The taste of chocolate slowly melting in your mouth cannot help but tempt you.
But not everyone can carefree indulge themselves with their favorite delicacy. Doctors' recommendations are especially contradictory about whether chocolate is allowed for stomach ulcers. Dessert can worsen the course of the disease, provoke heartburn, and even exacerbation of gastritis. On the other hand, some experts believe that natural cocoa butter and milk can help heal the stomach walls. But since it is almost impossible to find a completely natural dessert on the shelves, the above statement cannot be considered true. Moreover, regular consumption of treats can lead to a general deterioration of the condition.
What does the treat consist of, and how does it affect the course of a peptic ulcer?
Chocolate is made from cocoa beans that are fermented, dried, refined and finally roasted. The grains are finely ground into powder, which is added to the delicacy in its pure form or as oil. To make classic milk chocolate you need to mix cocoa butter, sugar and milk. Of course, a dessert made from such components cannot be stored for a long time, so manufacturers are expanding the composition of chocolate bars from year to year.
It is the additives that have an extremely negative effect on the lining of the stomach and the course of peptic ulcers. Of course, we are not talking about vanilla, dry nuts, or raisins. Stabilizers, flavorings, flavor enhancers, and preservatives have the most negative effect on ulcers. It is almost impossible to find a completely natural dessert on store shelves, so the question “is it okay to have chocolate if you have a stomach ulcer?” gastroenterologists answer negatively.
Chemical additives have a positive effect on the taste of the finished product, but at the same time irritate the walls of the stomach. Therefore, any “white”, milk, two-color, fruit chocolates are strictly prohibited for ulcers. Chocolate, which is made using basic, all-natural ingredients, tastes very bitter and most people with a sweet tooth do not associate with a traditional delicacy.
Such a dessert will cost much more than its analogues. Therefore, if you really want to treat yourself to chocolate, you shouldn’t save money and buy so-called “chocolate products”. And although such sweets in most cases have a more pleasant taste, they clearly lose in quality.
Advice from a gastroenterologist! When studying the composition on the packaging, you need to pay attention not only to the absence of preservatives, flavors and flavor enhancers. Hydrogenated vegetable oils (palm, soybean, corn) will also have a negative effect on ulcers.
Types of chocolate and their effect on the walls of the stomach
As with many other foods, different types of chocolate have different effects on the development of peptic ulcers. As mentioned above, conditionally, dark, completely natural chocolate brings the most benefit to the body. But milk chocolates are perceived extremely negatively by gastric bacteria.
A large amount of sugar activates excess fermentation processes in the intestines, which ultimately causes bloating and flatulence. Powdered milk, lactose and emulsifiers, when ingested regularly and over a long period of time, can cause exacerbation. People with ulcers are prohibited from eating chocolates with additives (nuts, raisins, cereal). But a sweet treat with alcohol can generally cause perforation of an ulcer.
Advice from a gastroenterologist! The best choice for an ulcer would be all-natural dark chocolate with a high cocoa content.
What symbols should you look for on the packaging? In addition to the fact that the chocolate should be dark and bitter, the label should contain a mention of:
- the amount of cocoa is at least 70%;
- complete absence or minimal amount of sugar;
- marked “without artificial sweeteners, flavors, preservatives, colors”;
- no trans fats;
- marked “non-GMO”.
An additional advantage will be the mention that the sweetness is completely organic, certified according to international quality standards.
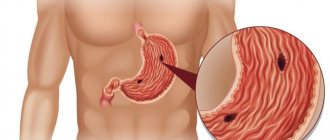
What is a stomach ulcer?
Peptic ulcer disease is formed due to poor circulation in the gastrointestinal tract. Due to lack of blood supply, the mucous membrane cannot withstand the aggressive effects of the produced hydrochloric acid and a special enzyme - pepsin. It is responsible for the process of protein digestion. As a result, small wounds form on the tissue - they are called ulcers. To stop their appearance and normalize the blood supply to organs, it is necessary to undergo examination by specialists. But the most important thing is to start following a diet. Several factors can lead to an ulcer:
- genetic predisposition;
- decreased immunity;
- bad ecology;
- recent infectious diseases;
- stress.
If treatment is not started on time, the disease will quickly become chronic. In addition, the ulcer is dangerous in the acute stage. It can lead to ulcerative colitis, and this will provoke ruptures of the intestinal walls, and subsequently hospitalization.
How much chocolate can an ulcer sufferer eat?
Even if the gastroenterologist has approved dark chocolate, this does not mean that you need to consume the treat on a daily basis. Moderation is important in everything. In general, the weekly dosage should not exceed 50 grams (this is less than half a bar). Don't fall for advertising gimmicks and expect benefits from milk chocolate bars.
Theoretically, such treats are really rich in antioxidants, calcium, and vitamin D, but any chemical additives will minimize all the benefits. Therefore, the allowed amount of milk chocolate for peptic ulcer disease = 0 grams.
Advice from a gastroenterologist! Chocolate is allowed to be eaten only during the remission stage of a peptic ulcer. It is also worth making sure that there is no dysbacteriosis. The fact is that an insufficient number of “useful” bacteria will not allow even the healthiest chocolate to be completely digested and fermented.
Can sweetener-based chocolate be considered a useful alternative for ulcers?
Everyone knows that sugar-free foods are a great way to enjoy dessert without the fear of gaining weight. But sugar-free chocolates will not be a healthy alternative to classic dark chocolate. Moreover, regular consumption of sweets with sweeteners can cause side effects. Sweeteners (sorbitol, xylitol, mannitol) cause digestive upset and irritate healed ulcers.
Some may argue that the ban should not apply to xylitol and sorbitol, because these natural elements are found in fruits (particularly apples and peaches) that are not contraindicated for ulcers. But you need to keep in mind that the average apple contains only a few milligrams of pure sorbitol, while the manufacturer will add tens of grams of sweetener in the form of alcohol to a chocolate bar.
Mannitol is another artificial sweetener derived from sugar alcohols. Mannitol is often added to chocolates with liquid fillings. This supplement contains far fewer calories than regular sugar, but even a completely healthy stomach can only partially digest mannitol.
In fact, all sweeteners are very poorly digested, and in severe cases they provoke the release of stomach acid. That is why people suffering from diabetes and regularly consuming foods with sweeteners often complain of flatulence, bloating, and diarrhea. If sweeteners constantly enter the stomach, then undigested and unabsorbed sugar alcohol will accumulate and eventually begin to ferment, thereby irritating the ulcerated areas. Thus, chocolate with sweeteners may be even more harmful than a bar with regular sugar.
What tests should I take for gastritis?
Timely, fast, accurate diagnosis of gastritis is the key to effective treatment. The disease has similar symptoms to other diseases, not only the gastrointestinal system.
Gastritis is determined using a diagnostic complex:
- visual examination of the patient, conversation;
- medical examination.
History is an important part of diagnosis. From a conversation with the patient, the gastroenterologist identifies the causes of attacks, exacerbations, applies a physical examination using palpation of the stomach, examines the throat, tongue, takes into account body temperature, general appearance of the condition,
After collecting diagnostic information and suggesting gastritis, laboratory research methods are prescribed to determine the nature and extent of damage to the stomach.
Methods of laboratory and instrumental research
What tests for gastritis are necessary first:
- general blood analysis;
- feces for occult blood, Helicobacter;
- Analysis of urine;
- blood biochemistry;
- examination of gastric juice.
Examination for acute gastritis is aimed at identifying microorganisms that cause intoxication, such as salmonella, staphylococcus, shigella and others.
Laboratory research
Initially, the patient is sent by a gastroenterologist for basic, general tests, for which blood, feces, and urine are taken, and they are also tested for Helicobacter pylori gastritis and cytology is performed.
Blood test
is a mandatory procedure, and general and biochemical tests are taken.
A general blood test is taken from a fingertip in the laboratory. This method determines the quantitative level:
- leukocytes;
- red blood cells;
- platelets;
- hemoglobin;
- ESR;
- change in the ratio of leukocyte types.
With gastritis, the analysis does not determine any specific indicators of differences from the norm, but attention is drawn to the presence of iron deficiency, low levels of hemoglobin, red blood cells, and an increase in ESR.
Biochemical - can show the following results:
- Pepsinogens I and II are in small quantities – their deficiency is a sign of gastritis.
- Increased bilirubin, gamma globulin, and a small amount of blood protein are signs of autoimmune gastritis.
- Blood antibodies IgG, IgA, IgM to Helicobacter pylori – bacterial gastritis.
- Increased levels of digestive enzymes indicate that this case is pancreatitis.
- An increase in acid phosphatase also indicates pancreatitis.
In chronic autoimmune gastritis, these tests show a decreased total protein, an increased amount of gamma globulins, and may reveal incorrect metabolism.
Blood levels of pepsinogen I and II are very important - their insufficiency is a harbinger of atrophy or the onset of a malignant process.
Blood serum testing reveals autoimmune disorders - their sign is the presence of Castle factor antibodies. Increased serum gastrin suggests A-gastritis.
Stool and urine tests
Using a laboratory method for examining human feces, you can find out the following disorders:
- acid balance;
- fermentation, the ability to digest food;
- the presence of undesirable substances: fatty acids, starch and others.
Separately, they conduct a stool test for occult blood - dark-colored stool suggests it.
Examination of stool helps to identify atrophic gastritis - the examined material reveals muscle fibers, a lot of connective tissue, digested fiber, and intracellular starch.
A urine test is carried out against the background of a general examination to exclude kidney pathology.
Specialized tests
To exclude other provocateurs of diseases of the digestive system, such infectious agents as:
- chlamydia, trichomonas and others;
- parasitic diseases.
Very often the cause of impaired digestion is associated with these infectious agents.
Definition of Helicobacter Pylori
To diagnose HP-associated gastritis, examine:
- Blood - specific IgG, IgA, IgM indicate the bacterial origin of the disease.
- Material taken for biopsy of the mucous membranes of the organ.
- Plaque.
There are many ways to conduct a breath test. It is recommended to undergo two different tests for the presence of bacteria. A urease breath test is performed to identify the gram-negative bacterium HP. It is mobile, survives in acidic gastric contents, and produces ammonia. This bacterium can enter a child’s body and develop for many years, causing stomach and duodenal ulcers, gastritis, and gastroduodenitis. To identify Helicobacter Pylori, a biopsy of the gastric mucosa is done; a good alternative is a breath test.
The advantage of the urease respiratory method is non-invasiveness and safety. Tests are carried out by examining the air blown out by a sick person.
The basis of this method is the ability of bacteria to induce enzymes that decompose urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia, carried out in the following stages:
- A medical specialist takes two background samples of exhaled contents: using special plastic tubes, the patient breathes for several minutes.
- Next, after ingesting the test liquid - a weak urea solution, the respiratory process continues. It is necessary to ensure that drool does not enter the tube with your breath.
- The patient's breath products are sent for testing.
Minimum rules must be followed to ensure that the results are not false:
- Testing should be carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach.
- Do not smoke or chew gum before the test.
- On the eve of the test, do not consume legumes: beans, peas, corn, soy,
- Do not take antisecretory or antibacterial drugs two weeks before the examination.
- Do not take antacids or analgesics before the procedure.
- Pre-treat the oral cavity: brush your teeth, tongue, rinse your mouth.
The urease breath test can be up to 95% sensitive.
It is used for the primary diagnosis of Helicobacter Pylori, also when anti-Helicobacter therapy is carried out.
Instrumental research
Such methods of analysis are carried out using various devices, medical equipment, and are most often used to monitor a patient with a chronic process.
FGDS
The main diagnostic method: fibrogastroduodenoscopy, gastroscopy - using a flexible probe with a video camera, which. FGDS shows places of inflammation of the stomach, damage to mucous tissues, and also to abstract from gastric ulcers. A device for performing FGDS transmits an image of the mucous membrane to a computer monitor, the doctor clearly sees all the changes in the mucous membrane that have occurred.
Tissue biopsy
When a gastroscopy is performed, small pieces of tissue from the gastric mucosa are removed and examined. The method is informative for determining the presence of HP bacteria. The material is taken from different parts of the stomach, since bacteria may not be active evenly across locations.
Acidity pH meter
Acidity often determines gastritis. The study is carried out in various ways:
- Carrying out an express analysis - a thin probe is inserted, equipped with an electrode that determines the level of acidity of the stomach.
- Daily pH metry - dynamics of changes in acidity over 24 hours, there are three methods of analysis:
- A pH probe is inserted into the stomach through the nasal sinuses, and a special information recording device (acidogastrometer) is attached to the patient’s waist.
- Swallowing the capsule, which gets on the gastric mucosa, transmits data displayed on the acidogastrometer.
- Collection of materials during gastroscopy - endoscopic RN measurement.
- Acid test – carried out if there are contraindications to the use of the probe. This method is studied using special drugs that react with hydrochloric acid of the stomach; their interaction changes the color of urine.
- Checking gastric juice.
The component is collected during gastroscopy. On the eve of the procedure, the patient is fed special food that enhances gastric juice. The study confirms gastritis and determines the causes of its occurrence. If a large composition of gastrin is detected, then the disease is caused by bacteria.
The most popular disease of the digestive tract is not difficult to diagnose - pain from FGDS and gastritis biopsies are minimal. Diagnosis of gastritis should be carried out as early as possible - it is better to prevent the disease than to detect ulcerative pathology or a malignant process late.