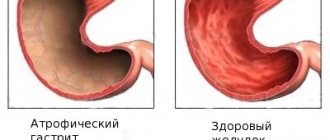
Diseases of the digestive system have similar symptoms. Patients complain of abdominal pain, nausea, and stool disorders. Such signs can occur in various diseases, so you should never self-medicate.
It is necessary to contact specialists and undergo a series of examinations. Most often, patients experience stomach problems. Modern diagnostics of gastritis allows not only to detect the presence of inflammation, but also to determine the type of disease. To make a diagnosis, a number of examinations are necessary.
Visual examination of the patient
When the first symptomatic signs appear in the form of spasmodic pain in the stomach after eating food, nausea, vomiting, unstable stool, or general malaise, you should immediately seek help from a gastroenterologist. At the first appointment, the doctor conducts a conversation with the patient, measures body temperature, and visually examines the patient.
Then the gastroenterologist palpates the epigastric area - palpating, pressing on the organ of the digestive system. The presence of pain when pressing indicates an inflammatory disease of the stomach. If a corrosive form of pathology is suspected as a result of chemical poisoning, the gastroenterologist examines the oral cavity for the presence of white, yellow or black coating on the tongue, depending on the substance. After a visual examination, the doctor determines methods for diagnosing gastritis.
Who will never become a donor
Permanent contraindications are established until the end of life. They do not depend on a person’s desire; they are caused by the presence of diseases of internal organs, in which a decrease in blood volume can cause exacerbation. Another reason is the risk of transmitting the donor’s disease through the blood. The list includes:
We also recommend reading: What blood type is a universal donor?
- chronic infectious diseases (regardless of the stage and success of treatment) - AIDS, HIV-infected persons, viral hepatitis, syphilis, tuberculosis, brucellosis, tularemia, typhus and leprosy;
- parasitic infections - echinococcosis, leishmaniasis, toxoplasmosis, trinanosomiasis, filariasis;
- neoplasms with a malignant course;
- blood diseases;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels (coronary and hypertension, atherosclerotic changes, defects, inflammatory diseases of the heart, arteries and veins);
- damage to the respiratory system (asthma, obstructive diseases with emphysema);
- diseases of the digestive system (gastric and duodenal ulcers, hypoacid gastritis, liver cirrhosis, calculous cholecystitis, unclear hepatitis);
- renal pathology (urolithiasis, glomerulo- and pyelonephritis);
- endocrine diseases with metabolic disorders;
- radiation sickness;
- complex connective tissue diseases;
- previous removal of an organ;
- high myopia (6 diopters or more);
- inflammation of bone tissue (osteomyelitis);
- purulent-inflammatory diseases of the eyes, nasopharynx;
- skin autoimmune, fungal and pustular diseases.
Sore throat should be treated
What types of tests are taken for gastritis?
Diagnosis of stomach disease is a complete medical examination after a clinical examination of the patient. To determine the form of gastritis, the following is prescribed:
- laboratory research;
- instrumental examination;
- passing special tests.
It is these methods that will allow us to determine the nature and extent of damage to the digestive system.
Laboratory research
Taking tests is the first stage in diagnosing stomach pathology. Laboratory research includes:
- blood tests (general, biochemical);
- submitting feces and urine to identify pathogenic bacteria in the body.
A general blood test for gastritis is collected from the ring finger to determine the number of leukocytes, red blood cells, platelets, and hemoglobin level. The biochemical procedure involves taking material from a vein to determine the content of pepsinogens, bilirubin, phosphatases, and antibodies. A blood test for gastritis allows you to identify the cause of the inflammatory process for an accurate diagnosis. Indicators different from the norm may indicate the presence of diseases of the digestive organ or autoimmune system, pancreatitis.
A urine test, which must be taken in the morning, can identify kidney problems. Fecal masses are collected to determine acidity, the presence of enzymes responsible for the digestion of food consumed, and harmful substances that lead to malfunction of vital organs and systems. There is a test to detect internal bleeding in the presence of black or bloody stool.
Instrumental research
After receiving the laboratory test results, an internal examination of the damaged stomach walls is necessary. To identify the severity of the disease, there are several instrumental diagnostic methods:
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- biopsy;
- analysis of gastric juice;
- radiography;
- pH measurement procedure.
Instrumental research is intended to detect gastric pathology in order to prevent the spread of pathogens that destroy the walls of the digestive system organ.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy
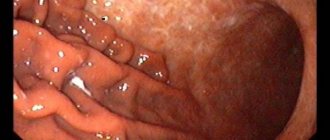
Gastroscopy is the most commonly used method for recognizing the presence of damage to the mucous membrane. To perform endoscopy, a smooth probe is inserted into the patient's stomach, at the end of which a camera is attached for inspection. A flexible hose - a gastroscope - is passed through the esophagus directly to the digestive organ. The camera displays an image of the stomach on a monitor, on which the doctor can see pathological changes. FGDS allows you to determine the form of gastritis by the depth and distribution of damage to the upper layer of the mucous membrane, the presence of an ulcer.
Biopsy
The gastroscope is intended not only for visual inspection of the digestive organ, but also for taking biological material from the walls of the stomach. The safe procedure is carried out painlessly by biting off the upper surface of the mucosa.
For a biopsy, cells from a healthy and pathologically altered membrane are taken to identify the location of damage to the stomach. The extracted tissue fragments will allow us to determine the activity of bacteria in the fundus, antrum and central region.
Gastric juice analysis
The material is collected during fibrogastroduodenoscopy using a gastroscope with built-in instruments. Before the analysis, you need to eat a special breakfast that contains foods that promote the active secretion of gastric juice. The substances contained make it possible to determine the causes of inflammation in the stomach.
Radiography
This procedure is an addition to gastroscopy in identifying the inflammatory process of the gastrointestinal tract. Before the x-ray, you should not eat anything for 12 hours. At the beginning of the procedure, the patient swallows a substance that allows one to visually examine the nature of the relief of the gastric mucosa, determining whether the pathology indicates the presence of an ulcer, gastritis and even cancer. During radiography, the patient must take different positions to assess the tone of the digestive system organ.
pH measurement procedure
To detect changes in acidity levels, a special procedure is prescribed, which is carried out in several ways:
- express analysis;
- daily analysis;
- acidotest.
A quick version of the analysis involves inserting an elastic probe directly into the stomach to detect the content of hydrochloric acid using fixed electrodes.
Daily pH-metry determines the level of acidity over a 24-hour period. This procedure is carried out by inserting a thin gastroscope through the nasal passage, the data of which is displayed on a special device attached to the patient. Another option is to use a miniature capsule, which, when it enters the stomach, attaches to the wall of the mucous membrane, determines the level of acid content, and after a day leaves the body naturally. pH-metry analysis can be performed during an endoscopic examination in order to collect material for measuring indicators.
The insertion of a probe is contraindicated after surgery. Therefore, to detect the level of acidity inside the stomach, special drugs that change the color of urine at low or high levels.
Endoscopic diagnostics
A more advanced method that requires certain skills and special equipment. It is carried out according to indications identified through clinical diagnostics, after visiting a therapist, most often with definite gastritis or suspicion of it.
It is based on an endoscope - a tube with various devices at the end, which is passed through the esophagus into the stomach. Diagnosis with an endoscope is a fundamental method in gastroenterology; without it, you can’t go anywhere, as they say. At the tip of the endoscope there may be devices such as a flashlight, a camera, forceps for taking biopsy samples, a laser for cauterization, etc. A detailed description of the entire procedure requires a separate article. Patients often call the procedure “gut swallowing.”
Endoscopy includes gastroscopy, FGS, FGDS, biopsy, probing.
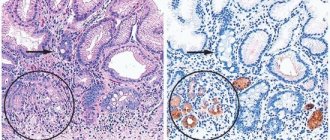
At this stage of diagnosis, we can already talk about the nature of the damage to the mucous membrane, but we still cannot talk about infection with H. pylori; for this, a laboratory analysis of the biopsy sample is done for bacterial culture.
Special examination
When carrying out basic comprehensive measures of laboratory and instrumental research, the doctor prescribes special tests aimed at identifying harmful microorganisms and bacteria, the ingress of which could cause the inflammatory process. Such pathogens include chlamydia, trichomonas, parasites, and infection (Helicobacter pylori).
To identify microorganisms, blood is drawn, a biopsy is taken, dental plaque is examined, and a breath test is performed, which is performed in several stages:
- the patient breathes into the tube for 2-3 minutes;
- the patient drinks the urea solution and then breathes into the tube again.
In the presence of an infectious bacterium, the content of carbon dioxide released during exhalation is high, which quickly reacts with the urea solution. Before the respiratory test, it is necessary to disinfect the oral cavity; you must not smoke, drink alcohol, chew gum, or eat peas, beans, corn, or soy.
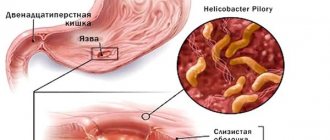
Detection of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori
Previously, the main causes of gastritis were considered to be frequent stress, eating food that irritates the mucous membranes, and irregular nutrition. Only recently have scientists discovered that more than half of the cases are associated with infection. Its danger lies in its oncogenicity - the bacterium can provoke the formation of malignant tumors.
Helicobacter pylori can be detected in the body using the following methods:
- Based on the results of a stool examination. For this purpose, feces are collected in a sterile pharmaceutical container. You cannot take samples from the toilet bowl, as there may be particles of disinfectants there. Feces must be delivered to the laboratory a maximum of 0.5 days after collection. The analysis must be stored in the refrigerator at a temperature no higher than 2 degrees. The results are ready after several hours of waiting and give an accurate answer to the question about the presence of Helicobacter pylori in the body.
- Enzyme immunoassay of venous blood. Detects antibodies to bacteria. If they are detected, a study is carried out using the Western Blot method. In the fluid from the vein, the amount of IgA antibodies to the microbe is determined, thereby establishing the stage of the disease.
Preparing for diagnosis
Before conducting laboratory and instrumental studies, it is necessary to undergo training to obtain reliable results. Patients must follow the general rules:
- Tests are taken on an empty stomach 12 hours before the material is collected;
- a few days before the examination, it is necessary to exclude harmful foods from the diet: spicy, salty, fried, smoked foods;
- giving up bad habits (alcohol, tobacco products) 2-3 days before diagnosis;
- Before donating blood, you must avoid physical activity;
- You should refrain from taking medications at least 7 days before the scheduled examination;
- Before donating feces, you should not eat foods that change the color and texture of biological material: beets, grapes, cabbage, carrots, radishes.
Test results can be affected by genetic characteristics, emotional tension, stress, physical fatigue, and recent illnesses. Therefore, these factors must be avoided before undergoing the study. Blood tests for gastritis, urine, and stool can be taken at a public clinic or private laboratories.
Diagnostics is a mandatory stage in identifying the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane of the digestive organ and prescribing treatment methods. Tests for gastritis are a necessary procedure to identify the causes of the development of pathology. Diagnosis involves various research methods depending on the nature of the symptomatic signs of the disease. Timely medical examination will prevent the progression of chronic, acute gastritis.
We recommend: What are the symptoms of gastritis - types, diagnosis and methods of treating the stomach
Other restrictions
The instructions do not allow people who have had:
- allergic reactions - two months;
- exacerbation of vegetative-vascular dystonia - one month;
- elevated temperature - one month.
In addition, it is necessary to take into account how much time has passed since the last vaccination. Contraindications are defined for each type of vaccine. The temporary delay in donation ranges from ten days to a year. During the examination, the infectious disease specialist indicates them exactly.
In case of an existing disease that is not included in the list, the order requires that all controversial issues be resolved by committee (by clinic specialists and the transfusiologist of the Blood Transfusion Station).
If a person really wants to, but cannot become a donor, do not be upset. Donation always needs help in organizing “Donor Days” and promoting the movement. Here you can bring no less benefit.