To prevent inflammation of the tonsils in the throat, for a long time surgeons simply removed them. This was considered an effective method.
But modern doctors, having studied all the pros and cons, insist on the great benefits of tonsils for the human body.
They explain this by saying that the tonsils produce large numbers of lymphocytes, white blood cells, that help fight infection.
How does the inflammation process begin?
Usually acute inflammation of the tonsils begins.
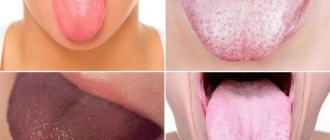
Symptoms: severe pain in the throat and when swallowing. There is a general feeling of weakness throughout the body, chills appear, a headache, and many begin to have aches in the joints. In this case, the temperature can reach 41 degrees. The lymph nodes under the jaw are very painful if you press on them. Tonsils are anatomical structures consisting of lymphoid tissue. There are six of them in total: two palatal (also often referred to as “tonsils”), two tubal, one pharyngeal and one lingual. Inflammation can affect any of the tonsils, but an independent examination of the pharyngeal cavity (pharyngoscopy) without special devices will allow you to see only the tonsils. The inflammatory process involving the tonsils is called “tonsillitis.”
Acute inflammation is characterized by active development and intense course, but it resolves after a short time and does not last longer than several weeks. Tissue damage can be quite extensive, but the likelihood of complete recovery is higher - especially if only the superficial layers are affected.
With chronic inflammation, the situation is different. An example is chronic tonsillitis, in which plugs form in the tonsils, and damage due to the proliferation of bacteria and the release of toxins by them continues constantly. We cannot exclude the possibility of the development of hypertrophy (increase in size), the existence of foci of necrosis, and the deposition of calcium salts.
You need to know that inflammation is considered a typical pathological process. This means that the cascade of reactions that initiate changes in the area of inflamed tissue will be the same, regardless of the location of the lesion and the type of etiological factor. Inflammation is the result of damage, a violation of adaptive capabilities, it always develops consistently and naturally, over a certain time. Symptoms of inflammation of the tonsils can be classified as:
- Local.
- Are common.
Among the local signs are:
- redness (hyperemia);
- swelling (edema);
- local hyperthermia (local heat);
- pain.
We also must not forget that local disorders may be accompanied by a change in the appearance of the tonsils due to the appearance of various plaques on the surface of the mucous membrane.
With pharyngitis, the back wall of the pharynx is affected, and the tonsils may turn red only partially, at the edges. Since sore throat as a symptom combines both diseases, it is important to conduct an objective examination for the correct choice of therapy.
Among the general signs of tonsillitis, one should mention, first of all, fever - it can reach different values, but one way or another accompanies the inflammatory process, since it is a protective reaction from the immune system. The severity of fever, as well as the severity of local changes, reflects the degree of reactivity of the body.
The most complete picture of the pathological process will be with an acute type of inflammatory reactions, since chronic inflammation of the glands, as mentioned earlier, has a less pronounced course and in a state of remission (between exacerbations) its signs are erased. In addition, most general and local signs (such as a violation of the general condition, an increase in general and local temperature, noticeable swelling and redness, severe pain) are not characteristic of chronic tonsillitis, unless we are talking about a relapse.
Hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils
The last disease on our list, which we will consider separately from the rest, is hyperemia of the tonsils. The disease looks like an increase in the size of the tonsils, but there is no inflammatory process at all. At the same time, adenoid enlargement may appear. At first glance, the disease seems simple, but its causes are so mysterious that even modern medicine has not figured them out. However, a certain connection has been identified between the number of colds and the manifestation of hyperemia. There are several degrees of the disease, which take into account the closedness of the space between the midline of the pharynx and the palatal arches:
- The first degree usually looks like a third of the space covered.
- The second is heavier, here we are talking about two-thirds of the space.
- And the last, the heaviest, is characterized by almost complete or complete overlap.
In some childhood cases, it happens that the tonsils on the sides enlarge so that they almost touch each other, thereby blocking even access to air.
At any stage of the disease, enlarged tonsils interfere with the adequate respiratory process, the passage of food into the esophagus, and sometimes the patient may have no speech. Externally, enlarged tonsils may have a yellowish or pinkish tint, and the surface is greatly deformed. In this case, plaque on the tonsils is completely absent, and plugs do not collect in the lacunae. Upon palpation, you can find that the tonsil is quite soft. For food, patients are usually prescribed liquid food or special loose porridges.
Symptoms during exacerbation
Signs of exacerbation of tonsillitis are similar to those of acute tonsillitis. A weakened immune system contributes to the appearance of this condition. Exacerbation of tonsillitis occurs with more severe symptoms than chronic inflammation. Tonsillitis in its acute form is called tonsillitis, and when the disease occurs:
- sharp pain in the throat;
- pain in joints, lower back;
- headache;
- enlarged and painful lymph nodes;
- difficulty swallowing;
- high body temperature;
- general weakness.
Varieties and atypical forms
According to the first classification, the following sore throats are distinguished:
- catarrhal;
- lacunar;
- follicular;
- phlegmonous (peritonsillitis, intratonsillar abscess);
- ulcerative-membranous (angina Simanovsky-Plaut-Vincent).
The second classification divides tonsillitis according to the type of course:
- spicy,
- chronic.
The acute form always implies a primary infectious attack and pronounced symptoms. Any sore throat, with the exception of phlegmonous, with an attack that occurs no more than once every 14-18 months, is considered acute. Phlegmonous tonsillitis, even with secondary abscesses, automatically becomes a chronic form. In this case, paratonsillitis almost always occurs against the background of the chronic course of other tonsillitis (lacunary, etc.). Because of this, some otolaryngologists generally consider it incorrect to divide phlegmonous tonsillitis into acute and chronic.
The chronic form means that the pathogen(s) remain in the body in small quantities for a long time. They become resistant to standard (i.e., not overpowered) immune responses and many antibiotics. With a sharp weakening of the immune defense, the number of pathogenic bacteria also increases sharply, and the chronic form turns into an active form, similar in its pattern to the acute form.
In 8 out of 10 cases, tonsillitis affects the palatine tonsils, but others (tubal, pharyngeal, lingual) can also be affected. However, with chronic tonsillitis, the infection always “sleeps” in the palatine tonsils. According to statistics, after an acute attack, chronic tonsillitis develops in 11% of children and 5% of adults. At the same time, about 2% of all cases of any sore throat were noted when the chronic form began immediately, without an acute primary attack.
The chronic form has one unique feature. Namely, any type of tonsillitis according to other classifications can become chronic. Those. Bacterial and viral tonsillitis, follicular and phlegmonous can be chronic. Moreover, the chronic form has negative dynamics. That is, for example, in the first couple of years there were relapses of trivial pharyngitis and catarrhal tonsillitis. And then exacerbations began with symptoms characteristic of follicular-lacunar varieties. And after a couple of years - relapses of intratonsillar abscess.
This is explained by the fact that the pathogen gradually develops protective mechanisms. Both against immunity and against antibiotics.
Chronic sore throat is divided into 3 gradations:
- simple form - has the most meager symptoms; it is with such chronic angina that the patient can simply be a carrier of the infection without suffering from its manifestations;
- toxic-allergic form of type 1 - here the symptoms are moderate and cause regular difficulties for the patient for a long time, but the ability to work outside of exacerbations is not impaired;
- toxic-allergic form of type 2 is the most severe version of the chronicity, and not only because of the abundance of constant symptoms that bring the patient closer to a state of permanent exacerbation, but also because of the serious risk of developing autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
The third classification divides sore throats into bacterial and viral. And those, in turn, can be divided into types of bacteria and viruses. For example, streptococcal tonsillitis, staphylococcal tonsillitis, enteroviral tonsillitis, etc.
Approaches to treating the disease in adults and children
Most often, the tonsils become inflamed with sore throat. This can sometimes also occur in the initial stages of acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections. The intensity of inflammation of the tonsils varies. If the sore throat is catarrhal, then the patient complains of a burning sensation and sore throat, and the pain when swallowing is not severe. There is a slight temperature that does not reach 38 degrees.
If the sore throat is follicular, then the temperature rises sharply to 38 degrees and above. A person suffers from general intoxication and chills. There is pain in the lower back. General weakness of the body appears. The pain is localized not only in the throat, but also “radiates” to the ear. Lymph nodes are painful and swollen. Children sometimes experience diarrhea and vomiting.
With lacunar angina, the symptoms are similar to follicular angina, but are more pronounced. There is an enlargement and inflammation of the tonsils, they are covered with a yellowish-white coating. This is the most severe form of sore throat.
The cause can be not only bacterial tonsillitis, but also fungal and viral ones. If it is monocytic, then the cause of inflammation is viruses. In this case, the patient experiences not only pain when swallowing, but also general malaise. Additionally, the spleen and liver enlarge, changes occur in all lymph nodes. The blood test also reveals a number of changes in the body.
Fungal tonsillitis is caused by infections that already exist in the body and are called opportunistic. If the immune system is weak, then their number increases sharply. This happens, for example, with long-term use of antibiotics. With such a sore throat, a cheesy coating appears on the tonsils. It is treated with antifungal drugs.
Children often experience herpetic sore throat, which is considered a highly contagious disease. A similar inflammation of the tonsils is spread by airborne droplets; the symptoms are as follows: small bubbles form on the back wall of the pharynx and tonsils, completely covering them. The bubbles contain a clear liquid. This type of sore throat is treated with antiviral drugs.
Like most diseases, inflammation of the tonsils in adults and children occurs differently. And their treatment is slightly different. Children under 12 years of age are not recommended to take analgesics, which speed up the cure of the disease.
When the form is advanced, doctors remove the tonsils. This is done very rarely in adults. Whereas in children this procedure is often performed. Doctors decide to remove tonsils only in the following cases:
- if a child suffers from tonsillitis more than 5 times during the year;
- when treatment does not produce any results;
- when, despite treatment, a large abscess constantly forms on the tonsils.
Removing tonsils is a simple operation. It takes place on an outpatient basis. Very soon the child is discharged and sent home.
Tonsillitis goes away, but removing tonsils can lead to a decrease in immunity. The child becomes more susceptible to viruses and infections.
Especially those that are transmitted by airborne droplets. Parents will have to ensure that the child does not walk in crowded places.
Traditional methods of treatment can sometimes give good results, and sometimes they can even cause harm. Although there is an opinion that nothing bad can happen from their use, you should still consult a doctor first.
The most common method of treating inflammation of the tonsils is rinsing the larynx with a solution of soda and salt. Rinse should be repeated every few hours. This type of traditional medicine can be very effective for this disease.
Water diluted with lemon can relieve a sore throat.
Honey is quite effective in relieving inflammation. You can simply eat it a few spoons a day, or you can add it to various rinsing solutions.
Propolis has no less effective effect. It also needs to be added to rinsing solutions. It is enough to carry out the procedures 3 times a day.
- recurrent form, that is, with frequently recurring sore throats;
- protracted form, when the inflammatory process in the palatine tonsils is characterized by a sluggish and prolonged course;
- compensated form, when episodes of sore throat and exacerbation of tonsillitis are not observed for a long time.
Chronic tonsillitis is the most common disease among all diseases of the pharynx and one of the most common diseases of all ENT organs, along with such a diagnosis as acute sinusitis.
Chronic tonsillitis can affect both adults and children, from the moment the palatine tonsils begin to develop (from 2-3 years). Moreover, the incidence of this disease in childhood is much higher.
Some respiratory diseases can also be classified as social diseases. For example, sinusitis and tonsillitis are among them. Poor environment, stress, lack of sleep, overwork, monotonous and poor nutrition, as well as poor heredity are predisposing factors to the development of the disease.
How to treat tonsils using traditional methods?
Before moving on to home treatment methods with folk remedies, it is recommended to consult with your doctor, especially if such methods are planned to be used for children.
The fact is that decoctions of medicinal herbs are noticeably inferior in effectiveness to simple antiseptics from the pharmacy, or even ordinary salt and soda. When choosing folk remedies, you should be prepared to consult a doctor in a timely manner if symptoms do not subside after 2-3 days.
Decoctions for rinsing
When the tonsils become inflamed, traditional medicine suggests using the following recipes for treatment at home.
- Sage decoction. Take a tablespoon of the medicinal plant, place it in a bowl and add 500 ml of water. Cook covered for 15-20 minutes over low heat. Then strain and cool.
- Propolis tincture. Grind 10 g of propolis, pour in 100 ml of vodka, placing the medicine in a glass container. Leave in a dark place for two weeks, shaking daily. Then use to gargle, dissolving a teaspoon of the product in a glass of water.
- Chamomile with honey. Prepare a decoction of one large spoon of chamomile flowers and a glass of water, cool to a temperature of 37 degrees and add a tablespoon of honey. Gargle with this remedy 4 times a day.
- Medicine with garlic. Squeeze 3-4 cloves of garlic into a glass, pour boiling water and leave until the water cools to a comfortable temperature. Gargle with this product morning and evening.
- Vinegar for gargling: add a teaspoon of vinegar to a glass of boiled water, mix thoroughly and use 3 times a day.
Such remedies are not recommended for treating tonsils in children at home. An adult can experiment with his health, but if a child has tonsillitis, it is necessary to visit a doctor as soon as possible.
Ointments and compresses
There are several other home treatments.
- Traditional medicine suggests lubricating the tonsils with honey to quickly cope with the disease. In general, honey does have antiseptic properties and strengthens the immune system, therefore it is useful for tonsillitis. However, candied honey can injure the tonsils, thereby causing a deterioration in health, so doctors recommend using it in the usual way - with warm milk.
- Another ointment is celandine juice mixed with cocoa butter. It is necessary to melt 100 g of butter in a water bath, add 5 drops of celandine juice, simmer a little over the fire, and then cool. A slightly warm ointment is applied to the tonsils 3-4 times a day.
- To reduce swelling in chronic tonsillitis, compresses with vodka are offered. They can be placed only after making sure that there is no fever or acute inflammatory process.
- A regular cabbage leaf will help relieve a sore throat. It must be kneaded with your fingers, then greased generously with honey mixed with melted butter and applied to the neck.
- Heat sunflower oil (50 ml), squeeze 10 cloves of garlic into it, mix everything and leave to cool. Then apply the product to gauze or bandage and apply to the neck.
- Grate a large onion, then strain the pulp through cheesecloth, squeezing out the juice. Mix the juice half and half with water, and then apply the product to the tonsils using a cotton swab. Repeat morning and evening.
Compresses should not be used in case of inflammation or enlargement of the lymph nodes, exacerbation of tonsillitis and high temperature. You need to keep the compress for an hour, it is better to do it before bed.
Warming up the throat
An effective folk remedy for sore throat (not recommended for people with high blood pressure)
The following method is prohibited for acute tonsillitis, but can really help with chronic tonsillitis. You need to boil 5-6 large potatoes in a large saucepan. When the potatoes are ready, mash them with a fork directly in the water. Wait until the water cools a little, and then lean over the pan and cover with a towel. Breathing steam is useful for chronic sluggish tonsillitis, as warm air helps clear the tonsils of congestion.
Another way to warm up is to breathe over a decoction of oak bark. To do this, you need to boil 50 g of oak bark for half an hour in a large saucepan (3-5 liters), and then breathe in the steam for half an hour.
To avoid re-infection or exacerbation of tonsillitis, traditional healers recommend hanging sprigs of lavender, bunches of celandine, sage and mint around the house. These herbs disinfect indoor air. To strengthen the immune system, you can take echinacea tincture.
Classification
More often, with angina, only the above-described symptoms are observed. If the standard symptoms are accompanied by disorders of the internal organs, persistent cervical or submandibular lymphadenitis, then such a sore throat is already toxic-allergic and there is a risk of developing serious complications. Chronic disease of the tonsils is classified depending on the stages of development:
- Compensated – stage of tonsillitis, which is a condition when local immunity still copes with pathogenic bacteria, but a dormant focus of infection has already appeared in the tonsils. There are no frequently recurring inflammatory diseases of the throat.
- Decompensated - at this stage of tonsillitis, frequent sore throats are observed, complications in the form of an abscess may occur, and damage to internal organs (kidneys, heart) may occur. At the decompensated stage, several infectious foci can be diagnosed in addition to the throat - diseases of the nose and ears.
Depending on the location of the inflammation and its characteristic signs, tonsillitis is classified:
- lacunar - inflammation is localized only in the lacunae (physiological depressions in the tissues) of the tonsils;
- sclerotic – there is an abundant growth of the affected tissue in the tonsils;
- lacunar-parenchymal – inflammation develops in lacunae and lymphadenoid tissue;
- phlegmonous - localized in the lymphadenoid tissue of the palatine tonsils.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures are determined by the cause of the pathology, because only by acting on the source of the problem can it be successfully eliminated. And with adequate treatment, hyperemia of the tonsils, which is one of a number of symptoms, will also go away. Based on the clinical situation, the doctor prescribes:
- Antiseptics (Decatylene, Givalex, Faringosept, Octenisept).
- Antibiotics (Bioparox, Sumamed, Augmentin).
- Antiviral (Groprinosin, Arbidol, Amizon).
- Antihistamines (Tavegil, Cetrin, Zyrtec).
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, nimesulide, paracetamol).
- Vitamins (ascorbic acid, retinol, tocopherol).
- Bio- and immunostimulants (Polyoxidonium, Apilak).
For chronic tonsillitis, non-drug therapy is also indicated (UHF, ultraviolet irradiation, ozokerite, laser), and in some cases it is necessary to resort to surgical correction (cryodestruction, galvanocaustics, tonsillectomy). Surgical treatment is also indicated for angina complicated by peritonsillar abscess.
Redness of the tonsils and surrounding mucous membrane most often occurs due to inflammatory processes. This is just one of the symptoms of various pathologies that require detailed diagnosis. And based on the results of the examination, the doctor will prescribe adequate treatment.
Causes of inflammation
There are six tonsils in humans. Three of them can be seen simply by looking into a wide open mouth: two on the sides are the palatine tonsils, and on top is the pharyngeal tonsil.
The two tubal tonsils are located deep in the pharynx - they are not so easy to see. Another one is lingual, located under the tongue. The palatine tonsils, also called tonsils, are the easiest to become inflamed.
The lymphocytes produced by the tonsils act as a kind of barrier. They block and destroy bacteria, viruses, harmful organisms and other infections that have entered the mouth area. If for some reason they cannot cope with this, inflammation of the tonsils of the throat begins, which must be treated immediately.
There are several risk factors for tonsils. Due to their influence, inflammation most often occurs:
- Changes in the shape of the larynx. Because of this, a change in breathing pattern occurs. The air enters not through the nose, but through the mouth. The circulation of cold air is disrupted, which affects the tonsils.
- Presence of chronic diseases in the mouth area. Because of them, the lymphatic system constantly has to fight infection. If there is too much of it, inflammation begins. Even chronic caries and stomatitis can be the cause.
- The immune system cannot cope with existing threats. There are many reasons for weakened immunity. But the main one is the lack of proper nutrition and an unhealthy lifestyle.
- Unfavorable working conditions. The greatest influence is exerted by gas and dust levels in the air at work.
- Poor environmental conditions, pollution from vehicle exhaust gases, harmful emissions into the atmosphere.
- Low quality of consumed water.
- Weak (low) immunity.
- Severe hypothermia of the body.
- Stressful situations.
- The presence of chronic diseases in the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses and oral cavity - dental caries, purulent sinusitis, etc., which often leads to infection of the tonsils.
- Irrational or poor nutrition, in which excess amounts of proteins and carbohydrates are consumed.
- Heredity (mother or father suffers from chronic tonsillitis). It is very important for a woman to undergo one or two courses of treatment for tonsillitis during pregnancy (depending on the severity of the process) in order to minimize the likelihood of the disease developing in the unborn child.
- Frequent overwork, fatigue syndrome, inability to fully rest.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
Chronic tonsillitis develops after infectious diseases of the throat and nose, more often after improperly treated tonsillitis. The immune function of the tonsils can be suppressed by human herpes virus type 4, which interferes with the functioning of the entire immune system. The reason for the appearance of tonsillitis and its development into a chronic form may be other chronic infectious diseases of the nasopharynx. For example, the disease often develops as a result of chronic pharyngitis and sinusitis.
Chronic tonsillitis in most cases develops after the patient has suffered an acute form of the disease - acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis. An untreated sore throat may reappear or worsen due to plugs in the lacunae and crypts of the tonsils, which are clogged with caseous-necrotic masses - purulent discharge, waste products of bacteria and viruses.
The main causative agents of the disease are most often:
- viruses - adenoviruses, common herpes, Epstein-Barr virus;
- bacteria - pneumococci, streptococci, staphylococci, moraxella, chlamydia;
- fungi.
In addition, the following factors can affect the appearance of chronic tonsillitis:
- non-compliance with safety regulations in production: a large amount of dust, the presence of smoke, gas contamination, suspensions of harmful substances in the inhaled air;
- chronic diseases of the oral cavity, ears, nasopharynx: chronic otitis, sinusitis, caries, pulpitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease, in which purulent discharge reaches the tonsils and provokes the development of the inflammatory process;
- decreased immune function of the palatine tonsils: the protective substances secreted by the lymphoid tissue can no longer cope with a large number of bacteria and viruses, which, in turn, accumulate and multiply;
- abuse of household chemicals;
- eating food containing low amounts of vitamins and minerals, irregular meals, poor quality food;
- heredity factor: one of the parents suffered or is suffering from chronic inflammation of the tonsils;
- bad habits - drinking alcohol and smoking, which, in addition to having a negative effect on the immune system, complicate the course of the disease;
- frequent stressful situations, prolonged stay in a state of strong emotional stress;
- lack of a normal work and rest schedule: lack of sleep, overwork.
Inflammation of the palatine tonsils most often develops against the background of ARVI. Among the predisposing factors:
- anatomical features of the structure of the nasopharynx,
- decreased immunity,
- the presence of a chronic focus of infection,
- Epstein-Bar virus.
The disease is seasonal and affects patients mainly in autumn and winter. Bacterial inflammation of the tonsils is caused by the action of streptococci, pneumococci and staphylococci.
Patients with a deviated nasal septum often encounter the disease. Difficulty nasal breathing leads to an increased risk of infection - the tonsils can become inflamed due to insufficient air purification when breathing through the mouth. A chronic focus of infection in the nasopharynx and oral cavity can also provoke inflammation of the tonsils. Potential dangers include:
- stomatitis,
- advanced caries,
- sinusitis.
Causes and mechanisms
Hyperemia is redness of the mucous membrane that occurs when the superficial capillary network expands. This local effect is observed in various conditions related to ENT pathology. Most often, the cause lies in acute or chronic inflammatory reactions that occur in the following conditions:
- Sore throat.
- Tonsillitis.
- Pharyngitis.
Hyperemia is provoked by various microbial flora (strepto- and staphylococci, corynebacteria, spirochetes, viruses, fungi) or other factors that have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane:
- Hot and spicy food.
- Chemicals (including alcohol and stomach acid).
- Voice load.
- Persistent cough.
- Dry air.
- Smoking.
Redness in the throat necessarily accompanies the group of acute respiratory viral infections (influenza and parainfluenza, adeno- and enterovirus infections, mononucleosis); it also occurs with other infectious diseases (diphtheria, scarlet fever, measles, listeriosis, tularemia, typhoid fever, syphilis). Agranulocytosis and leukemia also occur with tonsillitis syndrome.
It is necessary to note the role of other diseases characterized by inflammation of nearby structures. The mucous membrane of the palatine tonsils and arches is closely connected with the processes in the pharynx, nose and sinuses, and the oral cavity. Therefore, the following may contribute to redness:
- Rhinitis and sinusitis.
- Adenoiditis.
- Epiglottitis.
- Caries.
The chronic process can be accompanied by pathology of the digestive tract (with gastroesophageal reflux), endocrine diseases, tuberculosis (with an active form). Therefore, it is important to consider the problem as a whole, paying attention to the many factors that contribute to the appearance of tonsil hyperemia.
Redness of the mucous membrane of the tonsils occurs due to various factors that provoke a sore throat, chronic tonsillitis or pharyngitis.
Treatment or removal of tonsils?
Symptoms depend on the type of sore throat. Of course, if the cause of inflammation is precisely this disease. Symptoms also manifest differently depending on the state of a person’s immune system. If it is weak, then the disease begins much faster and progresses more intensely. With a strong immune system, symptoms are less pronounced.
The main signs of inflammation of the glands, which determine the onset of the disease:
- sore throat, which is expressed in varying degrees. With severe inflammation it can be very acute;
- redness of the tonsils (tonsils);
- increase in body temperature to 38 degrees or more.
Secondary symptoms appear periodically. It depends on the infection that caused inflammation of the tonsils. The manifestations are as follows:
- general weakness;
- Strong headache;
- hoarse voice;
- swollen tonsils;
- the appearance of pustules on the tonsils.
Modern medicine began to use this method a long time ago. The advantage of this procedure is that it relieves inflammation and pain. Rapid tissue regeneration occurs if they were damaged during surgery. The laser is completely harmless and does not disrupt processes occurring in the body. The operation takes place practically without blood.
Inflammation of the tonsils in the throat is called tonsillitis.
Symptoms of inflammation of the tonsils, depending on the severity of the disease and the strength of the immune system, can be noticed within a few hours after the infection, or only a few days.
Healthy and enlarged tonsils.
The first signs of the presence of the disease will be: soreness in the larynx, discomfort when swallowing water and food; tonsils increase in size and become red; a high temperature appears, the body aches, a headache, and there is a decrease in performance; after the infection penetrates the vocal cords, the voice becomes hoarse, it becomes difficult to speak, especially after a long silence.
Small children with this disease become capricious, often cry, and lose their appetite.
The course of tonsillitis depends on its form. If the tonsils are simply red and swollen, then this may be catarrhal tonsillitis. It is not as dangerous as other forms of tonsil inflammation.
With catarrhal tonsillitis, a high temperature may not even appear. If it is treated in time, the disease will quickly pass and complications should not be observed.
If catarrhal tonsillitis is not treated, it can develop into a more severe form, which is usually called tonsillitis. As a result, the temperature rises very high, and white dots can be seen on the tonsils.
It is important to treat inflammation of the tonsils in a timely manner, because the infection can enter the bloodstream and spread to other internal organs.
If you do not pay attention to inflammation of the tonsils for a long time, you can wait for it to become chronic. Chronic tonsillitis takes months to treat, while its simple form can be cured in a little more than a week.
Also, chronic tonsillitis can return several times a year. Its treatment is simply necessary in the initial stages of development.
If we talk about the removal of the tonsils, then the operation to completely remove the tonsil tissue is called a bilateral tonsillectomy.
Partial removal of the tonsils is called a bilateral tonsillotomy.
It is extremely rare that the palatine tonsil is removed routinely on one side. There is also a practice of a number of hospitals (they like to do this in the Pirogov City Clinical Hospital No. 1) of removing the palatine tonsil or tonsils in case of a paratosillar abscess. This operation is called abscessonsillectomy. But it must be remembered that against the background of severe pain caused by an abscess, removal of the tonsil is extremely painful.
Routinely, palatine tonsils can be removed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. Previously, this operation was performed only under local anesthesia.
Fortunately, there is now modern equipment that allows removal of palatine tonsils under general anesthesia or under anesthesia using cold plasma coagulation - Coblator.
Dear patients! If you have visited several specialists in this field, if a course of treatment for chronic tonsillitis has been carried out and none of the methods has brought the expected result, then only in this case should you think about removing the tonsils.
If a conservative approach gives lasting results for 4-6 months or more, then the palatine tonsils are able to fight on their own. Your task is to help the tonsils by regularly sanitizing them and stimulating their work physiotherapeutically.
Dear patients. I wrote this article for you long enough and scrupulously. This is due to the fact that the problem of chronic tonsillitis has accumulated a lot of information that I wanted to share with you, so that after reading this article everything will fall into place. So that there would be fewer or no questions left about the problem of tonsillitis.
Everything you just read was written, as I see it, impartially and true. I did not have the task of presenting this or that method of treatment as the best, most progressive and correct. The choice is always yours.
I hope that you will give a correct assessment of your condition and choose the optimal and effective method of treating chronic tonsillitis.
Be healthy!
Always yours, Dr. Zaitsev.
Drug treatment of tonsils at home
To treat tonsils at home, both medications and folk remedies are used. Doctors do not recommend self-medication, since acute sore throat requires antibiotics that cannot be selected on your own. Treatment without antibiotics is not always effective and can lead to the disease becoming chronic.
You can independently use various gargling solutions and tablets for sore throat.
Otolaryngologists warn: if symptoms have not decreased 3 days after starting home treatment, you should definitely go to the clinic.
In the case of chronic tonsillitis, doctors are not so categorical. Home treatment is allowed; it is not necessary to use antibiotics, but this does not mean that one can be negligent in one’s health. Professional therapy for chronic tonsillitis is more effective, but some methods of treating tonsils at home help improve overall well-being and reduce the frequency of exacerbations.
Gargling
Before rinsing, the product must be diluted with water.
Rinsing is the basis of therapy for chronic and acute tonsillitis. For treatment, special solutions with antiseptic properties are used. Moreover, these are not always potent drugs, because soda and salt are also antiseptics. Doctors also do not prohibit the use of such simple means.
The purpose of rinsing is to wash away plaque from the tonsils. The fact is that the palatine tonsils have small depressions or depressions called lacunae. Pathogenic microbes penetrate into these cavities, resulting in plaque or even plugs in the gaps. The use of antiseptic solutions helps get rid of plaque and prevent further proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
The following products can be used to gargle.
- Sea salt. Rich in iodine and other trace elements, it has an antiseptic effect. To prepare the solution, dissolve 1 teaspoon of the product in warm water. It is recommended to gargle 3-4 times a day.
- Soda. It effectively copes with fungal infections of the oral mucosa and tonsils, but with a bacterial infection it is noticeably inferior to salt. If you don’t have anything at hand, soda will also benefit your health. The rinse solution is prepared from one teaspoon of the product dissolved in a glass of water.
- Iodine. Iodine solution has a powerful antiseptic effect, but it must be used carefully. To prepare the medicine, you need to add only 5 drops of iodine to a glass of water. Contraindication – intolerance to this substance and pathology of the thyroid gland.
- Furacilin. This simple antibiotic will help relieve inflammation of the tonsils at home; moreover, it is actively used for treatment in the hospital. To prepare the solution, you need to take one tablet, grind it into powder and dissolve in a glass of water.
- Chlorophyllipt. The most popular pharmaceutical drug for the treatment of sore throat. It is affordable and available without a prescription. To prepare a gargle, mix 1 part of the drug with 5 parts of water.
- Lugol's solution. Essentially, it is the same iodine, but with the addition of potassium. It is used to lubricate the tonsils, but you can also prepare a solution for rinsing - 5 drops per glass of water.
Rinsing the tonsils is a treatment that allows you to relieve inflammation at home. The listed solutions refer to first aid products that can be used to relieve acute symptoms before visiting a doctor.
Lozenges
For inflammation of the tonsils, treatment at home is supplemented with special lozenges. They necessarily contain an antiseptic and an anesthetic component.
Important! Throat lozenges do not cure tonsillitis, but they are effective in relieving acute symptoms.
You can buy tablets for sore throat at any pharmacy. The most popular drugs:
- Septefril is the cheapest antiseptic for sore throat;
- Strepsils is a well-known product with a wide variety of different flavors;
- Faringosept - lollipops with a pleasant taste and powerful antiseptic effect;
- Angi Sept - lozenges with menthol and mint oil, act very quickly.
The tablets are suitable for treating tonsils in adults at home. They are prescribed to children with caution, as they have age restrictions for use.
Lozenges should be taken 3-4 times a day, preferably after meals. Within 1-2 hours after resorption of the tablet, you should abstain from food, as the drug creates a thin antiseptic film on the tonsils.
Spray for the throat
Use no more than four times a day
Children and adults are treated with tonsils at home using a spray. The drug in this form is sprayed onto the inflamed tonsils; this treatment allows you to quickly eliminate a sore throat at home. In general, sprays have the same composition as tablets, but do not require resorption.
The most popular means:
- Givalex;
- Angilex;
- Hepilor;
- Inhalipt.
The disadvantage of sprays is that they tingle and irritate the throat when sprayed. Lozenges do not cause such discomfort.
Inhalations
Treatment of tonsillitis at home can be supplemented with inhalations. The essence of the method is inhaling warm air with essential oils, which soothes inflamed tonsils and reduces sore throat. For inhalation use:
- green tea essential oil;
- pine or cypress oil;
- drug Pinosol;
- balm Zvezdochka.
Essential oils are added to a container of hot water or to an inhaler, 2-3 drops per liter. The drugs are used according to the instructions.
The disadvantage of inhalation is the presence of contraindications. This procedure is contraindicated at high temperatures and acute infectious processes in the body. Inhalations can be done for chronic tonsillitis.
Washing lacunae
The following treatment method is practiced for chronic tonsillitis and the presence of purulent plugs in the tonsils. Rinsing is carried out using a syringe with a special curved nozzle, or an irrigator.
It is necessary to prepare a solution of furatsilin and Lugol's solution. Open your mouth wide, place the tip of the syringe opposite the recesses in the tonsils and direct a stream of antiseptic solution into the gaps. Repeat the procedure 3-4 times, then rinse your mouth with an antiseptic and lubricate your tonsils with Lugol's solution. This procedure must be carried out twice a day.
What can't you do?
Mustard plasters should not be applied to sick tonsils.
Inflammation of the tonsils should be treated at home carefully. In case of acute inflammation it is prohibited:
- do warm-ups;
- rub your throat with vodka;
- make compresses;
- use mustard plasters.
All these methods can aggravate the course of the disease and provoke the spread of infection throughout the body, which is fraught with life-threatening complications.
It is also forbidden to try to clean off plaque with your fingers or squeeze out purulent plugs in the tonsils. All this is fraught with the development of extensive inflammation due to injury to the tonsil tissue.
Prevention of chronic tonsillitis
Dangerous protracted tonsillitis can not only be cured if you approach the problem comprehensively, but also prevent it. If a child often suffers from tonsillitis, then the problem lies in a weakened immune system. To avoid illness, you must:
- harden;
- eat right so that the body receives all the necessary elements and vitamins;
- give up cold carbonated drinks (carbon dioxide found in drinks irritates the throat);
- treat infectious diseases of the nasopharynx and colds in a timely manner;
- carry out sanitation of the oral cavity;
- monitor the health of your teeth and stomach.
Preventive measures to avoid relapse of the inflammatory process in the area of the tonsils include several comprehensive measures:
- proper nutrition: do not eat food that irritates the mucous membranes of the tonsils - citrus fruits, hot, spicy, fried, smoked foods, strong alcoholic drinks;
- strengthening general immunity: hardening, walking in the fresh air, taking vitamin and mineral complexes;
- rest and work regime: you need to get enough sleep, take time for proper rest, avoid working for long hours without breaks.
- Drug therapy. If an ENT patient undergoes treatment courses in the clinic once every 6 months, then in addition to six-month procedures, he is recommended to take the drug Tonsilotren, with a frequency of once every 3 months, i.e. 4 times a year. The course of taking (resorption) of the drug is for 2 weeks (more precisely 15 days). It is also possible to instill 0.01% Miramistin solution, 4 pumps 4 times a day for 2 weeks, in courses 4 times a year.
- Climatotherapy and spa therapy. An important point in the prevention of chronic tonsillitis is visiting seaside resorts. Sunbathing, humidified sea air, swimming and, as a result, the inevitable entry of sea water into the mouth have a beneficial effect on the prevention of chronic tonsillitis.
- Work and rest schedule. In order for the periods of remission to be long, it is necessary to fully rest and not expose yourself to stress. It is not without reason that chronic tonsillitis, like sinusitis, is classified as a social disease, in which the more stress and workload there is at work, the higher the likelihood of exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis.
- Diet. It is very important to eat right. Under no circumstances should you get carried away with fried, salty, peppery, sour, bitter, i.e. that food that irritates the mucous membrane of the back of the throat and palatine tonsils. Citrus fruits are contraindicated. The consumption of alcoholic beverages, especially strong ones, is also contraindicated. It is not advisable to eat very hot and very cold and solid foods.
Existing tonsil diseases
Before moving on to more hyperemia, we will understand what common typical diseases of the tonsils are. In general, all reactions that tend to occur inside the tonsils can be divided into two categories:
- Primary.
- Secondary.
The first usually includes viruses that infect the tonsils themselves. The second includes coverage of the organs closest to the tonsils: inflammation affects the nose, pharynx and larynx or oral cavity. It is also possible to identify the underlying infection for most cases of inflammation of the tonsils. This infection is tonsillitis, it occurs quite often, but it is relatively simple to treat and can be done either independently or using specific medications that can be prescribed in the hospital.
If tonsillitis is not noticed in time, it tends to quickly develop into a purulent sore throat. With it, purulent clots form in the lacunae of the tonsils. If you miss this moment, you can end up with a chronic form of the disease for many years to come.
Today, doctors have already been able to identify the main factors that contribute to the active manifestation of tonsil diseases:
- Regular breathing problems.
- Formation of permanent polyps.
- Nasopharyngeal injuries.
- Severe caries.
- Diseases of the ears and middle ear.
- Adenoids.
- Weak resistance to harmful organisms entering the body.
Tonsils: inflammation. Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment can sometimes be more effective than medications prescribed by a doctor. They can not only alleviate the general condition of the patient, but also speed up recovery. A warm (but not hot) drink helps a lot. Ideally, this is a tea that will contain herbs that have an anti-inflammatory effect:
- rose hip;
- viburnum;
- lemon;
- chamomile.
What to do if the tonsils are inflamed? Plaque or pustules can be rinsed with antiseptic agents. This procedure should be carried out several times a day, thirty minutes before meals. Another great medicine is regular lemon. Eaten half, without sugar and with the peel, can work wonders, killing inflammation. But after this you also need to wait about half an hour with food.
Symptoms
How to determine which particular form of sore throat has overtaken the patient? And is it a sore throat? There are symptoms that always appear in any form of angina according to any classification. There are those that are characteristic of several sore throats within the same classification. And there are completely unique symptoms that clearly indicate one, precisely specific, sore throat.
Nonspecific symptoms that are almost guaranteed to occur with absolutely any sore throat:
- Hyperthermia. The level and nature vary, but the very fact of increased body temperature does not bypass any sore throat. Temperature-free progression of tonsillitis is very rare even for adult patients.
- Hyperemia, swelling and sore throat. The symptom is perhaps even more obligatory than temperature. Pain when swallowing, redness of the tonsils, soft palate and its uvula - everyone who has suffered or is suffering from a sore throat is familiar with this.
- Absent symptom: no cough. If there is a pure sore throat, without laryngitis involved, then there will be no cough. Moreover, sore throat itself does not lead to hoarseness, the voice does not deepen, there is no hoarseness.
- And of course, there are symptoms of varying severity: headache, fatigue, lethargy, drowsiness, apathy, loss of appetite, decreased performance, nausea.
The listed symptoms appear during the period of exacerbation of the simple chronic form, when the immune system is most weakened (in spring or autumn). And also in the early stages of acute forms of other types of tonsillitis. Chronic disease in exacerbations is often limited to these four points (especially in adults).
The mildest type of sore throat - catarrhal - can be limited to four points. When the uppermost layer of the epithelium of the tonsils is affected. Even if the patient got sick for the first time. Another thing is that catarrhal tonsillitis is unlikely to immediately become chronic. If it is started, acute lacunar-follicular forms will first develop.
Acute lacunar-follicular tonsillitis is, in a way, the standard of the disease. Most people encounter them. And it is they, with inadequate treatment, or lack thereof, that give complications and/or lead to a chronic course.
Taking into account the features already mentioned above, the following symptoms are added:
- High rate of temperature increase (in a three-hour period). Hyperthermia can cross the bar at 39 degrees. The fever becomes wave-like: after sleep, low-grade fever or even normal, but in the evening there is a high fever again.
- The palatine tonsils noticeably increase in volume. The main thing is that already on the third day a purulent exudate of a yellowish or gray-whitish color is detected on them. With follicular angina - granular dots and spots, with lacunar - paths repeating the lines of the lacunae. Purulent discharge is easily removed with a spatula or a stream of liquid (especially when lacunae are affected).
- The lymph nodes become noticeably enlarged and become painful when pressed. First, cervical, but others may also be affected: axillary, inguinal.
- There is aching in the joints, especially in the lower back. The patient suffers from tachycardia.
If these symptoms appear, it means that there is follicular or lacunar tonsillitis in the peak phase. Another thing is - is it episodic, is it isolated, or has there been an exacerbation of a chronic infection?
The following points indicate the chronicle:
- the patient has already suffered similar tonsillitis less than six months ago, if several similar cases occurred within a year, the chronicle is confirmed;
- since the last illness, the patient noted regular mild sore throat, redness of the mucous membrane, increased fatigue, evening low-grade fever, periodic pain in the joints and behind the sternum, prolonged colds (toxic-allergic form of type 1);
- noticeable changes in heart rate (chronic tachycardia), persistent regular low-grade fever, pathologies in the kidneys and cardiovascular system are detected, the development of autoimmune connective tissue diseases begins (toxic-allergic form type 2);
- During the period between illnesses, the otolaryngologist recorded: increased looseness of the tonsils, scars and bumps on their surface, fusion of the tissue of the tonsils with the palatine arches, abnormally wide lacunae, small discharge when pressing on the tonsils;
- frequent bad breath, regardless of food intake.
However, the size of the tonsils is not an absolute indicator of the presence of infection. In children, tonsils are normally always enlarged, and their volume reaches its peak by the age of 7 years. There have been cases where pathogens settled in tonsils that were not visually enlarged (even small compared to the average of 2 cm in diameter).
Bacterial and viral tonsillitis also have their differences. Firstly, bacterial tonsillitis is usually more severe. This is due to the fact that viruses immediately begin to be affected by universal antiviral proteins - interferons, while bacteria require a longer immune response. Secondly, with a purely viral sore throat there is no purulent discharge, but rhinitis and laryngitis are often associated. Thirdly, with a diagnostic general blood test, changes in the leukocyte formula can immediately distinguish a bacterial sore throat from a viral one.
Phlegmonous tonsillitis is considered in a special manner. Based on the fact that its occurrence in 99 cases out of 100 occurs either against the background of another chronic form of tonsillitis, or as a complication of untreated or extremely severe acute lacunar-follicular tonsillitis. Immediately after the first infection, an intratonsillar abscess can occur only with a very aggressive pathogen in combination with a severely weakened immune system.
This type of tonsillitis cannot be confused with any other due to one characteristic feature - a unilateral purulent abscess. Already on the second day of the disease, a swelling is detected on the side of one of the tonsils (always only one!), which will increase over the next 72 hours (to the point that it closes almost the entire lumen of the throat). When a light tubercle (bulging pus) appears on the surface of the protrusion, it means that the phlegmon has matured and needs to be opened. The autopsy is performed by an otolaryngologist.
Chronic paratonsillitis is diagnosed if, after some time, a new abscess begins to mature. This can happen not only due to the constant presence of the pathogen, but also due to a previous abscess that was poorly washed out of pus. Chronic phlegmonous tonsillitis is an indication for tonsillectomy.
Causes of inflammation of the tonsils in the throat
Inflammation of the tonsils occurs more often in children than in adults. Since the viruses that cause tonsillitis are transmitted by airborne droplets, they most often spread in crowded places: in kindergartens, schools, public transport.
To prevent the occurrence of this disease, it is worth taking preventive measures and trying to strengthen the immune system.
If this failed and inflammation of the tonsils has already begun, there is no need to panic. If you notice it in the early stages, it is quite easy to treat.
Of course, if there are obvious signs of illness, you need to seek treatment with medications. But you can try to treat the disease at home. To do this, firstly, you need to go to bed.
The body needs bed rest and complete calm to restore strength.
Very effective for throat diseases - gargling. Solutions for them can be bought at the pharmacy, or you can prepare them yourself. To do this, you should prepare a mixture of water, salt and iodine.
If your body temperature has risen to 38 degrees or higher, then it needs to be brought down. There are antipyretic tablets for this.
You also need to drink a lot. Various decoctions are suitable for this: rose hips, currants, or just tea with lemon.
These methods can only be attempted for catarrhal tonsillitis. But at its more complex stages it is worth using antibiotics. To do this, you must consult a doctor.
Treatment of hyperemia
If the increase is insignificant and inflammation does not follow, then no specific treatment is required. In this case, doctors recommend simply gargling your throat with a solution of furatsilin or even regular soda from time to time. It is also necessary to ensure that the patient breathes only through the nose. This is due to the fact that the throat should not dry out, and the epithelium will not be exposed to dust.
If the increase is still significant, then you will need to resort to more serious methods other than antiseptic effects. With this development of events, the tonsils are usually cauterized with special astringents. Such drugs are usually prescribed by a doctor and treatment is carried out in special courses of several weeks. As for home treatment, we can note the effectiveness of treatment with a five percent glycerin solution and iodine solution.
As for the more complex situation with inflammation of the tonsils of the second or third degree, which is associated with complete or close closure of the throat, then only surgical intervention would be optimal. A tonsillotomy involves carefully removing part of the tonsils under local anesthesia. If there remains a certain possibility of keeping the tonsils intact, then doctors follow this path. And if not, then such an operation allows you to preserve some of the functions of the tonsils and return the throat to its full condition before the disease began.
How the infection is transmitted
There are two main ways in which the infection is transmitted from a sick person to other people. The first is from a person who has an active stage of inflammation. The infection is transmitted through coughing or sneezing (airborne), due to which a person spreads pathogenic microbes around him. As a result, healthy people can often get sick, especially those with weakened immune systems.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZgqjCEvULJg
Infection occurs even without direct contact with the patient. It is enough for microbes to get into the air through a cough, and after a while the person who inhaled them will feel that inflammation has now overtaken his tonsils. The reasons may also be domestic: sharing the same towel or cutlery with an infected person.
In the second case, the disease is transmitted from people who have passed the active stage of the disease, but the infection is not completely cured. It can also cause inflammation of the tonsils. In this case, bacteria spread throughout the body, and the lymph nodes, which act as a filter, trap them. As a result, the tonsils can still cope with the infection for some time, but then they weaken, and therefore inflammation of the tonsils occurs.
Questions for the doctor
Are tonsils and tonsils the same thing or are they different concepts?
Tonsil and tonsil are the same concept, these words have different origins: the word tonsil means “gland”, and the word tonsil comes from the ancient Greek “almond”. In medicine, the first term is more often used, although “tonsils” is also correct.
What is the amygdala and where is it located?
The amygdala, or amygdala, is a collection of nerve cells in the temporal lobe of the brain. It contains the center of fear and pleasure. It has nothing to do with the usual tonsils located in the oropharynx, except for a similar name.
Why does a person need such a complex throat structure?
The main function of the tonsils is to protect against infection; in addition, they play a role in the development of immunity and hematopoiesis. This structure allows them to perform their role well and protect the body.
I discovered holes in my tonsils. Is it a disease or are they needed for something?
The so-called “holes” are lacunae of the tonsils; in some people they are more pronounced, in others they are less pronounced. Pathological contents (plugs) may accumulate in the lacunae; in these cases, it is removed by washing.
Why is it recommended to remove enlarged tonsils if it is not a disease?
Hypertrophy (enlargement) can affect other organs: cause otitis media, reduce hearing, or cause inflammation. In these cases, it is recommended to get rid of the tonsils.
Other types
The use of antibiotics can lead to many side effects, but the benefits from them are still greater than the harm. That is why they are used in the treatment of inflammation of the tonsils. Antibiotics are mainly used for purulent plaque. In this case, the doctor prescribes a 5-day course of treatment.
Semi-synthetic drugs “Penicillin” and “Amoxicillin” (prescribed by a doctor for bacterial sore throat) have a wide spectrum of action. Contraindications for use are hypersensitivity to such drugs, renal failure and pregnancy. Side effects: tachycardia, dysbiosis, changes in consciousness and behavior, depression. These drugs are prescribed to adults and children.
Other antibiotics for inflammation of the tonsils: the drug "Amoxiclav" includes amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. It can be prescribed only after 12 years. The duration of treatment ranges from 5 to 14 days. When using this drug, strict control over the kidneys, liver and hematopoietic organs is necessary.
There are analogues of these drugs: Augmentin, Amosin and Flemoxin Solutab. When treating with antibiotics, the doctor may additionally prescribe products that support the intestinal microflora: these are Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Acipol and some others.
In addition to banal tonsillitis, inflammation of the tonsils can be caused by bacteria, viruses, and pathogenic fungi. Sore throat, in fact, is diphtheria of the tonsils, scarlet fever; symptoms of tonsillitis are observed with measles, herpetic infection, and may be present with leukemia, typhoid fever, and tularemia. It is impossible to describe a single picture that would accurately illustrate all the changes observed in all types of tonsillitis. Therefore, it is advisable to pay attention to the features of the most common pathologies:
- diphtheria;
- scarlet fever;
- herpetic sore throat.
Diphtheria is one of the most dangerous forms of tonsil damage. This is explained not only by a special type of inflammation (fibrinous), but also by the active production of a toxin by the pathogen, Corynebacterium. Local signs of diphtheria:
- enlargement of the tonsils due to edema;
- mild redness, sometimes with a cyanotic tint;
- the presence of dirty gray, whitish deposits with a smooth, sometimes wavy surface;
- moderate pain when swallowing.
Inflammation of the tonsils in diphtheria is characterized by the spread of dense plaque beyond their anatomical boundaries; When you try to remove it, the mucous membrane bleeds.
With scarlet fever, not only inflammation of the tonsils is observed, but also inflammation of the back wall of the pharynx and severe sore throat. Changes in the tongue are also characteristic - a dense white coating at the beginning of the disease and the acquisition of a bright pink hue after a few days. Symptoms of a sore throat are combined with a skin rash, the changes correspond to the picture of a common sore throat; with the necrotic form, areas of necrosis are visible in the form of ulcers on the surface of the tonsil.
Signs of inflammation of the tonsils with herpetic sore throat include:
- Redness, swelling.
- A sore throat.
- The presence of a blistering rash on the tonsils.
The rash can be located not only on the tonsils, but often spreads to the palatine arches, uvula, and pharynx. Bubbles appear with the formation of defects in the mucous membrane, usually not prone to fusion.
General signs depend on the form of the flow and a number of other factors. However, diphtheria is more often characterized by a moderate febrile reaction, while scarlet fever and herpetic sore throat are characterized by febrile and pyretic (38-39.9 ° C) indicators. The patient’s well-being is determined by the degree of intoxication - usually there is a headache, lethargy, pain in muscles and joints without a specific localization.
Diagnostics
If purulent plugs are observed on the tonsils, the tonsils become inflamed and swollen, you should consult an otolaryngologist. For oral ulcers that are accompanied by plaque formation on the tonsils, you should consult a physician or dentist. A pediatrician treats pus on a child's tonsils.
The diagnosis is made based on:
- visual inspection;
- analysis of patient complaints;
- oral swab.
A swab from the throat allows you to determine the nature of plaque on the tonsils, but the analysis is not mandatory and is prescribed for vague symptoms. Usually, it is enough for a doctor to examine the patient’s throat and listen to complaints in order to diagnose the cause of purulent plaque.
Complications
How dangerous is the inflammatory process in the tonsils? Sore throat can cause serious complications and lead to diseases of the cardiovascular system. With untimely diagnosis or inadequate treatment, the transition of an acute process to a chronic one is possible.
Streptococcal tonsillitis can cause purulent complications:
- otitis;
- sinusitis;
- mastoiditis;
- peritonsillar abscess;
- cervical lymphadenitis;
- meningitis;
- endocarditis;
- pneumonia.
Late non-purulent consequences are also possible:
- poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis;
- toxic shock;
- acute rheumatic fever.
The most dangerous complication of tonsillitis is rheumatism, which affects the joints and valve apparatus of the heart, leading to the formation of heart defects and the development of heart failure. Incompletely cured tonsillitis can lead to kidney disease (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis). Local complications of tonsillitis are paratonsillitis and paratonsillar abscess.
Inhalations for tonsillitis
Inhalations for tonsillitis are an additional method of therapeutic treatment, and during the procedure, drugs are applied to the surface of the tonsils, which will subsequently penetrate into the surface of the inflamed tonsils and help speed up recovery. The procedure itself can be carried out either at home using a nebulizer or steam inhaler, or in a physiotherapeutic treatment room at a clinic.
Inhalations for tonsillitis should be prescribed only by a qualified otolaryngologist, who evaluates not only the severity of local manifestations of the disease, but also the general condition of the patient’s body. In addition, it must be remembered that the use of antibiotic and antiseptic solutions for inhalation does not exclude the systemic prescription of antibacterial drugs, but only complements it.
The most important thing when prescribing inhalations is not to use drugs to which the patient’s body is hypersensitive, so antibiotics for local treatment of tonsillitis should be used with caution.
Most often, decoctions of plants with antiseptic and antibacterial effects are prescribed for inhalation for acute and chronic tonsillitis - sage, eucalyptus, chamomile, oak bark, pine buds, peppermint, calendula, coltsfoot, oregano, alcoholic solution of propolis, oil and alcohol chlorophyllipt solution, alkaline mineral waters, mucolytic agents.
You can also:
- Boil the potatoes “in their jackets” and breathe over them for 5-10 minutes, and then use the water drained after boiling the potatoes to make a warm compress on the throat. Rub the soles of your feet with garlic and wear woolen socks.
- Cut 1 head of garlic, put it in a saucepan, pour 1 liter of water into it, and as soon as the water begins to boil, add 1 teaspoon of baking soda and inhale (breathe over the saucepan) 3 times a day.
- If you suddenly become hoarse: boil the milk, skim it off and breathe over the pan, taking deep breaths as the steam rises.
- Chamomile flowers – 2 parts, sage leaves – 4 parts, eucalyptus leaves – 3 parts, peppermint herb – 2 parts, thyme herb – 2 parts, pine buds – 3 parts, elecampane roots – 4 parts
- 3 tbsp. l. pour the mixture into a kettle with 0.5 liters of boiling water, boil for 3-4 minutes. Then remove the kettle from the heat, put a paper funnel on its spout and breathe hot steam through your mouth for sore throat, pharyngitis, laryngitis, bronchitis.
The frequency of procedures and duration of treatment depend on the patient’s condition and the effectiveness of treatment.
Treatment of tonsillitis
Treatment of angina is broadly divided into conservative and surgical (sometimes it is also distinguished as conservative-surgical).
Conservative and conservative-surgical treatment is indicated for:
- acute catarrhal, lacunar, follicular tonsillitis;
- for chronic tonsillitis of simple form and toxic-allergic form of type 1.
Surgical treatment is used when:
- phlegmonous tonsillitis (acute, then the abscess is opened, and chronic, then the tonsils are removed);
- chronic tonsillitis of the toxic-allergic form of type 2 (to avoid further deterioration of the situation, they resort to tonsillectomy).
The type of pathogen (virus, bacteria or fungus) does not determine the type of treatment.
The determining factors here are:
- the degree of anatomical and physiological tissue damage;
- level of general intoxication of the body;
- degree of formation and dislocation of purulent exudate;
- development of complications.
Conservative treatment:
- antibiotic therapy - only during exacerbations, constant use of these drugs is unacceptable due to the negative effect on beneficial microflora and cellular immunity, antibiotics are clearly indicated for all bacterial sore throats (Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Cephalexin, Ceftibuten, Flemoxin, Spiramycin, etc. are used);
- antiviral agents are extremely important for viral tonsillitis (Acyclovir, Zovirax, Arbidol, Viferon, etc.), unlike antibiotics, they can be used cyclically in remissions with a chronic course;
- anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs - usually NSAIDs (Ibuprofen Analgin, Pentalgin, Tempalgin, Nurofen, Paracetamol, etc.) are taken spontaneously when appropriate symptoms occur (fever, pain), but with severe inflammation, especially in children, there is a risk of developing laryngeal edema ( false croup) and suffocation, then hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone) are used;
- rinsing, inhalation, lubricating the tonsils, resorption of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory tablets, compresses and heating - this is the most important component at the stage of healing of the acute form and the main therapy for the chronic form in remission, rinses are especially important, which wash away purulent formations, there are a huge number of remedies, including folk ones recipes, and every person knows at least a few - Kameton, Ingalipt, sea water, Gramicidin C, an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide, beet juice, a compress of fresh cabbage leaves and much more);
- physiotherapy - used only at the healing stage in the acute form and in cycles during the period of remission in the chronic form, this is a quartz tube (irradiation of the tonsils with ultraviolet rays). UHF (warming of the tonsil area from the outside with long-wave radiation), electrophoresis (local administration of various drugs using an electromagnetic field), galvanotherapy (treatment directly with weak currents), low-intensity laser therapy.
Surgical treatment is reduced to:
- puncture or cutting of phlegmon in case of paratonsillitis and subsequent washing of the resulting cavity from the remains of pus;
- removal of tonsils with a tonsillar loop or laser in case of repeated abscesses or in severe chronic cases, when an abscess does not form, but a number of systemic complications occur in the heart, kidneys, and blood vessels.
Conservative surgical treatment occupies an intermediate position and is a mild analogue of a more radical tonsillectomy. This treatment is considered lacunotomy. Shallow incisions are made between the lacunae (usually with a laser), which, after healing, stretch the surface of the palatine tonsils. And the gaps are smoothed out, which reduces the accumulation of pathogenic microflora.
Features in children
The main features of childhood sore throat:
- the most complete and pronounced symptoms, and therefore a higher severity of the course;
- increased risk of developing any complications, including transition to chronic disease;
- when moving into the chronicle - constant exacerbations, chronic tonsillitis in children is most often an indication for removal of the tonsils;
- the danger of false croup, when the larynx swells and breathing becomes critically difficult.
Otherwise, the disease progresses according to the standard scenario.
Traditional methods of treatment
There are many proven ways to treat purulent sore throat with homemade products and plants.
Chamomile and calendula decoction. To prepare the medicine, you will need to pour 2 tbsp into a small saucepan. l. herbs, pour 1 liter of boiling water over it and simmer the mixture over low heat for half an hour. The infusion cools for 2–3 hours, after which you need to start gargling.
Kalanchoe and aloe. Plants have anti-inflammatory properties. For the medicine you will need their leaves, which are more than three years old. The greens are crushed and squeezed, and the resulting juice is diluted with 1 glass of water. This natural product relieves swelling.
How to get rid of pus plugs in children
Before proceeding with therapeutic procedures, it is necessary to accurately establish the causes of the appearance of ulcers on the tonsils. Only after an examination and the necessary tests can a doctor with full responsibility recommend one or another method of combating the disease.
Do not try to remove ulcers from your child yourself using available home remedies. At best, such actions will be useless, but more often than not they will only further injure the mucous membrane of the tonsils, aggravating the situation.
How to treat tonsillitis: list of drugs
Topical preparations such as lozenges and lozenges have proven themselves to be effective in the treatment of sore throat, with complex preparations being more effective. For example, the drug Anti-Angin® Formula tablets/lozenges, which include vitamin C, as well as chlorhexidine, which has a bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect, and tetracaine, which has a local anesthetic effect. Due to its complex composition, Anti-Angin® has a triple effect: it helps fight bacteria, relieve pain and helps reduce inflammation and swelling1,2.
| Group of drugs | Mechanism of therapeutic action | Representatives | Mode of application |
| Antibiotics | They disrupt the formation of cell wall proteins, especially during division and growth. Causes the death of bacterial cells. | Ceftriaxone | Administer 1-2 g intramuscularly or intravenously once a day. |
| Ampicillin | Inside, regardless of food intake. Single dose of 0.5 g 4 times a day at regular intervals. | ||
| Amoxicillin | The dose is set individually, on average 0.5 g 3 times a day. | ||
| Sulfonamide drugs | They have a wide spectrum of action. They penetrate the bacterial cell and disrupt protein synthesis, preventing the growth and reproduction of microorganisms. | Sulfadimethoxine | Inside 1 time a day. On the first day the dose is 1-2 g, on the next 0.5-1 g. The duration of treatment is 7-14 days. |
| Sulfamonomethoxin | Take orally after meals. The first day 0.5-1 g 2 times a day. In the future, 5-1 g once a day. | ||
| Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs | Drugs for local treatment have an analgesic effect, reduce pain when swallowing and at rest. They also have an antimicrobial effect and reduce signs of inflammation. | Trachisan | Dissolve 1 tablet every 2 hours. |
| Neo-angin | 1 lozenge every 2-3 hours, preferably after meals. The maximum dose is 8 tablets per day. | ||
| Givalex spray | Use to irrigate the mouth 4-6 times a day. | ||
| Antiseptic solutions for rinsing | They disinfect and destroy bacteria in the oral cavity, help cleanse the lacunae of the tonsils from purulent contents. | Chlorophyllipt alcohol | The finished solution is diluted in a ratio of 1 tsp. per 100 ml of water. Repeat 4 times a day. |
| Chlorhexidine | 1 tbsp. rinse the mouth with the drug for 20-30 seconds 2-3 times a day. After the procedure, do not eat for 1.5-2 hours. | ||
| Antihistamines | Used for severe swelling of the tonsils. They help reduce swelling and reduce overall intoxication of the body. | Loratadine | 1 tablet 1 time per day. |
| Tsetrin | 1 tablet once a day. | ||
| Antipyretics | Take when the temperature rises above 38 degrees. Eliminates fever and body aches. | Paracetamol | 0.35-0.5 g 3-4 times a day after meals. |
| Ibuprofen | 400-600 mg 3 times a day after meals. |
What are tonsils: a brief description
This is an accumulation of lymphoid tissue in the pharynx, which begins to form in the womb. After a person is born, they actively grow until the age of 15, after which the reverse process begins. They are localized between the oral and nasal cavities and are represented by the palatine, tubal, pharyngeal and lingual tonsils. Normally they are small and imperceptible. The circular arrangement of these formations is called the pharyngeal lymphoepithelial ring. The granules of the posterior wall of the pharynx, its lateral ridges, the laryngeal tonsils and this ring form the lymphoid apparatus of the pharynx.
Forecast
With proper and timely treatment of acute primary tonsillitis of any kind, with a 95% probability everything will end well. Chronic tonsillitis is a little more complicated. Because the pathogens have already survived the primary immune attack and, probably, the main therapeutic methods. We can say that here the patient has a 50 to 50 chance. With persistent, systematic treatment, chronic tonsillitis will disappear without a trace. But there is exactly the same probability that certain consequences will still occur (problems with the heart and kidneys, damage to the immune system, removal of tonsils, etc.).
Is it contagious and how is it transmitted?
The acute form makes a person contagious for the entire period of the disease: from a two-day incubation period to complete recovery. The chronic form is dangerous for others during exacerbations. In remission, a person with chronic tonsillitis is considered conditionally non-infectious. But with prolonged close contact with a sick person (for example, this concerns the family circle), there is a chance of becoming infected during this period. Children of preschool and primary school age are especially vulnerable.
In severe chronic cases (type 2), the patient’s infectiousness practically does not subside. By the way, this is possible with
Complications and consequences
During the course of the article, most of the complications have already been mentioned.
The acute form of tonsillitis can cause two main complications:
- phlegmonous sore throat;
- transition of the disease to a chronic state.
And those, in turn, can give rise to a whole bunch of other diseases, many of which are life-threatening. With paratonsillitis, pus can begin to spread to other parts, causing abscesses in the mediastinum and cervical, purulent meningitis, damage to the cavernous sinus (connected to the veins of the brain) and blood poisoning when the walls of the tonsil arteries melt.
The chronic form is dangerous due to changes at the cellular and biochemical level. Streptococci synthesize proteins that are similar in structure to the structures of some tissue cells. And the immune system may mistakenly mistake the body's cells for foreign elements. This is one of the possible patterns of development of autoimmune diseases.
Doctors' recommendations
Therapy for sore throat necessarily includes gargling; if the deposits are localized deep in the crypts, it is better not to touch them so as not to provoke the development of complications. If it is necessary to remove accumulations, only a specialist in a medical institution can do this.
Opening and squeezing out purulent follicles on your own is very dangerous. At home, you cannot completely remove all the contents and clear your throat well. As a result of damage to the integrity of the mucous membrane, an unprotected wound surface is formed in the throat. It is an open gate for pathogenic bacteria to enter.
There is a high risk of developing an abscess, especially when pus penetrates deep into the tissue. Its occurrence can provoke a severe deterioration in the patient’s well-being. And the only method of getting rid of the problem is surgical intervention - opening the abscess.
Treatment of angina should be comprehensive and carried out under the supervision of a specialist. You should listen to your doctor's recommendations. This will help speed up the patient’s recovery and prevent the development of complications and side effects.
Photo of tonsillitis: what it looks like
Throat of a patient suffering from chronic tonsillitis of the toxic-allergic form of type 1.
Content may be difficult to view
A clear example of chronic tonsillitis, where increased looseness of the tonsils is especially clearly visible.
Content may be difficult to view
Typical picture of acute tonsillitis. Follicular and lacunar.
Content may be difficult to view
Content may be difficult to view
Prevention
To minimize the likelihood of developing tonsillitis in adults, it is necessary to begin strengthening the body’s defenses and immunity as early as possible.
- to harden;
- eat properly and balanced;
- ensure proper sleep;
- walk in the fresh air more often;
- carefully monitor oral hygiene;
- promptly sanitize foci of infection and treat teeth.
Tonsillitis in adults is a serious disease that needs to be treated as early as possible. If you take action in the early stages of the disease, you can recover quickly and prevent relapses and complications.
Tonsillitis is caused by various pathogens.
Therefore, careful diagnosis is required in order to correctly prescribe treatment. Self-medication for this disease is unacceptable and can lead to undesirable consequences. Sore throat in adults: treatment at home. How to cure a sore throat quickly Scarlet fever in children - symptoms and treatment at home Urticaria: symptoms and treatment
During pregnancy
The acute form of tonsillitis in pregnant women follows a general pattern. The only exception is that many antibiotics are highly discouraged for women during most of their pregnancy. Which creates an additional problem in selecting therapy. Macrolides often come to the rescue. The chronic form can lead to a child being born with an initially low immune status. Intrauterine infection of the child with sore throat pathogens may even occur. And this is especially harmful for the baby’s body. A pathogen in a newborn’s body can immediately attack the internal organs, “rewarding” him with a variety of chronic diseases. Therefore, allowing tonsillitis to become chronic during pregnancy is especially unacceptable. And if you already have one, then you need to try to keep the disease in deep remission for these 9 months.