Prevention of giardiasis in children
The risk of developing this disease can be minimized if parents teach their children to follow certain rules of behavior. It is much easier to prevent Giardia in children (their symptoms are unpleasant and debilitating): treatment requires a lot of time and effort. The following preventive measures are considered the most effective:
- Make sure your baby doesn't put dirty objects in his mouth.
- Wash your hands after walking, visiting the toilet and before eating.
- Give your child only filtered water.
- Avoid bathing your baby in polluted waters. This ban does not apply to the sea, since parasites do not live in salt water.
- Treat fresh vegetables and fruits with boiling water before giving them to your child.
- The child should play only in those sandboxes whose safety the parents are sure of.
- Giardiasis in children can be prevented if antiparasitic drugs are regularly given to pets. When animals are contagious, children should be prohibited from contacting them. It is advisable to resume communication with pets only after a course of antiparasitic therapy.
How does giardiasis manifest?
This disease is often asymptomatic. Nothing bothers the infected person, and clinical signs do not appear in any way. The affected intestines may cause abdominal pain, loose stools, rumbling and flatulence. From the gastrointestinal tract, this disease manifests itself as dermatitis, eczema, and urticaria that are difficult to treat. Less commonly, giardiasis affects the gallbladder. Most often, a person is bothered by pain in the area of the right ribs, an unpleasant taste in the mouth, etc. Intestinal lamblia affects a child much more often. This is explained by the fact that children rarely observe the rules of personal hygiene.
How to decipher the results of an ELISA test
It should be noted that the result of the blood test obtained is deciphered exclusively by a specialist. Since this analysis indicates several types of antibodies responsible for the stage of development of the disease.
A positive result is the following marking >1 OPD, which indicates that the body has a protozoal infestation of the intestines or an infection has existed in the past.
Figures less than 0.85 OPD indicate a negative result, which makes it highly likely that there are no parasites in the body.
Indicators between 0.85 and 1 OPD suggest repeat testing because the pattern of infection is unclear. In this case, additional research on Giardia is required: stool analysis and examination of duodenal juice.
Stool test for Giardia antigen
The essence of this method is simple: a laboratory assistant carefully examines a biological sample under a microscope and either detects Giardia antigen in the stool or not. Based on the data obtained, a conclusion is given: a positive answer means the presence of the parasite in the body, a negative answer means its absence. Such diagnostics are carried out in all medical institutions, including private clinics. A positive result is never false, but the probability of an erroneous negative answer is 20-30%.
Duodenal fluid examination
Since Giardia parasitizes not only in the small intestine, but also in the duodenum, duodenal juice can be quite informative material for research. If stool analysis raises some doubts, then examination of the immediate contents of the duodenum can detect these protozoan parasites.
For this purpose, fibrogastroscopy is done. In order for the procedure to take place with the greatest comfort, it is necessary to carefully prepare for it:
- three days before the proposed test, you must avoid spicy, fried, spicy foods, and avoid foods that contribute to excessive gas formation;
- the day before the procedure, eat light food;
- during 8 hours of research you cannot eat or drink anything;
- Also, three days before the procedure, you should refrain from smoking and alcohol, since smoking can stimulate the secretion of gastric juice, which can make an already unpleasant procedure even longer;
- if the patient uses certain medications every day, then treatment cannot be interrupted, but in addition you should consult with your doctor;
- the procedure lasts no more than 20 minutes.
A study of duodenal fluid will reveal the localization of Giardia in the body, which will simplify the treatment of Giardiasis.
Giardiasis is a dangerous infectious disease caused by microorganisms parasitizing the gastrointestinal tract. It is impossible to identify the disease solely by symptoms. Therefore, it is worth knowing what the Giardia test is and how to take it so that the result is as accurate as possible. The effectiveness of treatment directly depends on the objectivity of the test results.
If all symptoms indicate the presence of Giardia in the body, you should immediately consult a doctor. Usually a gastroenterologist helps to cope with this disease. This specialist should immediately send you for a full examination, which will help determine the exact cause of the ailment.
You can get rid of any parasites at home! You just need to drink it once a day...
The presence of giardiasis can only be determined by studying blood and feces; sometimes others can be added to these studies, but they are not so important. Since these parasites usually live in the intestines, their traces will be visible on the results of stool tests - Giardia cysts are usually found in it.
After all the studies have been completed, the correct treatment should be prescribed. Without an accurate definition of the pathogen, the approximate extent of infection and concomitant diseases, it is impossible to select suitable drugs.
How to collect feces from a child?
The existence of Giardia in the human body is difficult to determine by eye; there are a lot of medical diagnostics for this. They help doctors identify and fix the problem in a timely manner.
Since young children or teenagers often suffer from parasites, many parents are tormented by the question: how to identify Giardia in a child? First, you should pay close attention to the general condition of your child. In young children, giardiasis is usually accompanied by manifestations of intestinal infection:
- an increase in body temperature to 37.5 degrees;
- persistent diarrhea;
- nausea, vomiting and other symptoms of toxic damage.
If Giardia has managed to firmly establish itself in the child’s body, and the disease smoothly passes into the chronic stage of development, then the symptoms change. Appears:
- bloating and rumbling;
- the tongue is covered with a thick coating of a light or yellowish tint;
- liquid diarrhea alternates with constipation;
- the skin becomes pale, and a blood test does not reveal a lack of hemoglobin.
It is extremely rare that giardiasis is accompanied by peeling of the lips, dry mucous membranes, irritability, or, on the contrary, increased fatigue and apathy in the child. If you notice one or more characteristic symptoms, you should take your child for a preventive examination. The most inexpensive but popular method is stool analysis for Giardia in children.
However, this method is informative only for long-term infection. Therefore, an ELISA blood test is often performed along with it.
Giardiasis is a common disease among children.
Cysts enter the body with food, water, or through dirty objects. That’s why children often get giardiasis.
With giardiasis, the child has a stomach ache, fever, chills, vomiting, and an allergic reaction may occur. Children quite often have such symptoms, so it also happens that doctors cannot immediately understand the reasons for the child’s ailment - he is referred to a neurologist, dermatologist, allergist, etc. If treatment is not taken in time, the disease becomes chronic.
The consequences of this are intoxication or immune deficiency.
Giardia in a child's body is accompanied by a slight increase in body temperature, abdominal pain, diarrhea and vomiting. How to give this test to your child? Stool examination follows the same pattern as in an adult.
Treatment of children for giardiasis should include not only taking drugs against parasites, but also medications that will improve the condition of the digestive system. You can continue the course of treatment after using the drugs with herbal remedies and herbal medicine.
There are many traditional medicine recipes that will effectively affect the child’s recovery.
Important! Do not ignore the child’s symptoms in the early stages of damage to the body!
In order to find out where to take a stool test for Giardia, you should contact a specialist. He will suggest the most trusted laboratory.
Decoding the result
To ensure accurate results, you should take the test 2 times. It can show results like this:
- a positive result for Giardia antigens in the stool indicates that the human body is affected by parasites and treatment is required;
- a negative result means that Giardia was not detected in the body.
How long does it take to re-test stool for Giardia? The material should be re-examined for the presence of parasites after 1 week.
Where and how can you test feces for Giardia, features of the analysis
In order to detect giardiasis in time, it is necessary to submit stool for laboratory testing.
Methods for diagnosing giardiasis
Scatological method
To diagnose giardiasis, a scatological research method is used - testing stool for the presence of cysts or Giardia antigens. In addition, this disease can be diagnosed using a general blood test (detection of immune antibodies to parasites) and an additional research method - ultrasound. But the most accurate way is coprogram.
The results of a scatological study refute or confirm the presence of Giardia and their eggs in the feces, and also reveal acute or chronic forms of Giardiasis. It is necessary to test feces for Giardia cysts not only to diagnose the disease, but also during its treatment and seven to ten days after the end of the course. This is necessary to determine the effectiveness of the course of therapy.
Determination of antigens in stool
Determination of antigens in feces is a modern and promising method for diagnosing giardiasis. To examine stool for the presence of antigens, monoclocanal antibodies are used, which make it possible to identify parasites even during periods when they are not produced. Giardia antigen is excreted in the feces for two weeks after complete recovery.
You can donate stool at any medical laboratory. Research is carried out using modern equipment and powerful microscopes, where Giardia cysts can be detected in the presented material. The material for research is feces and their duodenal contents.
Features of donating feces
You need to take fresh stool for analysis (which is no more than twelve hours old). Before collecting material, you should not take laxatives. In addition, it is prohibited to take antiparasitic drugs for a week before the test.
Some laboratories will not accept stool that is more than two hours old or require warm stool. This is explained by the fact that in a fresh portion of feces, Giardia is active and does not hide its flagella. Over time, they begin to sense a change in living conditions and switch to the cyst form (they freeze, remove their flagella and “hide” under a dense shell). This condition persists for a long time, so twelve-hour feces are suitable for laboratory analysis.
Our readers successfully use Intoxic to get rid of parasites. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
It is very difficult to meet the requirements for the freshness of stool, especially for children, because they cannot stand waiting for the start of the working day. It is also very difficult for adults to deliver warm feces to the laboratory, because it quickly cools down on the way to the medical facility. Therefore, specialists who insist that feces should be two hours old can claim insufficient competence in this matter. After all, cysts are easy to detect in feces if you examine them under a microscope, since they do not collapse or disappear, but are excreted in feces.
It is best to test feces for detection of cysts in the first seven days after the first signs of giardiasis appear. This period is characterized by the largest number of parasites. They irritate the intestinal mucosa, cause the development of inflammatory processes and lead to serious digestive problems. Experts recommend that patients with giardiasis test feces daily for four to five days to see the full picture of the disease. Carrying out a laboratory test four times increases the reliability of interpretation to ninety percent. A one-time analysis may be inaccurate, since Giardia cysts are not released constantly, but intermittently.
For analysis, there is a special special container that is sold in any pharmacy. Feces should not be collected from one place, but samples should be taken from different places.
Interpretation of the results of a laboratory stool test for the determination of Giardia should take place in conjunction with the patient’s clinical blood parameters. If Giardia antigen was detected in the feces, this indicates giardiasis and does not exclude the presence of other parasitic microorganisms. If the antigen has not been identified, then in most cases there is no Giardia, but you should still take the test a second time, since there are cases of parasites of this type being detected during repeated testing.
Indications for the use of various laboratory tests and tests for Giardia
When diagnosing giardiasis, absolute preference should be given to direct methods of detecting giardia - microscopic examination, detection of microorganism DNA by PCR, detection of hypertension. AT detection can be used as an additional method.
Features of interpretation of laboratory research results.
The results obtained using direct diagnostic studies (microscopic studies, detection of hypertension and Giardia DNA in feces) have general principles of interpretation. Laboratory monitoring of the effectiveness of treatment of giardiasis is carried out 5–6 days after the end of taking the drugs. Criteria for the effectiveness of treatment: three negative results of microscopic examination with an interval of 1–2 days. When interpreting the results of AT detection, along with generally accepted factors influencing the level of AT (intensity of invasion, forms of the disease, etc.), one should take into account the possibility of cross-reactions of Giardia antigens with the antigens of pathogens of other parasitic diseases.
Copyright Federal Budgetary Institution Central Research Institute of Epidemiology of Rospotrebnadzor, 1998 - 2019
Central office: 111123, Russia, Moscow, st. Novogireevskaya, 3a, metro station “Shosse Entuziastov”, “Perovo” +7 (495) 788-000-1, [email protected]
Blood test for Giardia: explanation of how to take Ifa
Giardiasis is an infectious disease caused by protozoan microorganisms called Giardia. Despite the fact that this intestinal disease has been known to doctors for a long time, some problems in its diagnosis still exist, since it can be characterized by a variety of symptoms, or be completely asymptomatic. So, what is giardiasis, and what diagnostic methods (in particular, analysis for giardia) are used to identify it?
- Why are Giardia dangerous?
- What is a blood test for Giardia?
- How is analysis for Giardia deciphered?
- How to prepare for analysis
Why are Giardia dangerous?
In addition to the fact that giardiasis is a very unpleasant disease, it can also pose a direct threat to human health. Giardia is especially dangerous for infants (they can suffer from giardiasis starting from three months), since these parasites can cause serious delays in the development of the baby. That is why, at the first suspicion of invasion of the body by parasites, it is necessary to take an appropriate test (stool or blood) for Giardia, which will make it possible to diagnose the disease with great accuracy.
The most informative way to detect giardiasis is to analyze specific proteins (antibodies) to giardia. It involves the study of human venous blood using the Ifa method, which makes it possible to determine antibodies to these microorganisms in the sample, and hence the presence of the disease itself.
What is a blood test for Giardia?
The IFA (enzyme immunosorbent) method is a set of tests that detects the so-called AT (antibodies to Giardia antigens) of various classes (IgA, IgM, IgG), as well as total antibodies. A blood test for Giardia can be carried out immediately after the patient complains of symptoms of infestation, since specific antibodies appear in the body very quickly.
A blood test for giardiasis using the Ifa method consists in the fact that a human blood sample is examined in a special way over a certain period: this makes it possible to calculate the diagnostic density of certain at. The error of IFA is about 5-7%, so this particular test is recommended for all patients with suspected parasite infestation.
Approximately 10-14 days after infection, antibodies of the IgM class are detected in the patient’s blood, after which other antibodies of the IgG and IgA classes appear, which remain at a fairly high level in the body at all stages of the disease. The beginning of adequate treatment, as a result of which the parasites die, leads to the fact that specific and total antibodies decrease sharply and completely disappear from the blood within 2-6 months. At the same time, the level of atm in the blood of a particular person depends on many factors, including the state of his health, living conditions and much more.
How is analysis for Giardia deciphered?
It should be noted that in order to avoid misinterpretation of the results, deciphering the blood test for Giardia should be carried out exclusively by a specialist. Usually it indicates several types of antibodies, which make it possible to judge the presence of the disease, as well as one or another of its stages.
A positive test result for AT is considered to be a result of >1 OPD, which indicates that the body is infected with giardiasis or that the invasion took place in the past. Indicators less than 0.85 OPD are negative, that is, in this case we can speak with great accuracy about the absence of parasites, and if the analysis gives a result falling within the range from 0.85 to 1 OPD, then the study is best repeated after two to three weeks . In addition, to make an accurate diagnosis in such cases, experts recommend taking a stool test for the presence of Giardia cysts (larvae).
How to prepare for analysis
An analysis for antibodies to Giardia antigens should be prescribed by the attending physician, and the group of immunoglobulins (antibodies) for which the study is being carried out is indicated in the direction. A blood sample for Giardia must be taken in the morning on an empty stomach, having previously prepared for the procedure: at least 10 hours in advance, it is necessary to avoid drinking coffee, tea, juice or alcohol (you can only drink clean water), as these liquids can blur the clinical picture. Blood is taken from a vein using a regular syringe or a special system, and the turnaround time is approximately 3 days.
parazitu.net>
Research method
Blood microscopy to detect the pathogen is carried out using the ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) method of blood. The purpose of the study is to identify the pathogen and evaluate the body’s response. During a laboratory examination, the presence in the blood of antibodies, otherwise immunoglobulins (Ig), to specific antigens (foreign organisms) is determined.
Antibodies (AT) are protein compounds of the immune system whose task is to recognize and subsequently destroy antigens. Their active production indicates the presence of a foreign agent. In the case of diagnosing giardiasis, the antigen is Giardia.
Blood for allergens in a child
ELISA is carried out in stages. Initially, the antigen is placed on the testing surface, and blood serum is added to it. If the antigen is not recognized by the antibodies of the immune system as “native”, they try to destroy it. Thus, the formation of the antigen-antibody immune complex occurs.
Next, special reagents are added to the complex (in the case of Giardia detection, there are usually nine of them). The result is assessed by the degree of staining using an ELISA colorimeter (analyzer). The intensity of the color corresponds to the concentration of antibodies (the higher it is, the greater the amount of Giardia present in the body).
This study allows you to identify the main immunoglobulins IgA; IgM; IgG. Decoding of the results is carried out in the laboratory. An enzyme immunoassay blood test for giardiasis is prescribed two weeks later, after a previous stool microscopy, if parasites were not detected, but the patient’s well-being does not improve.
The timing of ELISA is determined by the fact that the production of immunoglobulins to foreign agents occurs within a certain period of time after their introduction into the body. To make an accurate diagnosis, it becomes necessary to identify the true pathogen and establish the form and stage of the disease. As an alternative to ELISA, the patient may be prescribed a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test.
Giardiasis
Giardiasis is a widespread disease caused by a member of the Protozoe family Lamblia intestinalis (Giardia Lamblia).
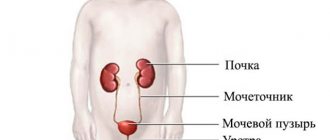
The source of infection is a person infected with Giardia. Transmission of infection occurs through the fecal-oral route. The main factor of transmission is water, but transmission can also occur through food products, on which Giardia cysts remain viable for 6 hours to 2 days; contact transmission from person to person is also possible. Giardia can cause serious intestinal diseases in humans, both in the form of epidemics and in sporadic cases. Children are more susceptible to Giardia infestation; their disease occurs with more pronounced clinical signs. Giardia infection may spontaneously disappear after 6 weeks or may persist for years. By colonizing the mucosa of the small intestine, Giardia trophozoites penetrate the epithelium and cause a systemic immune response.
Although giardiasis has been known for a long time, there are serious problems in its diagnosis. Traditionally, it is performed by detecting Giardia cysts or trophozoites in fecal samples or duodenal contents.
The effectiveness of these methods is about 50% due to the characteristic intermittency in cyst excretion associated with the characteristics of the reproduction of Giardia trophozoites. Detection of antibodies to Giardia antigens significantly complements methods aimed at identifying Giardia in feces, although this test is also not always sufficiently sensitive. It is advisable to carry out the test 1-2 weeks after the onset of clinical symptoms, if stool tests in an earlier period did not produce results.
According to clinical studies, antibodies to Giardia antigens are detected in 39 - 42% of patients with gastrointestinal pathology. In 89 - 92% of them, giardiasis is confirmed by a positive result of testing samples of feces or duodenal contents for the presence of Giardia cysts. There is a problem of cross-reactions of Giardia antigens with other parasitic and somatic antigens, which give false-positive results, therefore, to increase the reliability and reliability of the diagnosis of Giardiasis, a comprehensive examination is necessary.
Diagnosis of giardiasis
Giardiasis is a widespread everyday disease caused by the protozoan microorganism Giardia.
Pathogens enter the human body through water, unwashed fruits and vegetables, and raw meat. Almost 50% of the world's population are carriers of the infection, but most often the diagnosis of giardiasis is made in preschool children, although there are cases of infection in adults. The pathogenesis of the disease can affect almost all internal organs; reproduction of pests is impossible only in the gall bladder and ducts. It is not always possible to determine the presence of parasites in the human body by symptoms alone due to the absence of any signs of invasion. How to identify Giardia by other methods? For preventive purposes, it is necessary to undergo an examination and tests. There are two main ways to check for the presence of these helminths in the body:
- stool analysis for Giardia cysts;
- laboratory testing of feces for parasite antigens: detection of eggs or fragments of an adult.
Both analyzes are carried out using a precision microscope, and due to the fact that the outer shells of Giardia are almost transparent, the smear must be contaminated with a special dye or treated with Turdyev’s preservative. Research is carried out simultaneously with a repeat cycle after 3-4 days. The information content of the results will depend on the degree of damage to the body, the correctness of stool sampling and the time the sample arrived at the research center.
How is giardiasis diagnosed?
The variety of clinical manifestations of giardiasis and the absence of symptoms characteristic only of this disease require mandatory laboratory confirmation of the diagnosis. The material for research is feces and duodenal contents. Only trophozoids are found in the duodenal contents, only cysts are found in formed feces, and trophozoids and cysts are found in liquid and semi-formed feces.
Currently, a number of methods are used to diagnose giardiasis, which differ in sensitivity, specificity and general availability.
The most accessible method of laboratory diagnosis of giardiasis is scatological examination. When conducting research, it is necessary to remember that cysts in stool cannot always be detected. Intermittent excretion of cysts in feces requires repeated examination of feces, as well as the use of other laboratory research methods.
Antibodies to Giardia. In patients with clinical manifestations of giardiasis, but with a negative fecal examination, it is advisable to examine the duodenum or upper jejunum. As a rule, it contains a large number of Giardia, including trophozoids (they are visible in fresh smears).
Analysis of failures in identifying Giardia in the study of feces made it possible to systematize the main reasons for false negative results. These include:
- incorrectly collected research material;
- submission of stool to the laboratory while taking medications that damage the morphology of parasites;
- errors of laboratory research;
- examination of feces during the so-called “silent” period, when the excretion of Giardia cysts stops (8-14 days).
Giardia can be detected in 76% of patients if these causes are eliminated during the first stool examination. After the second study, the probability increases to 90%.
The most reliable method for diagnosing giardiasis is duodenal biopsy. Indications for duodenal biopsy are:
- typical clinical picture of giardiasis;
- negative result of scatological studies;
- one of the pathological symptoms (for example, edema and segmentation of the jejunum during endoscopic examination);
- pathological lactose tolerance test (i.e. the presence of abnormal bacterial flora during aspiration of intestinal contents);
- absence of secretory Jgd;
- hypogammaglobulinemia (deficiency of one of the types of proteins in the human body - gammaglobulin);
- achlorhydria (lack of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice).
Immunological methods (ELISA method for detecting Giardia lamblia antigen) have recently been widely used throughout the world to diagnose giardiasis. Such test systems have very high sensitivity and specificity, and allow the simultaneous detection of both cysts and trophozoids in stool samples. Typically, G lamblia is detected in 50-70% of patients after a single stool analysis. After three-fold analysis - in 90%.
Detection of antibodies of the total classes IgA, IgM, IgG to Giardia antigens (serological methods) is an indirect method for laboratory diagnosis of giardiasis. Can be used as an additional diagnostic method to determine the body's immune response to the introduction of a pathogen.
Giardiasis - description of the disease and the essence of diagnosis
Giardiasis is called the “disease of dirty hands.” This means that infection occurs through the fecal-oral route, and failure to comply with hygiene rules is the main predisposing condition. For this reason, the disease most often occurs in children, but can also be found in adults at any age. Helminthiasis can be asymptomatic (with minor invasion), but in most cases it manifests itself with characteristic symptoms:
- abdominal pain, digestive disorders - this is associated with mechanical injury to the intestinal mucosa;
- nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite and sudden weight loss;
- allergic reactions in the form of skin rash and itching - they appear in response to the accumulation of waste products of parasites.
Diagnosis of helminthiases is complex. Since different pathogens can cause similar clinical signs, the diagnosis is considered final only if the parasite is identified in any form. If you suspect giardiasis, you must first submit stool for testing. During its microscopy, cysts can be detected - durable round formations, in the form of which protozoa exist outside the human body. However, the formation of cysts does not occur constantly, and they are not found in every piece of research material.
Donating blood for Giardia is a more accurate diagnostic method. It will not be possible to find helminths or their cysts in this substrate, since they exist only in the human digestive tract. However, the results of blood diagnostics can form the basis for making a final diagnosis. The fact is that the human immune system produces specific antibodies - proteins that destroy bacteria and protozoa. DNA of any biological object, including Giardia, can also be detected in the blood.
The causative agent of giardiasis is a single-celled parasite that multiplies in the small intestine of humans.
When is it necessary to submit biomaterial for examination?
In patients of different ages, symptoms appear at different stages of the development of the disease; in addition, the signs may differ, which is determined by the protective functions of the body and the localization of helminths. In order to undergo treatment on time, any tests for giardiasis are recommended if a number of symptoms appear:
- The structure of the stool changes. Diarrhea or constipation may appear, often these conditions replace each other.
- Flatulence.
- Constant pallor.
- Central nervous system disturbances appear: the quality of sleep deteriorates, strength is lost, and frequent fatigue is noted.
- The condition of the skin, hair, and nails deteriorates, and persistent “jams” are visible in the corners of the lips.
Where can I go?
Upon the direction of the attending physician, the biomaterial is examined in a laboratory, which is available at any clinic; you can first contact your place of residence. In addition, biomaterial is collected to test for helminths in paid clinics, regional and city medical centers. When applying to a commercial organization, a referral is not required. Services in such laboratories are always paid.
It is necessary to outline a number of procedures that the patient must undergo:
The biomaterial is tested for cysts (feces) and antibodies to helminths (blood). It must be remembered that with long-term storage of feces, the effectiveness of the analysis is greatly reduced.
Preparation for analysis
A week before blood sampling, you need to follow a diet enriched with light, quickly digestible foods.
On the day of blood sampling, the patient is prohibited from eating and smoking; he can only drink still water - each factor can affect the final result.
It is recommended to stop taking medications a few days before the tests; if this is not possible, you need to notify your doctor. This will allow you to make a reliable diagnosis.
You need to enter the office without haste - increased physical activity provokes the release of certain substances into the blood that can distort the test results.
Blood test for parasites
More recently, to identify parasites in a patient, the method of stool probing was used, which helped to detect fragments of helminths, their eggs or larvae. If they parasitize the liver, pancreas, biliary tract or duodenum, then they can be found in bile and duodenal contents. Intestinal helminthiasis is detected by fecal samples. Urine is examined for genitourinary schistosomiasis, sputum for paragonimiasis.
However, the reliability of such a diagnosis depends on the professionalism of the laboratory assistant and the presence of eggs laid by the parasite (there is a possibility that it may not have time to lay them before the analysis is carried out). Most often, about 10 attempts are needed to identify, then the probability of a correct result increases.
Enzyme immunoassay blood test for parasites
At the moment, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for parasites is successfully used for the same purpose. It is used to detect antibodies (immunoglobulins) and antigens (parasites and their metabolic products). Immunoglobulin is produced in the human body and is an antibody to an antigen. This method is considered very highly sensitive: its accuracy is at least 90%. The results of a blood test make it possible to determine their type and quantity, and also make it possible to monitor the dynamics of parasitic diseases.
Due to its high sensitivity, this method is often used when there is a small number of parasites in the diagnosed material and when they are localized in tissues (echinococcosis). The downside of the method is its high cost, so this analysis is not carried out in all laboratories.
Blood test for parasites in children
Children are considered the main carriers of helminthiasis, since it is at a young age that the basic rules of personal hygiene are most often violated. Parasites lie in wait for children everywhere, be it a playground, a sandbox or a bed of delicious strawberries, so it is not difficult for children to catch such an infection. Statistics show that almost every child has become infected with worms at least once in their life.
If you suspect helminthiasis in a child, you should contact your pediatrician for a referral for testing. Currently, doctors use 3 methods to identify parasites: stool analysis for worm eggs, scraping for enterobiasis, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent test for blood.
Collecting stool for analysis is the cheapest, but not very informative method. It is used to determine only the presence of helminth eggs. The analysis will be negative if the parasites did not have time to lay them. For a reliable result, it is necessary to repeat the analysis several times.
Detection of worms by scraping for enterobiasis is considered more appropriate, as it is quite informative and painless. But, as with stool examination, the results of the analysis depend on the presence of a clutch of helminths, so this type of test also requires repetition in doubtful cases.
In children, it is more effective to test blood for parasites using the ELISA method. This method is considered the most informative, but at the same time more complex and expensive. For diagnosis, venous blood is collected in the morning on an empty stomach.
The interpretation of a blood test for parasites is based on the determination of antibodies to parasite antigens. To do this, testing systems measure the level of antibodies of the IgG and IgA classes. Detection of IgM antibodies occurs two to 2 weeks after invasion - penetration of the parasite into the body. Then IgG antibodies appear, which remain at high levels throughout the entire period of the disease.
After Giardia is eliminated, the amount of antibodies decreases, and after six months they completely disappear from the blood. When IgM antibodies are detected, we can confidently speak about the presence of an acute phase of the pathological process, and a high level of IgG antibodies indicates a chronic disease. High concentrations of IgM and IgG indicate an exacerbation of chronic giardiasis.
It is important to know that deciphering a blood test for parasites should only be done by doctors who are familiar with the working methods of the laboratory that carried out the tests, since the results of the study may vary depending on the equipment of the institution
Analyzes
Detection of helminths in stool samples in the laboratory is carried out using copro-ovoscopy (helminth-ovoscopy) methods.
Most often, 3 methods are used for this:
- Native smear microscopy is an examination under a microscope of a small drop of feces applied in a thin layer to a glass slide. To do this, a piece of feces is mixed with distilled water to the consistency of sour cream and then a small amount of the mass is transferred to glass. Add a drop of 50% glycerin and mix with the fecal mixture. After this, use a wooden stick to spread the mixture onto the glass surface in a thin layer, place a cover glass on top of the smear and examine the material under a microscope.
- The Fulleborn test involves mixing stool with salt water, which causes helminth eggs to float to the surface. To carry out the procedure, 10 grams of feces are combined with 100 milliliters of a 50% solution of table salt (450-500 grams of salt per 1 liter of hot water). Then the mixture of feces and water is left for 1.5 hours so that the helminth eggs float to the surface of the solution. After the specified time has passed, the film formed on the surface is removed with a special tool and transferred to a glass slide. The film is covered with a cover slip and examined under a microscope.
- Taleman's test - mixing stool with ether and hydrochloric acid, through which the presence of parasite eggs is determined. To carry out the procedure, feces are placed in a container and mixed with 4 milliliters of 30% hydrochloric acid, 15 milliliters of distilled water and 1-15 milliliters of ether. Then the container is tightly closed with a lid and tilted up and down several times, mixing the contents. Then the mass is filtered through gauze and centrifuged. The resulting sediment is placed on a glass slide, covered with a coverslip and examined under a microscope.
If helminth eggs were detected in at least one of the 3 samples, the test result is considered positive.
Consequences of giardiasis
The treatment of giardiasis should be taken seriously, since this disease leads to the development of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, damage to the gallbladder, intestinal tract and even the musculoskeletal system is isolated - the waste products of parasites negatively affect the cartilage tissue of the joints. The patient is concerned about the “products” of vital activity, which manifest themselves in constant headaches, the development of arrhythmia, irritability, and often an increased risk of fainting.
Chronic giardiasis always means poor skin condition, damage to the lip area, peeling of the eyelids and other problems.
When is it necessary to get tested for giardiasis?
It is necessary to be tested for giardiasis when obvious symptoms of parasite infection are observed.
The presence of the disease can be determined by signs of intoxication of the body:
- pale skin;
- periodic nausea, vomiting, flatulence;
- alternating diarrhea with constipation;
- formation of yellow plaque on the tongue;
- loss of appetite;
- anorexia;
- weight loss;
- the appearance of bitterness and dry mouth.
With giardiasis, there is a deterioration in general health (malaise, increased irritability, decreased immunity, headaches, etc.) and the appearance of aching or cramping pain in the hypochondrium, which eventually spreads throughout the abdomen.
Frequent abdominal pain may be caused by parasites
In some cases, the disease is accompanied by the appearance of an itchy rash, night grinding of teeth, hair loss, the appearance of cracks and cracks around the mouth, and enlarged tonsils.
If you discover the above-described signs, you must undergo a special examination, the results of which will help confirm the presence or indicate the absence of parasites in the body.
Particular attention should be paid to people who are at risk of infection. These include:
These include:
- children aged 1 to 5 years and people who live in the same household or have frequent contact with them (for example, caregivers);
- people who do not have access to clean drinking water;
- people who have anal sex without a condom;
- tourists traveling through disadvantaged areas with unsanitary conditions.
Where is the pathogen tested?
Laboratory testing is a fairly accurate medical diagnostic technique. Analyzes of stool, urine, blood and skin scrapings allow not only to determine the general health of the patient, but also to identify the pathological condition of various organs.
Where can I get tested for Giardia? This can be done in laboratories and private clinics, as well as in municipal clinics. In this case, the patient can choose which study is best for him to undergo.
Stool examination
This is the most common and easily accessible diagnostic option. How to test for Giardia? To do this, in the morning, biological material is collected in a container or other clean container. The sample is taken from different places in the feces, and it must be taken to the hospital as quickly as possible. If cysts are detected in the stool, the diagnosis of “giardiasis” will be confirmed. Live Giardia can be detected in biological material only if no more than 20 minutes have passed after its collection.
For the analysis to be carried out, three grams of feces are required, and it is best if it is liquid. If the collection of feces was carried out more than four hours ago, the effectiveness of the study is significantly reduced. If it is impossible to deliver the sample quickly to the hospital, then you can use a container with a special preservative, which is taken in advance from the laboratory.
Fecal analysis for Giardia is not reliable in all cases. This is explained by the fact that parasites that enter the intestines develop intensively only after 2 weeks, so it is not possible to detect them during this time. The accuracy of such an analysis is only 50-70%. For greater effectiveness, it is recommended to take stool samples four times, with three days between tests.
Causes of giardiasis
Giardiasis is a common parasitic disease caused by protozoa - intestinal lamblia.
The disease is caused by parasites belonging to the group of flagellates. Most often, Giardia enters the body due to the following factors:
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules.
- Drinking contaminated water.
- Poorly washed vegetables and fruits eaten fresh.
The main method of transmission of infestations is fecal-oral. A person infected with giardiasis is a carrier of cysts, which are expelled during defecation. These cysts are highly resistant to environmental factors.
Cysts can get into food and water. If a healthy person swallows them, they very quickly turn into adult parasites in the body, which begin to actively reproduce.
Sources of Giardia are often animals, mainly rodents, cats and dogs.
Giardiasis is often diagnosed in childhood. In school and preschool institutions, you can become infected with Giardia through dishes, linen, and toys.
Symptoms of the pathological condition
Signs of giardiasis are similar to diseases of the digestive system
For the development of giardiasis, the penetration of more than nine cysts into the body is sufficient. Depending on the degree of infection, the disease may be accompanied by the following signs of digestive disorders:
- Painful sensations in the navel area.
- Unpleasant-smelling stool.
- Constipation.
- Belching.
- Flatulence.
- Vomit.
- Nausea.
- Diarrhea.
- The stool is yellowish in color.
- Loss of appetite.
- Exhaustion of the body.
Such symptoms are due to the fact that giardiasis mainly affects the intestines. In addition, in rare cases, parasites can affect the liver and bile ducts. In this case, there is bitterness in the mouth, pain on the right side of the lower ribs.
An increase in body temperature, general weakness, and decreased performance are also often observed. Possible rashes on the skin, accompanied by itching, drowsiness or insomnia.
The acute form of giardiasis lasts up to one week; if the symptoms are ignored, the disease becomes chronic.
The disease is severe in infants, since it also affects physical development. Children experience hyperthermia, severe diarrhea, shortness of breath, and vitamin deficiency. Since parasites produce toxins, allergic reactions and a weakened immune system may occur. As a result, children often suffer from colds.
In adults, giardiasis can be asymptomatic. But if there are a large number of parasites in the body, signs of digestive disorders appear. Possible cracks and redness in the corners of the lips, allergic reactions, bruises under the eyes, fatigue. The skin takes on a gray tint. Therefore, if you have symptoms of the disease, you need to get tested for Giardia. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the specialist will prescribe the correct treatment.
How Giardia is isolated in feces during analysis
Stool test for Giardia antigen
Analysis of stool for antigens will allow the identification of Giardia fragments in samples. To carry it out you will need a small amount of feces. The results of the examination are accurate, but to be completely sure, you will need to test for the presence of antigens about four more times.
Antigens are not only released in feces. When examining the blood composition, Giardia cysts are also detected. An antigen is an immunoenzyme formation that resists foreign bodies entering the human body.
Sometimes they are present in the blood or stool even if a person is not infected. Strong immunity reacts by releasing antigens even when transit cysts or eggs enter the body, which immediately come out without infecting the person.
PCR research
Using PCR analysis, the source of infection is detected in the patient’s body and the type of invasion is determined.
Stool testing using the PCR method is informative and effective. PCR is an experimental method during which foreign bodies are isolated from a substance. Diagnostics are available in specialized laboratories that practice this analysis.
The Invirto laboratory network successfully engages in PCR research in the field of parasitology. You can view the price list for PCR diagnostics on the company’s website.
Tests for invasion at Invitro
For tests, you can always contact the Invitro medical laboratory.
Here, an individual approach to each patient and quick and accurate results are ensured. There is no need to tire yourself out with long queues, but simply come at a convenient time. Affordable prices, qualified staff, the latest technologies at your service!
Among different methods and means, everyone chooses the one that suits him best. But we must remember that no matter what parasite settles in our body, we must undergo a full examination and devote maximum time and attention to the problem. To prevent this from happening, you need to take care of your health.
Source
Giardiasis diagnosis
Giardiasis is a disease that is accompanied by irritation and inflammation of the intestinal mucosa caused by microscopic parasites.
The first symptoms of the disease appear 1-2 weeks after infection. During this time, parasites multiply and disrupt intestinal function. Mostly there is damage to the small intestine, in which the process of digestion and absorption of food occurs. How can you assume giardiasis in a patient? This disease is accompanied by obvious symptoms that are simply impossible to ignore. The main symptoms include:
- sudden increase in temperature to 38° and above;
- acute abdominal pain localized in the navel area;
- prolonged nausea and vomiting;
- weight loss;
- infrequent but prolonged diarrhea, which can last several weeks;
- the appearance of a pink itchy rash on the skin.
As you can see, the symptoms of giardiasis appear so clearly that anyone will pay attention to them. However, quite often the disease is practically asymptomatic and the patient may not even realize that he is infected with parasites. In this case, a blood test for Giardia can help. A blood test for Giardia can also be prescribed when all of the above symptoms are present to clarify the diagnosis. How is a blood test for lamblia performed?
Giardiasis is diagnosed by direct and indirect methods. Direct methods include identifying the parasites themselves in feces or duodenal contents (contents of the duodenum). Indirect methods include a blood test for antibodies to Giardia (ELISA method). In response to invasion, the body begins to produce specific immunoglobulins igg (each microbe has its own).
These methods do not guarantee the accuracy of the results. Therefore, if infection is suspected, the doctor can prescribe several types of tests at once in order to obtain summary results that increase the accuracy of the examination. Testing for antibodies will give a more accurate result in a chronic process, when stool analysis is uninformative.
Polymorphism of clinical symptoms and frequent co-occurrence with other infections make it difficult to diagnose giardiasis invasion. To correctly diagnose an invasion, the following research methods are used:
- fecal analysis
- analysis of duodenal contents
- blood tests - ELISA, PCR, general, biochemical
The most commonly used method in the laboratory diagnosis of giardiasis infection remains microscopy of feces and duodenal contents. A urine test is not done for giardiasis.
Parasitological research plays a primary role in diagnosis. The main drawback of the microscopic method is the difficulty of differentiating Giardia and other flagellates living in the intestine and the cyclical nature of cyst excretion.
Methods of enzyme immunoassay and immunofluorescence are considered promising in laboratory diagnostics. They have high sensitivity (60-95%) and specificity up to 92%. In clinical practice, serodiagnosis is used as a complement to traditional methods.
Typically, all three methods are used to make a diagnosis. In some modern laboratories, feces and blood are examined using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to detect the DNA of single-cell parasites.
Preparing for a blood test for giardiasis is the same as for any hematological examination:
- blood is donated on an empty stomach, after a 10-hour fast
- eliminate alcohol and nicotine
- After consultation with your doctor, stop taking medications 3 days before the procedure
- Eliminate spicy, salty, sour and fried foods for 3 days
On the day of the procedure, exclude physical and psycho-emotional stress. Reschedule X-ray examinations and physical procedures to another time. For giardiasis, a blood test is taken from the venous bed.
Since the symptoms of infection are very similar to those of other diseases, it is difficult for a doctor to make a correct diagnosis at the first examination, without additional examinations. Then he refers the patient for laboratory diagnosis of giardiasis. An ELISA blood test is considered the most informative, because it reveals the number of antibodies of different classes (immunoglobulin titers igm, iga, igg) to this disease. Pathogens often choose to parasitize the intestines, less often the gallbladder.
Ways of infection by parasites:
- water – swimming in a polluted (fresh) body of water and swallowing water;
- oral-fecal – through contact with an infected person, toy;
- food - unwashed food, poor heat treatment of meat.
Giardia are parasites that are characterized by a long life span and are localized for a long time in water, soil, on clothing or the surface of various objects. They become provocateurs of diseases such as giardiasis.
If an adult or child has been diagnosed with such a pathology, this may mean that he does not follow the rules of hygiene, since the penetration of one helminth into the body is enough for the development of helminthic infestation.
In most cases, parasitic forms may not make themselves felt in any way, therefore, with a well-functioning immune system, even if not treated, they disappear after 2-3 weeks. But in a number of situations, the disease still requires detection and drug therapy.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor needs to analyze the results of blood tests, so such a study simply cannot be done.
You should not hesitate to make a diagnosis in children, since their digestive system is poorly functioning or is still weakly expressed. Therefore, after parasites enter the intestines, pronounced symptoms appear. The worm contributes to the destruction of the intestinal mucosa, which provokes the development of the inflammatory process.
We suggest you read: Take a blood test for Giardia: price, explanation, how much is done