How the disease develops
Before considering symptoms and treatment, it is necessary to understand what esophageal obstruction is. With the development of such a pathological condition, the passage of the food bolus through the esophagus is disrupted. Obstruction can develop as an independent disease or as an exacerbation of other pathologies.
If there has been injury to the walls of the esophagus, then during healing, connective tissue is formed, which can cause obstruction. Next, we will consider the reasons for the development of pathology in more detail.
Stages
Pathology can occur at any age: in young children, adults and the elderly. The disease has several stages:
- the person feels slight discomfort at the moment of swallowing, severe pain occurs in the chest;
- the subsequent stage of development is manifested in the fact that large pieces of food are difficult to pass; drinking liquid will help alleviate the condition;
- It is difficult to consume ground foods;
- a feeling of pain occurs when drinking water;
- the further stage is critical, absolutely the entire lumen of the esophagus is blocked, even liquid is not swallowed.
To prevent this, it is important to start treatment at the first sign.
https://youtu.be/-9EtKBm9-Ww
Stages of disease development
This pathology goes through several stages in its development:
- The patient begins to feel some discomfort when swallowing, and pronounced unpleasant sensations appear behind the sternum.
- At the next stage, large pieces of food pass with difficulty; it becomes easier if you drink liquid at the same time as eating.
- It becomes difficult to eat even pureed food.
- Pain in the esophagus occurs even when drinking any liquid.
- Esophageal obstruction at the next stage is a critical stage when the passage of the esophagus is completely blocked. It becomes impossible to even swallow water.
It must be borne in mind that the earlier the pathology is detected, the more effective the therapy will be.
Classification of dysphagia
The development of the disease is distinguished into 4 stages:
- Inability to swallow only specific types of solid foods;
- Inability to swallow solid food. Semi-liquid or soft foods are easy to swallow;
- The patient can only eat liquid food;
- The act of swallowing is not performed.
Currently reading: Causes of inflammation of the throat and esophagus, how to treat correctly and reviews
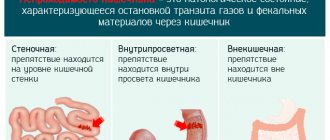
The disease, depending on the localization of the process, can be:
- Oropharyngeal or oropharyngeal. In this case, the bolus of food moves with difficulty from the pharynx to the esophagus;
- Esophageal or esophageal. It progresses if the lumen of the esophageal tract is blocked or as a result of disruption of its muscle structures. Experts divide this type into certain subtypes: upper, middle and lower;
- Cricopharyngeal incoordination.
Depending on the course, dysphagia can be:
- Constant;
- Intermittent (appears from time to time);
- Progressive. There is a gradual deterioration of the patient.
Forms and degrees of the disease
Two forms of pathology can be distinguished:
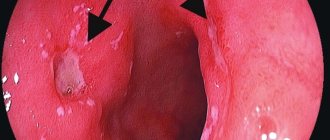
- Parts of the esophagus can narrow as a result of a benign lesion, for example, a chemical burn, consumption of various caustic liquids, or the presence of ulcers in the deep layers.
- Obstruction of malignant origin develops against the background of esophageal cancer.
The disease also has degrees:
- The first degree represents a narrowing of 9-11 mm.
- 2nd – narrowing diameter 6-8 mm.
- The next degree is 3-5 mm.
- 4th degree 1-2 mm.
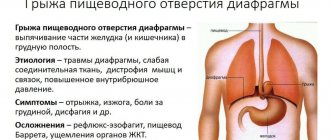
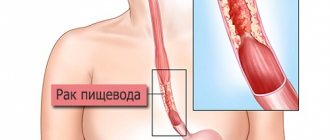
Esophagus
A long, hollow organ that resembles a tube that leads from the pharynx to the stomach is called the esophagus.
Its inner surface is lined with several layers of epithelial tissue. She is not prone to keratinization. Its characteristic property is the ability to recover quickly.
Muscle tissue consists of two layers. The outer one is formed by longitudinal fibers, their function is to ensure expansion of the organ.
The internal one is formed by circular muscles, they narrow it. A muscular seal is formed below - the sphincter. It separates the esophagus from the stomach cavity.
The outer surface is formed by connective tissue. Functionally, it is aimed at connecting the esophageal tube with the organs that are located in the chest. The looseness of the fabric allows it to stretch and contract.
In some places the esophagus has a natural narrowing. Its functions include:
- Transport. Due to the work of muscle tissue, food moves through the tube into the stomach.
- Secretory. The mucous membrane secretes a secretion that lubricates food.
- Protective. The sphincter prevents food from flowing back in.
Reasons for the development of pathology
There are a large number of factors and diseases that can trigger the development of esophageal obstruction. The most frequently noted are the following:
- Stenosis can be caused by ingesting chemical liquids or too hot drinks; it is for this reason that you should not drink very hot drinks.
- Malignant and benign neoplasms in the esophagus.
- Mechanical injury to the esophagus, which is possible as a result of foreign objects or injury.
- Irritation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus by the contents of the stomach and gall bladder.
- Obstruction can develop as a result of infectious, inflammatory diseases.
- Connective tissue pathologies.
- Parts of the esophagus can also be damaged as a result of pathologies of the thyroid gland, for example, nodular goiter develops.
- There is even congenital obstruction, which develops in the child during intrauterine development.
Symptoms
Abdominal, thoracic, cervical - these are the sections the esophagus has. Obturation (blockage) mainly appears in the thoracic region; it is this region that is most sensitive to the formation of malignant neoplasms.
The main symptoms of esophageal obstruction are as follows:
- dysphagia - impaired or difficult swallowing, manifested by discomfort at the time of eating food, the inability to swallow hard, dry or poorly chewed food, and subsequently the inability to take even liquid meals;
- unexpected vomiting immediately after eating food, while blood streaks are noted in the contents, belching occurs with a fetid odor of rotten eggs;
- odynophagia - pathological, unpleasant sensations in the sternum area, which worsen when swallowing. Sometimes it can be assumed that this is a heart attack, since the pain provokes changes in the blood circulation of the heart muscle;
- sudden weight loss - with difficulty swallowing, the patient often refuses to eat another meal, even if he has an excellent appetite.
Dysphagia - obstruction of food through the esophagus - occurs in several stages. Belching and vomiting occur at stages II and III of the development of the disease, and the very last stage (IV) is characterized by the inability to swallow liquid. Well, when trying to take a sip, a person begins to feel a burning sensation, squeezing, and discomfort.
How to recognize obstruction
The anatomy of the esophagus is such that pathology can develop very quickly, so it is important to detect it as early as possible. Symptoms may be as follows:
- The main symptom of the pathology is dysphagia, when there is painful and difficult swallowing. The degree may vary, from mild discomfort to difficulty swallowing water.
- Pain appears behind the sternum when swallowing. These symptoms can be confused with heart pain.
- There is vomiting of food eaten with blood impurities.
- Frequent belching with the smell of rotten eggs.
- Due to stenosis, the amount of food eaten is reduced, so the patient loses weight.
Even the slightest signs of esophageal obstruction in adults and children should not be ignored. The sooner therapy is started, the better.
Clinical picture
Thus, an unpleasant swallowing process indicates that a person has a pathology of one of the gastrointestinal tract organs, and it is necessary to consult a doctor. In parallel with the feeling that food is not passing well through the esophagus, patients may develop a number of accompanying symptoms that help establish the diagnosis. They experience pain when swallowing, after which coughing attacks or even suffocation may develop. Their voice becomes hoarse and hoarse.
Patients with dysphagia may experience a lump in the throat
Many patients complain of increased salivation. Between meals, people with dysphagia may experience a feeling of fullness behind the sternum or a feeling of a lump in the throat. Initially, people experience these unpleasant sensations if the food they eat is hard and rough. However, as the disease progresses, the condition worsens, and patients cannot eat even soft and then liquid foods normally.
When swallowing impairment is a consequence of paralysis of the pharyngeal muscles, or esophageal fistula, patients experience severe regurgitation, in which food enters the nose and trachea. With lesions of the lower esophagus (achalasia cardia, esophagitis, reflux disease, stricture), severe vomiting is observed, after which the discomfort disappears or its intensity noticeably decreases.
The voice of such patients becomes hoarse or even hoarse, which indicates damage to the larynx or pharynx. They lose body weight. Its rapid decline should alert doctors, as it may be a sign of esophageal cancer, which prevents food from passing into the stomach.
Dependence of the clinical picture on the location of the obstruction to the passage of food
With the first type of dysphagia, food accumulates in the mouth of the patient, who cannot swallow it. If the act of swallowing occurs, then subsequent unpleasant sensations arise almost instantly, no more than one second passes. Aspiration of food (its entry into the upper respiratory tract) is very often observed, resulting in coughing and suffocation.
In the case of esophageal dysphagia, people feel that food stops somewhere behind the breastbone, and these sensations arise only after a few sips.
From the moment of the last of them, it takes from two seconds (obstacle at the level of the cervical spine) to 4-5 seconds (pathological process in the middle third). If the obstacle is in the lower part of the esophagus, the clinic develops in 8-9 seconds.
Diagnosis of the disease
Making an accurate diagnosis is the first step towards effective treatment. The anatomy of the esophagus is such that it is almost impossible to visually determine the presence of pathology, therefore the following methods are used for diagnosis:
- Eophagogastroduodenoscopy is a technique that allows you to assess the condition of the esophagus and the structure of its epithelium. If necessary, a biopsy is taken during the examination.
- Ultrasound allows you to identify any pathologies of the organ.
- X-ray examination.
- Computed tomography and magnetic tomography help differentiate the disease, confirm the diagnosis and detect associated problems.
Since obstruction leads to changes in clinical parameters, the patient is referred for the following tests:
- Determination of hemoglobin and protein content in the blood.
- Examination of stool for the presence of occult blood.
- General blood and urine analysis.
After receiving all the results of the study and determining the cause, treatment of the esophagus is prescribed.
Manifestation of esophageal disease and its symptoms
Improper eating behavior manifests itself in the form of overeating, including before bed, drinking large amounts of carbonated drinks; sooner or later this leads to the symptom of sphincter insufficiency.
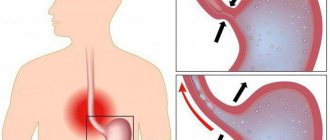
With the development of this pathology, there is a reverse reflux of the acidic contents of the stomach directly into the esophagus. These components irritate the mucous membrane, resulting in the development of a disease - esophagitis.
The disease is manifested by constant belching and heartburn. As the pathological process develops, the clinical picture changes. It is complemented by pain in the epigastric area and a constant feeling of fullness in the stomach.
Such unpleasant symptoms affect a person’s quality of life. He becomes overly irritable and aggressive, and his performance noticeably drops.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment tactics will entirely depend on the severity of the pathology and the cause of its occurrence. For example, if a foreign body gets into the esophagus, it is removed using an esophagoscope with expansion of the lumen. If there is oncology, then one method of treatment is not enough.
If we consider complex therapy of pathology, then treatment of the esophagus includes:
- Drug therapy.
- Surgery.
- The use of traditional methods of therapy.
- Diet therapy.
The best results can only be obtained with complex treatment.
Forecast
Since esophageal obstruction can be caused by very different diseases with varying degrees of severity, the prognosis is completely variable - from favorable to extremely difficult. Benign variants of esophageal obstruction are treated more successfully. The prognosis for obstruction of a burn or tumor nature is more complex and depends on the timeliness of treatment and whether it is fully carried out.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
9, total, today
( 212 votes, average: 4.58 out of 5)
Surgical treatment of obesity
Rectal bleeding: causes, symptoms, treatment
Related Posts
We treat obstruction with medications and surgery
Once the cause of the pathology has been established and the severity of the disease has been identified, treatment tactics are selected. It begins with the prescription of medications from the following groups:
- Antacids.
- Prokinetics.
- Preparations with astringent properties.
- Stimulants for recovery and acceleration of regeneration are prescribed.
- Proton inhibitors.
If drug therapy does not help and esophageal obstruction does not relieve symptoms, then surgical treatment is indicated. This method is usually necessary for esophageal cancer. Currently, several effective methods are used:
- Surgery with complete removal of the esophagus and replacing it with other tissues.
- Carrying out chemotherapy using anticancer drugs.
- Radiation therapy, combined with chemotherapy, helps shrink the tumor so it can be removed.
If the study reveals a benign tumor, it is removed by dilating the esophagus with special instruments.
Treatment options
Treatment of esophageal obstruction is based on eliminating the cause. Therefore, all therapy is divided into the following areas:
- medicinal;
- non-medicinal;
- invasive methods without surgery;
- surgical;
- folk methods.
In most cases, complex therapy is required. You should not self-medicate when the first symptoms appear. The causes of obstruction are varied. If you put off visiting a doctor, since treatment can only help in later stages, only surgery.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy consists of taking a specific list of drugs. These include:
- antacids;
- antisecretory;
- prokinetics.
Prescription of medications occurs in the early stages of development. This set of drugs is used in people with GERD or other concomitant gastrointestinal diseases. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor.
From the group of antacids, Almagel or Maalox are used. Their action is aimed at neutralizing the hydrochloric acid of the stomach. They are used to reduce the further aggressive effects of acid on the esophageal mucosa. Antacid medications reduce the risk of further scar tissue formation.
Antisecretory substances based on Omeprazole have the same direction as antacids. But their mechanism is based on reducing acid production by stomach cells. You should not abuse antisecretory drugs. The appointment of the first two groups is especially important if heartburn is present.
Prokinetics are used to improve bolus passage. These are all drugs with the active substance Domperidone . These include Motilium . The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. In cases of severe pain, painkillers and antispasmodics are prescribed.
Important! drug therapy is used only in the early stages, and after surgery on the esophagus.
Non-drug treatment
This type of treatment includes diet therapy. In case of esophageal obstruction, this is an important point for successful treatment. All food in the initial stages should be chopped or ground. You should avoid foods that increase acidity.
This includes:
- all products prepared by frying;
- adding various spicy spices;
- carbonated drinks and sweets;
- coffee and alcohol.
If there is an error in eating, you should take Almagel or Omeprazole . You should sleep with your head elevated. Particularly important for patients with reflux . Avoid work that requires bending forward.
Invasive treatment methods without surgery
Invasive methods include those in which an instrument is introduced into the cavity of the esophagus. But there is no dissection or cutting of tissue.
These include balloon dilatation of the esophagus . This procedure is carried out in several sessions. This method is otherwise called non-surgical endoscopic expansion. A balloon is inserted into the esophageal cavity, which is then inflated. During one procedure, about 2 balloons are used. Used for minor narrowing of the esophagus.
Another method is to insert bougies into the stenotic area. The endoscope string is passed below the narrowing area. Then, going up, the bougie is introduced into the stenotic area, thereby expanding it.
Surgery
One of the methods of surgical treatment is dissection of the narrowing site. Electrosurgical is performed . This method is used if it is not possible to perform balloon dilation of the esophagus. When the scar tissue is dense enough.
The cutting process itself is carried out using a special current of a certain frequency. Then a procedure is performed to dilate the esophagus with a balloon.
More severe narrowings are treated with the use of a stent . This is equipment that is inserted into the cavity of the esophagus, where it then opens to expand it. Normal nutrition is restored naturally.
If the cause of the narrowing is a tumor, it is removed. The foreign body can only be removed surgically.
Obstruction of the esophagus: treatment with folk remedies
Traditional recipes can come to the aid of drug treatment. Infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants will help alleviate the patient’s condition and reduce the symptoms of pathology.
Before using traditional recipes, you should definitely consult with your doctor, because you can only worsen the condition. To get rid of obstruction, use the following recipes:
- Oak bark decoction. You can prepare a healing potion like this: take 30 grams of oak bark and cinquefoil, 40 grams of walnut and St. John's wort leaves and 20 grams of oregano leaves. Combine everything, grind the mixture and take 30 grams, pour 700 ml of water at room temperature. Leave for 3 hours and then boil for 5 minutes. After filtering, take 100 ml of the medicinal mixture half an hour before meals.
- Composition based on wormwood. You need to prepare 50 grams of wormwood, 75 arnica and 100 grams of femoral root. Place 45 grams of the mixture in a thermos and add 400 ml of boiling water. Leave for 10 hours, and then take 100 ml 4 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
- Mix raisins, honey, olive oil and hay herb and take 1 tablespoon before bed with water.
- Prepare a tincture of young walnuts in alcohol and take a teaspoon after meals.
- Alder bark helps fight esophageal obstruction. The crushed raw materials must be poured with boiling water and left for 3 hours, and then taken 4 times a day after meals.
The most important thing in treatment is not to neglect the doctor’s recommendations and not to self-medicate.
Traditional methods
To start the stomach of a cow, folk remedies are also used - tinctures, mash, herbal decoctions. Let's look at some of them.
A pack of yeast
- A pack of yeast is diluted in a glass of warm water and left to swell. After half an hour, 100 grams of granulated sugar are dissolved in a glass of vodka, yeast is added to this mixture, and mixed thoroughly. Add water to the tincture to eventually get a liter of product. The medicine is given to the cow to drink half a liter in the morning and evening.
- A solution with vodka is not suitable for a calving cow; she can be offered herbal decoctions that stimulate digestion. For example, chamomile, flaxseed or yarrow. Prepare the product on the stove by brewing 20-25 grams of raw material with a liter of boiling water. The broth is simmered over low heat, then infused and filtered.
- If the calf's stomach has stopped, you can start it up using cucumber or tomato brine, mineral water or lactic acid.
Attention! It is unacceptable to give drink and food that causes fermentation to a cow if the foreign body has not yet been removed from the esophagus, as well as when gases accumulate in the rumen. First, they remove the object stuck in the esophageal tube, and then they work on starting the stomach.
Changing your diet
Nutrition for esophageal obstruction depends on the severity of the stenosis and the causes of the pathology. Nutritionists recommend several dietary tables:
- No. 1. Complete nutrition, but all dishes must be pureed and steamed or boiled. It is not recommended to eat foods that are too cold or hot. Throughout the day you need to eat often, but in small portions.
- Table No. 2 involves eating only liquid and semi-liquid foods. The interval between meals is no more than 2.5 hours. Salt intake should be limited, excluding bread, sausages and smoked meats, buns and pies, and sour fruits. Instead of strong tea and coffee, it is better to drink fruit drinks, compotes or decoctions of medicinal herbs.
- Table No. 3 allows low-calorie nutrition with the exclusion of all products that irritate the mucous membrane. All dishes must be ground and in a semi-liquid state.
It must be remembered that nutritional correction should complement the main course of therapy.
Diet for esophageal disease is the basis of therapy
The therapeutic diet for esophagitis (disease of the esophagus) allows you to solve several problems in this therapy at once. Firstly, diet helps relieve unpleasant symptoms. Secondly, it helps to normalize the functioning of the entire gastrointestinal tract system.
In addition, balanced nutrition has a positive effect on a person’s well-being. In a short period of time, he manages to get rid of several extra pounds, bring blood pressure and other vital indicators back to normal.
General recommendations - diet for esophageal disease
The diet for esophageal disease is complete, but it has a number of recommendations. Nutrition should be as balanced as possible. Therefore, the diet is selected by a doctor. Its daily calorie content is about 2000–2500 kcal.
The primary task of such nutrition is to reduce the mechanical load on the mucous membrane of the esophagus. It excludes all products that contribute to increased secretion of hydrochloric acid.
The main provisions of the diet for esophagitis:
- Diet. You need to eat often (up to 5 times a day), but in small portions. This approach allows you to reduce the amount of acid produced in the stomach. It also prevents excessive stretching of the walls of the organ and the reflux of food debris from it into the esophagus. After eating and for the next two hours, it is not recommended to lie down on the bed or bend over.
- Temperature conditions. Do not eat food that is excessively hot or taken directly from the refrigerator. The optimal temperature for the finished dish is 15–60 degrees. Otherwise, hydrochloric acid will be produced in excess.
- Rules for eating. You should eat slowly, chewing large pieces of food thoroughly. This approach greatly facilitates the work of the entire digestive tract. You should also not talk during a meal, since in this case a person begins to swallow large volumes of air. As a result, he will have to fight belching again.
- Alcoholic drinks. If you have esophagitis, you need to limit your alcohol consumption, it is better to give it up forever. Doctors do not advise drinking alcohol on an empty stomach. The liquid that gets into it activates the production of hydrochloric acid.
- Salt and drinking regime. A diet for this disease involves a sharp limitation of salt intake to 10 g per day. The amount of liquid must also be reduced to 1.5 liters per day. It is worth noting that you should not drink immediately after a meal. This can lead to stretching of the stomach walls.
- Heat treatment. It is recommended to cook all dishes in a double boiler or bake in the oven. Frying is strictly prohibited. The crust that forms on food during cooking can injure the gastric mucosa.
It may seem that the recommendations listed are impossible to implement. In fact, they allow you to get rid of unpleasant symptoms. A person gets used to this eating behavior very quickly. Most patients adhere to such advice even after recovery.
Allowed foods for consumption - diet for esophageal esophagitis
All lean foods are allowed to be eaten during a diet for esophagitis. However, preference should be given to foods that promote rapid restoration of damaged mucous membranes. These products include:
- mashed potatoes, soft apples, steamed green vegetables;
- porridge with oatmeal, rice, pearl barley;
- lean meat and fish;
- egg white;
- low-fat dairy products;
- herbal and green tea;
- dry bread and crackers;
- pasta made from premium wheat varieties;
- puddings.
Prevention of pathology
To prevent the disease you need to:
- Take measures to prevent the development of tumor processes in the esophagus.
- Store all chemical and caustic liquids only in containers with labels so as not to accidentally mix them up and in a place where a child cannot reach.
- If gastroesophageal reflux occurs, you must follow a strict diet: do not overeat, do not eat irritating foods.
- Do not eat before bed: last meal no later than 3 hours before going to bed.
- After eating, do not immediately take a vertical position.
- Watch your weight.
- Do not wear too tight clothes or tight belts.
- Don't overexert yourself physically.
It is much easier to prevent the development of the disease than to engage in long-term treatment later. When the first unpleasant symptoms appear, it is better to immediately visit a specialist rather than self-medicate.
What to do if food does not pass well through the esophagus, causing discomfort and pain
The first thing you need to do is contact a therapist or gastroenterologist for advice and referrals for examination. The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- X-ray with barium contrast (to identify scars, strictures, stenoses, cardiospasm);
- endoscopic examination (it is necessary to do a study to verify the diagnosis, determine tumor processes, foreign bodies);
- MRI;
- transesophageal ultrasound.
You should not delay your visit to the doctor, because difficulty passing food is one of the symptoms of a malignant neoplasm. Only after finding out the cause can you choose the right tactics: how and with what to treat the pathology.