What does the term atony mean?
In the wall of the stomach, muscle fibers are located in several layers, running in the longitudinal, oblique and transverse directions. Their coordinated work ensures mixing of the contents and movement of food masses towards the exit from the stomach into the duodenum (duodenum). In addition, muscle tone maintains the existing size and volume of the organ, preventing its excessive stretching .
The term “gastric atony” means that these muscles, due to various reasons, lose their strength or ability to contract. Therefore, the stomach becomes weaker, stretching and stretching (as if sagging), as well as mixing food worse and moving it into the duodenum.
https://youtu.be/1FRayDuz98g
Description of the disease
The walls of the intestine consist of muscles, with the contraction of which feces move from the upper zones of the digestive tract to the lower ones. This work is called peristalsis.
With atony, a violation of the tone of the intestinal walls occurs, and therefore they lose the ability to contract and relax normally to push feces to the rectum. Thus, food stagnates in the body, which leads to constipation and putrefactive processes.
Reasons for development
The immediate cause of gastric atony is a weakening of its muscle tone. The following pathological processes can lead to this condition:
- disruption of nerve innervation due to nerve damage during injury, surgery, or diseases of the nervous system;
- various myodystrophic processes;
- general serious condition;
- diseases of the stomach and intestines.
Acute atony can develop with:
- myocardial infarction;
- acute pancreatitis;
- peritonitis;
- vein thrombosis.
Other factors causing weakness of the muscles of the gastric wall:
- death of nerve fibers due to the action of various toxins;
- such severe infectious diseases as botulism, brucellosis, Lyme disease, typhoid fever, legionellosis;
- any injuries to the spinal cord;
- hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes of the brain when the corresponding areas are affected;
- exhaustion and excessive thinness, which occurs with nutritional dystrophy, anorexia and some other pathological conditions.
A predisposing factor to gastric atony is heredity and the characteristics of a person’s physique. For example, this disease often develops in people of asthenic physique, especially if they have stretched or flabby muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. Sometimes congenital elongation of the stomach or prolapse occurs, which also contributes to the appearance of this disease.
Causes of intestinal atony
Enhanced peristalsis of the intestinal walls is the key to the perfect functioning of the internal organs of the gastrointestinal tract, the process of defecation occurs regularly (1-2 times a day), painlessly.
In contrast, weak muscle function slows down the process of emptying and feces accumulated in the colon and rectum form constipation.
The causes of impaired peristalsis and healthy intestinal tone are largely determined by the patient’s lifestyle. Eating high-calorie, fatty fast food, a passive attitude towards sports and movement, uncontrolled medication use, stressful situations and psycho-emotional stress are the first signs that reduce peristalsis and lead to intestinal atony, both in an adult and a child.
Atony is caused by the following factors:
- There is an abundance of foods high in cholesterol, calories and fat on the menu. In contrast, the consumption of foods containing fiber and dietary fiber is minimized, which significantly affects the functioning of the intestines and reduces muscle tone.
- Inactive, sedentary lifestyle. Physical inactivity, especially in old age, reduces vascular tone, negatively affects metabolism, and in the gastrointestinal tract there is a decline in peristaltic contractions of the large and small intestines, leading to constant constipation and atony;
- The central nervous system, which controls the functioning of the digestive organs, is subjected to frequent stressful situations and negatively affects peristalsis.
- Long-term use of antidepressants, antiulcer drugs, combined analgesics and morphine-based painkillers can also lead to atony and impaired peristalsis.
- Abuse of nicotine, alcohol, and drugs that release toxins negatively affect not only the contraction of the muscles of the hollow organs of the gastrointestinal tract, but also the functioning of the entire human body.
- Intestinal infections and imbalanced intestinal microflora (dysbacteriosis) affect digestive functions, and toxic substances accumulated in the body contribute to decreased peristalsis.
Symptoms of gastric atony
Often, in the case of atony or hypotension of the stomach, patients note:
- periodic heartburn;
- nausea, vomiting;
- feeling of fullness, stretching;
- rotten belching, bad breath;
- due to impaired digestion of food - flatulence, bloating, bowel dysfunction.
Often this condition is accompanied by autonomic disorders. For example, cold sweat appears and the skin becomes pale. In addition, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, and general weakness may occur.
If food practically does not leave the stomach, then a feeling of rapid saturation occurs in very small portions, especially if the food is fatty. Appetite disappears, nausea increases.
With a long course of the disease, the processes of digestion and absorption of nutrients are disrupted. As a result, patients suffering from weak stomach muscles are characterized by symptoms such as exhaustion and relatively rapid weight loss. Due to impaired absorption of iron and vitamins, anemia, malfunction of the thyroid gland and other parts of the endocrine system, and even decreased immunity can occur.
pharmachologic effect
The pharmacological group of the drug is a cholinesterase inhibitor.
This is a synthetic anticholinesterase drug that reversibly blocks cholinesterase. As a result of this action, acetylcholine accumulates and its effect on tissues and organs increases. As a result, neuromuscular conduction is restored. Under the influence of the drug, the heart rate decreases, the secretion of the bronchial, salivary, sweat glands, as well as the glands of the digestive tract increases. In turn, this contributes to the manifestation of bronchorrhea, hypersalivation, and an increase in the level of acidity of gastric juice.
The active substance causes a spasm of accommodation, constriction of the pupil, lowers intraocular pressure, stimulates the tone of the smooth muscles of the intestines and bladder, tones the skeletal muscles, and provokes bronchospasm.
Prozerin is an antagonist of anti-depolarizing curare-like drugs. When taking large doses, the drug can provoke a disorder of neuromuscular conduction, which occurs due to the accumulation of acetylcholine. Produces a direct n-cholinomimetic effect. The effect of the drug coincides with the characteristic effects of excitation of cholinergic nerves.
After oral administration or parenteral administration, the active component of the drug has a pronounced stimulating effect on all tissues and organs. As a result, the conductivity of nerve impulses to the affected areas improves and metabolism is normalized.
The drug helps reduce blood pressure, heart rate, and intraocular pressure. At the same time, it stimulates the secretion and liquefaction of mucus in the bronchi and lungs, increases the production of digestive enzymes and gastric juice. As a result, the acidity level increases significantly.
The drug activates the salivary and sweat glands, which contributes to the development of hypersalivation and hyperhidrosis in the patient during its use. Prozerin also causes bronchospasm as a protective reaction of the body. It is noted that after ingestion, the active substance is quickly absorbed and processed in the liver.
Diagnostic methods
Gastric atony is diagnosed based on the patient’s characteristic complaints, medical examination, as well as additional laboratory and instrumental examination, including:
- contrast radiography of the stomach - barium suspension immediately settles to the bottom, elongation of the shape of the organ, lowering of the lower border, slow evacuation of the contrast agent, decreased peristaltic waves;
- FGDS - expansion of the organ cavity, the presence of stagnant contents;
- intragastric manometry (carried out in conjunction with FGDS) – muscle paresis;
- electrohystrography - weakening of peristaltic waves (registration of low-amplitude waves with large intervals in time).
In order to identify the underlying disease and assess the general condition of the patient, the following may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound;
- coprogram;
- general and biochemical blood tests, etc.
Preventive measures
Prevention of atony is as follows:
- performing a set of exercises to improve peristalsis;
- proper nutrition (excluding fatty foods);
- timely treatment of diseases that provoke a decrease in muscle tone;
- giving up bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking).
An active lifestyle, namely long walks, swimming and various sports, will help prevent the development of this disease.
If chronic constipation occurs, you must urgently contact an appropriate specialist for examination and treatment. The use of folk remedies and medicines at home should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, since self-medication can only aggravate the patient’s condition. With timely treatment and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations, the prognosis for this disease is favorable. Maintaining an active lifestyle can avoid the development of intestinal atony in the future.
Treatment of gastric atony
Treatment of atony is carried out by a gastroenterologist. It is comprehensive and includes:
- drug therapy;
- compliance with diet and dietary recommendations;
- lifestyle correction and physical therapy;
- treatment and prevention of concomitant diseases.
Medications
Depending on the specific situation, the doctor selects drugs from the following groups:
- prokinetics – Domperidone;
- antiemetics – Cerucal, Metoclopramide;
- medicines containing potassium, calcium;
- motor stimulants – Prozerin, Peristil, Cisapride;
- insulin.
If necessary, medications can be prescribed that improve the regeneration of the mucous membrane and blood supply - Methyluracil, Solcoseryl, as well as vitamin and mineral complexes, anabolic steroids. In case of digestive disorders and dysbacteriosis - pancreatic enzymes and probiotics.
Lifestyle and physical therapy
In cases of severe atony, wearing a bandage is recommended to prevent excessive prolapse of the stomach. It is worn in a lying position. It is especially necessary for a saggy belly. In order to improve your overall well-being, you need to:
- sleep at least 7-8 hours a day;
- take a contrast shower;
- take a walk before bed;
- develop stress resistance.
Prevention
An active lifestyle will benefit the patient.
Therapeutic exercise and moderate physical activity are the optimal means of preventing the appearance of atonic constipation in the elderly. You should not limit yourself to using only these methods.
The patient is recommended to lead an active lifestyle and move more, taking long walks. Swimming will be beneficial. It is extremely important to promptly adjust and balance your diet, removing high-calorie foods from your diet and optimizing it through the consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits.
How to eat with stomach atony
Stomach atony involves chewing thoroughly and eating food in small portions, since in this case it is easier to digest. Drinks and water should also be drunk in small sips and preferably in small volumes at a time. Usually, for atony, diet No. 2 according to Pevzner is recommended. Dishes are served warm.
All products are divided into 3 categories:
- Welcome:
- everything that contains fiber - bran bread, carrots, beets, buckwheat porridge, fruit and vegetable purees and juices;
- fermented milk products – kefir, yogurt;
- lean varieties of poultry, fish, meat.
- Limited to:
- astringent fruits;
- legumes;
- mushrooms;
- garlic;
- radish.
- Prohibited:
- alcohol;
- whole milk;
- chocolate, coffee;
- fried, smoked, pickles, marinades;
- cakes, pastries;
- too fatty foods.
A nutritionist and gastroenterologist is involved in drawing up a specific diet in case of concomitant diseases.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk recipes for atony will help to safely and effectively cleanse the intestines, as well as normalize peristalsis.
Recipes based on herbs and infusions
The most famous remedy for treating constipation
- To regulate stool, you can use a decoction of senna leaves. It is prepared at the rate of one tablespoon of chopped herbs per glass of water. The broth is boiled over low heat for 15 minutes, after which it is left to infuse for one hour. Take the product three times a day, one tablespoon for a week.
- An effective remedy is an alcohol tincture on the leaves of calamus, gentian, and rhubarb roots. All components are taken in equal proportions. The collection is poured with alcohol (1:10) and left for two weeks in a dark place. The tincture is filtered and stored in the refrigerator. You need to drink the product before meals, one teaspoon twice a day. Treatment lasts 7–10 days.
- Wash a few aloe leaves (about 150 g), remove the thorns, and cut into small pieces. Pour agave leaves into honey heated to 40 degrees (1.5 cups). The medicine is infused for 24 hours; before taking it, it needs to be warmed up again. Take one tablespoon of the remedy an hour before breakfast. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- An infusion based on burdock roots has a laxative effect. You need to pour two tablespoons of raw materials into a thermos and pour in 0.5 liters of boiled water. The drink should infuse overnight, after which it should be strained. Drink the infusion three times a day before meals, 1/2 glass. Treatment lasts two weeks.
- Take equal parts of celandine, dandelion and rhubarb root. Pour two tablespoons of the mixture into a thermos with one liter of boiling water and leave for 8–10 hours. Take the drink before meals, half a glass in the morning and evening. The course of treatment is usually 5–7 days.
- Tea with oregano is also effective for constipation. A tablespoon of crushed leaves is poured into one glass of boiling water and left for 15–20 minutes. This tea is drunk in the morning and evening before meals. You can take the infusion for 7 days.
Healers initially considered oregano to be a “female” herb, so men should not get carried away with tea based on it.
- A decoction of the string will be effective. Two tablespoons of chopped herbs are poured into 500 ml of cold water and brought to a boil. Then the broth is left to infuse for 30 minutes. The finished drink is filtered and taken 1 tablespoon three to four times a day. The course of treatment is one week.
- To restore the microflora, a decoction based on burnet root is used. 20 g of raw material should be poured into a glass of water and boiled for 20 minutes. Take the strained decoction one tablespoon five times a day. Treatment should be continued for two weeks.
- A decoction of calamus root will help with constipation. Three tablespoons of roots are poured into two glasses of water and kept over medium heat for 15 minutes, then filtered. This is a daily dose of medicine, taken in several doses. You need to drink the decoction for 7 days.
- Add half a teaspoon of honey and mint leaf juice to a glass of warm milk or water. Drink this remedy 3 times a day before meals, 1/2 cup. The recommended duration of treatment is two weeks.
We use seeds and fruits of plants
Flaxseed has been used for constipation since ancient times.
- A teaspoon of flaxseed is poured into a glass of boiling water and left to steep for 4 hours. The entire infusion should be drunk immediately before bed. You can take this remedy for 7 days.
- For chronic constipation, it is recommended to use a recipe for infusion of burdock seeds. One glass of boiling water should be poured into 20 g of seeds. The infusion is kept for one hour, then filtered. You need to drink the medicine one tablespoon 4 times a day for a week.
- There is a well-known recipe for an alcoholic tincture of red rowan. The washed berries are placed in a jar, sprinkled with sugar on top. The container is left in a sunny place for 4 weeks. When the berries are ready, squeeze out, and alcohol is added to the resulting syrup (25 ml of alcohol per 0.5 liter of syrup). The tincture is stored in the refrigerator and taken one glass in the morning on an empty stomach. The course of admission is no more than 14 days.
- Brew a teaspoon of fennel fruit with a glass of boiling water and leave for 20 minutes. Drink the infusion in four doses throughout the day. Duration of use is one week.
- 20 g of parsley fruits are poured into one glass of warm water and heated in a water bath for 30 minutes, after which the broth must be filtered. You need to take the medicine 4-5 times a day, one tablespoon. The course of treatment is 5–7 days.
- A decoction of cumin fruits has long been used to treat constipation. A tablespoon of raw material is poured into one glass of water and boiled for 5 minutes. Then the drink is cooled and filtered. It is recommended to take one teaspoon of the decoction 5-6 times a day for a week.
Cumin seeds will not only improve intestinal function, but also help you lose weight
- Blackberries stimulate peristalsis. You can simply eat 50 g of fresh berries a day or prepare an infusion of dried fruits. To prepare the drink, a teaspoon of berries is infused for 8 hours in one glass of cold water. The infusion should be drunk in three doses a day. Treatment lasts up to seven days.
- Dill seeds will help regulate your stool. To prepare the infusion, pour a tablespoon of ground seeds into a glass of boiling water and leave for two hours. The strained product is drunk 80 ml three times a day for 5–7 days.
- Atony is also treated with mustard seeds. They are simply swallowed in the morning, on an empty stomach, 30 minutes before meals. Start with ten seeds, increasing their number by two every day. The course will be completed when the number of seeds is twenty.
- Potato juice is useful for atony; you need to drink a glass of it a day one hour before meals. The course of such treatment is 10 days, then you need to take a week break.
Other folk methods
Wheat bran has a beneficial effect on intestinal motility.
Wheat bran can normalize intestinal function. To prepare the medicinal mixture, pour two tablespoons of bran into a glass of hot milk and leave for 30 minutes. Eat the product on an empty stomach; if desired, you can wash it down with water. Recommended course is 10 days.
Possible complications
Due to stagnation, atony itself can become a provoking factor for the occurrence of gastritis and gastroduodenitis, and as digestive disorders progress, diseases of the entire gastrointestinal tract, including colitis and intestinal dysbiosis.
Other possible complications:
- gastric circulatory disorders;
- rupture due to overstretching;
- thinning of the walls of this organ;
- weight loss due to digestive disorders;
- hypovitaminosis;
- nutritional deficiency.
General information
Intestinal atony is a condition in which a person complains of disturbances in the process of bowel movement. Such difficulties, first of all, are expressed in the fact that the intervals between acts of defecation are constantly increasing or stool is very difficult.
With intestinal atony, a characteristic symptom is constipation, which indicates a number of pathological conditions or is a consequence of the effect of certain negative factors on the human body. Intestinal atony occurs as a consequence of loss of intestinal muscle tone. With intestinal atony, both spasms and noticeable muscle relaxation can be observed. Such problems very often become chronic and continue for the patient for many years.
Treatment of sluggish intestinal motility
A decrease in the tone of the smooth muscles of the intestine, a slowdown in the wave-like movements of its walls (peristalsis) leads to the development of atony.
Intestinal atony develops as an independent pathology, is a complication of concomitant diseases, a consequence of taking certain medications, and the result of an unhealthy lifestyle. Provoking factors are:
- genetic predisposition;
- the predominance of heavy, high-calorie foods with insufficient fiber content in the diet;
- small amount of liquid;
- physical inactivity;
- the presence of intestinal infections, dysbacteriosis;
- worms, single-celled parasites;
- frequent use of cleansing enemas, laxatives;
- malignant neoplasms in intestinal tissues;
- unsuccessful cesarean section and other operations;
- being in a state of chronic stress (this disrupts the activity of the nervous system and causes disruption of the functioning of most internal organs);
- long-term use of painkillers and antispasmodics;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- drug use from the opiate group.
Features of atony in childhood
In children, atony is usually diagnosed as a consequence of a stressful situation. In addition, constant constipation with a lack of water consumption can cause pathology in a child. In infants, this condition is most often associated with the moment of weaning and potty training. The hereditary route of transmission of the disease remains important.
To avoid the onset of illness in a child, you can perform a preventative light abdominal massage. For an existing problem, treatment is carried out by revising the diet and administering glycerin suppositories.
Principles of therapy
Treatment for this disease is usually aimed at eliminating the underlying disease and restoring full motor function of the organ. Surgical intervention is required extremely rarely, since gastric atony often recurs after surgery.
Patients are usually treated by nutritionists, psychotherapists, gastroenterologists and specialized specialists. The latter are engaged in eliminating the underlying pathology. Immediately after confirmation of the diagnosis, patients are prescribed evacuation of gastric contents using a tube to prevent organ rupture.
Treatment of the disease involves taking medications, changing your usual diet, and using a special bandage. Some patients are recommended exercise therapy and acupressure self-massage. An integrated therapeutic approach helps with gastric atony. Treatment is not limited to one dose of pills.
Types of constipation
Atonic constipation occurs as a consequence of intestinal atony. However, there are other types of constipation, in which intestinal atony is also often a concomitant condition. The most common is nutritional constipation, which occurs as a result of an incorrect approach to nutrition. In addition, there are psychogenic, neurogenic, endocrine, toxic constipation, as well as constipation resulting from damage to the anorectal area and weakening of the muscles.
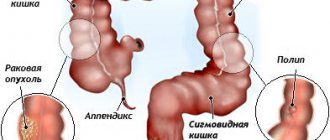
Constipation also occurs as a consequence of exposure to mechanical obstacles that interfere with the movement of contents in the intestines. These could be polyps or tumors, adhesions, or a number of abnormalities in the development of the large intestine.