Progesterone is a very important hormone that takes an active part in the functioning of the reproductive system. Fluctuations in its concentration indicate the presence of pathological processes in the body.
Lack of progesterone is one of the main causes of infertility and also increases the risk of spontaneous abortion.
Timely diagnosis, identification of the causes of hormonal imbalance and competent therapy, including taking medications, nutritional correction, and moderate physical activity, will help prevent the occurrence of serious complications.
In what cases does the concentration of the hormone decrease?
The concentration of the hormone is different on each day of the cycle. From the beginning of menstruation to ovulation, the lowest value of indicators is observed. This is a physiologically low level of progesterone, which will increase after ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum. In the second phase of the cycle, an increase in concentration is observed. With a normally functioning corpus luteum, the endometrium profusely grows with blood vessels and prepares for implantation of a fertilized egg.
A physiological decrease in hormone levels occurs during postmenopause. After the last menstruation, the maturation of eggs stops, the corpus luteum does not form, and the adrenal glands are not able to maintain concentration at the proper level.
If progesterone is low, the reasons for this may be the following:
- insufficiency of the luteal phase of the cycle;
- pathology of the thyroid gland;
- disruption of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland;
- placental insufficiency (in pregnant women);
- hypereprolactinemia;
- hyperandrogenism.
Indirectly, the concentration of the hormone can be affected by lifestyle, stress level, intensity of physical activity, and nutrition.
Luteal phase
Progesterone levels below normal may occur due to luteal phase deficiency. The functional factors of this condition may be determined by the condition of the ovaries themselves.
There are diseases that lead to such hormonal levels:
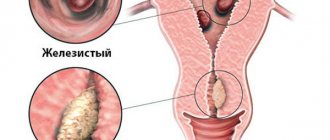
- Polycystic ovary syndrome is a disease in which the follicle matures, but does not rupture; it remains in a cyst state. When examined in such women, the entire surface of the ovary is covered with unruptured follicles resembling a honeycomb.
- Resistant ovarian syndrome is a loss of sensitivity of the organ to the effects of hypothalamic hormones; they do not respond to the action of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, and the egg does not mature.
- Ovarian hyperinhibition syndrome develops under the influence of unfavorable factors or medications that inhibit the influence of the pituitary gland.
- Premature exhaustion syndrome involves the early onset of menopause. The norm is considered to be the cessation of menstruation after 45 years, but sometimes women after 40 or 35 years old, under the influence of stress, radiation, chemotherapy, and taking medications, experience premature menopause.
Organic causes of low progesterone in the luteal phase lie in the presence of endometriosis, uterine or ovarian cancer, uterine polyps, fibroids, and endometritis. Intrauterine manipulations and operations (diagnostic curettage and abortion) influence the second phase of the menstrual cycle.
Effect of the thyroid gland
Hypothyroidism negatively affects fertility and hormonal levels. Under the influence of thyroid hormones, a protein is synthesized in the liver that binds and removes testosterone and estradiol. If this protein is not enough, an increased amount of active testosterone appears in the blood, which can suppress ovulation. This means that the corpus luteum does not mature, progesterone remains in minimal quantities.
Violation of estrogen inactivation under the influence of thyroid hormone deficiency leads to an increase in their concentration, which, according to the feedback law, affects the secretion of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones, which aggravates menstruation disorders.
Such women are characterized by infertility. Sometimes pregnancy occurs, but there is always a high risk of premature termination or congenital hypothyroidism in the child.
Influence of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland
The central glands that regulate the work of all the others are the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. A change in their function leads to the development of central types of hormonal secretion disorders. Tumors of these areas of the brain, insufficient blood supply will reduce the secretion of tropic hormones, and the work of all glands will be inhibited. Pituitary hypogonadism is one of the pathologies leading to miscarriage due to a lack of progesterone.
Hormonal function of the placenta
The placenta takes on the function of progesterone synthesis from the moment of its formation, usually after 16 weeks. If there are disturbances in the development of the placenta, its improper formation, calcifications and premature aging, then the progesterone content will be disrupted.
Hyperandrogenism
An increase in the amount of androgens leads to the development of anovulation. In this case, a dense capsule is formed on the ovaries, which prevents the release of a normal egg. The reason for the increase in hormone concentration is a tumor of the adrenal glands or ovaries.
Hyperprolactinemia
Prolactin is a hormone that promotes the growth of mammary glands and increased milk production. Its increase occurs naturally after childbirth. With tumors of the pituitary gland, blood supply is impaired, the regulation of the function of the hypothalamus changes, which affects the levels of FSH and LH. A lack of ovarian stimulating hormones leads to cycle disruptions.
In the postpartum period, there is a natural suppression of ovulation due to the fact that high prolactin inhibits the maturation of the egg. This is a protective reaction that is aimed at preserving the woman’s health: repeated pregnancy after a short period of time depletes the body and leads to serious complications for the mother and child.
Other factors of low progesterone are poor diet, lack of protein and animal products. Vitamin deficiency works the same way. Stressful situations and heavy physical activity, which are also perceived as stress, affect the secretion of neurotransmitters that suppress ovulation and hormone production.
Reasons for the decline
Why does a decrease in hormonal levels occur? Normally, physiological values decrease only after the onset of menopause, when the formation of the corpus luteum in the ovarian region stops. The adrenal glands are not able to maintain proper concentration on their own.
Causes of low progesterone:
- Endogenous (internal) - pituitary dysfunction, obesity, inflammatory processes in the pelvic area, infectious lesions of the reproductive system and thyroid diseases.
- Exogenous (external) - hormonal treatment or long-term use of oral contraceptives, abortions and regulation.
The female hormone is synthesized by the adrenal glands and ovaries. Maximum progesterone production occurs in the luteal phase. At this stage, it is recommended to undergo tests to find out the predisposing factor.
It turns out that with a decrease in hormonal levels, we can safely talk about pathologies of the corpus luteum. The cause of low progesterone is also a violation of metabolic processes, which is accompanied by characteristic symptoms (the appearance of colostrum, an enlarged thyroid gland). Lack of the hormone is observed against the background of ovarian dysfunction, severe stress and overload. The cause of the development of pathological abnormalities may be insufficient body weight.
You may be interested in: Intramural node: why it develops, how it manifests itself and how to treat
Disorders in the luteal phase
Low progesterone in the luteal phase is caused by ovarian disorders, which occurs against the background of the following diseases:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome. Accompanied by the maturation of the follicle, which does not rupture and the corpus luteum remains in a cyst-like state.
- Resistance. The ovaries lose sensitivity to the action of hormones produced by the hypothalamus. In this case, the egg is missing.
- Hyperinhibition. It develops when the body is exposed to such unfavorable factors as taking medications that inhibit the functions of the pituitary gland.
- Premature exhaustion. The cause of low progesterone is associated with the early onset of postmenopause (from 35 to 40 years), which occurs against the background of chemotherapy, radiation, stressful situations and taking medications.
LPF (luteal phase deficiency) may also be due to the presence of a malignant tumor of the ovaries and uterus. Endometriosis, fibroids and polyps should be considered as predisposing factors. Negative effects are possible during intrauterine manipulations (surgery, curettage, etc.).
Changes during pregnancy
It turns out that in the female body progesterone gradually increases until it reaches maximum values, after which its amount decreases. A similar pattern is present during pregnancy: in the 1st trimester - up to 468.4 nmol/l, in the 2nd trimester - up to 303.1 nmol/l, in the 3rd trimester - up to 771.5 nmol/l. The production of hormones decreases just before childbirth and does not increase, due to the fact that during the birth process the placenta leaves the woman’s body.
Lack of progesterone during pregnancy:
- Up to 4 months indicates the development of disorders of the corpus luteum.
- After 16 weeks - for abnormalities in the placenta.
A lack of female hormones is possible due to pathological processes in the pituitary gland, due to low stimulation of the ovaries. A decrease in its level also occurs when taking hormonal drugs after fertilization of the egg in large dosages and for a long time.
When to suspect a decrease in progesterone
Symptoms of progesterone deficiency in women include menstrual irregularities and problems with conception. The severity of symptoms depends on individual characteristics, the degree of decrease in the hormone and its relationship with estrogen.
In women of reproductive age, the menstrual cycle becomes irregular. Delays in menstruation can last up to several months. If menstruation occurs, it is long and with heavy bleeding. Discirculatory uterine bleeding often occurs. This is the appearance of bleeding of different intensity at uncharacteristic times of the cycle. In this case, medical intervention is required.
Signs of progesterone deficiency manifest themselves in the form of constant fatigue and rapid fatigue. The body retains sodium heavily, which is why swelling is common, which women mistake for excess weight gain.
Severe premenstrual syndrome owes its appearance to reduced progesterone. During this period, the mammary glands become engorged, mood swings and headaches appear, often turning into migraines.
An unprepared endometrium is not able to accept a fertilized egg.
Is it possible to get pregnant with low progesterone?
It depends on the degree of its reduction. Sometimes pregnancy occurs, but lack of hormonal support prevents it from developing.
Normally, the hormone should reduce the contractile activity of the muscles of the uterus, suppress local immunity, so that the fertilized egg, which is 50% foreign, is not rejected. But in early pregnancy, low progesterone leads to spontaneous miscarriage. If a woman knew about pregnancy, then the appearance of bloody discharge and abdominal pain should alert her. Ultrasound of such conditions reveals signs of detachment of the ovum; a hematoma forms under it, which does not allow the embryo to attach.
If a woman did not know about pregnancy, then its interruption will be like heavy, prolonged menstruation, which will force her to see a doctor.
In late pregnancy, signs of progesterone deficiency are post-term pregnancy. The normal gestation period is 40 weeks, a deviation of 2 weeks up or down is allowed. If labor has not begun by 42 weeks, the baby is at risk of birth injuries that occur due to ossification of the sutures of the skull. His head will not be able to configure enough to repeat the shape of the birth canal.
What are the consequences of a violation?
Low levels of estradiol and progesterone lead to very sad consequences:
- the menstrual cycle is disrupted;
- having difficulty conceiving;
- high risk of miscarriage (in the early stages);
- premenstrual syndrome is severe.
Lack of progesterone can provoke problems with conception.
The development of mastopathy and malfunction of the thyroid gland is possible. Sometimes long-term depressive states develop.
Ways to confirm suspicions
If a woman is concerned about menstrual irregularities, miscarriage or the threat of miscarriage, then she must undergo a progesterone test. For non-pregnant women, it is prescribed on the 22-23rd day of the cycle with a duration of 28 days, when the physiological value is maximum. For those whose cycles differ in duration, the day is determined by the attending physician. Pregnant women are examined regardless of the period.
If a woman has a long delay in menstruation, the study is carried out on any day, but it is not done in isolation, but in combination with other hormones:
- estrogens;
- prolactin;
- testosterone;
- hCG;
- cortisol;
- FSH;
- LG.
Blood for hormones is taken from a vein strictly on an empty stomach. The day before the test, you should not eat fatty foods or alcohol. On the day of the study, it is permissible to drink clean water.
Additional research will help determine why progesterone levels are low:
- A biochemical blood test reflects the functional state of the body and liver pathology. (With cirrhosis and liver failure, the utilization of hormones and protein synthesis are disrupted, so hormonal failure occurs).
- Thyroid hormones are needed to confirm or refute the condition of hypothyroidism.
- An ultrasound of the pelvic organs will show the condition of the ovaries, the presence of a ripening dominant follicle or a formed corpus luteum in them, and will also allow one to suspect polycystic ovary syndrome. The examination reflects the condition of the uterus, the presence of additional pathology in the form of fibroids, endometriosis, and neoplasms.
- An abdominal ultrasound is necessary to determine the condition of the liver and adrenal glands. An echo examination of the thyroid gland is required.
- An X-ray examination of the sella turcica, CT or MRI of the brain is necessary to exclude the central cause of a decrease in progesterone in the form of a pituitary tumor.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy is performed to visually determine the condition of the ovaries. For polycystic disease, treatment is also possible - dissection of the dense capsule.
Examination for low progesterone may include other methods, the choice of which is within the competence of the attending physician.
Effect of estrogen on the body
The hormone estrogen is produced in the ovaries - the female genital organs - in the first half of the menstrual cycle. Very little is produced in the adrenal glands. It has a feminizing effect on the entire body and determines, as the girl grows up, her body structure according to the female type:
narrow shoulders;
- wide rounded hips;
- growth and development of the genital organs.
Estrogen in adult women is responsible for the menstrual cycle, pregnancy and childbearing. It affects the thyroid gland and pituitary gland, has an anti-atherosclerotic effect in the cardiovascular system, regulates water-salt metabolism, stimulates the transition of fluid from the bloodstream directly into the tissues and thereby causes a compensatory retention of sodium and water in the body.
The more estrogen, the greater the risk of developing tissue edema. It regulates the exchange of phosphorus and calcium, affecting the quality of bone tissue, preventing its loosening, which prevents the formation of osteoporosis, is responsible for the condition of the sebaceous glands, and actively affects the condition of the mucous membranes and skin moisture in a woman’s body.
Correction of hormonal levels
Establishing an accurate diagnosis will tell you what to do if there is a hormonal imbalance. Treatment of the pathology depends on the underlying cause of the decrease in progesterone production. Tumors of the hyprophysis require treatment by an oncologist. Women with thyroid pathology should be referred to an endocrinologist.
Hyperprolactinemia is treated by prescribing Bromocriptine, Cabergoline, if the cause is functional impairment. Pituitary tumors are treated with surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.
Treatment must begin with lifestyle and nutrition adjustments. A woman should rest for at least 8 hours, and sleep at night should start from 10 p.m. Stressful situations are limited. Nutrition is normalized, it must be balanced in the amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, contain animal products, fresh vegetables and fruits.
Hormone therapy is prescribed by various types of drugs. For low progesterone in pregnant women with signs of threatened abortion, Duphaston is used. The drug is available in tablets that are taken daily every 8 hours. The dosage is selected by the doctor individually.
For endometriosis, Duphaston is used from days 5 to 25 of the cycle or continuously. When planning pregnancy, patients with infertility caused by luteal phase insufficiency use the drug from days 14 to 25 for at least 6 months, and then continue maintenance use of the drug with the onset of pregnancy until the placenta is formed.
Duphaston is also used to treat the following conditions:
- premenstrual syndrome;
- dysmenorrhea;
- irregular menstruation;
- amenorrhea;
- to stop and prevent dysfunctional uterine bleeding;
- in hormone replacement therapy in combination with estrogens.
Utrozhestan has a similar effect. The drug is available in the form of tablets for oral administration or intravaginal use. Indications for use coincide with those for Duphaston.
There is an oil solution of progesterone - Oxyprogesterone. It is used for intramuscular administration. The convenience of this form lies in the slow gradual release of the hormone into the blood. Therefore, the indication will be treatment and prevention of threatened miscarriage, amenorrhea. Using the solution you can induce the onset of menstruation. To do this, the drug is injected into the muscle every other day. Usually 3 to 5 injections are prescribed. 7-10 days after the last injection, sometimes earlier, the woman begins menstruation. From the first day of menstruation, a combined oral contraceptive is prescribed, which will set the ovaries to a normal rhythm of work and help cure amenorrhea.
The consequences of hormonal deficiency are felt by women of any age. If there are pronounced symptoms of premenstrual syndrome or difficulties with conception, then you should not try to solve them yourself or pretend that everything is normal. Delayed treatment is more difficult. And timely diagnosis will allow you to forget about unpleasant symptoms and live a full life.
A hormone that has a huge impact on a woman’s well-being. Its insufficient quantity leads to extremely unpleasant consequences for the female body.
Traditional treatment
If you suspect a hormonal disorder, you should consult an endocrinologist or gynecologist. After diagnosis, drug therapy is prescribed to stabilize hormonal levels. The main goal of treatment is to normalize the production of sex hormones. Therefore, as an addition to basic therapy, the endocrinologist can prescribe vitamins and homeopathic remedies that increase the synthesis of progesterone in the body.
Hormonal drugs
Lack of progesterone in women, the symptoms of which lead to temporary infertility, can be treated with the following drugs:
- Utrozhestan. Release form: capsules or vaginal suppositories containing 100 mg of micronized progesterone as an active ingredient. When administered orally, the female hormone analogue enhances the secretory activity of the endometrium for 24 hours. When using suppositories, Utrozhestan prepares the uterus for the implantation of a fertilized egg. The drug is taken 2 times a day, 100 mg. The duration of therapy is determined individually for each patient. Utrozhestan is contraindicated in cases of incomplete abortion, bleeding disorders, malignant tumors, and severe liver damage.
- Crinon. Release form: gel in disposable applicators for intravaginal use, containing 90 mg of progesterone. The active substance enhances the production of endometrial hormones, reduces the frequency of contractions of the uterus and fallopian tubes. The daily dosage is no more than 90 mg of the active substance. The average duration of treatment reaches 30 days. Contraindicated in women with a high risk of thrombosis, acute porphyria, incomplete abortion, renal and liver failure.
- Duphaston. Available in the form of tablets of 10 mg of active substance. The drug normalizes the plasma concentration of progesterone in the blood. Duphaston acts only on progesterone receptors located on the uterine endometrium. The medicine does not affect the egg and fallopian tubes. The medication should be taken 1 tablet 2 times a day from 11 to 25 days of the cycle. If there is a threat of miscarriage, in order to increase the pregnancy period, the daily dosage is increased 2 times. The drug is prohibited for use during lactation, in patients with malabsorption syndrome, glucose and galactose intolerance.
- Progesterone. Release form: ampoules for injection containing a 1% oil solution. Allows you to quickly normalize the level of progesterone in the blood, reduces the threat of miscarriage against the background of increased peristalsis of the endometrium of the uterus. The drug is contraindicated in cases of impaired renal and liver function. The daily dose of the drug is from 5 to 15 mg. The duration of treatment is from 18 to 20 days.
The duration of therapy and dosage are determined by a gynecologist or endocrinologist on an individual basis, depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle and the general condition of the woman.
Vitamins
Vitamins improve blood circulation in the pelvic cavity, which is why the endometrium of the uterus receives a sufficient amount of oxygen and energy. This effect on soft tissue enhances the effect of the drugs, normalizes the production of progesterone and its level in the blood plasma.
For sex hormone deficiency, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Actovegin. It is an antihypoxant, produced in the form of a solution for injection. The active substance of the same name saturates tissues with oxygen, normalizing metabolism and the production of endocrine hormones. The drug is contraindicated in people with individual intolerance to Actovegin, with heart failure, pneumonia and hyperhydration. Actovegin for progesterone deficiency is administered in a dosage of 100 to 200 mg intravenously once a day. The duration of treatment is 14 days.
- Ascorutin. Available in tablet form, which contains 50 mg of ascorbic acid and 50 mg of rutin. Vitamin C increases the activity of immunocompetent cells, improves tissue microcirculation and reduces vascular permeability. Vitamin P prevents the release of plasma from capillaries into soft tissues. Ascorutin should not be taken by people with increased blood clotting, fructose intolerance, hypokalemia, gout and hypercalcemia. The drug is taken 2-3 tablets per day for 3-4 weeks.
Herbal preparations
Homeopathic remedies based on the action of medicinal plants are taken to enhance the production of progesterone. Such drugs have a systemic effect on the entire body or act only on the hypothalamus, which regulates the functioning of the endocrine glands. These include the synthesis of female sex hormones.
Basic herbal preparations:
- Zhenimaks. The product contains stems and rhizomes of plants: morning glory, withania, turmeric and sandalwood. The active components in the product facilitate menstruation, increase libido and normalize hormonal levels. Zhensimax is available in the form of syrup. The product is taken 2 times a day, 1-2 tsp. within a month. The drug is prohibited for use by children under 18 years of age, people with diabetes mellitus and those with individual intolerance to the structural components of the drug.
- Cyclovita. The drug is available in the form of tablets, which contain a complex of vitamins, herbal ingredients and gum arabic. Cyclovita stimulates the production of progesterone by the corpus luteum and improves blood supply to the uterine endometrium. The medicine is taken 1 tablet per day. The duration of the course is 30 days. The drug is contraindicated in people with hypersensitivity to the structural substances that make up Cyclovita.
- Mastodinon. Available in the form of tablets or drops for oral use. The drug contains extracts of tiger line, violet, prutnyak, iris and cohosh. The drug suppresses the synthesis of prolactin, which inhibits the hormonal activity of the corpus luteum. Due to this effect, progesterone synthesis increases. The drug is prohibited for use by women with breast cancer, renal and liver failure, diabetes mellitus and glucose-galactose malabsorption. Mastodinon should be taken 1 tablet or 30 drops 2 times a day. Duration of treatment is 6 weeks.
Homeopathic remedies can only be taken with the permission of the attending physician. Plant extracts in their composition may increase the risk of side effects from hormonal drugs.
How do signs of deficiency appear?
The hormone is produced in the 2nd half of the cycle (in its luteal phase) by the corpus luteum of the ovary and the adrenal cortex.
During pregnancy, it is also produced by the placenta. In everyday life, together with other hormones, it is responsible for women's health , controls her ability to conceive, shapes the female body and even affects mental balance and psychological characteristics.
Both excess progesterone and its lack can lead to very serious consequences.
A lack of progesterone can be suspected if a woman suddenly begins to experience the following ailments:
- the mammary glands enlarge and become painful to the touch;
- painful and uncharacteristically heavy menstruation is observed;
- mood changes frequently and quickly;
- unusual irritability appears;
- headaches begin to bother you;
- the legs begin to swell or a feeling of heaviness appears in them;
- limbs become cold;
- weight increases;
- the skin turns pale and becomes drier;
- rashes appear on the skin;
- hair fall out;
- sweating bothers you;
- frequent constipation;
- problems with sleep appear.
Signs of progesterone deficiency (lack) in women
The following symptoms may indicate a lack of progesterone:
- migraine;
- emotional instability;
- mood swings;
- bloody issues;
- painful periods;
- swelling;
- increased vegetation;
- drying of the mucous membranes in the vagina;
- heaviness in the lower extremities;
- swelling of the mammary glands;
- weight gain before menstruation;
- hair loss;
- drying of the skin;
- the appearance of acne;
- sleep disturbance;
- pale skin, etc.
Climax
During menopause, hormonal changes occur in the female body. Due to a decrease in the functionality of the reproductive system, the concentration of progesterone decreases, so its deficiency is considered a natural phenomenon.
What can it lead to?
Almost any of the above symptoms can become so unpleasant that you need to see a doctor. However, this is not the worst thing that progesterone deficiency can lead to. A woman loses the ability to easily become pregnant or carry a child to term. Changes occurring in the endometrium of the uterine cavity depend on progesterone. The consequences of deficiency can be extensive endometriosis and other women's diseases.
Important! Among other things, progesterone during gestation suppresses myometrial contractions, preventing a possible miscarriage.
When a woman becomes pregnant, the center of hormone production changes . Initially, synthesis occurs in the corpus luteum. The synthesis function then passes to the placenta. In a pregnant woman, the main symptom of progesterone deficiency is miscarriage in the 1st trimester.
The level during pregnancy should reach a higher value than usual in phase 2 of the cycle, if conception does not occur. This happens because when an embryo appears in the body, the corpus luteum is activated, nourishing the fertilized egg.
In the absence or insufficiency of this process, there is a threat of miscarriage . This condition is manifested by bloody discharge and detachment of the fertilized egg, diagnosed by ultrasound.
Therefore, in the presence of progesterone deficiency, women are at risk for early miscarriages.
During menopause, the level of all hormones decreases. The body loses the ability to conceive children: for some this happens earlier - after 40 years, for others later - after 50. For a long time it was believed that the absence of progesterone during this period is normal, but in recent years doctors have come to the conclusion that the need to maintain balance during menopause.
A simultaneous decrease in progesterone and an increase in the amount of estrogen increases the risk of cancer processes in the uterus and endometrial hyperplasia. To find the required dosage you will have to take a hormone test. The restored balance during menopause will reduce its discomfort, eliminate heat and hot flashes, and also reduce the risks of developing pathologies inherent in this period.
Peculiarity ! Insufficiency of progesterone levels during menopause can be corrected with medication - hormone replacement therapy or a special diet.
The effect of foods on hormone levels
The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are the central glands that regulate the functioning of all the others. When they are not functioning properly, disturbances in hormonal secretion appear. Due to insufficient blood supply, the secretion of tropic hormones will decrease, and the work of all glands will begin to be inhibited. Pituitary hypogonadism is a disease that leads to miscarriage due to insufficient progesterone levels.
- menstrual irregularities;
- problematic conception;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- long delays in menstruation;
- During menstruation, a lot of blood is released;
- dyscirculatory uterine bleeding occurs;
- constant fatigue;
- fast fatiguability;
- the occurrence of edema;
- soreness in the mammary glands;
- frequent mood swings;
- migraine.
If one of the symptoms of low progesterone appears in women, doctors recommend undergoing a full study. It is important to consult a gynecologist-endocrinologist, since a lack of the hormone affects overall well-being and can provoke the development of serious diseases. To avoid serious complications, it is important to visit a medical facility in a timely manner and undergo all the necessary tests so that the doctor can make a diagnosis.
What foods increase progesterone in women? Avocado, raspberries, red peppers, nuts. To lower its level, it is necessary to exclude pork, poultry, and fats of plant and animal origin from the diet. Foods that lower progesterone in women are pumpkin seeds, nuts, legumes.
Why is there not enough and why is there a shortage?
There are many reasons that cause progesterone deficiency. Here are the most common ones:
- hormonal disbalance;
- presence of chronic untreated diseases;
- presence of gynecological diseases;
- dysfunction of the placenta or corpus luteum;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle;
- long-term drug therapy;
- oncological diseases;
- high emotional lability;
- excessive physical activity;
- smoking and excessive alcohol consumption;
- bad ecology;
- work in hazardous production;
- poor nutrition, lack of sleep and other delights of an unhealthy life.
Causes of progesterone deficiency
After conducting research and reviewing many clinical cases of progesterone deficiency, doctors have identified some patterns and the most likely causes of this pathology.
The most common causes of insufficient progesterone production by the glands include the following factors:
- Dysfunction of the corpus luteum or placenta, hormonal defects after abortion, disruption of the ovulatory cycle, frequent and heavy uterine bleeding.
- Pathological processes of various nature affecting the reproductive system.
- Kidney failure and other kidney pathologies.
- Violations of the psycho-emotional sphere of women.
- Excessive intensity of physical activity.
- Not the healthiest lifestyle (lack of sleep, unbalanced diet, excessively frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages, smoking and unfavorable environmental conditions).
- Taking a number of medications that can affect the synthesis of progesterone and estrogens.
Under these circumstances, progesterone deficiency develops quite rapidly and is characterized by certain symptomatic manifestations.
Features of synthesis
Progesterone begins to be synthesized only in the 2nd half of the cycle due to the fact that its formation depends directly on the corpus luteum, which is formed only after the follicle ruptures.
That is, the normal process of progesterone formation depends on estrogen , which regulates all processes occurring in phase 1 of the cycle. If there is not enough estrogen, the egg is unable to rupture the follicle, and progesterone production does not occur.
In the luteal (second) phase
The increase in the luteal phase promotes the formation of a dense endometrium. This is necessary so that the already fertilized egg can find its place and attach to the wall of the uterus.
With low progesterone, pregnancy will become impossible. The fertilized egg will not be able to attach to the uterus and pregnancy will not occur.
Attention ! The main reason for the lack of progesterone in this phase is the insufficient functionality of the corpus luteum.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for life is usually favorable; endocrine syndrome extremely rarely leads to severe life-threatening conditions. With regard to a woman’s ability to become pregnant and bear a child, the outcome of the pathology depends on many factors - the causes of progesterone deficiency, the duration of its course, and compliance with the treatment plan.
With correctly selected dosages of progesterone preparations, conception is possible within 2-3 months after the start of therapy; during pregnancy it is continued, taking into account changes in hormonal levels. To prevent the condition, you should mark the beginning and end of each menstruation on the calendar, thereby monitoring the duration of the cycle, and promptly treat inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, endocrine system, and kidneys. If you change the length of your menstrual cycle or the nature of your menstruation, you should consult a doctor.
Diagnostic methods
If a woman is concerned about the above symptoms, and in addition, problems with conceiving and bearing a child , it is necessary to take a test for the amount of progesterone.
Women should donate blood on the 22-23rd day of the cycle with an average length of 28 days, when the progesterone value is maximum.
If the cycle has a different duration, the day of the test is determined by the gynecologist. A pregnant woman can be tested any day.
If there is a long delay in menstruation, the analysis can be carried out at any time, but not only the level of progesterone alone is studied, but also all other hormones.
The following will also help determine the cause of the decrease:
- blood biochemistry - to determine the presence of liver pathologies;
- thyroid hormones - to determine the presence of hypothyroidism;
- Pelvic ultrasound to examine the condition and functionality of the ovaries, uterus and identify diseases in these organs;
- MRI of the brain to rule out a pituitary tumor.
Other tests may be prescribed for the examination, at the discretion of the attending physician.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
Diagnosis of progesterone deficiency is complex and multi-level. Some studies are carried out at certain periods of the menstrual cycle, so they may take a long time.
During the appointment, the doctor clarifies the phase of the menstrual cycle, how the last menstruation proceeded, and what unpleasant symptoms manifested itself. Based on the collected history and examination, further diagnostic methods are determined.
Determination of progesterone levels - blood is taken for analysis on days 21-23 of the cycle, in the morning on an empty stomach. In case of an irregular monthly cycle, the study is carried out several times. For women in menopause and pregnant women, tests are collected any day.
Using ultrasound, information is obtained about the condition of the endometrium, ovaries, and the presence of formations. Their correspondence to the day of the cycle is determined.
In some cases, additional examination is required: determination of the level of sex hormones, thyroid hormones, endometrial biopsy.
Hormone levels can be determined using a blood test.
Treatment
After identifying the reasons for the decline, its correction begins. First of all, the disease that caused this condition is treated. A woman should normalize her lifestyle - sleep should be at least 8 hours and must begin at 10 pm. You need to normalize your diet and adhere to a special diet. Stress should be avoided.
What to do?
Insufficient progesterone in pregnant women is treated with duphaston , which is taken every eight hours. For endometriosis, the medication is taken continuously or from the 5th to the 25th day.
When planning a pregnancy
When planning a pregnancy, women with infertility caused by luteal phase deficiency are prescribed duphaston from the 14th to the 25th day of the cycle for six months , and then switch to maintenance use until pregnancy.
Duphaston
Duphaston is also used to treat:
- premenstrual syndrome;
- irregular periods;
- dysmenorrhea;
- amenorrhea;
- uterine bleeding.
During hormone replacement therapy, duphaston is prescribed together with estrogens. Utrozhestan, which is prescribed in the same cases, has the same effect.
Oxyprogesterone
Oxyprogesterone oil solution is used for intramuscular administration. Oxyprogesterone is prescribed for threatened miscarriage and amenorrhea. The advantage of intramuscular administration is the gradual release of the hormone. The onset of menstruation is caused by the administration of Oxyprogesterone every other day. Typically, 3-5 injections are sufficient for these purposes. A week after the last one, menstruation begins.
Effective treatment
Most often, all doctors prescribe treatment with progestins. These are hormonal steroid drugs. They are one of the most effective ways to raise and normalize progesterone levels. After all, their structure is very similar to him. They can be used in several ways. Your doctor will help you choose the right one. For example, taken orally or intramuscularly.
Any hormonal drugs have a series of contraindications and side effects. It is recommended to start using them only after a doctor’s prescription. It is important to adhere to the dosage regimen. Do not forget that hormonal treatment is long-term and gradually disappears. But this is the only way to increase progesterone quickly and effectively.
Given the above, it is worth noting how important women's health and reproduction are. Unnoticed, everyday everyday problems, stress, and poor-quality food can cause serious health problems.
Therefore, it is very important to undergo examinations on time. Every woman should be examined by a gynecologist every six months. This way you can avoid many diseases. But the most important thing for all women is the opportunity to give birth to a child.
Nutrition
Nutrition during the treatment period should be rational . There are also specific foods that can positively affect progesterone production. This:
- legumes - beans, peas, lentils, etc.;
- almost all nuts;
- any dairy products, including fermented milk and cheeses;
- lean meat and liver;
- egg yolk;
- oatmeal and whole grain cereals;
- raspberries, avocado, olives.
Interesting ! The above foods do not themselves contain the hormone, but can stimulate its production in the body. To activate its synthesis, cholesterol is primarily needed. Therefore, meat and egg dishes, as well as fruits, potatoes, and fish are important in the diet.
Features of hyperprolactinemia
Thanks to prolactin, the mammary glands enlarge and milk production is activated. The level of this hormone increases after labor. If a patient is diagnosed with a tumor of the pituitary gland, the blood supply is disrupted, the regulation of the function of the hypothalamus has changed - the menstrual cycle is disrupted due to a lack of ovarian stimulating hormones.
There are several reasons that can affect hormone levels. Only after a thorough medical diagnosis can a doctor find out why a woman’s progesterone is low. Gynecologists and gynecological endocrinologists will help restore the patient’s health. Self-medication is prohibited, since the use of any medications not prescribed by a doctor can provoke the active development of diseases.
Symptoms and consequences
The severity of signs of progesterone deficiency depends on the degree of reduction in the amount of the hormone, the individual characteristics of the woman’s body, and the ratio with estradiol. Symptoms of progesterone deficiency are:
- uterine cycle disorders;
- problems with conception;
- fast fatiguability;
- swelling;
- severe premenstrual syndrome;
- loss of libido;
- miscarriages.
Pregnancy with progesterone deficiency is possible, but its further development is not. Functions of progesterone during pregnancy:
- decreased uterine muscle tone;
- suppression of local immunity (to prevent rejection of the fertilized egg, which is 50% genetically foreign).
If conception is successful and the woman knows about it, spotting or pain in the lower abdomen is a reason to immediately seek medical help.
Symptoms of low progesterone in women who did not know about pregnancy are heavy, prolonged bleeding, which indicates its termination. And in this case, examination and consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Low progesterone is dangerous in late pregnancy . This leads to post-maturity. Normally, delivery occurs after 40 weeks. A deviation of 2 weeks up or down is allowed. If labor does not occur by 42 weeks, the baby is at risk of injury. Postmaturity leads to ossification of the sutures (connections of bones) on the baby’s skull, the baby’s head cannot pass through the woman’s birth canal.
Symptoms of Low Progesterone Levels
Every woman can easily determine this based on her personal health. Characteristic symptoms:
- Frequent headaches;
- Unreasonable changes in mood;
- Constant feeling of fatigue;
- Hair begins to fall out a lot;
- The woman recovers quickly;
- The mammary glands swell;
- Irregular menstruation.
Most women do not consider these symptoms to be a sign of important changes. And in vain. If they are present, it is necessary to undergo examination and consult a doctor. Often when progesterone is low in women, symptoms do not appear immediately. It is important to listen to your own health and take it seriously.
Causes of low progesterone, external factors
The causes of low progesterone are not always pathological changes in the body. The amount of the hormone depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle.
- Low progesterone from the beginning of regulation until the onset of ovulation is a physiological norm. The lowest rates are recorded during this period.
- A natural decrease in progesterone concentration occurs during postmenopause. During this period, the maturation of germ cells in the woman’s body stops, the corpus luteum does not form, and the adrenal glands are not able to cover the deficiency. A decrease in progesterone and a relative increase in estrogen during this period increases the risk of developing malignant neoplasms in the uterus and excessive growth of the endometrium.
- Interfering factors, drugs that reduce progesterone - ampicillin, carbamazepine, cyproterone, danazol, epostan, estriol, goserelin, leupromide, oral contraceptives, phenytoin, pravastatin, prostaglandin E2.
- The performance of the endocrine glands is influenced by external factors, so a woman’s lifestyle indirectly affects the level of progesterone. Poor nutrition, physical inactivity, and especially chronic stress often lead to hormonal imbalance.
Between the ages of 35 and 50, progesterone production will drop by 75%
Beneficial changes in diet and lifestyle
During drug therapy, a woman needs to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
She will need to give up bad habits and adjust her diet by including:
- legumes;
- avocado;
- fish fillet of salmon, tuna, mackerel;
- nuts;
- poultry meat;
- sunflower seeds;
- eggs;
- cheese with a high percentage of fat.
Lack of progesterone in women, the symptoms of which lead to deterioration of the reproductive system, is eliminated with the help of B vitamins. They enhance the hormonal secretion of the corpus luteum, normalize the process of ovulation and the menstrual cycle.
It is recommended to take fish oil capsules once a day. It contains omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which stimulate hormone production. You should include foods rich in selenium and zinc in your diet. 70% of the diet should consist of vegetables and fruits.
A lack of progesterone in a woman’s body manifests itself as a result of improper functioning of the corpus luteum. The main reasons for this phenomenon are considered to be hormonal imbalances, infections or poor nutrition. Treatment of the pathology is carried out by a gynecologist or endocrinologist.
Luteal phase and deficiency
The luteal phase (or the corpus luteum phase, or progesterone phase) begins from the moment a mature and ready-for-fertilization egg leaves the follicle. This occurs on the 14th day of the cycle. Depending on the duration of maturation of the germ cell, the onset of ovulation is normal from the 12th to the 16th day. It is during this period that active synthesis of the pregnancy hormone occurs.
One of the reasons for low progesterone levels in the luteal phase is the condition of the ovaries. Pathologies causing physiological dysfunction of the gonads:
- Polycystic. With this disease, the mature follicle does not rupture. It remains in a cystic state. This is a pathological cavity with an overgrown wall and a non-viable egg inside. The ovaries are covered with unruptured follicles.
- Resistance (insensitivity). The female gonads do not respond to the follicle-stimulating (FSH) and luteinizing (LH) hormones of the pituitary gland, so the maturation of the egg does not occur.
- Hyperinhibition. Unfavorable environmental factors and the use of certain groups of medications cause organ dysfunction.
- Premature exhaustion. The pathology is caused by the early onset of menopause. The cessation of menstruation occurs in women aged 35-40 (normally after 45) under the influence of radiation, chemotherapy, chronic stress factors, and the use of certain pharmacological drugs.
Organic causes of progesterone deficiency in the luteal phase include the following diseases:
- endometriosis (excessive growth of the inner layer of the uterus);
- malignant tumor of the uterus, ovaries;
- uterine polyps (benign neoplasm);
- fibroids (hormone-dependent benign tumor of the uterus);
- endometritis (inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus);
- intrauterine manipulation (abortion, curettage).
What treatment
Treatment for progesterone deficiency in women involves the use of replacement therapy. Treatment tactics are determined individually and depend on whether the woman is pregnant or not, gestational age, the patient’s age, and the length of the menstrual cycle.
Hormone analogues are used in the form of tablets and suppositories for vaginal administration. The most frequently prescribed drugs: Duphaston, Utrozhestan.
Tablets are prescribed for the following progesterone deficiency conditions:
- infertility;
- mastopathy;
- premenstrual syndrome;
- menstrual irregularities.
Suppositories are used to prevent premature birth, in preparation for IVF to maintain the luteal phase, threatening abortion. During menopause, treatment with progestins is combined with estrogen-containing drugs.
Impact of pathologies
Hyperprolactinemia
One of the functions of prolactin is the production of breast milk. After childbirth, there is a natural increase in the concentration of the active substance. A pathological increase in the hormone occurs with pituitary tumors. The functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary system is disrupted and FSH and LH, which stimulate ovarian production, are disrupted. Disorder of the menstrual cycle is a consequence of pathological changes.
Hyperprolactinemia and low progesterone levels in the postpartum period are normal physiological phenomena . High prolactin inhibits the formation of eggs and protects the woman’s body from unwanted pregnancy during breastfeeding.
Disorders of the functions of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland
The pituitary gland and hypothalamus coordinate the work of all endocrine glands. Under the influence of their hormones (in particular, follicle-stimulating and luteinizing) the formation of active substances responsible for the maturation of the egg, conception, pregnancy, and childbirth occurs. Tumors of the pituitary-hypothalamic system and impaired blood supply to this part of the brain cause a lack of progesterone and lead to problems with pregnancy.
Placental insufficiency
One of the functions of the placenta is secretory. It is a temporary endocrine gland. Starting from the 16th week of pregnancy, the placenta begins to actively synthesize progesterone. If pathologies of its formation are observed, progesterone decreases, and problems arise with further bearing a child.
Hyperandrogenemia
The cause of an excess amount of male hormones in a woman’s body is a tumor of the ovaries and adrenal glands. Excess androgens cause anovulation. A dense capsule is formed in the gonads, which prevents the release of a mature egg.
Thyroid dysfunction
An insufficient amount of thyroid hormones (hypothyroidism) in the female body negatively affects fertility and hormonal levels in general.
Under the influence of thyroid hormones, a protein is synthesized in the liver that binds estradiol and testosterone. If the amount of this protein is insufficient, a large amount of free testosterone appears in a woman’s blood, which suppresses ovulation. In this case, the corpus luteum is not formed, and the concentration of progesterone remains minimal.
Pathology of the thyroid gland associated with insufficient secretion of hormones causes an increase in the concentration of estrogen . This disorder leads to a decrease in the production of FSH and LH (according to the feedback law) and disruption of the menstrual cycle. Women with thyroid hormone deficiency develop infertility. When pregnancy occurs, there is a risk of self-abortion or the newborn is diagnosed with congenital hypothyroidism.
What is progesterone responsible for in the female body?
Hormonal levels and the functionality of the endocrine system are the key to women's health. This hormone progesterone is responsible for:
- Regulating the menstrual cycle.
- Formation of libido.
- The ability to conceive and bear a child.
If the level of this hormone decreases, a woman cannot become pregnant. Progesterone is responsible for successful fertilization. Therefore, every woman should monitor its level. Especially if you are planning a pregnancy.
It is worth noting that during an interesting situation, progesterone levels increase 15 times. Until week 16, progesterone is actively produced by the corpus luteum. Then its functionality transfers to the placenta. At this time it is already fully formed.
Read about increased progesterone in women - causes and consequences here
Diagnosis of low progesterone
Indications for prescribing a blood test for progesterone are cycle disorders, miscarriage, and threatened miscarriage. With a 28-day cycle, laboratory material is submitted on days 22-23. In other cases, the day of the test is determined by the doctor. In pregnant women, blood sampling to determine the concentration of progesterone is done regardless of the period.
If there is a significant delay in menstruation, a comprehensive analysis takes place. In addition to the concentration of progesterone, the amount of the following hormones is determined:
- follicle-stimulating;
- luteinizing;
- human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG);
- estrogens;
- prolactin;
- testosterone;
- cortisol.
Complications
The most common complications of progesterone deficiency are infertility and miscarriage. The weakening of the feedback between the release of progesterone, follicle-stimulating hormone and estrogen leads to a greater imbalance in the endocrine part of the reproductive system. The consequence of this is the development of ovarian cysts and an anovulatory menstrual cycle.
Anomalies of endometrial trophism and changes in the nature of the secretion of the cervical canal increase the risk of infection of the uterine mucosa with pathogenic microflora (endometritis). Hormonal imbalance leads to pathologies of the mammary glands. Against the background of this condition, mastopathy occurs; during pregnancy with a lack of progesterone, galactorrhea is very often recorded.
What are the symptoms of hormonal deficiency?
You should know that estrogen-progesterone deficiency occurs either asymptomatically or with the presence of manifestations. In the first case, it is detected by chance. For example, when a woman cannot get pregnant for a long time and undergoes a comprehensive examination.
The following symptoms of progesterone deficiency are identified:
- the menstrual cycle becomes longer;
- attempts to conceive a baby for a long time do not give a positive result;
- the ensuing pregnancy ends in miscarriage;
- a disease of the mammary glands appeared;
- the lady has a low body temperature;
- limbs swell;
- spotting vaginal discharge appears either in the middle of the cycle or before menstruation;
- premenstrual syndrome has vivid manifestations of specific symptoms: irritability, tearfulness, frequent mood swings and others.
Expert opinion
Alexandra Yurievna
General practitioner, associate professor, teacher of obstetrics, work experience 11 years.
A decrease in the level of progesterone in a woman’s body may be indicated by such manifestations as the development of flatulence or the appearance of pain in the abdomen.
Often women do not associate them with the problem of prolonged non-pregnancy, and therefore do not report them to the gynecologist.
How is hormonal deficiency diagnosed?
In order to prescribe competent treatment, it is necessary to correctly diagnose.
What could be the reason?
For this purpose, the following methods are used:
- Screening of venous blood for hormones. In order to obtain adequate results of blood tests, with a 28-day menstrual cycle, it is necessary to take a blood test to determine the estrogen level on the 3rd day of the cycle, and to determine the progesterone level on the 21-22nd day.
- When a woman’s menstrual cycle exceeds 28 days or is shorter, the dynamic ultrasound diagnostic method is used. It allows you to monitor the stage of ovulation and the development of the corpus luteum.
- If it is not possible to use ultrasound, then the woman measures her basal temperature. This is a very simple but effective method that allows you to determine the onset of ovulation by a sharp drop in basal temperature. During the luteal phase of the cycle, basal temperature gradually increases.
- A special study is carried out - a smear to check for infections in the genitourinary tract.
In order to obtain the maximum amount of information, doctors prescribe all diagnostic methods in combination. The lady measures her basal temperature on her own.
To obtain reliable information, you must adhere to the following requirements:
- use the same thermometer every day;
- measure temperature at one time;
- Carry out the procedure without getting out of bed.
There are several ways to measure basal temperature. The thermometer can be taken into the mouth or placed in the vagina or anus.
The most reliable indicators of basal temperature are obtained by placing a thermometer in the anus at the same distance every morning.
If there is not enough progesterone in males
Not only women suffer from a decrease in progesterone; a lack of this hormone in the male body can also negatively affect his health. As a result, male sexual desire decreases. If the activity of the adrenal cortex decreases, in addition to low levels of progesterone, impotence develops.
Therefore, a man is also recommended to promptly seek medical help in case of problems with the genitourinary system.
Characteristic symptoms
A deficiency in the production of the hormone progesterone affects a woman’s well-being and health. To a greater extent, a hormonal imbalance or deficiency occurs, which provokes the development of various kinds of symptoms in the form of diseases. The female reproductive system suffers.
The reasons for low progesterone levels in a woman’s body are symptoms:
inflammation in the ovarian area , or formations of various types .
This list of provoking factors is supplemented by numerous stressful situations. This concerns the emotional state, hormonal imbalance. The lack of the basics of a healthy lifestyle and balanced nutrition only aggravates the situation. After all, abuse of alcoholic beverages and excess fatty and floury foods provoke low progesterone. This situation occurs quite often after crossing the 35-year mark.
In addition to bad habits and frequent stressful situations, a number of other reasons can be identified. We are talking about physiological disorders when the development of the ovaries is impaired. Hereditary factor , or taking medications also plays a significant role. In particular, this applies to taking antidepressants and hormonal contraceptives.
If a girl is overly keen on diets, or has some kind of infectious disease, the situation only gets worse.
It should be noted that jumps in the concentration of symptoms of the hormone progesterone do not always depend on the age category; signs of deficiency can also occur in a woman under 35 years of age. In order to avoid negative consequences, you should pay attention to the following signs of deficiency:
- quite severe headaches, attacks of nausea and vomiting are also possible. There is a decrease in blood pressure;
- the digestive process is disrupted. This manifests itself in flatulence and fairly persistent constipation. A woman suffers from regular bloating;
- fluctuations in body temperature;
- a woman suffers from excess hair;
- A typical situation for a lack of symptoms of the hormone progesterone is vaginal dryness. During sexual contact, a female representative feels discomfort and pain;
- the abdomen and breasts increase before the onset of menstrual periods;
- difficulty controlling body weight, regular weight fluctuations.
Article on the topic: Normal levels of the hormone 17-OH-progesterone in women: reasons for increase and decrease
If a woman is expecting the birth of a baby, then it is necessary to pay attention to the following signs of hormone deficiency:
- pain that is localized in the lower abdomen. They can have both a pulling and a sharp character;
- The lower back also suffers during this period, pain is noticeable;
- Blood discharge is also possible. All this indicates uterine hypertonicity.
It is worth seeking help from a doctor in a timely manner. Thanks to this, it becomes possible to normalize the symptoms of a woman’s hormonal imbalance. Thanks to this, she can carry the baby normally and ensure its development. You should not ignore the fact that one or several symptoms characteristic of this condition appear. After all, this is fraught without taking appropriate measures, the development of infertility, or a number of diseases accompanying this condition.
Progesterone norm
Before discussing the problem of progesterone deficiency, it is necessary to understand where this substance comes from and what its normal concentration in the blood is.
Progesterone is a female sex hormone secreted by the corpus luteum, a formation that emerges from the follicle after the release of the egg during ovulation. The place of synthesis of this substance is the ovaries, and a small part of it is produced in the adrenal cortex and placenta during pregnancy. FSH plays a major role in the synthesis of progesterone, a hormone that stimulates the growth and maturation of follicles. If the latter is lacking, the corpus luteum may not appear at all.
There is no single indicator for the norm of progesterone, since the amount of this hormone varies greatly at different periods of the menstrual cycle. For example, before ovulation, when the follicles are just maturing, its content in the blood may not exceed 0.35-2.25 nmol/l, while in the ovulatory phase this value reaches 0.5-9.5 nmol/l.
In postmenopausal women, when follicle maturation and ovulation no longer occur, progesterone levels are low - up to 0.65 nmol/l, which does not negatively affect health.
Treatment of progesterone deficiency
It is necessary to treat progesterone deficiency only together with a gynecologist, since self-administration of any hormonal medications can only aggravate the situation and harm the reproductive system. Therapy depends on what stage of deficiency the girl has.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to undergo a full examination: do an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, do a blood test for biochemistry and hormones, and also do an MRI to detect abnormalities in the pituitary gland.
Oral contraceptives
Low progesterone during the first half of the menstrual cycle, when ovulation has not yet occurred, can be corrected with the help of oral contraceptives, which will gradually stimulate the maturation of the follicles, and after their rupture, prolong the life of the corpus luteum. Progesterone-containing OCs include the following drugs:
- Duphaston;
- Ingesta;
- Utrozhestan.
Usually, OCs are able to correct the reduced level of the hormone to normal within a few months, but with such treatment it is necessary to strictly observe the regularity of taking pills, because skipping even one can significantly reduce the effectiveness of therapy.
Hormone therapy
If low progesterone is observed in the luteal phase, when the corpus luteum should produce the hormone most actively, treatment with hormonal birth control pills will be powerless. In this case, therapy should consist of Progesterone in ampoules or injections, and sometimes it is replaced with Endometrin, a drug with the same active ingredient.
Such hormonal therapy gives a significant effect, but can be dangerous because it disrupts the functioning of the entire endocrine system if the dosage is incorrect or the drug is not selected correctly. Additionally, many women experience hair loss and weight gain after progesterone treatment.
Low progesterone in women signals problems in the pituitary gland or abnormal maturation of the follicles, which is why this hormone is produced in small quantities. Such a deviation rarely goes away on its own, but the consequences of lack of treatment can be serious, so you should contact a gynecologist and undergo the necessary tests if symptoms of progesterone deficiency are detected.
httpss://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SrMbLXfZQSs
What are the functions of the hormone
Progesterone production occurs in the second part of the menstrual cycle. When the follicle bursts, progesterone is produced after the corpus luteum appears. Then the egg matures and further ovulation occurs. After which the follicle ruptures and the egg is released from the ovary.
If there is a lack of progesterone, the egg does not mature and the follicle cannot rupture; as a result, ovulation does not occur and this hormone is not synthesized further. And if there is an excess of tarragon, then the menstrual cycle increases and progesterone is suppressed. In the absence of conception, hormone production decreases. Such circumstances eventually lead to rejection of the mucous membranes of the uterus, as its smooth muscles rapidly contract.
Thanks to the normal production of this substance, the mucous membrane of the uterine part remains normal, and the glandular epithelium in the milk ducts is not disturbed. Nothing prevents the eggs from moving freely through the fallopian tubes to the uterus.
The production of progesterone and estrogen is influenced by the hypothalamus, located in the cortical part of the brain. This area regulates endocrine processes in the body. When certain areas of the brain, including the hypothalamus, are damaged, progesterone production is noticeably reduced. This may be indicated by a blood test or the detection of pregnanediol in the urine.
As a result, we can summarize what functions the hormone progesterone affects:
- The endometrium has an effect, which contributes to the preservation of the fetus.
- Prepares the uterine walls for attachment of the embryo to them, making them more loose.
- Slows down the contractility of the uterus.
- Prepares the mammary glands for milk production.
Consequences of progesterone deficiency
Every girl should regularly visit a gynecologist, because this is the only way to notice the manifestation of a lack of hormones. To diagnose a lack of progesterone, it is necessary to do a blood test every 1-2 years to determine the content of sexually active substances, this is especially important for those who have once had problems with reproductive health.
If a girl ignores the symptoms of progesterone deficiency, then gradually she may develop other problems:
- prolonged disruption in the frequency of the menstrual cycle;
- lack of ovulation;
- very painful and heavy periods;
- vaginal dryness;
- diseases of the reproductive organs (uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, too thin endometrium);
- infertility;
- obesity.
Low estradiol and progesterone during puberty can negatively affect the development of the reproductive system, often causing serious problems with fertility in girls in the future.
Low progesterone during pregnancy is also dangerous, because this hormone “protects” the baby’s health - it constantly reduces the synthesis of estrogen, which can cause miscarriage. That is why pregnant women must undergo tests every 2-3 months and be under the supervision of a doctor.
Can thyroid hormone levels be affected?
Progesterone in women - what is it? How does the thyroid gland affect its indicator? This is a hormone that is responsible for the regularity of the menstrual cycle and the possibility of bearing a fetus. During the development of hypothyroidism, hormonal levels may be disrupted. Under the influence of thyroid hormone, a protein is synthesized in the liver that removes testosterone and estradiol. With protein deficiency in the blood, active testosterone increases, which suppresses ovulation. Under such conditions, the corpus luteum cannot mature. If there is a deficiency of thyroid hormones, estrogen is inactivated, which leads to an increase in their concentration, resulting in disruption of the menstrual cycle. Under such conditions, women are often diagnosed with infertility. In some cases, conception occurs, but it is not always possible to bear a healthy baby. Quite often, newborns are diagnosed with hypothyroidism.
Recommendations for patients
It is very important not only to undergo proper treatment for low progesterone in the luteal phase, but also to follow the following recommendations:
- Healthy diet. Meals should include whole foods, plenty of high-quality protein, fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Women are advised to drink plenty of water and avoid alcoholic beverages, caffeine and sugar.
- Avoid stress. In the luteal phase, a decrease in progesterone may be associated with prolonged or chronic stress. The body then requires more progesterone to produce cortisol. This means that during LF progesterone is not enough to carry out its direct functions.
- The use of medications that help normalize the functioning of the adrenal glands and glands that produce cortisol, which can also be useful in increasing progesterone levels and stabilizing the luteal phase.
- Experts recommend using special supplements to maintain progesterone: Wild Yam, Vitex, Melatonin and vitamin B6.
- Elimination of genital infections and inflammatory processes in the appendages and uterus. This is done by taking antibacterial medications.
- Maintaining hygiene and rules of intimate life. A woman is recommended to have regular sex life with a regular sexual partner, which will help avoid many serious consequences such as contracting sexually transmitted infections and disrupting the vaginal microflora.
Standard therapy for progesterone levels below normal in the luteal phase is based on the use of medications. Vitamin complexes, the use of antiestrogens, the use of human chorionic gonadotropin preparations, follitropins - all this is recommended to be done at the same time. Complex treatment allows you to increase progesterone and prevent such serious consequences of this condition as infertility, miscarriage, placental insufficiency, endometrial and breast cancer, the formation of polyps and fibroids.
Low progesterone: treatment
If you ignore treatment for low progesterone, the following complications may occur:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding that can last more than a week. As a rule, in such a situation one cannot do without drug intervention.
- The cycle may be severely disrupted or menstruation may stop altogether.
- Miscarriage.
Before you begin drug treatment for low progesterone, you need to:
- Adhere to the rules of rational nutrition.
- Increase the amount of vitamin E consumed, since it is it that is involved in the production of progesterone and has a decisive role in its proper distribution.
- Avoid stressful situations as much as possible.
- Do not overuse trips to the gym. Perhaps intense running should be replaced with yoga.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Get more rest.
- Do not make your own decision regarding the choice of oral contraceptive.
As for medications, today they can effectively solve the problem of low progesterone. They produce drugs of both synthetic and natural origin. Particular care should be taken when choosing a drug during pregnancy. Only a doctor can prescribe a hormone! Remember that this is not a vitamin and has a number of contraindications. The most popular drugs containing progesterone are Utrozhestan and Duphaston.
Symptoms of high progesterone
High progesterone in the second half of the monthly cycle is characterized by the following symptoms:
- hypersensitivity of the mammary glands;
- mood changes;
- the appearance of bloody discharge from the vagina;
- pain in the head;
- decreased sex drive;
- flatulence;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- frequent and prolonged migraines.
Sometimes acne appears in large numbers on the patient’s body. They are very deep and occupy almost the entire thickness of the skin. Sometimes women's hair becomes terribly brittle and gradually begins to fall out.
What to do if there is a lack of hormone?
Treatment with drugs
The plan for correcting hormonal levels depends on the causes of the pathology - an oncologist deals with tumor processes, and an endocrinologist deals with thyroid dysfunction.
Hyperprolactinemia of a functional nature is treated using the drugs Cabergoline, Bromocriptine.
Hormonal therapy is prescribed for infertility, if there is no menstruation (due to illness or psychosomatics) or progesterone is low in pregnant women with a threat of miscarriage, to stop uterine bleeding, with PMS, amenorrhea, with early or severe menopause (in combination with estrogen).
Progesterone replenishment pills
The most effective are Utrozhestan (contains a natural hormone of the corpus luteum), Duphaston (an artificially developed analogue of endogenous progesterone), Oxyprogesterone (an oil solution of a natural hormone for intramuscular administration).
Folk remedies for low hormones
Plants that can initiate the independent production of progesterone by the female body:
- crushed twig fruits (2 tbsp) are poured into 0.5 liters of boiling water, the mixture is set aside until it cools - the infusion should be drunk (consumed little by little) 2 days before;
- plantain seeds (1 tsp) are mixed with chopped cuff leaves (1 tbsp) and poured with a glass of boiling water, after cooling, the product is taken 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. l.;
- astragalus root (1 tbsp) is crushed, poured into a thermos, into which 0.5 liters of boiling water is poured, after half an hour you can drink the infusion - take 70 ml after meals three times a day;
- mix dried raspberry and wild yam leaves (take 1 tablespoon of each herb), pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, drink the infusion warm throughout the day;
- Baikal skullcap (100 g of roots) is placed in a dark glass container, 250 g of alcohol or vodka is poured in, infused for a month, and taken for a long period of time, 30 drops 3 times a day.
An infusion is made from the roots of skullcap and taken for a long period of time.
With low progesterone, it is recommended to drink herbal infusions in the second half of the menstrual cycle, that is, from 15 to 25 days.
To maintain the correct level of hormones, women are advised to monitor their diet, walk as often as possible in green areas, get enough sleep, avoid stress, regularly (once a year) undergo preventive examinations and do not hesitate to go to the doctor if any symptoms begin in the body. problems.
Rate this article ( 2 ratings, average 5.00 out of 5)
The most important female hormones
The female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone are synthesized in overwhelming quantities by the ovaries. A small amount of them is produced by the adrenal cortex. The menstrual cycle has 3 phases, which occur under the influence of a certain sex hormone.
What do the gonads influence?
Let's take a closer look:
- The follicular phase is influenced by the hormone estrogen. Under its influence, a dominant follicle is released in the ovaries, in which an egg develops for subsequent fertilization. At the same time, the endometrium, the inner layer of the organ, grows in the uterus under the influence of estrogen. In order for a fertilized egg to implant into the endometrium, it must have a thickness of 11-12 mm. Against the backdrop of rising estrogen levels, the endometrium is saturated with blood and nutrients so that in the event of pregnancy, the egg has all the conditions for growth and development.
- The ovulatory phase lasts one day. Approximately 12-16 days from the beginning of the menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs - the egg leaves the follicle and moves along the fallopian tubes towards the sperm. If all circumstances are successful, conception will occur in the woman’s body.
- The luteal phase occurs under the influence of the hormone progesterone. It is produced by the corpus luteum, a temporary endocrine gland that forms in the ovary at the site of the released egg. If fertilization of the egg has occurred in the female body, then pregnancy will occur under the influence of progesterone, and if not, then menstruation will begin.
As you can see, estrogen-progesterone deficiency will lead to either a lack of ovulation or a pregnancy failure.
Help with folk remedies
To eliminate the lack of progesterone, in addition to medications, traditional medicine is also used. A variety of herbal infusions are commonly used. However, before starting a course of treatment, it makes sense to consult a doctor so as not to increase its level too high.
Traditional healers recommend using the following remedies to raise the level of this hormone in the blood:
- Raspberry infusion. It is prepared from the dry leaves of this plant, poured with 2 cups of boiling water. This collection will have to brew for an hour, and then it will be drunk in small portions during the day.
- Infusion of raspberries and yams. Dry raspberry and wild yam leaves are required. They are poured with boiling water and infused for several hours, but the finished drink is drunk before meals, 1 tbsp. 3 times a day.
- Infusion of plantain seeds. 1 tbsp. seeds and cuffs are poured with boiling water. The infusion is taken regardless of meal time three times a day.
- Infusion of twig. The fruits of the plant are crushed and poured with 2 cups of boiling water. The infusion sits for 2 hours, after which it is taken in small portions throughout the day.
It is worth remembering that all the recipes described here can be used starting from the 15th day of the menstrual cycle.
Another way to improve low hormone levels is through diet. Women with low levels should definitely include chicken, eggs, fatty cheeses, seeds and nuts in their diet. Fatty sea fish, such as tuna, salmon, and mackerel, are very useful for increasing progesterone levels.
Hormone levels and causes of deficiency in different periods of life
- the occurrence of painful menstruation, while bleeding can appear even in pauses between menstruation;
- the appearance of pain during sexual intercourse due to vaginal dryness;
- the occurrence of stomach problems in the form of constipation or increased gas formation;
- a sharp enlargement of the mammary glands and the occurrence of pain when touching the nipples;
- sudden swelling of the legs, a feeling of heaviness in them;
- sudden weight gain during the premenstrual period;
- capriciousness, suspiciousness, the appearance of hysterics and general emotional instability, manifested in causeless sobs or laughter;
- constant debilitating headaches;
- presence of cold feet and hands;
- sudden hair loss;
- the appearance of skin rashes such as pimples and acne;
- the appearance of painful menstruation with foul-smelling discharge;
- insomnia;
- violation of the body's thermoregulation in the form of freezing or excessive sweating;
- the occurrence of skin problems in the form of stretch marks, dryness and pallor of the epidermis.
We should also talk about the symptoms of progesterone deficiency during pregnancy. The fact is that during this period this hormone is busy suppressing contractions of the smooth muscles of the uterus. When it is not produced enough in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, there may be a risk of miscarriage.
Signs of this disease in pregnant women usually include changes in the composition of the blood and urine, so it is vitally important to be under constant medical supervision during pregnancy. Giving birth at home is strictly prohibited, as this is fraught with unplanned termination of pregnancy, threatening the woman’s life.
- improper formation and functioning of the corpus luteum or placenta;
- abortion and subsequent disruption in the hormonal system;
- congenital and acquired diseases of the female reproductive system;
- diseases of the genitourinary apparatus and excretory system;
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- long-term use of a number of medications;
- the presence of malignant tumors;
- stress and increased physical activity;
- poor diet and lack of sleep, smoking and drinking alcohol.
It is worth highlighting separately the cases when a woman “sits” on a fashionable diet and, as a result, loses her weight uncontrollably. So she can reach an extreme degree of exhaustion, which will force the body to stop producing hormones. In addition, if she begins to use hormonal contraceptives without any control, this will cause a disruption in the endocrine system, which will lead to a lack of progesterone.
A frozen pregnancy leads not only to miscarriages, but also to the fact that a woman develops an inferiority complex. As a result, she cannot find a man, conceive and bear a child.
- when taking oral contraceptives;
- depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle;
- during pregnancy;
- during lactation.
Lack of progesterone in women
| Phase of the menstrual cycle | Progesterone content, nmol/l | Hormone norm when taking oral contraceptives, nmol/l |
| Follicle maturation | 0,32-2,25 | less than 3.6 |
| Release of the egg into the uterine cavity | 0,49-9,4 | 1,52-5,45 |
| Corpus luteum phase | 6,95-56,63 | 3,01-66,8 |
| Postmenopause | less than 0.64 | less than 3.19 |
Symptoms of progesterone deficiency in the female body occur for the following reasons:
- violation of the secretory function of the corpus luteum;
- hormonal imbalance after abortion;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- alcohol intoxication;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system;
- kidney damage;
- sleep disturbances, unbalanced diet;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle, frequent intrauterine bleeding;
- malignant neoplasms;
- stress, emotional turmoil;
- heavy physical activity.
Pregnancy
The concentration of progesterone in the blood may vary depending on the trimester of pregnancy. Moreover, its content in plasma can reach up to 771 nmol/l, which is due to constant changes in the emotional and physical state of a woman.
| Trimester | Hormone norm, nmol/l |
| 1 | 8,9-468,5 |
| 2 | 71,5-303,2 |
| 3 | 88,7-771,5 |
Progesterone production increases toward the end of pregnancy due to fetal growth. The embryo increases in size, stretching the uterus, which leads to a reflex contraction of the smooth muscles of the organ. To prevent endometrial contraction, glands on the placenta begin to synthesize progesterone. The hormone has a sedative effect on the muscles of the uterus, reducing the risk of miscarriage.
The cause of hormone deficiency during pregnancy is:
- poor nutrition;
- exhaustion;
- dehydration;
- antibacterial therapy;
- uterine bleeding;
- chronic pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- infections;
- placental abruption.
After childbirth, progesterone synthesis decreases - the woman’s body prepares for lactation, which activates the production of prolactin. The latter suppresses the synthesis of female sex hormones.
After 40 years, metabolism slows down, aging processes are activated, which negatively affects ovarian function. As a result, the production of progesterone and estrogen gradually decreases. The main reason for the decrease in progesterone concentration is the depletion of the endocrine glands.
Climax
During menopause, the norm of progesterone is 0.64 nmol/l. The reason for the decrease in the concentration of sex hormones is age-related changes in the body. Progesterone levels may drop to 0 nmol/L during menopause. This phenomenon is considered normal, because during this period the endocrine glands are depleted and do not receive enough oxygen and nutritional compounds.
Against the background of hypoxia and impaired tissue trophism, the ovulation process stops. As a result, the egg does not enter the uterine cavity and in its place the corpus luteum does not form, which would produce progesterone.
If progesterone deficiency is observed during pregnancy, the uterus begins to actively contract, which can lead to miscarriage in the first trimester. In late pregnancy, placental abruption and premature birth with complications are possible.
She will need to give up bad habits and adjust her diet by including:
- legumes;
- avocado;
- fish fillet of salmon, tuna, mackerel;
- nuts;
- poultry meat;
- sunflower seeds;
- eggs;
- cheese with a high percentage of fat.
Lack of progesterone in women, the symptoms of which lead to deterioration of the reproductive system, is eliminated with the help of B vitamins. They enhance the hormonal secretion of the corpus luteum, normalize the process of ovulation and the menstrual cycle.
It is recommended to take fish oil capsules once a day. It contains omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which stimulate hormone production. You should include foods rich in selenium and zinc in your diet. 70% of the diet should consist of vegetables and fruits.
A lack of progesterone in a woman’s body manifests itself as a result of improper functioning of the corpus luteum. The main reasons for this phenomenon are considered to be hormonal imbalances, infections or poor nutrition. Treatment of the pathology is carried out by a gynecologist or endocrinologist.
Features of treatment
There is no single scheme that can successfully treat estrogen-progesterone deficiency in different patients. Treatment is always individual. It depends on the results of the diagnosis and the causes of hormonal imbalance. The doctor will prescribe a specific hormonal drug, its dose and course of treatment.
It is strictly not recommended to treat hormonal disorders on your own. Each medicine has its own indications and contraindications. Only a specialist will be able to select the optimal drug, based on test results and taking into account the patient’s health condition.
The most popular medications for the treatment of such hormonal disorders are Duphaston and Utrozhestan. Treatment of estrogen-progesterone deficiency can be carried out with the following hormonal drugs: Janet, Novinet, Mercilon, Ovidon, Tri-Regol and others.
Expert opinion
Roman Andreevich
Candidate of Medical Sciences, gynecologist-obstetrician, 14 years of work experience.
To get a consultation
In case of deficiency of only estrogen, the following drugs are prescribed: Proginova, Ovestin, Ovepol, Estrogel, Hormoplex, Hormoplex and others.
Video about progesterone deficiency
There are more than sixty hormones in the human body, and the balance between them creates a hormonal background. They are sometimes called angels of life. They determine a woman’s appearance, her well-being, and dictate her body parameters:
- weight;
- height;
- the constitution;
- skeletal structure;
- condition of the skin and mucous membranes;
- psycho-emotional state.
If a woman pays enough attention to herself not only during Balzac and old age, but throughout the entire reproductive period, she will be able to delay the changes that occur in the body with age. Sex hormones that are produced in the body determine the level of female reproductive health and, to some extent, influence it.
In general, the level of this hormone affects the psycho-emotional sphere: resistance to stress, emotional stability, and good mood depend on it. If an estrogen deficiency develops in the body, a woman stops liking not only herself, but also those around her:
- Her skin becomes dry, premature wrinkles appear, her hair becomes dull and thin, her nails become brittle and brittle.
- Excess hair may appear in areas of the skin where it should not be.
- Body weight changes and adipose tissue accumulates.
- Disorders of the central nervous system appear.
With an increased level of estrogen, body weight increases. Fat is deposited on the stomach and thighs. Sexual desire decreases and premenstrual syndrome may develop. Sometimes a disease such as migraine appears and develops. There is a threat of developing benign tumors of the mammary glands and ovaries. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment to reduce the level of the hormone.
In the first days of pregnancy, more precisely, up to eight weeks, progesterone plays a leading role in maintaining pregnancy. After the eighth week, the leading role is played by the placenta, which is formed before twelve weeks. Progesterone plays a huge role during pregnancy, but there are significant features in its production that many do not know.
The first feature is its short half-life. In the blood, its indicator is not constant, it changes during the day: it increases, then it can decrease. It begins to be produced in a pulsating mode and disintegrates very quickly. The only purpose of checking progesterone levels during pregnancy is to determine whether the level is high or low in the early stages, as it is a test for the viability of the pregnancy.
- A mid-luteal phase serum progesterone test in women planning pregnancy to determine whether ovulation has occurred. If it was, the hormone level will be high, if it was not there, it will be low.
- A test in the early stages of pregnancy to determine its viability.
Indications for the use of progesterone today:
- Progesterone deficiency, which has been proven. However, during pregnancy it is quite difficult to prove this. Therefore, this question remains exploratory and empirical.
- Habitual miscarriage.
- Artificial ovulation.
- Defective corpus luteum of the egg during the follicular period.
The age of a woman is decisive in the development of menopause (Greek - “step”). At a certain period in the life of any biological individual, not only humans, a period begins that is characterized by involution, the extinction of the function of the reproductive system. This is the transition from productive age to old age. However, the high frequency and severity of sex hormone symptoms significantly reduce quality of life.
In past centuries, menopause was not talked about as a disease. At about 40 years of age, the involutionary process begins. At this age, the ovaries no longer respond to hormones produced by the pituitary gland. Menstruation stops, which indicates the onset of menopause. The life period when the menstrual cycle completely stops is called menopause. A woman’s entire life—from puberty to old age—is divided into three stages:
- Premenopause, the period from the moment of the first menstruation until its cessation.
- Menopause is the time of life after one year from the last menstruation.
- Postmenopause is life two years after the cessation of menstruation.
The following factors influence early menopause:
- regular active smoking;
- serious illnesses;
- gynecological operations, including numerous abortions;
- removal of the ovaries (so-called castration);
- severe prolonged stress;
- underweight, exhaustion caused by diets;
- type 1 diabetes mellitus.
During menopause, weight typically increases. This is normal: it should increase, normally - plus 5 kg to its usual weight. This happens because fatty tissue produces hormones, such as estrogens. You can't lose weight using fad diets. It is very important to establish proper, nutritious nutrition and drinking regimen. You need to drink water at the rate of 30 mg per 1 kg of weight.
The level of progesterone in the female body constantly changes depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. In the follicular phase its amount is small. And after ovulation, the place of the burst follicle is replaced by the corpus luteum (temporary secretion gland). It produces progesterone, preparing the uterus for the implantation of an embryo, and the woman’s body as a whole for pregnancy.
If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum regresses on its own, the hormone level decreases and menstruation begins. When the embryo implants into the uterus, the gland continues to produce progesterone until the placenta takes over this function.
A natural cause of low progesterone is the onset of menopause, when the ovaries stop functioning properly and producing eggs. In this case, the adrenal glands cannot provide normal concentrations of progestins in the blood. In other cases, low progesterone indicates the development of pathology.
The pituitary gland and hypothalamus are responsible for the functioning of the endocrine glands, so disruption of their functions negatively affects the production of hormones in the body. The cause of this pathology may be:
- neoplasms in the area of these brain structures;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- pituitary dwarfism (dwarfism).
Causes of low progesterone in the luteal phase include:
- benign or malignant neoplasms in the pelvic organs;
- polycystic ovary syndrome (the mature follicle does not come out, and a cyst forms in this place);
- the use of drugs that suppress the functions of the pituitary gland;
- endometriosis or endometritis;
- premature ovarian failure (cessation of menstruation in women under 45 years of age as a result of chemotherapy or radiation).
Hyperandrogenemia
The cause of low progesterone may be neoplasms in the ovaries or adrenal glands, which produce the male sex hormone testosterone. As a result, the ovaries are covered with a dense capsule that does not allow the egg to pass through. The woman does not ovulate, and the corpus luteum, which secretes the hormone, is not formed.
Pathologies of the thyroid gland lead to the fact that thyroid hormones, which affect the synthesis of a special protein that binds and removes testosterone and estradiol from the body, are produced in insufficient quantities. As a result, their number in the body increases, which negatively affects ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum.
Progesterone levels may be affected by thyroid disease
Hyperprolactinemia
Prolactin is a hormone that in the female body is responsible for the growth and development of the mammary glands, and also stimulates lactation in the postpartum period. It suppresses the production of progesterone, thereby protecting the woman from re-pregnancy while breastfeeding.
But in some cases, an increased amount of prolactin is also observed in non-pregnant women. This is possible with neoplasms in the pituitary gland or cerebrovascular accidents. Excessive amounts of the hormone negatively affect egg maturation and ovulation.
Normally, after the sixteenth week of pregnancy, the placenta takes over all functions of producing progesterone. But there are certain pathologies that can disrupt this process. These include:
- disruption of the formation of the placenta (as a result of genetic abnormalities);
- premature aging of the placenta (due to metabolic or circulatory disorders in certain areas);
- placental calcification (causes may be bad habits, urogenital infections, systemic diseases).
Other factors
Other factors that negatively affect progestin levels in women include:
- heavy physical activity;
- stressful situations;
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- unhealthy diet, in which the diet contains little fat and protein of animal origin.
Symptoms of low progesterone in women:
- fatigue that occurs in the absence of physical activity;
- menstrual irregularities, prolonged heavy menstruation;
- severe premenstrual syndrome;
- swelling;
- skin disorders: stretch marks on the skin, the skin becomes pale and dry, may peel, skin rashes;
- insomnia;
- hair loss;
- violation of the body's thermoregulation, resulting in severe sweating or frequent chills;
- threat of miscarriage or termination of pregnancy in the early stages;
- infertility.
Swelling may indicate a decreased hormone level
The fact that a man has low progesterone may be indicated by such signs as excessive emotionality, increased irritability, and frequent mood swings. Representatives of the stronger sex, whose amount of the hormone is too low, often become depressed.