Women quite often have to deal with various ailments. The most popular reason for patients to visit a gynecologist is pain in the lower abdomen (in the middle). In women, these sensations may occur periodically or be permanent. You can learn about the reasons for such discomfort from the article below.
Is it normal for women to have pain in the lower abdomen (middle)?
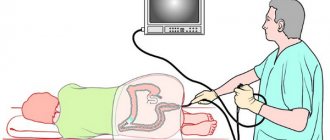
When a patient comes to see a gynecologist, she is first of all interested in whether such sensations are normal or if it is a pathology. The doctor will not be able to answer this question right away. To find out what caused the pain in the lower abdomen (middle) in women, it is necessary to conduct some examination. Usually it includes a gynecological examination, taking a smear, and ultrasound diagnostics. Based on the results obtained, the doctor may prescribe additional studies. These include colposcopy, hysteroscopy, magnetic resonance imaging, laparoscopy, and so on.
Depending on what caused the pain in the lower abdomen (in the middle), women are given a diagnosis. It is worth noting that such sensations are not always a symptom of pathology. Sometimes this can be an absolute norm or a physiological feature. Let's look at the main causes and symptoms of lower abdominal pain in women.
Principles and approaches to the treatment of such pain
Treatment for this symptom depends on the cause that caused it. The most correct decision would be to visit a specialist who will clarify the nature of the pain and offer a competent treatment regimen. If abdominal pain is associated with cramps, then antispasmodics (Drotaverine, etc.) will help eliminate it. In cases of severe severe pain, it is better not to take painkillers and antispasmodics before the doctor arrives, so as not to blur the clinical symptoms.
For any cause of pain, before consulting a specialist, you can play it safe and provide the body with hunger, cold and rest to make it easier to endure this condition. Heat or heating pads on the abdominal area can only be used in cases of spastic pain. If the patient is not sure, then it is better not to do this.
Intestinal problems
Pain in the lower abdomen (in the middle) in women can occur due to intestinal pathologies. So, most often it is fecal retention or frequent bowel movements. Usually such symptoms appear due to poor nutrition. However, they can also be caused by more serious problems, such as inflammation or dysbiosis.
If discomfort arises due to problems in the intestines, then the fairer sex often notices other symptoms. These include increased gas formation, lack of appetite, nausea, and so on. If you have problems with your intestines, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible and get qualified help.
Digestive system disorders
Both men and women initially associate the occurrence of discomfort in the abdominal area with digestive disorders. This is a completely logical and often correct assumption. The most common causes of discomfort are the following pathological diseases:
- Appendicitis is an acute inflammation of the appendage of the cecum. In the acute course, the patient experiences sudden severe pain in the right iliac region. At first the pain is vague, but after a few hours it concentrates in the right side of the lower abdomen, intensifying when coughing, laughing and subsiding slightly when lying down.
- Enterocolitis is a digestive disorder caused by infectious non-infectious inflammation of the intestine. The disease is characterized by acute symptoms: vague abdominal pain, heaviness, rumbling. Enterocolitis is often accompanied by diarrhea; when it is infectious, mucus and blood are found in the stool.
One of the common causes of pain in this area is gastrointestinal pathology. Let's list the most common diseases and conditions.
- Appendicitis (inflammation of the appendix of the cecum). In the first hours/days, the pain is localized in the middle of the abdomen, then the right side in the lower abdomen begins to hurt. In addition, this acute surgical pathology is characterized by nausea, vomiting, digestive disorders and general condition. Check for characteristic symptoms of peritoneal irritation: muscle tension in the right iliac region, Voskresensky, Shchetkin-Blumberg, Sitkovsky, etc. symptom.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases (colitis, enteritis). These diseases are accompanied by disorders of the digestive tract: nausea, bloating, stool disorders, mucus or bloody discharge in the stool. They are characterized by bursting pain in the abdominal area.
- Acute and chronic intestinal obstruction. The pathology is caused by a violation of the movement of contents along the digestive tract. Accompanied by abdominal pain, vomiting, retention of stool and gas, bloating and asymmetry.
- Diseases of the biliary tract. Problems with the biliary tract (stones, stricture, cholecystitis) lead to discomfort in the lower abdomen on the right and indigestion due to insufficient flow of bile into the intestines. In addition to pain, the patient complains of nausea, heaviness in the stomach, belching, heartburn and other dyspeptic disorders. With severe obstruction of the biliary tract, the patient may develop jaundice. Hepatic colic develops due to blockage of the bile ducts by a stone. It is characterized by paroxysmal stabbing pain in the right hypochondrium, which spreads to the shoulder, shoulder blade and abdomen. The pain can be cramping or constant and is often accompanied by frequent vomiting, which does not improve the patient’s well-being.
- Liver diseases (hepatitis, jaundice). Problems with the liver occur with unpleasant sensations in the area of the right hypochondrium. With cirrhosis of the liver, in addition to pain, the patient experiences many other symptoms: nose and gum bleeding, jaundice, appetite and digestive disorders, swelling, change in the color of stool, telangiectasia, spider veins, redness of the palms, change in the color of the tongue.
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. Outside of an exacerbation, the patient only experiences digestive dysfunction. During an exacerbation, sharp pain in the abdomen is disturbing, usually in the upper part, but it can also move lower.
- Poisoning. Food poisoning is accompanied by abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Vomiting brings noticeable relief. The duration of the disease depends on the reactivity of the body and the damaging agent.
- Helminthiases (enterobiasis, etc.). The presence of parasites in the body can manifest as unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen. With enterobiasis, the patient is concerned about itching of the anus, loss of appetite, weight loss and changes in the character of stool.
- Complications of peptic ulcer and duodenum (bleeding, penetration, perforation). These complications are accompanied by a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition, abdominal pain and other symptoms: vomiting mixed with blood, signs of peritoneal irritation, etc.
- Acute pancreatitis. It is suspected if the left side in the lower abdomen hurts. The disease is accompanied by nausea, bloating, repeated vomiting and dehydration.
Onset of pregnancy: implantation
Pain in the lower abdomen (in the middle) in women can be a sign of fertilization. So, after the fusion of the male and female gametes, the cells begin to actively divide and gradually descend into the uterine cavity. Here the implantation of the membranes into the wall of the organ occurs. This process is accompanied by minor damage to small capillaries and pain.
It is worth noting that not all women feel such discomfort. In more than half of the cases, implantation occurs asymptomatically. This is explained by the fact that this pain is very insignificant. Sometimes implantation of the fetus into the uterus is accompanied by a short one-day bleeding. After just one week, a woman can take a home pregnancy test and get a positive answer.
Can a symptom indicate the development of a myomatous node?
Spasmodic feelings in the lower abdominal cavity are also a manifestation of a myomatous node. In this case, the symptoms resemble the beginning of the birth process. The uterus functions in an enhanced mode. The muscles are actively contracting.
If you experience recurring pain, you should be checked for uterine fibroids.
Signs indicate that the body is trying to get rid of the existing tumor on its own. When a growth forms, intense pain occurs. The pain also extends to the genitals.
The disorder can only be corrected through surgery under general anesthesia. In the absence of therapy, there is a high probability of painful shock. It is important to regularly visit a gynecologist in order to promptly detect the course of the disease and begin elimination.
Myomatous nodes are also accompanied by heavy and prolonged menstruation.
Menstruation
Pain in the lower abdomen in women before menstruation is a very common phenomenon. Approximately 80 percent of all representatives of the fairer sex feel this discomfort. Sometimes this is explained by a physiological feature and a low pain threshold. In other cases, pathology is detected.
Painful sensations may begin several hours before bleeding begins and persist for the first few days. To alleviate your condition, try not to engage in physical activity during this period, but rather rest more. It is also worth visiting a gynecologist and finding out whether this is a normal reaction of the body to monthly bleeding.
Pathologies of the nervous system
Neuropathies are often the cause of discomfort. Pathologies are not widespread. However, there are often cases when neuropathies reduce performance for quite a long period of time, and sometimes lead to disability.
Damage to the femoral nerve is characterized by sharp, shooting pains. Not only the surface of the thigh hurts, but also the pelvic area, lower abdomen, the unpleasant sensation spreads all the way to the foot. The cause of discomfort can also be damage to the femoroinguinal and iliohypogastric nerves.
Pregnancy and the threat of termination
A dull pain in the lower abdomen in women (in the middle) can occur during pregnancy. In this case, you need to immediately put aside your business and visit a doctor, or better yet, call an ambulance. At the same time, symptoms such as bleeding from the genital tract, a decrease in the strength of toxicosis, and so on may occur.
The normal state of the uterus during pregnancy is maintained by a hormone called progesterone. It ensures that the reproductive organ is in a relaxed state and does not try to push the fetus out. If the amount of this substance decreases, contractions begin, leading to similar pain.
Unpleasant sensations in the abdomen during pregnancy
The weaker sex is sensitive and emotional. Any discomfort, first of all, causes psychological inconvenience. The woman immediately tries to find the cause of the unpleasant sensation in the abdomen, and, as is known, pathology is better treated in the early stages. Unpleasant sensations can be different. Based on their nature and accompanying symptoms, you can independently identify the probable cause of discomfort:
- Dull pain accompanied by spotting may indicate inflammatory processes in the urinary system.
- Intense pain, copious discharge with blood, high temperature are often signs of infectious diseases of the pelvis.
- Blurry cramping pain in the abdomen, bloating, and nausea may indicate gastrointestinal disorders.
During gestation, any discomfort in a woman’s body causes her to panic. Expectant mothers react especially acutely to pain. Before you panic, you should understand the causes of discomfort in the lower abdomen during pregnancy.
All types of pain are divided into obstetric and non-obstetric. Obstetrics are directly related to pregnancy, non-obstetrics are gastrointestinal disorders, structural changes in the abdomen, inflammatory diseases of internal organs.
Obstetrics:
- Ectopic pregnancy is the development of a fertilized egg outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. The initial symptoms are the same as during normal pregnancy: signs of toxicosis, delayed menstruation. Then unpleasant sensations appear in the abdominal area, which quickly become intense. Such pain indicates termination of a tubal pregnancy; the woman needs immediate hospitalization.
- Premature placental abruption is always accompanied by sharp pain, spasms of the uterine muscles, and bleeding.
- Risk of miscarriage. Symptoms of spontaneous abortion are nagging suprapubic pain and spotting.
Non-obstetric:
- Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Strained abdominal muscles and round ligament.
- Diseases of internal organs of an inflammatory nature: cholecystitis, pancreatitis, inflammatory processes in the kidneys, urinary tract.
The cause of pain is a neoplasm
A nagging pain in the lower abdomen (in the middle) in women is sometimes a symptom of a tumor. Often this is a benign functional formation that has grown due to a slight hormonal imbalance. Such cysts on the ovaries go through several cycles and do not cause any harm to the woman’s health. However, sometimes a tumor can still have the same benign nature, but be non-functional. In this case, it begins to grow for some reason, affects neighboring organs and causes a feeling of heaviness, pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen in the middle.
Malignant tumors are much less common. They usually appear in older women. Such neoplasms must be treated as soon as possible. To correct the condition, a surgical operation and a subsequent course of recovery of the body are performed.
Pain due to disorders in the genital area
Gynecologists divide lower abdominal pain in patients into functional (physiological) and organic. Functional reasons are caused by temporary underdevelopment of the genital organs in girls, associated with menstruation, pregnancy. They are associated with excitement, hypothermia, and the onset of sexual activity.
Organic causes always manifest themselves in acute or chronic pathology of the uterus and appendages. The pain varies in nature and may be accompanied by uterine bleeding and vaginal discharge.
Differences between physiological pain and organic pain:
- lack of a clear connection with the previous action, spontaneous onset and disappearance;
- short-term nature;
- moderate intensity;
- relatively satisfactory health.
Physiological pain in women
To figure out why a girl’s lower abdomen hurts before and during each menstruation, gynecologists will need to study the patient’s hormonal levels and regimen. Primary algodismenorrhea is associated with functional disorders caused by underdevelopment of the endocrine and nervous systems.
In girls, the production of prostaglandins and estrogens increases, which increase uterine contractions. It is often observed with overload in studies, little physical activity, poor diet (coffee, sandwiches, chips), and emotional stress.
In 75% of cases, the diagnosis is defined as “premenstrual syndrome”. In addition to pain, a few days before menstruation, the following occur:
- headache and nausea;
- dizziness and fainting;
- vomit;
- The mammary glands swell and hurt.
During pregnancy, pain is caused by stretching of the ligamentous apparatus. Most often they bother primiparous women over the age of 25 with poor physical fitness.
It is impossible to exclude the occurrence of an acute disease or an exacerbation of a chronic disease during pregnancy, therefore every expectant mother is obliged to closely monitor her well-being and inform the doctor about any changes.
Ovulation pain occurs on days 14–15 of the normal menstrual cycle. Lasts for several hours or days. Women experience regular nagging pain in the lower abdomen that intensifies during sexual intercourse. They are caused by hormonal changes with increased blood supply to the ovary. Usually one-sided. Women require observation by a gynecologist.
Pain due to pathology of the genital organs in women
Organic pain, depending on pathological changes in the uterus and appendages, is provoked by: hypothermia, heavy physical work, sports, increased nervous tension, and the use of intrauterine contraceptives.
Adenomatosis (endometriosis) is caused by the proliferation of epithelium from the inner layer of the uterus into the muscular layer. The most affected are nulliparous women over 30 years of age and those suffering from infertility. Symptoms are associated with constant nagging pain above the pubis, prolonged menstrual bleeding, and brown vaginal discharge.
The epithelium forms “pockets”. Menstrual blood gets into them and puts pressure on the surrounding tissue. Therefore, during menstruation, the pain intensifies, radiating to the groin and lower back.
Hormonal drugs are used for therapy.
Inflammatory diseases (endometritis, adnexitis) are accompanied by bursting or cramping constant pain. With adnexitis (inflammation of the ovary), the pain is one-sided. Irradiation to the sacrum and lower back is observed, and the general condition worsens.
The risk of inflammation is highest in women:
- who have undergone diagnostic curettage and abortion;
- refusing long-term therapy.
Additional signs include:
- weakness, dizziness;
- muscle pain;
- temperature increase;
- unpleasant odor from vaginal discharge due to an admixture of pus;
- insomnia;
- irritability.
In 60% of women, inflammation is caused by a sexually transmitted infection. Treatment must include a temporary cessation of sexual intercourse and examination of the partner.
Congenital and acquired anomalies - in girls they are detected during a painful first menstruation (contamination of the vagina, cervix). The accumulation of blood in the cavity causes expansion and constant pain. In adult women, blood retention is facilitated by the curvature of the uterus (retrodeviation) and fusions in the cavity (synechia).
Girls need to be shown to a gynecologist and examined urgently. Special exercises are selected for women, and if the situation cannot be corrected, surgery is performed.
Tumors of the genital organs in women have benign growth and a malignant course. Benign ones include cysts and fibroids. As they grow, they stretch the organ and cause bursting pain. At the same time, stretching of ligaments and adhesions (in case of chronic inflammation) takes part in the mechanism.
Manifestations can be an acute attack due to cyst torsion or rupture. In this case, the pain is one-sided, accompanied by dizziness and nausea, and shock is possible. With fibroids, the pain is accompanied by severe uterine bleeding and signs of anemia.
Malignant tumors of the appendages are accompanied by bilateral localization, intensity in stages II–III. Signs of cancer intoxication appear:
- nausea;
- lack of appetite;
- weight loss;
- hormonal disorders;
- weakness.
Unilateral pain is caused by fallopian tube cancer. Early symptoms include intermittent, profuse, watery discharge. Uterine sarcoma is detected during examination for uterine bleeding. The tumor is characterized by rapid growth, increased pain and metastasis.
Tubal pregnancy with rupture - accompanied by sudden pain on one side of the abdomen, severe dizziness, and possible loss of consciousness caused by internal bleeding. A woman has a delay in menstruation, secondary signs of pregnancy.
Endometriosis is an insidious enemy
Pain in the lower abdomen (in the middle) in women can have hormonal causes. Often this is the development of endometriosis. It is worth noting that doctors still cannot find out the main reason for the development of pathology. Some say that sex during menstruation leads to endometriosis. Others argue that it is purely a hormonal disease. Be that as it may, with this pathology the patient may feel quite severe pain in the lower part of the peritoneum. They intensify during menstruation and subside somewhat towards the middle of the cycle. Bleeding is more abundant with the presence of chocolate-colored clots.
With endometriosis, the contents of the inner layer of the uterus grow where this should not happen. The most common pathologies detected are the ovaries, fallopian tubes, abdominal cavity, and so on. Treatment can be conservative or surgical. After correction, the pain in the middle of the abdomen in women goes away without a trace.
Reasons for men
As a rule, men do not suffer from such discomfort, but its occurrence should not be excluded.
More often the problem appears above the pubic bone, the pain moves to the lower back and sacrum. With such symptoms, there may be a problem with the seminal vesicles.
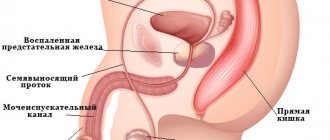
If you have prostatitis, it hurts when walking on the right or left, difficulty urinating, and possible pain during urination.
As a rule, with prostatitis, pain appears on the lower right and in the groin at the same time, and symptoms also arise in the form of elevated temperature and purulent discharge.
The last reason why a man’s lower abdomen hurts is inflammation of the testicles and appendages. This disease is called orchiepididymitis.
Pathology appears after infectious diseases, including influenza.
During the course of the disease, people feel severe pain in the testicles, the scrotum enlarges, and the skin becomes smooth and shiny. If you touch the testicles, the pain increases significantly.
Bladder pathologies
Often pain in the lower abdomen in the middle occurs with cystitis. In this case, we are talking about an inflammatory process in the bladder. Often, a woman also complains of a frequent urge to urinate, during which pain, burning and itching appear.
Cystitis must be treated with antimicrobial and diuretic drugs. However, before this you need to undergo tests that will help identify the sensitivity of microorganisms to certain drugs. After the correction, the pathology disappears, and along with it, the pain and discomfort in the abdomen in the middle is eliminated.
Classification of pain
A common cause of pain in the lower abdomen is inflammation that occurs in the pelvic organs.
Such symptoms occur in men and any woman. The main thing is to understand not only the characteristics of pain, but also the location.
If pain appears below, immediately after the pubic bone, then it is more likely that a disease of the genital organs or reproductive system is developing. There may also be pathologies of the bladder and intestines.
If the lower abdomen hurts even more when walking, then in a woman this may be a sign of inflamed ovaries.
If it hurts on the right side, then often the cause is an inflamed appendix.
In men, it may hurt on the right due to the inflammatory process in the seminal vesicles, and in women, due to inflammation of the appendages.
Pain on the left indicates inflammation of the ovary in a woman or rectum in both sexes.
Based only on the location of the pain, it is impossible to establish the cause and diagnosis with 100% accuracy. So the treatment will be incorrect and can lead to negative consequences.
During the onset of symptoms, it is necessary to pay attention to the duration of the pain, as well as its nature and intensity. Any human disease is characterized by pain of different characteristics.
Inflammation of the uterus and its appendages
Pain that appears in the lower abdomen in women and is localized in the middle may indicate an inflammatory process. Doctors call it metritis, endometritis, and also use other terms. Inflammation is often the result of an untreated infection that was acquired through sexual contact. In the acute form of the disease, women note an increase in body temperature, weakness, headache, and so on. When the inflammation becomes chronic, we can talk about the addition of discharge of an unusual color with an unpleasant odor, a feeling of pain during sexual intercourse, and so on.
Treatment of inflammation takes quite a long time using numerous medications. However, after the correction, the pain disappears and no longer bothers the patient. It is worth noting that women who have had inflammation are at risk. Often the pathology recurs and symptoms reappear.
Diagnosis and treatment methods
When a person complains of cutting pain in the lower abdomen, diagnosis in a medical institution begins with a visual examination of the patient by a doctor. He assesses the person’s condition based on external signs, after which he palpates the abdomen. This technique allows you to determine the localization of the pathology, the nature and intensity of pain.
The doctor must collect anamnesis, that is, conduct a survey of the patient. You should be prepared to answer the following questions:
- The nature of pain.
- Specificity of accompanying symptoms.
- Presence of chronic diseases.
In addition, it is necessary to remember when pain first appeared and characterize it by intensity and duration.
For an accurate diagnosis, you will definitely need to take laboratory tests of blood, urine and feces, and:
- a general blood test
will most likely show the presence of inflammatory processes; - stool analysis
allows you to understand whether abdominal cramps are associated with malfunctions of the digestive system, and can also confirm the presence of parasites; - A urine test
if the indicators deviate from the norm indicates the presence of urinary tract diseases of an infectious-inflammatory nature.
Additionally, an ultrasound is prescribed. Thanks to such hardware research, it is possible to obtain the most complete information about the state of all parts of the intestine. A colonoscopy may also be necessary to examine the condition of the colon. Additionally, radiography and fibrogastroduodenoscopy may be prescribed.
When treating diseases that are accompanied by cutting pain in the lower abdomen, an individual approach is used. Antibiotic therapy is often given. In addition, painkillers are prescribed to relieve spasms. For the treatment of various pathologies of the digestive system, various physiotherapeutic procedures may be additionally indicated. An individual diet is almost always prescribed.
Surgical treatment is used only in cases of extreme necessity.
Surgeries are required for the following pathologies:
Formation of stones or sand in the organs of the urinary system.