Medicine considers colon cancer to be a collective concept, including more than one malignant formation at once; the formations differ in their structure, scale, intensity, and localization.
If we are talking about the large intestine, then the malignant tumor can be localized in the cecum, in the anus, in the rectum or colon.
Residents of countries with a stable economy and standard of living are most susceptible to the disease: for example, more than 15,000 residents of the country die from this type of cancer per year in England, in the United States the situation is no better - about 145,000 residents of the country are diagnosed with a colon tumor, and a third of them die.
The CIS countries occupy almost the leading place in terms of mortality from this type of tumor.
Classification of colon cancer
There are quite a lot of distinctive signs when diagnosing, therefore the classification is different.
Based on their outlines, experts distinguish exophytic, endophytic, and saucer-shaped forms.
Depending on the cellular structure, such types of cancer are distinguished as: mucous and ordinary adenocarcinoma, mucocellular, undifferentiated and unclassified forms of the disease.
The most common form, which forms in the large intestine, manifests itself as adenocarcinoma: about 80% of cases are identified during examination.
Development of a tumor in the left side of the intestine
If the tumor is localized on the left side, then the symptoms of colon cancer will be slightly different, more complex, in contrast to the symptoms that appear on the right side. The patient complains of constant constipation, difficulties during excretion of feces, and bloating. There is a frequent alternation of loose stools with constipation, through narrowing and relaxation of the lumen of the colon. Excretion of feces occurs with great difficulty, often with blood and mucus, and is accompanied by painful sensations.
Colon cancer stages
A colon tumor has four stages, which differ in symptoms and course of the disease:
- Initial stage of the disease. During this period, the tumor formation is small and localized to the intestinal mucosa. Chemotherapy at this stage almost always helps, if there are no concomitant pathologies.
- The next stage is conventionally divided into stages: “a” and “b”. In both cases, metastases do not begin to act.
- In the third stage, most of the intestine is affected. The lesion extends along the entire length of the intestinal wall and throughout its thickness. Stage “b” predisposes to the onset of metastases, which will spread to the nearest lymph nodes.
- At the last stage, the neoplasm reaches a large size, is capable of affecting organs that are located nearby, and metastases spread to distant organs and lymph nodes. Treatment with chemotherapy is no longer able to help, and the survival rate is less than 20%.
Stages of development of colorectal cancer
There is a classification of the stages of development of the type of cancer that interests us. It is based on changes that occur with three main phenomena characteristic of this disease, namely:
- the occurrence of tumors;
- changes in lymph nodes;
- the occurrence of metastases.
Stages of development of bowel cancer
To understand what specific changes occur at each stage of the disease, you need to pay attention to the table below.
Table 1. Stages of colorectal cancer and changes characteristic of each of them
| Stage | Characteristic processes |
| First stage | At the first stage of the type of cancer we are interested in, clinical manifestations are considered minimal or absent in principle. Provided that they do occur, most likely we will talk about symptoms of intoxication of a minor nature. As for the actual changes, a new formation of a dense structure appears in the rectum, its size is insignificant. The location may be:
|
| Second stage | At the second stage, the main changes occur primarily with the neoplasm, which rapidly increases in size. At this stage, relative to the intestinal lumen, it can be:
|
| Third stage | At this stage, the tumor increases even more. Now it can reach the size of the full size of the intestinal lumen, but in some cases, it can also maintain its original size. If by this stage the development of damage to the lymphatic system has already occurred, then, most likely, it will spread to all large vessels (or it will not manifest itself at all, which also often happens). Metastases also do not form at the third stage of colorectal cancer. |
| Fourth stage | The fourth stage of this disease can truly be called critical, since it is at this stage that metastases arise and spread. It is believed that at this stage it is very difficult, almost impossible, to reverse the process. |
What is the intestine
Before you trace the symptoms of this disease, you should know the structural features of the human digestive system.
The food that a person has consumed, passing through the esophagus, ends up in the stomach, where the digestive process occurs.
The next step is the passage of food through the large intestine. The body begins to take nutrients from food.
The colon (large intestine) collects water from food. The large intestine begins on the right side at the bottom in the abdominal region.
Its first part (the ascending colon) passes upward, and then extends to the left side of the peritoneum - called the transverse colon.
The descending colon descends to the bottom of the abdominal cavity.
The large intestine ends with the sigmoid colon, rectum and anus.
Those wastes that were obtained as a result of the digestive process accumulate in the rectum.
They leave the body as a result of defecation through the anus.
Lymph nodes are located near the intestine and are no larger than the size of a pea.
Causes
Among the many reasons that can provoke pathology, the following are particularly distinguished:
- Poor nutrition. With the predominant inclusion in the menu of a large number of meat products and the absence or low fiber content. This combination leads to stagnation and the release of toxins, damaging the intestinal walls.
- Chronic intestinal diseases without appropriate treatment . The main risk group includes people with polyps in the rectum. Long-term pathologies lead to disruption of metabolic processes, which can serve as a factor in the development of cancer.
- Papillomavirus. Scientists have proven that papillomavirus can cause the development of cancer in the organ that it affects.
Causes of Colon Cancer
In almost all cases, an intestinal tumor means damage to the colon.
More than half of the cases are a tumor of the colon (large intestine) and a third are a disease of the rectum.
Recognition of a colon tumor is considered a secondary issue.
Important factors that influence the appearance and spread of the disease:
- Dietary disorder;
- Bowel disease;
- Heredity;
- Taking alcohol, nicotine, and narcotic substances.
Diet
A tumor develops under the influence of one or more factors (pathogens).
According to scientists, the food consumed has the greatest impact on the development of colon cancer.
The risk of developing a cancer predisposition is caused by foods rich in proteins and animal fats, especially for food consumed without vegetables and fruits.
Alcoholic drinks also have a negative effect on the body, killing and changing cells, and the general state of the immune system worsens.
Hereditary predisposition
Heredity also affects the digestive system.
If there have been previous cases of colon cancer in the family, then the chance of the disease developing in relatives increases.
People whose close relatives are diagnosed before the age of 45 are more likely to get sick.
The more cases of the disease in the family, the greater the likelihood of predisposition to the disease.
If this has happened in your family, you should contact an oncology facility to determine the risk of the disease in yourself.
Such examinations help prevent the formation of malignant tumors. You can be examined once every six months.
There are two genetic conditions in which the risk of developing a colon tumor becomes many times higher.
The first condition is NAP, medically known as hereditary adenomatosis-polyposis in the lining of the colon.
With this pathology, there are a large number of benign neoplasms.
People with this type have a very high chance of getting any type of cancer.
The second condition is called NPOCC, or hereditary nonpolyposis colon tumor.
This case is quite severe, since cancer can develop in several places simultaneously.
Intestinal diseases
These include disorders of the intestinal lining, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis, which increase predisposition to cancer.
After establishing such diagnoses, it is better to check for the presence of neoplasms.
In addition to determining the presence of this disease, you should find out the cause of the lesion, since oncology may be accompanied by other diseases that will complicate the treatment process.
Causes of colon cancer
After many years of studying this cancer, experts have identified several factors that contribute to an increased risk of developing cancer in the intestines:
- Heredity. A family history of cancer increases the likelihood of developing colorectal cancer. Particularly dangerous is familial colon polyposis, which is characterized by a high risk of hereditary malignancy.
- Precancerous pathologies. These include: Lynch syndrome, Crohn's disease, intestinal polyps, chronic and ulcerative colitis, and inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Nutrition. A low level of plant fiber in the diet and regular consumption of animal fats and proteins contribute to the onset of cancer in the intestines.
- Bad habits. Persons suffering from alcohol and nicotine addiction are also at risk. It has been proven that the likelihood of the formation of cancer cells in the intestines increases significantly with regular consumption of alcoholic beverages and a long history of smoking.
- Exposure to carcinogens. Chemical substances have a high mutagenic effect, in particular metabolites, nitro compounds, inorganic salts, metals, steroids, etc.
Risk factors for the development of colorectal cancer also include insufficient physical activity of the body, obesity, and chronic constipation. In addition, long-term use of antibiotics at the age of 20-40 years can lead to the development of adenomatous polyps, which are prone to malignancy.
Colon Cancer Symptoms
Experts often confuse the symptoms of colon cancer in the early stages.
Since not only a colon tumor can be diagnosed, the symptoms are very similar to rectal disease.
With a colon tumor, the following is observed:
- There is blood on the excrement, the discharge may be enveloping or located inside;
- Weight loss due to lack of appetite;
- Constipation and diarrhea alternate for more than a month;
- Pain is felt in the abdominal cavity or anus, not acute;
- After defecation, a feeling of incompleteness;
- Acute intestinal obstruction.
With rectal cancer, you can observe:
- In addition to blood, pus or mucus is observed in the excrement;
- Pain in the perineum, coccyx, sacrum, lower back;
- The urge to defecate is often accompanied by pain;
- There is a feeling of something foreign in the rectum;
- The shape of the feces also changes and takes on the appearance of a ribbon;
- Frequent constipation, but no diarrhea.
These symptoms can be the main reason for contacting a specialist for people over 45 years of age.
Those younger than this age may have a completely different problem, for example, SRCT or ulcerative colitis.
First signs
Cancer, like any other disease, has symptoms that are difficult to diagnose at an early stage in women. The incubation period can be several years. And when the patient is critically ill, the disease begins to show a signal. Signs of bowel cancer include:
- Rapid weight loss This is one of the symptoms that indicates that something is happening in the human body. Almost all women do not pay any attention to this symptom. Especially those who previously had a lot of weight, quickly acquired the desired body. If a person eats right and eats everything, but the weight goes off, then this should be a signal to visit a doctor.
- Appetite decreases The greater the stage of the disease, the more appetite will decrease. If the disease develops too rapidly, then the person almost completely refuses to eat. In some cases, a person will want to eat one of the foods. Most people who suffer from colon cancer eat a lot of meat. Such a rapid desire can be explained by the fact that the body eats to reduce the load on itself, so a person wants to eat meat.
- Presence of anemia If there is some pathology in the intestines, then anemia cannot be avoided. Often, there may be internal bleeding.
- Frequent fatigue At the initial stage of the disease, fatigue may occur periodically. But, at a more complex stage of development, fatigue becomes a habit. In addition, a person may also experience headaches and nausea, which are practically untreatable.
- The temperature rises The presence of an elevated temperature does not mean that there are tumors in the body. But if the temperature rises and lasts too long, this may indicate the presence of a tumor in the intestine. In most cases, this is the basis for a terrible diagnosis. This can be explained by the fact that an inflammatory process occurs in the intestines. Thus, the body becomes intoxicated, which is the reason for the increase in temperature.
- Local symptoms This type of symptoms includes the presence of a tumor in the intestinal area.
- Frequent and unpleasant belching If you have intestinal cancer, you will belch with a rotten smell. This is explained by the fact that food is not processed in the body for too long, which ultimately leads to its breakdown. It is because of this that ammonia smells from a person’s mouth.
- Presence of heartburn During heartburn, an acidic taste is felt in the mouth. This is because when the food breaks down, the acidity has not yet completely left the stomach. Therefore, it is thrown out, burning the tissue, which is called heartburn.
- Sometimes heaviness may appear in the abdomen. Since the intestines are in the process of developing a disease, they cannot fully cope with their tasks. Food is not completely processed, which ultimately leads to heaviness in the abdominal area.
- Presence of ascites According to doctors, ascites is the most important symptom of the onset of pathology. If there are cancer cells in the body, then the fluid will not completely leave the body. If such a symptom is present, the patient has little chance of recovery.
- The appearance of frequent disorders If there are any diseases in the intestines, then this will be accompanied by symptoms - the appearance of nausea, and frequent pain during bowel movements. In this condition, medications are of little help. Over time, the stool becomes like water. The person begins to go to the toilet frequently. In some cases, on the contrary, constipation may appear. But, constipation will only occur if the tumor is located in the area where the intestines are bent.
- Blood appears in the stool If there is blood and mucus in the stool, this may also indicate the presence of oncology in the body. At the same time, a person’s health deteriorates. The skin turns pale and the functioning of the urinary system is disrupted.
Diagnosis of colon cancer
Unfortunately, the symptoms that determine the presence of a tumor cannot always help in treatment.
People don't take them seriously. Therefore, as soon as the first signs of intestinal disease appear, you must immediately contact a special medical institution.
The modern level of medicine makes it possible to diagnose a colon tumor as clearly as possible, which is why the most accurate diagnosis is made.
And treatment is carried out in a short time. Diagnosis of colon cancer has its own specific scenario, so you should take all the necessary tests on time, strictly following all the doctor’s instructions and recommendations.
The initial diagnostic order does not change.
The first step is to question the patient for symptoms; signs and sensations are carefully assessed from a medical point of view.
The specialist examines the patient, palpating the intestinal area.
The next stage is sigmoidoscopy. The patient undergoes a general blood, stool and urine test, and a colonoscopy is performed.
In the initial stages of intestinal disease, the results of the above diagnostic methods may not appear.
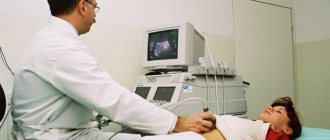
For a clearer picture, the doctor prescribes other studies: the patient is sent for an ultrasound of the abdomen, an endorectal ultrasound of the pelvis.
To perform a biopsy, a piece of tissue is taken from the patient; this helps to thoroughly study the structure of the cells and their damage; the method is not used so often, in some cases.
If the person showing symptoms is over 50 years old, then the doctor is required to test for colon cancer, a treatment that involves the intestines in one way or another.
Most often, the tumor is localized in the upper intestinal sections, so conventional diagnosis of colon cancer does not always give the desired results.
Regarding the tumor in the lower parts of the intestine, it can be detected during simple palpation.
When diagnosing colon cancer, in any case, one should not neglect the diagnostic methods offered by modern medicine.
Diagnostics
Rectal cancer can be diagnosed by naked eye examination. However, more cases of advanced cancer occur than in the early stages. The diagnostic algorithm consists of several important points:
- Gathering complaints is the initial stage of diagnosis. The list of signs of rectal cancer in women at an early stage has been described above. The conversation with the doctor also includes a life history. The doctor asks questions about cases of cancer in blood relatives, which helps assess the likelihood of hereditary pathology. A history of obligate precancerous diseases indicates a high probability of having rectal cancer.
- Objective examination includes inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation. With palpation, you can feel the tumor in the left half of the abdomen if it is large. It will be informative to conduct a digital examination of the rectum if the cancer grows in the lower third of the intestine or in the anorectal area. The use of rectal mirrors and examination of the intestinal cavity also has great diagnostic value.
- Laboratory diagnostics. A clinical blood test will show anemia. A stool occult blood test is required if rectal cancer is suspected.
- Instrumental methods. Sigmoidoscopy will make it possible to visualize the rectal cavity and, if there is a formation, perform a biopsy - pinch off a part of it for histological examination. In the pathology laboratory, the doctor will examine the tumor and give an opinion on the morphology of the formation.
- X-ray with contrast enhancement. The tumor will look like a mass in the intestinal cavity.
- Ultrasound is informative when examining the abdominal and pelvic organs for distant metastases.
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are studies necessary for a thorough examination of the tumor - its blood supply, fusion with surrounding tissues, and the possibility of radical treatment.
- Positron emission tomography is the newest method necessary for diagnosing tumors less than a centimeter in diameter.
Treatment of colon cancer
After diagnosing the disease, the specialist prescribes a series of therapeutic actions.
They depend on the characteristics of the human body and the presence of allergic reactions. Treatment must include a strict diet.
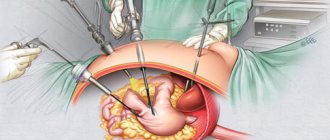
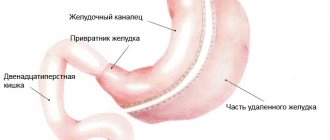
At earlier stages of a colon tumor, removal of the malignant tumor is used, as well as elimination of metastases that have spread beyond the intestinal walls.
Surgical intervention in the treatment of oncology can completely eliminate the affected tissue, and feces that do not pass are removed during the operation.
The intestines are carefully prepared before the surgical procedure.
A diet is prescribed, and a few days before the procedure the patient must undergo a colon cleanse and an enema. The digestive tract is washed if necessary.
The operation can be quite risky; colon cancer can be affected along the entire perimeter of the organ: the doctor does not touch the tumor itself during the operation, since the tumor cells, along with the blood flow, can move through the tissues of the body and spread to nearby organs.
When metastases develop, treatment is more difficult; the possibility of removing part of the intestine is sometimes pointless, since they will go further.
If a malignant tumor is removed during surgery, the risk of complications is reduced.
This applies to pain and bleeding. In such a case, the operation will only stop the process of damage.
In the final stages, when there is no longer a chance for a full recovery, they try to improve the patient’s condition.
For this purpose, a colostomy is formed; this method allows you to normalize intestinal functions; there are no other methods better than this.
If colon cancer has pathological complications, then surgery at later stages is prescribed immediately; surgery is performed in several stages.
The first stage is determined by removing the tumor and eliminating complications. The colostomy is formed during the second operation.
Earlier stages make it possible to eliminate the tumor without surgery: chemotherapy for colon cancer can bring a positive result if there are no metastases, and radiation can also stop the impact of the lesion.
Adenocarcinoma is considered an effective method in the treatment of some complex types of intestinal cancer.
Such irradiation destroys pathogenic cells, so the colon tumor decreases in size.
Radiation is combined with surgery, which reduces the risk of cells spreading through the blood and eliminates the possibility of tissue inflammation.
For clearly defined tumors, this treatment method will be most effective.
But the human body does not always allow certain methods of treating a tumor, since sensitivity to radiation can interfere with treatment. In this case, chemotherapy is prescribed.
For colon cancer, chemotherapy is usually aimed at reducing the growth rate of the malignant neoplasm.
Typically, chemotherapy for such an intestinal disease is prescribed after completion of surgery, its purpose is to minimize the risk of relapse of the disease.
Chemotherapy does not always completely get rid of a colon tumor, but it does inhibit its growth and action.
Metastases also do not develop. In addition to the intervention, medications are prescribed to improve the mucous membrane and normalize the immune system.
When treating with a diet, the doctor prescribes a diet that does not irritate the human membrane.
Food helps normalize the gastrointestinal flora.
You should not eat too hot and spicy foods, this aggravates the situation, also causing gastritis.
You should not drink alcohol, otherwise the cells will continue to die at a faster rate.
Each treatment method can give both positive results and complications.
This depends on the number of metastases, their intensity of spread, lesions of other organs, the effectiveness of drug treatment and the stage of development of the disease.
Treatment
To treat cancers localized in the rectal area, standard methods are used:
- Surgical intervention. This method is fundamental in the treatment of this type of cancer. The tumor is removed along with some of the healthy tissue surrounding the growth. In case of an extensive lesion, an entire segment is excised, which is then restored by suturing the edges.
If it is necessary to remove the anus, the operated intestine is removed in the form of a colostomy.
- Radiation therapy. Represents the impact on the affected area by radiation rays. For this type of cancer, both contact and remote techniques can be used.
- Polychemotherapy. Involves the administration of intravenous or injection infusions. For this pathology, combination therapy is used, which includes several anticancer drugs: oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin. Chemotherapy is carried out in the presence of metastases. Treatment requires several courses of chemotherapy.
Survival prognosis for colon cancer
How quickly a person turns to a specialist will determine how soon colon cancer will be cured; the prognosis in this regard depends only on the patient.
Many people ignore the first symptoms, paying attention to their health when the formation of metastases begins.
If at least one symptom appears, you should consult a specialist.
Cancer may not be found, but other diseases of the digestive system can also contribute to further problems.
How long do you live after treatment for colon cancer?
Prediction is based primarily on the stage of oncological pathology and the characteristics of a low-quality tumor. In patients with the first stage of intestinal cancer, subject to timely diagnosis and quality treatment, the five-year survival rate is more than 95%. In patients with the second stage of intestinal neoplasia, remission is observed in 70% of cases. Five-year survival rate at the third stage is 45-50%, at the fourth stage it is 5-7%.
The main reason for the high mortality rate is late diagnosis, so oncologists strongly recommend undergoing regular screening tests of the gastrointestinal tract, immediately consult a doctor if the most minor symptoms occur, and adhere to preventive measures.
What are the differences between bowel cancer symptoms in men and women?
When the tumor begins to grow into the intestinal walls and spreads to other nearby organs, then the disease manifests itself with slightly different symptoms. Signs of intestinal cancer in men and women with this course are practically no different. Later, if the tumor progresses and spreads to neighboring organs, the prostate is the first to be affected in men, and the vagina is the first to be affected in women; the rectal space and anal canal are also affected. In this case, the patient begins to experience severe pain in the anus, coccyx, sacrum, and lumbar region; men feel difficulty during urination.
The fact is that in men, a cancerous tumor of the intestine begins to grow in the tissue of the bladder, manifested by a strong increase in temperature and the manifestation of an ascending infection of the urethra.