Rotavirus gastroenteritis is a pathology that represents a wide branch of viral acute diarrhea, which occurs against the background of serious damage to the gastrointestinal tract, as well as the respiratory tract. The nature of such gastroenteritis is determined by febrile or subfebrile temperature, abdominal pain, repeated vomiting, hyperemia of the pharynx, as well as diarrhea within five to fifteen times a day. Gastroenteritis can be confirmed by appropriate PCR analysis of bowel movements and serological blood tests using a variety of methods. The treatment course consists of a mandatory diet, the use of antiviral agents, enterosorbents and enzymes. If suspicious symptoms are detected, it is undesirable to self-medicate, since improper treatment of gastroenteritis can cause serious dehydration.
Causes
The causes of gastroenteritis are, as a rule, dysbiosis and poor nutrition. In this case, inflammatory processes form on the intestinal mucosa or other organs of the digestive system.
In addition, various infectious diseases can cause the first symptoms of gastroenteritis in infants.
In newborns, gastroenteritis can be caused by the following reasons:
- Introduction of a new product into the child’s diet that causes inflammation;
- Breastfeeding, it is worth noting that before feeding the woman ate foods that were unusual for the child;
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- Rotavirus, a fairly common cause of disease in children, occurs in a fairly severe form and is accompanied by dehydration in the child;
- The influence of Coxsackie and Norfolk viruses, which can cause an attack of diarrhea;
- The entry of bacteria into the child’s body, which, when multiplied, can affect both the intestines and other organs of the digestive system.
https://youtu.be/O5YssCJYeJU
Reasons for appearance
The most common cause of acute gastroenteritis is rotavirus. A child can become infected through contact with another child who is a carrier of the bacteria. Prolonged incubation does not make it possible to timely identify problems in the child’s body - at the initial stage of development of the disease there are no signs.
Rotavirus can be infected by shaking hands, exchanging personal items, etc. The harmful microorganism can remain for a long time on television remote controls, door handles, sockets, switches and other open places. Therefore, if a child has been diagnosed with bacterial gastroenteritis, he needs to be given separate dishes for the duration of treatment.
Pathogenic bacteria, once in the gastrointestinal tract, begin to damage the mucous membranes. The first symptoms of the pathology may appear 2-3 days after infection. Negative consequences can be avoided only with timely treatment. The acute form of the disease can be provoked by the following factors:
deterioration of intestinal microflora and dysbacteriosis,
- ARVI, flu,
- entry of amoebae and lamblia into the digestive system,
- etching with plant and animal poisons, acids and alkalis, heavy metal impurities and some medications,
- overeating, consuming too many spices and salt (dietary disease).
https://youtu.be/3jW3tLxORwg
If you do not start treating the child, gastroenteritis will progress to the chronic stage. From time to time, relapses will appear, and concomitant foci of infection will form inside the body.
Some minerals and vitamins accumulate in the intestinal cavity. However, against the background of pathological symptoms, their absorption is impaired. As a result, the child becomes very irritable, lethargic, and problems begin at school due to deteriorating memory. Acute gastroenteritis can occur for the following reasons:
- failure to comply with hygiene rules,
- improper food preparation,
- eating stale food,
- improper or untimely care: changing diapers, poor care of mucous membranes and skin.
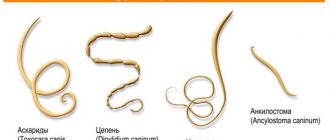
In some situations, worms act as provocateurs of gastroenteritis. As parasites reproduce inside the body, they release toxins that damage the mucous membranes.
If a child is prone to allergies, intestinal infections may also appear. This is due to impaired functioning of the immune system. Many medications also irritate the walls of the intestines and stomach. In this case, doctors are trying to find the optimal dosage or replace the drugs with more suitable drugs.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of gastroenteritis in a newborn are:
- Bloating, which may go away on its own after passing gas;
- The appearance of contractions and pain in the child in the navel area;
- Increased body temperature in a child caused by the effects of viruses on the body;
- Stool disorder manifested in diarrhea;
- Vomiting or gagging;
- General weakness in the child;
- Decreased amount of urine;
- Rapid weight loss;
- The appearance of dry skin;
- The appearance of a white coating on the child’s tongue;
- Salivation decreases.
It is important to consult a doctor when the first signs of the disease appear, in order to carry out treatment as early as possible and prevent further development of the disease and the occurrence of complications.
Diagnosis of gastroenteritis in a newborn
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out only by a doctor, for this purpose palpation and visual examination of the child is carried out. In this case, obvious symptoms are expressed in the following:
- Presence of fatigue and weakness in the child’s muscles;
- The presence of extraneous sounds in the intestines;
- Severe swelling in the child’s throat;
- Changed heart rhythm.
Additionally, stool is examined in the laboratory and a blood test is taken to determine the presence of inflammatory processes in the child’s body.
It is worth noting that the acute course of the disease is accompanied by high fever and severe dehydration of the body, which generally leads to impaired circulation and cessation of urine production by the body.
Diagnostic techniques
Using palpation, the specialist identifies swelling of the digestive organs. The disease may be accompanied by severe rumbling in the stomach. Before deciding on therapy, the doctor must identify the type of harmful microorganism, as well as identify the child’s sensitivity to antibiotics and antivirals. For this purpose, tests of vomit, feces, urine and blood are taken. Having deciphered the examination results, the doctor may discover:
- excessive accumulation of protein breakdown products and leukocytes in the urine,
- decrease in the amount of hemoglobin, platelets and red blood cells in the blood.
In addition, the patient is prescribed a stool test for the presence of protozoa and parasitic worms. If a child is suspected of having chronic gastroenteritis, then an additional endoscopic diagnosis of the gastrointestinal mucosa is prescribed.
https://youtu.be/O4AjkJqAiWo
Complications
Complications of gastroenteritis in newborns include:
- Manifestation of chronic gastroenteritis;
- Development of dysbacteriosis.
The greatest danger is posed by such a complication as dehydration of the body, which contributes to blood thickening, disruption of brain function and weakening of the immune system.
In case of dehydration, it is necessary to carry out immediate treatment and restore the water content in the body with special preparations. If help is not provided for dehydration, death cannot be ruled out, so parents should pay special attention to a disease such as gastroenteritis in their child and consult a doctor.
Also, among the consequences of gastroenteritis in a baby, it is worth noting the development of diseases such as pharyngitis, which is an inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa in a child, and rhinitis, expressed in inflammation of the nasal mucosa. These forms of inflammation are characteristic of the rotavirus form of the disease and, as a rule, occur quite often.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis is favorable . The acute form usually lasts up to a week. For a complete and speedy recovery, diet is of great importance. However, final restoration of digestive function may take up to 6 weeks.
However, the development of diseases such as gastritis and enterocolitis (in their chronic form) after gastroenterocolitis is possible if the episode of the disease was preceded by cases of stomach or intestinal diseases, helminthiasis and other gastrointestinal diseases.
Among the preventive measures:
- compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards for food storage and preparation,
- following the rules of personal hygiene,
- rational nutrition and its regime.
Treatment
What can you do
Treatment of gastroenteritis in an infant must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, while timely diagnostic measures and treatment as soon as possible contribute to the child’s rapid recovery and improvement of his general well-being.
Therefore, it is important not to try to treat your child on your own, but to seek help from specialists; as a rule, the first contact is made to the local pediatrician and a doctor is called to your home.
What does a doctor do
To treat gastroenteritis in an infant, the doctor, first of all, collects information on the disease; for this purpose, laboratory tests are carried out on tests taken from the child and the cause of the disease is determined.
It is worth noting that in infants, treatment excludes the use of antibacterial drugs, so doctors use more gentle drugs and medications.
When a child has gastroenteritis, dehydration occurs, therefore, first of all, the child is provided with fluid. This can be done by drinking water frequently or drinking a weak infusion of tea or herbs and avoiding milk and dairy products, which can aggravate the gastroenteritis situation. In some cases, a drip may be prescribed to prevent dehydration in case of concomitant diseases, such as rotavirus.
Therapeutic measures
Before treating gastroenteritis in children, the type of pathogen is identified. A long incubation period often causes delayed treatment. Gastrointestinal infections are very dangerous, so medical specialists begin treatment immediately. Antibiotics and antiviral drugs are used.
Simultaneously with the treatment of the disease, the consequences of dehydration are eliminated by introducing special solutions with minerals and glucose. This allows you to restore water and salt balance in the body, as well as compensate for fluid loss. To prevent dysbacteriosis, the following may be prescribed:
- probiotic preparations containing lacto- and bifidobacteria,
- prebiotics that improve intestinal microflora,
- drugs to reduce nausea,
- adsorbents and enterosorbents,
- enzyme agents,
- antispasmodics,
- antacids,
- non-steroidal drugs for high fever,
- antihistamines.
The child is prescribed long-term therapy with microelements and vitamins. Immunostimulants help improve the functioning of the immune system.
Prevention
Due to the fact that the cause of the disease is the entry of bacteria and microorganisms into the child’s body, it is necessary, first of all, to keep the house clean and prevent dirty toys and objects from entering the child’s mouth.
It is necessary to monitor the baby’s hygiene yourself, wash your hands and his hands more often, and periodically clean and disinfect both personal items that can get into the child’s mouth and toys.
In cases where a child is given water to drink, it is necessary to control its quality and source. Water must be boiled or bottled from the store.
Gastroenteritis in children: symptoms and treatment
Gastroenteritis in children most often occurs in the first five years of life. Parents most likely will not be able to avoid this. Microorganisms that a person encounters every day can be both beneficial and very harmful to his body.
It is easier for a child to catch an intestinal infection due to the imperfection of his gastrointestinal tract. A disease such as gastroenteritis depends on how active the gastric juice is.
It is this acid that keeps the digestive organs intact from the harmful effects of harmful bacteria. In children, this protective mechanism is not developed and stomach acid is not secreted in sufficient quantities.
According to statistics, intestinal infections affect children as often as common acute respiratory viral infections.
Gastroenteritis
- inflammatory disease of the stomach and small intestine. More often it occurs in an acute form, less often in a chronic form. With simultaneous damage to the large intestine, gastroenterocolitis is diagnosed. Accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, internal pain and spasms.
Consequences of the disease
The most serious complication of gastroenterocolitis is dehydration in children. Constant vomiting and frequent loose stools lead to a critical lack of fluid in organ tissues. This condition threatens the life of a small patient, especially if the body is weakened by concomitant diseases.
Lack of treatment may be the cause of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - chronic enteritis, dysbacteriosis.
With a long, severe course of the disease, there are known cases of the formation of malignant polyps on the intestinal walls.
Causes of infections
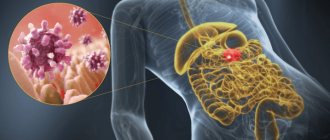
When the lining of the stomach and small intestine becomes irritated and inflamed for any reason, gastroenteritis occurs. Parasites and bacteria, as well as some viruses, can act as irritants. Gastroenteritis can occur in acute and chronic forms.
Gastroenteritis is caused by:
• parasites, including Giardia and Cryptosporidium.
In addition to unwashed hands, the infection can be transmitted to a healthy person by:
• contaminated water and food;
Types of diseases in infants
Infants and children under 3 years of age are most likely to get rotavirus or enterovirus infection. It accounts for 95% of all intestinal infections in young children. Rotavirus is transmitted by the oral-fecal route, and the carrier of the virus will remain infectious to others for another month.
Once in the body, rotavirus infection, first of all, negatively affects the respiratory tract, and then descends lower into the small intestine. Enterocytes, the intestinal epithelial cells that are responsible for the absorption of nutrients from food, are also exposed to pathogenic effects.
Thus, beneficial substances do not enter the necessary cells of the body, but simply rot in the intestines.
Under favorable conditions, the virus multiplies successfully and continues the process of destruction of the gastrointestinal tract. The development of gastroenteritis syndrome for the patient means a rapid release of water from the body in all possible ways. Lack of fluid in a child's body can even cause pneumonia.
Symptoms of gastroenteritis in children
The nature and severity of the disease directly depends on the type of gastroenteritis and the location of the source of infection in the body, and the general state of the immune system of the infected person is also important. The incubation period for gastroenteritis lasts two to three days.
Then acute symptoms and manifestations begin to appear:
• loose stool streaked with blood and mucus;
• pain around the navel;
• nausea and vomiting;
• severe pain with rumbling in the stomach;
• sore throat and dry cough.
For infants, the main danger is dehydration. A slight loss of water in the body, only 10%, can be fatal for a child under 1 year of age. Together with the fluid, the baby loses vital sodium and potassium salts.
When the child’s body temperature reaches 37.5 °C, toxins from the intestines that did not have time to be excreted in the urine begin to be absorbed into the blood and poison important organs and systems. Fever also leads to increased sweating.
Therefore, the higher the temperature, the more fluid the child needs. Parents should closely monitor the amount of fluid lost. You will even have to weigh the diapers used per day.
Characteristic symptoms
This infection is very difficult in children, especially if it occurs in an infant. Regular vomiting and diarrhea severely dehydrate the body, which can lead to very sad consequences. Important substances and salts are removed with loose stools and vomit.
An increase in body temperature increases the absorption of toxins into the blood. The child's intoxication gradually increases, accompanied by profuse sweating and convulsions.
Symptoms of gastroenteritis in children begin to appear several hours or even days after exposure to the virus. This depends on the strain of the virus, the characteristics of the body and the age of the child. The following signs of gastroenteritis in children may first appear:
bowel dysfunction: constipation or diarrhea,
- disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract: vomiting, increased gas formation,
- pain and discomfort in the navel area,
- headache,
- pressure surges,
- sudden weight loss, loss of appetite,
- change in color of feces.
In the absence of proper therapy at this stage, various complications may appear. Pathology gradually affects all internal organs and systems:
- the child’s temperature rises and falls sharply, perspiration appears on the forehead,
- lower and upper limbs may tremble slightly,
- the skin becomes very moist and pale,
- the baby is in a very lethargic mood, he constantly wants to sleep,
- dizziness and fog appear,
- pressure decreases sharply.
The acute form of the disease is accompanied by signs of intoxication and dehydration. The following changes may be observed:
- the skin becomes less firm and elastic,
- the mucous membranes of the eyes, larynx and nose become very dry.
Regular vomiting also adds to the problems - children do not have the opportunity to drink water, the liquid simply does not have time to be processed by the body. Loss of minerals through the kidneys causes urination problems. The urine begins to smell bad and changes color. It is imperative to remember that the loss of even 10% in an infant often leads to death.
Diagnosis of gastroenteritis in children
The diagnosis of gastroenteritis can be made independently based on the symptoms, but the cause of the disease can only be determined after all tests have been completed. The cause itself will be treated in a hospital setting, not the effect. For most intestinal infections, treatment methods are the same.
The following laboratory tests are carried out:
• blood diagnostics using the PCR method;
• general blood and urine analysis;
If a child allegedly caught the virus in kindergarten, at a party or at home, the attending physician should be informed about this. Perhaps someone from your environment also needs to get tested and undergo treatment. Sometimes food is tested in the laboratory when intestinal poisoning is suspected.
Diagnostic scheme
To make a diagnosis and identify the cause of gastroenterocolitis, the following methods are used:
- Examination by a therapist or gastroenterologist. A primary diagnosis can be made based on a typical clinical picture.
- General and biochemical blood test. In chronic gastroenterocolitis, anemia and failure of lipid metabolism are observed. In the acute stage, a disturbance in the ionic balance of the blood is possible.
- Coprogram. Stool examination allows you to evaluate the functioning of the digestive tract.
- Bacteriological culture of stool. Used when the infectious nature of the disease is suspected. Allows you to identify the causative agent of gastroenteritis.
For chronic damage to the digestive tract, other methods are added:
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy. Used to diagnose lesions of the stomach and duodenum.
- Colonoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the intestine. Allows you to see the mucous membrane from the inside, identify tumors, ulcers, polyps, and signs of inflammation. During a colonoscopy, a small section of the mucous membrane is removed for histological examination.
- Sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic method for diagnosing diseases of the final sections of the colon.
- X-ray examination. Allows you to identify defects in the intestinal wall or space-occupying formations and assess the patency of the organ.
We recommend reading:
Small intestine: location, structure and functions
Treatment of gastroenteritis in children
The main treatment for intestinal infections and poisoning is replenishing fluid in the body. In modern medicine, there are special oral rehydration products that can be used from birth.
You should drink in small sips. It is also necessary to limit nutrition and remove meat and all dairy products, legumes, vegetables, fruits and any sweets from the diet. You can eat porridge with water, biscuits, crackers and rice water.
Diet is very important in the treatment of gastroenteritis, so as not to further irritate the intestinal mucosa. It is better to feed your baby according to appetite, not according to the clock.
As a preventive measure, you need to wash your hands, avoid meeting with infected people if possible, and get vaccinated against rotavirus. Modern vaccines are developed for children from 2 months of age, and vaccination must be completed before 7-8 months, otherwise it makes no sense.
The rotavirus vaccine is administered orally and has no side effects. Children over 10 months of age are no longer given this vaccine due to its inappropriateness.
Emergency medical care for severe gastroenteritis in a child may be needed:
• when the child drinks little;
• when there is blood in the stool;
• when the skin turns pale and body temperature increases rapidly;
• any signs of dehydration (dry tongue, sunken fontanel and eyes, lack of urine for several hours, crying without tears);
• for headaches;
• child's age up to one year.
Any medicines to restore microflora, absorbents and enzyme preparations can only be prescribed by a doctor.
Parents, in addition to the therapeutic therapy itself, must disinfect the house in order to protect the family from the further spread of intestinal infection.
Gastroenteritis in infants
Gastroenteritis is a fairly common disease among 1 year old children. The reason for this is poor nutrition and dysbacteriosis. Inflammatory processes appear on the mucous membrane of the intestines or other organs of the digestive system. In addition, various infectious diseases can cause the first symptoms of gastroenteritis in infants.
Children under 3 years of age are most susceptible to diseases, since the immune system is still quite weak. This disease requires immediate treatment, as deaths are common among newborns.
How does the disease manifest?
In children, acute inflammatory damage to the mucous membranes of the digestive canal in the vast majority of cases occurs violently and rapidly.
A few hours (4-8) after the microorganism enters the digestive system, in the midst of complete health, severe malaise, heartburn, nausea and vomiting occurs, after which severe weakness, paleness, and cold sweat appear.
I am concerned about acute paroxysmal spasmodic pain in the abdomen, localized in its upper half and in the umbilical region. Or it could be diffuse pain, i.e. involving all areas of the abdomen.
A sick child takes a forced position in which his suffering is slightly alleviated: lying on his side with his knees bent, his hands pressed to his stomach.
Characterized by repeated loose stools (diarrhea), the color of the stool is dark green with mucus or even streaks of blood.
It is possible that the temperature may rise in the first 2-3 days to subfebrile or even moderate levels - 37.2-38.5 C. Then follows an approximately 1-3-day plateau.
And only after this a gradual decrease in temperature to normal begins. In general, the temperature reaction lasts up to 5-7 days.
Causes of gastroenteritis in an infant
In young children, the disease can be caused by the appearance of a new product in the diet, which causes inflammation. In an infant, gastroenteritis may occur during breastfeeding if the mother has eaten foods that are unusual for the baby. Failure to comply with hygiene procedures can often provoke the appearance of gastroenteritis in infants.
For one-year-old children, rotaviruses are a common cause of illness. This disease is very difficult for young children to tolerate, so it can be severe, accompanied by dehydration in the infant. After prolonged contact with a child, adults can also become infected.
At 1 year of age, Coxsackie and Norfolk viruses are very dangerous for a child, as they can cause severe bouts of diarrhea, the treatment of which requires immediate hospitalization.
Symptoms of gastroenteritis in infants
The first sign is severe, cramping pain in the navel area. The child experiences bloating, which may go away on its own after the gases pass.
Eating low-quality food can cause the entry and development of parasites, which, multiplying in the body, affect not only the intestines of a one-year-old child, but also the walls of other organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
All this causes the following symptoms of gastroenteritis in infants:
- increased body temperature caused by the presence of viruses in the body;
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- vomit.
- weakness.
Causes and risk factors
According to the nature of occurrence, gastroenterocolitis is divided into two large groups:
Infectious gastroenterocolitis
Causes:
- bacterial infection: E. coli, salmonella, shigella, etc.;
- viral infection: ECHO, Coxsackie, etc.;
- fungal infection: mainly Candida;
- invasion of protozoan microorganisms: amoeba, lamblia.
Non-infectious gastroenterocolitis
Causes:
- nutritional factor: irrational and monotonous diet, overeating, eating hot or cold food, strict diets;
- allergic reaction;
- parasitic infestation;
- alcohol intoxication;
- poisoning with medications, alkalis and acids, poisons, heavy metals, etc.
Gastroenteritis in infants
Gastroenteritis is a fairly common disease among 1 year old children. The reason for this is poor nutrition and dysbacteriosis. Inflammatory processes appear on the mucous membrane of the intestines or other organs of the digestive system. In addition, various infectious diseases can cause the first symptoms of gastroenteritis in infants.
Children under 3 years of age are most susceptible to diseases, since the immune system is still quite weak. This disease requires immediate treatment, as deaths are common among newborns.
Causes of gastroenteritis in an infant
In young children, the disease can be caused by the appearance of a new product in the diet, which causes inflammation. In an infant, gastroenteritis may occur during breastfeeding if the mother has eaten foods that are unusual for the baby. Failure to comply with hygiene procedures can often provoke the appearance of gastroenteritis in infants.
For one-year-old children, rotaviruses are a common cause of illness. This disease is very difficult for young children to tolerate, so it can be severe, accompanied by dehydration in the infant. After prolonged contact with a child, adults can also become infected.
At 1 year of age, Coxsackie and Norfolk viruses are very dangerous for a child, as they can cause severe bouts of diarrhea, the treatment of which requires immediate hospitalization.
Symptoms of gastroenteritis in infants
The first sign is severe, cramping pain in the navel area. The child experiences bloating, which may go away on its own after the gases pass.
Eating low-quality food can cause the entry and development of parasites, which, multiplying in the body, affect not only the intestines of a one-year-old child, but also the walls of other organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
All this causes the following symptoms of gastroenteritis in infants:
- increased body temperature caused by the presence of viruses in the body;
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- vomit.
- weakness.
Gastroenteritis in infants, accompanied by diarrhea and vomiting, causes dehydration. Some fluid is also lost through the skin, and urine output becomes very scanty. In this case, infants experience rapid weight loss and the child becomes very weak. The skin becomes unnaturally dry. A white coating appears on the baby's tongue and salivation decreases. The presence of these manifestations of the disease requires contacting a specialist to prevent severe consequences of gastroenteritis in a newborn.
Treatment of gastroenteritis in an infant
A doctor will be able to diagnose gastroenteritis in an infant through laboratory tests, taking all the necessary tests. Antibacterial therapy is not accepted for the treatment of newborns and infants.
Since the disease most often causes dehydration, it is necessary to provide the newborn with fluid. The child needs to be given water, tea or herbal infusions very often. It is not recommended to consume dairy products, as during illness this product can cause stomach upset in an infant.
In the first hours of gastroenteritis, it is best to refuse food in order to improve the functioning of the baby’s stomach and intestines. You can restore the balance of fluid in a baby’s body with the help of special medications.
The diet for illness should be very gentle - fatty, fried, too sweet foods are contraindicated.
Diagnosis and treatment of gastroenterocolitis in childhood
A diagnostic examination of children suffering from gastroenterocolitis is to determine the cause of the disease. Consultation with two specialists is required - an infectious disease specialist and a gastroenterologist. They conduct a detailed study of the diet of foods consumed over the past three days, examining those that cause concern. This procedure allows you to most accurately determine the causative agent of infection.
There are no radical methods for destroying pathogens. After five to seven days, the immune system produces antibodies that independently fight the infection. Therefore, treatment of the disease is aimed at replenishing lost fluid and restoring intestinal function.
To do this, in the presence of gastroenterocolitis, dietary nutrition is used using the following scheme for children:
- For the first two days of the illness, it is best to completely abstain from food and drink only plenty of fluids.
- On the third day, add pureed soup from boiled vegetables, baked apple with honey.
- Steamed cutlets made from dietary meat are included in the menu on the fourth day.
- On the fifth day, you can allow the child to eat several biscuits, prepare boiled low-fat fish, and add one egg.
Next, use the usual diet, from which fried, spicy, fatty foods, marinades, and smoked foods are excluded. A small child who needs milk can be given it in diluted form.
It must be remembered that meals during this period should be fractional, food should be taken in small portions 5-6 times a day.
Depending on the severity and cause of the disease, medications with an absorbent effect (“Polysorb”, “Smecta”, “Atoxil”), probiotics (“Bifiform”, “Linex”, “Acilact”), and enzymes to improve digestion (“Bifiform”, “Linex”, “Acilact”) are prescribed. Festal", "Pancreatin").
With progressive symptoms of gastroenterocolitis, hospitalization is recommended; infants are treated in a hospital.