Epidemiology and pathogenesis
According to the International Classification of Diseases No. 10, hypertrophic gastritis is registered under code 29.6 . This type of gastric disease is diagnosed less frequently than other forms of gastritis. Middle-aged and older men are more often affected; 40% of patients with the identified superficial hypertrophic form have chronic alcoholism.
Among women over 45 years of age, multiple polyposis of the upper areas is more common. Hyperplastic adenomas develop after long-term use of medications from the group of proton inhibitors.
Mechanism of proliferation
The growth of epithelial cells, during which the internal relief changes, cannot always be clearly traced. Gastroenterologists note that pathology develops due to the structural features of the inner membrane, as well as the functions that it performs.
- secretory surface cells secrete alkaline exudate for increased regeneration of damaged areas;
- underneath them is the basal layer, it is formed by fibroblasts and lymphoid matter;
- mast cells, phagocytes, B-lymphocytes secrete antibodies, interferon, histamine for local protection of the inner layer.
When the surface is disturbed by any pathogenic factor, an inflammatory reaction occurs with significant growth of the epithelium in the place where the gastric glands come to the surface. Dense foci form there, which then thicken and form pathological folds.
Symptoms of pathology
The intensity of symptoms may depend on the stage of development of the disease, the age of the patient, and the state of his immune system.
The main symptom of the disease is dyspepsia, which is similar to the erosive chronic form. The following symptoms are observed:
- Belching with the smell of rotten eggs.
- “Hunger” pain an hour after eating.
- Heaviness in the stomach.
- Heartburn.
- Having an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Diarrhea.
- Possible vomiting.
With severe deformations of the gastric tissue, severe pain occurs immediately after eating. Appetite disappears, weight decreases sharply, the body becomes exhausted, anemia and pale skin are observed. The main distinguishing signs of this pathology are shortness of breath and tachycardia, which occur half an hour after eating food.
What causes the appearance of hypertrophic gastritis?
The causes of chronic hypertrophic gastritis are quite diverse and have a wide range of infectious, parasitic, and nutritional factors.
Hypertrophic inflammation of the inner membrane is associated with damage by microorganisms, the most famous of which is the bacterium Helicobacter pilori . It is also possible to be affected by the fungus Candida , Cryptococcus , Histoplasma capsulatum . Long-term invasion by these microorganisms is manifested by inflammatory reactions in the stomach cavity, duodenum and small intestine. The following conditions contribute to pathological growth of the mucous membrane:
- autoimmune diseases (lupus, scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis);
- chronic reflux gastritis;
- lack of proper eating behavior;
- decreased general and local immunity.
- long-term use of proton pump inhibitors, nonsteroidal medications for inflammation, anticancer cytostatics, corticosteroids, and iron supplements sometimes lead to the growth of folds on the surface of the stomach.
Provoking mechanisms that increase the risk of hypertrophic gastritis include poor nutrition, frequent alcohol consumption, smoking, and stressful situations. A genetic disposition cannot be ruled out; sometimes deformation of the mucosa is associated with a gene mutation that causes familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome.
Classification by type
The type of deformation of the mucous epithelium is identified during a diagnostic study and is divided into the following types:
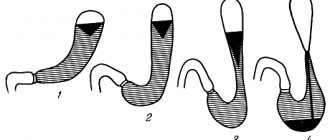
- Menetrier's disease - the folds thicken more than 2-3 cm, this is a giant hypertrophied gastritis with the development of multiple cysts, adenomas, and decreased secretion of gastric secretions. There are dyspeptic, pseudotumor and asymptomatic types; the disease is quite rare.
- Hypertrophic granular gastritis - growths in the form of ovals of 3-6 mm form on the inner surface of the mucosa. The advanced stage of granular gastritis often develops into oncology or gastric ulcer.
- Warty form - this subtype of hypertrophic pathology is characterized by the direct growth on the surface of the stomach of huge, separately located growths, similar to papillomas or warts. In the development of this pathology, hereditary disposition transmitted through the male line plays a role.
- Polypous type - accompanied by polyps of varying sizes of inflammatory or unknown origin. This form is considered a precancerous condition.
Growths and tubercles on the surface are located singly or in groups. As the disease progresses, polyps and growths affect the entire inner surface of the stomach.
Causes
In the development of hypertrophic gastritis, an important role is played by the influence of harmful factors - external and internal. In some cases, the pathology is a consequence of the acute form, while in others it develops independently, as a result of prolonged and constant exposure to irritants.
Among them, prolonged consumption of alcoholic beverages, overeating, eating dry food, not chewing rough food well enough, hasty eating “on the go,” and poor dental condition are of great importance.
In addition, there are many factors that have a negative impact and lead to inflammation in the stomach:
- long breaks in eating (accompanied by the release of gastric juice, which corrodes the walls);
- smoking tobacco (impairs the secretory function of the stomach);
- insufficient content of complete proteins in the diet (lack of vitamins A, B, C impairs the function of the stomach and its ability to heal, leading to atrophy of the mucosa);
- long-term use of medications (salicylic, mercury drugs have an aggressive effect on the walls of the stomach);
- food allergies (food antigens irritate the walls and cause tissue swelling);
- circulatory disorders as a result of stress (insufficient oxygen supply in the blood).
Significant causes in the development and origin of hypertrophic gastritis are acute infectious diseases (tuberculosis, diphtheria, influenza, intestinal infections), as well as focal infections (sinusitis, tonsillitis, adnexitis).
Dysfunctions of the digestive organs (biliary tract, intestines, pancreas), as well as parasitic diseases (helminthiasis, trichocephalosis, ascariasis) are of great importance in the development of hypertrophic pathology.
It is necessary to note the professional causes of hypertrophic gastritis. For workers in hot shops and heavy industry, the disease occurs as a result of constant inhalation of toxic fumes - acids, mercury, ammonia.
It is important to know! Hypertrophic gastritis is a chronic form of the disease that affects men more than women. This is explained by the fact that the “strong half of humanity” is more susceptible to physical activity and bad habits - the use of tobacco and alcohol.
How does the disease manifest itself?
At the first stage of the disease, the mucous membrane has minimal changes, which is why clinical signs are sometimes absent. Hypertrophic gastritis is characterized by a chronic course. The first symptoms of surface deformation are manifested by heaviness and discomfort in the epigastrium. Since digestive processes slow down, discomfort is especially noticeable after eating.
- aching pain appears of cutting attacks ;
- with reflux gastritis, the patient experiences heartburn ;
- salivation, nausea , and possible vomiting , which does not bring relief;
- distension of the abdominal cavity, increased flatulence .
Since all the unpleasant signs are associated with food intake, the patient refuses to eat, his appetite decreases, and sometimes is completely absent. As a result, a person quickly loses weight. Irregular filling of the stomach disrupts stool, rare and poor nutrition provokes worsening inflammation.
Why is the disease dangerous?
- the digestive functions of the organ decrease;
- glandular tissue decreases in size, the mucous membrane atrophies;
- the production of hydrochloric acid decreases;
- gastrointestinal motility works more slowly;
- the stomach increases in size or narrows.
The level of protein in the blood plasma decreases abnormally; such patients often develop ascites - this is abdominal dropsy when the amount of free fluid reaches 25 liters.
Forecast
Medical experts say that hypertrophic gastritis has a chronic form, and it is impossible to guess how the disease will develop. There is a high risk of serious complications: possible gastric bleeding and transformation into a cancerous tumor.
Diagnostic methods
In the early stages of hypertrophic gastritis, diagnosis is difficult. In an advanced form, with pronounced clinical signs, gastroenterologists make a primary diagnosis. After instrumental and laboratory tests, a final diagnosis is made and treatment for hypertrophic gastritis is prescribed.
One of the main studies is gastroscopy. Using this method, a superficial examination of the gastric mucosa is made and the extent of damage is determined. For a detailed study of the disease, the following methods are used:
- blood test (a reduced number of red blood cells indicates the development of anemia);
- targeted biopsy (sampling of mucosal tissue and histological examination of large areas of the surface);
- study of the secretory functioning of the stomach (carried out using a probe);
- microbiological method (study of mucosal cells in order to detect infection and the bacteria “Helicobacter pylori”).
An objective examination reveals characteristic signs - pain when palpating the abdomen, thick plaque on the teeth and tongue, cracks in the corners of the mouth. The results of radiological, endoscopic and histological studies are decisive. It is important for a specialist to distinguish hypertrophic gastritis from cancerous tumors.
In doubtful cases, the examination is repeated after 2–2.5 months and after the final diagnosis is made, treatment is prescribed. Therapeutic methods are aimed at relieving inflammation and restoring the epithelial function of the gastric mucosa.
How does a doctor make a diagnosis?
The general appearance of the patient does not indicate inflammation; hypertrophied areas are determined using fibrogastroscopy. Acidity must be measured, then bile is taken for study. At the same time, a biopsy is performed to take histological material.
How is Helicobacter bacteria detected?
- Using stool analysis, a special laboratory diagnostic method calculates the antigen of a bacterium.
- An air test is used - the exhaled air contains products of the bacteria. A person takes a drug with labeled carbon atoms. After some time, the patient breathes into a special device, which notes an increase in the content of H. Pilori .
For differential diagnosis, computer and/or magnetic resonance imaging , as well as blood tests for antibodies and tumor markers .
Diagnostics
This disease cannot be seen during a general examination, so careful diagnosis is required to select treatment. An anamnesis of the disease is collected, the skin and visible areas of the mucous membrane are examined, the abdomen is palpated, during which pain begins in the upper part - the epigastrium. The acid level in the stomach is then determined. For this purpose, esophagofibrogastroduodenoscopy (EFGDS) is used, in which probing of the digestive tract is performed, accompanied by the collection of bile. At the same time, a biopsy can be done, as a result of which the resulting material will be studied.
Sometimes there is a need for an acid test, in which a person takes a certain drug, after which urine is collected. The level of acidity in the urine is equal to that in the stomach. There are ways to identify the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which include:
- analysis of stool, which determines the antigen of the microorganism in humans;
- a respiratory test allows you to determine what percentage of bacterial waste products is in the patient’s body;
- fibrogastroscopy, in which the mucous membrane is examined using a device that visualizes its condition.
How to treat hypertrophied gastritis?
A mild form of hypertrophic gastritis is treated on an outpatient basis. The patient receives symptomatic therapy, which consists of reducing pain and neutralizing inflammation. A person receives medications to reduce the production of hydrochloric acid, as well as to protect the affected mucosa.
- Antacids - exist in the form of gels, syrups, tablet forms. The products envelop the surface and promote regeneration;
- proton pump blockers - suppress receptors that produce enzymes and HCl;
- If the bacterium H. Pilori is detected, a course of treatment with antibiotics .
When conservative methods do not work and gastritis progresses, a decision is made to surgery for growths or partial removal of the stomach.
Classification of gastritis
Hypertrophic gastritis is divided into several types, which are characterized by the duration and intensity of the development of the pathology. The main feature by which they can be combined is the transformation of the mucosal relief; it appears against the background of secretory insufficiency.
Under the influence of irritants, the gastric mucosa becomes inflamed and regenerates; these ongoing processes lead to the appearance of one of the types of hypertrophic gastritis:
- warty. A characteristic feature of this form is the presence of growths on the mucous membrane that resemble papillomas (warts) in appearance;
- giant gastritis (Menetrier's disease). With this type of gastritis, very large folds are present - up to 3 cm, atrophy of the secretory glands occurs, and the number of mucus-forming glands increases. This type of gastritis is divided into 3 forms: asymptomatic, pseudo-tumor, dyspeptic;
- granular form of gastritis. It is characterized by the formation of small (less than 1 cm) growths resembling grains. Pathological cavities appear inside the gastric walls, which are filled with liquid contents. This form of hypertrophic gastritis is formed against the background of the appearance of cysts of different types and sizes (from 2–3 mm to 1.5–2 cm);
- polypous form. It is typically characterized by the presence of both single and multiple growths (polyps) of connective tissue, which are formed as a result of increased regeneration (the size of the lesions is 0.5-2 cm in diameter).
Growths that form in the stomach can be of various types: benign or formations of a complicated inflammatory process. The hypertrophic process can penetrate into the parenchyma of the walls, that is, into the muscular layer of the digestive organ.
In addition, the pathology is divided into acute and chronic forms:
- The acute form is a dangerous pathology, due to the fact that the cause of its appearance is chemical intoxication. Penetration of caustic alkalis and acids into the gastrointestinal tract promotes deformation of the gastric walls and leads to tissue degeneration.
- The chronic form of gastritis is a sluggish pathology that has stages of exacerbation and remission.
Hypertrophic gastritis: treatment with folk remedies
In order to cure hypertrophic gastritis, you should be regularly examined and observed by a gastroenterologist. As a supplement to the main treatment, it is useful to use methods from a folk pharmacy.
For high acidity:
- Herbal tea – 2 tbsp. Mix tablespoons of medicinal chamomile, yarrow, St. John's wort, and celandine. Take one tablespoon of the mixture, pour a glass of boiling water, cover with a lid, and cool. Drink 100 grams before meals 6 times a day, course 2 months.
- Herbal infusion - prepare a mixture of St. John's wort, nettle, chamomile. Place two tablespoons of the mixture in a thermos, add hot water, and leave overnight. Drink the infusion before meals for 2 months.
For low acidity: Prepare cabbage juice using a juicer. Pour half a glass of juice and heat slightly. Drink every day in the morning on an empty stomach. Freshly squeezed cabbage juice can be stored on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator for no more than 24 hours.
Diet for hypertrophic gastritis and its role
The use of a gentle diet is a mandatory rule in the treatment of chronic gastritis of the hypertrophic type. It is very important to eat frequently and in small portions, at least 5 times a day in small portions. The total volume of food per single dose should be no more than 350 g.
For the first six months after surgery, a person takes only pureed food; the food should not be too cold or hot.
Do not use:
- alcohol, strong tea, coffee, carbonated drinks, kvass, kefir, cocoa;
- hot spices, fatty sauces, seasonings;
- chocolate, brown bread, fresh baked goods, mushrooms, grapes;
- lard, sausages, smoked meats, semi-finished meat and fish products, fatty meat and fish.
Recommended to eat:
- pureed cereal soups, oatmeal, semolina porridge with milk, soft-boiled eggs, steamed omelet;
- mild cheese, low-fat cottage cheese, yogurt, fermented baked milk, baked milk;
- For meat dishes, preference should be given to turkey, rabbit, chicken breast, and lean beef. Meat products are cooked in a double boiler, then minced in a meat grinder or crushed in a blender. Vegetable dishes are also prepared.
The diet should maintain the integrity of the epithelial layer and normalize the digestive process. Compliance with nutritional rules should become the norm of life. Patients wishing to achieve maximum results from treatment should accept restrictions and follow all instructions of the gastroenterologist.
Treatment: which methods are effective?
Drug therapy
The treatment regimen is prescribed by a doctor; self-medication is prohibited. Gastric hypertrophy requires complex treatment, which includes the drugs given in the table:
PAY ATTENTION! Do not prolong gastritis or an ulcer until stomach cancer, it is better to be on the safe side, but this will be necessary. read the story of Galina Savina >>
Painkillers
| "No-Shpa" | |
| "Besalol" | |
| "Papaverine" | |
| "Drotaverine" | |
| Proton pump blockers | "Omeprazole" |
| "Esomeprazole" | |
| "Lansoprazole" | |
| "Rabeprazole" | |
| "Gastrozol" | |
| Normalizing digestion | "Festal" |
| "Mezim" | |
| "Creon" | |
| "Pancreazim" | |
| "Pancreatin" | |
| Vitamins | Complexes containing groups B, C, P |
Return to contents
Surgical intervention
When conservative treatment of hypertrophic gastritis is ineffective, especially if the granular form is diagnosed, surgery is recommended. Abdominal surgery is performed to excise polyps and cysts or eliminate a hypertrophied area of the organ. A laparoscopy method is also used, in which a device is inserted into the stomach to remove pathological areas.
Physiotherapy
Hypertrophic gastritis can be treated using the following methods:
- magnetic therapy;
- electrical stimulation;
- ultrasound;
- cryotherapy;
- mud therapy;
- aerotherapy;
- electrophoresis;
- paraffin applications.
Physiotherapeutic treatment is contraindicated during periods of exacerbation of the disease.
Physiotherapy has the following therapeutic effect on a diseased organ:
- eliminate pain;
- stimulate the production of gastric secretions;
- saturate tissues with oxygen;
- relieve inflammation;
- reduce the activity of leukocytes;
- improve blood and lymph flow;
- promote tissue regeneration;
- normalize local metabolism.
Return to contents
Therapeutic diet
For hypertrophic gastritis, it is recommended to adhere to the correct diet. You should avoid alcohol, as well as fatty, spicy, pickled, fried and smoked foods. Food portions should be divided into 5-6 meals. Food should be warm, steamed or boiled, baked, stewed. The diet for hypertrophic gastritis includes the following products:
- lean meats and fish;
- low-fat dairy products;
- mild varieties of cheese;
- soft-boiled eggs or steam omelet;
- dried white bread;
- cereal porridges, including oatmeal, wheat, buckwheat;
- berry jelly;
- lean broth;
- vegetable or butter;
- puree soups;
- baked apples;
- boiled or stewed vegetables;
- sweet varieties of fruit;
- honey.