Updated: March 4, 2020, at 16:09
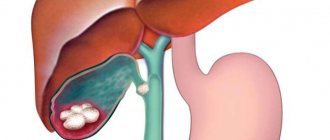
Cholecystitis is considered the most common disease of the abdominal organs, occurring in approximately 20% of adults. In most cases, the development of pathology is caused by microbes: E. coli, staphylococci, enterococci, streptococci. The initial symptom of the disease is a sudden sharp pain in the side on the right side. An attack of cholecystitis is manifested by symptoms of varying intensity, depending on the form and degree of development of the disease.
Symptoms of the disease
Basically, exacerbations can occur at the time of a breakdown in nutrition.
Often an attack occurs while drinking alcohol or fatty foods. After consuming one portion of contraindicated foods, the patient feels aching pain in the right side, under the rib, heaviness, vomiting, and loss of appetite. Sometimes the temperature rises. Only at the initial stage the disease manifests itself without pain. Symptoms during an attack of pain are much more serious:
- During an acute attack, pain occurs in the right side, radiating to the collarbone, scapula, and back.
- Nausea and debilitating vomiting with bile last for a long time.
- Increased temperature, fever.
- Stool upset, belching, flatulence.
- The skin may be yellow, and the color of stool and urine may change.
The pain increases with palpation in the stomach or right side. The pulse becomes rapid. The more serious the patient's condition, the more frequent the pulsation.
The most serious is an attack of stones coming out of the bladder. The ducts begin to close, and bile has nowhere to enter. Pain becomes very frequent. Severe symptoms can be dangerous to humans.
Stones can injure the walls of the bladder and cause inflammation. As a result, infected formations can enter the abdominal cavity and cause peritonitis. It is very unpleasant to look at a patient in pain. His blood pressure drops sharply, his skin turns pale, and the pain does not subside for a long time. Medical assistance, hospital monitoring and urgent treatment are urgently needed.
The disease manifests itself as a defensive reaction to intoxication and poisoning. Occurs due to bile stagnation. Symptoms of cholecystitis may indicate other diseases: ulcer, appendicitis; pancreatitis, poisoning. If bloody clots occur during vomiting, then some other disease has arisen. A secondary sign is considered to be a change in stool. These problems may suggest the presence of gastrointestinal pathologies.
Clinical manifestations of cholecystitis
This gallbladder disease is a protective reaction of the body to poisoning. It develops as a result of bile stagnation.
But do not forget that many of the symptoms that are characteristic of cholecystitis can also mean other phenomena:
- stomach ulcer;
- appendicitis;
- renal colic;
- pancreatitis;
- duodenal ulcer;
- poisoning;
- pregnancy.
Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor V. M. Savkin:
Cleansing the liver will help rejuvenate the body in a few days and give you an additional 15 years of life...
To determine the cause of nausea and vomiting, you should pay attention to when they occur. Equally important is the duration of the attack and the frequency of its occurrence. If blood clots come out when vomiting, then some other disease has probably developed.
Another sign of cholecystitis is bowel dysfunction. Such problems mean the presence of gastrointestinal pathologies.
The following complications can cause the development of diarrhea during therapy:
- toxic infection;
- dysbacteriosis that developed while taking antibacterial drugs;
- bloating and fecal retention that appeared after complications of cholecystitis or intestinal peritonitis;
- impaired motor skills as a result of pathologies of the digestive organs;
- passive lifestyle;
- prolonged inflammation leading to a reflex effect on the stomach.
First aid for an attack
The rapid proliferation of microbes, pressure inside the inflamed gallbladder is dangerous due to the destruction of the walls. Contact of internal organs with the contents of the gallbladder, saturated with pathogenic microbes, can cause negative health consequences.
Therefore, an attack of acute cholecystitis should be stopped as quickly as possible.
Actions during an attack:
- provide rest to the patient;
- put a cold compress on the area of severe pain (right side of the abdomen);
- give an antispasmodic drug (no-spa);
- after attacks of vomiting, serve mineral water without gas on a sodium chloride, bicarbonate basis.
- call emergency help.
An attack of acute cholecystitis is always sudden and has acute symptoms.
In the chronic form of the disease, the pain is dull, bursting, and an attack often occurs after eating.
How long does an attack of cholecystitis last?
In the chronic form, attacks are short-lived, rarely lasting more than an hour. In the “calculous” form of acute cholecystitis, the attack lasts 1-3 hours. If the attack is provoked by a stone, the pain can persist for up to 6 hours.
Which side should you lie on during an attack of cholecystitis?
The patient should be placed on his right side and allowed to take a comfortable position. In the absence of severe pain, the patient can lie on his back.
How to treat a patient during an attack
It is forbidden to carry out warming procedures: placing heating pads on the area of pain.
You cannot do enemas, so as not to provoke an increase in pressure in the internal organs.
It is not recommended to take analgesic drugs before the doctor arrives, so as not to “blur” the picture of the disease.
It is allowed to administer an antispasmodic to relieve spasmodic pain (no-spa, drotaverine, papaverine).
Treatment of microbial flora requires antibiotics. Depending on the form of cholecystitis, the doctor prescribes antibiotic drugs of different groups.
To relieve pain, take analgesics with an anti-inflammatory effect. To maintain the functions of the liver and gallbladder - enzymatic agents.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Depending on the course and symptoms, this disease is divided into acute and chronic forms.
Acute cholecystitis manifests itself in the form of sharp and acute pain localized in the right lower abdomen. They are accompanied by nausea, vomiting and low-grade body temperature up to 38–39ºС. Painful sensations arise spontaneously and, as a rule, are unbearable. In this case, the patient becomes restless and cannot find a comfortable body position in which pain is significantly reduced.
Usually, 2-3 days after an attack of cholecystitis, yellowness of the skin appears, which is a consequence of the cessation of bile secretion into the intestines. Urine becomes dark in color.
The number of complaints about the symptoms of acute cholecystitis especially increases after holidays, which are accompanied by overeating, excessive consumption of fatty foods and alcoholic beverages. Failure to maintain a balanced diet leads to severe attacks of acute cholecystitis, resulting in the patient requiring immediate hospitalization and often surgical intervention.
Chronic cholecystitis develops as a result of repeated attacks of acute cholecystitis. Its symptoms include pain under the ribcage on the right side, a feeling of heaviness in the upper abdomen, nausea and a feeling of bitterness in the mouth.
Diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
Diagnosis of acute cholecystitis is based on clinical and additional data:
1. The presence of complaints of the following nature – pain in the right hypochondrium for more than 30 minutes, nausea, vomiting, change in body temperature. Previously, 50% of patients could experience hepatic colic.
2. A medical examination reveals a characteristic Murphy symptom - involuntary holding of breath as a result of sharp pain when pressing in the area of the right hypochondrium; Tension of the abdominal muscles is also detected, an enlarged gallbladder can be felt in 30-40% of patients; 10% of patients have jaundice;
3. Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics:
- a blood test shows an increase in the number of leukocytes - leukocytosis, the magnitude of which will depend on the severity of inflammation; blood biochemistry will reveal an increase in C-reactive protein, bilirubin with the development of jaundice, alkaline phosphatase, AST, ALT (specific liver enzymes);
- urine analysis changes only when the process worsens - with the development of jaundice, bilirubin appears in the urine, with the development of necrosis and severe intoxication, protein and casts are detected;
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder is the most accessible and informative method that allows you to identify stones and inflammatory thickening of the bladder wall. During the study, Murphy's symptom is observed in 90% of cases, which is a diagnostic sign of acute cholecystitis;
- scintigraphy cannot always be carried out practically, but is the most reliable method of proving occlusion of the cystic duct;
- MRI is performed to detect acute cholecystitis in pregnant women when abdominal pain occurs;
- X-ray is informative in 10-15% of cases when the stones contain calcium and are visible through X-ray. X-rays also reveal the presence of gas in the wall of the bladder, which occurs with acute emphysematous cholecystitis in the elderly and patients with diabetes.
How to treat acalculous cholecystitis
If the disease is diagnosed for the first time, the patient does not have stones or purulent complications, then conservative treatment of acute cholecystitis is indicated. In such situations, antibiotic therapy is prescribed to eliminate pathogenic microflora.
To eliminate pain and dilation of the bile ducts, taking antispasmodics is indicated. For symptoms of intoxication, detoxification therapy is carried out. When cholecystitis occurs, treatment involves following a therapeutic diet.
Diet therapy is based on compliance with the following rules:
- Fractional meals up to 6 times a day in small portions;
- Refusal of alcoholic beverages, fried, fatty and spicy foods;
- Food must be freshly prepared; heat treatment involves boiling, baking and steaming;
- To prevent the development of constipation, it is necessary to introduce foods enriched with dietary fiber into the menu.
Treatment options
In the hospital, an attack of the disease can be relieved quickly, and it will take 10 days to relieve inflammation. When stones pass out, surgical intervention is necessary. There is a problem when the gallbladder is closed and the ducts are blocked. There is only one way out - removal of the diseased organ. The extreme method helps save the patient’s life, because specialists try in any way to ensure the preservation of organ function, even resorting to endoscopic techniques.
A puncture is made in the abdomen, experienced surgeons insert an endoscope, and with the help of ultrasound the process of removing stones from the ducts is completely visible. The organ is saved.
Follow-up diet
During a relapse, to make life easier for the patient, fasting is required for a couple of days. You can drink mineral water and green tea without sugar. As general health improves, the patient may be offered lean broths and viscous porridges. You should eat small meals often. Coarse fiber contained in raw vegetables is prohibited.
Food is only steamed and boiled. A strict diet excluding junk food is indicated for the future. It is based on dietary meats, steamed and pureed, low-fat fish, dairy products, and sweet fruits. Non-acidic juices are recommended, you can drink still mineral water, berry fruit drinks, mint and green tea.
Traditional medicine to help with cholecystitis
Many herbs can reduce pain: choleretic decoctions and infusions. Such properties include: yarrow, chamomile, immortelle, leaves and buds of birch. You can use herbs only after consulting a doctor. Some herbs dilute bile, while others stimulate its formation and expel it.
There are known ways to take one spoonful of vegetable oil on an empty stomach.
Rowan juice is useful. You need to drink 100 g three times a day.
Grate horseradish root 200 mg. Pour four glasses of hot water. Place in the refrigerator for a day. It is advisable to strain and reheat before use. Drink 50 g before meals three times a day.
Plantain decoction: you will need one tablespoon of seeds or leaves, pour boiling water. Leave for 15 minutes, take small sips within an hour. The benefits of beets in the fight against disease have been proven. Boil the peeled vegetable until the consistency of the broth resembles syrup. Drink 1⁄4 cup of the decoction before meals.
Oatmeal jelly has good results. Pour boiling water over half a kilogram of oat grains and leave for half an hour. Strain and consume 0.5 cups three times a day. Another way is to cook jelly from oatmeal, add milk, and bring to a boil. Add honey. Drink a glass three times during the day, warm.
The causes of stagnation in the gallbladder are:
- Bacterial infections;
- Anatomical features of the structure of the organ;
- Stones in the bile ducts;
- Changes in the chemical composition of bile.
In order to promptly recognize and stop an attack of acute cholecystitis, it is necessary to clearly know the causes of this disease, its characteristic symptoms, the mechanism of development and the correct algorithm for assistance.
Duration and frequency of attacks
Pain in people suffering from cholelithiasis occurs suddenly. The duration of the attack can range from 15 minutes to 8 hours. Sometimes the pain continues for 12 hours. This happens with the development of acute cholecystitis. When the attack of the disease passes, the pain disappears. All that remains is an unpleasant sensation in the abdominal area.
The frequency of attacks during the disease varies from person to person. In some sick people, symptoms of biliary colic may occur every day, in others - once a week, in others - once a month. It is extremely rare to have just one pain attack.
Diagnostics
To confirm the diagnosis, it is important to take into account existing and previously suffered pathologies of the digestive system. Pain during digital examination of the abdomen indirectly indicates the course of cholecystitis
Instrumental methods include ultrasound and duodenal probing. With their help, the condition of the smooth muscles of the gallbladder and the condition of the lumen of the bile ducts are assessed.
An attack of cholecystitis can be confirmed by positive results from the use of methods of artificial provocation of pain:
- Shchetkin-Mussy symptom - the appearance of pain when pressure is applied to the area of the right hypochondrium with subsequent weakening;
- Ortner's symptom - pain from light tapping with your fingertips on the extreme rib on the right;
- Mussi-Georgievsky's symptom is pain and discomfort when applying slight pressure on the sternocleidomastoid muscles.
Therapy
Having determined the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes infusion, antibacterial and analgesic therapy. If breathing is impaired, provides oxygen through a nasal catheter.
Traditional methods
If it is not possible to save the organ with medication, then they resort to cholecystectomy.
In acute cholecystitis, doctors do everything possible to preserve the gallbladder and treat it with medication. It is removed only if the stones have blocked the bile duct. However, with the help of endoscopy, in many cases it is possible to remove stones while preserving the gallbladder.
The operation begins with a small puncture in the abdomen, and then the surgeon removes the stones using laparoscopy. What is happening inside the patient’s abdominal cavity is monitored on the monitor of a special device.
In less serious cases, doctors first prescribe injections (clarophan, cephobid, cefazolin, gentamicin), then oral antibiotics: amoxiclav, amoxicillin.
For acute pain and disruption of the gallbladder - injections of No-shpa, Papaverine. In the hospital, an attack of acute cholecystitis is usually relieved within 3 days. It takes about 12 days to completely get rid of the characteristic signs of the disease and eliminate the inflammatory process.
Folk remedies
To prevent the formation of gallstones, drink a decoction of Solyanka Kholmovoy: 1 tbsp. l. dry raw materials pour 1 tbsp. hot water. Boil for 10 minutes, cool, filter and take 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day before meals.
In autumn they are treated with red rowan juice. To obtain it, ripe berries are pounded in a mortar, and then the resulting pulp is filtered through cheesecloth. The drink is consumed at 0.5 tbsp. 3 times a day half an hour before meals. The course of treatment can be continued until the rowan fruiting ends.
Another recipe: dry plantain leaves, chop them, take 1 tbsp. l. raw materials and pour a glass of boiling water. Leave covered for 40 minutes, strain and drink in small sips for an hour. And so once a day. The duration of the course is a week.
In case of an acute attack of cholecystitis, you should not eat at all for the first three days. Drinks allowed include warm non-carbonated mineral water and green tea with mint leaves. After fasting, the diet consists of:
- weak broths;
- puree soups;
- pureed food;
- well-cooked porridge with a viscous consistency.
You need to eat little, but often: every 3 hours. Food can be eaten steamed, boiled and baked, but in no case fried or stewed. When you return home, it is recommended to cook using a double boiler or multicooker. You should not eat foods that are too cold (below 15°C) or hot (above 50°C).
Avoid foods that cause bloating
- broccoli;
- peas and other legumes;
- zucchini;
- potato;
- onion;
- carrot;
- cucumbers;
- radish;
- radish;
- beet;
- Bell pepper;
- green beans;
- tomatoes;
- pumpkin;
- cauliflower.
It is recommended to switch to steamed omelettes, salads with olive oil, boiled lean meat (can be put through a blender or cut into small pieces), boiled cod, navaga, pollock and other dietary fish, viscous porridges, fermented milk products with a small percentage of fat content.
Among sweets, preference is given to dietary oatmeal cookies without additives (preferably not store-bought). Butter dough, alcohol, smoked meats, pickles, fatty foods, marinades, ketchups, mayonnaise, and seasonings are still on the black list.
What provokes an exacerbation
Chronic cholecystitis can be calculous (with stones) or acalculous. Exacerbation of the latter can be provoked by:
- consuming large amounts of fatty, fatty, smoked or pickled foods, as well as combinations of these unhealthy foods;
- binge eating;
- drinking alcohol;
- severe stress;
- allergies - especially food allergies;
- a diet that lacked fiber and plant fiber for a long time.
In the case of calculous cholecystitis, exacerbation can be additionally caused by:
- bumpy ride;
- physical activity (especially after a long period of physical inactivity);
- a sudden change in body position, especially if the person has eaten a heavy meal beforehand.
Exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis is more likely to occur in a person with the following conditions:
- abnormalities in the development of the biliary tract;
- obesity;
- dyskinesia (impaired coordination of muscle movements) of the biliary tract;
- during pregnancy;
- during hypothermia, colds or exacerbation of chronic pathologies of internal organs.
Causes of an attack of cholelithiasis
Problems associated with the formation of gallstones are quite common. The causes of an attack may be:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- poor and/or irregular diet;
- eating large amounts of fatty foods;
- chronic diseases of the pancreas;
- systematic nervous overstrain and/or nervous stress.
All these factors can lead to salt deposits and the formation of stones of various sizes.
As a rule, the disease can occur in people after forty years of age, but recently it has begun to occur very often among young people. At the initial stages of salt deposition in the gallbladder, there are practically no painful sensations or cramps, only slight bloating is present.
People who suffer from cholecystitis should undergo timely treatment from a specialist. To prevent an attack of hepatic colic from occurring in a person, it is recommended to follow all doctor’s recommendations and eliminate conditions that provoke spasms and the advancement of stones.
The very first cause of this disease is poor nutrition. It doesn't have to be just eating the wrong foods. These include frequent fasting, which causes stagnation of bile in the organs, and frequent overeating, which place a heavy burden on the body, in particular on the organs of the digestive system. Frequent consumption of excessively fatty, fried, spicy and pickled foods leads to disruptions in the food digestion system.
The main predisposing factors in the development of a crisis state include:
- Diseases of inflammatory origin, regardless of form - acute or chronic.
- Helminthic infestations and parasitic lesions.
- Constant overeating, frequent consumption of spicy, fatty, fried foods, and alcoholic beverages.
- Frequent psycho-emotional stress, depression, prolonged stay in a traumatic situation.
- Past acute respiratory viral diseases and colds, infections of the oropharynx and nasopharynx (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, sinusitis).
- Infectious mononucleosis or adenovirus.
Living in unfavorable environmental conditions and genetic predisposition can cause the development of gallstone disease. Such factors provoke disturbances in the normal functioning of the gallbladder.
Possible complications
If signs of acute cholecystitis appear against the background of migration of stones, then perforation of the ducts or organ walls may occur. This condition poses a direct threat to the patient’s life, as it provokes inflammation of the abdominal cavity.
The listed complications of acute cholecystitis are characterized by the following symptoms:
- Acute pain that intensifies during palpation;
- Intense thirst;
- Increased body temperature;
- A sharp decrease in pressure against the background of tachycardia;
- Severe weakness;
- Increase in size of the abdomen;
- Vomiting of green contents;
- Pale skin and tongue.
In advanced forms of the disease, the following complications of acute cholecystitis develop:
- The appearance of emphysema of the gallbladder;
- Fistulas;
- Development of purulent inflammation;
- Sepsis (the occurrence of a generalized infection);
- Necrosis of the digestive organ.
Drotaverine
So, what painkillers are taken for acute cholecystitis? One of the most common drugs is Drotaverine. The medicine is intended to eliminate spasm by dilating blood vessels and reducing smooth muscle tone. Drotaverine promotes the supply of oxygen to organs and tissues. Thanks to this effect, the patient can quickly get rid of pain.
Drotaverine is quite effective, and the effect of the drug lasts a long time. The maximum concentration of the drug in the body is reached 40 minutes after application. The medicine is available in the form of yellow-green tablets, as well as in the form of injections.
The drug is used to reduce pain and spasms when:
- stomach ulcer;
- pyelite;
- intestinal colic, etc.
The tablets are taken orally, washed down with warm water. The maximum daily dose is determined by the doctor based on each specific situation.
The drug is contraindicated in case of individual intolerance to the components that make up the tablets. In addition, the product is not recommended for use in cases of heart disease, kidney failure, and women during lactation. During pregnancy, taking the medicine is allowed, but with great caution under the constant supervision of a specialist.
Side effects that occur when using the drug are extremely rare. In rare cases, the drug causes nausea, vomiting, headache, sweating, arrhythmia, decreased blood pressure and tachycardia. However, with the right course of treatment, these symptoms can be avoided.
Diet
The basis for treating an attack of cholecystitis is a strict diet, since unhealthy eating habits and fatty foods most often disrupt the functioning of the gallbladder, liver and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract. During an attack and the manifestation of its symptoms, it is forbidden to eat any food at all. Green tea and still mineral water are acceptable, as they help cope with nausea.
Within 2-3 days after the attack, you need to lighten your diet as much as possible, eating only foods of plant origin and in small quantities. Liquid porridges are allowed, as well as low-fat chicken broth. You need to eat in minimal doses, a few sips every 2 hours. Foods that increase flatulence remain prohibited - these are baked goods, fresh fruits and vegetables.
Healthy foods include all low-fat fermented milk products, natural yoghurts, and starter cultures. Baked apples and pears, as well as carrots, fresh or baked, can also help the digestive system and gall bladder.
It is very important to drink 2 to 3 liters of clean water during the day.
What can you eat during an attack of cholecystitis? It is not recommended to eat during an attack.
To support the body and relieve symptoms of nausea, you can take green tea and still mineral water. After an attack, diet plays an important role in recovery.
For the first 2-3 days, you should adhere to a strict diet and lighten your diet as much as possible. Low concentration chicken broth and liquid cereal porridge are useful.
You need to eat in small portions (1-2 tablespoons), every 2 hours. It is forbidden to take foods that can increase flatulence: raw vegetables, fruits, baked goods.
By following a diet following the principle of cholecystitis, they achieve the outflow of bile, unload the liver, and improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
As the patient’s condition improves, it is allowed to include a variety of steamed dishes, pureed soups, and white bread croutons in the diet.
Baked apples and pears, carrot casseroles, and fresh low-fat dairy products are useful during recovery.
Features of therapeutic nutrition
Patients with cholecystitis are prescribed a strict diet. It provides the following:
- The patient is prescribed fractional meals. You should not combine hard-to-digest foods at one meal.
- The diet should be well balanced and rich in nutrients. The basis of the menu should be porridge and vegetable dishes.
- The consumption of lean boiled meat and fish, cereals and puddings, rosehip infusion and green tea is encouraged.
- You can eat low-fat fermented milk products and a little honey.
- Non-sour apples, bananas, and all dried fruits are allowed.
- You can eat nuts and steamed protein omelettes in limited quantities.
The following products are strictly prohibited:
- Coffee.
- Mushrooms.
- Pickles.
- Salty fish.
- Sausages.
- Smoked meats.
- Bakery.
- Hot sauces.
- Fatty meat and fish.
- Sweet confectionery with creams.
- White bread.
- Candies.
Causes of acute cholecystitis
The cause of the attack may be a calculus that has blocked the duct
Acute cholecystitis begins to actively develop when an obstruction occurs in the path of bile outflow from the gallbladder. E. coli is often the culprit of the pathology. Staphylococci and other bacteria are also dangerous. Their entry into the gallbladder is accompanied by severe pain.
An attack of illness can occur due to the following reasons and conditions:
- improper diet, snacks on the run, dry food;
- abuse of fatty and spicy foods, fast food, sweets, carbonated drinks, alcoholic drinks;
- inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity;
- fasting, strict mono-diets;
- pressure on the abdomen (for example, the wrong size jeans belt cutting into the flesh);
- developmental anomaly or bending of the gallbladder;
- deformation, compression, displacement of ducts due to injury, tumor, inflammation of nearby organs;
- stones inside the bubble;
- lack of physical activity;
- overweight;
- stress, nervous exhaustion, depression;
- disruptions in the functioning of the biliary tract;
- atherosclerosis;
- pancreatitis;
- diabetes;
- viral hepatitis.
Watch a video about acute cholecystitis:
- sharp, ever-increasing pain in the right side under the ribs, radiating to the shoulder, shoulder blade and lower back on the right side;
- belching, nausea, vomiting with bile and blood;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- chills, fever;
- bloating;
- lemon-yellow skin tone, whites of the eyes;
- darkening of urine;
- bowel dysfunction;
- tachycardia;
- lethargy, drowsiness.
When palpating the right side, the pain worsens. If the patient gets worse, his temperature and pulse jump even more. After an attack of vomiting, the expected relief does not come.
The most dangerous attack is calculous cholecystitis, which occurs when stones are moved. When the bile ducts are blocked, a person begins to suffer from severe biliary colic. This condition is fraught with death.
If the migration of stones disrupts the integrity of the walls of the gallbladder, then its contents, along with the infection, will enter the abdominal cavity. The most likely outcome will be peritonitis.
In this case, the patient’s condition will worsen significantly, he will become very pale and weakened, the pain will become unbearable, and the pressure will drop sharply. With such symptoms, self-medication is not only useless, but also dangerous. You need to call an ambulance as soon as possible.
Symptoms
Cholecystitis can occur in chronic and acute forms, and the disease can be either acalculous or with the formation of stones.
The symptoms of an attack are pronounced, so it is impossible not to notice it. It all starts with severe and sharp pain in the right hypochondrium. It resembles an attack of pancreatitis - the pain radiates to the shoulder, lower back, and shoulder blade. If you press on the right hypochondrium, then the unpleasant sensations will immediately become stronger.
Other symptoms of an attack of cholecystitis may be observed:
- Bloating and excessive tension in the abdominal area.
- Decreased blood pressure, severe weakness, dizziness.
- Yellow tint to skin and eyes.
- Bitter taste in the mouth, nausea.
- Vomiting of bile, without relief.
- Stomach upset, increased gas formation.
- A sharp increase in body temperature.
- Tachycardia. The pulse is more than 120 beats per minute.
- Heavy sweating.
The patient experiences severe anxiety and cannot find a place for himself. The pain does not go away for a long time, which indicates the need to call a doctor.
How to relieve an attack of cholecystitis
In chronic cholecystitis, painful sensations occur periodically, due to the consumption of too fatty, salty, spicy foods, smoked foods or alcohol. The nature of the pain is dull, bursting, the attack lasts no more than an hour, it can be stopped by taking painkillers or antispasmodics.
Treatment of attacks of chronic cholecystitis is carried out with medication. The treatment regimen includes drugs that improve the flow of bile, antibacterial agents to relieve the inflammatory process and antispasmodics to relieve spasms of the biliary tract and eliminate pain. The patient is prescribed a diet, and subsequently, as the inflammatory process subsides, treatment is prescribed to prevent repeated relapses of the disease. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe drugs that help dissolve gallstones (Ursofalk, Ursosan).
What to do if you have an attack of cholecystitis if it strikes you at home or at work? How to provide first aid during an attack of cholecystitis at home? First of all, you need to call your local therapist. The patient needs to be put to bed, provided with rest and a cold compress applied to the right side. If nausea occurs, you can drink warm still mineral water or green tea with mint. To relieve pain before the doctor arrives, you can take a tablet of noshpa or papaverine.
Taking analgesics is not recommended; this may blur the clinical picture of the disease. Under no circumstances should you apply a hot heating pad to your stomach, take choleretic drugs, or give a cleansing enema.
In case of an acute attack of cholecystitis, you cannot hesitate; you must immediately call emergency medical care and send the patient to the hospital. If during an ultrasound examination no stones are found in the gallbladder, after pain relief the patient will be sent home with recommendations for treatment. Otherwise, the issue of performing a surgical operation will be decided.
Treatment methods
In a hospital setting, an attack of non-calculous cholecystitis can be relieved in 3 days, and to completely eliminate the symptoms and inflammatory process it will take 10-12 days. With calculous cholecystitis, a decision is usually made about surgical intervention. In severe cases, when the gallbladder is completely clogged with stones, cholecystectomy (removal of the organ) is resorted to.
If it is possible to preserve the gallbladder and its functions, endoscopic methods are used, which are easier to tolerate by patients, cause fewer complications and do not require a long recovery period. The intervention is carried out through a small puncture in the abdomen. The progress of the operation is monitored using ultrasound; the surgeon monitors all manipulations on the monitor of a special device. Using laparoscopy, it is possible to remove the stone from the bile ducts and thus avoid removing the gallbladder.
Diet after an attack of cholecystitis
During an acute attack of cholecystitis, fasting for 2-3 days is recommended. At this time, you are allowed to drink warm still mineral water or unsweetened green tea with mint.
As the patient’s condition improves, weak broths, pureed soups, pureed food, and boiled viscous porridges are recommended. You need to eat small portions every three hours. Food should be gentle; raw vegetables with coarse fiber are prohibited during this period (cabbage, radishes, radishes, turnips, bell peppers). Dishes are steamed, boiled or baked.
In the future, fats and “fast” carbohydrates are excluded from the diet; pickles, marinades, smoked foods, baked goods, sweet carbonated drinks, spices and seasonings, and alcohol remain prohibited. The basis of the diet is pureed or boiled dietary meat, boiled lean fish, steamed omelettes, viscous porridges, fresh vegetable salads with vegetable oil, low-fat fermented milk drinks, sweet fruits and berries. For drinks, warm mineral water without carbon, non-acidic juices half diluted with water, compotes, fruit drinks, rosehip decoction, herbal and green tea are recommended.
Symptoms of acute cholecystitis
The appearance of symptoms is often associated with errors in diet, in the form of consumption of fatty foods, alcohol, and is also observed after emotional shock. The severity of symptoms depends on the stage of the disease and the activity of the inflammatory process.
The symptoms of catarrhal cholecystitis are as follows:
- acute pain. With cholecystitis, it may first be paroxysmal, then it becomes constant. Often radiates to the shoulder blade, shoulder and neck on the right;
- nausea, vomiting that does not bring relief;
- body temperature is moderately elevated – 37.5-38° C;
- moderate increase in heart rate up to 80-90 beats per minute, slightly increased blood pressure;
- slight tension in the abdominal muscles, but it may be absent.
Symptoms of phlegmonous cholecystitis:
- intense pain in the right hypochondrium, which intensifies when changing body position, coughing, breathing;
- nausea in this form of cholecystitis is more pronounced and more frequent than in the catarrhal form, vomiting is repeated;
- body temperature above 38° C;
- pulse rate increases to 100 beats per minute;
- the tongue is wet, the stomach is swollen;
- when breathing, the patient tries to consciously not involve the right half of the abdomen in movement, so as not to increase pain;
- when palpating the abdomen on the right, under the ribs, a sharp pain occurs, and protective muscle tension is also expressed there;
- sometimes an enlarged gallbladder can be felt in the right hypochondrium.
The development of the gangrenous form of cholecystitis occurs if the body’s weakened defenses cannot contain the further development of the infection.
Initially, a period of “imaginary well-being” may occur, which is manifested by a decrease in the intensity of pain. This is due to the death of the sensitive nerve cells of the gallbladder. But then all the symptoms intensify, and when the wall of the gallbladder breaks through (perforation), clinical signs of inflammation of the peritoneum appear - peritonitis:
- severe pain emanating from the right hypochondrium spreads to most of the abdomen;
- high temperature 39-40° C;
- pulse 120 beats per minute or higher;
- breathing becomes rapid and shallow;
- the patient becomes lethargic and lethargic;
- the tongue is dry, the abdomen is swollen, the abdominal muscles are tense;
- the stomach does not participate in breathing.
Gangrenous cholecystitis often occurs in older people. This is due to the liquefaction of the ability of tissues to recover, impaired circulation due to atherosclerosis and a general slowdown in metabolism.
Therefore, in older people, a mild course and mild symptoms are often observed: there is no severe pain and tension in the abdominal muscles, there is no increase in leukocytes in the blood, which significantly complicates timely diagnosis.
Antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed by doctors in cases where the disease is bacterial in nature or complicated by infection. Treatment is carried out in the early stages of cholecystitis, its course usually does not exceed a week. If therapy is continued, taking the drug will lead to disruption of the intestinal microflora and weakening of the immune system.
Antibiotics are indicated for vomiting, nausea, diarrhea and severe pain in the right hypochondrium. Before starting treatment, it is recommended to identify the pathogen.
The use of antibacterial drugs may cause side effects in patients. Among them are decreased immunity, allergic reactions (up to angioedema or anaphylactic shock), bronchospasm, and dysbacteriosis.
Erythromycin
This is one of the first and most popular antibiotic drugs. Has a powerful antibacterial effect against various microorganisms. Available in the form of tablets and solution for injection.
Reaching the lesion, Erythromycin stops the growth and development of gram-positive bacteria, streptococci, and gram-negative microorganisms. The drug is absorbed and absorbed by the body unevenly, which is why part of the drug remains in the kidneys and liver.
The drug is contraindicated in case of allergies to the components of the composition, carrying and feeding a child, severe liver diseases.
The cost of the drug Erythromycin is from 20 rubles.
Levomycetin
Levomycetin is an antibiotic characterized by a wide spectrum of activity against pathogenic bacteria. It disrupts the synthesis of proteins that form the basis of microorganisms, which is why the latter are unable to grow and die. Shows activity against gram-positive and gram-negative cocci, various bacteria, spirochetes, rickettsia and a small amount of large viruses.
The drug has a number of contraindications:
- Allergy to the components of the drug;
- Porphyria – a disorder of pigment metabolism;
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency;
- Kidney and liver failure;
- Skin lesions, psoriasis, eczema;
- Bearing and feeding a child.
The drug is not recommended for newborns. If therapy is necessary, first consult a specialist, and then treat the child with Levomycetin.
The drug can be purchased in pharmacies from 117 rubles.
Ampioks
Ampiox is a combination drug from the penicillin group. Shows activity against gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Contraindicated in case of a tendency to allergic reactions and individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
The cost of the product is from 67 rubles.
Before and after surgery, antibacterial treatment is mandatory. Cholecystitis is quickly eliminated with drugs of this pharmacological group, since it is a variety of microbial agents that cause inflammation of the gallbladder.
Most often modern gastroenterologists and surgeons use the following drugs:
- fluoroquinolones;
- cephalosporins;
- macrolides.
Ofloxacin and Norfloxacin are well-deservedly popular among fluoroquinolones. Both medications penetrate the wall of the gallbladder better than others and remain in it for a long time. They do not have a negative effect on their own intestinal microflora. The development of resistance of microbial agents to these fluoroquinolones has not been observed. Conveniently, Norfloxacin is available in injection and tablet form, that is, injections can be used first, and then the tablet.
Cephalosporins are the most widely used group of antibiotics in surgical practice. A medicine from this group quickly and effectively eliminates the manifestations of inflammation of the gallbladder due to a wide spectrum of antibacterial effects. There are only two limitations in the use of cephalosporins: the injection form of release (only Cefuroxime and Cephalexin have a tablet) and a negative effect on the intestinal microflora.
Modern macrolides, for example, Azithromycin, Spiramycin, Clarithromycin, are effective against most microbes (Gram-negative and Gram-positive). The medication of this group does not affect the intestinal microflora, quickly penetrates into the tissue of the bile ducts and bladder, and has a convenient combination of release form (injection solution and tablet).
Other antibacterial agents for cholecystitis are less popular. Metronidazole does not penetrate the gallbladder tissue and accumulates only in its lumen, so the strength of the antimicrobial effect is reduced. Almost any drug from the group of aminoglycosides (Tetracycline, Gentamicin) is characterized by a pronounced toxic effect.
Antiparasitic drugs for cholecystitis are necessary if the fact of infestation by helminths or protozoa is confirmed. Most often, tapeworms (ascaris) cause blockage of the bile ducts and the subsequent development of inflammation of the gallbladder. A good effect is observed only if the duration and dosage of the anthelmintic drug is observed.
Antifungal medications for cholecystitis are also only necessary in cases of confirmed fungal infection. Antimycotic agents (Clotrimazole, Fluconazole) also require careful and balanced use. A good effect is observed if treated with an antifungal agent for a long time.
Helping a sick person at home
When diagnosed with chronic cholecystitis, pain and colic occur periodically due to a change in diet, namely the inclusion of harmful and prohibited foods in the diet. Dull pain lasts one hour. You can relieve pain with antispasmodics.
Treatment of the chronic stage of the disease occurs with the help of medications. Antibacterial drugs, antispasmodics, and painkillers are selected to promote the discharge of bile to relieve inflammation. The patient is prescribed a strict diet to prevent colic. The doctor prescribes medications and prescribes certain procedures to dissolve stones.
There are situations when a disease takes you by surprise at home or in the workplace and first aid is needed. The patient must be laid down, kept calm, and cold applied to the right side. To do this, take a heating pad with cold water or a cold product and wrap it in a towel.
If nausea occurs, offer the patient water or tea. To relieve pain at home, the drugs Drotaverine, No-shpa or Papaverine are effective. It is prohibited to use analgesics, hot heat, bile removers without medical indications, and to give an enema. Within the walls of the hospital, a person will undergo an ultrasound examination of the gall bladder for the presence of stones. If there are none, the patient will be sent home with established recommendations and treatment. Sometimes surgery is required as a last resort.
Prevention
Home treatment for cholecystitis involves following a diet. A prerequisite for exacerbation is the consumption of large amounts of water. After eliminating pronounced symptoms, you can eat steamed meat, fish and vegetables.
If you have cholecystitis, you cannot place increased stress on the digestive system, so it is recommended to exclude fiber products from your diet.
Food should be consumed in small portions. The last snack should be a few hours before bedtime.
Prohibited products for this disease include:
- canned and smoked products;
- products that affect the acidity of gastric juice;
- products that produce gases in the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms of acute cholecystitis in humans
The clinical picture of new-onset cholecystitis is similar to biliary colic. An attack of cholecystitis is an acute pathology requiring emergency care.
The main signs of acute cholecystitis:
Pain Pain sensations occur in the right hypochondrium, can spread to the upper abdomen and radiate to the right side (back, shoulder blade, neck, chest, arm).
Acute pain with cholecystitis is quite intense and constant, in contrast to cramping pain with biliary colic, which occurs without inflammation. The patient tries to lie on his right side with his legs crossed.
Nausea, vomiting An attack of biliary colic may be preceded by a feeling of bitterness in the mouth; this feeling does not go away even when pain appears. The developing attack is accompanied by nausea, often bilious vomiting.
After the contents of the stomach are released, the vomit is yellowish in color. In this case, vomiting brings the patient some relief, albeit temporary.
General symptoms Acute inflammation always provokes a rise in body temperature. At the same time, temperature indicators can be used to judge the severity of the inflammatory reaction. Catarrhal cholecystitis (common inflammation) is accompanied by low-grade fever - 37.5 - 38ºС.
Gangrenous (purulent melting of the bladder walls) and phlegmonous (necrotic) form of inflammation of the gallbladder is always accompanied by a rise in temperature to 39ºC and above.
Gangrenous and acute phlegmonous cholecystitis occur with symptoms of an acute abdomen: “board-shaped” abdomen - tension in the abdominal wall due to severe pain and rapidly developing inflammation. Yellowness of the eyeballs and tachycardia up to 120 beats/min are often observed.
At the same time, failure to provide timely medical care is fraught with the development of peritonitis.
Diagnostics
In case of acute symptoms in the abdominal cavity, it is important to quickly make a diagnosis. Pre-acute cholecystitis is diagnosed based on the patient’s complaints and characteristic symptoms of the disease
The doctor receives confirmation of the diagnosis through the following studies:
- general blood test - leukocytosis and ESR, as signs of inflammation in the body;
- blood biochemistry - increased liver function tests;
- Ultrasound of the abdomen - the gallbladder is enlarged, the walls with a double contour reach more than 4 mm in thickness, Murphy's symptom (tension of the gallbladder with slight pressure with an ultrasound sensor), stones may be detected, dilated bile ducts;
- Cholangiography (X-ray examination of the biliary tract) and CT are prescribed in cases of suspected destructive inflammation (vesical phlegmon or gangrene).
Share the article on social media. networks:
Drug treatment of cholecystitis: list of drugs
Drug treatment of acute or chronic calculous cholecystitis differs from usual. It is very important that the treating specialist take this fact into account and make adjustments to the treatment regimen. In addition, calculous cholecystitis is always complicated by colic caused by blocking of the neck of the gallbladder with a calculus. Because of this, the normal flow of bile is disrupted.
If this procedure is delayed for a long time, a person may experience peritonitis or rupture of the gallbladder.
If there are no indications for surgery, therapy with ursodeoxycholic acid is prescribed. It is capable of dissolving stones. The minimum duration of therapy in this case should be at least six months, but in most cases it continues for several years. Usually the tablets are taken immediately before bed.
Most often prescribed:
- Ursohol.
- Ursosan.
- Ursofalk.
- Ursodes.
To achieve the greatest effectiveness from such therapy, the doctor may additionally prescribe sanatorium and physiotherapeutic methods of influence. It is very important to maintain proper nutrition: you must completely avoid harmful foods.
Cholecystitis is a fairly common pathology of the gallbladder, which is diagnosed in approximately 20% of the adult population.
Inflammation of the gallbladder can be provoked by impaired blood circulation in the walls of the organ, stagnation and infection of bile.
Effective treatment of the disease requires proper diagnosis and exclusion of all factors influencing the development of the pathology. Treatment of cholecystitis with medications helps eliminate the manifestations of the disease and alleviate the patient’s condition.
About cholecystitis
Chronic cholecystitis can be calculous (with the formation of stones in the bladder cavity) and acalculous. Under the influence of damaging factors, a sluggish inflammatory process begins to develop on the walls of the gallbladder.
As the pathology progresses, the walls of the organ thicken, the walls lose mobility, and scars and ulcerations form on the mucous tissues. This aggravates the disruption of bile outflow and promotes the formation of stones.
The development of cholecystitis can be caused by the influence of the following main factors:
- microbial infection;
- unhealthy irregular diet;
- inflammation of the pancreas (which can progress to the gallbladder);
- dyskinesia (violation of the tone of the gallbladder and biliary tract);
- the presence of stones in the gallbladder;
- parasitic diseases (giardiasis, opisthorchiasis, amoebiasis, etc.).
The most common is chronic calculous cholecystitis, the development of which is provoked by cholelithiasis.
This form of pathology is characterized by periods of remissions and exacerbations (attacks of biliary colic). Exacerbation is often caused by dietary errors (fatty and fried foods).
In addition, an attack can be caused by hypothermia, decreased immunity, shaking, or physical exertion.
An attack occurs when a stone hits the neck of the gallbladder, causing a spasm. The main symptom of biliary colic is severe pain in the right hypochondrium, radiating to the area of the scapula, shoulder or collarbone.
Often an attack of biliary colic is not controlled by conservative treatment methods.
If additional symptoms appear, for example, high body temperature and vomiting mixed with bile, which does not bring relief, this indicates acute calculous cholecystitis, requiring emergency surgical care.
The main symptoms of cholecystitis are:
- weak aching pain in the right hypochondrium, which gradually intensifies and becomes pulling and stabbing;
- feeling of discomfort after eating fatty and fried foods;
- increased pain after drinking alcohol (including beer);
- loss of appetite;
- decreased intellectual and physical performance, lethargy;
- sudden weight gain;
- rare stools, constipation;
- decreased immunity;
- nervousness and irritability.
Very often, cholecystitis occurs in women who are overweight. Weight control and dietary nutrition significantly reduce the possibility of developing this pathological process.
The treatment regimen for cholecystitis is selected by a gastroenterologist individually in each case and depends on the clinical picture, form of the disease and functional state of the gallbladder.
Typically, in the chronic form of cholecystitis, conservative treatment methods are used, the main purpose of which is:
- Eliminate inflammatory changes in the walls of the gallbladder.
- Eliminate symptoms of the disease.
- Prevent complications.
- Improve the patient's quality of life.
| Group of drugs | pharmachologic effect | Titles |
| Antibiotics | Eliminate bacterial infections and local inflammation |
|
| Sulfonamide drugs | Destroy pathogenic microorganisms in the intestines (with concomitant diseases) | |
| Antimycotics | Destroy fungi that actively multiply during antimicrobial therapy |
|
| Choleretic agents | Normalizes the production and flow of bile | |
| Antispasmodics | Relieves muscle spasms, eliminates pain |
|
| Hepatoprotectors | Restore liver function, accelerate hepatocyte regeneration |
|
| Enzymes | Normalizes and facilitates digestive processes | |
| Anti-inflammatory drugs | Have long-term analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects |
|
Antibiotics
For cholecystitis caused by bacterial pathogens, antibiotics are prescribed. In acute forms of the disease, such drugs are almost always used.
The advantage of antibiotics is their ability to penetrate well into bile and a wide spectrum of action.
Antibiotics in the treatment of cholecystitis must be specifically active against pathogenic microflora that have colonized the walls of the gallbladder. In most cases, cephalosporins are used, which have high activity. If inflammation is severe, the erythromycin group of drugs is recommended.
When treating pregnant women, elderly patients and children, the penicillin group of antibiotics is used, which are effective and absolutely safe.
Sulfonamides replace antibiotics when:
- it is impossible to carry out classical antimicrobial therapy;
- the course of the pathology is complicated by the inflammatory process of the intestinal mucous tissues.
Antimycotics are prescribed when fungal flora is activated in the body, which is often provoked by antimicrobial therapy. Therefore, many doctors use antimycotics as a preventive (prophylactic) measure.
When parasites are detected in the bile during the diagnosis of cholecystitis, treatment is prescribed to help destroy them and remove them from the body. Drugs are selected depending on the pathogen:
- For opisthorchiasis, fascioliasis, clonorchiasis, Chloxyl (in powder) is used simultaneously with Furazolidone, which is recommended to be dissolved in milk.
- For strongyloidiasis, trichuriasis, hookworm, Vermox tablets are used.
- For giardiasis and amoebiasis, Macmiror and Trichopolum are prescribed.
The use of choleretic drugs in the treatment of cholecystitis in adults is a mandatory part of therapy. Such medications contain bile components that help increase its production by the liver and slow down the process of stone formation in the gallbladder. The following drugs are often used:
- Allohol. Prevents fermentation processes in the intestines, reduces flatulence;
- Nikodin. It has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects and is used in combination with antibiotics;
- Digestal. Improves the process of food digestion;
- Gepabene. Has a hepatoprotective effect (protects liver cells).
Antispasmodics relax the gallbladder, ducts and sphincter of Oddi of the duodenum, which improves the outflow of bile and relieves pain. The most effective antispasmodics are:
- Mebeverine. Selectively affects the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, and therefore does not affect blood vessels and the heart. Has a pronounced analgesic effect.
- Odeston. Has a choleretic effect, reduces the formation of bile.
- Olimethine. It has an anti-inflammatory and choleretic effect.
- Meteospasmil. The composition contains two components: Alverine (good for relieving spasms);
- Simethicone (anti-flatulence).
Cholekinetics
Cholekinetics have an irritating effect on the mucous layer of the small intestine, which promotes the release of the hormone-like substance cholecystokinin. Cholecystokinin contracts the gallbladder and relaxes the ductal system, thereby improving bile production. The most commonly used cholekinetics:
- Magnesium sulfate (25% solution). It should be borne in mind that this remedy has a strong laxative effect;
- Berberine;
- Carlsbad salt.
Cholelitholytics
Cholelitolytics dissolve cholesterol stones in the gallbladder. However, they are not always effective. They can be taken if:
- The size of the stones is no more than 15 mm and they occupied 1/3 of the GB.
- Attacks of pain are observed infrequently.
Even in these cases, the risk of exacerbation is high. It is recommended to treat cholecystitis with cholelitholytics under ultrasound control once every 3-4 months. If no positive effect is observed, this indicates treatment failure. Cholelitholytics are used when there are contraindications to surgery to remove the gallbladder or when the patient refuses surgery.
These drugs, in addition to their cholelitholytic effect, have a choleretic effect:
- Ursosan;
- Uro- and chenodeoxycholic acid;
- Ursofalk.
Prokinetics
Prokinetics are used as agents that provide symptomatic relief and eliminate nausea and vomiting:
- Domperidone.
- Cerucal.
- Metoclopramide.
- Motilium.