- To which organs does stomach cancer most often metastasize?
- Symptoms
- Diagnostic methods
- Modern methods of treatment
- How long do you live with stage 4 stomach cancer?
The stage of stomach cancer is determined by three indicators, which are indicated by letters of the Latin alphabet:
- T ( tumor) - the size of the primary tumor, the depth of its germination into the stomach wall and spread to neighboring tissues.
- N ( nodes) - spread of cancer cells to the nearest (regional) lymph nodes.
- M ( metastasis) - the presence of metastases, secondary foci that arose as a result of the spread of cancer cells through the blood or lymph from the stomach to other organs.
In stage 4 gastric cancer, the primary tumor can have any size, grow into the stomach wall to any depth, spread or not spread to neighboring organs and lymph nodes. But there are always distant metastases. This is a key sign.
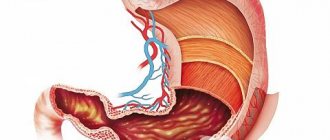
To which organs does stomach cancer most often metastasize?
Tumor cells can spread from the stomach to other organs in different ways:
- Cancer can directly grow into neighboring organs. Most often - into the pancreas, less often - into the transverse colon, the left lobe of the liver.
- Sometimes cancer cells spread along the surface of the peritoneum , a thin film of connective tissue that lines the inside of the abdominal wall and covers the internal organs. In this case, women often have metastases in the ovaries ( Krukenberg tumor ).
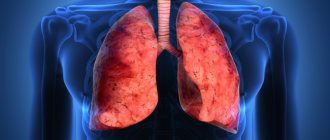
- By hematogenous route (through the bloodstream), stage 4 stomach cancer most often spreads to the liver, less often to the lungs and bones.
- Lymphogenic spread of cancer cells occurs along the hepatoduodenal ligament , celiac trunk , and splenic vessels.
With stomach cancer, specific metastases can occur. There are special names for them:
- Virchow's metastasis - in the lymph node located above the collarbone.
- Metastasis of Sister Mary Joseph - to the navel.
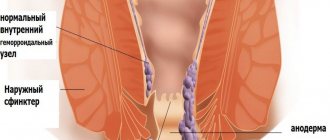
- Schnitzler metastases - to the lymph nodes located around the rectum.
- Irish metastases - to the lymph nodes located in the axillary region.
According to statistics, stage 4 gastric cancer most often metastasizes to the liver (48% of patients), peritoneum (32%), lungs (15%), and bones (12%).
TYPES AND FEATURES
Lung cancer is divided into central or peripheral forms. Neoplasms of the central form of cancer begin their development in the large bronchi. Primary symptoms of this type occur early (chest pain, dry cough, shortness of breath, hemoptysis). In the peripheral type, the tumor spreads to nearby organs and quickly increases in size. Cancer of this type is asymptomatic in the first stages of development. The first signs, shortness of breath, chest pain, appear after a significant increase in the tumor.
Symptoms
With stage 4 stomach cancer, nonspecific symptoms such as poor appetite and weight loss, up to severe exhaustion ( cachexia ), discomfort, a feeling of heaviness, bloating and pain in the abdomen, heartburn, nausea and vomiting (sometimes with blood), constipation, blood in the stool.
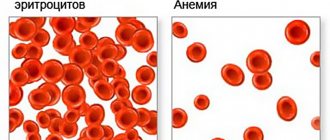
Specific symptoms are gastric bleeding due to tumor disintegration and anemia due to blood loss. Damage to peritoneal tumor cells leads to ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity). Also characteristic are foul-smelling black stools and vomiting in masses resembling coffee grounds.
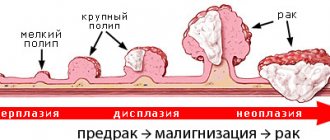
Stomach cancer does not make itself felt for a long time. In the early stages, many people do not experience symptoms and do not know they have the disease. In four out of five patients, the diagnosis is made when the tumor has already spread to other organs.
People at increased risk of stomach cancer should undergo regular screening - gastroscopy . This helps diagnose the tumor in the early stages.
Why do they die?
At the fourth stage of cancer, irreversible processes in the body begin, and it is almost impossible to save the patient. The cancerous tumor grows and quickly becomes huge and aggressive. Malignant cells spread, affecting other healthy organs. To reduce pain and prolong the patient's life, chemotherapy and radiation are prescribed, which reduce the aggressiveness of cancer cells.
The aggressiveness of the myeloma form of the disease quickly kills a person.
People with cancer die due to the following complications:
- oncology has spread throughout the body;
- major organs have been damaged;
- aggressive forms of cancer emerged: myeloma, melanoma.
Diagnostic methods
For stage 4 gastric cancer, different diagnostic methods are used, they help to identify the primary tumor and secondary lesions in other organs:
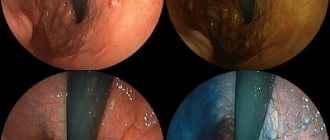
- Endoscopic examination (gastroscopy, FGDS) helps to detect pathological changes in the gastric mucosa.
- Endoscopic ultrasound is essentially the same as FGDS, but there is an ultrasound sensor at the end of the gastroscope. It can “illuminate” neighboring organs and lymph nodes through the stomach wall. This is often much more informative than a regular ultrasound.
- Biopsy . A study during which the doctor obtains a sample of tumor tissue and sends it to a laboratory for analysis. At the moment, a biopsy can be called the most accurate method for diagnosing cancer. You can examine the tissue of the stomach, lymph nodes, and other organs.
- Contrast enhanced radiography . This diagnostic method is used quite rarely, since gastroscopy is more informative (in addition, during it you can take material for a biopsy). But radiography is a less invasive method; during it, no instruments are inserted into the stomach. Sometimes this advantage is important. The essence of the method is that the patient is given a solution of barium sulfate, which is impenetrable to X-rays, to drink, then photographs are taken.
- CT scan . A more “advanced” type of radiography allows you to obtain layer-by-layer images - “slices” of the entire body, on which the stomach tumor and lesions in other organs will be visible.
- MRI is, in a sense, an analogue of computed tomography, but during this study, instead of X-rays, a powerful magnetic field is used. It's safer. MRI “sees” soft tissue better. The disadvantage of the method is that it is more complicated; you need an expensive device, which not all clinics have.
- Positron emission tomography (PET) . Ideal for searching for metastases that cannot be detected by other diagnostic methods. Safe radioactive sugar is introduced into the body. It accumulates in cancer cells as they actively consume energy, and makes them visible in special images.
- Chest X-ray . Used to search for metastases in the lungs.
Causes
So far, scientists have not figured out the exact cause of any oncology. But there are certain statistics of patients who were exposed to certain factors. For now, based on it, oncologists can provide data on risk factors.
- Genetics and the presence of oncogene.
- Smoking and alcohol have a detrimental effect and destroy the walls of the stomach.
- Junk food - canned food, food with dyes, carcinogens and flavoring additives is foreign to the body.
- Radiation and ecology - back in the last century, scientists proved that radiation rays cause cancer, and ecology worsens health and suppresses immunity.
- Chemical poisoning.
- Long courses of medications.
- Ulcer, gastritis, pancreatitis.
Modern methods of treatment
Treatment for stage 4 gastric cancer has two goals:
- Reduce the size of the tumor and slow its progression.
- Eliminate symptoms: pain, anemia, gastric obstruction, ascites.
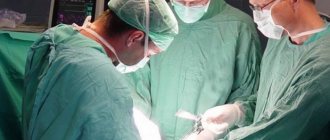
Surgery
Surgery for stomach cancer is usually aimed at restoring patency if the tumor interferes with the movement of food. Sometimes it is possible to perform a subtotal resection - to remove part of the stomach. bypass surgery is performed : a connection is created between the upper part of the stomach and the jejunum, bypassing the area blocked by the tumor.
In cases where surgery cannot be performed, gastric stenting . a stent is installed using an endoscope - a hollow frame with a metal mesh wall. Sometimes endoscopic ablation : a laser beam is delivered through the endoscope, which destroys the tumor tissue.
If a person with stage 4 stomach cancer is unable to eat normally and surgery does not correct it, a gastrostomy tube or jejunostomy tube . The stomach or jejunum is sutured to the skin and an opening is formed. Nutrition will occur through it.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy
For gastric cancer with metastases, palliative chemotherapy and radiation therapy are performed. Their main task is to reduce the size of the tumor and prolong the patient’s life. Different combinations of chemotherapy drugs are used:
- Epirubicin + cisplatin + 5-fluorouracil.
- Docetaxel + cisplatin + 5-fluorouracil.
- Irinotecan + cisplatin.
- Irinotecan + 5-fluorouracil.
- Irinotecan + capecitabine.
- Oxaliplatin + 5-fluorouracil.
- Oxaliplatin + capecitabine.
Three-drug combinations, as well as chemotherapy combined with radiation therapy (chemoradiotherapy) are more effective, but are less well tolerated and carry a higher risk of side effects.
Targeted therapy
Targeted drugs may be effective in cases where chemotherapy does not help. This is a modern group of antitumor drugs; they attack certain target molecules that are important for the growth of tumor tissue. For stage IV gastric cancer, two targeted drugs are used:
- Trastuzumab HER2 receptor protein , which is found on the surface of cancer cells and causes them to multiply. The activity of this protein is increased in every fifth malignant stomach tumor (such cancer is called HER2-positive ).
- Ramucirumab blocks VEGF , a protein produced by cancer cells that stimulates the growth of new blood vessels that supply the tumor with oxygen and nutrients.
Targeted drugs are used alone or in combination with chemotherapy. They are effective when cancer cells have certain molecular genetic characteristics, when the activity of the corresponding “target substance” is increased in them.
Immunotherapy
The human immune system is very complex. It has many links and various regulatory mechanisms. For example, in order to restrain itself from attacking its own healthy tissues, the immune system uses special substances - checkpoints . Sometimes they are used by malignant tumors to protect themselves from immune attack. Modern medications that belong to a class of immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors .
For stage 4 stomach cancer, a checkpoint inhibitor called pembrolizumab (Keytruda ) is sometimes effective.
Treatment of anemia
Bleeding from stomach cancer can lead to anemia, a condition in which the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin in the blood decreases. As a result, the quality of life and survival rate deteriorate. It is necessary to reduce the doses of chemotherapy drugs and shorten the duration of chemotherapy courses, the treatment becomes less effective.
Anemia in stage 4 stomach cancer is combated with the help of iron supplements, folic acid, vitamin B12, and red blood cell transfusions. There are drugs analogous to the hormone erythropoietin , which is produced by the kidneys and activates the formation of new red blood cells in the red bone marrow. Some dietary recommendations can help provide the body with additional iron.
Treatment of ascites in stage 4 gastric cancer
Ascites, an accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, is one of the most common complications of stage IV gastric cancer. This condition occurs for two reasons:
- Due to cancer metastases into the peritoneum . At the same time, the permeability of the walls of blood vessels increases, the fluid from them enters the abdominal cavity in greater quantities. The functioning of the lymphatic vessels is disrupted, they cannot remove fluid.
- Due to metastases in the lymph nodes . The outflow of lymph is disrupted; the lymphatic vessels, which normally should remove fluid from the abdominal cavity, can no longer perform their function.
For ascites, laparocentesis : a puncture is made in the wall of the abdominal cavity and excess fluid is removed through it. In order to ensure gradual removal of fluid over a period of time, special peritoneal port systems . Intraperitoneal chemotherapy, when the chemotherapy drug is injected into the abdominal cavity, helps destroy metastases in the peritoneum. Any type of treatment requires a special diet and a number of medications to reduce nausea.
Last days of life
The care of loved ones is very important for a dying person.
It is close people who create favorable conditions for the patient, which at least for a short time alleviate his suffering. Patients with the fourth stage of cancer are usually not kept within the walls of the hospital. Such patients are sent home. Before death, patients take strong painkillers. And yet, despite this, they continue to experience unbearable pain. Death from cancer may be accompanied by intestinal obstruction, vomiting, hallucinations, headaches, epileptic seizures, and hemorrhages in the esophagus and lungs.
By the time the last stage occurs, almost the entire body is affected by metastases. The patient is entitled to sleep and rest, then the pain torments him to a lesser extent. The care of loved ones is very important for a dying person at this stage. It is close people who create favorable conditions for the patient, which at least for a short time alleviate his suffering.
How long do you live with stage 4 stomach cancer?
The main prognostic indicator for cancer is five-year survival rate . It indicates the percentage of patients who are alive 5 years after diagnosis and initiation of treatment for a malignant tumor. For stage IV gastric cancer this figure is 4%. Within five years, 96 out of 100 patients die, 4 remain alive. But such depressing statistics are not a reason to give up. Treatment methods are improving, and oncologists can do much more today than they could decades ago. Patients who do not respond to standard treatments can take part in clinical trials of new drugs.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+78
Disease prevention
Preventing the development of stomach cancer involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This means giving up bad habits (alcohol, smoking), following a diet and normalizing your daily diet (eating in small portions 5-6 times a day). Once a year, undergo a preventive examination by a gastroenterologist. Only a specialist can detect the first signs of the disease. These measures do not act as a 100% guarantee that a person will not get stomach cancer; they will help to significantly reduce the risk of this terrible disease.