It is the largest gland in the human body and is a vital organ. It is located in the abdominal cavity, just below the diaphragm, on the right side. It participates in metabolic processes, cleanses the body of toxins, promotes digestion, synthesizes cholesterol and bile acids. It accumulates fats, proteins, minerals, carbohydrates and vitamins. It is very important to maintain a healthy liver, and for this you need to know the symptoms of liver diseases and the causes that cause them.
Classification of diseases
Medicine has not yet come to a unified classification of diseases of this organ and the biliary tract due to the fact that the main criteria by which diseases are systematized: causes, changes in structure, causative agent, clinical manifestations are intertwined. According to morphology (pathological processes of the disease), all pathologies of the liver and biliary tract are conventionally divided into three main groups.
- Parenchymal - diseases associated with disruption of the cells that provide the basic functions of the organ. These include: cirrhosis, hepatitis, all neoplasms: cysts, various tumors.
- Hepatobiliary - these include various inflammatory processes in the bile ducts that are of medicinal, toxic and infectious origin. This group also includes diseases associated with disorders of the outflow of bile, resulting from spasm, blockage or neoplasms of the ducts.
- Vascular - any dysfunction of an organ associated with the condition of the blood vessels.
In addition to this classification, all diseases can be divided according to the etiology (causes and conditions of occurrence) of the disease and other criteria.
Types of clinical examination
After examining the patient, during which the size, density, location, and pain of the liver are determined, the hepatologist prescribes laboratory and instrumental studies. Their results will help to correctly formulate an overall picture of the disease. That is, its course, stage, cause of occurrence and further prognosis.
Laboratory examination of the liver
Laboratory diagnostics of the biomaterial shows whether there are malfunctions in the functioning of the internal organ. Based on the violation of one or more functions, a set of manifestations of the disease is formed, which helps to make a correct diagnosis. During a liver examination, the following tests are prescribed.
General blood analysis
CBC values are not specific to accurately make a diagnosis. However, they help to see if there are any abnormalities in the liver and give a general idea of a person's health.
Sample information about the study's implications:
- A change in the number of leukocytes will indicate that there is an inflammatory process in the body.
- With reduced levels of total protein, disturbances in liver function are possible, as well as the rapid development of malignant neoplasms.
- During elevated glucose levels, chronic hepatitis may occur. A decrease in data indicates intoxication of the body with alcoholic drinks and poisons, as well as other liver diseases.
- An increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate indicates infectious diseases and inflammatory processes, including hepatitis.
- A reduced platelet concentration serves as a signal of liver dysfunction.
The RDV indicator also plays an important role in liver diagnostics. With elevated numbers, genetic and chronic diseases can be diagnosed.
Blood chemistry
To examine the liver, each patient will have to donate blood for biochemistry. This analysis allows us to judge all disorders of internal organs associated with the gastrointestinal tract system.
Main indicators of liver damage:
- ALT and AST. The predominance of alanine aminotransferase values over the amount of aspartate aminotransferase indicates damage to hepatocytes. Increased levels of both values are observed in viral and toxic hepatitis.
- Bilirubin. Its high concentration indicates liver pathology, tumors, blocked ducts, and gallbladder disease.
- GGTP. An increased amount of the enzyme is observed with stagnation of bile, hepatitis of various etiologies, and cancer.
- Cholesterol. A reduced concentration indicates liver failure, an increased concentration indicates bile stagnation.
- Alkaline phosphatase. High readings indicate obstruction of the bile ducts. Most often, blockage and disruption of outflow are caused by cancerous tumors or gallstones.
An increase in all fractions of GGTP, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase and a decreased level of albumin protein will indicate the presence of liver cirrhosis.
Tests for markers
If viral hepatitis is suspected, the hepatologist recommends testing for their markers. The purpose of the method is to detect antigen in blood plasma, the amount of virus, determine its activity and genotype.
There are two types of examination:
- Specific. This analysis determines the type of infectious agent. Individual parts of the hepatitis virus act as markers.
- Non-specific. This analysis is based on antibody markers that resist viral pathogens.
The detection of antibodies to antigens is an accurate confirmation of the pathological process.
Tests for tumor markers
This liver examination allows you to timely diagnose cancer tumors, as well as determine their extent and severity. However, this method is only used for additional clinical research purposes. The fact is that an increased amount of proteins can be observed both in malignant neoplasms and in diseases of other etiologies.
When examining the liver for tumor markers, the following types of biomolecules are used:
- AFP. An elevated level of alpha protein marker highly accurately confirms the presence of hepatocellular carcinoma.
- CA 15-3, 19-9, 242, 72-4. A slight deviation in the values of these substances indicates liver dysfunction. The presence of malignant tumors will be indicated by their high rate.
- REA. The values of this tumor marker determine liver metastases.
Based on the totality of these data, a general picture of liver damage is compiled.
Analysis of urine
A general urine test is an important informative method for examining the liver. In the results of the study, doctors pay attention to the appearance of bilirubin, the amount of urobilinogen, microhematuria, and proteinuria.
The following urine parameters are considered abnormal:
- dark color, similar to strong tea;
- increased density;
- high protein levels;
- glucose detection;
- presence of ketone bodies;
- increase in leukocytes;
- red blood cells in the field of view above 3;
- high coefficient of calcium oxalate crystals;
- presence of bacteria.
In this case, bilirubin should be completely absent. Its detection will indicate advanced diseases of the liver, gallbladder and ducts.
Coprogram
An examination method such as a coprogram can evaluate the functioning of the entire digestive system. After conducting a chemical, physical, macro and microscopic examination of feces, the specialist gives a complete description of its composition.
Coprology interpretation table indicating liver dysfunction:
| Index | Norm | Deviation | What does this indicate? |
| color | cinnamon | light | pathologies of the liver and its ducts |
| consistency | rather dense | ointment-like | blockage of the biliary tract |
| liquid | pathological process | ||
| acidity | pH 6.8–7.6 | pH 5.5–6.7 | failure of fat metabolism |
| smell | not sharp, characteristic | burnt oil | dysfunction of the pancreas |
| soluble protein | absence | Availability | malignant neoplasms |
| stercobilin | 75-350 mg | reduced | stones in the bile ducts |
| leukocytes | absence | Availability | inflammatory process |
| fatty acid | absence | Availability | violation of the outflow of bile or a small amount of it |
| neutral fats | absence | detection | failure of bile synthesis |
In order for stool tests to be reliable, it is recommended to follow the preparation procedure, as well as the rules for collecting and storing biomaterial.
Instrumental examination
In the event that laboratory tests confirm the presence of liver pathologies, the patient is prescribed one or more instrumental examinations to make a final diagnosis. The choice of diagnosis depends on what information the doctor needs to obtain about the internal organ. The most common instrumental methods for examining the liver are:
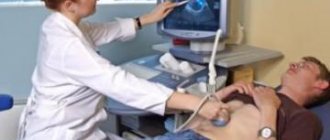
Ultrasound
Ultrasound examination is a non-invasive technique for visual examination of the human body using ultrasonic waves.
To carry out these manipulations, the patient is placed on a couch. Then the skin in the liver area is lubricated with gel. A sensor is placed over the treated area, which transmits ultrasonic waves. The structure of the liver is displayed on the monitor.
This diagnostic method makes it possible to detect heterogeneity in the structure of the internal organ, changes in its size, and enlargement of the bile ducts.
CT
Computed tomography is performed using X-rays. During this procedure, the patient needs to lie down on the table. Next, under some pressure and at a certain speed, a contrast agent is injected into his blood. Then the table, together with the person, begins to move in the tomograph tunnel, stopping only at those moments when it is necessary to capture a certain part of the liver in the picture.
Such an examination of the liver allows you to determine the nature, degree, type of disease, as well as identify its relationship with other nearby organs.
During the CT scan, the patient must remain motionless. Otherwise, the survey results will be unreliable.
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging is a method of examining internal organs using tomographic images on a machine monitor.
To examine the liver, the patient lies along the tomograph tubes in a special room. Then the survey area is determined. A strong magnetic field is concentrated at this point. With its help, the state of the organ is transmitted to the device monitor.
This examination method allows you to examine the blood vessels of the liver and its ducts, determine the nature of the tumors, the patency of the bile ducts and much more.
Needle biopsy
A puncture biopsy is considered one of the most reliable methods for examining the liver. Diagnosis is carried out by sucking the biomaterial through a syringe with a thin or thick needle. A long, thin, pointed instrument is inserted repeatedly into the human body. During these manipulations, sharpened needle jaws capture and cut off pieces of the liver. They are then removed from the syringe and sent for histological examination.
Thanks to this examination, the doctor can accurately determine the severity of liver damage and evaluate its functioning. In addition, these results help to create the correct treatment regimen and monitor its effectiveness.
Causes of the disease
Liver tissue is very resistant to various negative influences. This is the only human organ that can heal itself. Despite this, the constant influence of unfavorable factors leads to various diseases. The main causes of ailments that are taken into account when diagnosing liver diseases are the following:
- Injuries. They occur during a fall, at work, or in an accident. There may be no visible signs, and symptoms will appear much later in the form of cysts, which are discovered quite accidentally during an ultrasound examination.
- Viral infections. Hepatitis A, B and C viruses pose a serious threat. They give rise to tissue inflammation, which occurs in acute or chronic form, subsequently causing cirrhosis. The safest of these is hepatitis A, called jaundice. It does not become chronic and does not have serious consequences. The greatest danger is posed by hepatitis B, which does not show a clinical picture for a long time, becomes chronic and has a risk of developing cirrhosis or cancer.
- Presence of parasites. Their various types cause organic and functional disorders. Necrosis appears, combining into an amoebic abscess, and liver failure develops.
- Medicines. Unsystematic use of medications, especially antibacterial, hormonal and antifungal agents, leads to disruption of the functioning of a vital organ.
- Poisoning. Systematic exposure to toxic substances on the human body as a result of working in hazardous industries leads to liver damage. A single exposure to heavy metal vapors or chemical compounds can cause acute necrosis of the gland. Liver failure occurs, as a result of which the remaining healthy cells cannot perform all the functions assigned to them. Over time, dead cells are replaced by connective tissue, which leads to the development of cirrhosis.
- Alcohol poisoning. Alcohol abuse also leads to cirrhosis.
- Poor nutrition. A high content of fatty, spicy, fried and smoked foods in the diet impedes the flow of bile, which leads to stagnation, resulting in the formation of stones both in the gallbladder and in the ducts.
- Genetic predisposition. Disturbances in the structure of the liver cause a narrowing of the ducts and vessels, which impedes the flow of blood and bile; poor development of a vital organ or its parts leads to decreased functioning.
- The presence of purulent foci in the peritoneum. This affects the functioning of the biliary tract, and cholangitis or abscess develops.
- Exposure to radiation. Radiation or ionizing phonation causes the degeneration of liver cells into cells that are malignant.
There are a lot of factors that influence the condition and functioning of the organ, but most of them are related to lifestyle, so a person can maintain his health.
Liver examination using medical equipment
In modern medicine, to check liver pathology, objective indicators are used from devices created on the basis of the penetrating and reflective ability of ultrasonic vibrations, the resonating capabilities of magnetic radiation, and the accumulation of isotopes in “related” tissue.
Ultrasound diagnostics of the liver is carried out routinely and urgently in any hospital. The procedure is safe for small children and pregnant women. Allows you to identify the exact size of the organ, the density of the parenchyma structure, the node and localization of the neoplasm, cysts, and the degree of damage.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are even more informative. They give results in a multidimensional image, allowing you to see the degree of replacement of the parenchyma with scar tissue. Better display of intrahepatic ducts and vessels. Scanning is carried out using intravenous injection of isotopes, which are delivered by blood to the liver. Here they are distributed throughout all functioning cells.
When scanning, it is possible to identify areas of scar changes in non-functioning tissue, establish tumor growth (the isotope does not pass into malignant cells), and the extent of the remaining healthy parenchyma. Biopsy is prescribed only if the results of other types of studies are insufficient, for differential diagnosis with tumors.
During a biopsy, a needle is inserted into the liver, with which material is removed and subsequently processed in the laboratory.
What are liver diseases?
In medicine, the main diseases are considered to be the following:
- Hepatitis is inflammation of a different nature. They can be acute or chronic, toxic, medicinal or viral in nature. In the absence of timely treatment, the general condition of a person worsens significantly.
- Primary cirrhosis. The disease is more common in women. Symptoms of liver disease include itching, ulcers, yellowing of the mucous membranes and dermis.
- Cholangitis. Inflammatory processes occur in the ducts of the organ.
- Vascular abnormalities – congestive liver, venous thrombosis.
- Tuberculosis - bacteria usually enter from the intestine through hematogenous or lymphogenous routes, and sometimes spread through the bile ducts.
- Fatty degeneration - organ cells are replaced by adipose tissue.
- Liver failure is characterized by a violation of one or more functions. Appears due to damage to the parenchyma.
- Hepatomegaly is a pathological increase in the size of a vital organ. This condition is characteristic of many diseases.
- Volumetric (focal) liver formations are single and multiple areas of structural changes, the origin of which can be very different: benign and malignant.
- Steatosis is fatty infiltration of an organ. Fat accumulation occurs in the cells.
- A cyst is a benign cavity formation filled with fluid inside. Located in various segments of the liver.
- Hepatic coma is caused by deep depression of the organ. The person loses consciousness, his blood circulation and breathing are impaired.
Most often, when examining patients, hepatitis, cirrhosis and liver steatosis are detected.
How to determine the severity of a process based on analysis?
Several blood values are used to determine Child-Pugh severity. These are bilirubin, albumin, prothrombin time. A certain level corresponds to a particular number of points. The higher the total score, the more severe the cirrhosis.
Other features included in this table are ascites, encephalopathy, and nutrition.
What bilirubin, albumin, prothrombin time and other factors provide 1 point for liver cirrhosis? Bilirubin levels are less than 2 mg%, albumin is more than 3.5 g%, prothrombin time (PTT) is increased by 1-3 seconds (normal 11-16 seconds), there is no ascites or encephalopathy, nutrition is good.
2 points are given for the following indicators: bilirubin - 2-3 mg%, albumin - 2.8-3.5 g%, PTT - increased by 4-6 s, ascites is moderate, mild encephalopathy, average nutrition.
3 points are provided by the following numbers: bilirubin - more than 3 mg%, albumin - less than 2.8 g%, PTT - increased by more than 6 s, significant ascites, reduced nutrition to the point of exhaustion, severe encephalopathy.
The total score will determine the class of liver cirrhosis: 5-6 – A (mild), 7-9 – B (moderate), 10-15 – C (severe).
We have put a lot of effort into making sure you can read this article and would welcome your feedback in the form of a rating. The author will be pleased to see that you were interested in this material. Thank you!
Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis must be comprehensive. At the initial examination, the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis based on clinical signs and write a referral for abdominal ultrasound and laboratory tests. Cirrhosis is a severe lesion of the liver parenchyma, in which normal functional tissue is replaced by dense connective tissue. Changes in the body are irreversible; tests can only help determine the severity of the damage and give the patient a prognosis.
The first signs of the disease
To recognize the symptoms of the disease, you need to know where the liver is. Its shape is similar to an obtuse triangle, which consists of two lobes and has rounded edges. The liver is located in the peritoneum on the right side. Its upper part is located from the left nipple to the right, and the lower part is located at the right ribs. In the early stages of the disease there may be no signs. This organ does not contain nerve fibers, so pain may not appear for a long time.
In case of liver disease, the very first sign is weakness and fatigue. But it should be remembered that a number of other diseases also have such symptoms, or they may simply appear with excessive stress. If you are constantly feeling unwell without any apparent reason, it is advisable to consult a doctor. In diseases, these symptoms are associated with intoxication of the body, since the liver ceases to cope with its cleansing. In addition, there may be a violation of metabolic processes: vitamin, carbohydrate and protein. Only a doctor can understand all the intricacies. The most important thing is to contact him promptly at the first signs of liver disease.
What should a doctor identify during an appointment?
To determine liver disease, the doctor has the opportunity to question the patient, find out the most typical complaints and perform an examination. The result is a presumptive diagnosis. To confirm, the doctor decides which tests to order to check the liver. This is important, since not all high-quality studies can be carried out by the laboratory of the clinic; it is possible that some tests will have to be taken in private institutions on a paid basis.
During diagnosis, doctors use such an ancient method of determining the boundaries of the liver as Kurlov percussion. The method cannot be considered reliable in modern conditions, since it depends on the doctor’s practice and the ability to detect the slightest change in sound.
Percussion is carried out with short blows on the middle phalanx of the third finger of the pressed palm, the finger moves to the place where a change in sound is heard
The liver percussion technique involves determining the boundaries of the lower and upper edges of the organ along the right midclavicular and parasternal (runs along the outer border of the sternum) lines. Then the distance between the extreme points is measured. Sometimes there is a need to percussion along the anterior axillary line on the right.
The position of the left lobe is clarified by percussion from the upper point of the midline of the sternum to the left at an angle of 45 degrees. The table shows the norm for children and adults.
| Line names | Size for children under 7 years old in cm | Size for children 7–10 years old in cm | Adult size in cm |
| Right midclavicular | 5,5–6,5 | 6,5–9,5 | no more than 10 |
| Right parasternal | 4,5 | 6,5 | 7–8 |
| Deviation at an angle | 5,5 | 7,5 | 7 |
Pediatricians believe that percussion is suitable for diagnosis in children after 7 years of age. Small deviations are possible with different body types (asthenics and hypersthenics). The given dimensions should not be confused with the size revealed by ultrasound. Most often, a displacement of the lower edge is detected, which is confirmed by further palpation (hepatitis).
The upper border of the liver is in contact with the right lung. An increase is possible with a large cyst, tumor, or abscess. Fixation of reduced sizes is possible. This symptom accompanies primary biliary cirrhosis and other types of fibrosis of the liver tissue.
Main symptoms of pathology
Diseases of this organ pass for a long time without any signs; pain appears even with severe damage to the liver, when it increases in size and begins to compress the fibrous membrane where the pain receptors are located. The following symptoms may appear with various liver diseases:
- weakness and general malaise;
- heaviness under the ribs on the right side;
- yellowness of mucous membranes and skin;
- dark color of urine;
- feces have a liquid consistency and grayish-white color;
- the appearance of swelling;
- formation of hematomas as a result of vessel fragility;
- increased sweating;
- frequent bleeding;
- in the morning there is a bitter taste in the mouth, a yellow coating on the tongue and an unpleasant odor;
- papules on the skin, burning and itching;
- sudden weight loss;
- the appearance of a venous pattern on the abdomen and an increase in its volume;
- frequent headaches, loss of memory and mental abilities;
- hormonal imbalance and dysfunction of the nervous system;
- significant increase in volume.
Symptoms of liver disease include numbness in the muscles, coldness in the fingers and toes, and nails that become brittle and brittle with white streaks or spots. Hepatitis and cirrhosis are accompanied by a slight increase in temperature. When its values are more than 39 degrees, one should expect that a purulent process develops. The nervous system reacts with sleep disturbances, apathy, and fatigue due to incomplete elimination of toxins due to poor functioning of the organ.
Fibrotest
In modern laboratories, a new non-invasive method for diagnosing liver lesions is being actively introduced - fibrotest. It is an alternative to biopsy. The main task is to determine the stage of fibrosis and necroinflammatory activity. Indications for fibrotest may include chronic hepatitis. Since 2008, in France, this study has been recognized as a reliable method for determining hepatitis C in an advanced stage. Fibrotest is safe and can therefore be used during pregnancy.
Diagnostics
To establish a diagnosis, the doctor conducts the following studies:
- Conversation with the patient – listens to the patient’s complaints.
- Examination – visual examination: abdominal volume, skin and tongue color, presence of rashes.
- Palpation - the size of a vital organ, density, and outline are determined.
- A biochemical blood test for liver disease helps diagnose hepatitis, metabolic disorders and cirrhosis.
- General analysis of urine - the color, transparency, smell, and nature of the foam are examined.
- Stool analysis - determines physical and chemical indicators.
- Analysis for viral hepatitis and HIV infection.
- Ultrasound – to identify the source of the disease.
- CT and MRI - the lesion is determined, the size and condition of the tissues are specified.
- Puncture – to collect material for histology.
- Duodenal intubation - assesses the function of the gallbladder, collecting bile for analysis.
The diagnosis of liver diseases allows us to accurately establish the diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Markers of viral hepatitis
Antibodies can be divided into 2 types: IgM and IgG. The former indicate an acute stage of the process, the latter indicate a past infection and persist throughout life.
For hepatitis A, it is enough to determine IgM. The most accurate indicator for viral hepatitis B is HBeAg. This nuclear antigen indicates the presence of active reproduction of the virus in hepatocytes and high blood contamination. Hepatitis C is also detected.
It is important to monitor the increase in antibody titer over time. Since viruses can pass from mother to child, you need to be tested for hepatitis before pregnancy.
Skin changes due to diseases
In diseases associated with this internal organ, specific changes occur in the skin. They may include the following manifestations:
- Jaundice color of the dermis. First of all, the mucous membranes, eye sclera, the lower surface of the tongue, palms, feet, face change color, and then the whole body takes on a yellowish tint, especially noticeable in natural light.
This process is associated with increased levels of bilirubin in the blood.
- Skin rash. Rashes in liver diseases manifest themselves in the form of: pustular lesions, boils, dermatitis, eczema, hemorrhagic rash. All this is associated with functional disorders in the functioning of the internal organ - the inability to synthesize immunoglobulin, neutralize toxic substances, and produce prothrombin.
- The appearance of stretch marks. They often appear on the abdomen in the form of thin bluish stripes. A hormonal imbalance occurs in the body, as the liver cannot cope with excess steroid hormones.
- Body itching due to liver disease is explained by an increased concentration of toxic substances in the epidermis as a result of poor functioning of the organ. Irritated skin on the abdomen, thighs and forearms scratches and is very difficult to treat.
- Spider veins are small blood vessels. They appear on the face, neck, and then spread throughout the body and are considered signs of cirrhosis.
- Pronounced pallor of the skin. Impaired absorption of nutrients and a reduced amount of protein for the formation of hemoglobin leads to anemia.
- Spots on the skin due to liver diseases. They appear in the groin and axillary area. The pigmentation has a bronze or smoky color and is a symptom of hemochromatosis.
Serum enzyme determination
Aspartate aminotransferase - AsT. This enzyme is found in large quantities in the heart, liver, kidneys and muscles. Its level in the blood increases when the tissues of any of these organs are damaged. Alanine aminotransferase AlT. The content of this enzyme is higher in the kidneys than in the heart or muscles. Therefore, an increase in its blood level is a more specific sign of liver cell damage than an increased AST level. An increase in the blood levels of these two transaminase enzymes in the blood serum helps diagnose liver cell damage, most often caused by viral hepatitis. Sometimes the level of transaminases increases with other liver disorders caused by taking any medications, or insufficient blood supply to the liver. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGTP). High levels of this enzyme in the blood can be caused by both hepatitis and blockage of the bile ducts. The content of this enzyme increases with prolonged alcohol abuse or when taking certain medications (anticonvulsants). In some cases, increased GGTP levels are not associated with impaired liver function. Alkaline phosphatase. The content of this enzyme increases when the bile ducts are blocked or inflamed, and sometimes when liver cells are damaged by the hepatitis virus. High levels of alkaline phosphatase may also indicate a blockage of the bile ducts by a stone, tumor, or adhesions. Sometimes the enzyme level increases during hepatitis that occurs against the background of normally functioning bile ducts (congestive or cholestatic form of hepatitis). Blood proteins. The liver produces a number of proteins important for the body: albumin, fibrinogen and many substances involved in thrombus formation (blood coagulation factors). In severe forms of hepatitis or chronic liver diseases, the protein content in the blood decreases markedly.
Liver pain
Based on the intensity and nature of the pain, one can assume the type of gland disease:
- Acute – occurs due to pathological phenomena in the gallbladder. A spasm of the bile ducts occurs, which leads to disruption of the outflow of bile, and hepatic colic begins.
- Burning – appears in acute cholecystitis. At the same time, bitterness appears in the mouth, the temperature rises, nausea and vomiting begin. Pain from liver disease can radiate to the right arm and collarbone.
- Dull – characteristic of chronic inflammatory diseases: cholecystitis, hepatitis. Additional signs will be: poor digestion of food, flatulence, nausea.
- Aching – characteristic of cirrhosis or malignant tumors.
In some cases, pain in the right hypochondrium can cause diseases that are completely unrelated to the internal organ in question.
Basic liver functions
The liver is involved in all significant transport and redistribution flows in the body. Neutralizes harmful substances and toxins that enter the body with inhaled air and food. Participates in the digestion process, converting consumed foods into nutrients and energy.
Stores vitamins and microelements that the body may need at the right time. Participates in the processing of fat and controls its level in the body. Synthesizes proteins necessary for the body to clot blood and protect the body from infections. And this is not the entire list of functions that the liver provides.
The liver is quite resistant to external destroyers and is able to recover (renew) after damage or an inflammatory process. However, increasing the load on it may disrupt the update process. Such painful processes in the liver are promoted by alcohol and cigarettes, which add additional toxins to the blood.
An irregular and unbalanced diet (fatty foods, fried foods, smoked foods) has a harmful effect. The liver suffers from uncontrolled use of antipyretic and painkillers. Liver damage is caused by infectious diseases, such as viral hepatitis, as well as metabolic disorders.
When the liver, for one reason or another, can no longer restore its tissues, its destruction begins. Due to cell damage, liver functions are impaired and liver failure develops.
Damage can lead to fatty deposits (fatty liver), liver inflammation. It is possible for normal liver tissue to turn into connective (scar) tissue. Gradually, the liver becomes deformed, changes its structure, shape and ceases to disinfect toxins. Liver cirrhosis develops.
The liver is involved in all significant transport and redistribution flows in the body
When the liver, for one reason or another, can no longer restore its tissues, its destruction begins. Due to cell damage, liver functions are impaired and liver failure develops.
Damage can lead to fatty deposits (fatty liver), liver inflammation. It is possible for normal liver tissue to turn into connective (scar) tissue. Gradually, the liver becomes deformed, changes its structure, shape and ceases to disinfect toxins. Liver cirrhosis develops.
The main danger of liver diseases is that the initial stage of the disease occurs without pain symptoms. There are no nerve endings in the liver. The main signals of liver disease may be fatigue and weakness. As well as loss of appetite, recurring attacks of nausea and pain in the right side.
Clinic for men
All people, regardless of age, suffer from various ailments of the key human organ. There is no difference between the signs of liver disease in men and women. According to medical statistics, it is believed that women are less susceptible to these diseases than men. This is most likely due to the way of life, and not to the constitutional characteristics of a person. Some diseases are more common in women. For example, long-term use of hormonal contraceptives provokes disruption of the hepatobiliary system (removal of metabolic and digestive products from the body). Others suffer more often than men. For example, cirrhosis, which occurs from excessive alcohol consumption or working conditions with toxic substances. Certain types of pathology affect sexual activity in men. Signs of liver disease, which appear with the massive death of hepatocytes, lead to a decrease in potency.
Preparing for a blood test
It is advisable to come to the laboratory in the first half of the day. Before diagnosis, it is important not to eat food for 8-12 hours; you are only allowed to drink water. It is prohibited to undergo examination after drinking alcohol, this will greatly distort the result, because iron will actively process toxins. Avoid alcoholic beverages at least 24 hours before the test, and do not smoke 1 hour before donating blood.
Avoid physical activity for several days (ideally a week). Eliminate fatty foods at least a day before the examination, and in the evening, on the eve of the diagnosis, do not consume coffee and dairy products (consuming skim milk is allowed). Avoiding severe stress is also necessary for reliable results. A number of medications can distort the examination result. It is necessary to notify your doctor in advance about taking any medications.
Liver diseases have a huge impact on the entire body. The best prevention is proper nutrition, getting rid of bad habits and refusing to take uncontrolled medications. Advanced gland diseases lead to irreversible consequences. At the slightest suspicion of organ pathology, you should consult a doctor, he will conduct the necessary check of the condition, and give an explanation of the diagnostic results.
Blood analysis
When analyzing the biochemistry of blood, its composition is revealed, the results of which are entered into a certain form, which lists the main components and their content in the blood. The values of the indicators may vary depending on the age and gender of the patient. Their deviations from the norm are a symptom of a malfunction of the organ. Only the attending physician can correctly evaluate all the results of the analysis and compare them with other signs and causes of the disease. The main indicators of liver disease in blood biochemistry are:
- proteins – total, creatine, albumin, uric acid, urea;
- lipids and lipoproteins – cholesterol, apolipoprotein, triglycerides;
- carbohydrates – fructosamine, glucose;
- specific proteins – transferrin, C-reactive protein, ferritin, myoglobin, troponin;
- electrolytes;
- pigments – bile acids, bilirubin;
- vitamins.
Only blood biochemistry reflects the functional state of the internal organ and will significantly help the doctor make a diagnosis.
MRI, CT scan of the liver
Non-invasive liver studies include computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. These techniques allow you to obtain a picture of the organ in the form of sections with a step of 5–10 mm. Contrast enhancement is used to identify the most common focal pathology. The methods make it possible to determine any deviations from the norm in size and structure. Disadvantages include the high cost of research and the presence of contraindications (pregnancy, presence of a pacemaker).
Coated tongue
The tongue is not only a participant in the digestive process, but also an indicator of human health. When visiting a doctor, you can often hear the phrase: “Stick out your tongue.” This interest of doctors is not accidental; the tongue is one of the first to sense the onset of abnormalities in the body. An experienced doctor can determine the symptoms of certain ailments by the appearance of this vital internal organ. The color of the tongue in liver diseases usually becomes yellow.
This color is caused by disorders associated with the outflow of bile from the gallbladder. The most common cause of this phenomenon is the occurrence of cholecystitis due to stagnation of bile or hepatitis infection. In addition, a bitter taste appears in the mouth and painful sensations in the right hypochondrium. Sometimes the appearance of a yellow coating indicates stomach diseases or prolonged smoking. Of course, it is impossible to make a diagnosis based on the color of the tongue. To do this, it is necessary to take into account other symptoms and reasons that caused the change in the color of the tongue and the results of laboratory tests. In case of liver disease in complex cases, instrumental studies are also carried out.
What is done to detect cirrhosis?
To identify cirrhosis, the patient undergoes all the described diagnostics. Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is also necessary. In conclusion, the doctor notes the blood-filled and dilated veins of the stomach and esophagus, signs of concomitant gastritis, duodenitis. To determine the type of cirrhosis, all immunological and biochemical tests are necessary.
In addition to the alcoholic cause, the disease can be a consequence of chronic viral hepatitis C. It is important to consider that for a long time the pathology is asymptomatic. Much more than for other pathologies, a liver biopsy is indicated.
In some cases, it is necessary to resort to laparoscopy under general anesthesia (insertion of an optical tube into the abdominal cavity). Anyone can have their liver checked if they feel something is wrong with their health or find typical symptoms. The main thing is not to delay and get an answer to solve your problem.
Ultrasound and fibroelastometry of the liver.
If the blood test is suspicious, the doctor will prescribe an ultrasound examination, during which structural changes in the liver can be seen.
But fibroelastometry will help you get an answer to the question of what exactly happens to the organ tissues.
Fibroelastometry or fibroscanning of the liver is similar in appearance to ultrasound. A special sensor is installed between the patient’s ribs, which generates electromagnetic waves. They are reflected differently from healthy and diseased fibrous areas of the liver due to the density of the tissue, which is why fibroelastometry is also sometimes called measuring liver stiffness.
The procedure lasts 15 minutes. 10 measurements are taken from one point to obtain an average.
It is important that fibroelastometry must be done strictly on an empty stomach, otherwise the result may be erroneous.
Ultrasound and fibroelastometry make it possible to see in what place and to what extent the liver tissue is affected. But how do we understand what exactly this lesion is: a parasitic cyst, oncology, hepatitis?