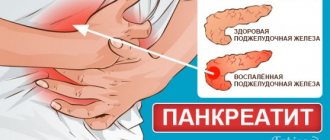
In 24 hours, the liver produces about 2 liters of bile. This unique and complex liquid is involved in the breakdown of fats, the absorption of many vitamins, and stimulates movement through the intestines. If the gallbladder (GB) works normally, many people do not even know where it is located. But if the functionality of this organ is impaired, problems arise.
Biliary or biliary colic is a sharp pain in the gallbladder. A gallbladder attack is usually provoked by cholelithiasis (cholelithiasis), cholecystitis, pancreatitis, cholangitis. This condition is accompanied by various symptoms and can occur due to the consumption of certain foods. To eliminate biliary colic, you need to identify the cause of its occurrence and carry out treatment.
Symptoms of an attack
Symptoms of gallstone disease may not appear for a long time. Large stones can remain in the ducts for several years and not move anywhere. Very often, gallstones are first detected during an ultrasound examination performed for another disease.
Exacerbation occurs due to the movement of stones in the gallbladder or its ducts. The most common symptom of gallstone disease is hepatic colic. This clinical form of the disease is detected in seventy-five percent of people suffering from cholelithiasis.
How an attack manifests itself:
- Hepatic colic is manifested by severe pain in the epigastric region and right hypochondrium,
- Pain can also radiate to the right arm, cervical spine and area of the right shoulder blade,
- Pain during an exacerbation of cholelithiasis can be cramping, stabbing or pressing,
- Increased pain is observed when lying on the left side,
- Typically, attacks begin at night and last about thirty minutes.
The frequency of attacks of gallstone disease varies from person to person. In some patients, symptoms of biliary colic occur every day, in others - once a week, in others - once a month. As a rule, after the first attack of cholelithiasis, a second one develops. During the period between exacerbations the person feels well.
In addition to pain in the right hypochondrium, exacerbation of cholelithiasis has the following symptoms:
- nausea,
- vomiting mixed with bile,
- diarrhea,
- yellowness of the skin,
- increased heart rate up to one hundred beats per minute,
- bloating,
- sleep disturbance,
- darkening of urine
- increased fatigue,
- lack of appetite.
At first, recognizing the symptoms of gallstone disease is quite difficult. Only an experienced doctor can make a correct diagnosis.
Non-infectious colic
It occurs spontaneously, without warning signals, and is caused by eating disorders, drinking alcohol, or sudden prolonged shock to the body. The pain symptom manifests itself extremely variable:
- The patient describes stabbing, cutting, tearing sensations, but dull or pressing pain may also be present. The intensity makes it difficult to find a comfortable position, so the patient constantly changes it, becomes agitated, and even screams. In rare cases, it comes to painful shock.
- Localization can be felt in the right hypochondrium (subchondral region), to the right of the xiphoid process or directly above it.
- Radiating pain depends on the location of the main symptomatic manifestation and its intensity. They can radiate to the scapula and subscapular region, to the shoulder, to the cervical, jaw, frontal, periorbital region - in the right half of the body. There may be irradiation to the left side; this is more dangerous, because in some patients it causes a parallel attack of angina.
- The duration varies from a few minutes to 48 hours.
Taking medications gradually leads to the subsidence of pain, and subsequently there are no traces of changes in the areas of the suspected pathology. The person feels quite healthy, only in some cases the consequences of an attack can be considered fatigue, weakness and weakness.
Causes of gallstone disease
Gallstone disease is called a disease of civilization. A sedentary lifestyle and irregular diet provoke its appearance at a young age. According to medical statistics, ten percent of people under forty-five years of age already have gallstone disease.
There are the following main causes of an attack:
heavy weight,
- consumption of fatty, spicy foods, as well as foods rich in cholesterol,
- frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages,
- disturbance of cholesterol metabolism in the body,
- biliary tract infection,
- acute pancreatitis,
- presence of cholecystitis and hepatitis,
- diabetes,
- taking hormonal drugs,
- severe stress.
An attack of cholelithiasis can be triggered by eating fatty foods, spices or smoked foods. Often biliary colic occurs while working with the body tilted. Even pregnancy can cause an attack of cholelithiasis. Due to mechanical compression of the bile ducts, bile stagnation occurs, which can lead to the formation of stones.
Nutrition rules
The key reason for exacerbation of an attack of gallstone disease is an unbalanced diet. After consuming a large amount of fried, fatty foods, or alcoholic beverages, an attack of biliary colic may occur. After the attack has stopped, you should not eat food for another 12 hours. After this, you are allowed to eat light vegetable broth, drink compote or herbal decoction.
After a day, the diet can be expanded by adding porridge with water, meat broth, boiled fish or boiled poultry, non-acidic fruits and vegetables. Mineral water and alkaline drinking are recommended. You should not eat fried and fatty foods, baked goods, pasta, sausages, smoked meats, pickles, pickled foods, sweets, chocolate, and alcoholic beverages. Meals should be fractional, the number of meals should be at least five per day, two to three hours should pass between meals.
If drug treatment does not bring the desired result, the doctor prescribes radical stone removal. But in most cases, with a correctly prescribed therapeutic algorithm, surgery can be avoided. In the future, you need to maintain proper nutrition, lead a healthy lifestyle, and introduce feasible physical activity into your life.
To avoid an attack of gastrointestinal tract, the patient must follow a diet. It is recommended to eat foods that contain minimal amounts of fat and cholesterol. Your daily diet should be supplemented with fiber-rich foods.
Improper diet provokes biliary colic
The patient should eat more fresh vegetables, fruits, wholemeal bread, brown rice, and bran. In addition, meat and fish (low-fat varieties), and fermented milk products with low fat content are not contraindicated. It is recommended to cook oatmeal, rice, semolina porridge, and soups in vegetable broth. You should also include cold-pressed vegetable oils in your menu. It is better to eat warm foods and drinks.
Some foods increase the likelihood of cholelithiasis and biliary colic:
- fatty, fried, spicy foods;
- whole milk and products made from it;
- alcohol, soda;
- coffee, tea, cocoa;
- red meat.
Compliance with nutritional rules will not help dissolve existing stones, however, by changing the diet, unpleasant symptoms are alleviated, and attacks of gastrointestinal tract occur less frequently.
It is important to know that with biliary colic you cannot sharply limit the number of calories. If the patient is overweight, he should reduce it gradually (no more than 1 kg in 7 days). If after changing your diet rules the pain does not disappear, then you need to visit a doctor.
An attack of cholelithiasis, the symptoms of which are known to every gastroenterologist, is familiar firsthand to many people. However, not everyone thinks about prevention. Changing your daily menu will greatly help in preventing attacks of gallstone disease.
First, you should avoid refractory fats. Due to insufficient bile supply, the activity of a special enzyme, lipase, decreases. This, in turn, leads to a deterioration in the breakdown and absorption of fats. People feel pain, cramping, and bloating. Only butter and vegetable oils are allowed.
Secondly, you should exclude rye bread, mushrooms, peas, beans, nuts, millet, chocolates, coffee, cocoa, and pastry from your menu. These products cause aggravation, because their digestion requires tension in the enzyme systems of the human body.
How to relieve an attack at home
To prevent the development of painful shock, you need to relieve an attack of gallstone disease as quickly as possible. First aid to the patient consists of performing the following actions:
- Place the patient on his right side with his knees bent,
- let the patient take one of the anti-spasm medications,
- if you have a chill, wrap the patient in a blanket,
- call an ambulance.
On the first day after an exacerbation, you should stop eating. Food stimulates the liver to produce a new portion of bile, which can worsen the condition. There is an opinion that to relieve spasm you need to apply a warm heating pad to the right hypochondrium. However, as medical practice shows, such an action can cause a serious complication of the disease in the form of peritonitis.
If the pain does not go away after taking antispasmodics, you need to urgently take the patient to the surgical department of the hospital. Based on diagnostic procedures, the doctor will decide on further treatment.
Antispasmodics will help relieve acute pain during an attack of gallstone disease:
No-Shpa . To relieve an attack of hepatic colic, No-shpa is administered intravenously at a dosage of two milliliters.
- Bellasthesin . The drug has an antispasmodic effect, reducing the tone of the muscles of the gallbladder and bile ducts. Adults take one tablet of the drug twice a day before meals, dissolving the tablets but not swallowing them, as they are vomited.
- Dicetel . According to the instructions, the drug in a dosage of fifty milligrams is taken with meals three times a day.
- A complex of Papaverine and Analgin is prescribed intravenously or intramuscularly. The effect of this combination is enhanced by the addition of Diphenhydramine.
- If colic is accompanied by pain in the area of the heart muscle, use Halidor or Curantil - 2-4 ml intramuscularly.
All of the above drugs effectively relieve pain caused by cholelithiasis. If the pain does not subside after taking antispasmodics, the solution to this situation is surgical removal of the gallbladder.
How to help yourself
If the attack takes you by surprise, you will need to relieve the attack of cholelithiasis yourself.
First aid is as follows: you need to lie down on a sofa, bed or chair - a place where you can stretch your legs and feel peace. If the patient is alone at home, it doesn’t hurt to call friends and relatives asking for help. Ask your friends to come, there may be a case of vomiting or an intensification of the attack (painkillers do not always help) so much that you will have to call an ambulance.
Painkillers are often:
- no-shpa;
- drotaverine;
- papaverine;
- antispasmodics of any order.
The attending physicians prevent the problem in advance - offer the patient a painkiller in case of an attack. If you have not received a proposal from your doctor, discuss the names of the medications at your appointment.
Some doctors recommend taking a bath. The water is at a pleasant, warm temperature (from 37 to 39C), and should not burn the human body. There is no need to lie in the bath for a long time: just relax for 10-15 minutes. Then it is recommended to quickly go to bed so that the warmed body does not cool down again and the body temperature does not change. An alternative option that allows you to “warm” the body and improve the functioning of blood vessels is to apply a heating pad to your legs. It is recommended to wrap the patient as much as possible in blankets and warm clothes; in case of cholelithiasis, warmth will serve a good purpose. If the patient's temperature fluctuates, the patient feels chills, wrap the person in a blanket more tightly.
To avoid dehydration, drink plenty of water. Mineral, filtered water is recommended; tap water and carbonated drinks are strictly prohibited.
As a rule, serious attacks last 20–30 minutes; after the specified time has elapsed, you are allowed to leave the bed or bath and continue doing business. If the attack does not end, then the matter is serious and a doctor’s consultation is urgently needed. You'll have to call the hospital and call an ambulance.
Remember: the sooner a stone (or several) is detected in the gall bladder and the patient complains to the doctor, the higher the likelihood of avoiding surgery.
Complications of cholelithiasis and concurrent diseases
If you do not see a doctor in time for gallstones, you may encounter a number of quite serious complications that greatly affect the condition of your body. At first, the stones are small, painkillers cope with the task of dulling the pain, but gradually the formations become more massive, and passage through the biliary tract becomes more difficult. When stones get stuck, blocking the bile ducts, unpleasant phenomena occur:
- biliary cirrhosis of the liver;
- jaundice;
- cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder);
- cholangitis.
Cholecystitis is accompanied by recognizable symptoms:
- the pain is localized on both sides of the body, acquiring a girdling character;
- yellowed skin;
- change in body temperature;
- pain radiates to the back, creating a sensation of pulsation;
- problems with processing food - vomiting, nausea.
When the stones enlarge and the ducts are blocked, the scary thing is that the pain does not stop and is very intense. In order not to delay treatment until surgery, it is better to worry about preventing consequences in advance.
The following diseases will serve as a prerequisite for the appearance of gallstones:
- Crohn's disease;
- gout;
- diabetes.
The common reason for the transition of diseases into each other is the deterioration of the body’s condition. As a rule, clinics remember this relationship and take preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of gallstones.
Due to complications and parallel diseases that are not treated in time, a person suffers many times: the first time when he tries to cope with a diagnosed disease, the second time when an additional disease appears, and the patient has to fight on several fronts at the same time. The metabolism and life of a person depend on complications of gallstone disease; symptoms indicating the occurrence of complications require an urgent need to call an ambulance. The attending physician will be able to decide whether it is worth hospitalizing the patient or whether it will be possible to get by with a set of basic measures.
During hospitalization, further treatment course is prescribed individually depending on the cause of the attack in addition to the neglected gallbladder.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Surgery for cholelithiasis is indicated if the size of the stones exceeds one centimeter in diameter. As a rule, doctors resort to laparoscopic removal of not only stones, but also the gallbladder. If you leave the organ, it can become inflamed again in the future and cause other diseases.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is performed under general anesthesia after preliminary preparation of the patient.
The advantage of this treatment method is the presence of small punctures in the patient’s abdomen, through which the laparoscope and surgical instruments are inserted. The duration of such surgery does not exceed forty minutes. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the safest and most effective surgical method for removing the gallbladder.
Diagnostics
Ultrasound examination helps in accurately diagnosing the disease.
The doctor diagnoses cholelithiasis based on characteristic clinical data: the occurrence of biliary colic with vomiting, flatulence, jaundice, itching of the skin, changed color of urine and feces. For more accurate data, additional research is carried out:
- Ultrasound and X-ray examinations. Based on the data obtained, the exact dimensions of the gallbladder and its tract are determined. The stone or stones are also inspected.
- Clinical blood test. Detects the presence of inflammation and its nature.
- Biochemical blood test to detect bilirubin and transaminases. The analysis shows the presence of inflammation in the gallbladder, stagnation of bile and problems in the liver.
- ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) and EUS (endoscopic ultrasonography). They are used for more specific information on the location of formations and violations associated with them.
How to prevent gallstone disease
To prevent gallbladder attacks, follow these preventive measures:
- Maintain normal body weight
- Take hormonal medications only when absolutely necessary
- Play sports
- Eat right
- Take a walk in the fresh air
- Do morning exercises
- Do not drink alcoholic beverages,
- Don't overeat
- Avoid strenuous physical activity during the stone formation stage.
- If the disease worsens, call emergency medical help.
When the first symptoms of cholelithiasis appear, try not to delay treatment. Regarding the issue of removing the gallbladder, it is necessary to consult a gastroenterologist. You should not self-medicate, as complications of the disease can be very serious.
Prevention
A single gallstone attack is a warning and reminder of the need to take care of your health. To protect yourself from recurrence, it is enough to follow a number of preventive measures. The demands become extremely important after an attack. Eg:
- You should fast for 12 hours after the onset of pain;
- then they move on to drinking rosehip decoction, eating soups prepared with fresh vegetables;
- on the third day after inflammation, cereals boiled in water, cottage cheese (necessarily low-fat), milk (low-fat), broths with lean meat, bread (rye), fresh vegetables and fruits are returned to the diet - eliminating the sour taste;
- With great caution, after an attack occurs, river fish, turkey meat, and chicken (without skin) should be added to food. Discuss with your doctor the possibility of a therapeutic course of taking mineral water.
The diet, developed by nutritionists solely to prevent new attacks of gallstone disease, is accompanied by a list of prohibited foods:
- pasta (even the highest grade);
- sausage;
- spinach;
- dairy products with high fat content;
- dishes subject to heat treatment, in addition to boiling and steaming;
- forget about seasonings, pickled and highly salted foods;
- coffee;
- alcohol.
It is required to adhere to a diet during an attack and after it. The diet helps reduce the load on the gallbladder and the processing system as a whole. Take care of your diet, it is not difficult and does not require much effort.
If you are diagnosed with gallstone disease, you will have to temporarily forget about intensive weight loss methods. Quite often, women mistakenly believe that fitness can improve health; gallstones become an exception. Such diets disrupt metabolism, food processing and the secretion of bile from the bile ducts are impaired. It is better to discuss the need to lose weight with your doctor, finding a way out that suits both parties.
Recommendations for eating
The diet has a list of permitted and prohibited foods, recommendations regarding dosage and frequency of daily meals. The daily intake of nutrients varies from person to person; only a doctor can give clear, individual advice. However, there are known rules that are common to each case.
For example, you will need to plan the menu and the quantitative ratio of dishes on the list in the morning. A large portion of food should be divided into 5-6 meals. The size of the dish should not be massive, so as not to overload the inflamed organs.
By following simple preventive rules, you will be able to forget about stones in the bile ducts for a long time. It is important to remember that you should not provoke attacks, so that later you do not have to deal with unwanted pain.
Structure of the gallbladder and bile ducts
To understand the mechanism of spasm development, it is necessary to study the structure of the gallbladder. The gallbladder is an internally hollow organ, up to 15 cm long and about 5 cm wide. The average capacity of bile is 60-80 ml, but if necessary, the bladder can stretch up to 200 ml.
It is located directly under the liver, not far from the duodenum, in the area of the right hypochondrium. In its normal state, it cannot be felt by palpation, and its size and condition can be determined using ultrasound.
The walls of the organ consist of three membranes:
- serous (external);
- muscular (medium);
- mucous membrane (internal).
The main bile duct is formed as a result of the connection of the hepatic and cystic ducts, and consists of several sections. It is through the ducts that bile is removed from the liver, enters the gallbladder and is subsequently released into the intestine.
When food enters the stomach, an involuntary contraction of the gallbladder occurs, which opens the main valve, then the sphincter, after which the bile enters the horizontal part of the duodenum (duodenum). There the digestion process begins, during which fats and carbohydrates are dissolved by bile.