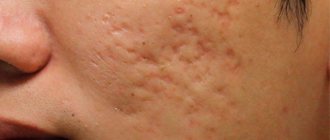
Discharge from the penis is one of the symptoms of the disease
Chlamydia is an infectious disease transmitted through sexual contact. Among all sexually transmitted infections, this is in first place; more than 100 million people suffer from it every year.
Chlamydia in men often results in complications, and all because not all representatives of the fair sex pay attention to the symptoms and go to the hospital. People who are unaware of their illness are potentially dangerous to others.
Pathogens of chlamydia
The causative agent of chlamydia in men is a stationary spherical microorganism - chlamydia, which is neither a virus nor a bacteria. When chlamydia enters the male body, damage occurs to epithelial cells of various organs:
- urethra,
- Oral cavity,
- seminal ducts,
- Mucous membrane of the eye.
The life activity of the microorganism and its structure are much more complex than those of other viruses. Unfavorable conditions contribute to the fact that they fall into “hibernation”, wait for a certain time and become more active at the moment of reduced immunity of a man.
Features of the disease
The development of chlamydia in a man is caused by the entry of the chlamydia bacterium into his body, which can affect the urethra, rectum, eyes and other organs. In rare cases, the parasite can settle in the throat. Constant stress and lack of adequate nutrition can lead to this condition, as a result of which the body’s natural defenses are reduced.
The main method of transmission of infection is unprotected sexual intercourse. Due to the fact that chlamydia bacteria quickly die in environmental conditions, it is almost impossible to become infected with it through household means. A separate method of transmission of chlamydia is vertical - from an infected mother to a child during childbirth.
Dermatovenerologist Vyacheslav Vasilyevich Makarchuk will talk about the symptoms and manifestations of the disease:
The risk group includes men and women aged 16-25, although anyone can be diagnosed with chlamydia, regardless of age. The infection became widespread due to:
- Long incubation period.
- The absence of symptoms or their insignificant expression.
It is with this that doctors attribute the fact that chlamydia often leads to various kinds of complications. After all, an infected person who is unaware of the disease can transmit it to a huge number of other people.
How does chlamydia develop?
Once in the body, chlamydia, like viruses, penetrates the tissue of epithelial cells and sticks to the membranes. Because they have minimal mobility, adoption is very slow. The epithelial cells themselves begin to absorb the adhered pathogenic microorganism. Once inside, chlamydia becomes invulnerable to harmful factors from the outside and begins to have a detrimental effect on the affected cell by exchanging information with it at the genetic level. After introduction, it is no longer possible to influence the microorganism with drugs - in this it is similar to a virus.
Chlamydia that has invaded human tissue provokes each infected cell to form new ones. Their quantitative composition regularly increases and over time, with the greatest number, the affected epithelial cell is already destroyed. After its destruction, new chlamydia, which escape, invade healthy cells and this cycle repeats. There are two forms of chlamydia in the body: extracellular and intracellular.
With the help of blood and lymph flow, chlamydia spreads throughout the body, and as a consequence of chlamydia, damage occurs to the internal organs of a person, the oral cavity and the mucous membranes of the eyes.
Unprotected sex (vaginal or anal) increases the likelihood of infection from a sick person by 50 percent. Since chlamydia practically cannot live outside the body, the likelihood of household infection is minimal. Therefore, the toilet, swimming pool, bathhouse, sharing dishes, towels are not the cause of the disease.
Pathogen information
Chlamydia are pathogenic microorganisms of very small size, and they are found mainly inside the cells of the human body. In the systematic series they are located between bacteria and viruses.
Chlamydia located inside the cell exists and develops for three days, then the cell is completely destroyed, and the microorganisms begin to spread to other areas of the affected tissue. It is practically impossible to take a fragment of material for analysis at this moment, therefore the microscopic technique for studying smears and scrapings has low information content.
According to statistics, if sexual contact was carried out without the use of barrier contraception, then infection with this disease occurs in ninety cases out of a hundred. Globally, half of all adult women and men are diagnosed with chlamydia. The incubation period is asymptomatic, so it is almost impossible to detect infection at an early stage. Because of this, the disease becomes chronic, leading to infertility.
In addition, during pregnancy, various fetal development disorders occur, miscarriages occur, and autoimmune somatic diseases such as arthritis occur. Therefore, chlamydia in men and women must be diagnosed as early as possible and promptly treated.
Methods of infection
Chlamydia can enter a man's body in the following ways:
- Sexual route – by engaging in unprotected vaginal or anal sex, people expose themselves to 90% of the risk of infection. There is a possibility of a pathogenic virus entering the body during oral sex.
- The everyday route - the likelihood of the disease is minimal, since chlamydia can only live for a few days outside the body.
- Vertical route - bacteria are transmitted from mother to baby through the birth canal. In this case, a diagnosis is made: a congenital type of disease.
Many men are interested in the question of after what period the disease manifests itself. From the moment chlamydia enters the human body until the appearance of primary symptoms, two to four weeks pass.
Mechanism of disease development
The manifestation of chlamydia in men does not begin immediately. First of all, chlamydia enters the body, penetrates the epithelial cells of tissues, and begins to adhere to their membranes. Since they are practically deprived of the process of movement, the process of implementation itself is extremely slow.
In medicine, many doctors believe that it is the epithelial cells that absorb microorganisms when they come into contact with them. Once chlamydia is inside, it becomes invulnerable to adverse factors. Once introduced, medications will be useless; this is similar to viruses.
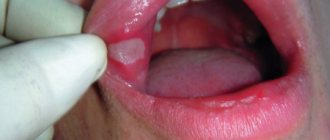
Possible chlamydial infection in the mouth
The number of microorganisms grows rapidly; after some time, the affected cell is completely destroyed. The newly formed chlamydia then come out and search for a new home for themselves, that is, they are introduced into new, healthy cells.
In the human body, chlamydia can exist in two forms:
- extracellular;
- intracellular.
With the blood and lymph flow, chlamydia spreads throughout the body, affecting more and more organs. Contaminated hands can get on the mucous membranes of the eyes or mouth.
The main route of infection is through unprotected sexual intercourse
Types of pathogen
There are several types of chlamydia, each of them provokes the development of the disease, which proceeds in its own way:
- Chlamydia trachomatis;
- Chlamydia pneumonia;
- Chlamydia pecorum;
- Chlamydia psittaci.
The first two types are considered the most dangerous for humans, since they are the ones that cause the development of serious complications. In men, chlamydial infection most often affects the reproductive and urinary systems. Other organs and systems may also be affected: hearing, joints, teeth, genitals, heart, vision, etc.
Such microorganisms can cause diseases such as trachoma, chlamydial conjunctivitis, etc. Many unpleasant symptoms and discomfort may bother you.
Many men may be bothered by problems in their intimate lives.
Possible routes of infection
The causes of chlamydia in men can be varied. As practice shows, infection most often occurs during unprotected sexual intercourse, both vaginal and anal. There is also a small chance that infection can occur through oral sex.
Common household items also cannot be excluded:
- toilet seat;
- towels, dishes;
- when visiting a public bath or sauna;
- dirty hands.
Pathogenic microorganisms, being outside the human body and in the presence of favorable conditions, can maintain vital activity for up to two days. Thus, we can conclude that the whole family can be affected; there are known cases of so-called familial chlamydia.
Chlamydia
The possibility of infection through unprotected sexual intercourse is 50%, that is, it does not occur in all cases. The incubation period lasts from two to four weeks. Chlamydia can be detected in many married couples.
Interesting! Women are more sensitive to the disease than men.
The first symptoms of chlamydia in men
In fifty percent of the male population, chlamydia occurs without pronounced symptoms, but the person is already infected and dangerous for a sexual partner. How does the disease manifest itself?
- Pain when urinating - usually mild, but can be severe and sharp,
- Scanty and clear discharge from the glans penis,
- Unpleasant smell
- Swelling of the testicles,
- Itching near the opening of the urethra,
- Cloudy urine with streaks of pus, blood,
- If the rectum is affected, there is discharge and slight pain in the anus,
- Mild pain in the scrotum, testicles, urethra and lower back,
- Increase in body temperature to 38 degrees,
- Intoxication causes weakness of the body and reduces performance.
Symptoms are expressed in different ways, usually without causing discomfort to the man, and after a certain time, the symptoms of chlamydia may disappear altogether. It is for this reason that men often do not go to the doctor, because they believe that there is no need to waste time on checks, while there are no pain symptoms. Meanwhile, chlamydia disease becomes chronic, which ultimately leads to serious and unpleasant complications.
Signs of the disease
The incubation period for chlamydia lasts from two weeks to a month. The first signs of chlamydia in men may be as follows:
- the appearance of pain of varying intensity during urination, pain and burning may occur;
- clear discharge is observed, accompanied by an unpleasant odor, but may have a yellowish-cloudy color (most often in the morning);
- the testicles and the area around them swell and turn red;
- itching in the area of the urethra occurs;
- chlamydia symptoms in men may be accompanied by a rise in body temperature (for a long time the thermometer may show 37-37.5 degrees);
- Pain in the abdomen, scrotum, testicles, and lower back may occur;
- urine may become cloudy and streaked with pus.
Against the background of general intoxication of the body, the symptoms of chlamydia in men are complemented by a feeling of weakness, decreased performance, sleep disturbance, and the appearance of irritability.
Male chlamydia is dangerous due to complications. If you do not see a doctor in time and do not start treatment, serious health problems may arise.
How chlamydia manifests itself in men
when complications occur is indicated below:
- against the background of an infectious disease, inflammation of the testicles may occur. Pain appears in the groin area and lower back. The scrotum swells, body temperature can rise to high levels;
- prostatitis – inflammation of the prostate gland. The condition is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, and rectum. There is a clear mucous discharge from the urethra, and difficulties with urination appear. Potency is impaired;
- vesiculitis - leads to inflammation of the seminal vesicles. Erection is disrupted, weakness, headache occurs, and body temperature rises. There may be discharge in the form of mucus with blood;
- Epididymitis is an inflammation of the epididymis. There is a high body temperature. The appendages become swollen and inflamed;
- Urethritis is characterized by itching and burning in the urethra. I am worried about the periodic urge to urinate, accompanied by discharge with pus.
Against the background of chlamydia trachomatis in men, the amount of sperm production decreases and their motility decreases. The situation leads to infertility.
Complications can also arise during medical therapy if it is chosen incorrectly. The body cannot cope with the active proliferation of bacteria when the immune system is reduced.
Tests and diagnostics for chlamydia
Diagnosis of the disease is a rather complicated procedure, since chlamydia is an intracellular parasite and the results of a smear from the urethra do not provide a full opportunity to establish a diagnosis. They only allow one to suspect the presence of a disease, since the required number of leukocytes in the blood may correspond to the norm or slightly exceed the permissible percentage. The ability to determine the presence of chlamydia in this case is no more than 15%.
To carry out a more accurate diagnosis, other methods are used and for them blood, urine, semen and scrapings from the surfaces of the tissue of the affected organ are taken for analysis.
The following methods will allow you to detect a pathogenic microorganism:
- PCR – polymerase chain reaction. Currently, this is the most accurate method for diagnosing the presence of chlamydia in the body.
- RIF – fluorescence reaction. The material for analysis is examined using a special fluorescent microscope. The method does not provide high accuracy - about 50%. The result will depend on the qualifications of the doctor. There are also the following disadvantages: the disease must be active at the moment, the maximum amount of material for research is required, there is the possibility of getting a false positive result if staphylococcus or another virus is mistaken for chlamydia.
- ELISA – analysis for the presence of immune enzymes. A scraping and blood is taken for it. The method identifies the necessary antibodies to the microorganism that the human body is capable of producing in response to an infection. It allows you to identify both the existence of the causative agent of chlamydia and determine the stage (acute or chronic) of the disease. The disadvantage of this method is that the diagnostic accuracy is 60%. Reasons: antibodies are also detected in healthy people; the presence of such antibodies is associated with other diseases.
- Culture for chlamydia, which determines their sensitivity to medications (antibiotics), is a labor-intensive, expensive method with which you can find out which antibiotic will be detrimental to chlamydia. Accuracy ranges from 70% to 90%.
Routes of transmission of chlamydia
Chlamydial infection is a leader among sexually transmitted diseases. Every year in Russia alone, 1.5 million cases of urogenital chlamydia are registered. Chlamydia in men is often diagnosed at the age of 20-40, although in recent years the percentage of patients aged 13-17 has increased sharply.
Pathogens can be transmitted from people with asymptomatic chlamydia and active disease. Sexual partners become infected through contact. This is the most common route of transmission of chlamydia, which does not depend on the method of contact.
Sometimes the infection is transmitted in everyday life, through clothing, hygiene items, bedding, and touch. The disease can be transmitted from mother to child: antenatally (during pregnancy) and intranatally (during childbirth).
Treatment options for chlamydia
The faster the symptoms are identified, the less likely it is that the disease will become chronic and will not cause serious consequences. Since chlamydia is an intracellular microorganism, only those drugs are selected that have the ability to penetrate inside the epithelial cell. The main group of antibiotics for the treatment of chlamydia in men: the group of macrolides (Azithromycin, Erythromycin), tetracyclines (Doxycycline), penicillins (Ampicillin).
In addition to antibiotics, the following medications are used to treat chlamydia:
- Enzymatic - the medicine contains biochemical active substances of both plant and animal origin. Thanks to them, the permeability of cell membranes in the male body increases. As a result, the drugs easily penetrate the cell and destroy harmful chlamydia, and also relieve signs of intoxication, which is very important during the acute period of the disease. Drugs such as Flogenzym and Wobenzym are considered effective.
- Immune – stimulating the body’s defenses is necessary when treating chlamydia. Strong immunity helps antibacterial agents fight infection. The patient is prescribed the following drugs: Amiksin, Cycloferon.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes - the patient is prescribed ascorbic and glutamic acid to stimulate the immune system.
- Hepatoprotectors - increased and long-term use of medications during treatment disrupts the activity of the liver. Hepatoprotectors reduce the negative effects of both drugs and infection on the body. The following effective drugs are recommended: Linex and Lactobacterin.
- Antiseptics - intended for treating inflamed areas. These solutions include: Miramistin and Chlorhexidine.
The main profiling drug in the treatment of chlamydia in men today is Azithromycin - taken once a day in the dose prescribed by the doctor.
In addition to antibiotics, antifungal medications and immunomodulators are sometimes included in the treatment regimen. If there is excessive discharge from the urethra, antimicrobial medications are prescribed. Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial ointments and suppositories are also used.
During the treatment period it is not recommended to drink alcoholic beverages. It is also necessary to maintain a diet, eliminating salty, fatty, sweet and spicy foods. During treatment, it is advisable not to have sexual contact with your partner. Examination and treatment are necessary for all sexual partners of the patient.
Before starting treatment for chlamydia, the treating specialist determines the duration of infection, signs of the disease, intolerance to any medication, the possibility of an allergic reaction, etc. Based on the analysis results obtained, he clarifies the following:
- The state of the male immune system,
- Condition of the pancreas, liver and gallbladder,
- Intestinal condition for microbiosis,
- Urogenital tract.
Treatment
Unlike other diseases caused by bacteria entering the body, treatment for chlamydia in men is quite long-term. This is due to the fact that only those antibiotics for chlamydia that are capable of destroying the infection located inside the cell are suitable for it.
The main groups of antibacterial drugs used for treatment include:
- Macrolides (“Midecamecin”, “Azithromycin”, etc.).
- Tetracyclines (“Doxycycline”, etc.).
- Fluoroquinolones (“Ofloxacin”, etc.).
Using some injections or tablets for chlamydia does not always bring the desired result. This is due to the fact that chlamydia is very resistant to the action of many medications. Therefore, the treatment regimen for chlamydia in men is often based on several antibiotics belonging to different groups. Additionally, antifungal medications (Fluconazole, etc.) may be prescribed.
To increase the body's defenses and help it cope with infection, the patient is advised to take immunomodulatory drugs, multivitamin complexes and follow a special diet.
If chlamydia in a man is manifested by discharge, then it is necessary to prescribe local antimicrobial agents. To protect the liver from the negative effects of a large number of medications, hepatoprotectors are used.
The course of treatment for chlamydia in men is prescribed individually for each patient and depends on:
- Features of the body of a particular patient.
- Which organs were affected by the infection.
- Stages and severity of the disease.
If the treatment was chosen incorrectly, then chlamydia goes into a chronic phase, the treatment of which is significantly difficult due to the fact that the bacteria have become resistant to the drugs used.
As a rule, the average duration of treatment is 25 days. However, there are situations when for a complete cure a man needs to undergo several courses of antibacterial therapy. Treatment at home using folk remedies is unacceptable. They can only be taken in addition to the main therapeutic course.
The following procedures help cure chlamydia:
- Enemas.
- Sitz baths.
- Prostate massage.
- Patient reviews have proven the effectiveness of physiotherapeutic procedures (iontophoresis, electrophoresis, ultrasound, etc.).
For the entire period of treatment, the man must exclude sexual contact. In addition, you should avoid drinking alcohol and dairy products.
Due to the fact that chlamydia is transmitted sexually, the sexual partner of a sick man is also subject to treatment.
Chronic form of chlamydia in men
Chronic chlamydia can be successfully cured with antibiotics, but the treatment has certain features that both the doctor and the patient need to pay attention to.
Basic principles for the treatment of chronic disease:
- Search for an atypical focus of the disease,
- Detection of infections,
- Selection of effective drugs,
- Taking antibiotics as recommended.
Due to the fact that therapy is very complex, situations sometimes arise in which treatment does not lead to complete recovery, but only to temporary remission. Often the fault lies in insufficiently detailed diagnosis or a man’s frivolous attitude towards treatment, but there are also doctors’ mistakes.
Treatment of the chronic stage requires three to four courses and lasts several months. In the advanced stage of chlamydia, a man who did not receive timely treatment or received ineffective treatment is at risk for the following diseases: prostatitis, epididymitis, urethritis, Reiter's disease.
Signs of prostatitis - with inflammatory processes in the prostate gland, pain appears in the rectum, lower back and groin. Sexual potency is impaired, difficulty urinating, and mucous and watery discharge is observed in the urethral area.
Signs of urethritis are itching, the urge to urinate frequently, mucous and purulent discharge; with chronic urethritis, urethral stricture develops.
Signs of epididymitis are inflammation of the epididymis, causing fever, enlargement of the epididymis, which can lead to male infertility and failure of the spermatogenesis process.
Reiter's disease is arthritis due to chlamydia and conjunctivitis.
Specifics of diagnostic measures
Only a doctor can prescribe medications for chlamydia, but before this the patient needs to undergo an appropriate examination. This will help confirm the diagnosis. The process of detecting an intracellular parasite is extremely complex, so an analysis is taken - a smear from the urethra. The total number of leukocytes remains within the normal range or slightly exceeds the values. At home, you can use a special test for chlamydia, but it cannot be trusted 100%.
To obtain an accurate result, a number of laboratory tests are carried out: urine analysis, blood analysis, spermogram, as well as scraping from the surface of the infected organ. The most proven method is PCR.
Important! To increase the accuracy of the results, tests are taken during the period of exacerbation. You will need a lot of research material. If a person has a staph infection, the answer may be a false positive.
It is mandatory to culture the bacteria on a nutrient medium; this makes it possible to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to medications such as antibiotics. The proposed method is very expensive and time-consuming. However, it is he who will help determine which drug can provide effective treatment for the disease.
Risk factors
The following factors increase the rate of infection:
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse and frequent changes of partners,
- Failure to comply with basic rules of personal and intimate hygiene,
- Homosexual activities,
- Using other people's intimate hygiene products,
- Excessive drinking of alcohol, which often results in casual sex,
- Reduced immunity.
Factors influencing the exacerbation of the chronic process of the disease and subsequent complications of chlamydia:
- Hypothermia,
- Overwork – physical and emotional,
- Bad habits,
- Past bacterial and viral infections,
- Frequent sexual intercourse.
Prevention of chlamydia
Regarding infectious diseases, it is safe to say that they are easier to prevent than to cure. Prevention of chlamydia is quite simple.
Measures to prevent urogenital chlamydia in men:
- healthy sexual behavior;
- use of contraception;
- sexual intercourse with one partner;
- regular preventive examinations (checking opportunistic and pathogenic flora);
- timely response to symptoms of diseases of the genitourinary system.
Since the treatment of chlamydia involves taking antibiotics, after it it is necessary to restore the microflora and strengthen the body's protective functions.
All kinds of complications with chlamydia
First of all, chlamydia affects the reproductive system and urinary tract. The signs of the disease are similar to the symptoms of inflammation that occur in the genitourinary system and on this basis the initial stage of chlamydia is called primary chlamydial urethritis. If appropriate treatment is not started in time, the infection will begin to spread further and cause inflammatory processes in the testes, epididymis and prostate gland.
Constant stressful situations, poor nutrition, lack of rest, and immune system disorders provoke chlamydia damage to the cardiovascular system, respiratory system (chlamydial pneumonia), musculoskeletal system (chlamydial arthritis), and visual organs. This type of infection is dangerous because it has many complications: potency is impaired, joints, blood vessels, and heart are affected and the risk of male infertility increases.
If there is the slightest suspicion of disorders in the genitourinary organs, a man should undergo an examination by doctors in order to completely exclude the diagnosis or confirm the presence of chlamydia. Urologists, venereologists and infectious disease specialists treat the disease.
Features of chlamydia
Chlamydia is a group of diseases that are caused by chlamydia. These microorganisms are mistakenly called bacteria or viruses, but in reality they are parasitic agents that reproduce intracellularly, which greatly complicates the diagnosis and treatment of chlamydia in representatives of the stronger sex. The danger of this disease lies in the fact that it often does not manifest itself at all.
Urogenital chlamydia is often confused by its symptoms with cystitis, urethritis and prostatitis. It is possible to accurately determine the nature of the disease only with the help of laboratory tests: enzyme immunoassay, serological and molecular biological. Infections caused by chlamydia pose a great danger to health, mainly because they are fraught with serious complications.
Possible consequences of chlamydia:
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- infertility;
- joint diseases;
- violation of potency.
If any symptoms occur, you should contact a specialist: a venereologist, urologist or infectious disease specialist. Even the most minor signs of genitourinary system disease need to be checked and advanced chlamydia excluded.
Why are joints affected?
Chlamydia does not go away without treatment.
The infection may lurk, but it does not leave the body.
Therefore, the first and main cause of chronicity is the lack of treatment.
1. They do not go to the doctor because their chlamydia does not show symptoms.
That is, they do not know that their reproductive health is threatened.
2. They don’t go to the doctor, ignoring the symptoms.
Many patients try not to pay attention to discharge, itching in the genitals and other obvious signs of infection.
They are afraid to go to doctors.
After all, being examined and treated, in their opinion, is expensive, scary and painful.
It’s better to endure it, maybe it will go away on its own.
Of course, it doesn’t go away on its own.
Chlamydia becomes chronic.
Often, the symptoms subside, and the patient believes that everything is fine.
Exactly until the moment when complications begin.
3. Self-medicate.
A person is trying to be treated without knowing the diagnosis, the characteristics of the disease, or the correct treatment regimens.
Naturally, he achieves no results.
Self-medication does more harm than good.
Especially if not antibiotics are used, but folk remedies or dubious dietary supplements.
4. Sees a bad doctor.
Many people go to a free clinic.
There are good doctors there, but there are also very mediocre specialists.
Therefore, patients often remain underexamined and undertreated.
5. They don’t take control tests.
Even the best regimens from the most reputable doctor sometimes do not work.
Simply because chlamydia may be insensitive to the antibiotic.
All patients must be tested again after treatment.
This is necessary to understand whether a person has been cured or not.
If not, a repeat course of therapy is required.
Otherwise, chlamydia remains in the body for many years.
Before getting acquainted with treatment for women and men, it is necessary to understand why the infectious process becomes chronic.
According to doctors, there are several main factors:
- Ignoring symptoms of illness
Chlamydia is a rather insidious disease, characterized by a rather blurred course.
The disease is characterized by mild complaints, which are significantly expressed only in women, and even then not always. A person ignores a mild illness, which gives the infectious process a chance to become chronic.
- Self-medication
Patients often refuse to seek help from medical personnel. The result is quite predictable. Attempts to treat yourself using traditional methods and symptomatic therapy give the microorganism the opportunity to penetrate deep into the body, which leads to chronicity.
- Wrong therapy
In some cases, the doctor makes a mistake in choosing antibacterial drugs that can be used in the fight against chlamydia.
This happens if the patient has not been tested for sensitivity to antibiotics. Naturally, in this case, medications have to be prescribed blindly. The certainty that the pathogen will be sensitive to them is questionable.
Joint damage due to chronic chlamydia is not uncommon. Many patients do not understand the connection between STDs and joints, but it exists.
In fact, everything is simpler than it seems.
The fact is that chronic chlamydia causes Reiter's disease. This does not happen to all patients, but only to those who are genetically predisposed to it. In this case, arthritis of the joints is noted, and the eyes are also involved in the pathological process, which is manifested by conjunctivitis. Naturally, damage to the genital organs also persists.
As doctors note, autoimmune reactions are responsible for the development of Reiter's disease, and not just an infection that has entered the body. The body, trying to defeat the pathogen, begins to destroy not only it, but also itself.
Reiter's disease is considered a rather severe complication of STDs, which is not so easy to cope with. Treating it at home is strictly prohibited.
Diagnostics
How to determine the presence of a disease? This question also needs to be answered, since we are talking about chronic chlamydia in men.
Diagnosis is carried out by urologists. However, it is also necessary to make an appointment with a venereologist in order to exclude the possibility of infection with other sexually transmitted infections based on the results of the examination.
What about diagnostic measures? A general cytological smear does not give a complete picture of the presence of chlamydia. Therefore, PCR diagnostics are now being carried out. This method makes it possible to detect the pathogen in the test material even in very small quantities. Its accuracy reaches 95%.
Another informative method is enzyme immunoassay. It helps to detect the presence of antibodies to the pathogen. Sometimes they resort to direct immunofluorescence, which involves microscopy of smears stained with a special substance.
In addition to the above, bacteriological culture is often used to diagnose chronic chlamydia in men, the photo of which shows an unpleasant picture. The doctor may also prescribe antibiotic sensitivity testing.
As a rule, the material for carrying out all the above-mentioned procedures is blood, semen, urine, cell scrapings, as well as discharge from the genitals.
Causes of chlamydia
Chlamydia is the main cause of chlamydia. The following factors play an important role in the successful infection and development of infection within a sick person:
- unprotected sex;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- neglect of personal hygiene;
- close contacts with infected birds and animals;
- decreased immunity as a result of a lack of vitamins, taking antibiotics, a chaotic lifestyle, systematic hypothermia, and constant stress.
Features of therapy
Now we can talk about the treatment of chronic chlamydia in men. It is immediately necessary to make a reservation that therapy for this disease, no matter what form it occurs, involves taking antibiotics. It is strictly forbidden to select them yourself.
The doctor prescribes drugs of the tetracycline group - macrolides and fluoroquinolones. But, as a rule, the course of rational treatment of chronic chlamydia in men is not limited to medication alone. Often the patient has to take two drugs from different groups. The doctor may prescribe bacteriophages, antifungals, enzymes, enzymes.
If necessary, the patient is prescribed physiotherapy. The most popular are magnetic therapy, ultrasound and electrophoresis.
Tetracycline drugs
It is necessary to talk in detail about how to treat chronic chlamydia in men. Tetracycline drugs have the ability to disrupt the process of protein synthesis of parasitic cells, penetrating into the intracellular space. They are produced in the form of ointments and tablets. For chlamydia they are used in both versions.
The most famous medicine is the drug “Tetracycline” in tablets. It is prescribed if the patient does not have liver or kidney pathologies. The course of treatment is 1-2 weeks. It must be taken four times a day, 0.4 g. The ointment is usually prescribed for chlamydial conjunctivitis.
Metacycline is also effective. It has diverse antimicrobial activity. Capsules must be taken for one week. The daily dose is 600 mg.
Minocycline is also prescribed. This is a medicine of semi-synthetic origin, which is available in the form of a suspension, capsules and tablets. It should be taken 40 minutes every day, 200 mg before meals, also for one week.
But the most effective drug from this group is Doxycycline. It is available in the form of a powder (a solution is prepared from it, which is administered parenterally) and capsules. The active substance destroys most strains of the pathogen. In the pharmacy the drug can be found under the names “Dorix”, “Vibramycin”, “Unidox Solutab”. Take one of these remedies twice a day, 0.1 g, for 1-2 weeks.
When talking about the drugs taken in the treatment of chronic chlamydia in men, it should be noted that side effects may occur. Most often these are headaches, nausea, hypertension, vomiting, gastrointestinal problems, and increased skin sensitivity to ultraviolet rays.
Disease prevention
To avoid a grueling course of treatment for chlamydia, it is easier to avoid infection than to visit doctors later.
Therefore, it will be useful to learn simple precautions:
- If you have a non-regular sexual partner, it is recommended to use personal protective equipment - condoms, or to refuse promiscuity in general.
- Both partners should be systematically tested for chlamydia.
- It is not recommended to use other people's underwear.
- Before wearing, new underwear must be washed on a delicate cycle at 40°C.
- If there are suspicions about the presence of a disease in the body, you must go to a diagnostic center for tests and, for the duration of the diagnosis, refrain from alcohol, sexual intercourse and consumption of dairy products.
Chlamydia is an insidious viral disease that causes unpleasant complications if treatment is delayed. Therefore, if the first signs of the disease are observed, it is necessary to immediately seek medical help from a venereologist, without self-medicating or letting the problem take its course.
We bring to your attention a video in which a specialist explains the nuances of treating chlamydia at home:
What consequences occur after infection with chlamydia?
Having considered the signs (chlamydia in men is a common problem), it is necessary to understand what complications this infection can lead to. It can affect many organs and systems of the body. This is an insidious disease - chlamydia. For men, the consequences can be very serious.
The most basic ones are impotence and infertility. As the infection spreads, it affects the seminal vesicles in chlamydial vesiculitis, as well as the bulbourethral glands, which causes chlamydial cooperitis. The result is complete irreversible infertility in men.
Anal sexual intercourse with a carrier of this virus leads to the fact that the infection begins to spread to nearby organs. Proctitis occurs, causing damage to the rectum. If sexual oral contact is practiced, chronic pharyngitis develops.
Cardiovascular diseases and joint inflammation are complications that arise from chlamydia. If the infection gets into the eyes, chlamydial conjunctivitis develops, which can lead to complete blindness. The disease also contributes to the occurrence of inflammation in the inner ear and dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus.
How does chlamydia manifest in men? A pathology such as Reiter's disease, which includes the classic triad: conjunctivitis, urethritis, arthritis, may indicate the presence of this infection. Each pathology individually brings great trouble to a person, and their combination reduces the quality of life several times. This disease causes damage to the upper layers of the epidermis and can also affect the nervous system. Various encephalopathies and encephalitis occur, accompanied by seizures and nervous convulsions.
How and what to treat at home
Everyone's favorite folk recipes not only will not help in the treatment of chlamydia, but can also significantly aggravate the problem. There are only preventive measures to prevent infection:
- avoid casual sex;
- sex should be protected, especially if there is no confidence in the health of the partner;
- sexual partners must undergo preventive examinations;
- If the slightest symptoms of the disease appear, consult a doctor immediately.
If intimacy occurs without using a condom, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- wash the external genitalia with soap;
- inject an antiseptic solution into the urethra;
After anal sex, be sure to rinse the intestines with water with the addition of antiseptics.
Chlamydia is a fairly common sexually transmitted disease. It is extremely difficult to treat, so it is better to adhere to preventive measures that will help reduce the chances of infection.
How to cure chronic and acute chlamydia
Even if the body is damaged, symptoms may be completely absent. Only after undergoing tests and consulting with the attending physician will it be possible to prescribe the correct treatment, and it would be best to combine several medications at once:
- broad-spectrum antibiotics prescribed by a doctor;
- drugs that can enhance immunity;
- complexes of vitamins and minerals that are beneficial for men;
- refusal of alcohol;
- often limiting the number of cigarettes smoked.
If a chronic form of chlamydia is diagnosed in men, then the treatment regimen will necessarily include the following drugs:
- “Doxycycline” (two hundred milligrams twice a day);
- “Pulse therapy” (one tablet for ten days, after a week’s break);
- “Azithromycin” (a tablet in a five hundred milligram dosage approximately twice a day, the course of administration does not exceed five or seven days);
- eubiotics that normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- drugs that can get rid of thrush (“Nystatin”);
- drugs that can enhance immunity.
Features of the pathogen
Before analyzing the signs, it is necessary to understand the characteristics of the disease and the pathogen itself. The disease is caused by pathogenic microorganisms called chlamydia.
Chlamydia can enter the human body in several different ways. The most common route of infection used in medical practice is the sexually transmitted route. This means that chlamydia is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person during sexual contact.
Moreover, doctors note that it is not only the standard form of sexual contact that poses a threat. But there are also other options (for example, oral and anal sex). In addition to the sexual route, you can become infected through contact and household contact. This happens when basic personal hygiene recommendations are ignored.
It is also worth keeping in mind that chlamydia can affect children's bodies. At the moment when a child passes through the genital tract of a sick woman at the moment of birth.
Mostly pathogenic microorganisms affect the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system.
However, depending on the characteristics of sexual contact, they can inhabit the oral cavity and anal area. In young children born from infected mothers, involvement of the eyes and respiratory tract may be detected. The eyes are affected due to the fact that they are the most accessible mucous membranes for the pathogenic microorganism at the time of birth.
Characteristics of the pathogen
The causative agents of chlamydia (chlamydia) are gram-negative bacteria that have a round shape. Chlamydia affects the urinary and reproductive systems and has the ability to penetrate the intestines, causing disturbances in the intestinal biocenosis. Due to the lack of the ability to independently synthesize ATP, bacteria can only exist inside the cells of a living organism, and most often affect the columnar epithelium of the urethra and rectum in men and the cervical canal in women. Chlamydia reproduce by division and have an antigen specific to their group, which makes it possible to detect bacteria using the immunofluorescent method.
Chlamydia and reproductive function
There are many causes of male infertility. However, the most common are genitourinary infections transmitted through unprotected intercourse. Unfortunately, the active progression of parasitic microorganisms leads to irreversible changes in the composition of sperm.
Scientifically speaking, there is hyperproduction of the active form of oxygen radical by sperm polymorphonuclear leukocytes. This leads to damage to the sperm membrane. And this phenomenon, in turn, has a depressing effect on the ability to fertilize.
It is also important to take into account that such a pathology often leads to abnormal development of the fetus.
Is chronic chlamydia curable?
Even people with an advanced form of the disease have nothing to fear. Chronic chlamydia can be treated, but the process of suppressing the parasites takes longer. The problem is that antibiotics have a strong effect on secondary manifestations of the disorder (conjunctivitis, bronchitis, changes in the joints).
In the fight against chlamydia, a long course of antibiotics is selected. Medicines are prescribed in high doses, because otherwise the therapy will be useless.
Another problem is that medications are taken only during an exacerbation; the rest of the time, chlamydia is not susceptible to antibiotics. To cure the disease, 3-4 courses of medications will be required, so therapy takes several months.
Chlamydia: general information
The causative agent of the infection is chlamydia - a stationary spherical and coccoid microorganism that cannot be classified as either a virus or bacteria. Once in the male body, chlamydia, just like viruses, infects the epithelial cells of various organs from the inside:
- in the seminal canals;
- in the urinary tract;
- in the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- in the oral cavity.
But the life activity and structure of chlamydia is much more complex than that of viruses. In an unfavorable situation, they can, as it were, hibernate, waiting for their time and become activated when a person’s immunity decreases.
The mechanism of chlamydia in men
When chlamydia enters the male body, like the virus, it passes into the epithelial cells of organs and adheres to their membranes. Since they are almost deprived of the ability to move, the implementation process is very slow.
Having penetrated inside, chlamydia becomes resistant to unfavorable factors and begins a harmful effect, exchanging its genetic information with the affected cell. After this introduction, it is almost impossible to influence chlamydia with the help of medications.
Having penetrated the tissue, microorganisms force all “captured” cells to create new chlamydia. Their number grows steadily and over time becomes very large - the infected cell is destroyed . Then the newly formed chlamydia come out of it and begin to search for another home, infecting other cells. The development cycle of the microorganism repeats itself again.
That is, chlamydia is found in two forms in the body:
- Intracellular;
- Extracellular.
Spreading with the flow of blood and lymph throughout the body, chlamydia infects various organs, and through contaminated hands it can reach the conjunctiva of the eyes and the mucous membrane of the oral cavity.
Types of infection
There are several types of chlamydia that cause different diseases:
- Chlamydia pneumonia;
- Chlamydia trachomatis;
- Chlamydia psittaci;
- Chlamydia pecorum.
The first two types of chlamydia are the most dangerous for people - these are the microorganisms that can cause serious complications . Most often, the infection in men infects the reproductive and urinary systems, but sometimes it leads to a huge range of serious diseases that affect different organs:
- tissue of blood vessels and heart;
- external and internal genitalia;
- hearing organs;
- teeth, joints;
- organs of vision;
- lymphatic system;
- mucous membrane of the lower and upper respiratory tract.
Among the diseases caused by microorganisms are genitourinary tract infections , trachoma, lymphogranuloma venereum, chlamydial conjunctivitis. Among homosexual men, infection of the rectum can often be found.
Methods of infection with chlamydia
As a rule, chlamydia infection occurs through unprotected sexual intercourse . There is a minimal possibility of infection in everyday life, for example, through:
- toilet seat;
- towel, dishes;
- dirty hands;
- visiting the sauna or swimming in the pool.
Symptoms of chlamydia
The presence and severity of symptoms of chlamydia in men will depend on the state of the body's immune system and the ability of the infection to cause inflammation. In approximately 50% of cases, chlamydia is asymptomatic . It is this feature that is the most dangerous for a man, since the absence of any sensations explains the late diagnosis and treatment. The risk of complications in these cases increases significantly.
The first symptoms of chlamydia in men are not clearly expressed:
- mild pain during urination;
- the appearance of discharge from the urinary tract;
- sometimes the temperature increases to 38 degrees;
- the appearance of mild pain in the lower back, urethra, testicles and scrotum;
- possible change in the color of urine, the appearance of blood and pus;
- weakness as a result of intoxication of the body.
Possible complications
First of all, chlamydia in men infects the reproductive system and urinary tract. As a rule, the symptoms of infection are similar to the symptoms of the inflammatory process of the genitourinary system - urethritis, therefore the initial degree of chlamydia is called primary chlamydial urethritis . If timely treatment is not carried out, the infection continues, causing inflammation of the testes, epididymis, and prostate gland.
Subsequently, the disease becomes sluggish, chronic and can last for years, creating significant symptoms and complications. The most common complications of chlamydia are as follows:
- Orchiepididymitis or inflammatory process in the epididymis. It is characterized by narrowing of the vas deferens and death of cells that are responsible for the formation of sperm. As a result, the negative impact of chlamydia leads to infertility, since the quality of sperm deteriorates greatly.
- Chronic pyelonephritis is an inflammatory process in the kidneys.
- Vesiculitis is an infection of the seminal vesicles, which is characterized by impaired potency and may be accompanied by an increase in temperature, headache, and weakness. Bloody mucus may be discharged from the urethra.
- Urethritis (infection of the urethra - urinary tract). Accompanied by the appearance of purulent discharge and disruption of the urination process.
- Chronic prostatitis. It affects the prostate, leading to a decrease in its ducts and a deterioration in the quality of sperm, and subsequently to infertility. It is characterized by the manifestation of unpleasant sensations in the area of the sacrum, rectum and perineum, the process of urination is painful and frequent. Sexual function also suffers - orgasm is lost, premature ejaculation appears, and erection weakens.
- Reiter's disease. This disease can cause severe complications, including disability. The disease is characterized by the simultaneous development of three diseases - arthritis, urethritis and conjunctivitis, which affects the joints, urogenital organs and eyes. Also sometimes balanoposthitis (inflammatory process of the head of the penis) and various types of skin lesions are added to them.
- A narrowing of the urethra, which is caused by scarring of the mucous membrane. The only treatment option in this case is surgery.
Currently, the role of chlamydia in the occurrence of prostatitis has not been fully proven, but it is believed that chlamydia is one of the causes of this disease . It should be taken into account that repeated lesions significantly increase the risk of complications.
Popular drugs - rating of antibiotics
- Hilak - Forte - 30-40 ml 2-3 times a day for 14 days.
- Linex - 1-2 capsules 3 times a day, 10-14 days.
- Normaze - 5-10 mg 3-5 r. in a day.
- Dufalac - 5-10 mg 3-5 r. in a day.
Separately, enzymes should be highlighted - Wobenzym - 3 tablets. 3 times a day, 14 days.
The treatment regimen for urogenital chlamydia is very extensive and there are a lot of drugs for treatment. You can endlessly list the list of antibacterial drugs, but among them there are the most or least popular tablets for chlamydia. Currently, macrolides are considered one of the most effective antibacterial drugs for the treatment of chlamydia; they are prescribed in the very first days of treatment.
- Josamycin and Macropen are new generation macrolide agents. A huge plus is that they have the fewest side effects. Prescribed 500 mg 3 times a day, 7-14 days (mostly 7 days).
- Azithromycin takes second place. Prescribed 2 tablets. 500 mg on day 1, then 500 mg 1 time per day on days 2, 5, 7 of treatment or 1 g 1 time per day on days 1 and 7 of treatment.
- Doxycycline, although considered one of the most polar drugs, has a large number of side effects. Prescribed 200 mg for the first dose, then 100 mg 2-3 times a day, 7-14 days (mostly 7 days).
- Klacid is the most frequently prescribed drug by doctors, but the least popular. Prescribed 250 mg 2-3 times a day, 7-14 days.
- Ceftriaxone is the least popular broad-spectrum antibiotic. Prescribed 1 injection per day, 7-10 days
- Clarithromycin is a less popular drug. Prescribed 500 mg 2 times a day, 7-14 days (mostly 7 days).
- Erythromycin is considered a highly effective treatment for chlamydia. Prescribed 500 mg 4 times a day for 10 days.
- Rulid is a less popular drug. Prescribed 150 mg 2 times a day for 2 weeks.
Description
Urogenital chlamydia is an STD that develops when the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis enters the body, which affects the mucous membrane of the urethra and appendages of the human genital organs . An incorrect diagnosis and treatment regimen lead to the pathology becoming chronic. In its chronic form, the disease is sluggish and asymptomatic, so it is difficult to detect. The disease can develop in the body for many years, causing the development of various complications. This is what makes many people go to a medical facility. Patients complain of itching in the urethra, swelling and redness of the genitals. Female representatives have no discharge.
Chlamydia first affects the human genitourinary system, in particular the genitourinary canal, so very often the patient develops urethritis, but the disease can develop in different ways. Quite often the eyes, nasopharynx, and lungs are affected.
Diagnosis of chlamydia
Chlamydial infection is diagnosed according to the same principles as other infections. To test for chlamydia, discharge from the cervical canal of women and the urethral canal of men is used. Urine sediment can be used for testing Chlamydia is often found with pathogens of other diseases that are sexually transmitted - gonococci, mycoplasmas, trichomonas and ureplasmas due to the same route of transmission.
Molecular biological methods
Diagnosis of chlamydial DNA (PCR) is a highly sensitive technique. Its specificity reaches 80 – 100%. When conducting this study, it is possible that the study is greatly simplified.
Culture diagnostic method
and allows the detection of viable bacteria. However, its sensitivity is low and amounts to 40 – 60%. In addition, the technique is quite labor-intensive and time-consuming. But the delivery of material to bacteriological laboratories and its storage have certain limitations.
Direct immunofluorescence method (DIF)
The results of the study depend on the quality of the material obtained and the qualifications of the laboratory personnel. Quick results are a clear advantage of this method.
Bacterioscopic method
To carry out this method, it is necessary to have a scraping of the affected mucosa, since chlamydia multiplies intracellularly, where they are located in the form of reticular bodies.
Serological methods
Serological methods are not recommended for diagnosing chlamydia in the Russian Federation.
If you are young and sexually active, get tested for chlamydia infection once a year or whenever you change sexual partner.
Rice. 11. In scrapings from the conjunctival epithelium, intracellular inclusions of pathogen bodies are visible.
What is persistence of chlamydia
Chronic chlamydial infection is not only a form of this disease, but also its stage.
There are four of them:
- acute – when a person is sick for less than 2 months;
- chronic – if the duration of the disease exceeded 2 months;
- reactivation – the occurrence of chlamydia against the background of a long absence of any signs of infection;
- reinfection – re-infection after laboratory-confirmed cure.
The chronic form can last for years.
Often it does not cause a person significant discomfort.
But it is still dangerous for his health.
Some people have no symptoms of chronic chlamydia for years.
This is possible if chlamydia persists.
The condition develops if:
- treatment destroyed most of the chlamydia, but some bacteria remain in the urogenital tract;
- human immunity “thinned out” the population of pathogens, and the rest “hid” in the secluded corners of the genitourinary system.
A feature of the persistence of chlamydia is that signs of inflammation are not detected even during laboratory testing.
There is no redness of the mucous membrane of the urogenital tract, nor increased levels of leukocytes.
Clinically the person is completely healthy.
Chlamydia exists only in the form of isolated microcolonies.
They can only be detected by highly sensitive methods.
These include PCR and culture testing.
The absence of an inflammatory response is due to the fact that chlamydia “resets” some antigens, which are a “target” for the immune system.
The amount of membrane antigen on the surface of the cell wall decreases.
The amount of lipopolysaccharides also decreases.
The heat shock protein of chlamydia disappears.
When chlamydia persists, it often becomes resistant to antibiotics.
The mechanisms of its formation are different.
Resistance is usually associated with:
- the disappearance of some proteins on the surface of the cell wall that facilitate the penetration of the antibiotic into the cell;
- preservation of chlamydia inside neutrophils, leukocytes and macrophages;
- the presence of bacteria in the membrane zone of epithelial cells.
Just because bacteria are lurking does not mean they are safe.
The risk of complications remains high.
The pathology can recur at any time.
It is transmitted to another person through sexual contact, although with a much lower likelihood than acute chlamydial infection.
Symptoms
The symptoms of the pathological process should be well known to any person. After all, there is always a possibility of encountering this disease. Therefore, it is necessary to imagine the complaints that will appear during the disease, and also understand when to see a doctor.
It is important to remember that symptoms can be quite subtle. This means that the patient will not see a doctor for a long time.
Despite the presence of any abnormalities in your health.
In men
In representatives of the stronger sex, the chronic form of chlamydial infection, like its acute version, is often completely asymptomatic.
A man may not even suspect that he is a carrier of infection, and that a pathogen lives in his body, which slowly but inevitably destroys his body. This, as doctors note, is the main danger of chlamydia. The disease will most likely progress with exacerbations and periods of remission.
In exacerbation, a sick man will complain of:
- the appearance of a low temperature, which rarely exceeds 37.5ºC
- the appearance of suspicious, glass-like discharge from the channel through which urine and sperm are normally excreted
- attacks of weakness, general malaise
- the appearance of impurities in the urine, which makes it cloudy and gives it a non-standard consistency
- attacks of itching, irritation, burning in the genital area, which are quite difficult to ignore
- the appearance of redness in the area of the urination channel, possible swelling of the tissues, etc.
Read also Norms for the positivity rate for chlamydia
However, in most cases, any clear symptoms are not typical for chronic chlamydia in men.
A representative of the stronger sex can lead a standard sex life with his wife or sexual partner. Without even imagining what is the source of the infectious process. Because of this feature of the disease, it is not uncommon for a woman to seek help in a couple.
Among women
Chronic chlamydia in women, unlike men, usually occurs with more severe symptoms. Doctors believe that the severity of the symptoms is associated, first of all, with the structural features of the genitourinary system.
The short and wide female urethra allows the pathogen to quickly reach the key organs. This explains the vivid symptoms of the inflammatory process even during the period of chronicity.
A woman's symptoms will be as follows:
- pain in the area of the projection of the uterus, its appendages, bladder
- the appearance of problems with urination
- complaints of attacks of pain during sexual intercourse
- increased pathological vaginal discharge after sexual intercourse
- the appearance of itching, burning, pain in the mucous membranes of the genital organs
- bleeding from the genital tract
Often in the fair sex, the disease is accompanied by various menstrual irregularities.
It is pathological changes in the cycle that force the fair sex to seek help in the first place. However, by the time disruptions appear, the infection in most cases has already become chronic and causes damage to the body over a long period of time.
Effective treatment regimens and drugs
The chronic form of the disease is treated with antibacterial agents. The doctor selects tablets taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen. Both partners must take medications to avoid re-infection. Medicines are prescribed according to an individual regimen.
To suppress chlamydia, tetracyclines (doxycycline, Unidox Solutab, Vilprafen), fluoroquinolones (levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin) and macrolides (sumamed, azithromycin, clarithromycin) are used.
In order to cure a patient from a chronic form of the disease, the use of several drugs at once will be required.
In addition to antibiotics, plant enzymes are used to stimulate normal kidney and liver function and prevent intoxication. Vitamins and probiotics are also prescribed to normalize the intestinal microflora. During treatment of chronic chlamydia, sexual contact is prohibited.
For inflammation of the genital organs, local medications are prescribed. The doctor may prescribe ointment, vaginal suppositories, or rinsing with herbal solutions. It is dangerous to use folk remedies without a doctor’s recommendation. In chronic chlamydia, they can aggravate the course of the disease and develop immunity in the parasites. Incorrectly selected medications will form a protective shell around the bacteria, making antibiotics useless.
Prognosis and prevention
If the disease is detected in time and the doctor prescribes effective treatment, then the prognosis of the disease will be favorable, since the patient can be completely cured. If the pathology is advanced, this can take a long time. In addition, one should take into account the development of complications of the disease, which negatively affect the health and life of the patient; self-medication in this case is contraindicated. The attending physician must strictly monitor the patient's compliance with all recommendations and prescriptions.
Prevention of chlamydia is based on the use of contraception during sexual intercourse. A person must also have one sexual partner. If you have unprotected sexual intercourse with an unfamiliar partner, it is recommended to immediately get tested for chlamydia, even in the absence of symptoms and signs of the disease.
When planning a pregnancy, both partners must comply with preventive measures; they must pass all tests to detect hidden infections, as well as STDs. Such preventive measures help maintain health at the proper level.
Prevention
Urogenital chlamydia causes a huge blow to health, and therefore it is necessary to protect yourself from this disease. For prevention, the following measures must be taken:
- Avoid casual sex. The more sexual partners a man has, the greater his risk of contracting an infection.
- Use a condom. This contraceptive not only prevents pregnancy, but also protects against STIs. If a man is in a long-term monogamous relationship, this is not a reason to refuse condoms. Read articles on this topic: How to choose the right condom by size and quality and How to quickly and correctly put on a condom
- Do not have sexual contact with a carrier of the infection. During treatment, the patient is prohibited from any sexual contact. And if a man knows about his partner’s illness, it is better to refuse the act.
- Avoid stress. It is important to limit yourself from nervous breakdowns and unnecessary worries. Depression caused by problems at work or in your personal life takes a toll on the body. Therefore, the key to success is a positive attitude.
- Eat properly. It is important to include fresh fruits and vegetables, fish, meat, and dairy products in your diet. It is advisable to avoid empty carbohydrates, which are found in sweets, soda and flour. However, it is not necessary to completely eliminate the consumption of these products.
- Follow the regime. Good sleep and organized leisure will relieve stress and replenish the body's defenses. A fresh, rested body is always ready to fight harmful microorganisms.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle. Hardening, playing sports, daily walks - all this has a positive effect on your health. For example, pump up your abs, learn how to do pull-ups on the horizontal bar, and do exercises to increase your biceps. These activities will strengthen the immune system and increase resistance to pathogens. It is important to stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Get examined in a timely manner. Both partners need to be periodically examined by a venereologist. You should go to the hospital for help after the first, even mild, manifestations of an STI.
Complications of the chronic form
Among the main complications are:
- a long-term inflammatory process leads to the formation of adhesions, which limit the spread of pathology beyond the lesion and at the same time lead to structural and functional changes in the organs of the reproductive system. In men, adhesions block the testes; in women, obstruction of the fallopian tubes develops. Against the background of ongoing processes, infertility may develop;
- A long-term pathological process in advanced disease progresses and “spreads” not only to neighboring organs (bladder, urethra), but also affects distant systems of the body, for example, vision, lungs. Often one of the pathologies, called Reiter's disease, occurs, accompanied by simultaneous damage to the eyes, urinary organs and joints;
- deformation of the urethra in the form of narrowings and kinks. Her only treatment option is surgery;
- narrowing of the sperm ducts leads to impaired sperm formation and infertility in men;
- prostatitis, first acute and then chronic, is accompanied by a change in the quality of the secretion secreted by the prostate gland and the death of male germ cells, and, consequently, infertility;
- the chronic form of the disease is fraught with the spread of infection to the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, and heart.
Causes of pathology
Causes of pathology
The cause of the formation of urogenital chlamydia is Chlamydia trachomatis, which penetrates the human body through sexual, contact-household, intranatal and transplacental routes. Chronic chlamydia in women can occur due to non-compliance with hygiene rules in the sauna, swimming pool and other recreational areas. The bacterium spreads throughout the body through the bloodstream, settling in organs and tissues, so the disease has several lesions. It causes the development of adhesions in the affected organs as a result of the inflammatory process, weakening of the immune system. In the external environment, chlamydia easily perishes under the influence of boiling, ultraviolet radiation, and antiseptics. Chronic chlamydia in men most often develops as a result of unprotected sexual intercourse or oral sex, and affects about 10% of men under the age of thirty.