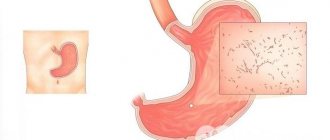
Briefly about the duodenum
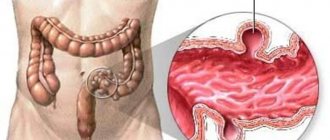
It is the initial section of the small intestine; its length averages about 30 centimeters. It is fixed with the help of connective tissue fibers to the walls of the abdominal cavity. The common bile duct and the main pancreatic duct open into the lumen of the duodenum. At the site of their exit there is a major papilla (Vaterov), and in the area of the accessory duct of the pancreas there is a small papilla (Santorini). With their help, the release of pancreatic secretions and bile into the intestinal lumen is dosed. The duodenum consists of 4 main membranes:
- mucous membrane;
- submucosa;
- muscular;
- serous.
With duodenitis, various layers of the intestine can be affected, but most often the inflammatory process affects the mucous membrane.
The main functions of the duodenum are:
- neutralization of the acidic contents of the stomach, turning it into an alkaline environment with the help of Brunner's glands located in the submucosal layer. They are the ones who produce a thick mucous secretion that neutralizes acids;
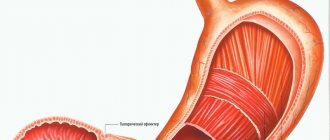
- regulation of the reflex closing and opening of the pyloric sphincter of the stomach, thereby allowing the bolus of food to enter the small intestine;
- initiation and control of the production of bile and pancreatic enzymes depending on the chemical composition and acidity of the food gruel.
With duodenitis, disturbances occur in almost all functions of the duodenum, which leads to negative consequences for the entire body.
What causes chronic duodenitis
Reasons leading to the appearance of chronic duodenitis:
- Intestinal pathology leading to deterioration of peristalsis, stagnation of intestinal contents, stretching of the walls and atrophy of the duodenum mucosa: prolonged constipation, intestinal adhesions, impaired blood supply and nervous regulation of the intestine.
- Chronic gastritis with high acidity causes acid damage to the intestinal epithelium with the gradual development of its atrophy. Gastritis-duodenitis is formed.
- An abnormality of the liver, gallbladder and pancreas leads to disruption of the release of enzymes into the lumen of the duodenum, which impairs its functioning.
- Regular violation of diet and nutrition.
- Food allergies.
- Prolonged stress.
- Taking a lot of medications.
- The presence of bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking, substance abuse).
Types of duodenitis
First of all, the following forms are distinguished:
- spicy. It develops against the background of poisoning with heavy metals (mercury, lead), concentrated acids or alkalis. It is also detected in some infectious diseases, such as salmonellosis. In this case, it is combined with inflammation of the stomach and other parts of the intestines. It is characterized by the development of superficial inflammation of the duodenal mucosa, the appearance of erosive defects and rarely phlegmon (diffuse purulent foci). Depending on these processes, erosive, phlegmonous and catarrhal duodenitis are distinguished;
- chronic. It is characterized by a long course, with alternating phases of exacerbation and remission (absence of symptoms of the disease). Often combined with other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (chronic pancreatitis, gastritis, peptic ulcer). The following types are distinguished: superficial, atrophic (with atrophy of the mucous membrane and a decrease or complete absence of goblet enterocytes necessary for the production of mucus) and erosive duodenitis.
Also distinguished:
- limited form , the inflammatory process in which is localized in a certain area of the duodenum (descending, ascending, horizontal or upper part - the bulb);
- widespread - inflammation can affect several parts of the intestine at once.
The duodenal bulb is most often affected.
Causes of development of superficial gastritis (superficial duodenitis)
The following are the main reasons for the development of this pathology:
- Poor nutrition. Lack of a routine, dry food, fast food snacks on the go, as well as excessive consumption of heavy and fatty (smoked, spicy) foods and marinades are very harmful to the stomach and duodenum.
- Constant stress, depression and moral tension also negatively affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Unhealthy lifestyle: drinking alcohol, smoking and lack of physical activity.
- Exposure to chemicals.
- Treatment with medications. Long-term use of many of them injures the mucous membrane of the duodenum and stomach. Steroids are especially dangerous in this regard.
- The presence of diseases of the biliary tract and liver.
- Development of Helicobacter pylori bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract. In children, pathology can occur through infection from adults, due to poor nutrition, salmonellosis and helminthic infestations.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Genetic predisposition and decreased immunity. In such cases, the pathology very quickly takes on an atrophic form.
- Anemia.
- Allergy.
- Penetrating radiation.
- Severe infections.
- Cardiac and pulmonary pathologies.
Superficial gastritis and duodenitis are the initial stage of development of a full-fledged pathology.
Symptoms of duodenitis
Acute forms occur with more pronounced clinical symptoms, which are characterized by the following manifestations:
- severe pain in the epigastric region, intensifying after eating after 1 - 1.5 hours and when palpating the abdomen;
- nausea;
- sometimes vomiting once or twice;
- significant weakness, malaise;
- lack of appetite;
- increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels (up to 37.5°C).
When the phlegmonous form of duodenitis occurs, the general condition noticeably worsens: abdominal pain can be diffuse, body temperature rises to more than 38°C, and vomiting occurs more often.
Chronic superficial duodenitis may not make itself felt for a long time. Other forms are characterized by alternating periods of remission and exacerbation (usually in the spring and autumn). The latter is characterized by:
- pain in the epigastrium with the erosive form, a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the stomach for the atrophic one. Painful sensations can also be permanent, and with local inflammation of the papilla of Vater, they can resemble similar sensations to those with hepatic or renal colic (they arise due to a pronounced violation of the outflow of bile);
- periodic feeling of nausea;
- increased gas formation, rumbling and bloating (flatulence);
- bowel disorder - constipation may alternate with diarrhea.
Some clinicians identify the following forms of chronic duodenitis:
- ulcer-like, manifested by “hungry” and “night” pain in the epigastric region, frequent sour belching and persistent constipation;
- gastritis-like - with heartburn and pain after eating;
- cholecyst-like, which is characterized by a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, severe pain in the right hypochondrium, vomiting bile;
- neurovegetative, manifested by a feeling of weakness, general malaise, increased sweating, rapid heartbeat;
- pancreatic-like, expressed in the form of pain in the left hypochondrium or encircling nature, vomiting, instability of stool, prone to diarrhea;
- mixed, which is expressed in various combinations of the above options.
If you have similar symptoms, you can contact general practitioners or gastroenterologists.
Therapy
As data from the tests is received, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment to the patient. Therapy is selected on a purely individual basis, based on the indications and characteristics of the human body. Taking into account all indicators, drug therapy, physiotherapy, as well as some traditional methods of treatment (if there is such a need) are prescribed separately.
Also, the patient must adhere to a diet. The diet is developed taking into account the patient’s personal needs, tolerance and intolerance to certain foods. It is worth noting that dietary nutrition is a key point in the patient’s recovery.
Important: To develop a balanced and healthy diet, you must visit a nutritionist. This way the diet will bring more tangible results.
Medication
Drug treatment of the duodenum is prescribed based on the cause that provoked the development of the inflammatory process. So the treatment might look like this:
- For an anti-inflammatory effect, the patient is prescribed special enveloping drugs - de-nol, almagel, maalox, phosphalugel.
- When helminths and giardiasis are detected, effective chemotherapy is necessary - Chloxin, Flagyl.
- If pathogenic bacteria are detected, the patient must undergo a course of antibiotics. At the same time, it is recommended to take drugs that restore the microflora.
- with increased acidity, antacids and agents that reduce the production of hydrochloric acid - omeprazole, ranitidine - are recommended.
When taking medications, be sure to read the instructions for them. Increasing or decreasing the dose on your own may lead to not just a lack of effect, but also the possibility of developing complications.
Important: If there is no effect from taking the pills, you should consult your doctor again. In the future, he will replace the existing drugs with more suitable ones. A complete change in treatment tactics is also possible.
Traditional methods
In the treatment of duodenitis, the presence of traditional methods of treatment is also allowed. They are relatively safe for almost everyone with any health condition. In addition, they provide truly worthwhile and effective results.
Shows excellent results in the treatment of duodenitis:
- chamomile decoction;
- yarrow decoction;
- honey;
- Melissa;
- sage;
- rose hip;
- sagebrush;
- thyme;
- St. John's wort;
- shepherd's purse.
Freshly squeezed vegetable juices perform well - potato, carrot. During the treatment period, it is strongly recommended to drink the required amount of water and green tea (without sugar).
Before using any folk remedies, it will not be superfluous to obtain a preliminary consultation with a doctor.
Diagnostics
A competent specialist may suspect inflammation of the duodenum even when interviewing the patient. But for a more detailed and accurate diagnosis, the following laboratory tests and instrumental types of research are used:
- fibrogastroscopy (FGDS) with biopsy is the “gold standard” of diagnosis. Allows you to identify various changes in the mucous membrane of the duodenum (atrophy, erosion, hemorrhage, superficial inflammation, metaplasia - a precancerous condition);
- Fluoroscopy of the duodenum using contrast agents. Helps in detecting violations of the motor-evacuation function of the intestine, gross thickening of the mucosa or erosions, allows you to identify various deformations of the bulb or other parts of the intestine;
- determination of Helicobacter pylori using urease, bacteriological, enzyme immunoassay or other tests;
- duodenal intubation, with the help of which the quality of digestion and duodenal secretion is determined. It is a fairly informative, but almost forgotten diagnostic method;
- computer gastroenterography or duodenokinesiography are one of the new ways to determine the motor function of the duodenum;
- examination of blood and feces for parasitic infestation.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Treatment of superficial duodenitis involves an integrated approach using medications, diet and traditional medicine recipes. In addition, it is important to strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations and instructions.
The following medications may be required:
- Antispasmodics (Drotaverine, No-Shpa) - to relieve painful symptoms.
- Enveloping medications (Almagel, Maalox) – when inflammation of the duodenum is associated with erosive damage. Additionally, you can take Omeprazole, De-nol.
- Antiemetics (Domperidone, Motilium) - for vomiting, intramuscular administration of drugs is used.
- To reduce stomach acid - Gaviscon, Rennie.
- To reduce irritation on the mucous membrane, use Kvamatel, Famotidine.
- Antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Furazolidone) may be needed to eliminate Helicobacter pylori.
The disease can be cured if you additionally take medicinal infusions with calendula, chamomile, and more.
As an additional measure, patients may be prescribed physical therapy. Conducted:
- magnetotherapy - the method is based on the process of exposure of problem areas to a static magnetic field;
- balneotherapy - the therapeutic effect is achieved by taking a bath with mineral water;
- mud and paraffin applications;
- ultrasonic influence;
- UHF of the epigastric zone - a therapeutic effect on the zone using a high-frequency electromagnetic field.
The procedures help restore blood circulation, increase the body's defenses and rapid regeneration of damaged duodenal mucosa.
Treatment of duodenitis
Therapy is selected individually for each person and, depending on the form, may include:
- antibacterial drugs to combat Helicobacter pylori (Amoxicillin, Tinidazole, Clarithromycin, Levofloxacin);
- antisecretory agents - Lansoprazole, Omeprazole, Kvamatel, Ranitidine;
- antacids (reduce acidity) - Almagel, Phosphalugel;
- antispasmodics (eliminate spasms and help reduce pain) - Papaverine, Duspatalin, Mebeverine, Drotaverine;
- regulators of duodenal motility - Cerucal, Domperidone;
- multienzyme preparations (to improve digestive function in atrophic duodenitis) - Creon, Mikrasim, Panzinorm;
- Cholespasmolytics (to relax the sphincter of the duodenal nipple) - Platifillin, Odeston;
- reparants (accelerate the healing of the duodenal mucosa) - sea buckthorn oil, Solcoseryl;
- anthelmintics (for helminthic infestation) - Macmiror, Praziquantel, Aldazole.
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate such a serious disease.
Folk remedies
To treat duodenitis, decoctions, tinctures, and oils are used.
- Mix chamomile, mint, lemon balm, St. John's wort, calendula in equal proportions, pour in 1 tbsp. spoon of the potion with a glass of boiled water, let it brew for 15 minutes. Or put it in a saucepan on the stove. Boil after boiling for a minute, leave under the lid closed for half an hour. You can drink it like regular tea three times a day, you can add 1 spoon of sugar.
- Take 1 teaspoon of sea buckthorn oil on an empty stomach. The product quickly stops inflammation, relieves pain, destroys pathogens, and helps restore microflora.
- Pour flax seeds with water and place on the stove. After boiling, cook over low heat for 60 minutes. Allow to cool slightly, drain the mucus. It is used to treat the stomach and intestines. Take a tablespoon up to 5 times a day.
- Burdock root is poured with water, left for at least 30 minutes, and 100 ml is taken.
- Raw quail eggs are used to treat the intestines and stomach. They act like antacids. You should drink 2 pcs daily on an empty stomach. Within 60 days, more is possible. Quail eggs cope with acute symptoms, strengthen the immune system, and prevent exacerbation.
- Non-carbonated mineral water reduces acidity and removes toxins. They drink it in small sips. During the day, drink up to 2 liters of the drink.
Self-prepared yogurt with the addition of bifidobacteria helps cope with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Sunflower and pumpkin seeds reduce acidity. You just need to click them.
Diet for duodenitis
A prerequisite for successful treatment of duodenitis is adherence to a diet. Its main principles are:
- food should be prepared in gentle ways. Suitable soups, steamed dishes, various cereals;
- food should be served warm;
- You should avoid overeating and eating at night, and eat small meals four to six times a day.
Products allowed for consumption:
- lactic acid products - cottage cheese, kefir, fermented baked milk;
- baked and boiled vegetables, vegetable purees;
- lean varieties of meat, boiled or chopped in a blender - chicken, rabbit, nutria;
- eggs;
- low-fat fish - hake, cod;
- vegetable and butter;
- crackers and day-old bread, preferably whole grain;
- porridge - buckwheat, oatmeal, wheat;
- honey, jelly.
Prohibited:
- raw vegetables and fruits;
- smoked meats;
- canned food;
- fatty meat and fish, as well as mushroom broths;
- garlic, onions, spicy dishes;
- alcoholic and carbonated drinks;
- coffee;
- ice cream;
- fatty fish - mackerel, carp, silver carp, etc.
You should stick to a diet only in acute and exacerbation of chronic forms of duodenitis.
In other cases, you should not limit yourself to food, because it is one of the main pleasures in life. You can eat those foods that are individually tolerable.
Prohibited Products
- Food that is too hot or cold.
- Alcohol.
- Carbonated and caffeinated drinks.
- Chocolate.
- Spices.
- Flour products and sweets (including honey and sugar).
- Garlic (onion).
- Fast food.
- Sour fruits and berries.
- Smoked meats.
- Fried and salty foods.
- Canned foods.
- Citrus.
If the patient follows such a diet, he will quickly experience a weakening of the symptoms associated with superficial gastritis and duodenitis. You should move to a balanced diet carefully, gradually expanding your diet. Important! A healthy diet helps you recover faster and prevent the development of possible complications.
What is duodenopathy?
Duodenopathy is not an independent disease; it reflects some signs of pathological changes in the duodenum. Most often found:
- erythematous duodenopathy, manifested by redness of various parts of the intestine;
- erosive, characterized by the formation of cracks and erosions on the mucous membrane;
- cirrhotic - with cirrhosis of the liver, expressed in changes in vascular components and the relief of the mucous membrane;
- diabetic - manifested by thinning of the mucosa and other changes.
The danger of duodenopathy is that under certain conditions it can turn into a real disease that will require long-term therapy and recovery.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for chronic duodenitis is favorable, subject to proper and timely treatment . Unfortunately, the disease is difficult to treat; the chronic form is incurable, but long-term and even lifelong remission can be achieved. With a complicated course (in 10% of cases), the prognosis becomes significantly more complicated.
Prevention consists of timely examination, cyclic anti-relapse therapy, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and food discipline, and eliminating bad habits.
How to avoid duodenitis in modern conditions?
It is always easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. To reduce the likelihood of developing duodenitis you need to:
- stop drinking alcohol and smoking;
- strictly control the intake of medications, especially non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Aspirin, Diclofenac, etc.);
- normalize your diet, significantly limit the consumption of foods that irritate the mucous membrane of the duodenum - chips, crackers, too hot, spicy dishes;
- promptly treat other chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - cholecystitis, pancreatitis, gastritis.
Basic forms
Experts distinguish between acute and chronic. In the first case, the clinical picture is pronounced and is present for about a week. The condition gradually normalizes even without special treatment, but there is a risk of becoming chronic if the impact of unfavorable factors is not eliminated. Chronic duodenitis manifests itself mildly, but there is always weakness, discomfort in the abdomen, signs of indigestion and stool problems. Periodically, exacerbations occur with increased symptoms.
Foreign body
Accidental ingestion of any foreign objects can also lead to proximal duodenitis. In this case, a foreign body can settle in the intestinal bulb and compress its wall, which will provoke the development of an inflammatory reaction around it. Especially often in young children, the development of the disease in the proximal part is caused by intestinal parasites along with helminths and Giardia.
Many people are interested in what it is - proximal duodenitis.
Symptoms
If the patient has been diagnosed with duodenitis, then the existing symptoms will strongly resemble the manifestation of gastritis. The main signs of this disease in the proximal region are divided into several groups:
- The development of an ulcer-like pain syndrome in the intestines and stomach, which occurs some time after eating food.
- Dyspeptic symptoms, that is, digestive dysfunctions, which are characterized by excessive gas formation, a tendency to constipation and nausea. In this case, frequent vomiting is also possible.
- Symptoms of intoxication and inflammation can manifest as general weakness, and at the same time dizziness, fever, loss of appetite and, very often, sudden weight loss.
Antacid and adsorbent drugs
Almagel . Reduces the acid content in gastric juice, preventing the occurrence of heartburn. It has a slight local anesthetic and choleretic effect. Take 1-2 teaspoons half an hour before meals. The maximum period of continuous use is no more than 2 weeks.
Vis-Nol - has a gastroprotective effect due to the formation of a protective film on the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. Has activity against Helicobacter pylori. Take 1 capsule 30 minutes before meals. The course of treatment can last up to 8 weeks.
Manti – reduces acidity in the stomach, adsorbs bile acids and lysolecithin. Eliminates flatulence. Take 2-3 tablets at intervals between meals, but no more than 12 tablets per day. Drug treatment of duodenitis with this drug is allowed for 2 weeks.
Doctors' advice
Doctors say that proximal duodenitis, like any other pathology, must be subject to appropriate preventive measures. Experts consider it mandatory not so much to treat with medications or other special means, but to maintain general health along with timely treatment of diseases of the stomach and the entire digestive system as a whole.
Doctors advise patients not only to eat a balanced diet, but to completely give up bad habits, namely nicotine and alcohol. In addition, experts insist that patients engage in moderate physical activity and lead a healthy lifestyle. It is very important to take daily walks along with physical exercises and other activities that improve the metabolic process and other physiological activities.
In particular, doctors advise annual endoscopic examination to assess the condition of the inner surface of the esophagus, stomach and intestines. In addition, according to experts, a mandatory step in the treatment of this disease is taking a biopsy.
Reviews
Dear readers, your opinion is very important to us - therefore, we will be happy to provide feedback on proximal duodenitis in the comments, this will also be useful to other users of the site.
Alina:
“I drink herbal tea almost constantly. I buy it in sachets at the pharmacy. I just fill it with water, leave it for 5 minutes, add a little sugar.”
Svetlana:
“During an exacerbation, I drink Almagel, Omez, probiotics, sorbents. I always eat healthy and don’t drink alcohol.”
Provoking factors are:
- unhealthy diet: fasting, overeating, especially at night;
- abuse of unhealthy foods and drinks;
- smoking, especially on an empty stomach;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- infectious diseases that weaken the immune system;
- regular nervous stress, psycho-emotional stress and breakdowns, causing spasm of the duodenum and a decrease in the protective properties of the mucous membrane;
- bad heredity;
- entry of a foreign body into the digestive tract.
Other causes of the disease:
- helminthic infestations;
- Crohn's disease;
- Giardiasis
Classification
The two basic forms of duodenitis are acute and chronic diseases. However, they are divided into varieties.
Acute duodenitis
- Catarrhal. The simplest type, easy to treat
- Erosive-ulcerative. Requires complex treatment, in some cases surgery.
- Phlegmonous. Extreme degree of acute gastritis, an advanced form of the disease, requiring immediate hospitalization and surgery - otherwise complications may develop.
Chronic duodenitis
This type of disease is classified according to the following criteria.
The following options are available:
- Papillitis. A disease that develops in a small area, often manifesting as peripapillary diverticulitis.
- Bulbits. Clearly localized minor duodenitis of acidopeptic origin.
- Combination of the underlying disease with enteritis and gastritis. It lasts longer and requires additional therapy.
- Duodenitis with duodenostasis. A complex form of the disease requiring hospital treatment.
According to the endoscopic picture:
- Surface. Does not affect the middle and deep layers of the intestine.
- Atrophic. Most often, a combination of superficial disease with partial degeneration of the membranes.
- Interstitial. Large-scale damage to the duodenum, requiring complex treatment.
- Erosive-ulcerative. The most complex form of chronic duodenitis, requiring hospital treatment.
Reasons for appearance
Infection of the proximal intestinal mucosa with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori can lead to the development of proximal duodenitis. But besides this, there is an additional set of different reasons that can provoke the occurrence of the disease:
- Hereditary factors when there are close relatives in the family suffering from inflammatory diseases of the digestive system.
- An unbalanced diet, when a person often overeats, especially before bed, or, conversely, goes hungry too often.
- Consumption of large quantities of junk food in the form of marinades, pickles, smoked foods, fast food, and also fatty, spicy and especially fried foods.
- Abuse of bad habits, be it alcohol or smoking.
- Uncontrolled use of drugs.
- The influence of psycho-emotional factors in the form of frequent stressful situations and nervous disorders.