Important: the frequency of atrial contractions during AF reaches 350-600 beats/60 seconds. A prolonged attack of such a heart rhythm disorder (lasting longer than 2 days) significantly increases the risk of thrombosis and the development of ischemic stroke.
The constant form of atrial fibrillation is the factor that causes the rapid progression of chronic circulatory failure.
Important: according to statistics, 30% of clinical cases associated with hospitalization of patients with arrhythmias are caused by atrial fibrillation. The prevalence of AF is directly proportional to the age of the “victims”: atrial fibrillation is diagnosed in 1% of patients who are not yet 60 years old, and in 6% of patients who have crossed this age limit.
Classification
The main criterion for typing a problem is the duration of the course. Based on this, three forms of the pathological process are distinguished:
- Paroxysmal form. Most common. At the same time, it poses the least danger to health and life. Paroxysm of atrial fibrillation (attack) lasts from 2 hours to a week and is accompanied by a minimum of symptoms. The efficiency of the heart and muscle contraction is significantly reduced. Hence tissue hypoxia. At this stage, the problem can only be identified through electrocardiography, and even then not always. It has the ability to transform into more complex types and progress. Symptoms are attributed to fatigue, lack of sleep, and physical activity.
- Persistent form. An attack of atrial fibrillation continues for more than 7 days, but not on an ongoing basis. This is a more resistant variety. It requires increased attention and urgent treatment. The manifestations are pronounced, but also nonspecific.
- Finally, the chronic or permanent form. The most dangerous in terms of consequences. Thus, the risk of developing a heart attack or stroke in persistent and terminal stages of atrial fibrillation is 30%, and increases in proportion to the duration. The incidence of coronary disease or heart failure is 65% and even higher. Treatment reduces the risks significantly (see forecast).
There are also less informative classification methods. Depending on the manifestation, a primary type is distinguished (formed as an initial, newly identified pathology) and a recurrent type (there was once a paroxysm, now it is repeated).
Clinical variants of atrial fibrillation are as follows:
- Normosystolic variety. Against the background of an adequate heart rate, from 60 to 80 or a little more beats per minute.
- Tachysystolic. Pulse over 90 beats. per minute
- Bradysystolic. Heart rate less than 60 beats. per minute
In this case, where are the 300-600 abbreviations mentioned here? The devil, as they say, is in the details. As already noted, these are not blows, these are tissue flutters, which are recorded by objective methods. The patient does not feel them. Example on ECG:
Principles of treatment of atrial fibrillation
When planning treatment for atrial fibrillation, the doctor is faced with a choice: try to return the correct rhythm or maintain the arrhythmia, but with a normal heart rate. Recent studies show that both treatment options are good, and pulse control even in the presence of arrhythmia improves survival rates and reduces the incidence of thromboembolism as complications.
Treatment of patients with atrial fibrillation aims to eliminate the negative symptoms of arrhythmia and prevent severe complications. To date, two patient management strategies have been adopted and used:
- Heart rhythm control - restoration of sinus rhythm and drug prevention of arrhythmia relapses;
- Control of heart rate (heart rate) - the arrhythmia remains, but the heart rate is reduced.
All persons with an established diagnosis of arrhythmia, regardless of the chosen strategy, are given anticoagulant therapy to prevent thrombus formation in the atria, the risk of which is very high in atrial fibrillation, both permanent and during paroxysm. Based on the manifestations of arrhythmia, age, and concomitant pathology, a treatment plan is drawn up individually. This may include cardioversion, drug maintenance of the target heart rate, and prevention of repeated episodes of fibrillation and thromboembolic syndrome is mandatory.
Anticoagulant therapy
Atrial fibrillation is accompanied by an extremely high risk of thrombus formation with embolism in a large circle and the manifestation of the most dangerous complications, in particular embolic stroke, therefore it is very important to prescribe anticoagulant therapy - antiplatelet agents, direct or indirect anticoagulants.
Indications for prescribing anticoagulants are:
- Age up to 60 years, when there is no structural damage to the myocardium or with it, but without risk factors - acetylsalicylic acid is indicated;
- After 60 years, but without predisposing factors, aspirin and cardiomagnyl are prescribed;
- After 60 years, with diagnosed diabetes or coronary heart disease, warfarin under INR control is indicated, possibly in combination with aspirin;
- At the age of 75 years and older, especially women, as well as in cases of severe concomitant diseases (thyrotoxicosis, congestive heart failure, hypertension), warfarin is prescribed;
- Rheumatic heart defects, previous valve surgeries, previous thrombosis or embolism require the mandatory use of warfarin.
Anticoagulant therapy includes:
- Indirect anticoagulants - warfarin, Pradaxa - are prescribed long-term under the control of a coagulogram (INR is usually 2-3);
- Antiplatelet agents - acetylsalicylic acid (thrombo ass, aspririn cardio, etc.) at a dose of 325 mg, dipyridamole;
- Low molecular weight heparins are used in acute situations, before cardioversion, and reduce the length of hospital stay.
It should be borne in mind that long-term use of blood thinners can cause adverse consequences in the form of bleeding, therefore, anticoagulants are prescribed with extreme caution to persons with an increased risk of such complications or decreased coagulability based on the results of a coagulogram.
A. Rhythm control strategy
A rhythm control strategy involves the use of pharmacological agents or electrical cardioversion to return the rhythm to normal. In the tachysystolic form of arrhythmia, before restoring the correct rhythm (cardioversion), it is necessary to reduce the heart rate, for which beta-blockers (metoprolol) or calcium antagonists (verapamil) are prescribed. In addition, cardioversion requires mandatory anticoagulant therapy, because the procedure itself significantly increases the risk of thrombosis.
Electrical cardioversion
Electrical cardioversion is the normalization of rhythm using electric current. This method is more effective than administering medications, but is also more painful, so patients receive sedatives or undergo superficial general anesthesia.
Direct restoration of sinus rhythm occurs under the influence of a cardioverter-defibrillator, which sends an electrical impulse to the heart, synchronized with the R wave, so as not to cause ventricular fibrillation. The procedure is indicated for patients in whom the administration of pharmacological agents does not produce results or in cases of circulatory instability due to arrhythmia. It is usually performed externally, by applying a shock to the skin, but intracardiac cardioversion is also possible if the superficial method is ineffective.
Cardioversion can be planned, then the patient takes warfarin for 3 weeks before and 4 after. The planned rhythm restoration procedure is prescribed for those whose arrhythmia lasts more than two days or its duration is unknown, but the hemodynamics are not impaired. If the arrhythmia paroxysm lasts less than 48 hours and is accompanied by severe circulatory disorders (hypotension, for example), urgent cardioversion is indicated, subject to the mandatory administration of heparin or its low-molecular-weight analogues.
Pharmacological cardioversion
To restore sinus rhythm through drug therapy, antiarrhythmic drugs are prescribed:
- Procainamide;
- Amiodarone;
- Propafenone;
- Nibentan.
Procainamide is administered intravenously, but causes many side effects - headache, dizziness, hypotension, hallucinations, changes in the leukocyte formula, which is why it is excluded from the list of drugs for cardioversion by European specialists. In Russia and many other countries, procainamide is still used due to the low cost of the drug.
Propafenone is available in both solution and tablet form. In case of persistent atrial fibrillation and flutter, it does not have the desired effect, and is also contraindicated in chronic obstructive diseases of the pulmonary system and is extremely undesirable for use in persons with myocardial ischemia and reduced contractility of the left ventricle.
Amiodarone is available in ampoules, administered intravenously and is recommended for use in the presence of organic lesions of the heart muscle (post-infarction scars, for example), which is important for the majority of patients suffering from chronic cardiac pathology.
Nibentan is available as a solution for intravenous infusion, but can be used exclusively in intensive care units, where rhythm control is possible throughout the day after its administration, since the drug can provoke severe ventricular arrhythmias.
Indications for pharmacological cardioversion are cases when atrial fibrillation has occurred for the first time or a paroxysm of arrhythmia occurs with a high frequency of heart contractions, leading to negative symptoms and hemodynamic instability that cannot be corrected with medication. If the likelihood of subsequent maintenance of sinus rhythm is low, then it is better to refuse drug cardioversion.
Pharmacological cardioversion gives the best results if it is started no later than 48 hours after the onset of the arrhythmia attack. The main drugs for atrial arrhythmia occurring against the background of congestive heart failure are amiodarone and dofetilide, which are not only highly effective, but also safe, while the use of procainamide, propafenone and other antiarrhythmics is undesirable due to possible side effects.
The most effective drug for restoring rhythm during paroxysmal atrial fibrillation is amiodarone. According to research results, when taken for two years by patients with chronic heart failure, overall mortality is reduced by almost half, the likelihood of sudden death by 54%, and the progression of heart failure by 40%.
Antiarrhythmic drugs can be prescribed for a long time to prevent recurrent arrhythmias, but in this case the high risk of side effects along with the relatively low effectiveness must be taken into account. The question of the advisability of long-term therapy is decided individually, and the preferred medications are sotalol, amiodarone, propafenone, and etacizine.
b. Rate control strategy
When choosing a strategy for controlling heart rate, cardioversion is not resorted to at all, but drugs that slow down the heart rate are prescribed - beta-blockers (metoprolol, carvedilol), calcium channel blockers (verapamil, diltiazem), amiodarone if the previous groups are ineffective.
The result of the chosen strategy should be a pulse no higher than 110 per minute at rest. If the symptoms are severe, then the heart rate is maintained at a level of up to 80 beats per minute at rest and no more than 110 during moderate exercise. Pulse control reduces the manifestations of arrhythmia, reduces the risks of complications, but does not prevent the progression of the pathology.
V. Catheter ablation
Catheter radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is indicated when electrical and pharmacological cardioversion are ineffective or the normal rhythm is not maintained by antiarrhythmic drugs. RFA is a minimally invasive endovascular intervention when an electrode is inserted through the femoral vein and then sent to the heart, where an electric current destroys the atrioventricular node, His bundle fibers, or isolates areas of pathological impulses at the mouths of the pulmonary veins.
In the event of destruction of the atrioventricular node or His bundle, complete transverse block occurs when impulses from the atria do not reach the ventricular myocardium, so this ablation is followed by the installation of a pacemaker.
For rare paroxysms of atrial fibrillation, which, however, occur with severe symptoms, intra-atrial cardioverter defibrillators can be implanted, which do not prevent arrhythmia, but effectively eliminate it if it occurs.
The mechanism of pathology development
The mechanism is always approximately the same. As a result of disruption of the conductivity of the heart fibers, a chaotic distribution of the electrical impulse occurs.
All parts of the organ contract “haphazardly”, there is no coordination of the atria. At the same time, the sinus node continues to work as it should: it generates new signals. Partial coordination of reductions is possible, but positive dynamics are still not observed.
Why are fibrillations dangerous?
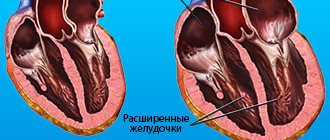
heart function in atrial fibrillation
The heart is a hollow muscular organ whose main function is to pump blood through the vascular system. As a result of its periodic contractions, all tissues of the body receive oxygen and nutrients in a timely manner, and carbon dioxide and toxic metabolic products are quickly removed from it. The work of the “blood pump”, consisting of four sections - two atria and two ventricles, must be coordinated. The organ sections function sequentially: the contractile movement of the atria is followed by that of the ventricles. The contraction frequency of the first and second mentioned chambers of the heart should be the same.
Fibrillation is characterized not only by its increase to frightening numbers, but also by the lack of coordination of the movements of the organ departments. The atria and ventricles begin to contract unevenly.
When chaotic, unregulated contractions of the heart muscle occur, the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the organs stops; the nervous system, in particular the brain, is especially sensitive to this. The lack of blood supply for just 5-6 minutes leads to the death of a person.
Also complications of cardiac fibrillation are:
- The formation of thrombotic masses in the atria and their blockage of arterial vessels (brain (stroke) and other organs).
- Cardiomyopathy (dilated form). Overload of the myocardium leads to expansion of all organ cavities.
- Cardiac arrest due to cardiogenic shock.
Causes of cardiac profile
In 70% of cases, the disease is of purely cardiac origin, the remaining 20 are due to noncardiac causes and 10% to mixed factors.
- Severe heart failure. To tell the truth, you need to try hard for atrial fibrillation to occur against the background of the disease.
The patient population consists of older people or people who have recently suffered a major myocardial infarction. Functional tissues are replaced by scar tissue, hence the decrease in the conductivity of the structures.
- Arterial hypertension. This kind of problem begins to arise at stages 2-3, in patients with a decent history of the pathological process. Another reason to promptly contact your treating specialist for help. Better early. The symptoms are typical: headaches, vertigo, nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, flickering of spots before the eyes, tinnitus.
- Inflammatory lesions of cardiac structures. Myocarditis, endocarditis. They can result in total destruction of the atria with the need for emergency prosthetics.
The essence of the process is the same as during a heart attack. The replacement of functional connective tissue occurs.
The disease has several nonspecific symptoms: increased heart rate, chest pain, shortness of breath and discomfort when walking.
- Congenital and acquired malformations of the heart. Requires surgical correction. Identified in childhood and adulthood. More often on the pathologist’s table, after the fact.
Diverse in nature, but typical in clinical picture, accompanied by chest pain, nausea, shortness of breath and rapid fatigue, problems with physical activity.
- Rheumatoid pathologies that destroy cardiac structures. They make themselves known extremely poorly. It can only be identified by objective methods. Therefore, every six months to a year you should undergo general and biochemical blood tests. Attention is drawn to increased levels of ESR and C-reactive protein (in particular).
- Myocardial infarction and subsequent cardiosclerosis. The intensity of the changes depends on the severity and extent of tissue damage. Read more about post-infarction cardiosclerosis and treatment methods here.
Differential diagnosis
In addition to atrial waves, AF is distinguished from sinus rhythm by different distances between the ventricular complexes and the absence of the P wave.
When intercalary complexes occur, diagnosis with ventricular extrasystoles is required. With ventricular extrasystole, the coupling intervals are equal to each other, there is an incomplete compensatory pause, and the background is normal sinus rhythm with P waves.
Emergency care for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation consists of stopping the action and treating the cause of the disease and hospitalization in a cardiology hospital; to stop the attack, the tactics of medicinal rhythm restoration are used - 300 mg of cordarone intravenously.
Extracardiac causes
Besides cardiac reasons:
- Hyperthyroidism. An excess of specific hormones of the thyroid gland, and, partly, the pituitary structure. Accompanied by increased blood pressure, body temperature, weakness, swelling of the neck (goiter), drowsiness, headaches, and bulging eyes. Atrial fibrillation is the result of excessive stimulation of cardiac structures.
- Nervous-mental stress. In this case, the change in cardiac activity is temporary, paroxysmal in nature and lasts no more than 1-2 hours. You can even cope with the problem on your own, using products from your home first aid kit.
- Intoxication with harmful substances: salts of heavy metals, glycosides and antihypertensive drugs.
In some cases, even after a complete diagnosis, it is not possible to determine the causes. In such a situation, they speak of the idiopathic form of atrial fibrillation. Treatment is symptomatic.
Why does cardiac fibrillation occur?
The vast majority of patients diagnosed with ventricular or atrial fibrillation suffer from various ailments. Conventionally, they can be divided into groups:
Pathologies of the heart itself and surgical operations on it
- Angina pectoris (coronary heart disease) and its consequences - myocardial infarction;
- Inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis);
- Rheumatic organ defects;
- Cardiomyopathies (myocardial pathologies as a result of various hormonal disorders, metabolic disorders, alcoholism, drug use);
- Cardiosclerosis (replacement of part of the muscle fibers with connective tissue);
- Anomalies in the development of the heart and its conduction system;
- Surgical intervention (coronary artery bypass grafting).
A sharp decrease in total blood volume
- Volumetric blood loss. As a result, a sudden drop in blood pressure occurs, and the body compensates by increasing the strength and frequency of contractions of the heart muscle.
Diseases of other organs
- Severe poisoning (hypokalemia occurs with increased excitability of the heart muscle).
Disorders of the nervous or endocrine systems
- Pathologies of the thyroid gland with hormonal imbalance.
- Severe chronic stress or severe simultaneous nervous strain.
Overdose of cardiac glycosides, diuretics
Sometimes this type of arrhythmia occurs in people who do not suffer from any of the above ailments, and the cause cannot be determined. In this case, fibrillation is called idiopathic.
Characteristic symptoms
They are nonspecific, which, on the one hand, does not motivate the patient to see a cardiologist, on the other hand, it does not make it possible to quickly make a diagnosis and complicates the examination.
Among the manifestations:
- Weakness in the legs. The person cannot move normally and tends to lie down more.
- Sweating. Even with minimal physical activity.
- Polyuria. Increased volume of urine output. As a rule, paroxysm ends with this phenomenon; it is necessary to distinguish this type of arrhythmia from classical tachycardia.
- Trembling, tremors in the limbs.
- Feeling of unreasonable fear. Accompanies a panic attack: the vegenative component of an acute attack.
The tachysystolic form is much more difficult to tolerate: the patient feels disturbances in the functioning of the heart. In addition, the following signs of atrial fibrillation are observed:
- Headache for no apparent reason.
- Vertigo.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Fainting.
- Attacks of a sharp drop in blood pressure (Morgagni-Adams-Stokes), which can lead to a stroke.
The duration of the picture corresponds to the duration of the paroxysm. With persistent or chronic varieties, the symptoms are blurred, the patient learns not to notice them, which is not good: the process does not go away and is gaining momentum every day, slowly bringing death closer.
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation depend on the form, degree of disturbance, individual characteristics of the patient’s body and the electrical activity of the heart.
What are the forecasts?
Following the doctor's recommendations will help a person stay healthy.
The chances of successful recovery depend on the underlying cause of the atrial fibrillation. If the pathology occurs against the background of congenital or acquired heart defects, the prognosis is disappointing. The patient's heart failure rapidly progresses, and the risk of death increases. If severe cardiac disorders are not identified, the heart generally functions normally, the patient can lead a normal lifestyle, but do not forget about the diagnosis and apply the doctor’s preventive recommendations to maintain the health of the cardiovascular system.
Diagnostic measures
Cardiologists are involved in the management of patients with this problem. Other specialists join as assistants to combat the cause of the condition. Statement of fact is possible at the initial appointment.
Among the events:
- Determination of patient complaints. Usually they are minimal or absent altogether.
- Anamnesis collection. Lifestyle, family history, somatic and mental illnesses, etc.
- Physical examination. Assessing the peripheral pulse, listening to heart sounds (they are erratic and differ in volume). The number of beats is higher than the number of waves. A characteristic feature of the pathogenic process.
- Verification of the diagnosis is carried out using classical methods:
- Electrocardiography. Determines the type of condition, the degree of functional impairment.
- Daily Holter monitoring to identify the dynamics of changes in the pulse rate within 24 hours (duration of attacks, their relationship with physical activity).
- Load tests (veloerogmetry).
- Echocardiography. To assess the characteristics of cardiac structures.
- TEE in rare cases to determine the nature of atrial fibrillation.
In the absence of data for cardiac causes, you need to look further. You will need: thyroid scintigraphy, ultrasound, MRI, blood tests.
Clinical and instrumental research
Upon examination and auscultation, irregular pulse and heart rhythm . The difference between heart contractions and pulse is determined. Laboratory tests are necessary to determine the etiology of the disease.
The diagnosis is confirmed by electrocardiography.
ECG signs of atrial fibrillation : instead of P waves, f waves are recorded with a frequency of 350-600 per minute, which are especially clearly visible in lead II and the first two chest leads. With tachyform, along with waves, the distance between QRS complexes will be reduced.
This is what atrial fibrillation looks like on an ECG:
If the form is not constant, daily monitoring is indicated, which will help identify attacks of atrial fibrillation.
To stimulate possible myocardial activity, transesophageal stimulation and intracardiac EPI . All patients require echocardiography to establish hypertrophic processes in the heart chambers and identify the ejection fraction.
Therapy depending on stage
Treatment of atrial fibrillation is systemic: using drugs, electrical methods and, in extreme cases, radio wave ablation of the heart.
The paroxysmal form is eliminated by medication and minimally invasive methods.
Among the necessary drugs:
- Cardiac glycosides. Digoxin and lily of the valley tincture. They normalize the rhythm by enhancing the contractility of the myocardium.
- Alpha and beta blockers. Anaprilin, Carvedilol and analogues.
- Calcium channel blockers. Diltiazem, Verapamil.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs (Hindin).
Cardioversion is used to urgently stop an attack. Normalization is carried out by electrical discharge. This is a safe and effective procedure (the result is achieved in 90% of cases). Therapy is carried out under the control of cardiography and blood pressure levels.
Chronic and persistent forms are eliminated by medication. In addition to the drugs already mentioned, the following are used: Atenolol, Bisoprolol (adrenergic blockers). Radical surgical therapy is possible.
Radiofrequency isolation of the pulmonary veins allows achieving results in 70% of situations.
In exceptional cases, ablation (or cauterization) of the atrioventricular node using an electrode is prescribed. This is a method of treating a resistant (unresponsive to drugs) form of the disease.
If controlled, people with atrial fibrillation live a long time, the duration does not differ from the national average (possible deviation - minus 5 years, however, this is a solvable problem).
Traditional recipes are not used due to ineffectiveness and danger. Lifestyle changes also have very little effect, which is due to organic persistent disorders. The specific names of drugs and their combinations are selected by the doctor; self-medication is excluded.
Types of MA
The classification of atrial fibrillation can vary. Thus, types of MA are distinguished on the basis of etiological (causing) factors, clinical course, as well as electrophysiological mechanisms of occurrence.
Thus, the main classification of atrial fibrillation includes persistent, chronic (constant), paroxysmal (transient) forms. The duration of an attack of paroxysmal MA is from 1 to 7 days, and signs of chronic and persistent MA can be detected for longer than 1 week.
Types of atrial fibrillation based on exactly how myocardial functions are disrupted:
- Flicker.
- Atrial flutter.
During fibrillation, only individual groups of muscle fibers contract, therefore, as such, the coordinated work of the atrium is not determined. A large number of electrical impulses converge at the atrioventricular junction: some remain “in place”, others diverge in the direction of the ventricles, as a result of which they function with a different rhythm.
Based on the frequency of ventricular contraction, experts identify the following forms of atrial fibrillation (measurement units – beats/minute):
- tachysystolic (from 90);
- normosystolic (60-90);
- Bradysystolic (less than 60).
Atrial flutter is a type of arrhythmia, which is characterized by rapid (200-400 beats/60 sec) contractions, provided that a consistent “healthy” atrial rhythm is maintained.
Possible complications
The likelihood of developing adverse consequences is determined by the form and duration of the process.
Among the phenomena:
- Thromboembolism. Formation of blood clots. The result of the adhesion of formed cells. Blockage of a large vessel will lead to death or gangrene.
- Heart failure and ischemic heart disease. The most likely outcome of the pathological process. Ends with myocardial infarction.
- Cardiogenic asthma.
- Pulmonary edema as a result of impaired drainage and venous-lymphatic outflow.
- Cardiomyopathy. It doesn’t make itself felt at all until the muscle organ stops working.
- Mitral valve stenosis.
- Cardiogenic (arrhythmogenic) shock. It is almost impossible to get out of this state. Mortality is close to 100%.
Risks are further influenced by current medical conditions: cardiac problems are associated with a worse outcome.
Prevalence
The prevalence of atrial fibrillation is 0.4%. Among the group under 40 years old this figure is 0.1%, over 60 years old – up to 4% .
It is known that in patients over the age of 75 years, the probability of detecting AF is up to 9%. According to statistics, the disease occurs one and a half times more often in men than in women.
The disease is based on the mechanism of re-entry of excitation into the atrial structures. This is caused by myocardial heterogeneity, inflammatory diseases, fibrosis, stretching, and previous heart attacks.
The pathological substrate cannot conduct the impulse normally , causing uneven contraction of the myocardium. Arrhythmia provokes expansion of the heart chambers and failure of function.
Forecast
The prognosis for life with atrial fibrillation is differentiated, depending on the stage and type of the disease:
- Paroxysmal is associated with a low likelihood of complications (5-7% within 3 years).
- The persistent form has a slightly worse outcome, the numbers are 8-12% over the same 3 years.
- A permanent or chronic type of atrial fibrillation causes a probability of 30-40%, regardless of the prospects: trouble can strike this very moment, tomorrow or in a year.
Subject to treatment, you can safely divide all the numbers presented by 1.5-2 or even more; with a good response to therapy, the risks are minimized.
Relapse prevention and prevention measures
Primary prevention of AF is used in cases of focal myocardial diseases and open heart surgery. It is necessary to eliminate risk factors for cardiovascular diseases : treat hypertension, lose weight, give up smoking, and fatty foods. You should also limit your consumption of strong coffee and alcoholic beverages.
To prevent relapses and complications, prescribed antiarrhythmic therapy should be used daily and follow the doctor’s instructions. It is very important to control blood clotting and INR levels.
If all instructions are followed and risk factors are eliminated, the prognosis is favorable . It is necessary to carefully prevent thromboembolic complications, take anticoagulants, and monitor the heart rate.
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: treatment
Treatment of paroxysmal AF depends on the length of the attack:
- if the last attack is at least 48 hours ago, then the main task of doctors is to restore sinus rhythm,
- when more time has passed, the likelihood of embolic complications is so high that strong treatment methods must be used. Use anticoagulants that prevent the formation of blood clots by forced blood thinning. And only after a month can we talk about restoring the heartbeat rhythm.
Preventive actions
Measures to prevent heart disease and arterial hypertension:
- avoid abuse of alcoholic beverages, and it is best not to take,
- do not do serious physical activity. But walking in the fresh air at a leisurely pace is beneficial.
- Eliminate fatty and salty foods from your diet. It's better to eat more fresh vegetables and fruits.
- As a preventive measure, the attending physician may prescribe medications, for example: sulfate or aspartate.
How to use folk remedies
Folk remedies used for arrhythmia are mostly safe. However, their use requires caution. A person with heart problems should be careful when using any medications, including natural ones.
How to use folk remedies:
- Medical consultation is required.
- The treatment is long-term - the drugs are taken in weekly or monthly courses. A single or double dose will not have a healing effect on the body.
- Each product is prepared according to a specific recipe. It is necessary not only to observe the proportions of ingredients when preparing them, but also recommendations for their use. Prepared infusions, decoctions and other folk remedies must be consumed in the exact dosage and frequency specified in the recipe.
- Products prepared in a water bath have the greatest effect. Such preparations retain much more useful substances than infusions.
- Plants used to prepare traditional recipes should be collected only in environmentally friendly areas.
- After taking the drug for the first time, you must carefully monitor your condition. If negative signs appear, use should be stopped and the product should not be used again.
- It has been proven that the human body better perceives medicinal plants grown in the area where he lives. It is not recommended to take drugs with exotic ingredients.
Attention! Plants used for folk remedies cannot be collected in cities; the minimum distance to the highway, landfills, and industrial complexes is 5 km.
If the drug contains highly toxic herbal ingredients, it is necessary to take supporting medications in parallel. It is recommended to take decoctions based on tartar and thistle.
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: symptoms
Signs of cardiac arrhythmia may vary from patient to patient. Some people experience pain in the heart area. While most patients with arrhythmic fibrillation are characterized by the following symptoms:
- a sudden single attack of palpitations,
- a sharp deterioration in health and weakness,
- lack of fresh air,
- feeling of coldness in the hands and feet,
- extreme sweating
- trembling throughout the body and more.
In some cases, pale areas of the skin and bluish lips are observed.
When the pathology is severe, the symptoms worsen. The following symptoms are observed:
- dizziness to the point of loss of consciousness,
- panic attacks caused by a sharp deterioration in general well-being and its normalization. As a result, the patient does not understand what is happening to him and worries about his own life.
Important! Whatever happens, first of all, do not panic and contact a specialist. Only after an examination (ECG) can you find out the cause of symptoms and health problems.
As soon as the paroxysmal rhythm disturbances, more precisely, seizures, are over, the patient experiences increased intestinal motility. The latter causes profuse urination. When there is a significant decrease in the number of heartbeats, the patient experiences a decrease in blood flow to the brain. Therefore, loss of consciousness occurs, breathing stops and the pulse cannot be felt. In this case, the patient needs urgent resuscitation.
Disease prevention
Primary preventive measures consist of intensive and extremely early treatment of “possible precursors” of arrhythmia. This could be heart failure or high blood pressure.
As for secondary prevention, it is aimed at:
- Maintaining specialist advice regarding anti-relapse drug therapy.
- Limiting psychological and physical stress.
- If necessary, undergo intervention by cardiac surgeons.
- Categorical refusal of alcohol and smoking.
If you suspect atrial fibrillation, you should immediately be examined by a doctor. It is important to promptly identify deteriorating health, establish the most accurate diagnosis, and undergo the necessary therapy.
(
1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Traditional medicine against arrhythmia
Of course, arrhythmia that occurs against the background of serious diseases of the cardiovascular system cannot be cured using traditional methods. But if irregular heart rhythms are associated with external causes, then it is possible to normalize heart function without resorting to medications.
To cure arrhythmia, you need to get rid of excess weight. It is important to avoid fatty foods and minimize the consumption of flour products. A balanced diet enriched with vitamins, microelements and nutrients will bring undoubted benefits and normalize heart function class=”aligncenter” width=”700″ height=”325″[/img]
Playing sports is beneficial for the heart; the main thing to remember is that physical activity should be moderate and selected in accordance with age. Swimming, walking and running strengthen the heart muscle well.
Advice! It should be remembered that morning exercises for arrhythmia should become a mandatory event.
In addition, to strengthen the heart muscle and prevent heart rhythm disturbances, traditional healers suggest regularly taking hawthorn infusions. Decoctions from:
- Motherwort;
- Valerian;
- Melissa.
Natural vitamin complexes that are prepared at home are considered very effective additional remedies in the treatment of arrhythmia:
- Rosehip decoction: boil 50 g of dried berries in a liter of water for ten minutes, after which the decoction is infused in a thermos for six hours;
- Viburnum decoction with the addition of honey: three glasses of pureed berries are poured with two liters of cooled boiled water and infused for six hours, and then half a kilogram of natural honey is added.
- A mixture of natural honey, freshly squeezed lemon juice and crushed apricot kernels.
- A mixture of dried fruits ground in a meat grinder, lemon with walnut peels and raisins with the addition of natural honey.
Radical therapy
To treat this pathology, more radical measures are provided:
- Electrical cardioversion (a small electrical shock is delivered through the chest);
- Catheter amblation (a thin tube is inserted into the heart muscle through a blood vessel, which allows pathological impulses to be generated);
- Operation Labyrinth. Incisions are made in the area of the atria and then reconnected. In their place, scars form, which prevent the occurrence of incorrect impulses.
Diet
Dietary nutrition for PF is mandatory. The diet should be based on foods enriched with potassium, magnesium and calcium. These substances are found in:
- bran and grain bread,
- buckwheat,
- green beans,
- pumpkin and sunflower seeds,
- wheat bran,
- cocoa,
- wheat and soy sprouts,
- red rice,
- oats and oatmeal,
- potatoes,
- bananas,
- cilantro,
- hard cheese,
- homemade fat cottage cheese,
- nuts,
- fish fillet,
- fermented milk products,
- vegetable oil.
The patient should not eat:
- sweets,
- homemade sour cream,
- scrambled eggs
- spicy dishes,
- canned food,
- fat meat,
- chocolate,
- rich meat broths,
- salo.
The consumption of alcoholic beverages and energy drinks is prohibited. Table salt and sugar can be used in minimal quantities.
What it is
Cardiac fibrillation is a condition in which the heart muscle, instead of normal contractions that help push blood through the vessels, makes too frequent or too infrequent movements.
When the disease occurs, chaos affects the entire heart muscle, but the provocateur is one section, so doctors distinguish between fibrillation of the heart in its upper and lower sections.
The heart is normal and with fibrillation
The normal human heart rate is between sixty and eighty beats per minute. When pathology occurs, it can increase in the atria up to seven hundred times, and in the ventricles up to four hundred and fifty. As you can see, there is a significant difference in the rhythmicity of the upper and lower parts of the heart, so the forms of fibrillation in them also differ.
Atrial arrhythmia:
- Flutter. It is characterized by a contraction frequency of up to four hundred and fifty times per minute. There is some coordination between the atria and ventricles so that the overall rhythm is balanced.
- Flicker . Here the rhythm of the atria is so fast that the ventricles cannot keep up with it, so chaotic behavior occurs in the contractions of the lower and upper sections.
In accordance with the course of the disease, fluttering is distinguished:
- Paroxysmal type. This diagnosis is made by doctors when the disease goes away on its own within seven days, or when the rhythm is restored with the help of a specialist’s intervention within two days.
- Persistent type . An attack of arrhythmia lasts more than one week; with the intervention of devices that restore rhythm, heart contractions are restored only after two days.
- Constant. With this type, heartbeat disorders cannot be treated. Seizures occur frequently.
When the heart flickers, the classification looks like this:
- Tachysystolic . From the name it is clear that the frequency is too high - more than ninety times per minute;
- Normosystolic - up to ninety contractions;
- Bradysystolic - less than sixty times per minute.
The arrhythmia of the ventricles of the heart is also divided into flutter (up to three hundred times per minute) and atrial fibrillation (up to four hundred and fifty times). Here are the stages that are clearly visible using such a diagnostic method as an electrocardiogram (ECG of the heart):
- Large-wave has large, not wide waves (better to treat).
- Shallow wave - wide, small waves.
Most patients with cardiac fibrillation suffer from various diseases, which are divided into several groups.
Heart diseases:
- insufficiency of oxygen supply to the heart muscle through the coronary arteries and its consequences (oxygen starvation);
- inflammatory process in the area of the heart muscle;
- damage to the heart valves in the form of inflammatory marginal fibrosis of the valve leaflets or heart disease formed after acute rheumatic fever;
- heart disease due to hormonal disorders, metabolism, abuse of alcoholic beverages, drugs;
- replacement of a section of heart fibers with muscle tissue;
- abnormal processes in the development of the main circulatory organ and vascular system;
- surgical intervention.
Anemia:
- With a sudden loss of a large amount of liquid tissue, the heart muscle reflexively begins to increase the frequency of contractile manipulations in order to restore the current.
Diseases of other organs:
- In case of poisoning, potassium deficiency in the cells may occur, which leads to high sensitivity of the heart.
Disorders of the central nervous system and glandular system:
- Thyroid diseases and hormonal imbalance. Constant or one-time, but very strong stress. Overdose of diuretics.
It also happens that doctors cannot accurately determine the cause of cardiac fibrillation, then they talk about idiopathic arrhythmia.
Symptoms of cardiac fibrillation are not always identified. Therefore, it is difficult to determine what happened to the person. This happens when the atria malfunction.
The lower parts of the main circulatory organ are always accompanied by the following symptoms:
- The patient has a strong heartbeat;
- Pain in the chest area;
- Loss of orientation in space;
- Chronic fatigue;
- Inability to perform actions requiring great physical strength.
External signs of cardiac fibrillation:
- Pale skin;
- Symptoms of shortness of breath, frequent breathing actions;
- Pulsation of blood vessels located in the neck area;
- The patient may lose consciousness.
Strong beating and pain in the heart - may be symptoms of fibrillation
Upon a more precise examination, the specialist notes:
- Strong pulse;
- The contraction frequency increases, and the correct rhythm is not observed between the upper and lower chambers of the heart;
- There is no difference between the first and second tone;
- Wheezing in the lungs.
In case of cardiac arrest:
- The person loses consciousness, the skin is pale;
- There is no breathing;
- It is impossible to determine the pulse in the cervical arteries, there is no heartbeat;
- Pupil dilation.
Electropulse therapeutic method for the treatment of paroxysmal AF
If the previous treatment method does not bring results, the attending physician may prescribe an electrical discharge or electropulse therapy:
- To begin with, the patient is placed under anesthesia.
- Two electrodes are connected under the collarbone on the right, in the area of the motor actuator.
- The medical worker switches the device to synchronization mode so that the correspondence between the discharge and contraction of the ventricles is identical.
- The current indicator should be in the range of 100-360 J.
- An electrical shock is delivered.
In this case, the body receives a reboot and the rhythm is restored. This method is almost 100% effective.
What does fibrillation look like on an ECG?
The most informative method of additional diagnostics for a pathological condition is an electrocardiogram (ECG).
With atrial fibrillation the following are observed:
- Absence of P waves.
- There are waves f of different heights and smoothly transitioning into one another without a pronounced isoline between them.
- QRS complexes are frequent, chaotic (RR intervals are not the same), but their shape is correct.
Ventricular fibrillation on the ECG is manifested by the following:
- Frequent, chaotic, irregular waveforms instead of normal QRS complexes.
- When fluttering they are rhythmic, when flickering they are not.
- P waves are rarely observed before the ventricular complexes.
If there are previous pathologies of heart fibrillation, for example, myocardial infarction, other types of arrhythmias, blockades of the conduction system, there will also be signs of them.
Actions during an arrhythmia attack
Critical conditions are considered very dangerous with arrhythmia, when disturbances in heart rhythms can lead to loss of consciousness. In a person suffering from arrhythmia, the symptoms of an attack are:
- Dizziness;
- Feelings of nausea and vomiting;
- Pallor of the skin;
- A feeling of shortness of breath occurs.
In this case, you should immediately call an ambulance, and before the specialists arrive, you need to do the following:
- Place the person in a horizontal position and ensure maximum intake of fresh air, that is, open all windows and unbutton the top buttons of clothing.
- If a person is conscious, give him a sedative to drink in order to remove the feeling of fear that always accompanies an attack of arrhythmia. Suitable medications are corvalol, valerian tincture or valocardine.
- If a person has an antiarrhythmic drug that he usually takes, you need to help him drink the available drug;
- If it was not possible to prevent loss of consciousness, then indirect cardiac massage and artificial respiration should be performed before the arrival of specialists.
In difficult cases, specialists use defibrillation to restore heart rhythms, which involves applying an electric current to the heart muscle. The procedure is carried out as follows:
- Two electrodes, pre-moistened in a solution that prevents burns, are applied to the chest.
- An electrical impulse is applied to them. As a rule, a few pulses are sufficient for resuscitation.
- Defibrillation should be accompanied by artificial respiration and chest compressions.
If a person’s condition during an attack of arrhythmia is not critical, but it is not possible to normalize heart rhythms with the help of medications, then a less radical method is used - cardioversion. It is also based on the use of electric current, but it differs in that the procedure is carried out in a medical facility after an electrocardiogram.
The method of treating cardiac arrhythmia is always selected by a cardiologist. If you follow all the instructions, have the right lifestyle and a balanced diet, in most cases the prognosis is positive. All you need for arrhythmia is to have the necessary medications with you so that if rhythm disturbances occur, use them in a timely manner.