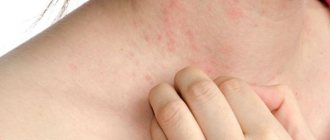
Itching of the skin of the body in liver diseases in the vast majority of clinical cases is the first, and for a long time the only symptom of the beginning pathological process in the hepatobiliary sphere. Which indicates the appearance of signs of chronic cholestasis (stagnation of bile).
Hepatic itching and accompanying rash with pigmentation are diagnosed in every fourth patient with jaundice, as well as in all patients with manifestations of primary biliary cirrhosis. Such symptoms are a very important diagnostic sign, allowing the doctor in a number of ambiguous cases to promptly assume that the patient has functional liver disorders.
Causes of itchy skin in liver diseases
At the moment, there is no exact etiology for the appearance of itchy skin associated with liver diseases. However, there are a number of assumptions as to why diseases of this internal organ manifest themselves in this way. The most common hypothesis is the increased content of toxic bile acids in the epidermis. Normally, they do not penetrate the human bloodstream and do not accumulate in the body. However, at the slightest malfunction of the liver, itching will begin to manifest itself, ranging from light scratching to painful, unbearable itching that disrupts the usual rhythm of life.
Liver problems can be caused by:
- Medicines: chemotherapy, antibiotics, hormones.
- Viral diseases, such as hepatitis.
- Alcohol intoxication due to large intake of alcohol-containing substances.
- Pathological changes in the liver: cirrhosis.
- Damage by parasites: giardiasis.
Itchy skin is a symptom of a number of other diseases, ranging from banal food allergies. To rule out other causes of itching, an in-person visit to the doctor is necessary. Incorrect treatment can cause irreparable harm to health!
Diagnostics and therapy
Skin itching itself in the presence of liver problems is not treated, since it is only a symptom of a true disease. It is necessary to find out what disease of the liver or gallbladder caused such a symptom, and treat it. The sooner the diagnosis is made and treatment is started, the faster the cholestatic itching of the skin will disappear.
If there is skin itching, the doctor prescribes the following diagnostic methods:
- General and biochemical blood test. He is especially interested in indicators of bilirubin, liver enzymes, serum protein, cholesterol;
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder, liver, pancreas;
- coagulogram.
The best treatment option is to eliminate the cause that caused the itching and, if necessary, additional use of groups of certain drugs.
Complex treatment of skin itching in cholestasis is usually used, the main drugs of which and their effect are discussed in the following table:
| Drugs. | Purpose. |
| Allohol, Festal, Holenzim. | Designed to increase the digestibility of fats and fat-soluble vitamins. If itching occurs due to cholestasis, treatment with these drugs helps well, since they contain bile components that stimulate its outflow. |
| Hepatoprotectors. Essentiale Forte N, Gepatrin. | Drugs that restore the function of liver cells. |
| Drugs that eliminate intoxication of the body (Hemodez, Polysorb). | Sorbents, special solutions for droppers to cleanse the blood. |
| Glucocorticoids (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone). | They help relieve itching caused by exposure to bile acids. |
| Antibacterial and antiviral, anti-inflammatory drugs. | It is especially important to use them for viral hepatitis. But before you get rid of itching due to hepatitis C, you need to consult a doctor. Only he can prescribe specific medications and their dosage. |
| Ursosan, Ursofalk. | Preparations containing ursodeoxycholic acid. They bind with bile acids to form non-toxic compounds, which suppresses skin itching. |
Liver diseases accompanied by itching of the body skin
Cholestasis. Cholestasis is a violation of the full outflow of bile. Occurs against the background of cancer and gallstone disease. Occurs in acute or chronic form, inside the liver or outside the organ. Itching occurs due to the penetration of bile acids into the skin, irritating its receptors. It is accompanied by a number of other symptoms: digestive failure, weakness and general malaise, insomnia and elevated body temperature.
Hepatitis, including hepatitis C. Viral hepatitis is currently, unfortunately, quite common. The routes of transmission are different - drinking contaminated water or food (hepatitis A), sexual intercourse and the bloodstream (hepatitis B and C). Often the symptoms of hepatitis C are not pronounced. The patient feels only general fatigue and attributes this to some external reasons. Therefore, for many people, the acute phase of the disease turns into a chronic phase, which is very difficult to treat. With this disease, toxins accumulate in the body due to disruption of the liver. Bilirubin and bile acids enter the bloodstream. Against this background, a person develops both itching and a rash, as well as yellowing of the sclera and skin.
Alcohol damage to the liver. The World Health Organization has calculated an approximate safe dose of alcohol consumption - 20 grams. ethyl alcohol per day. Exceeding this dose, and especially drinking alcohol-containing drinks too often, puts the liver at risk. Cells are unable to resist toxins. Connective tissue grows and is replaced by fibrous tissue. Hepatosis and, in more severe cases, cirrhosis may occur.
Cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is a disease in which fibrous connective tissue replaces liver cells that die due to various factors. In this case, the blood supply to the liver is disrupted and the organ ceases to function fully. As a result, the death of the patient may occur. It is dangerous in its asymptomatic course and manifests itself in severe and sometimes critical cases.
Diabetes. In diabetes, uncontrolled breakdown of fat occurs, which leads to the development of fatty hepatosis, i.e. accumulation of fat in liver cells. The organ stops functioning normally, bile does not drain well, and its acids cause itching.
Hepatosis. Hepatosis occurs against the background of excess weight in both obese people and junk food lovers. Leads to fatty liver degeneration. Characterized by pain in the right side, nausea, general malaise, and digestive problems.
Hepatosis in pregnant women is also unexplored. The exact cause of this disease has not yet been identified, but it does exist.
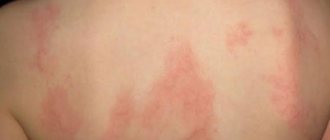
Liver diseases are often accompanied by skin rashes that look like an allergic rash. May appear as:
- Spider veins localized on the back, arms, neck;
- Abscesses manifested as a result of impaired immunoglobulin synthesis and immune imbalance;
- Red spots - due to the accumulation of toxins;
- Yellow plaques characteristic of hepatitis;
- Bruising.
The location of the rash varies: it can affect the upper and lower extremities, small areas on the neck, back, even feet and palms, but rarely affects the entire body.
Itching in liver diseases does not need to be tolerated; it will not go away on its own and requires complex treatment, since it is a concomitant symptom of problems with the internal organ. In other words, itching can only be overcome by eliminating and treating liver disease.
How is the treatment carried out?
Drug therapy
If a person has an itchy and itchy head and skin, it is important to go to the hospital as soon as possible. At the appointment, the physician will conduct a survey of the patient, during which he will find out how long ago cholestatic itching has occurred and what additional symptoms are present. Then appropriate diagnostics will be carried out, which will identify liver diseases, as well as the reasons that contributed to their development. After receiving the test results, the doctor begins prescribing a course of therapy.
First of all, they resort to sorbents, which allow the removal of waste and toxins from the body. The most popular medication from this group is activated carbon. It is taken according to the following scheme: 1 tablet per 1 kg of the patient’s weight. Because this medication may irritate the lining of the gastrointestinal tract, it is not prescribed to patients who have erosions or bleeding in the digestive system.
They often resort to the help of Enterosgel, which does not irritate the mucous membrane. “Atoxil” can also be prescribed, which removes not only toxins, but also allergens, as well as rotting products. The medication is not prescribed to patients with peptic ulcers.
Additional medications
Itching due to cholestasis will need to be treated with lipid-lowering medications. Cholestyramine is often used, which effectively relieves a person of this unpleasant symptom. They often resort to the help of hepatoprotectors, which normalize the functioning of the filtration organ. This group of drugs includes Heptral, which has antioxidant, neuroprotective, and regenerative properties. It is prescribed with caution, since the medication has a considerable number of adverse reactions. Itching due to hepatitis C, as well as other liver diseases, can be eliminated with the help of Karsil and Gepabene.
Skin problems caused by jaundice or other pathologies of the filtration organ are also treated with anti-inflammatory, antiviral and antibacterial medications. Treatment is also not complete without the administration of probiotics and vitamin-mineral complexes. It is important to remember that the correct medicine and the duration of its use can only be prescribed by the treating specialist, who takes into account the type of disease and the severity of its course.
Diet food
Itching of the skin of the body in liver diseases suggests prescribing a diet to the patient. They often resort to the help of diet table No. 5. However, if, against the background of pathology of the filtration organ, the patient is diagnosed with disorders in the gastrointestinal tract, then such a diet is not prescribed. To get rid of skin problems, the patient will need to remember the following nutritional principles:
- Reduce your intake of fats, especially animal origin.
- Avoid eating essential oils, cholesterol and oxalic acid.
- Reduce salt intake to 6 g per day. It is recommended to salt dishes already prepared.
- Add enough fruits and vegetables to your diet.
- Avoid frying foods. Cook food using a steamer, baking, stewing or boiling.
- Monitor your drinking regime and drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day.
How to distinguish itchy skin in liver diseases from allergies?
As mentioned above, hepatic itching always appears against the background of additional symptoms. Do not self-medicate and do not start taking antihistamines uncontrollably; they will be useless and will not provide any therapeutic effect, since the cause of the rash is a malfunction of the internal organ. Rule out allergies if the rash is accompanied by:
- Changes in skin color;
- Increased sweating;
- Swelling of the face and limbs;
- Pain in the right side;
- Cracks on the body;
- Peeling of the skin.
In addition, itching in liver diseases most often occurs at night and is intense. This is due to the fact that the production of bile increases in the body during this period, which means that the amount of bile acids entering the bloodstream increases sharply, causing unpleasant and uncomfortable sensations. The more severe the disease and the more acute its form, the more unbearable the itching becomes, often tormenting the patient and preventing him from leading his usual way of life.
If you notice similar symptoms, along with changes in your body, do not delay your visit to the doctor and do not prolong the course of the disease. Remember that liver diseases are asymptomatic for a long time. The appearance of characteristic signs, and especially pain, indicates that the condition is close to critical.
Preventing itching
Itching is a manifestation of some disease, and not an independent disease. Therefore, its prevention is to prevent the causes of itching. To do this you need:
- Treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, and endocrine disorders in a timely manner.
- Detect and treat infectious and fungal skin diseases.
- To prevent parasitic infections, you should maintain hygiene, wash your hands thoroughly, eat only well-washed vegetables, fruits and herbs, and heat-treated meat and fish.
- Undergo regular medical examinations by a neurologist, oncologist, or therapist in order to promptly identify neurological and general diseases and tumors.
- If severe itching is caused by allergies, you should avoid contact with the allergen, follow a diet, and organize a hypoallergenic lifestyle.
- Itching in the intimate area is a sign of sexually transmitted infections and inflammatory diseases. To avoid them, you need to maintain personal hygiene, have a reliable sexual partner, dress for the season and avoid hypothermia.
- Itching caused by stress will help prevent a calm, measured lifestyle, sound and healthy sleep, and taking special sedatives.
- A balanced, healthy diet is good for the skin. Be sure to include vegetables, herbs, lean meat and fish in your diet, and drink a lot of water.
- Almost any type of skin on the face and body needs moisturizing with cosmetics. To avoid itching, you should use balms, milk, creams - this is especially important after water procedures.
- To compensate for the deficiency of vitamins and microelements, it is useful to use special vitamin and mineral complexes. Products containing vitamins A and E will help improve skin condition.
Itching is a kind of signal from the body. Like pain, it indicates trouble in a certain area:
- Skin – for general and psychiatric diseases, dermatological diseases, endocrine disorders, allergies.
- Anal itching - for diseases of the rectum, helminthic lesions.
- Itching in the intimate area in women is a sign of problems in the field of gynecology. Itching in men is due to diseases of andrology/urology.
Itching in the groin, on the skin, and in the perianal area is treated in completely different ways. The choice of the appropriate treatment method depends on what disease is causing the irresistible desire to scratch.
Treatment of skin itching in liver diseases
Treatment of hepatic itching will certainly be combined with the fight against the underlying disease. Once an accurate diagnosis has been established, begin appropriate therapy.
To relieve itchy skin, try to follow these recommendations:
- Avoid visiting baths, saunas, steam rooms, and swimming pools for a while. Do not overheat or steam the damaged skin, thereby increasing blood flow - the itching will make itself felt with renewed vigor.
- Do not rub your skin with a towel or other hard cloth. After taking a bath or shower, just blot off the moisture.
- Keep hygiene products and linen clean.
- Avoid synthetic materials that come into contact with the skin.
- The use of cooling and itching-relieving gels is permitted.
- If possible, eliminate smoking, alcohol, and review your diet.
- Stop taking toxic medications for a while or replace them with analogues with less harmful effects on the liver.
- Avoid unnecessary stress and emotional unrest, against the background of which skin problems tend to worsen.
Watch your health, do not ignore the signals that your own body sends you, lead a correct lifestyle, and then not only the liver, but your entire body will never experience serious illnesses.
Methods and methods of treatment
To establish a diagnosis, you should consult a doctor. Based on the diagnostic results obtained, treatment is prescribed. It is complex and includes the use of medications and special nutrition. Medicines are selected in accordance with the disease, which is the primary source of the problem.
In some cases, surgery is required. If the cause of cholestasis is a failure in the outflow of bile, which arose due to blockage of the channels, which led to intoxication, then drainage is installed. Drainage helps remove excess dangerous components, which quickly eliminates negative symptoms.
Use of medications
In drug therapy, opioid acid antagonists, bile acid derivatives and ursodeoxycholic acid preparations are used in high dosages.
To get rid of itching sensations, you need to take medications:
- Sorbents – help remove toxic components from the intestines (Enterosgel).
- Vitamins – ascorbic acid, tocopherol, retinol, vitamin K.
- Anti-inflammatory medications to reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process.
- Immunostimulants - used against the background of a reduced immune status.
- Probiotics normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Hepatoprotectors – help restore gland cells, improve the functionality of the organ, and accelerate regeneration processes.
Forecast
Itchy skin requires immediate diagnosis to identify its cause and further treatment of the disease. Violation of the integrity of the skin when scratching can lead to infection with staphylococci and streptococci, which manifest themselves in the form of pustular skin diseases (boils, abscesses).
To summarize, I would like to note important points regarding skin itching:
- Itchy skin is a symptom of diseases associated with disruption of the body's functional systems. It can also be caused by allergens, viruses and parasites.
- Complex treatment of the disease is carried out only by a specialist. To relieve and eliminate itching, antihistamines (Suprastin, Zodak and others) and antipruritic ointments for external use (Beloderm, Triderm) are used. At home, you can eliminate itching with the help of talkers, powders, and baths with medicinal herbs.
- Prevention of itchy skin includes maintaining good skin hygiene and a healthy lifestyle.
Itchy skin causes
The Itch Center has been created on the basis of the Clinic of Dermatovenereology and Allergology of the European Medical Center. Specialists from various fields provide outpatient and inpatient care to patients with acute and chronic itching. During treatment, the patient is offered a detailed examination in accordance with the protocol of the AWMF-Leitlinie (Association of Scientific Medical Societies in Germany) and European protocols for the management of patients with chronic itching.
The experience of highly qualified doctors, combined with a wide range of possibilities and examination methods at EMC, in most cases helps to identify the causes of itching, which, together with comprehensive, individually selected treatment, allows you to achieve maximum results from therapy.
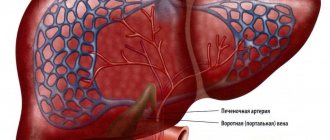
What are bile acids and what are the reasons for their release into the blood?
Bile acids are complex biochemical compounds that are formed from cholesterol and produced by hepatocytes. Together with bile, fatty acids enter the gallbladder, and from there along the duct into the duodenum. The main functions of bile acids:
- participate in digestion, emulsify fats and help their further absorption;
- stimulate intestinal motility, prevent food stagnation and constipation;
- regulate intestinal microflora, suppressing the growth of pathogens;
- participate in maintaining normal cholesterol levels in the blood;
- promote the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.