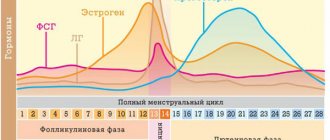
Diseases of estrogen deficiency include neuroendocrine disorders, osteoporosis, urogenital problems and pathology of the cardiovascular system. Everything is explained by the presence of estrogen receptors in many tissues: bone, epithelial, adipose. Estrogen deficiency can occur naturally as we age. There is also artificial menopause, when ovarian function is stopped by medication or surgery. In this case, the symptoms of menopause appear in the same way as during its natural onset.
Causes of colpitis
The content of the article
If in children and adolescents the main cause of the disease is non-infectious factors, then in adult women the trigger for colpitis is pathogenic microorganisms that have entered the vaginal mucosa, for example, after unprotected sexual intercourse.
But it cannot be said that colpitis occurs only in women who have sexual relations with a man without a condom, which protects against viruses, fungi and infections. The main cause of colpitis is a change in the composition of the vaginal microflora, where normally lactic acid microorganisms should predominate, protecting against the penetration of pathogenic bacteria.
Flora can change its biological composition under the influence of the following factors:
- stress and depression (they provoke a decrease in immunity);
- endocrine disorders (problems with the thyroid gland, adrenal glands);
- incorrectly selected antibiotics (or a long course of treatment) - antibiotics destroy everything indiscriminately;
- changes in diet (during a vacation in an exotic country);
- infections (staphylococci, pneumococci), STDs (STIs), genital herpes, HPV;
- injuries to the vaginal mucosa (during a gynecological examination, use of sex toys);
- climate change (travel to hot countries in winter);
- failure to comply with hygiene standards;
- promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- menopause;
- ovarian dysfunction.
Whatever the causes of colpitis, the disease causes a lot of inconvenience to a woman and gives serious complications, and therefore requires mandatory treatment.
Causes
The development of the disease is based on hypoestrogenism, which can be either physiological (after the last menstruation) or artificial (surgeries and other manipulations on the ovaries). In women of childbearing age, hypoestrogenism can develop under the following circumstances:
After childbirth, especially in lactating women
In the postpartum period, restoration of hormonal balance occurs gradually, especially in mothers who are breastfeeding (prolactin is produced), which leads to long-term hypoestrogenism and often to the development of atrophic colpitis.
Hormonal ovarian dysfunction
Long-term hormonal imbalance causes persistent hypoestrogenism and the development of the disease.
- Strong psycho-emotional experiences (disturb the level of hormone ratio).
- Endocrine pathology
Women suffering from diseases of the thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus, and pathology of the adrenal glands are prone to the occurrence of atrophic colpitis.
Other reasons
- Ovariectomy (removal of the ovaries). The ovaries synthesize estrogens, and in their absence, the production of female sex hormones stops automatically.
- Radiation therapy of the pelvic organs. Irradiation of the pelvic area also affects the female gonads, which disrupts the production of hormones, including estrogens.
- Carriers of HIV or patients with AIDS.
- Weakened immunity (negatively affects the hormone-forming function of the ovaries).
Predisposing factors
Predisposing factors for the development of the disease include:
- incorrect intimate hygiene;
- frequent, promiscuous and unprotected sexual intercourse;
- use of aromatic intimate hygiene products, fragrances, antibacterial soaps, lubricants;
- wearing tight synthetic underwear (prevents the access of air and promotes the development of anaerobic flora);
- errors in the diet (lack of fermented milk products, eating unwashed vegetables and fruits, drinking poor-quality water);
- chronic inflammatory processes of the genitals;
- common chronic diseases.
Symptoms of colpitis
Every second woman who comes to see a gynecologist has encountered colpitis at least once in her life. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- There is a burning and itching sensation in the vagina, and there may be a burning sensation when urinating;
- mild or unbearable itching occurs;
- the discharge is characterized by purulent inclusions and a cheesy consistency;
- during sexual intercourse, friction, burning and pain are felt in the genitals;
- urination is painful;
- lower abdomen hurts.
All signs of colpitis may be present at the same time or 2-3 symptoms. It all depends on the degree of development of the disease.
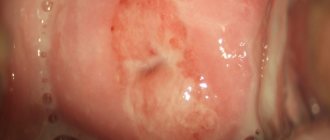
When examined in a gynecological chair for colpitis, the doctor notes the following:
- hyperemia - redness due to blood filling of the mucous surfaces;
- swelling of the vaginal walls;
- petechiae - small rash in the form of pinpoint hemorrhages;
- pigmentation (color change) of the epithelial (skin) cover;
- the natural acidity level of 3.8-4.2 pH is increased to 6.
Sometimes mild colpitis goes away on its own within a few days. Many women do not attach importance to painful sensations in the vagina and burning sensation when urinating. Moreover, colpitis is not characterized by high temperature, even in acute form. This is the danger of the disease - it easily develops into a chronic form, creating favorable conditions for infection by pathogenic microflora and the development of serious inflammation of the internal female organs.
Colpitis - what is it?
Colpitis is an inflammatory process in a woman’s vagina, which can be a source of chronic inflammation. It can spread to the uterus, ovaries, tubes, ureters and bladder. In other words, colpitis can cause not only generalized inflammation, but also infertility, which can develop if this disease is not treated in any way or self-medicated.
Nature has created many natural barriers to the entry of infection into the vagina. The following protective mechanisms help to resist microbial, viral and fungal aggression:
- Epithelium of the vaginal wall. It is multilayered, that is, “deeply layered,” and blocks the path of microorganisms when penetrating deep into its walls;
- The presence of normal lactic acid microflora in the vagina (Dederlein bacillus). Naturally, it is much more difficult to get to where the place is “occupied”;
- The acidic environment created by the rods. Normally, its pH ranges from 3.8 to 4.5. It protects tissues from microbial aggression.
The condition of vaginal dysbiosis, or bacterial vaginosis, is known. In this condition, the acidic environment is replaced by an alkaline one - a ready substrate for the development of many chronic infections;
- There is a special mucus plug in the cervical canal that reliably prevents infection of the uterus;
- Regular “self-cleaning” of the uterus during menstruation from the old epithelium and replacing it with a new one;
- Contraction, or peristalsis, of the fallopian tubes towards the uterine cavity. Although the vagina is the “final stage” of uterine protection, it takes an active part in the formation of local immunity (presence of immunoglobulins, lysozyme, activity of macrophages and neutrophils, presence of vaginal secretions).
But, alas, sometimes an inflammatory process occurs - which can have a different nature. What types of vaginitis (colpitis) are there?
Types of colpitis
Depending on the nature of the manifestation and the type of pathogen, colpitis is divided into types:
According to the intensity of the course: acute, subacute, chronic. In the acute period, colpitis can have maximum manifestations - it is during this period that you should immediately contact a good gynecologist. With chronic colpitis, the symptoms are blurred and worsen for a short time.
According to the type of pathogen:
- Specific
. It is caused by pathogenic pathogens that cannot be found on the vaginal walls of a healthy woman. This type of colpitis occurs when infected from a sexual partner. - Non-specific
. It is provoked by opportunistic microorganisms that exist in an amount of no more than 10% in the body of a healthy woman. Under the influence of unfavorable factors (weakened immunity, stress), opportunistic bacteria become pathogenic, causing inflammation of the vaginal walls.
Regarding the patient's age:
- Children's
. It is combined in childhood with vulvitis (inflammation of the external labia), and is typical for girls under 10 years of age, who often suffer from respiratory viral infections and take antibiotics. All this affects the immune system, which leads to colpitis. - Reproductive age
. It often occurs due to poor personal hygiene, when bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract enter the vaginal walls. This is possible with improper washing, wearing pads for a long time, or anal sex. Pantyliners with different scents, synthetic tights and aggressive hygiene products also contribute to colpitis. - During menopause
. In women during menopause, the production of the hormone estradiol decreases, which maintains an optimal acidity level of 3.8-4.2 pH. The thickness of the walls of the mucous membrane becomes thinner, lactic acid bacteria give way to pathogenic flora.
Atrophic colpitis in menopausal women: why the problem arises
The period of menopause is characterized by the occurrence of a complex of urogenital disorders, which include the following conditions:
- atrophy of the vaginal mucosa;
- urinary incontinence;
- prolapse of the pelvic organs.
The causes of these conditions are atrophic changes in tissues that are sensitive to estrogens:
- vaginal epithelium;
- lower third of the urinary tract;
- pelvic floor muscles;
- ligamentous apparatus.
Rarely does change occur in isolation; it is usually a combination of several problems. Moreover, the frequency of their occurrence is related to age. If at 50 urogenital disorders occur in 10% of cases, then after 55 years - in 50%. For women 75 years old, this figure reaches 80%.
According to ICD-10, the code for atrophic colpitis is N59.2, but if menopause is caused by surgery, then it is assigned code N59.3.
How the norm turns into pathology
In women of reproductive age, vaginal pH is maintained at 3.5-5.5 due to the metabolism of lactobacilli. They convert glucose into lactic acid. The nutrient medium for their life is formed from desquamated epithelium, in which a large amount of glycogen has accumulated. In addition to lactic acid, lactobacilli produce many other beneficial substances, including hydrogen peroxide. Normal mucosal microflora is maintained by the following mechanisms.
- Glycogen. Its amount in desquamated cells determines how many microorganisms are able to survive.
- Acidity. Normal pH not only affects beneficial flora, but also prevents opportunistic pathogens from multiplying.
- Estrogens. Their concentration is the determining factor. Under the influence of hormones, the epithelium intensively stores glucose, and glycogen is formed.
- Sex life. Full sex increases the transudation of fluid into the vagina if the woman is aroused, and promotes desquamation of the epithelium. Sufficient humidity allows lactobacilli to thrive.
But once estrogen deficiency develops, the amount of glycogen in epithelial cells will significantly decrease. This means that lactobacilli will not receive a nutrient medium for themselves. Their number gradually decreases until it disappears completely. The disappearance of lactobacilli leads to a decrease in the production of lactic acid and a change in pH towards the alkaline side. This creates favorable conditions for opportunistic and pathogenic flora. The protective properties of the vagina are significantly reduced.
Then symptoms of atrophic colpitis appear, such as dryness and thinning of the epithelium.
Causative agents of colpitis
Specific colpitis occurs against the background of infection with an STI, one of the symptoms of which is inflammation of the vaginal wall. The main pathogens are gonococci, trichomonas, chlamydia, Treponema pallidum (the causative agent of syphilis), Koch's bacillus, mycoplasma and ureaplasma. It is not uncommon for several types of pathogenic bacteria to be detected at once - a complex infection of the reproductive system, guaranteed to lead to infertility.
Non-specific pathogens of colpitis include opportunistic microflora, which is necessarily present in a healthy woman. The limit between the normal and dangerous content of conditional pathogens in the microflora is 10% in relation to “good” bacteria.
Conditional pathogens instantly become dangerous pathogens under the influence of the following factors:
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards (this is especially typical for girls, who often come from health camps with colpitis);
- Wearing synthetic underwear, tight-fitting trousers and leggings that do not allow air to reach the genitals. Dampness, warmth and lack of oxygen are an ideal environment for the development of colpitis;
- Using panty liners (they have various flavors, which actually have an aggressive effect on the microflora and block the access of oxygen);
- Introduction of cocci from the anus into the vagina;
- Stress, which weakens the body’s natural defenses, long-term treatment with antibiotics, frequent colds and ARVI, food poisoning, diarrhea, diets that provoke a lack of vitamins and fiber;
- Abortions, which weaken the entire system and dramatically change hormonal levels;
- Diabetes mellitus - with this disease, metabolism in cells changes, immunity decreases, and the acidity of the mucous membranes changes.
In mature women who have reached menopause, atrophic colpitis, caused by age-related thinning of the mucous surface, often occurs. During intimacy, they do not produce lubrication, as a result of which sexual intercourse becomes painful. Only hormone replacement therapy can help the situation.
Treatment of atrophic colpitis
Since the reason for the development of colpitis in the postmenopausal period is a hormonal imbalance, gynecologists use hormone therapy to treat this problem in mature women. Treatment with hormone-containing drugs is carried out in two ways. The first treatment option is local therapy. Tablets and vaginal suppositories are used. The second method is systemic, that is, taking tablets (orally, of course) and injections. The most effective and widely used drugs for the treatment of colpitis are considered to be Gynodian Depot, Ovestin and some others.
The following methods are used as auxiliary therapy:
• Physiotherapeutic procedures (most often this is a magnetic laser effect on the external genitalia).
• Treatment of the vagina and labia with soda solution.
• Use of vaginal suppositories with sea buckthorn oil.
Treatment of both acute and chronic colpitis involves complete abstinence from sexual intercourse until the tests return to normal and the symptoms of the disease disappear.
Why is colpitis dangerous?
Colpitis itself is not dangerous, although it causes a lot of unpleasant sensations; its complications, leading to serious health problems, are much more dangerous. Many women expect that the disease will go away on its own, refusing treatment; as a result, colpitis becomes chronic.
Among the possible consequences of colpitis are:
- The chronic form of the disease is dangerous due to relapses, which significantly worsen a woman’s quality of life. Constant burning, pain during sexual intercourse, thrush and other surprises become a serious obstacle in your personal life.
- Colpitis with insufficient treatment turns into cystitis and urethritis, cervical erosion, endometritis (inflammation of the upper layer of the uterus).
- Chronic colpitis of a specific nature leads to female infertility or ectopic pregnancy.
- In little girls, synechiae (fusion of the labia) occurs.
- Sores appear on the walls of the vagina, through which infection enters the body.
- Inability to perform operations on the genitals. If infected, if surgery is not delayed, blood poisoning may even occur.
Treatment of colpitis
Modern gynecology offers patients with colpitis general and local therapy. The tactics and treatment regimen in each clinical case are selected by a specialist on a strictly individual basis. The type of pathology, the presence of concomitant gynecological problems, the woman’s age, as well as her medical history are taken into account.
Local treatment of colpitis involves sanitation (douching/washing) of the vagina and external genitalia with special solutions of certain medications. Most often this is a solution of potassium permanganate (the notorious potassium permanganate), zinc sulfate, chlorophyllipt or a solution of rivanol. As a supplement, it is recommended to use decoctions of herbs that have antiseptic properties (for example, chamomile or sage).
General therapy includes restorative treatment, the purpose of which is to increase immunity. After all, as mentioned above, the low protective ability of the female body is the right path to health problems, including colpitis.
During diagnosis, the doctor determines the type of bacteria in order to treat them with antibacterial drugs during the treatment process. Antibiotics can be prescribed either topically or orally, and in some cases, both.
The patient is required to adhere to a special diet. The diet excludes dairy and fermented milk products and dishes, and also minimizes the amount of salty, fatty and spicy foods consumed. Also, during treatment, alcoholic and sweet carbonated drinks are completely excluded.
To reliably assess the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment, vaginal smears are taken from the patient at regular intervals for analysis. In patients of childbearing age, a smear is taken on the fifth day of the cycle; in young patients, as well as in the elderly, a control smear is taken after completing the full course of therapy for colpitis.
Diagnosis of colpitis
Diagnosis consists of two types of examination:
- Visual inspection
. The doctor examines the external genitalia, examines the vagina, and determines the type of discharge. Also, using mirrors, a dilator and a colposcope, the inner surface of the vagina is examined. Smears are taken for microflora. - Laboratory and clinical examination of smears.
Microflora is studied under a microscope to identify pathogenic bacteria, fungi and viruses. Bacteriological culture helps determine the sensitivity of microflora to antibiotics. Additionally, a smear is taken for cytology. - If there is a suspicion of a more serious disease, the patient undergoes a blood test for RW, HIV, and a gonococcus culture. If an STI is detected, the woman undergoes a colposcopy.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease must be comprehensive and include:
- Examination of the walls of the vagina and mucous membrane of the cervix in the speculum;
- Taking smears for microbiological examination
A large number of leukocytes are detected (with the addition of a secondary infection), which indicates inflammation, an almost complete absence of lactic acid bacteria, a high content of opportunistic flora, it is possible to identify specific pathogens (Trichomonas, fungi, Gardnerella, “key cells”, etc.).
PCR
If there is an obvious inflammatory process in the vagina and questionable microbiological results of smears, the patient is referred for testing using the PCR method (gynecological smears, urine, blood) to identify hidden sexually transmitted infections. It is possible to detect chlamydia, uro- and mycoplasmas, cytomegalovirus, genital herpes virus and human papilloma and other pathogens.
Determination of vaginal acidity
This is done with a special test strip. Normally, the pH should be between 3.5 and 5.5. In the case of atrophic vaginitis, the pH increases to 5.5 - 7 or even becomes alkaline (more than 7).
Colposcopy
Examination of the cervix and vaginal walls under magnification (colposcope). Pallor and atrophy of the mucous membranes of the vagina and cervix, the smallest injuries (cracks), a weak vascular pattern, and possibly foci of dysplasia on the walls of the vagina and cervix are revealed. Schiller's test (staining with Lugol's solution) weakly positive or uneven staining (depletion of the epithelial layer, an indirect sign of dysplasia).
Taking a smear from the cervix and from the posterior vaginal vault for cytological examination
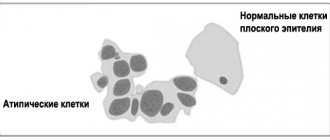
The cervical mucosa consists of several types of cells:
- keratinizing (those that are exfoliated - this is the topmost layer);
- intermediate (represented by 2 layers, located under the keratinizing ones and replace them subsequently);
- parabasal;
- basal (ripen, become parabasal, then intermediate, and finally keratinizing).
Since in this disease the epithelial layer is depleted (not only on the vaginal walls, but also on the cervix), the cytogram for atrophic colpitis will be dominated by parabasal and basal cells.
Classification of cytological smears:
- Type 1 – no atypical cells, the cytological picture is normal;
- Type 2 – the structure of epithelial cells is slightly changed due to the inflammatory process in the vagina and/or cervix;
- Type 3 – cells with altered nuclei are present, but in a single quantity (repeated cytological examination is required) and colposcopy;
- Type 4 – individual epithelial cells with obvious signs of atypia (malignancy) are detected – colposcopy and histology are necessary;
- Type 5 – many atypical (cancerous) cells.
In atrophic colpitis, as a rule, a cytogram of inflammation is diagnosed, which requires the prescription of anti-inflammatory treatment.
How is colpitis treated?
Treatment of specific and nonspecific colpitis is different. With nonspecific colpitis, the causes that provoke the disease are first eliminated. Women are advised to wear underwear made from natural fabrics, avoid douching, and take immunostimulants. When the cause of colpitis is established, the pathogenic microflora itself, which provokes inflammation, is eliminated. For this, vaginal antiseptics Miramistin, Dioxidin, Nitrofural are used.
Additionally, vaginal suppositories containing antibiotics are prescribed.
| Medicine | Active components |
| Betadine | Povidone iodine, which kills bacteria and fungi |
| chlorhexidine | Diklyukonat |
| metronidazole | 5-nitroimidazole interferes with protein synthesis in the virus cell, causing its death |
| Dalacin | Klindamitsin |
| Gaynomax | Ioconazole + tinidazole, disrupt intracellular metabolism |
| natamycin | Natamycin inhibits protein synthesis inside the virus cell |
| Vagical | Salicylic acid |
Treatment is complex, combining several types of antibiotics. If a woman is diagnosed with colpitis, her sexual partner is also treated.
Prevention
Women who are susceptible to atrophic colpitis should follow a number of recommendations to prevent this disease.
- Do not eat spicy or salty foods.
- You should give up bad habits (smoking and alcohol).
- Control your weight.
- Have a quiet sex life.
- Wear natural, comfortable and breathable underwear.
- Maintain personal hygiene. Do not use hygiene products containing chemical additives.
- Follow the doctor’s recommendations if you have diseases that contribute to the development of senile colpitis.
- To live an active lifestyle.
- Take fish oil, which helps strengthen tissue elasticity.
- Do Kegel exercises.
To avoid complications, you should consult a doctor if you experience any discomfort.
Treatment of specific colpitis: medications
When treating specific colpitis, the sexual infection that caused inflammation of the vaginal walls is eliminated first.
| Disease | Medicine |
| Gardenelez | Ginalgin (metrodinazole + chloroquinaldol), Klion-D (metrodinazole + miconazole nitrate), Terzhinan (meratin-combi + mycoginax) |
| Trichomoniasis | Suppositories Metronidazole, Fazizhin, Trichomonacid, Neo-Penotran |
| Yeasts | Suppositories Nystatin, Natamycin, Pimafucort, Clotrimazole, Canesten |
| Genital herpes | Acyclovir cream, Bonafton ointment, Epigen aerosol, interferons Poludan, Viferon, Gepon, antiviral drugs Megosin ointment, Alpizarin |
Then the woman restores the natural microflora with the help of the drugs Bifidumbacterin, Bifikol, Vagilak, Lactobacterin. To strengthen the immune system, the patient is recommended to take a course of vitamins Multitabs, Vitrus, Centrum, Riboflavin, and ascorbic acid.
It is more difficult for little girls to cure colpitis due to the low protective abilities of the vagina. Children are recommended to take baths with antiseptics, special powders, and ointments.
Physiotherapy is also effective in the treatment of colpitis. In the acute stage of the disease, the patient is recommended:
- Exposure to a high-frequency electromagnetic field with a current power of 20-30 W for 10 minutes daily for 5-8 days. The procedure relieves inflammation, destroys pathogenic bacteria, and accelerates tissue healing.
- Ultraviolet radiation, course of 6 sessions 2 times a day
In the chronic stage, doctors use:
- Zinc electrophoresis according to Kellat with a current of 10 mA for 10 minutes once a week for 6-8 weeks;
- Centimeter wave therapy, which penetrates tissue to a depth of 4 cm;
- Laser irradiation of the vulva for 5-10 minutes every day for 10 days;
- Ultraphonophoresis (exposure to a drug under current).
Treatment
What and how to treat for atrophic colpitis can only be determined by a gynecologist. The main and effective method of treating atrophic colpitis in women of both postmenopausal and reproductive age is the prescription of hormone replacement therapy or HRT. It is the intake of hormones that helps to mislead the vaginal mucosa, forcing the epithelium to renew itself cyclically (the influence of estrogens), which improves the nutrition of the mucosa, reduces the degree of its atrophy and prevents the formation of microtraumas.
HRT can be carried out in two ways: administering hormones systemically, in the form of tablets, injections or hormonal patches, or locally (suppositories, ointments, creams). Hormonal therapy should be carried out for a long time, at least 1.5 - 3 years, although a positive effect is observed after 3 - 6 months from the start of treatment. But if the course of HRT is stopped, the symptoms of senile vaginitis return again, often complicated by the addition of a secondary infection.
Local treatment
Suppositories that are prescribed for atrophic colpitis:
- Estriol
Suppositories contain the main active ingredient - estriol (an estrogenic component) and an additional one - dimethyl sulfoxide. The drug is available without a prescription. Treatment regimen: in the first month, intravaginal administration once a day, then (after a month) twice a week. The medicine reduces vaginal itching, excessive dryness, and eliminates dyspareunia. Effective for urinary disorders and urinary incontinence caused by atrophic processes in the vaginal mucosa.
- Ovestin
Available in the form of suppositories, vaginal cream and tablets. The main active ingredient is estriol, additional substances: potato starch, acetyl palmitate, lactic acid and others. The drug has the same properties as estriol. The treatment regimen is similar to estriol (first, daily intravaginal administration of suppositories for 4 weeks, then, if the condition improves, the dosage is reduced to 2 suppositories per week). Dispensed in pharmacies without a prescription.
- Gynoflor E
Available in the form of tablets for intravaginal administration. The drug contains lyophilisate of lactobacilli acidophilus in a dosage of 50 mg and estriol in an amount of 0.03 mg. They effectively restore the normal microflora of the vagina (the effect of lactobacilli acidophilus), improve the trophism of the vaginal epithelium, stimulate the growth of the epithelium (the effect of estriol), due to the glycogen included in the drug, they support the growth and development of the vagina’s own lactic acid bacteria. Treatment regimen: insertion of one tablet into the vagina daily for 6 to 12 days, then one tablet twice a week. Available without a prescription.
- Elvagin
Available in the form of vaginal suppositories and cream. The main active ingredient is estriol. Injected into the vagina daily once a day for 2 - 3 weeks, then the dose is reduced to twice a week. Dispensed from pharmacies without a prescription.
- Ortho-gynest
Available in the form of vaginal cream, suppositories and tablets. The drug contains estriol. Directions for use: administration of cream (tablets or suppositories) at a dosage of 0.5 - 1 mg per day for 20 days, then a break for a week, if symptoms weaken, continue treatment for 7 days a month. Therapy should continue for at least 6 months.
- Estrocard (cream and suppositories)
- Estrovagin (cream, vaginal suppositories)
- Ovipol Clio (suppositories).
Systemic therapy
Prescribed drugs for systemic treatment:
- Climodien
Available in the form of tablets for oral use. One package contains 28 tablets. The drug contains estradiol and dienogest. The medication is taken one tablet daily, preferably at the same time. After finishing the package, they immediately begin taking a new one. Climodien is prescribed to women with severe menopausal symptoms (hot flashes, disturbed sleep, increased sweating) and signs of senile vaginitis, but not earlier than a year after menopause. Available in pharmacies by prescription.
- Cliogest
One blister contains 28 tablets. You can start taking the drug on any day, but not earlier than a year after your last menstruation. The medicine contains estradiol propionate and norethisterone acetate. The drug is prescribed as HRT to women over 55 years of age, for the prevention of osteoporosis and the treatment of senile vaginitis. Dispensed by prescription.
- Divina
Available in the form of white (11 pieces) and blue (10 pieces) tablets. The package contains 21 tablets. The white tablets contain estradiol, and the blue tablets consist of estradiol and medroxyprogesterone. Taken daily, at the same time for 3 weeks, then a 7-day break is required, during which menstrual-like bleeding will occur. The drug is prescribed for estrogen deficiency (atrophic vaginitis), menopausal syndrome and for the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Dispensed by prescription.
- Pauzogest
The drug contains estradiol and norethisterone (monophasic drug). The package contains 28 tablets. Pauseogest is taken daily, one tablet for 4 weeks. After completing the package, they immediately begin taking a new one. Pauzogest is prescribed no earlier than one year after the last menstruation. Dispensed by prescription.
- Aktivel
- Revmelid
- Eviana.
Herbal preparations (phytohormone therapy)
- Cliophyte
Available in the form of syrup or elixir. The composition of the drug includes: rose hips, cedar seeds, hawthorn, coriander seeds, chaga, chamomile and other plant components. Treatment regimen: 10 - 15 ml of the drug is diluted in 100 ml of water and taken three times a day 15 minutes before meals for 2 - 3 weeks. If necessary, the course of treatment is repeated after 7–14 days. Available without a prescription.
- Klimadinon
The medicine contains cohosh rhizomes, which has an estrogen-like and anti-menopausal effect. One blister contains 15 tablets, a package contains 4 or 6 blisters. The drug should be taken 1 tablet twice a day at the same time, the duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. Available without a prescription.
- Qi-klim
The drug contains black cohosh root extract and is available in tablets and in the form of face and body creams. Take 1-2 tablets daily for at least a month. The duration of the course is prescribed by the doctor.
- Klimadinon Uno
- Klimaksan
- Feminal
- Remens (drops)
- Menopace (multivitamins and minerals)
- Menopace Plus (herbal ingredients)
- Bonisan
- Tribestan
- Estrovel
- Inoclim
- Lefem.
Where to cure colpitis in St. Petersburg, prices
Treatment of colpitis is a complex and lengthy process (do not confuse it with healing and temporary relief of symptoms, which is usually done by inexperienced or unscrupulous doctors), therefore, such a problem should be addressed to gynecologists with the highest category. There are such specialists at the Dina clinic in St. Petersburg.
Here you can take all tests for colpitis, undergo colposcopy, pelvic ultrasound and other important procedures. At the same time, treatment of colpitis will be quite inexpensive. For example, an appointment with the best gynecologist costs 1,000 rubles, and a consultation on test results will cost only 500 rubles. A comprehensive ultrasound of the pelvic organs using a new device in our medical center will cost only 1000 rubles. The cost of smear analysis for flora is 350 - 400 rubles.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Treatment - drugs and methods
What to do first?
Treatment of colpitis in women must be comprehensive. The most important thing is not to self-medicate, and under no circumstances use antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription. After all, vaginitis may turn out to be fungal, or even viral, and antibiotics will only cause intestinal dysbiosis and completely upset the balance of the vaginal microflora, which has still resisted aggression.
It should be a rule: antibiotics should be prescribed only after isolation of the pathogen (this can be done using PCR), and ideally after growing a pure culture and determining the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics. Only in this case their use is not only justified, but also advisable, since it allows you to avoid a lot of mistakes.
The only “minus” of this method is the long period of isolating a pure culture of the pathogen. And in this case, according to the doctor’s decision, before the results of the smears arrive, treatment can begin empirically - that is, with the most effective antibacterial drugs against a wide range of microorganisms that cause gynecological inflammation. Gynecologists know which pathogens are most active in a given region in women of different age groups, and they even prescribe empirical antibiotics with much greater efficiency than self-medication.
In the case of viral colpitis, etiotropic therapy (directed at the pathogen) should use interferons and their inducers, as well as agents that increase local antiviral immunity. In this sense, treatment of colpitis with suppositories, for example, Viferon, is highly effective.
Local treatment of inflammation must be a prerequisite. Instillations, douching, and also washing of the genitals are used.
Attention! The direction of washing should always be from front to back, as well as the direction of fluid flow, so as not to introduce flora from the rectum into the genital tract.
For acute vaginitis, the following douching solutions are used:
- Light pink solution of potassium permanganate;
- Chlorophyllipt solution;
- A solution of chlorhexidine, furacillin, hydrogen peroxide, Miramistin is also used as one of the universal antiseptics;
- To thin out thick mucus, douching with a solution of baking soda is used, and then with the above solutions. Soda helps well in the complex treatment of candidal colpitis;
- A decoction of chamomile, sage, St. John's wort and calendula, and other herbs is also used.
In addition to antiseptics, as prescribed by a doctor, tampons with antibiotics, for example, streptomycin emulsion or syntomycin liniment, are used.
Intramuscular and, even more so, intravenous administration of antibacterial drugs is necessary in case of a pronounced general reaction of the body and fever, a purulent process, as well as when a specific infection is detected, for example, with gonorrhea or trichomoniasis.
An obligatory component of the treatment of any colpitis is the strengthening of local and general immunity, as well as the introduction of lactobacilli into the vagina after finishing taking antibiotics. This will allow you to quickly normalize the vaginal microflora in the fastest way.
Treatment of atrophic colpitis in women often comes down to relieving the symptoms of inflammation and discomfort. To do this, it is necessary to “remember” the vaginal epithelium the effect of the hormone estriol, so it is prescribed both locally and in the form of tablets and patches. Phytoestrogens, for example, Klimadinon, often help.
Treatment prognosis
It all depends on three factors: the nature of the inflammatory process (the severity and severity of the lesion), the pathogen (gonococci, chlamydia, anaerobic flora, fungi), as well as the state of the immune system. It is known that it is much easier to cure banal purulent colpitis in a practically healthy and pain-free woman than indolent candidal vaginitis in an HIV-infected patient.
In the case of atrophic senile lesions, the prognosis is usually favorable with timely administration of estrogens and symptomatic therapy. In the case of a microbial, viral or fungal infection, you should not “rely” on the prognosis - after all, there is a reliable means of monitoring the quality of treatment - this is taking PCR and smears from various places - the vestibule, vaginal vault, cervix. If, after treatment, three test results did not reveal the pathogen, then the clinical case can be considered cured.
In conclusion, we must add that at the same time it is necessary to carry out prevention, and sometimes even joint treatment of a regular sexual partner is required, even preventive. For example, a woman has been diagnosed with an acute gonococcal infection, but her sexual partner is “clean”. But unprotected sex is too much of a risk, and treating just one woman can lead to re-infection. It is when all possible options for re-infection or relapse of infection are taken into account and eliminated that we can talk not only about successful treatment of colpitis, but also about a favorable prognosis.
Tags:
women Health
Colpitis during pregnancy - is it dangerous?
Pregnancy is accompanied by a natural decrease in immunity. Against this background, many “dormant” chronic pathologies, not only of the reproductive organs, but also of the systemic ones, are often activated. However, even if they were not there, physiological immunosuppression often causes an increase in the activity of opportunistic flora, and at the same time candidal colpitis or bacterial vaginosis develops.
- Such conditions cannot be left without attention.
And although a limited list of drugs is used for treatment, you should never refuse therapy. The inflammation will begin to rise upward, affecting the cervix and the uterus itself. Possible intrauterine infection of the fetus, threat of miscarriage or premature birth, or infection of the child during natural delivery.
The following drugs are allowed during pregnancy:
- ointment "Dalacin";
- suppositories “Pimafucin”, “Itraconazole”, “Natamycin”, “Trichopol”;
- tablets "Trichopol" (from 20 weeks).
Forecast
If the cause of the disease is correctly established and therapy is started on time, colpitis responds well to treatment and does not cause complications. Otherwise, the pathology may become chronic and inflammation may spread to other organs of the reproductive system.
If vaginitis persists, a comprehensive examination is indicated. Perhaps it will reveal any systemic disease that became the cause. Only by eliminating it will you be able to get rid of colpitis.
Infectious colpitis is the most dangerous during pregnancy, as it threatens the life and health of the fetus.
Tags: gynecology
- Hypotension - what is it? Causes, symptoms by type,…
- Tuberculosis - first signs, symptoms by type and...
- Vulvitis - symptoms and treatment in women, medications
- Hyperthyroidism - symptoms in women, treatment and medications...
- Hypothyroidism - symptoms and treatment in women, hormones +...
- Cystitis in women - symptoms and treatment at home...
Treatment prognosis and consequences
If all recommendations are followed, the treatment prognosis is favorable. The vaginal mucosa is restored, atrophic changes are reduced. In some cases, they do not disappear completely, but replenishing the hormone deficiency is sufficient to activate protective functions and eliminate the conditions for the long-term existence of the infection.
Types and treatment of acute vaginitis:
However, relapses of atrophic colpitis are likely, since the natural level of hormones in older women is reduced. Therefore, a preventive course of local hormone therapy and herbal treatment must be taken on the recommendation of the attending physician.
What happens if you don't get treatment?
If treatment is not started on time, the following consequences and complications are possible:
- Dysuric disorders - urinary incontinence, frequent urge. This is due to the fact that the bladder tissue (sphincter) also has estrogen receptors. An insufficient amount of this hormone leads to weakening of muscle elements and the development of urinary disorders.
- Purulent discharge from the genital tract, indicating the addition of a coccal infection.
- Pain in the lower abdomen. This symptom indicates an ascending infection. In this case, signs of intoxication may occur - fever, chills, general weakness.
Symptoms
The cause of atrophic colpitis is the physiological changes that occur with age in a woman. Against the background of hormone deficiency, other signs of the disease appear. But the occurrence of inflammation can also be provoked by the patient herself.
Colpitis during menopause, symptoms and treatment
The main risk factors in old age are:
- Excessive sexual activity increases the risk of damage to the vaginal mucosa.
- Unprotected intimate life - when a woman constantly changes sexual partners, insecurity in sexual life leads to constant infection of the woman’s vagina.
- Underwear made from synthetic fibers first brings discomfort, and then pathogenic bacteria appear on the mucous membrane, which leads to inflammation.
- Insufficient hygiene of the genital organs leads to colpitis.
- Using an antibacterial product for genital hygiene. This remedy leads to the destruction of lactobacilli in the vagina.
At risk for the occurrence of pathology in the vagina are older women with excess body weight, with a weak immune system and pathologies of other body systems.
Prevention of atrophic vaginitis
To prevent or delay the development of atrophic vaginitis as much as possible, it is necessary to give up bad habits (as is known, menopause occurs faster in women who smoke), visit a gynecologist annually, eat right, and have an active sex life (this stimulates the production of sex hormones).
In addition, if indicated, doctors prescribe hormone replacement therapy to menopausal women even before the development of atrophic vaginitis - for preventive purposes.
Zubkova Olga Sergeevna, medical observer, epidemiologist
16, total, today
( 63 votes, average: 4.25 out of 5)
Back pain during pregnancy: causes and treatment
Thrush and menstruation
Related Posts
Definition of the concept
Colpitis is one of the gynecological diseases characterized by an inflammatory process affecting the vaginal mucosa.
It often occurs with damage to adjacent structures - the urethra (urethra), cervix, labia minora and labia majora. According to statistics, every second girl suffered from this disease at least once, even in a mild form. This disease is also known under another name - vaginitis.
From the Greek vagina means “vagina”, and the suffix “itis” means an inflammatory process.
Symptoms
The disease develops gradually, so the appearance of its symptoms occurs almost the same.
The first signs of a pathological condition in women include:
- Itching of the labia;
- Dry vaginal environment;
- Pain during intimacy;
- Redness of the vagina;
- Increased urination;
- Vaginal discharge.
With increased physical activity, involuntary release of some volume of urine may occur. White, sometimes cheesy, masses that have a repulsive odor are released from the vagina. Sometimes they contain blood impurities.
With secondary infection, purulent grayish masses may be released from the vagina. Any of these symptoms already signals the presence of pathology, and therefore requires medical intervention.
Signs
The onset of the pathological process is most often sluggish and asymptomatic. The woman is a little worried about discomfort after sexual intercourse and periodic discharge in small quantities. The increase in atrophic changes under the influence of progressive hypoestrogenism leads to the appearance or intensification of symptoms. Over time, the entire symptom complex of the disease develops:
- Dryness and itching.
- Discomfort during bowel movements.
- Pain of varying intensity during gynecological examination and sexual intercourse (dyspareunia).
- Discharge with an unpleasant odor and an admixture of pus.
- Increased frequency of contact sanguineous discharge.
- Petechial bleeding.
- Chronic cystourethritis, characterized by frequent urination and pain when passing urine.
- Alopecia in the pubic area (partial or complete).
Due to pathological changes in the bladder and urethra, urinary incontinence develops under the influence of physical stress.
Despite the presence of predisposing factors to the development of a bacterial infection (changes in the vaginal microbiocenosis, pH level, constant appearance of microtraumas), some researchers note that vaginitis in many cases occurs in an aseptic form. Therefore, they assign the main role in the development of the main symptom complex of the disease not to disruption of the vaginal environment, but to changes in the blood flow of the vaginal wall.
It is believed that changes in microflora during this period are only a response to aging, and it (the reaction) is quite natural.
Description
Atrophic colpitis is a disease associated with the aging of a woman’s reproductive organs and a decrease in the level of female sex hormones. The mechanisms of aging of the female reproductive system are quite complex. The processes begin even before menopause, from about 45 years of age.
The postmenopausal period of life (2 years after the persistent cessation of menstruation until the age of 60–65) is characterized by progressive changes in the woman’s reproductive system of an involutive nature. The size of the uterus decreases, its muscles are replaced by connective tissue, the ovaries shrink, and the vaginal epithelium becomes thinner. Changes occur in the epithelial layer of the vaginal mucosa, affecting the stroma of its walls and choroid plexuses:
- The epithelial layer becomes thinner due to a decrease in the proliferative ability of its cells (the ability to divide). The epithelium becomes less elastic due to decreased glycogen production. The microcenosis of the vagina (bacterial environment) changes. The changes are characterized by the elimination (mass death) of lactobacilli. Because of this, the acidity of the vaginal environment changes. Increases the risk of developing a secondary infection.
- The collagen structures of the vaginal walls (stroma) are depleted due to impaired collagen metabolism. The walls of the vagina “sag.”
- The choroid plexuses also undergo changes. The vascular network becomes impoverished (reduces). Ischemia of the vaginal walls is observed. This leads to disruption of transudation (sweating of the liquid part of the blood from the venous walls) and vaginal dryness.
- The secretory activity of the glands of the vaginal vestibule decreases.
Excessive dryness and thinning of the vaginal epithelium leads to its trauma during sexual intercourse, periodic leucorrhoea and sanguineous discharge.
In parallel with changes in the tissues of the vagina, the tissues of the urine excretion system (bladder, urethra) also atrophy, and the muscular system of the pelvis suffers. This leads to prolapse of the uterus and vaginal walls and increased urine output.
Postmenopausal atrophic vaginitis occurs in almost half of women (about 40%) and it develops 6 years after the onset of menopause. Already 9–11 years after menopause, about 70% of women suffer from this disease.
Folk remedies: chamomile, St. John's wort, aloe, sea buckthorn oil
The use of herbs is an auxiliary component of therapy, however, in the presence of serious cardiovascular diseases or cancer, it becomes the only way to combat this problem.
For treatment, sitz baths, douching with a decoction of herbs and tampons are used.
For douching use:
- A decoction of a mixture of herbs: oak bark, chamomile flowers, St. John's wort and nettle leaves.
- A rich decoction of calendula flowers.
- Diluted alcohol tincture of peony flowers (three tablespoons per 500 ml of boiled water).
The douching solution should be at room temperature. The procedure is carried out once a day at night for two weeks.
For sitz baths use:
- A rich decoction of Rhodiola rosea.
- Decoction of juniper fruits.
The procedure is carried out once a day at night for 35–40 minutes. The solution should be warm, but not hot. The course of treatment is 7–10 days.
Additionally, it is recommended to use tampons with freshly squeezed aloe juice or sea buckthorn oil.
Photo gallery of folk remedies
Sea buckthorn oil has a wound healing effect
Aloe juice reduces swelling of the mucous membrane
Chamomile has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect
St. John's wort has antiseptic properties