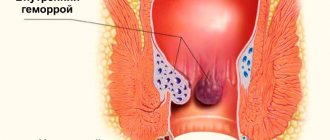
The initial course of hemorrhoidal disease is the most dangerous. If treatment is not taken, the disease quickly becomes chronic.
Itching, burning, abdominal pain are the first signals about the onset of hemorrhoids development
Hemorrhoids are a delicate condition that people are embarrassed to share with their doctor. The disease gradually becomes chronic and is already difficult to treat. It is at the initial stage that hemorrhoidal disease can be cured quickly and without complications.
Table: Stages of hemorrhoids
| Stages of development | Symptoms |
| Stage 1 | Development of bleeding |
| Stage 2 | Bleeding, prolapse of hemorrhoids with spontaneous reduction into the anal canal |
| Stage 3 | Bleeding, prolapse of nodes with the need for manual reduction |
| Stage 4 | Constant prolapse of nodes without the possibility of their reduction, bleeding |
An insidious illness can take both strong men and fragile girls by surprise. In recent years, doctors have more often stated the fact that the disease is getting younger. Hemorrhoids often occur in women due to pregnancy and childbirth, and in men due to heavy physical activity.
Stage 1 of the disease often occurs latently and without symptoms
If you experience discomfort in the anal area or any signs of early hemorrhoids, you should definitely see a proctologist. Otherwise, the consequences can be sad. The disease from the first stage can progress to the second, with more serious and painful symptoms that take longer and more difficult to treat.
What influences the development of stage 4 hemorrhoids
Inflammation of blood vessels in the anal area, called hemorrhoidal, has several stages of development. The fourth is the most severe form of the disease, usually related to the external or combined form of the disease. For the development of stage 4 hemorrhoids, it is enough not to be treated in the presence of the third stage of the disease. At the same time, the disease gradually gains momentum, deepening and periodically exacerbating. More rapid development can occur with:
- insufficient amount of physical activity (the so-called sedentary lifestyle);
- excessive amounts of physical activity (overexertion, heavy lifting, prolonged standing, etc.);
- sudden change in body position;
- severe cough;
- release of gas formations;
- severe constipation;
- diarrhea.
When the time comes for the development of this stage, exacerbation can begin even with minimal changes in pressure in the abdominal cavity. The vascular nodes simply fall out of the anus, creating a lot of unpleasant sensations. If the patient independently pushes them back inside, then the nodes will rarely remain there for a long time; they will constantly strive to fall out again.
Friction of the venous walls, as well as their frequent injuries, lead to the appearance of wounds that begin to bleed. During this period, inflammation and strangulation of hemorrhoidal formations occurs.
https://youtu.be/j3N-0aGDkVs
Features of treatment
Treatment of mixed hemorrhoids is prescribed depending on the stage of development of the disease:
- At the initial stage, conservative methods are used. The patient is prescribed drugs that improve blood circulation, strengthen vascular walls and eliminate unpleasant manifestations of pathology.
- Second degree hemorrhoids are eliminated using cryodestruction. During the procedure, hemorrhoids are exposed to low temperatures, which causes them to freeze and die. Cones can also be tightened using latex rings.
- If the treatment was not carried out on time and the development of the third degree was allowed, then medications alone cannot be used. The dimensions of the internal and external units in this case are quite large. Therefore, treatment of combined hemorrhoids of the 3rd degree is carried out using surgical intervention. This method involves pulling the nodes up with special titanium plates.
- At the last stage, hemorrhoids must be removed surgically. Other therapeutic methods will not bring results.
In the initial stages of the disease, the doctor prescribes medications
At the beginning of the development of pathology, it is possible to save a person from suffering. The main thing is that the patient follows all the doctor’s recommendations, even after the condition has improved.
Consequences of neglect of the disease
Some people think that stage 1, 2 or 3 hemorrhoids are one of the diseases that are not worth spending a lot of time on. They delay the meeting with a specialist for an indefinite amount of time, aggravating their condition. But when the fourth and final stage of hemorrhoids arrives, they are surprised that they feel unwell. After all, if this disease is not treated, then you can get a whole bunch of troubles:
- the first trouble is pain that seems to follow the patient everywhere, especially in the toilet;
- Lack of treatment for hemorrhoids leads to frequent bleeding, which causes the development of severe anemia. As a result, a number of complications develop, such as heart failure, respiratory failure and many others;
- According to statistics, the greatest likelihood of developing rectal cancer is in those patients who “gave up” and, accordingly, did not treat hemorrhoids. The cancerous tumor is “masked” against the background of hemorrhoidal formations and develops quietly. It is extremely difficult to notice it in such an environment, so the tumor develops to stages 3-4.
Symptoms of the disease
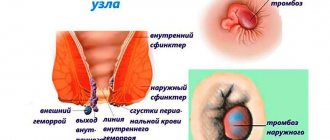
The fundamental symptom of stage 2 hemorrhoids, which distinguishes it from the initial stage, is the regular exit of pathologically altered hemorrhoidal veins of the rectum beyond its boundaries.
Hemorrhoids of the 2nd degree (attached photos) also differ from more severe forms of the disease (3rd and 4th degrees). Cavernous accumulations are still able to independently return to the anal passage after bowel movement. However, the nodules gradually grow larger and lead to more and more discomfort.
In addition to the occasional hemorrhoidal cones emerging from the anal canal, other unpleasant symptoms also occur:
- intense itching and burning sensations in the anus and anorectal area;
- bleeding, often massive. Bloody discharge occurs after bowel movements and appears in the form of small droplets or thin streams. The flow of blood is observed after almost every act of defecation;
- a feeling of the presence of a foreign object in the rectum, as well as a feeling of an incompletely emptied anal canal;
- painful sensations when visiting the restroom. Hemorrhoids of uncomplicated degree 2 are characterized by a less severe pain syndrome than in severe forms of the pathology, but they can no longer simply be ignored.
Thus, the clinical picture of the second stage of hemorrhoids is characterized by a greater severity of the main symptoms than with stage 1 of the disease. However, even in this case, not all patients go to the proctology office.
Such a sign may indicate the development of not only varicose hemorrhoidal veins, but also the presence of much more serious diseases, for example, a malignant tumor of the rectum.
Signs of stage 4 hemorrhoids
How to find out about the onset of stage 4 hemorrhoids?
It's not difficult at all. Since by this time the anal muscles and connective tissues have atrophied, external hemorrhoids appear that do not retract inward, requiring manual intervention to tuck them in. The patient often feels itching, and dermatitis appears on the skin in the anal area. The reason for this is vascular nodes stuck in the passage, preventing the sphincter from closing. In this case, the inflamed surface of the rectum produces an inflammatory exudate, which, when it gets on the skin around the anus, irritates it, causing irritation and dermatitis, causing severe discomfort and the desire to scratch. At stage 4 of hemorrhoids, the pain does not decrease, but becomes more noticeable and almost constant. All this negatively affects the character of patients, causing them to become very irritable and restless. Participate in an anonymous survey:
Which symptom of hemorrhoids bothers you most?
Diagnosis of hemorrhoids in the hospital
When a patient finally decides to go to a proctologist with the question of how to treat stage 4 hemorrhoids, he undergoes a series of procedures necessary to diagnose the disease and prescribe treatment before surgery, so be prepared for the following procedures:
- external examination of the patient. In this case, the patient takes a knee-elbow position or is placed in a special chair. The doctor notes the presence of scars and nodes, as well as other abnormal formations on the outside of the anus and on the skin near it;
- analysis of line stimuli. This is how the doctor checks the condition of the sphincter muscles;
- examination of the dilated anus will make it possible to determine the presence of cracks;
- finger diagnostics is one of the unpleasant, but extremely necessary methods. With its help, the tone of the sphincters, the intensity of pain during examination, and the presence of abnormalities on the surface of the rectum are determined. To evaluate hemorrhoids, the doctor asks the patient to push. The reason is that these formations change their size when pressed;
- a blood test that detects the presence of anemia accompanying hemorrhoids due to frequent hemorrhages;
- coprogram (analysis of feces). Before taking the test, you should eat light, non-coloring foods, and also remove beets and other coloring foods from your diet 3 days before the test;
- colonoscopy, in which the doctor visually assesses the condition of the mucous surface of the rectum using an endoscope;
- irrigoscopy, that is, x-ray examination of the rectum. Before conducting the study, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the intestine from feces.
Types of surgical intervention for stage 4 hemorrhoids
At stages 2 and 3 of the disease, the use of minimally invasive methods of getting rid of hemorrhoids is common, but treating stage 4 hemorrhoids without surgery is almost impossible. Before the operation, drug treatment is carried out, since during an exacerbation, operations cannot be performed.
Surgical operations required for the treatment of stage 4 hemorrhoids are divided into:
- traditional;
- hemorrhoidectomy;
- laser surgery;
- Longo's method.
Let's look at them in more detail.
Longo method
This method is good in cases where there are no external nodes. Minimal trauma and quick results allow you to recover in the shortest possible time.
Flaw:
Cannot be used for external nodes. In addition, the cost of such an operation is quite high.
Laser surgery
Removal of nodes using a laser is possible even in the presence of an exacerbation. In addition, laser surgery is almost painless and quick.
Flaw:
Removing large hemorrhoids using a laser is ineffective. Part of the node remains, and over time it begins to remind itself of itself with new attacks of hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoidectomy
This type of surgery is combined with hemorrhoidopexy. In this case, a special tube-like device is inserted into the anus. This device stitches all the nodes at the base with threads, by which they are pulled by another device, which cuts off all the nodes and stitches their base with special clips. Hemorrhoidectomy is low-traumatic. In addition, in the process the mucous membrane is tightened.
Flaw:
The cost of such an operation is quite high.
Minimally invasive methods
Treatment of internal hemorrhoids, as well as external forms of the disease, also occurs with the help of minimally invasive techniques. This type of surgical intervention, characterized by low trauma, is used if conservative therapy is ineffective.
In the second stage of the pathological process, several minimally invasive interventions are available. The choice of the preferred method is made after diagnostics and in-depth examination of the patient.
- Desarterization of hemorrhoidal nodules. The essence of the technique is to ligate the arteries that feed the cavernous formations. To find such vessels, an anoscope equipped with a special sensor is required. The discovered arterial branches are tied up with a special self-absorbing material, after which the nodule, deprived of nutrition, “dies”. After a few weeks, the venous collection is replaced by connective tissue.
- Sclerotherapy for hemorrhoids. Another popular technique involves injecting special drugs into the venous collections - the so-called sclerosants. These solutions glue the blood vessels together, causing the hemorrhoid to collapse and then disappear altogether. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and is usually not accompanied by any complications. Another advantage of sclerotherapy is a short rehabilitation period.
- Cryodestruction. Liquid nitrogen is used to destroy anal varicose veins. The node is removed by exposing it to extremely low temperatures, as a result of which the pathological tissues freeze and die. The procedure is painless and free of bleeding. In addition, frost activates local immunity, enhances metabolic processes and improves microcirculation in the rectum.
- Infrared coagulation. This minimally invasive method of removing hemorrhoids involves exposure to infrared rays. Using a special device, infrared waves are directed to the “leg” of the varicose formation, causing coagulation (clotting) of the protein substances contained in the tissues. As a result, the nodule stops receiving nutrition and dries out.
- Ligation of nodes with latex rings. It is used for formed internal nodes. The essence of the technique is to tighten the base of the cone with a special latex ligature. This ring isolates the node from the blood supply, as a result of which after a couple of weeks it dries out and leaves the rectum along with the feces.
Minimally invasive techniques for the treatment of hemorrhoidal nodules are a promising direction in proctology. However, most of them are not able to overcome this disease forever, since they “fight” not with the cause, but with the effect.
It is important to exclude provoking factors, and then you can forget about hemorrhoids for a long, long time.
Complications
After removing hemorrhoids with any type of surgery, complications may arise. These include:
- severe pain (you have to use anesthetics);
- problems with urination in men (catheter inserted);
- a symptom of fear, a negative psychological attitude (for relief, a light diet and laxative are prescribed. Sometimes analgesics);
- bleeding in the first hours after surgery;
- narrowing of the anal canal (appears due to a doctor’s mistake, and can only be treated by a specialist. It can appear even 2 months after surgery);
- relaxation of the sphincter and rectal prolapse (due to doctor error. Treated surgically);
- fistula (conservative treatment);
- suppuration (antibacterial therapy and anti-inflammatory procedures).
The list of complications is quite long, but complications appear extremely rarely.
How to live after surgery to remove hemorrhoids?
Bad habits should be eliminated.
After removal of hemorrhoids and the rehabilitation period, you can return to your normal lifestyle. However, if the patient wants to avoid relapse of the disease, then some things will still have to be changed. In order to avoid this, it is advisable to completely reconsider the power system. Watch what you eat. Try not to eat foods that cause constipation. Eat small meals at least five times a day. The diet should consist of fruits and vegetables. It is better to cook dishes by steaming. It is better to forget about fast food, sausages, canned foods, sweets, baked goods and bad habits forever. Go in for sports, any type of gymnastics, yoga, Pilates, fitness, swimming, skiing will do. By following these simple rules, you can easily become one of the percentage of people who, after surgery, never experience hemorrhoids again.
Diet
During illness and after surgery, you need to follow a special diet, so make sure that your food is balanced and nutritious.
You need to eat at least 6 times a day, but in small portions. Choose gentle foods that leave your stool soft.
Remove from your diet white cabbage, spinach, turnips, onions, garlic, raspberries, beans, beans, grapes, tangerines, black bread, kvass, smoked meats, hot and spicy dishes, marinades and canned food, alcohol (including low-alcohol drinks), sorrel, radish , radishes, dates, apples, gooseberries, peas, lentils, raisins, nuts, milk and soda. In addition, limit your consumption of sugar, baked goods, fatty meats and mushrooms.