive mucous membrane, causing an inflammatory process.
The disease can manifest itself after severe stress, when a person is under constant nervous tension, works a lot, when his sleep and nutritional patterns are disrupted. Constant fasting, abuse of rough food, fast food, spicy, fried and fatty, as well as strong coffee, tea, and alcoholic beverages can become a stimulus for the manifestation of pathology.
Catarrhal duodenitis can appear after severe poisoning with drugs that negatively affect the walls of the duodenum. Duodenitis often develops against the background of various diseases: in the presence of advanced dysbiosis, parasites living in the intestinal lumen, long-term untreated dysbiosis, cirrhosis of the liver, decompensated pathologies of the heart, lungs, and kidneys. As a result, the body is poisoned by the products of its own metabolism. The cause of catarrhal duodenitis may be injury to the duodenum by foreign objects.
Factors that cause the disease also include:
- Emotional breakdowns, nervous system disorders, lack of proper rest, stress, depressive situations, poor diet;
- Regular consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- Taking anti-inflammatory drugs, salicylic acid, some antibacterial or hormonal agents that can have a destructive effect on the intestinal walls;
- Exposure of a person to harmful environmental factors or unfavorable workplace conditions;
- Decreased immunity, which leads to inhibition of the body's protective abilities.
Forms of the disease
Catarrhal duodenitis is conventionally divided into separate forms. The following types are distinguished:
- ulcer-like. Characterized by the presence of ulcerative symptoms;
- gastro-like. With this form, the symptoms of gastritis are recorded;
- cholecyst-like. Characteristic of this form is the manifestation of signs of cholecystitis;
- nervously - vegetative. It occurs with frequent dizziness, headaches, fatigue, increased excitability;
- asymptomatic. Signs of the disease are completely absent;
- mixed. There are many symptoms characteristic of different forms of the disease;
- flagmetose. The inflammatory process is purulent in nature;
- erosive. Erosive formations are observed on the mucous membrane;
- atrophic. Thinning of the intestinal wall and atrophy of intestinal hairs occurs;
- hyperplastic. Excessive growth of hairs is recorded, the walls of the organ become thicker;
- interstitial. Damage to the pancreas is not recorded.
Clinical picture
There are many classifications of this disease.
| Sign | Classification |
| By etiology |
|
| Depending on the location of the foci of the inflammatory process, there are forms |
|
| By type of endoscopic picture (according to FGDS) |
|
| Individual forms (depending on the causative factor) |
|
Clinical taxonomy of inflammation of the duodenum identifies such forms as:
- long-term bulbitis in combination with gastritis;
- prolonged duodenitis with inflammation of the small intestine;
- duodenitis that developed due to duodenostasis (impaired evacuation of the contents of the duodenum);
- local duodenitis (with damage to the papillary or peripapillary areas).
ICD 10 code
Duodenitis rarely occurs as an independent symptomatic pathology. Often duodenitis is a consequence of chronic gastritis in the patient or vice versa. These diseases are closely related to each other. Therefore, during the 10th revision of the ICD, a separate code was adopted - K29.9, which belongs to the K20 - K31 group (diseases of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum). Duodenitis is defined by code K 29.8.
Why is inflammation of the duodenum dangerous?
If the patient does not want to treat duodenitis, the inflammation lasts long enough, this can lead to atrophy, which cannot but affect the patient’s digestion: the breakdown of food, the production of enzymes, and the absorption of substances will worsen. Because of this, over time, the patient may develop anemia, a lack of vitamins or microelements, which will affect their well-being.
And that is not all. Some patients may experience the following complications of duodenitis:
- Intestinal bleeding.
- An ulcer in which both the duodenum and the patient’s stomach suffer.
- Stenosis of the pylorus of the stomach. With this pathology, the passage between the patient's duodenum and the stomach is greatly narrowed, which can even cause intestinal obstruction.
- Malignant tumor of the patient's intestine.
- Purulent inflammation of the tissues that surround the duodenum (phlegmonosis) of the patient.
Therefore, when the first unpleasant symptoms appear, it is advisable for patients to immediately consult a doctor, undergo examination and begin treatment while duodenitis proceeds without complications.
Treatment methods
A correct diagnosis is important for effective treatment. During a catarrhal form of duodenitis, during an examination of a patient, a doctor can record plaque on the surface of the tongue and pain of varying degrees upon palpation. In this case, the hemogram and urine analysis are normal in most cases. To fully understand the nature of the disease and for accurate diagnosis, instrumental studies are prescribed.
Currently reading: Symptoms of chronic duodenitis and methods of treating the disease
Conducted:
- X-ray of the stomach and duodenum using a barium suspension. This method allows you to assess the condition of the walls of the organ and record defects, if any;
- FGDS. The method is an endoscopic examination. Allows you to accurately visualize the epithelium of the duodenum, identify the root cause of symptoms, and, if necessary, take a sample from suspicious areas to examine the nature of the disease.
Based on the research results, treatment is prescribed. The treatment regimen is chosen by a specialist on a purely individual basis.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is based only on one or more of the following criteria:
- Clinical. The presence of pain and (or) dyspeptic disorders of any severity.
- Endoscopic. FGDS reveals edema and hyperemia of the inner lining of the duodenum, multiple erosions and hemorrhages. The inflamed inner lining of the duodenum is extremely sensitive to contact with the endoscope: easy vulnerability, bleeding, etc.
- Histological. When taking a biopsy during FGDS and subsequent histological examination, there are no signs of proliferative diseases or any other pathologies, but there are indicators of inflammatory infiltration, atrophy, and degenerative changes.
- Laboratory. There may be hidden blood in the stool, signs of anemia (according to a general blood test), vitamin B12 deficiency (with mucosal atrophy).
At the stage of mandatory instrumental and laboratory examination, the following is carried out:
- Complete blood count (detects signs of bacterial or viral damage and anemia associated with blood loss or vitamin B12 deficiency).
- Determination of total protein and its fractions. Reduced in the course of inflammation and atrophy of the underlying parts of the gastrointestinal system.
- Determination of iron content in blood serum (a decrease in the indicator allows one to suspect chronic blood loss).
- Analysis of stool for the presence of occult blood.
- Detection of Helicobacter Pylori (by breath test) - to establish an accurate diagnosis, according to etiology.
- Histological and cytological examination of biopsy material (if degenerative changes and tumor pathology are suspected).
- FGDS – for visual confirmation of the diagnosis.
Drug therapy
When the disease is caused by Heliobacteria, antibiotics are prescribed. The doctor chooses the treatment regimen and cycle based on the course and severity of the disease, also taking into account the specific reactions of the patient’s body.
The doctor also determines which medications the patient can take at the same time. Antibiotics from the penicillin group and bismuth-containing agents are often prescribed.
To neutralize the aggressive effects of gastric juice on the walls of the duodenum, antacids are prescribed. Proton pump inhibitors are also used, which inhibit the functioning of cells that produce hydrochloric acid. The course of treatment includes antispasmodics that help reduce the pain threshold.
Types and forms of duodenitis, features
In addition to acute duodenitis, it is also possible to develop chronic inflammation, in which not only inflammation of the mucous membrane is formed, which is permanent, but also a change in the functional activity of the intestine. Its peristalsis decreases, duodenostasis occurs, or difficulty in the passage of food into the jejunum.
Typically, chronic duodenitis occurs in waves, with alternating periods of exacerbation and remission. Often these periods coincide with times of national feast and errors in diet.
Chronic duodenitis is a time bomb. From the duodenum, inflammation can spread to the pancreas, as well as to the bile ducts. Thus, it is possible to obtain complex damage to the hepatobiliary zone.
What other forms of duodenitis occur?
Surface
It is worth saying a few words about this form of the disease. It is known that all forms of intestinal inflammation begin precisely from the surface of the mucous membrane.
If the inflammatory reaction stops here (as most often happens in an acute process), then there is a chance of recovery. If the inflammation does not stop there, then more severe forms of duodenitis occur, for example, an erosive process.
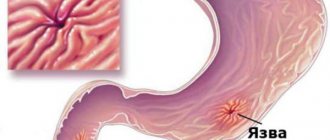
Erosive
Erosion is a painful area where the mucous membrane is simply absent. Erosive duodenitis is a more severe form.
To understand what erosion is, just look at a fresh callus: if the bubble is opened and the remaining skin is removed, then meat is revealed - a red surface, any touch of which is sharply painful. The same thing happens on the inner surface of the duodenum.
Now imagine that you sprayed this surface with acid. Introduced? This is exactly what happens in the duodenum during digestion. Therefore, if the FGD results in the conclusion “erosive duodenitis”, then treatment must be started urgently. A general diagnosis of “erosive gastroduodenitis” is often made.
The only consolation is that erosions heal easily. A new mucous membrane forms on them, and no defect occurs, as with an ulcerative lesion.
It must be remembered that erosive gastroduodenitis can occur with the abuse of NSAIDs, which induce an erosive process and even ulceration.
Therefore, drugs such as Nalgesin, Diclofenac, ibuprofen, Nise, meloxicam and many others from this group should be used in short courses, according to strict indications, and also under the cover of proton pump inhibitors - omeprazole.
You need to be even more careful when prescribing corticosteroid hormones. In the event that even a very short course of administration is planned (for example, pulse therapy with prednisolone for only three days), then an FGDS must be done before this. The stomach and duodenum should be “calm”.
A little about ulcerative lesions
Everyone knows that usually, when talking about ulcers, the name of the diagnosis is pronounced as “peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum.” Many will argue that peptic ulcer is a completely different disease, and this has no place in the article about duodenitis. This is a deep misconception, since an ulcer is always accompanied by inflammation.
Speaking about ulcerative duodenitis, one can only note that the outcome of the ulcer in any case, even with timely treatment, will not go unnoticed: a scar will form. In unfavorable cases, the outcome may be cicatricial stenosis (narrowing of the lumen), perforation of the ulcer with the development of peritonitis, profuse bleeding that can lead to death, or even malignancy of a chronic ulcer.
Folk remedies
One of the effective ways to treat catarrhal duodenitis is alternative medicine. It is recommended to use various decoctions and infusions that have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. However, before use, the chosen method must be agreed with your doctor.
Decoction of oats and nettles
You need to take a glass of unpeeled oats, pour half a liter of cold water and put on low heat until you get a slimy mass. You also need to take dry nettle and pour boiling water (1:3). Decoctions of oats and nettles are mixed, the resulting healing drink is taken 100 ml 30 minutes before meals.
Medicinal fee
St. John's wort, marshmallow root, and chamomile are taken in equal proportions. 2 tbsp. l. The mixture is brewed with 400 ml of boiling water and left for 10 hours in a dark place. Afterwards, the infusion is filtered and topped up with boiling water until the original volume is obtained. Take 100 ml 4 times during the day, taking into account that the last dose is immediately before bedtime.
Honey with plantain
Squeeze 2 tbsp from fresh plantain leaves. l. juice, mixed with 2 tsp. natural honey and leave for 2 hours. Use 1 tbsp three times a day. l.
Currently reading: What is moderate duodenitis - photos, symptoms and treatment
Anti-inflammatory collection
Mix lavender, chamomile flowers, lemon balm, marshmallow root and shepherd's purse in equal proportions. Take a tablespoon of the mixture and pour 250 ml of boiling water. The resulting composition is heated in a water bath, without bringing to a boil. Take three times a day, half an hour before meals.
A decoction of flaxseeds, homemade jelly with sweet fruits, and sea buckthorn oil are useful.
Diet
Diet is an important part of the treatment of catarrhal duodenitis. The diet should be varied and consist of a minimum amount of carbohydrate products. It is necessary to use food rich in proteins. It is recommended to use juices from fresh vegetables and fruits, compotes, and jelly. It is necessary to eat regularly so as not to overload the stomach; the patient is advised to eat food in small portions (about 150 g each portion) 5 times during the day.
Eating a variety of dairy products is beneficial. The diet should include cottage cheese, low-fat sour cream, and kefir. An ideal breakfast consists of vegetable puree and a hard-boiled egg.
Sweets are allowed to be used in very small quantities. It is best to replace them with natural honey, fruits and berries. Spices and seasonings should be excluded from the diet, and the amount of salt used should be limited.
It is recommended to use a large amount of liquid per day in the form of herbal teas, jelly, freshly squeezed juices from fruits and vegetables. The use of canned food, sausage, chips, coffee, fatty, fried and spicy foods, hot and cold food is not allowed.
Prevention
To prevent the development of duodenitis, it is recommended to adhere to a proper diet. You need to eat a balanced diet, including fresh fruits, vegetables, berries, and dairy products in your daily menu.
You need to give up bad habits, smoking, drinking alcohol, carbonated drinks, coffee, hot and cold food.
It is necessary to timely identify and treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and periodic examinations to prevent the development of such pathologies. Regular moderate physical activity, physical exercise, walks in the fresh air, and avoidance of stressful conditions are also recommended.
Catarrhal duodenitis can be cured in a very short time if you follow a diet and take the treatment prescribed by a specialist.
When is hospitalization necessary?
If symptoms of gastroduodenitis appear, you should consult a gastroenterologist. The specialist conducts an objective assessment of the person’s condition to find out under what conditions the patient should be treated for gastroduodenitis.
For moderate manifestations of the disease, you can conduct an examination and prescribe medications on an outpatient basis. However, therapy and its results should be monitored. Positive dynamics indicate the effectiveness of the measures taken.
Pronounced changes, which are characterized by severe pain, poor general health, and increased temperature, indicate severe gastroduodenitis and require hospitalization. If the patient cannot eat, weight loss is noted, infusion therapy with glucose-saline solutions is performed. If necessary, some medications are administered intravenously.
The gastroenterologist also refers the patient to the hospital if complications arise. Because some cases require surgery as soon as possible (eg bleeding, perforation).
Reviews
Dear readers, you can leave your opinion about catarrhal duodenitis in the comments (form below)
Victor
Against the background of chronic gastritis, I developed catarrhal duodenitis. The symptoms were similar to gastritis, so I did not suspect that the duodenum was affected. I was worried about dizziness, bitterness in the mouth, and nausea, which only went away after vomiting. The doctor prescribed appropriate treatment and diet. A week later, the condition began to improve.
Paul
I was treated for catarrhal type of duodenitis on an inpatient basis. They prescribed complex treatment and a gentle diet (diet table number 1). The treatment process began by washing the stomach with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. After two days of the treatment course, I began to feel better, the urge to vomit stopped, and my digestion and stool normalized.
https://youtu.be/RyGln1s-6II