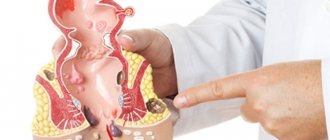
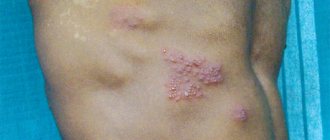
Types of purulent hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids with pus are a clear symptom of inflammation in the intestines. The disease has characteristic sensations:
- pain syndrome;
- burning;
- severe itching;
- swelling of the hemorrhoidal area;
- discharge of fluid from the anus.
Hemorrhoids can cause purulent discharge of various compositions.
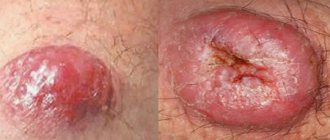
When a blood clot forms in the area of the hemorrhoid or suppuration of the tissues surrounding the rectum, purulent hemorrhoids occur
Depending on the form of the disease, the affected area and the cause of the disease, there are different forms of hemorrhoids:
- by localization: acute: subcutaneous, retrorectal and submucosal;
- chronic, according to the location of the focus: front, side and back.
- acute: simple, anaerobic, after injury and specific;
- simple;
Blood from the anus
Excessive enlargement of the venous nodes, their proliferation and prolapse from the anus can be another cause of blood discharge. The bleeding that accompanies hemorrhoidal disease can be mild, usually occurring during bowel movements, or heavy, which is observed both during bowel movements and outside of this process.
There are a number of factors that provoke the appearance of blood from the rectum.
- Chronic constipation, in which hardened feces, passing through the rectal cavity, scratch the mucous membrane, as well as the hemorrhoidal formations themselves, thereby causing bleeding from the rectal canal.
- Cracks and tears in the anus, also appearing due to injury to the mucous membrane and skin by compressed feces.
- Frequent diarrhea, which causes thinning and further damage to the mucous membrane.
- Prolonged stay on the toilet, accompanied by strong straining, which leads to bleeding.
To eliminate this symptom, wound healing and hemostatic agents are usually prescribed, for example, Anestezol, Anuzol, Proctosan, Detrolex, Phlebodia 600, Hemoroidin.
What are the prerequisites for the occurrence of purulent hemorrhoids?
Not in all cases, hemorrhoids fester; inflammation can occur in a simple form and cause a minimal amount of negative effects.
Hemorrhoids with suppuration are formed due to 3 main conditions:
- the presence of a thrombus in the node. If treated, discharge from hemorrhoids begins only after the inflammatory process worsens. Swelling in the rectal area gradually increases and an abscess appears. The development of inflammation leads to the formation of a blood clot, which contributes to the appearance of swelling in the nearby area. Necrosis and festering hemorrhoids soon appear;
The appearance of such a pathology indicates the presence of severe inflammatory processes in the rectum
- paraproctitis in purulent form. Refers to inflammation in the intestines, but in a complicated form. When the disease appears, the quality of the microflora of the stomach and intestines is disrupted. Soon the prerequisites for the appearance of acute and severe forms of inflammation appear;
- anal fissures trigger processes with negative consequences for the intestines. Purulent discharge from hemorrhoids does not appear for no reason; they are complications from the long-term chronic course of the disease.
The discharge of pus is not always provoked by suppuration of the nodes; there are other disorders in the body that provoke a similar condition.
Purulent discharge and hemorrhoids can provoke the following conditions:
- Ulcerative colitis is an acute inflammation localized in the gastrointestinal tract. The disease is often accompanied by patches of blood in the mucus;
- the presence of tumors regardless of their quality;
- fistula of the perirectal space. Pus is not released from the anus, but through the fistula. It can be seen just behind the nodes;
- negative reaction of the body to surgery performed in the rectal area or intestines. This is a dangerous condition because the pus from hemorrhoid removal leads to the opening of the area where the operation was performed. Feces with all dangerous microorganisms can enter the site of the intervention, which creates a risk of various complications.
Read also
Rehabilitation after hemorrhoid removal surgery
Types of purulent hemorrhoids depend on its shape, location and causes of formation
Mucus discharge
One way or another, a healthy intestine secretes a small amount of mucus necessary to maintain its normal dynamics. When any inflammatory processes occur, the mucous membrane tends to change its structure, and in such a situation, the function performed by the mucus present is undeniable, since it prevents the intestinal tissue from sticking together.
However, an increased amount of pathological secretions produced is a deviation, the internal cause of which must be sought. Ignoring this fact can lead to a number of subsequent logical symptoms that are often found with hemorrhoids. We are talking about constant irritation of the skin by mucus and the resulting formation of various erosions, the presence of which only increases the sensation of itching, a traditional companion of hemorrhoidal disease.
Very often, excessive secretion of clear, viscous fluid from the anorectal canal occurs in combination with constipation or diarrhea, colic and bloating. Moreover, any mucous discharge can be observed not only during the act of defecation. A very advanced form of hemorrhoids can lead to anal sphincter insufficiency, and in such a situation, mucus is able to remind itself regardless of bowel movements.
The clinical picture under consideration is a serious reason for an urgent visit to the doctor, since mucus can be not only one of the symptoms of hemorrhoids, but also a sign of other developing diseases, which include:
- rectal fistulas;
- ulcers;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- condylomas;
- colon infections, such as gonorrhea or tuberculosis;
- inflammatory processes: proctitis, paraproctitis, sigmoiditis, proctosigmoiditis;
- irritable bowel syndrome.
First symptoms
The disease is a consequence of a passive lifestyle, excess body weight, consumption of large amounts of junk food, alcoholic beverages, etc. Hemorrhoids appear in half of all women after childbirth.
Discharge from hemorrhoids - symptoms:
- discomfort in the hemorrhoidal area;
- burning and itching are manifestations of mucous secretions that have an irritating effect on the skin. The appearance of fluid is a consequence of the inflammatory process in the walls;
- bleeding occurs in most cases of the disease. It can be almost invisible, and given the appearance of fluid only after bowel movements, blood may not be noticed. To determine the presence of blood clots, you need to examine the surface of the stool. In some cases, drops or stream may appear after defecation;
- nodes falling out. Initially, the symptom becomes noticeable only with severe stress, often with constipation. Over time, loss occurs every time you have a bowel movement, and then for no apparent reason or with minimal exertion. At the initial stages, the nodes do not require reduction; they return on their own. If the condition worsens, you have to contact a specialist for adjustment.
If the listed symptoms appear, perhaps some of them, you need to contact a proctologist. The delicacy of the problem leads to embarrassment for some patients, which is why people often seek help in the later stages of the disease. As it progresses, the risk of complications increases.
The disease manifests itself as pain, burning and itching in the anus
What to do and how to treat
If the first signs of the disease appear, the following will help alleviate the condition:
- physiotherapy;
- diet to eliminate chronic long-term constipation;
- taking mild laxatives, preferably on a natural basis;
- cool lotions and baths that have an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect;
- use of sanitary napkins and antibacterial agents after bowel movements, careful adherence to personal hygiene.
If the discharge becomes complicated, the temperature rises, hemorrhoidal cones fall out, or heavy bleeding begins, then hospital treatment will be required, and in some cases, surgery.
Today, the following minimally invasive methods are used to remove nodes in late stages:
- Sclerotherapy - a special substance is injected into the node to stop the arteries.
- Ligation - latex rings are used to compress the nodes, the blood supply is stopped, they dry out and come out during defecation.
- Cryotherapy – cauterization with liquid nitrogen at low temperatures.
- Desarterization is the most modern and effective method, which involved stopping each artery and suturing the node to the walls of the mucosa, which prevents its loss.
Traditional methods
They are often recommended by doctors themselves as an addition to general conservative treatment.
The most effective and proven:
- decoction of camel thorns for baths;
- medicinal fume juice - 0.5 tbsp. l 3 times a day;
- woodlice juice - 0.5 tbsp. l. every 2 hours;
- black nightshade - a decoction for baths is prepared at the rate of 8 tbsp. l. for 2-3 liters of boiling water. Dry branches are infused for four hours and sitz baths are made.
- borage juice to stop bleeding - a dessert spoon 4 times a day.
Causes of paraproctitis
The appearance of paraproctitis can be provoked by the general condition of the body or illness. Among the main causes and risk factors:
- decreased immune function;
- exhaustion of the body;
- chronic pathologies;
- infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in chronic or acute form;
- frequent diarrhea or constipation;
- proctological diseases: simple hemorrhoids, fissure, papillitis, proctitis, cryptitis.
Pus from hemorrhoids can also mask other diseases that affect the intestines.
Features of the treatment of hemorrhoids with pus
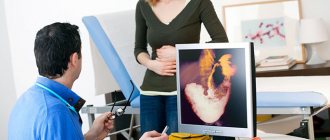
An abscess with hemorrhoids should be treated only under the supervision of a proctologist. With timely treatment, a specialist will help prevent complications and speed up recovery. Based on what pus looks like in hemorrhoids, you can learn about the involvement of other organs and the degree of neglect of the condition. As the source of inflammation spreads, the pelvic organs are involved in the pathological process. For men, the most common lesion is the urinary canal, and for women - the vaginal area.
Read also
Hemorrhoids and anal fissures
In advanced stages of the disease, surgical intervention is required
More often, the doctor prescribes surgical intervention, but with a small focus of suppuration, an alternative in the form of drug treatment may be offered.
Treatment with medications is based on antibiotics and ointments for external use with anti-inflammatory effects.
If the doctor strongly recommends surgery, it implies the need to eliminate the abscess. Treating purulent hemorrhoids surgically means opening the abscess and eliminating the exudate. After the operation, the patient notes a general improvement in well-being: the body temperature decreases and the severity of intoxication symptoms decreases. For complete treatment, 2 operations are indicated, the second is required to eliminate the hemorrhoid.
Treatment of purulent hemorrhoids in the final stages becomes especially difficult; the disease cannot be easily eliminated. If the disease has led to the appearance of fistulas, additional surgery will be required to eliminate them, otherwise there is a high probability of relapse. Therapy will require subsequent use of medications, as there is a risk of oncology.
Drug therapy
At the initial stage of the disease, it is recommended to use drug therapy. The specific treatment regimen is prescribed by the treating proctologist. The therapy uses enemas, suppositories and ointments that target the problem area to provide maximum benefit.
Purulent hemorrhoids at an early stage of formation can be treated with medication
Effective drugs for purulent hemorrhoids:
- “Phlebodia” eliminates venous congestion and increases vascular tone;
- "Betiol" accelerates wound healing and prevents erosion;
- "Detralex" restores the tone of the veins in the anus and strengthens the blood vessels;
- “Relief” stimulates rapid healing of wounds;
- "Troxevasin" eliminates inflammatory reactions;
- "Procto-Glivenol" is a symptomatic drug to eliminate pain and discomfort;
- Proctosan reduces the risk of bleeding and accelerates regeneration processes.
If the medication regimen does not have the desired effect, the doctor prescribes surgery.