Causes
All causes of intestinal perforation are divided into traumatic and non-traumatic. In the first case, perforation occurs from the outside, in the second - from the inside. Regardless of the location, perforation can be caused by the following factors:
- oncological diseases of the intestine;
- diverticulitis;
- volvulus;
- infections, for example, tuberculosis, typhoid fever;
- intestinal obstruction;
- ulcerative colitis;
- organ transplantation;
- ingestion of sharp objects into the intestines;
- blunt abdominal trauma;
- AIDS;
- inflammatory processes in the intestines;
- toxic megacolon.
Small bowel perforation
This section of the intestine is less susceptible to perforation. In addition, perforation of the thin section carries fewer dangerous complications. Perforation may occur in the ileum or duodenum. The main causes of such damage:
- obstruction of the small intestine;
- infectious diseases, including tuberculosis, typhoid fever;
- viral pathologies;
- progressive gastric or duodenal ulcer;
- tumor in the organs of the reproductive system (uterus, ovaries);
- penetrating wounds;
- blunt trauma to the peritoneum;
- hit by sharp objects;
- intrauterine anomalies of intestinal development.
Colon
Perforation of the large intestine ranks second in frequency after perforation of the duodenum and stomach. Men encounter this pathology more often. Perforation occurs in the area of the cecum. The reasons for perforation are as follows:
- Crohn's disease;
- ulcerative colitis;
- toxic megacolon;
- intestinal obstruction of non-oncological nature;
- colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy;
- acute diverticulitis;
- immunodeficiency virus;
- sigmoiditis;
- intestinal obstruction;
- volvulus;
- spontaneous rupture;
- condition after transplantation of skin, organs, tissues;
- taking immunosuppressants and some hormonal drugs.
https://youtu.be/3fyyk0WQUTw
Pathology of the small intestine - the main causes
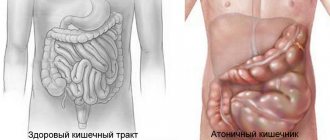
The small intestine is less susceptible to this kind of pathology. Based on WHO (World Health Organization) statistics, we can conclude that such a disease carries fewer dangerous complications.
However, the disease requires urgent surgical intervention. Perforation can affect the duodenum and ileum. As a rule, pathology occurs in adulthood and most often in men. The main reasons provoking the development of perforation.
- Mechanical impacts, injuries: falls, accidents, intense impacts.
- Severe intestinal obstruction. Over time, stretching occurs to critical values, after which a rupture or acute loss of integrity occurs.
- A progressive ulcer of the stomach or duodenum (perforated type) without therapeutic effect, the development of an inflammatory process may be observed.
- Penetration of a foreign body into the body. In this situation, a gradual endogenous mechanical effect on the intestines occurs.
- Various kinds of infectious pathologies - typhoid fever, a sharp decrease in the protective functions of the immune system, tuberculosis, diseases caused by viruses or bacteria.
- The presence of a tumor in the organs of the reproductive system: uterus, ovaries.
- Wounds penetrating into the abdominal area - puncture injuries, gunshot.
Small intestine
Symptoms
A characteristic sign of intestinal perforation is severe abdominal pain. It is localized on the left side, near the ribs and can radiate to the shoulder. Due to pain, a person takes a forced position on his side or back with his legs bent. Other characteristic symptoms of intestinal perforation:
- temperature increase;
- nausea and vomiting;
- absence of bowel sounds;
- diarrhea, weak pulse;
- bile in vomit;
- gray skin color;
- loss of appetite, development of anorexia;
- weak heartbeat;
- tension in the peritoneum, which can be felt by placing your hand on your stomach;
- blood in stool and urine;
- peritonitis.
Intestinal perforation in newborns
In infants, the pathology manifests itself with specific symptoms. The endurance of newborns compared to adults is much lower, so intestinal perforation can quickly lead to death. To prevent this, it is important to notice the following symptoms in time:
- dry epithelium;
- low skin temperature that feels cold to the touch;
- gray or white tint, pale skin;
- vomiting with bile.
Intestinal perforation: symptoms and clinical picture
Signs of pathology vary depending on the location where the wall is damaged. Intestinal perforation, symptoms and treatment in adults differ from manifestations and treatment in newborns, infants and children.
Common signs of pathology include:
- severe acute pain in the abdominal region;
- intense nausea, urge to vomit;
- stool disorders, blood streaks and mucus are observed in stool and urine;
- reduction in heart rate;
- strong tension in the peritoneal area, easily determined by palpation of the abdomen;
- development of anorexia, loss of appetite;
- manifestation of the inflammatory process in the stomach, peritonitis;
- absence of characteristic bowel sounds.
Pain syndrome
The main symptom of perforation is the inability to breathe freely due to acute pain. As the pathology develops, fecal impurities appear in the urine.
- dry skin, the shade changes and approaches gray;
- intense vomiting occurs, the vomit includes streaks of bile;
- pronounced causeless cooling of the skin.
Suspicion of perforation in both the adult age group and children is a reason to seek emergency medical help. Timely treatment means a significant reduction in the risk of complications; otherwise, there is a high percentage of deaths.
Diagnostics
First, the doctor conducts an external examination of the patient, palpating his abdominal cavity. Next, to confirm the diagnosis, the following laboratory and instrumental procedures are performed:
- Plain radiography of the abdominal cavity. Detects the presence of free gas, which is clearly visible under the diaphragm.
- Peritoneal lavage. This is a procedure for washing the abdominal cavity. During the study, fluid is taken to study it for the content of bacteria, leukocytes, intestinal contents, and blood.
- Blood analysis. Detects leukocytosis - an increased level of white blood cells. With peritonitis, electrolyte disturbances may be detected.
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging. Allows you to detect the localization of perforation by the presence of gases in the peritoneum.
Treatment
Conservative therapy serves only as a stage of preparation for surgery. If there are no signs of peritonitis and there is a risk of surgical intervention, then exclusively medicinal treatment methods can be used. Immediately before the operation, the following procedures are carried out:
- Discontinue oral administration of fluids and food. A urethral catheter and a nasogastric tube are installed in the patient.
- Administration in the form of infusions of complex solutions to restore water and electrolyte balance.
- Antibacterial therapy. For intestinal perforation, Cefotetan, Metronidazole, Cefoperazone, Cefoxitin, and Gentamicin are most often used.
The main treatment method is surgery. All operations have a common scheme - removal of areas of necrosis, feces, clots. Intestinal perforation is often eliminated using the following methods:
Beware - scammers
Leaky gut syndrome is a disease that is controversial from the point of view of traditional medicine. Therefore, promises of healing and expensive treatments from “specialists” are very common. There is still no scientific evidence that measures to improve or restore the intestinal barrier have an impact on the onset or course of various diseases.
Important! Before using traditional or alternative medicines, it is recommended to consult a doctor. Reckless use of high doses of medicinal herbs or drugs with unknown clinical effect can lead to unpredictable consequences.
Consequences
The intestine contains a large number of bacteria, so if it is perforated, there is a high risk of bacterial complications. Among the possible consequences of intestinal perforation, other pathologies stand out:
- bleeding;
- abscess (phlegmon);
- peritonitis;
- hypovolemia;
- sepsis;
- shock;
- multiple organ failure;
- hypoproteinemia;
- violations of acid-base and electrolyte composition;
- fistulas
- Pale skin
- Abdominal pain
- Severe abdominal muscle tension
- Intoxication
- Exhaustion
- Blood in stool
- Blood in urine
- Fever
- Diarrhea
- Feces in urine
- Spread of pain to other areas
- Vomit
- Vomiting bile
- Weak pulse
- Nausea
- Cold skin
Intestinal perforation is a dangerous pathological condition that develops as a result of the aggressive impact of various exogenous and endogenous factors on the walls of the small and large intestine, resulting in a violation of the integrity of its mucous membrane. This condition in the medical literature is also called perforation of the small or large intestine (depending on the location). The disease requires emergency medical care, as without it death can occur. Intestinal perforation can develop in people of various age categories, including newborns. That is why, if its first symptoms appear, you should immediately contact a medical institution for qualified help.
Sometimes the cause of perforation in the intestine is colonoscopy (endoscopic examination of the intestine). There are several reasons for this, and the first of them is the incompetence of a medical specialist. For this reason, you should only trust a highly qualified specialist to perform a colonoscopy. It is worth noting that in the event of a perforation during colonoscopy, the symptoms of the disease appear immediately, and doctors will be able to quickly stop this condition.
Leaky Gut Diet: Basic Nutrition Principles
There are countless nutritional tips or supplements surrounding leaky gut syndrome. Because the disease is still poorly understood, there are no scientifically proven treatment guidelines.
High-fiber foods—whole grains, vegetables, and legumes—make sense because bacteria break down dietary fiber into butyric acid. According to studies, it significantly reduces intestinal permeability.
5 common tips for healthy eating:
- Oily fish - salmon, herring and mackerel - are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D. 1 to 2 servings of oily fish per week are recommended.
- Zinc helps strengthen the intestinal barrier. The microelement is found in seafood, nuts and beef.
- A lack of vitamin A contributes to the development of leaky gut syndrome. The richest sources are animal products - liver and cheese. The precursor of beta-carotene is found in peppers, carrots, spinach and apricots,
It is assumed that artificial additives in industrially produced foods - flavor enhancers and emulsifiers - increase the permeability of the mucous membrane. It is recommended to avoid processed foods.
Dietary guidelines promote elimination diets, which recommend eliminating various foods from the diet. One-sided eating plans are not recommended as they lead to chronic nutritional deficiencies.
Causes
With perforation, there is a violation of the integrity of the mucosal area in the intestine, as a result of which its contents can leak into the abdominal cavity, thereby provoking the development of severe complications such as peritonitis, sepsis, etc. Under no circumstances should you try to eliminate this condition yourself, as you can only worsen the patient’s condition and waste precious time. You should immediately consult an experienced doctor. Parents of newborns especially need to be attentive. Often, perforation can be congenital, so it is important to know its first signs in order to get the child to the doctor in a timely manner.
Most often, the following factors can provoke a rupture of the intestinal mucosa:
- blunt trauma to the abdominal area;
- stab, cut, gunshot wound of the abdominal cavity;
- swallowing an object with sharp edges;
- the occurrence of infectious pathologies in the human body;
- diverticula;
- colitis;
- the presence of an oncological tumor in the intestine;
- AIDS;
- inflammatory processes in the organ.
In newborns, intestinal perforation can be caused by congenital pathologies or abnormal development of the fetus in the womb. Colonoscopy can also cause symptoms of perforation in both adults and newborns. And this is not a rare case. During a colonoscopy, a special probe with a camera is inserted into a person's large intestine through the anus. An unqualified or inexperienced specialist may insert it incorrectly, thereby damaging the intestinal wall. In this case, the symptoms of the disease appear immediately. Colonoscopy is often performed to remove polyps localized in the large intestine, which can also cause burns on the walls of the organ. In the future, they may become necrotic, and this will lead to perforation. In this case, after the colonoscopy, it will take 3 to 5 days before characteristic clinical signs appear.
Intestinal perforation
Intestinal perforation is a pathology that, if incorrectly diagnosed or treated, leads to death. The disease can develop in both adults and newborns.
It is important for a person to monitor his health and consult a doctor at the slightest sign of illness.
In medical practice, there have been cases when pathology was detected at the time of colonoscopy, which allows immediate assistance to the patient.
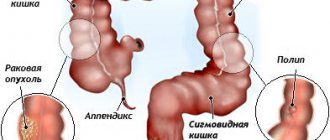
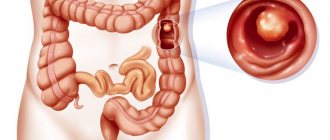
When perforation occurs, the integrity of the walls of the organ is violated, and the contents from the intestine exit into the peritoneum. Diseases are quite often diagnosed in the area of the cecum, and in other parts of the large intestine, perforations occur less frequently.
This condition of the small intestine can be formed under the influence of such factors:
- abdominal injuries;
- penetrating injuries;
- sharp objects in the intestines;
- intestinal obstruction;
- development of infection.
The following reasons contribute to the formation of the disease:
- malignant formations;
- colitis;
- complications after ulcers;
- infections;
- foreign bodies in the stomach;
- unexpected breakup;
- complication after organ, skin or tissue transplantation;
- wounds upon diagnosis.
Intestinal perforation in newborns can develop in the womb and may be a congenital disease. Colonoscopy is often the cause of the condition in children and adults. During the examination, the doctor guides the probe incorrectly, which irritates the mucous membrane. In this case, symptoms of intestinal perforation appear immediately.
When compiling the classification, clinicians relied on the location of the disease.
In this regard, the following types of pathology are distinguished:
- perforation of the small intestine;
- large intestine.
Large and small intestines
The disease can develop under the influence of improper medical procedures. Based on this fact, pathology can manifest itself in three groups:
- minor injuries;
- moderate severity;
- severe breakup.
Intestinal perforation is a disease in which symptoms indicate rapid inflammatory changes in the abdominal cavity. The patient needs immediate assistance if the following symptoms are noticed:
- pain that intensifies during movement, coughing and when inhaling;
- the temperature rises, chills may begin;
- pale skin is noted;
- reduced performance;
- nausea and vomiting;
- urination decreases;
- pulse quickens;
- breathing is impaired.
When the large intestine is perforated, the patient develops additional signs of intestinal perforation. During palpation of the area of inflammation, a dull sound disappears, which indicates the accumulation of gas or liquid in the peritoneum.
A perforation can form not only under the influence of other ailments or examination, but there can also be a spontaneous rupture of the rectum. It can form due to a blow to the stomach, increased pressure in the abdominal cavity, lifting weights, urination or other factors.
Characteristic signs are noted:
- pain attacks in the lower abdomen and anus;
- discharge of blood from the anus;
- there may be prolapse of loops of the small intestine from the anus.
Perforation can be identified by the following symptoms:
- bloating;
- strong gas formation;
- bleeding;
- sharp pain in the abdomen;
- intoxication;
- moderate tension in the abdominal muscles.
The patient needs to be helped as quickly as possible, since a few hours after the formation of the perforation, all symptoms fade away. This is due to the fact that the nerve endings of the peritoneum get used to the changes that have arisen. The reduction in symptoms is temporary. After some time, the symptoms increase again and begin to progress, which worsens the patient’s condition.
If the intestinal walls are affected and the above symptoms develop, the patient urgently needs to seek professional help. As part of diagnosing the disease, the doctor must examine and palpate the peritoneum. Then it is necessary to carry out general tests, x-rays of the affected area, and tomography.
When an emergency condition is established, the doctor must find out the cause of organ damage. The assistance provided will depend on the factors that provoked the formation of perforation.
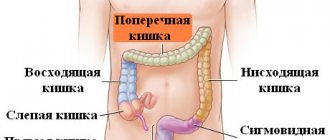
During the examination, the patient needs to undergo a complete examination of the condition:
- small and large intestine;
- cecum;
- ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid colon;
- rectum.
In addition to the mentioned methods of instrumental research, the doctor can refer the patient to undergo:
- Ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract;
- X-ray of the stomach and duodenum;
- Ultrasound OBP.
Since the disease is similar in its symptoms to some other gastrointestinal problems, the doctor needs to conduct a differentiated analysis. The disease has common characteristics with colon cancer, ischemic or amoebic colitis, steroid ulcer, and spontaneous rupture.
If a patient is diagnosed with a violation of the integrity of the large intestine, then intestinal perforation can only be treated with surgery. Such radical measures can be taken only after diagnosing and determining the location of the perforation.
The operation can be performed if the person has not been diagnosed with peritonitis and there are no significant holes in the intestines.
Sometimes colostomy is used in therapy.
- In the postoperative period, the patient is prescribed antibiotics and intravenous administration of electrolyte solutions.
- Doctors can also use an alternative method of treating pathology.
- The algorithm of action according to the Taylor method consists of the use of antibiotics and constant suction of contents from the intestine in the area of \u200b\u200bthe rupture.
- This method allows the intestines to heal faster, but as practice shows, such treatment does not lead to recovery, and sometimes can only worsen the patient’s condition.
- Since the disease can develop from the appearance of ulcers, doctors advise treating all gastrointestinal pathologies in a timely manner, otherwise the patient may die.
Survival rates for gastric perforation can be determined after symptoms are identified. Only time can tell the doctor how effective the treatment will be. Indeed, during inflammation and before surgery, such a disease can develop in different ways and at different speeds. The patient's age and the presence of other concomitant diseases are also taken into account.
Doctors report that up to 50% of patients can survive after surgery. Successful surgery is not a guarantee of recovery.
Source: https://OkGastro.ru/kishechnik/446-perforatsiya
Symptoms
It is important to note that the symptoms of the disease may vary slightly depending on where the rupture occurs. But the general signs are as follows:
- severe intoxication of the body;
- nausea and vomiting;
- abdominal tension. It can be felt simply by placing your hand on the anterior abdominal wall;
- severe pain in the abdomen;
- pain in the left side of the abdomen, closer to the ribs, which can radiate to the shoulder area;
- hyperthermia;
- There are no sounds characteristic of the intestine;
- presence of blood in excrement and urine;
- diarrhea;
- anorexia;
- pulse weak;
- Peritonitis often progresses.
Diagnosis and treatment
First of all, the specialist conducts an external examination of the patient, palpating his abdominal cavity. Next, laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are prescribed. In particular, radiography and computed tomography are highly informative.
If the diagnosis was confirmed during diagnosis, then the patient begins to immediately prepare for surgical intervention, since this is the only way to eliminate the pathology. Preparation lasts on average from 2 to 4 hours. But if the patient is in shock, then the operation is performed without preliminary preparation. The essence of the intervention is that, under general anesthesia, the surgeon makes an incision in the abdominal wall, sutures the tear in the intestinal wall and then rinses the abdominal cavity. This type of operation is performed in case of a small tear and in the absence of peritonitis. In other cases, a colostomy is indicated - the removal of the large intestine to the abdominal wall.
After the operation, the patient is prescribed antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and painkillers. Fasting is mandatory in the first few days after the intervention.
https://youtu.be/NNsiAxSMyMQ
Intestinal perforation is a serious pathology in which holes appear in the intestinal wall, opening inward into the abdominal cavity. When perforation occurs, many organs of the gastrointestinal tract are affected, as a result of which peritonitis can even occur, resulting in death if not treated in a timely manner. In medicine, intestinal perforation is also called intestinal perforation.
Other Ways to Improve Gut Health
While eating right is key to improving your gut health, there are many other steps you can take.
Here are some more ways:
Take probiotics (dietary supplement) : Probiotics contain beneficial bacteria that are naturally present in fermented foods. Taking probiotics as a supplement may improve digestive health if you are not getting enough probiotics through your diet.
Reduce stress: Chronic stress has been shown to harm beneficial gut bacteria. Activities such as meditation or yoga can help.
Avoid smoking : Cigarette smoke is a risk factor for several negative GI conditions and can increase inflammation in the digestive tract. Quitting smoking can increase the number of healthy bacteria and reduce harmful bacteria.
Get more sleep: Lack of sleep can lead to poor distribution of healthy gut bacteria, which can lead to increased intestinal permeability.
Limit your alcohol intake: Research has shown that excessive alcohol consumption may increase intestinal permeability by interacting with certain proteins ().
If you think you have leaky gut, consider getting tested for celiac disease. These two disorders may have overlapping symptoms.
In addition to eating clean, to heal leaky gut, try taking probiotics, stressing less, getting more sleep, and giving up bad habits. All of this will definitely improve your gut health.
Causes
The causes of intestinal perforation will largely depend on what part of the intestine is affected (small or large intestine).
| Causes of perforation of the small intestine | Causes of colon perforation |
| blunt or puncture abdominal injuries (falls, knife and gunshot wounds, blows); | during colonoscopy, damage to the intestines by the device itself is possible; |
| ingestion of sharp objects that are not digested in the stomach (needles, toothpicks, glass, plastic); | colitis of various etiologies; |
| in newborns, perforation may occur due to intrauterine anomalies of intestinal development; | infections affecting the gastrointestinal tract; |
| intestinal obstruction (when a large amount of feces accumulates in the small intestine, over time the walls cannot withstand the pressure and rupture occurs); | volvulus; |
| intestinal infections and their complications. | intestinal diseases (diverticulitis, fistulas); |
| AIDS | |
| entry of a foreign body into the intestines (possibly during anal sex using sharp objects); | |
| organ transplant or other abdominal surgery. |
Intestinal perforation can occur in both adults and children. You should not delay treatment, as delay can be fatal; it is better to go to the hospital immediately. If the disease is not diagnosed in time, then even the latest medicine and the best specialists will not be able to help.
One of the main causes of constipation and diarrhea is the use of various medications.
.
To improve bowel function after taking medications, you need to drink a simple remedy
.
Hypothetical holes in the intestinal walls?
The phenomenon of “increased permeability of the intestinal mucosa” really exists. The intestinal wall protects the body from pollutants and pathogens. Nutrients must pass through the walls because they are simply absorbed by the body.
In order for the system to function properly, the lining of the small intestine has specially designed transport channels, so it is not completely dense in nature. The degree to which the channels are permeable is controlled by special substances, most of which have not yet been studied.
Symptoms
Typical signs of intestinal perforation:
- abdominal pain is acute, can radiate to the left shoulder, and is often localized under the ribs;
- the perforated area hurts more when pressed;
- nausea and vomiting;
- blood in stool and urine;
- if the bladder is affected, urine may come out with feces;
- hard abdomen; upon palpation, tension in the abdominal wall is felt;
- the temperature rises sharply up to 39 degrees;
- when listening, there are no sounds of normally functioning bowels;
- diarrhea also accompanies the disease in some cases;
- loss of appetite;
- weakness;
- the patient takes a forced position lying on his side or back, does not inhale deeply and holds his stomach with his hands;
- heartbeat is very weak.
What came first?
German scientists have found that in some diseases the mucous membrane is more permeable than usual. Increased permeability occurs in inflammatory bowel diseases - Crohn's disease, wheat protein intolerance (celiac disease), food allergies and irritable bowel syndrome.
Anti-inflammatory analgesics such as ibuprofen or aspirin and chronic alcohol abuse weaken the connections between cells in the small intestinal wall. Therefore, chemicals also increase the permeability of the walls.
However, there is a big “but”: a certain disease is not necessarily caused by greater permeability of the intestinal walls. It is quite possible that it is a result (consequence), and not the cause of disease. The classic chicken and egg problem: you don't know which came first.
When it comes to the causes of intestinal diseases, science is still in the dark. Why irritable bowel syndrome or chronic inflammatory bowel disease occurs is unknown. The occurrence of food intolerances - celiac disease - and allergies are also poorly understood.
Diagnostics
It is important to diagnose intestinal perforation in the first hours after the onset of rupture. If this is not done in a timely manner, the patient runs the risk of developing peritonitis, after which there is a direct path to the operating table. To diagnose a perforation, the doctor will first perform palpation of the abdomen and percussion.
To confirm the diagnosis, instrumental studies are performed:
- X-ray of the intestines.
- CT scan.
- Blood analysis.
Diagnostics using instruments is not carried out; if clinical signs are obvious and the situation worsens, then a diagnostic operation can be immediately prescribed, during which appropriate measures will be taken to eliminate the perforation.
One of the main causes of constipation or diarrhea is poor diet.
.
Therefore, to improve bowel function, you need to drink a simple drink
.
Sample menu for one week
Below is a healthy one-week menu to improve your digestive health and heal leaky gut. It focuses on including foods that promote the growth of healthy gut bacteria while eliminating foods that are known to cause digestive upset.
Monday
Breakfast : Blueberries, banana and Greek yogurt.
Lunch : Mixed green salad with chopped hard-boiled eggs.
Dinner : beef with stewed vegetables (broccoli, zucchini) and sauerkraut.
Tuesday
Breakfast : omelette with vegetables of your choice.
Lunch : Leftovers from Monday lunch.
Dinner : Seared salmon with fresh green salad.
Wednesday
Breakfast : Blueberries, Greek yogurt and unsweetened almond milkshake.
Lunch : Braised salmon, egg and vegetarian frittata.
Dinner : Grilled chicken salad with sauerkraut.
Thursday
Breakfast : Gluten-free oatmeal with a quarter cup of raspberries.
Lunch : Leftovers from Wednesday dinner.
Dinner : Grilled steak with Brussels sprouts and sweet potatoes.
Friday
Breakfast : Kale, pineapple and unsweetened almond milkshake.
Lunch : beets, carrots, kale, spinach and brown rice salad.
Dinner : Baked chicken with roasted carrots, beans and broccoli.
Saturday
Breakfast : coconut milk pudding with papaya and chia seeds.
Lunch : chicken salad with olive oil.
Dinner : Brussels sprouts and brown rice.
Sunday
Breakfast : Mushroom, spinach and zucchini frittata.
Lunch : Sweet potato halves with spinach, turkey and fresh cranberries.
Dinner : Grilled chicken wings with fresh spinach and sauerkraut.
A healthy diet is the treatment for leaky gut syndrome. This diet should be rich in fruits, vegetables and protein. Fermented vegetables such as sauerkraut or fermented dairy products such as Greek yogurt are also great additions as they are a rich source of healthy bacteria.
Treatment
Patients with intestinal perforation after diagnosis are immediately indicated for preparation for surgery or urgent surgical intervention. During the operation, patients most often undergo suturing of part of the intestine. If there are a lot of holes and gangrene begins to develop, then a colostomy on the anterior abdominal wall is indicated.
This passage allows stool to be passed out not through the usual anus, but through a special tube. A colostomy can be temporary; after a few days, when the patient’s condition has stabilized, the intestines will be sutured in the usual position and the patient will be able to go to the toilet as before. But sometimes a colostomy, if indicated, can remain for life.
Surgery may also take the form of a bowel resection. In this case, the affected part is cut out, and the healthy areas are sewn together. If symptoms of perforation reappear within a few days, a repeat laparotomy is performed.
Video
After the operation, the patient is prescribed bed rest. His bandages are changed every day and antibiotics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are administered to his body.
In the first few days after surgery, a fast is indicated; food is replaced with intravenous glucose and fluid.
This is necessary so that the intestines go through the healing period faster and the sutures heal faster. After which, food is introduced gradually, in small portions and mashed, so that constipation does not occur.
Less severe changes after the study
In addition to perforation and bleeding, there are other complications that resolve on their own without the use of special measures.
If the CS is performed under general anesthesia, after the examination the general condition associated with the influence of narcotic drugs may be impaired.
The remaining consequences are quickly corrected and normalized in a short time. These include:
- flatulence;
- unstable stool;
- rectal discharge;
- temperature increase over 38°C;
- discomfort or pain in the intestines.
Violation of general condition
General weakness and other minor manifestations that worsen the general condition are not always a sign of pathology. During the first 1-2 days, this is a common occurrence after a CS. If the symptoms increase and your health worsens, you need to look for the cause and carry out adequate treatment.
If there is a violation of the general condition associated with the consequences of anesthesia, complaints about the following appear:
- nausea and uncontrollable vomiting;
- headache;
- respiratory disorders;
- muscle spasms.
In such situations, the patient is transferred to the ward for further observation and removal from this situation.
The general condition may worsen for other reasons. This occurs due to blood loss during other complications, infection, and may also be associated with forced fasting in preparation for the procedure.
Defecation disorder
After a CS, diarrhea or constipation may occur due to inadequate preparation or poor nutrition. Reasons for stool changes include:
- dysbacteriosis - disruption of the normal intestinal microflora;
- injury to the mucous membrane with a probe;
- decreased intestinal motility.
Diarrhea develops most often due to a violation of the main function of the intestine - the absorption of water from feces. As a result, all the liquid remains in the intestines, and bowel movements take on the appearance of diarrhea.
Forecast
The prognosis for intestinal perforation is not very good, which is due to the late presentation of patients for medical help. Half of the patients die due to the development of peritonitis. If the disease is diagnosed within the first four hours, the outcome is more favorable. After the operation, most patients return to their normal lives.
In children, the survival rate even after surgery is lower. Therefore, it is extremely important to quickly call an ambulance so that they can diagnose and find out where the intestinal rupture occurred, and quickly provide assistance to the patient.
Lack of fluid in the diet is one of the main causes of constipation. To get rid of it in 3 days, you need to drink a simple remedy every day.
Video
How to treat leaky gut?
Treatment for a scientifically unproven “diagnosis” is questionable. Advocates suggest a wide range of measures - enemas, dietary supplements or the use of probiotics. It is impossible to test whether the measures will help cure leaky gut syndrome because there are no clear diagnostic criteria.
Probiotics
Considering that the microbiological balance of the gut plays an important role in the development and treatment of intestinal diseases, the use of probiotics to treat leaky gut syndrome seems reasonable. A 2011 study found that Lactobacillus casei may prevent intestinal barrier breakdown.
Important! The clinical effectiveness of probiotic agents has been proven for diarrhea. According to a meta-analysis from the Cochrane Collaboration, regular use of probiotics reduced the duration of diarrhea by 1.3 days. However, clinical effectiveness in reduced intestinal permeability has not been proven.
Biologically active additives
In a Spanish study, researchers examined the effect of regular use of butyrate and omega-3 fatty acids on inflammatory bowel disease. It was found that dietary supplements reduced the intensity of inflammation and pain by 29%.
Zinc and vitamin D have a positive effect on wall permeability, but clinical effectiveness has not been fully proven. According to two French studies, zinc not only reduces the permeability of the intestinal wall, but also regulates intestinal microflora. Vitamin D improves the bioavailability of calcium, therefore normalizing the activity of intestinal cells.