Kinds
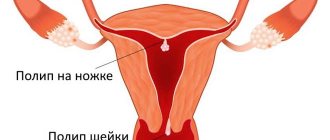
Polyps can be single or multiple. The outer part of the polyp consists of epithelial cells, the same as the cells of the mucous layer of the uterine cervix. Types of epithelium covering the polyp:
- Cylindrical
- Multi-layer and flat
By type, a uterine polyp can be:
- Fibrous;
- Glandular polyp;
- glandular fibrous polyp;
- atypical or adenomatous endometrial polyp.
| View | Description |
| Fibrous | Formed from the connective endometrial layer. It is more often diagnosed in premenopausal or menopausal women. The risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor is high. |
| Glandular fibrous | They are formed from the glandular and connective endometrial layer. Their size can be above average (from 2 cm). After therapy, patients are prescribed a course of hormonal medications and constant medical supervision to prevent relapses. |
| Glandular | One of the simplest types of education. Formed from the mucous membrane of the uterus. They are usually small and more common in young women who have not given birth. The likelihood of degeneration and reappearance after treatment or other complications is minimal. |
| Atypical | Large neoplasms with a homogeneous structure. The risk of degeneration into a malignant form is highest. Therefore, they need to be removed as quickly as possible. And the patient may be prescribed chemotherapy to prevent the development of cancer cells in the cervix or uterine cavity. |
https://youtu.be/DkiikCSLrzs
Why do they appear?
The reasons for the appearance of cervical polyps have not yet been precisely discovered. The most common factors provoking education:
- chronic infections;
- hormonal imbalance;
- mechanical injuries of the uterine cervix.
Inflammatory processes
A polyp in the cervical canal can provoke a number of inflammatory and chronic pathologies.
- The inflammatory process in the lining of the uterus is endometritis.
- An inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the cervix caused by an STI – cervicitis.
- Infection with the human papillomavirus – HPV.
These pathologies affect the structure of the epithelium, the functioning of the glands, and the regenerative processes in tissues. Therefore, the likelihood of polyp formation is high.
Article on the topic: cervicitis of the cervix - what is it?
Hormonal disorders
If the ovaries do not work properly, then a hormonal imbalance occurs in the female body, the amount of estrogen increases sharply, and progesterone decreases. Excess estrogen leads to thickening of the mucous membrane in the cervix, which can cause polyps to appear. Reduced progesterone provokes the formation of cystic neoplasms
Injuries
During mechanical abortions, curettage for diagnostic examination, and cleansing, the tissue structure of the uterine cervix is disrupted. If injuries are complicated by infectious pathologies, then the progress of damage recovery slows down significantly. Polyps grow on injured areas of the epithelium.
Causes of polyps
There is no consensus among experts about the root cause of polyps in the cervical canal. Modern gynecology puts forward the following theories:
- inflammatory processes;
- hormonal imbalance;
- genetics;
- structural features of the internal lining of the cervical canal;
- metabolic disorders.
Inflammatory processes in the uterus and its cervix, which occur over a long period of time, cause disruptions in the division of tissue cells. As a result, an excess of these cells forms in the form of polyps. Microorganisms such as ureaplasma, mycoplasma, gardnerella and others can play a special role. Chronic inflammation can also be caused by an incorrectly installed intrauterine device.
The tissues lining the cervical canal are very sensitive to changes in hormonal levels. Experts have proven a pattern between the high content of estrogen in a woman’s blood and the presence of polyps.
If polyps were observed in a woman’s relatives, most likely this pathology will be observed in her herself. Scientists have identified several genes that determine an increased number of sex hormone receptors in women. The more of these receptors, the more sensitive the tissue is to hormonal imbalances. Accordingly, the formation of polyps is more likely.
Common chronic diseases lead to disruption of metabolic processes, such as:
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- hypertension.
Symptoms
There are no specific symptoms of polyps in the cervical area. But the signs may be associated with concomitant pathologies that caused the tumors. The size and type of polyps directly affect the intensity of the symptoms. If the polyps are small, then the symptoms practically do not appear, and you can only find out about them during a routine examination by a gynecologist. What symptoms should you pay attention to:
- discharge;
- pain;
- cycle disorders;
- difficulty conceiving.
If you have one or more signs, you need to consult a doctor and undergo diagnostics, which will help you recognize the type of formation and draw up a plan for further treatment.
Discharge
Discharge from polyps occurs frequently. They usually occur during sexual intercourse or after it, if the tumor is located in the vaginal canal. The polyp is damaged, which causes bloody smears. Also, such smears can be done before and after the end of menstruation. If smears appear during menopause, this is a very alarming sign; it is possible that a benign polyp will transform into a malignant formation. That is, uterine cancer appears. In addition to bloody discharge, there may be strong serous or serous-purulent discharge with a specific odor if there is infection and inflammation in the reproductive organ.
Pain
If the polyp is larger than average, then pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen may periodically bother you. There may be pain during sex because the polyp is injured.
Menstruation disorders
Polyps of the cervical canal cause prolonged periods, with large blood loss. Because a high level of the female hormone (estrogen) promotes thickening of the lining of the uterus, which causes longer periods. Heavy bleeding also provokes the development of anemia.
Infertility
Destabilization of hormonal levels often leads to difficulties in achieving pregnancy. The ovulatory process is disrupted. Polyps prevent male reproductive cells from entering the uterus and fertilizing the egg.
Is it necessary to remove a polyp of the cervical canal, and by what method?
To stop the polyp surgically, there are various ways to remove the polyp of the cervical canal. But the favorite and effective method of polyp removal is hysteroscopy. Usually this method is combined with curettage. After surgical removal is completed, this material is sent to the laboratory for diagnostic histological examination.
Also, other methods can remove a polyp: curettage, diathermocoagulation, conventional polypectomy or cryodestruction. But according to doctors, they are less effective than hysteroscopy. But any doctor chooses a technique based on the different age or clinical data of the patient.
Also, clinical manifestations dictate further treatment. As soon as the polyp is removed, conservative treatment is prescribed. That is, certain hormone preparations can completely restore a woman. In some rare cases, it is necessary to remove the entire uterus along with the polyp. This is done when a woman is at risk (polyp growth, malignancy, metastases). It’s bad when a malignant polyp is detected in the uterus - the uterus must be removed. A large polyp of the cervical canal must be stopped quickly.
Diagnostics
If signs of polyps are detected, you need to contact a gynecologist and undergo diagnostics. Detection and diagnostic methods:
- Visual control - the cervix is examined on a gynecological chair using mirrors. So, the doctor can see the polyps.
- Ultrasound examination - ultrasound reveals inflammation in the pelvic organs, and sees polyps that are not visible during visual diagnosis.
- Colposcopic examination – for a thorough visual diagnosis.
- Hysteroscopic examination - a microvideo camera is inserted into the cervix through the vaginal canal so that the doctor can see the full picture of the disease and associated complications.
Types of studies for diagnosing uterine polyps
An ultrasound is not always enough to fully assess the functionality of the pelvic organs or the reproductive system as a whole.
In some cases, the following types of research may be required::
- Abdominal ultrasound - viewing the pelvic organs through the peritoneum;
- Transvaginal ultrasound - examination of the cervix and its cavity with a vaginal sensor;
- Hysteroscopic examination - assessment of the uterine cavity using optical equipment;
- Biopsy - targeted biopsy is performed under ultrasound imaging control for further tissue histology;
- Hysterosonography with contrast agent;
- Dopplerography is an assessment of the state of blood circulation in the uterine cavity.
The reliability of ultrasound data is highly accurate if the study meets the requirements.
Each method has its own disadvantages and advantages. The larger the visualization of the pelvic organs, the higher the power of the optical capabilities of the equipment, the higher the information content of the study, and the higher the chances of identifying other asymptomatic pathologies.
Treatment methods without surgery
Treatment of polyposis without surgery is possible, but not always. Since conservative therapy does not remove polyps, it only stops their development and reduces symptoms. To eliminate symptoms and stop the growth of tumors, medications are prescribed:
- hormonal;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antibacterial;
- vitamins;
All therapy is complex and is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor.
Hormone therapy
Treatment with hormones is effective if the formations appear due to hormonal imbalance in the body. Progestin agents or COCs are prescribed.
- COCs stabilize the balance of estrogen and progesterone in the body.
- Gestagens – stop bleeding, normalize the functions of the endocrine system.
How hormones affect formations in the cervix:
- neoplasms stop developing;
- the likelihood of transformation into a malignant form decreases;
- vaginal discharge stops or decreases in intensity;
- the cycle stabilizes;
- less risk of uterine bleeding;
- pain sensations are reduced.
The type of drugs for treatment is determined by the doctor after tests for hormones, which reveal their excess or deficiency.
COOK
Combined oral contraceptives contain two main female hormones - progesterone and estrogen. The drugs are prescribed to women of reproductive age suffering from uterine polyps of the glandular or glandular-fibrous type. What a doctor from the COC can prescribe:
- Regulon course;
- Yarina;
- Janine;
- other means of similar action.
They need to be taken from the first day of the 21-day cycle. Then there is a seven-day break. At this time, menstruation begins. Then we will resume taking the drug. The duration of treatment is determined individually, usually from three months to six months, but there may be other periods.
Gestagens
The active substance here is progesterone. The course is prescribed:
- Norkoluta;
- Duphaston;
- Utrozhestan.
It is better to take these drugs according to the following scheme: from 116 to 25 days of the cycle. You need to take the pills for 10 days. The dosage is determined by the doctor. Course duration is from 3 to 9 months.
Antibiotics
If the cause of the appearance of polyps is infectious and inflammatory pathologies, antibiotics will help. Depending on the type of infection, appropriate groups of antibacterial agents are prescribed.
- Chlamydia - tetracycline, macrolide antibiotics.
- Mycoplasmosis – tetracycline, fluoroquinolone.
- Trichomoniasis - nitromidazole.
- Gonorrhea – fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins.
- Ureaplamoz - macrolides, tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones.
- Adnexitis is the same as with ureaplamoz.
- Cervicitis - the same as with ureaplamosis and adnexitis.
The antibiotics used to treat these diseases are described in detail in the table.
| Antibiotic group | Product name | How it works | How to use |
| Macrolides | "Azithromycin" | Suppresses the activity of microorganisms and bacteria | Two tablets daily, twice a day or as recommended by a physician. |
| "Erythromycin" | Bacteriostatic and bactericidal effect | Four tablets per day. The course of treatment is seven to ten days | |
| Tetracyclines | "Tetracycline" | Suppresses the action of microorganisms | Four tablets per day. The course of treatment is five to seven days |
| "Doxycycline" | Suppresses the action and proliferation of microorganisms | Half a tablet morning and evening. The course of treatment is ten days. | |
| Fluoroquinolones | "Ofloxacin" | Destroys infection | Two tablets twice a day (200 mg). Or one tablet once a day (400 mg). |
| "Ciprofloxacin" | Destroys infectious microorganisms | One or two tablets a day. During the week. | |
| 5-nitroimidazole derivatives | "Metronidazole" | Kills bacteria and protozoa. | Two tablets morning and evening. Course – 10 days. |
| "Ornidazole" | Kills bacteria and protozoa. | Four tablets twice a day. The course is five to seven days. | |
| "Tinidazole" | Acts on protozoan microorganisms that destroy the genitourinary system | Half a tablet twice a day. | |
| Cephalosporins | "Ceftriaxone" | Destroys bacterial infection | Intramuscular single injection. |
| "Cefotaxime" | Destroys bacterial infection | Intramuscular single injection. |
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Treatment of cervical polyps with anti-inflammatory drugs is effective for cervicitis, adnexitis and other inflammatory pathologies. They are usually prescribed along with antibiotics. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are also effective; they relieve pain, relieve inflammation, and reduce fever. Applicable:
- Ketoprofen;
- Ibuprofen;
- Diclofenac.
The dosage and regimen of use is determined by the doctor. You cannot self-medicate.
The essence of pathology
This disease is otherwise called a cervical polyp; in essence, it is an abnormal proliferation of cellular structures of the cervical mucosa.
Polyps can be diagnosed at any age; as an independent disease, they form quite rarely; most often, their formation occurs against the background of hormonal imbalance, or during a long-term chronic inflammatory process in the genitals.
If more than one growth forms in the cervix, doctors call this disease polyposis . The features of this disease depend not only on the location of the pathological growth, but also on its cellular composition.
Read about the symptoms of cervical polyps here.
Treatment with folk remedies
It is completely impossible to cure a polyp with folk remedies. But you can stop its growth and reduce symptoms. Folk remedies are used only as an auxiliary therapy. Herbal tampons based on herbs and oils work most effectively. Manufacturing instructions:
- take sterile cotton wool and gauze bandage;
- cut a small strip of bandage, about 15 cm, and fold it in half;
- Roll a small ball out of cotton wool;
- place a cotton ball in the central part of the workpiece;
- bring the edges of the gauze together and tie tightly with cotton thread.
After inserting the tampon inside, the ends of the thread should be on the outside so that the tampon can be easily removed later. Cut off the excess parts of the thread and bandage with scissors.
The tampon must be inserted deep enough into the vagina, closer to the cervical canal. You need to keep it for about two hours, but you can put it on overnight. Effective preparations for impregnating a tampon:
- calendula;
- sage;
- celandine;
- chamomile;
- sequences;
- sea buckthorn oils.
Let's take a closer look at the effects of herbs on the body.
- Calendula - heals wounds, relieves inflammation, disinfects and relieves pain. Recipe for calendula decoction: for 20 grams of dry herb, one glass of boiling water. Leave for half an hour with the lid closed. Filter through double gauze. If you do not have time to prepare a decoction, the oil of this plant can replace it; it is sold at the pharmacy. Soak the tampon in oil and leave it in for two hours, or better yet, overnight. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- Sage – disinfects, stops bleeding and relieves inflammation. For 1 tbsp. - a glass of boiling water. Simmer the mixture over low heat for about 10 minutes. Leave the broth for twenty minutes after turning off the heat. Strain. Moisten a tampon generously in the broth. Keep the tampon on for three hours.
- Celandine is a natural antiseptic, relieves inflammation, prevents polyp growth, and relieves pain. The collection is prepared in the same way as calendula decoction. Leave for half an hour. Use as impregnation for tampons. Leave it overnight.
- Chamomile – relieves inflammation, kills infection. For 1 tbsp. chamomile flowers - a glass of boiling water. Cover and leave for about 45 minutes. Soak the tampon in the decoction and leave it for a couple of hours or overnight.
- The sequence - heals wounds, destroys bacteria and microbes, reduces the inflammatory process. For 25 grams of grass 250 ml. boiling water Leave for about one and a half hours. Use as a tampon impregnation. Leave it for two hours, but you can also leave it overnight.
- Sea buckthorn oil regenerates the epithelium and has an anti-inflammatory effect. The oil is sold in pharmacies. Before use, it can be heated in a water bath. The tampon is soaked in oil. You can keep it on all night. The course of treatment is two weeks.
Application of candles
For polyposis, vaginal suppositories are prescribed as an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agent. If polyps appear due to inflammation or infection, suppositories are effective and do not depress the kidneys and liver, like similar tablets.
Vitamins
Vitamins and minerals activate the body's immune system. Doctors recommend taking complexes containing a complex of biotins (B vitamins) and minerals: iron, zinc, copper, selenium, magnesium. They help improve blood composition, stimulate cellular metabolism, metabolism and protein synthesis.
Removal of cervical polyp
Conservative therapy is not always effective; for large polyps, it has practically no effect, but only reduces symptoms. Therefore, doctors use surgical removal.
How to remove polyps on the cervix:
- hysteroscopy;
- diathermocoagulation;
- cryodestruction;
- radio wave method;
- polypectomy;
- complete removal of the cervix.
During the operation, local or general anesthesia is used, depending on the chosen surgical method. Sometimes it is enough to remove the polyp without touching the cervix, but in some cases its complete amputation is necessary, for example, when cancer develops.
Should I delete
The only correct way is surgery to remove the formations, but many patients do not want to resort to surgery and are interested in whether removal is necessary and whether it is possible to do so using conservative methods.
You can completely get rid of polyps only by removing them, but if you categorically refuse surgery, the polyp is small and there is no risk of degeneration into a cancerous tumor, then you can be treated with medication. Factors influencing the choice of treatment are as follows.
- The size of polyps is smaller than average - up to 1 cm.
- Type of formation - fibrous polyps respond best to medication.
- Stage of development - the earlier the growth is detected, the easier it is to cure.
- The patient’s age – if she is reproductive, they try to preserve the cervix.
- Individual susceptibility to drugs.
If medications are prescribed correctly and all instructions are followed, conservative therapy can give good results. But, if the polyp is large, there are complications and the risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor, the tumor must be removed surgically.
How to prepare properly
Preparation for surgery includes a thorough ultrasound and hysteroscopic diagnosis of the cervical canal. General urine and blood tests, tests for HIV, hepatitis and HPV are taken. If the patient has problems with the veins, then before the operation a consultation with a phlebologist is necessary, and during the procedure you need to wear compression stockings or an elastic bandage.
If the operation is performed under general anesthesia, the patient is prescribed an ECG to identify possible risks and consequences of anesthesia.
12 hours before the procedure, it is advisable not to eat or drink anything and to do a cleansing enema.
Hysteroscopy
Removal of a cervical polyp by hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical method. Its advantages:
- painless;
- no postoperative stitches;
- safe - minimal blood loss, no cavitary wounds.
- effective - through a micro-video camera, the doctor can see even the smallest polyps and carry out complete curettage without damaging healthy tissue.
The polyp is removed through an optical hysteroscope. Forceps and abortsang (special polyp forceps) are also used. First, a hysteroscope is inserted into the vaginal canal. The device shows the overall picture, and the doctor, watching what is happening on the monitor, excises or unscrews the polyps using auxiliary instruments. The operation is performed after the end of menstruation, no later than the 10th day of the new cycle.
When hysteroscopy is contraindicated:
- during pregnancy;
- if there is infection and inflammation;
- with stenosis;
- in oncology.
The presence of contraindications is determined by preliminary diagnosis. It is possible to use medications if they help eliminate contraindications.
Diathermocoagulation
Diathermocoagulation is the cauterization of a formation with high-frequency current. This is a relatively cheap procedure that has a good effect, but it has disadvantages:
- the procedure is quite painful;
- scars may remain - this complicates labor and prevents conception;
- wounds heal slowly after cauterization;
- bleeding is possible when the crust falls off the wound.
After cauterization with electric current, a wound remains at the site of the removed polyp, which then becomes covered with a crust. The crust protects the wound from germs and stops bleeding.
Diathermocoagulation cannot be done during pregnancy, with infectious and inflammatory pathologies, decreased blood clotting, if the woman has not yet given birth.
Cryodestruction
Cryodestruction is the cauterization of polyps with a stream of liquid nitrogen. The tissue freezes and dies, and normal epithelium appears in its place. Advantages of cryodestruction:
- no scars remain;
- painlessness;
- minimal risk of complications;
- can be performed on nulliparous girls.
The disadvantage of the procedure is the slow regeneration of tissue in the wound area, which is why it takes a long time to heal. Supportive drug treatment will help speed up the healing process. Contraindications:
- endometriosis;
- scars in the cervical canal;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases.
Radio wave treatment
Removal of polyps using the radio wave method is widely used in gynecology. Advantages of radio wave cauterization:
- minimal risk of injury to healthy epithelium;
- no scars remain;
- painlessness;
- Possible for young women.
Before performing the operation, it is necessary to exclude infectious and inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs and chronic pathologies.
Classic or laser polypectomy
- Classic cervical polypectomy is done with an electric loop. The polyp is grabbed and cut off.
- In laser removal, a laser is used as a tool.
A significant disadvantage of polypectomy is that it can only be used for small and medium-sized formations without complications.
Cervical amputation
Amptuation of the cervix is performed in case of severe complications and the presence of an oncological process (cervical cancer). Amputation is resorted to in extreme cases, especially when the girl is still planning to become pregnant.
What is the price
In a hospital hospital, surgical removal of the uterus is free of charge. The type of operation depends on the technical capabilities of the institution. Prices in a private clinic vary from 5 to 20 thousand rubles.
Prices for laser removal are up to 10 thousand rubles. Other removal methods may be more expensive or more expensive depending on the clinic and the need for the patient to continue to be in a hospital and receive medication support.
What happens after polyp removal?
In rare cases, as a complication of the removal, thermal burns and cervical stenosis may occur, which are formed due to excessive cauterization of the polyp attachment site. Therefore, after removal of a cervical polyp, for 3 weeks - pain in the lower abdomen, the appearance of bloody or more abundant mucous discharge, therefore during this period the following is highly undesirable:
- Have sex
- You cannot take a bath, go to the steam room, sauna, you should only take a shower
- You cannot douche with any means after removal.
- You can't use tampons, only pads
- Avoid heavy physical labor, sports, any physical exercise
Sometimes, if tissue is not completely removed, a relapse is possible, when a fresh neoplasm can again be found at the site of the former polyp. Therefore, it is very important to determine the possible cause of the growth of polyps in the female body and choose preventive treatment tactics - antiviral, hormonal therapy, anti-inflammatory, as well as promptly and correctly treat any inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs. And remember, treatment with folk remedies is possible, but only on the recommendation of your doctor. In most cases, traditional methods are used only after surgical treatment as a prevention of relapse.
Author:
Selezneva Valentina Anatolyevna physician-therapist
Prevention
You can prevent the appearance of cervical polyps by applying simple preventive recommendations:
- avoid stress and depression;
- eliminate alcohol and smoking;
- eat right - less fatty, salty and sweet;
- treat infectious and inflammatory processes in a timely manner;
- undergo regularly scheduled gynecological examinations - once every six months;
- use a barrier method to protect against STIs;
- strengthen the immune system.
The earlier you detect cervical polyps, the more successful the treatment will be. If the disease is neglected, polyps can develop into cervical carcinoma.
Answers to possible questions
Before surgery, many women have a whole list of questions. We will try to answer the most popular ones.
Does it hurt to remove
Most polyp removal methods are virtually painless. If the patient is highly sensitive, doctors use local anesthesia. The most painful method is diathermocoagulation. Otherwise, a woman may experience only minor pain during and after the procedure.
Is it possible to have an intimate life?
After surgery, the patient should follow the following precautions:
- do not have sex for four weeks;
- do not lift weights, do not give your body serious sports loads;
- don't douche.
All this must be observed for 1-2 months until the tissue heals. Otherwise, you can get an infection and cause complications.
Polyp on the cervix during pregnancy
Polyps do not affect the course of an already existing pregnancy; a woman can carry and give birth to a child without problems. During pregnancy, there is no need to touch the polyps, but after the birth of the child, treatment can begin. If the formations were discovered in the early stages of pregnancy (up to three months), they can be removed.
If polyps are present during pregnancy planning, they often cause difficulty conceiving and a woman cannot become pregnant for a long time. Why is this happening:
- The cause of polyps is hormonal. A reduced level of progesterone, the hormone responsible for pregnancy, prevents conception. The course of ovulation and the menstrual cycle is also disrupted and fertilization of the egg becomes more difficult.
- Large polyps located in the cervix can block the passage to the uterus and make it difficult for sperm to pass through and attach to its walls.
If you are planning a pregnancy and you have polyps, you need to cure them, and only then you can get pregnant.
Is it possible to get pregnant after surgery to remove
After removal of the formations, a woman must undergo gynecological control for about a month. The doctor looks at how the epithelium is healing, to see if there are any complications. The first examination is carried out 5-7 days after surgery. As soon as the wounds heal, you can plan a pregnancy. The sooner the better, since sometimes the disease can return if the cause of its occurrence has not been eliminated. Typically, pregnancy occurs within six months after removal of the formations. If growths reappear in the cervix after pregnancy, then there is nothing to worry about. They do not affect the development of the fetus and the upcoming birth.
Postoperative period
In general, the recovery period after removal of a polyp in the cervix proceeds without complications . After a couple of days, all unpleasant symptoms disappear.
After surgery, a woman is required to be prescribed hormonal medications that will reduce the concentration of estrogen in the blood, as a rule, this is Urozhetsan.
The course of taking this drug is determined by the doctor, but on average it is recommended to take it for three months.
If the removal was performed using a laser, you may need to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which will reduce the risk of developing an inflammatory process.
As for antibiotics, they are prescribed only if the cause of the polyp is an infection. The doctor may also recommend taking vitamins and immunostimulants.