The leading position among gynecological diseases in women of reproductive age is cervical erosion. There are many known prerequisites for the development of pathology, but only a gynecologist can determine exactly what caused the erosion after a preliminary differential diagnosis. Based on the results obtained, you can decide on the need for treatment or choose a wait-and-see approach. Sometimes cervical erosion is a sign of dangerous conditions and requires immediate medical intervention.
Brief anatomy of the uterus
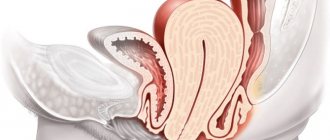
The uterus is conventionally divided into sections: fundus, body and cervix. In the latter, in turn, there is an upper part (supravaginal), into which the uterus passes, and a lower part, located in the vagina and accessible for examination by a gynecologist. A narrow cervical canal runs along the entire cervix, opening with an internal os into the uterus and an external os into the vagina.
All departments differ in their functions, histological structure and, accordingly, diseases. The upper layer of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal is represented by columnar epithelium, and the surface of the cervix on the vaginal side is multilayered flat non-keratinizing, which slightly passes into the canal in the area of the external pharynx. The boundary between these types of epithelium is called the transformation zone. This is exactly the area where erosion forms.
Causes of the disease
The disease and its causes have been discussed by doctors for a long time. Several main reasons are now known due to which this female ailment occurs:
- Inflammation of the genital organs - increases the secretion of the glands; with inflammation of the vagina and cervical canal, abundant mucous discharge is observed.
- Mechanical damage - inflammation develops when there is a strong impact on the epithelium during difficult childbirth or forced sexual intercourse.
- STIs – chlamydia, genital herpes, papilloma virus, staphylococci, yeast and others.
- Early intimate life - the mucous membranes begin to mature only by the age of 20-22 and, if infections intervene before this period, pseudo-erosion appears.
- Menstrual irregularities are caused by hormonal imbalance.
- Early or late birth - during early childbirth, the epithelium is damaged and the immature mucous membrane is destroyed.
- Changes in hormonal levels - with ovarian tumors, age-related changes, dysfunction of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
Erosion and other pathologies can also occur due to reduced immunity and its protective functions. What is cervical erosion and why does this disease often cause no symptoms? Doctors call this disease a cancer provocateur and the reason is the absence of nerve endings in the organ. In this regard, pathological processes: dysplasia and erosion may not bother a woman for a long time and only upon examination a gynecologist discovers them. Sometimes, by bleeding after intercourse or spotting, you can suspect something is wrong.
Classification
In most cases, cervical erosion is a completely normal condition for young women. Moreover, it occurs in almost all girls who have not yet reached adolescence. Often this pathology has no symptoms, so only a doctor can detect it during an examination. In this regard, it is worth noting that every woman should definitely undergo a routine medical examination several times a year. In some cases, erosion does not cause any problems and does not require treatment.
Sometimes ectopia can still cause some inconvenience. Namely: women often complain of discomfort, which often occurs after sexual intercourse, as well as excessive vaginal discharge. In this regard, it is worth noting that doctors distinguish several types of erosion, each of which has its own symptoms. Depending on the type of erosion, treatment is prescribed or not. There are three main types of cervical erosion: true, pseudo-erosion and congenital.
- True erosion . Often it is damage to the squamous epithelium, which is located on the outside of the pharynx of the cervix. Less commonly, cervical erosion appears on the lip or back of the pharynx. This defect appears as a small, bright red rounded area. But sometimes the entire epithelium can be damaged - large erosion of the cervix. In addition, this type of cervical erosion is characterized by inflammation.
Since endocervicitis is often the cause of true cervical erosion, purulent discharge appears on the affected areas of the squamous epithelium. It is also worth noting that during a colposcopic examination, traces of blood, fibrin, mucous secretions, as well as swelling and dilated vessels are visible on the damaged surface.
- Pseudo-erosion . 1-2 weeks after the onset of true erosion of the cervix, it enters the healing stage and the development of pseudo-erosion begins. As a result of healing, the squamous epithelium is replaced by a cylindrical one, the cells of which have a brighter and more saturated color. Therefore, the damaged surface of the epithelium remains bright red. Replacement of squamous epithelium with cylindrical epithelium is the first stage of healing of true cervical erosion. Often it is at this stage that it is diagnosed by a gynecologist.
It is worth noting that the proliferation of columnar epithelium can occur not only along the surface of the pharynx of the cervix, on which erosion has formed, but can spread to other areas in the form of branching glandular ducts. In these glands, a gradual accumulation of secretion may occur, due to the difficulty of the outflow of which cysts begin to form over time. Their size can vary greatly: from very small to very large, which resemble polyps. It is worth noting that multiple cysts gradually provoke thickening of the cervix.
If pseudo-erosion is not treated, it can persist for several years until it is eliminated. The result of treatment of pseudo-erosion is the reverse process of replacing the columnar epithelium with squamous epithelium. At the second stage of healing of erosion, the epithelium of the cervical pharynx is restored. But it is worth noting that treatment must be timely. Otherwise, this can lead to changes in epithelial cells, which may even be considered a precancerous condition. Symptoms of pseudo-erosion may include bleeding during sexual intercourse or examination.
- Congenital erosion . There is also congenital erosion, which is a displacement of the columnar epithelium of the cervical canal. As a rule, it is discovered in childhood or adolescence. It is often asymptomatic. Since displacement of the epithelium occurs in the fetus during the prenatal period, this type of erosion is called congenital. Typically, such erosion occupies a small area near the external pharynx, has a smooth surface and a bright red color. If congenital erosion persists until puberty, infection and inflammation may occur.
Symptoms2
The situation with cervical erosion is complicated by the fact that this disease does not have pronounced symptoms and in most cases does not manifest itself at all. But as erosion progresses, patients may begin to notice:
- bloody and sometimes purulent discharge between menstruation, which can appear, for example, after sexual intercourse.
- copious vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor.
- longer and heavier menstruation.
- pain in the lower abdomen during urination or sexual intercourse.
During the examination of the patient, the gynecologist first examines the cervix in the speculum. As a result, an epithelial defect may be found on its mucous membrane (epithelium is the cells that cover the vaginal part of the cervix and protect it) in the form of a bright red spot against the background of healthy tissue, which will bleed upon contact with a gynecological instrument. Depending on the type of erosion, other external signs of the disease will be present.
But in any case, they additionally perform colposcopy (examination of the cervix and vagina under magnification) and examination of a cellular smear from the surface of the erosion to exclude oncological diseases. Examination of the cervix using an optical device that magnifies the image 25-32 times is absolutely painless. These manipulations enable the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment. In addition, tests are carried out for infections and sexually transmitted viruses, HIV and hepatitis, smears are taken for flora, etc.1
Reasons for development
The main cause of ectopia (pseudo-erosion) is the displacement of the cylindrical layer of the epithelium to the outer part of the cervix. Blood vessels are visible through the columnar epithelium, so during examination the gynecologist can tell you about the presence of an eroded surface. But with cervical ectopia, the mucous membrane is not damaged, therefore calling it a disease is not correct. Ectopia can develop against the background of hormonal changes during pregnancy, after childbirth, while taking or after stopping birth control pills. When hormonal levels stabilize and mechanical or chemical stimuli cease to act, cell replacement (metaplasia) will begin again, and the cervical epithelium will again become flat and pink.
True cervical erosion is always a pathology. The covering epithelium (the upper layer of the cervix) can be damaged:
- mechanically (during intense or frequent sex, careless insertion of tampons or intrauterine contraceptives, after abortion, childbirth);
- chemicals (douching, using spermicides, improper local treatment);
- due to infectious diseases (mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, gardnerellosis, pathogenic effects of streptococci or E. coli).
Cervical erosion can also develop against the background of ovarian dysfunction, menstrual irregularities, early menarche, excess estrogen, decreased immunity, frequent changes of sexual partners and the presence of chronic diseases (diabetes, etc.)
Complex surgical procedures in the treatment of the cervix
- The operation (conization of the cervix - used in case of poor biopsy results) - is performed under local anesthesia and consists of excision and removal of the affected tissue of the cervix. It is performed using laser radiation, thermal cauterization (with a loop electrode), and excision with a scalpel. Conization is carried out immediately after the end of menstruation. Before the operation, you should refrain from sexual contact, and after its completion, it is forbidden to visit the bathhouse and take a bath, and it is also forbidden to engage in sexual relations for 6 weeks;
- Cervical plastic surgery (prescribed after difficult childbirth) - the operation is aimed at restoring the functions of the vagina and returning the anatomical norm of the cervix. Performed using different methods.
The drugs used in the treatment of cervical erosion have anti-inflammatory activity, are intended to restore hormonal levels, have antimicrobial and antibacterial activity and help strengthen the immune system. Only an experienced doctor can determine the correct diagnosis and cause, as well as prescribe the best treatment, based on the patient’s examination data.
Self-medication of the disease is unacceptable, as it can aggravate the situation and lead to serious and irreversible consequences. Specialists from the Diana Gynecological Department offer advice on choosing the most effective and safe treatment package.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Symptoms
Unfortunately, very often cervical erosion has no symptoms and does not make itself felt at all. That is why it is usually diagnosed during the next medical examination. In other cases, the clinical picture is accompanied by typical symptoms of pathologies that are sexually transmitted.
In particular, cervical erosion may have the following symptoms:
- infertility;
- difficulty urinating;
- bloody or watery vaginal discharge that appears on its own or immediately after sexual intercourse;
- violation of the monthly cycle;
- the presence of genital warts in the genital area;
- pain during intercourse.
During a gynecological examination, the specialist will notice the cervix, which has a red color, signs of inflammation and a granular surface.
The inflammatory process occurs due to the fact that the cylindrical epithelium, which is not in a typical place, is quickly populated by bacteria and viruses. Thus, erosion of the cervix becomes a source of chronic infection in the vagina, from where it spreads upward (cervix - uterine body - tubes - ovaries).
When erosion exists on the mucous membrane for a long time, and treatment does not produce results or is not carried out at all, then the cells of this area acquire the ability to undergo atypical division, growth and irreversible changes. This means that untreated erosion greatly increases a woman’s risk of developing cervical cancer. This is why it is very important to undergo regular preventive examinations every 6 months.
Cervical erosion is classified as a background process, due to which complications arise much more often and other pathologies develop. The presence of a confirmed human papillomavirus in the patient is particularly highlighted. It is with it that an increased level of risk of malignant degeneration of erosion is associated.
Diagnostics
Symptoms of cervical erosion are characteristic of other gynecological diseases. Therefore, it is important to distinguish the problem from other pathologies and determine the severity of the patient’s condition and determine the severity of the change in epithelial tissue.
For this purpose they prescribe:
- vaginal smear to assess quantitative indicators of the components of the intimate sphere;
- a smear from the cervical canal and cervix to determine the identity of the cells located here;
- colposcopy allows you to analyze the reaction of tissues to chemical solutions and collect cells from suspicious areas;
- a biopsy provides detailed information about the structure of the tissue taken and allows you to determine how dangerous the true erosion is.
If large cervical erosion is detected, it is necessary to perform a blood test to determine the types of human papillomavirus that are present in the body. The obtained indicators make it possible to assess whether the disease is dangerous and whether the altered cells can develop into a malignant tumor.
Inspection
A gynecological examination and examination of the condition of the cervix in mirrors makes it possible to make a preliminary diagnosis. Since the doctor knows exactly what erosion on the cervix looks like, he immediately determines the change in the tissue. At the same time, a specialist cannot provide more accurate information about the origin of erosion and is unable to determine visually how dangerous it is.
During a gynecological examination, a specialist takes a smear from several areas of the intimate organs. The analysis allows not only to assess the state of the microflora, but also shows atypical cells, if they are present.
Colposcopy
To distinguish between false and true cervical erosion, it is necessary to perform colposcopy. The doctor will tell you what it is and how to prepare for it. Often the procedure causes fear in women and forces patients to refuse. However, gynecologists reassure women and say that colposcopy is a highly informative procedure. The examination is absolutely safe and can be performed even during pregnancy.
During diagnosis, the true erosion of the cervix is increased and its boundaries are studied in detail. After this, acetic acid or iodine solution is applied to the pathological area. After such a reaction, the healthy mucosa changes, and the pathological areas become visible as clearly as possible.
In case of false erosion, the examination is completed after the chemical reaction. If true erosion of the cervix is detected, the doctor takes part of the tissue for a more detailed study.
Required laboratory tests
Before treating cervical pathology, laboratory tests must be performed. A blood test for infections allows you to identify the causative agent of the inflammatory process and determine HPV levels in a woman’s body.
Using a vaginal smear, the state of the intimate microflora is assessed. Cytological examination makes it possible to detect atypical cells on the cervix and suspect dysplasia.
Laboratory diagnosis for erosion of the entire cervix is an integral part that determines therapy. Thanks to the examination, it is possible to establish the sensitivity of microorganisms and identify what caused the changes in the cervical mucosa.
Cervical erosion and pregnancy
Due to the fact that cervical erosion is found quite often in women of childbearing age, one of the most pressing issues in this case is the question of how cervical erosion and pregnancy are combined. In particular, women are interested in whether erosion could become an indication for termination of pregnancy.
According to many years of observations by specialists, the presence of cervical erosion does not affect the development of pregnancy and the condition of the expectant mother. In some cases, during erosion, a pregnant woman may periodically experience bloody discharge from the genitals. But this phenomenon is not associated with termination of pregnancy. However, in this case, it is important that the diagnosis is confirmed, since discharge during pregnancy can be associated not only with erosion, but also with some dangerous conditions.
However, during childbirth, unpleasant consequences of pregnancy may appear. In particular, tissue affected by erosion stretches less well and may tear. But during pregnancy, doctors do not practice conventional treatment methods: a pregnant woman is prescribed only restorative treatment or medications strictly according to indications. All procedures practiced for effective therapy are applied only when the young mother returns to menstruation.
Symptoms of erosive cervix
Usually erosion is asymptomatic. There are no particularly acute indicators or obvious manifestations of the pathological condition of the uterine cavity. Most often it is detected during routine gynecological examinations. But some signs by which erosive inflammation can be recognized can still be identified:
- increase in the volume of secretions;
- profuse leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor;
- long menstrual regularities;
- pain when urinating in the lower abdomen;
- convulsive tingling during sexual intercourse.
The symptoms of erosion on a woman’s cervix are very similar to many other diseases of the reproductive system, so they often ignore it or try to heal it on their own, without medical intervention. However, this is a wrong decision, because starting such a disease and bringing it to a severe form is extremely dangerous.
Complications
Many women are afraid or lazy to treat cervical erosion, meanwhile, it is not harmless to a woman’s body. Not only is it a source of chronic infection, which can lead to disastrous consequences, for example, miscarriage or infertility. The presence of cervical erosion is a ticking time bomb. There is always a risk that ectopic epithelial cells will degenerate into cancer - then there will be a need to remove the uterus and appendages and long-term chemotherapy.
Treatment of erosion in an advanced stage is always long-term, traumatic and problematic. When the cervix is cauterized, it is injured, which cannot but affect the reproductive function in the future. Problems may arise when carrying a child.
That is why, after 30 years of age, developed countries offer all women to undergo regular examination with a simple test - a cervical smear PAP test. The smear is painted with a special substance and examined under a microscope. If cells suspicious for cancer are found, more detailed and in-depth treatment is carried out to identify and quickly cure the problem.
Signs of advanced pathology
The main feature of the uterine cervix is the absence of nerve endings. In view of this, when the damage is formed, the feeling of discomfort does not bother the woman. As a rule, patients more often turn to a gynecologist with complaints about other pathologies of the reproductive system. And during the examination, erosion is revealed.
If the disease in question is diagnosed in a timely manner, there is a chance of defeating the pathology with conservative treatment. It is necessary to take into account the fact that in the initial stage of development, symptoms are practically absent. And often the problem that has arisen can only be determined by inspection. Therefore, a planned visit to the gynecologist should not be ignored.
If a woman develops symptoms such as:
- the appearance of discharge with small fragments of blood on any day of the cycle that is not related to menstruation;
- discomfort felt in the groin area and spreading to the abdomen;
- discomfort that occurs during intimacy;
- Excessive whitish discharge with blood streaks that appears after intimacy.
Important: If a woman is bothered by pain in the abdomen, increased discharge of leucorrhoea and discomfort during intimacy, she should immediately consult a doctor. Since such symptoms signal the formation of many diseases of the reproductive system.
Pain in the lower abdomen, caused by erosion, can occur any day. In this case, discomfort intensifies during menstruation. In addition, inflammation is often associated with erosion, as a result of which the pain intensifies and the discharge becomes more abundant. Moreover, if the inflammation is in an acute stage, the woman’s body temperature often rises.
Photo
Cervical erosion is often discovered by chance during a routine examination using speculum at a gynecologist. The damaged area usually has a round shape, bright red color, without signs of inflammation. But there are erosions and irregular shapes. The damaged epithelium is most often located around the opening of the cervical canal. Touching the area with any instrument may cause slight bleeding.
To determine the depth and extent of the lesion, the uterine pharynx is stained using various dyes (3-5% acetic acid, Lugol's solution). With such staining, erosion becomes clearly visible.
Types of cervical erosions1
In gynecology, there are several types of cervical erosion: true, pseudo-erosion and congenital. The true appearance refers to exactly that bright red spot that bleeds when pressed and is detected during a routine gynecological examination. Such erosion is dangerous because pus can form on the affected area. As a rule, true erosion lasts about two weeks, then it becomes covered with connective tissues and develops into pseudo-erosion.
Pseudo-erosion of the cervix is a rounded red area about 5 mm in size, on top of which pus may also appear, especially if the disease has been going on for a long time, which is what most often happens. Pseudo-erosion is typical for girls with elevated levels of female hormones in the blood and can extend beyond the cervical canal. The danger of pseudo-erosion is that it can develop into a malignant formation.
Sometimes, when examining girls or adolescents, a gynecologist may discover that the columnar epithelium in the cervix is displaced, and on colposcopy it will be seen that it is colored bright red. This is the so-called congenital erosion, which does not need to be treated, since it almost never develops into an oncological formation.
How to treat erosion?
In the treatment of cervical erosions, practical gynecology adheres to the following rules:
- monitoring of congenital erosions, no need for their treatment;
- true erosions and pseudo-erosions are treated simultaneously with the underlying diseases that caused or maintain them;
- if there are signs of inflammation, therapy should be aimed at infectious agents (trichoionases, chlamydia, gonococci, etc.);
- erosion in the active stage of inflammation is treated with gentle methods (vaginal tampons with sea buckthorn oil, fish oil, syntomycin emulsion, aerosols containing antibiotics - chloramphenicol, etc.).
Modern approaches to the treatment of cervical erosion are based on the use of the mechanism of destruction of columnar epithelial cells, their rejection and subsequent restoration of squamous epithelium on the surface of pseudo-erosion.
Stages of erosion
Currently, there are 3 stages of cervical erosion:
1st degree: inflammation of cervical erosion. A negative phenomenon is formed as a result of infection entering the cervical epithelium. In turn, this degree is classified into three stages of development:
- attack of pathogenic microorganisms, alteration;
- formation of swelling followed by effusion of serous or purulent exudate into the vaginal lumen, exudation;
- intensive tissue growth with subsequent replacement of the defect, proliferation.
In the absence of adequate treatment, this stage progresses to the next stage;
2nd degree: formation of a wound on the surface of the mucosa. As a result of the destruction of the epithelium and lack of therapy, a wound forms on the surface of the cervix, which does not heal for a long time;
3rd degree: transformation of the wound site into ectopia. With this abnormal process, the wound does not heal properly, causing the surface to become covered with cells from the cervical canal. And the multilayer epithelium is replaced by single-layer cells.
Important: To determine the stage of the defect, the doctor uses a colcoscope. This technique allows you to accurately determine the extent of damage to the mucous membrane of the neck.
Lack of timely therapy leads to the development of dysplasia, which can gradually turn into cancer.
Conservative treatment
If the patient has a concomitant inflammatory and infectious process, they usually begin with conservative therapy.
It is necessary to eliminate the cause that caused the erosion. Depending on the identified concomitant diseases, a course of broad-spectrum antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators, and traditional medicine is prescribed. The cervix is locally treated with medications that cause chemical coagulation of the affected area, which contain organic acids (acetic, nitric). These drugs are intended exclusively for the treatment of benign formations of the cervix and are more suitable for nulliparous girls, since they do not leave any scars on the cervix after treatment.
The disadvantage of this technique is a possible relapse. The method can be used for all types of erosion.
Discharge after cervical erosion after radio wave cauterization: is this normal, what should I do?
Cervical erosion
The radio wave method of treating cervical erosion is currently considered the most effective and modern. It is suitable for nulliparous girls and women of reproductive age, since it does not leave scars at the site of tissue excision. Many women after such a procedure are concerned about the presence of discharge. Let's figure out whether this is normal and what is important to know and need to do.
- During the healing of the cervical surface, discharge after cervical erosion after radio wave cauterization is a normal physiological process.
- In the first week after cauterization, clear ichor fluid may be observed.
- Its quantity will depend on the area of the lesion and the individual characteristics of the organism. Over time, it will become less watery and a slight yellowish tint may appear.
- On days 10-15, a small amount of blood may be released. This is due to the tissue moving away from the wounded surface.
- If the bleeding becomes intense and does not stop for several days, you should consult a gynecologist.
- The appearance of a pungent odor and purulent green discharge should alert you. This indicates the development of an infection.
During the entire period of rehabilitation, the woman is only required to follow the rules of hygiene. By the time of the next menstruation, the cells have almost completed their restoration. Experts allow you to return to your normal lifestyle.
Surgical methods
There are many methods of surgical treatment of cervical erosions, which allows you to choose the most suitable one in each specific clinical case.
For surgical treatment to be successful, the accompanying infectious inflammation must first be eliminated and normal hormonal function restored. When a control laboratory test confirms the success of antibacterial therapy, they begin to stabilize the state of the vaginal microflora. Preparations containing lactic acid, lacto- and bifidobacteria (Femilex, Lactogel and the like) are used.
In the absence of infection and the presence of normal indicators of the composition of the vaginal environment, surgical treatment begins. It is always short and painless with any chosen method. Regardless of the method of removing the pathological focus, the ultimate goal of therapy is the destruction (destruction) of the zone formed by “wrong” cells, so that a normal mucous layer is restored in its place.
To surgically eliminate pseudo-erosion of the cervix, the following are used:
Diathermocoagulation
Quite an old method with a lot of disadvantages. The essence of diathermocoagulation is to cauterize the ectopia with a high-frequency current, that is, a black scab forms at the site of erosion, like after a burn. Currently practically not used.
Disadvantages of DTK:
- soreness;
- risk of bleeding occurring during cauterization and after;
- altered by cervical scars, and this makes it impossible to use the method in nulliparous girls and in women planning a pregnancy.
Complete healing occurs by 4–6 weeks. Cauterization is carried out in the second phase of the cycle, on the eve of menstruation, so that menstruation “washes” the scab, which contributes to its more “gentle” rejection.
Positive aspects of DTK: the possibility of performing conization of the cervix if necessary, the simplicity and low cost of the method.
Chemical coagulation
This method of removing cervical ectopia involves treating the pathological area with chemical solutions, for example, the drug Solkovagin. Its constituent components are organic acids (oxalic and acetic) and zinc nitrate with nitric acid. Chemical destruction is used only when treating small areas of ectopia.
Not so long ago, Vagotil was popular, with tampons applied to the erosion for 7–10 days. Today, Vagotil treatment is not used, since the depth of its penetration into the altered tissues is small, and therefore the effectiveness of therapy is low. After cauterization of the erosion by the solkovagin, a scab forms on its surface, which is torn off after a few days. Complete regeneration occurs after 6 – 8 weeks.
The advantages include:
- almost complete painlessness;
- ease of processing (twice with an interval of several minutes);
- relatively inexpensive (the cost of Solkovagin ranges from 750 to 1200 rubles: the package contains 2 ampoules of 0.5 ml);
The disadvantages include low efficiency; treatment is carried out only for small-sized ectopia of the cervix.
Cryodestruction
Cryocoagulation is based on treating the pathological focus with liquid nitrogen cooled to 100 - 150 degrees (replacement is nitrous oxide), which is sprayed by the device. The treated area turns white and loses sensitivity. The fluid in the cells crystallizes, causing them to collapse. The duration of the manipulation is 15 minutes. After treatment, significant watery discharge appears, restoration of most of the ectopia begins by day 7, and complete healing occurs after 4 to 6 weeks.
Advantages of the method:
- quite effective (85 – 97%);
- simplicity;
- almost complete painlessness;
- does not disturb the structure of the cervix.
Disadvantages include the possibility of bleeding after treatment and the risk of incomplete treatment of pathological cells.
Laser vaporization
A widely used method that involves treating the pathological area with a laser beam (non-contact method). Before manipulation, the cervix is wiped with a solution of acetic acid to spasm the blood vessels and with an iodine solution to determine the boundaries of ectopia. Under the action of laser beams, the liquid from the pathologically altered cells evaporates and they are destroyed.
Pros of the procedure:
- the method is practically painless;
- high efficiency (98% cure);
- do not form scars on the cervix.
The disadvantages include the high cost and the need for special equipment, which makes the method’s accessibility relative and a larger zone of decay of healthy tissue (1.2 mm) than with radio wave treatment of erosion.
Radio wave method
This method of treating ectopia and more has become very popular lately. Gynecological oncologists consider the treatment of cervical diseases with radio waves to be the most optimal method among all those used. The method is non-contact and is based on the conversion of electric current into radio waves (Surgitron apparatus), which are directed to the affected area using an electrode.
During manipulation, the electrode does not come into contact with tissues and does not heat up, that is, the risk of burns is completely eliminated. Under the influence of radio waves, the liquid from the cells evaporates and they disintegrate. The zone of altered epithelium at the border of healthy and pathological tissue is 0.04 mm, that is, we can say that radio waves stop at the affected area without affecting healthy cells. The method is relatively painful, but requires only local anesthesia.
Advantages of the method:
- cicatricial deformation of the cervix does not occur after manipulation;
- efficiency reaches 100%;
- the risk of bleeding is almost zero.
Healing occurs in 2–3 weeks. The procedure can be performed on any day of the cycle.
The only disadvantage is that not all antenatal clinics have special equipment.
Treatment methods for this disease
Today, medicinal (drug) and non-drug methods are successfully used to treat cervical erosion.
Drug therapy consists of the local use of anti-inflammatory drugs and drugs that affect the cause of erosion and promote the restoration of damaged tissue. If the disease is caused by infections such as trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis or chlamydia, effective treatment is possible only after they are eliminated.
In order to accelerate the regeneration of damaged cells, various ointments, solutions, vaginal suppositories, as well as chemical coagulation agents are prescribed (when applied to damaged erosion cells, they accelerate their death and replacement with healthy ones).
The choice of a particular drug is made only by the attending physician based on the results of the examination.
Non-drug treatment of cervical erosion can be carried out using the following methods:
- Cryodestruction - it is performed by freezing damaged cells with low-temperature liquid nitrogen, after which they die. This method is absolutely safe for healthy cells and does not lead to the formation of scars on the cervix;
- Laser coagulation - the method consists of cauterizing erosion with a laser, which penetrates to a certain depth of tissue without affecting neighboring cells;
- Diathermocoagulation - it is carried out using electric current. After such thermal cauterization, a small scar remains in place of the damaged cells. For this reason, this method of treating erosion is not recommended for nulliparous women.
How to behave after cauterization of the cervix?
After cauterization, there is a wound on the mucous membrane of the cervix. For its optimal healing, it is necessary to create optimal conditions, functional rest, normalize the microflora, and follow the hygienic recommendations of the attending physician. In this regard, any form of genital contact should be excluded. It is necessary to take medications that stimulate healing, antibacterial medications and eubiotics to create optimal conditions for speedy healing.
The duration of sexual rest is determined individually. However, this period in most cases is at least 4 weeks. To more confidently determine the timing of the recovery period, it is necessary to regularly visit the attending gynecologist and conduct an examination in the mirror. The duration of drug treatment is determined by the attending gynecologist individually, depending on the general condition of the patient, the cause of erosion and the dynamics of the process.
Preparation for cauterization includes several stages:
- restoration of normal vaginal microflora
- conducting research for sexually transmitted diseases.
- in case of detection of sexually transmitted diseases, it is necessary to carry out comprehensive treatment of the identified infections.
- in some cases, it makes sense to conduct a preliminary biopsy (sampling a normal area of the vaginal mucosa) for subsequent microscopic examination.
- in the case of immunodeficiency conditions, it is necessary to carry out complex treatment that stimulates the body’s protective properties.
Prevention
Prevention is based on an annual scheduled visit to the gynecologist, the use of external local methods of contraception, and personal hygiene.
Traditional medicine helps reduce the risk of development and spread of erosion.
- Sea buckthorn oil is effective against inflammation and diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria. Tampons are impregnated with it. This remedy also helps prevent the spread of erosion.
- For vaginal douching, use an infusion of calendula. This remedy also serves to prevent sexually transmitted infections.
- Tampons are also soaked in a solution of aloe juice mixed with honey and castor oil. Used at night, it causes a feeling of warmth. The product has healing properties.
- Peony tincture prepared with alcohol is used for douching and cauterization. The finished product is diluted in warm water based on a ratio of 1 to 25. The tincture can also be taken orally no more than 4 times a day, one teaspoon.
Many women have heard from doctors what erosion is. Ulcers on the cervix appear after childbirth, due to hormonal imbalances, and infectious diseases. Surgical methods are mainly used for treatment.
Treatment of cervical erosion during pregnancy
The presence of erosion does not affect pregnancy in any way, just as pregnancy does not affect erosion. Surgical treatment (cauterization) is not carried out throughout pregnancy, since after cauterization it will be more difficult to give birth. The cervix will dilate and stretch worse during childbirth if it is cauterized during pregnancy, so it is better to postpone all manipulations until the postpartum period.
You can use traditional medicine (the same sea buckthorn oil). The use of phytotampons is contraindicated during pregnancy. If there is an infectious process, a course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs is prescribed locally. Most gynecologists simply carry out dynamic monitoring of pregnant women with a similar pathology.
Signals of disease at different sizes of pathology
Does the size of the formation affect symptoms? Of course, small-scale erosion rarely makes itself felt. This pathology is most often asymptomatic. The first signs of the disease occur with the development of cervicitis - inflammation of the cervix or in the presence of other concomitant pathology.
It is also useful to read: What is useful for a woman to know about cauterization of cervical erosion
A completely different situation arises with extensive erosion. Larger lesions are much more likely to manifest as bloody vaginal discharge. Huge erosions are always an alarming sign, since they may hide cervical cancer.
How to treat cervical erosion in nulliparous women?
Women should be warned right away: they should not delay treatment of erosion for a long time, because it can develop into a more serious disease. And the fact that a woman has not yet given birth or is currently pregnant is not a contraindication to treatment. But the choice of treatment method in this case is crucial. Considering that some cauterization methods can cause undesirable consequences in the future, it is necessary to choose a method that does not affect the ability to become pregnant or give birth without problems.
The most gentle methods include chemotherapy and laser treatment. If the size of the erosion is small, you can choose a chemical treatment method; Laser therapy is suitable for eliminating defects of any depth and size. In cases where the size of the erosion is up to 2 cm, it is possible to use an alternative treatment method - physiotherapeutic stimulation of healing using ultraviolet rays.
If the disease is detected in a pregnant woman, cauterization of the erosion can be postponed until after childbirth. This is possible when the size of the erosion is minimal, there are no signs of cell degeneration and inflammation. In the presence of inflammation, but with a small area of damage, anti-inflammatory and regenerating (healing) agents are prescribed - Olazol, Levovinisol, Miramistin, Vaginorm S, sea buckthorn oil, solcoseryl ointment.
Prevention of pathology
In order not to look for ways to eliminate uterine lesions in the future, you need to follow some rules of prevention:
- visit a gynecologist 2 times a year for a routine examination;
- observe basic hygiene rules;
- when having intimate contact with a casual partner, use contraceptives;
- to prevent infection, it is recommended to adhere to monogamy and have regular sex life;
- if you are not planning to conceive a child, you should use contraception to avoid abortion;
- if erosion is detected, it is recommended to immediately begin treatment, while at the same time adhering to a healthy lifestyle;
- When menstruation occurs, you need to regularly change your personal hygiene products and take a shower 2 times a day.
Erosion itself is not dangerous for a woman and is a benign process. However, in some cases, a disease not detected in a timely manner at a late stage of development can transform into dysplasia, and then into oncology. Considering this important point, experts recommend regular examinations and, if erosion is detected, immediately begin its treatment.
Folk remedies
Self-treatment of large true cervical erosion is impossible; it requires mandatory medical intervention, removal and control using modern technology. All methods of traditional medicine are only preventive or auxiliary, for example, in cases where operations are postponed for objective reasons. But the use of folk remedies greatly reduces the risk of erosion.
- Ointment "Levomekol". A miraculous ointment that has proven itself excellent for wounds. Squeeze the ointment onto a tampon and insert it into the vagina at night. In the morning, remove the tampon and douche. Carry out daily for two weeks.
- For cervical erosion, it is recommended to inject aloe juice into the vagina every day, and then lie down for 20 minutes.
- Douching. St. John's wort infusion: 4 tbsp. l. St. John's wort herb pour 2 liters of hot water, boil over low heat for 10 minutes and leave for 30 minutes.
- For treatment, a decoction of boron uterus is used (the decoction is used both for douching and in the form of tampons soaked in the decoction). To prepare a decoction, 2 tablespoons of raw materials are mixed with half a liter of water. The mixture is brought to a boil, filtered and cooled. Douching should be done once a day, at night. The course of treatment is about a week (5-7 days on average).
- Thoroughly dissolve 2 mummy tablets in 1 tsp. warm water, add sea buckthorn oil. Place a tampon soaked in this solution according to the scheme described above.
- Bergenia root extract: 3 tbsp of crushed plant root is poured into 1 tbsp of boiling water, simmer over low heat until the liquid has completely evaporated. Drink 30 drops three times a day half an hour before meals.
- Calendula infusion is used for vaginal douching in cases of congenital erosion and mechanical damage to the mucous membrane. The product serves as a preventive measure for many STDs.
- Pour two tablespoons of chamomile into a liter of boiling water in a saucepan. Place the pan with a lid in a water bath for 15 - 20 minutes. Turn off the heat, leave the solution for 40 minutes, then cool to room temperature.
- Treatment with honey, for this you need to wrap one teaspoon of honey in a bandage or gauze, make a tampon from it, tie it with a thread, insert it inside the vagina as deeply as possible. This should be done at night, in the morning you will notice a little blood, this is normal.
The basis for the prevention of any disease of the female genital area is regular visits to a gynecologist, at least once a year, and compliance with the main rules of sexual culture, one sexual partner and the use of protective methods of contraception.
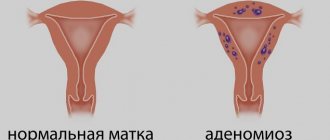
Cervical dysplasia Cervical cancer Uterine fibroids Uterine prolapse Uterine adenomyosis Human papillomavirus
Consequences of erosion
The main danger of the pathology in question is that it does not disappear, but transforms into a chronic form, which contributes to the manifestation of other, more serious defects. In this case, therapy largely depends on the type and likelihood of complications.
If ectopia progresses, this leads to the formation of cervical dysplasia. In addition, the structure of cells is disrupted and atypical structures appear. Such processes have several types of development:
- first, the changes affect the deepest layer, located next to the muscle wall;
- further, the deformation concerns the layer on the surface;
- if the mucous membrane is affected 1/3 deep, a diagnosis of grade 1 dysplasia is made;
- a lesion affecting 2/3 indicates stage 2 pathology;
- a complete change in the mucosa indicates that grade 3 dysplasia has formed;
- the next stage of change is a malignant neoplasm.
Important: If a woman is a carrier of the papilloma virus, the risk of developing dysplasia, and then a malignant neoplasm, increases several times.
The last stage is characterized by the appearance of metastases. Therefore, urgent surgical intervention is required to remove the uterine organ and appendages.
Interpretation of the results of cytological examination
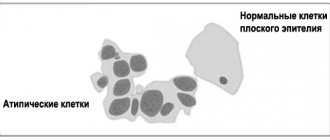
| Options | Cytological picture |
| 1 | Normal structure of stratified squamous epithelial cells |
| 2 | The structure of cells is changed due to the inflammatory process in the vagina and (or) cervix |
| 3 | Single atypical cells with nuclear anomalies appear, and malignancy is suspected |
| 4 | There are individual cells with obvious signs of a malignant process |
| 5 | A large number of cancer cells |
Secondly, he will take a vaginal smear for flora. The smear may contain elevated leukocytes and pathogenic microflora, which indicates inflammation of the vagina. The inflammatory process in the vagina makes it difficult to identify atypical cells, therefore, if one is detected, then it is necessary to treat it, and then repeat the cytological examination.
For sanitation of vaginal inflammation, topical preparations in suppositories or vaginal tablets are used: Terzhinan, Hexicon and others. In some cases, it may be necessary to prescribe antibiotics, and to treat thrush - antifungal agents. The doctor will select all medications taking into account the causative agent of the disease.
To speed up the healing of erosion, all existing inflammatory diseases in the vagina should be cured, as they can affect the development of the focus of an existing pathological area.
It's important to understand
All of these medications are not used to treat erosion. The purpose of their purpose is to sanitize the vagina so that microbial agents do not provoke the transition of an uncomplicated form of erosion, which does not need to be treated, into a complicated one. Complicated erosion has a less favorable prognosis and always requires therapy.
Thirdly, if a cervical defect is detected, the gynecologist will suggest taking an HPV (human papillomavirus) test. Cervical pathology is usually caused by two oncogenic types of HPV - 16 and 18.
And finally, a colposcopic examination. The doctor will examine the cervix in detail under a microscope and evaluate the structure of the cells of the spot seen, the nature of the surface, color, edges of the affected area, and vascular pattern. Colposcopy complements cytological examination and makes it possible to identify a group of healthy women - those who do not require treatment for ectopia. The purpose of this study is to identify the lesion and substantiate the indications for targeted biopsy of the cervix. There is no need to be afraid of this procedure - it is absolutely painless.
A cytology smear allows you to determine the presence of cervical diseases and identify the risk of neoplasms.
How is the cervix structured?
To clearly understand what we are talking about, you need to have minimal knowledge of anatomy and know how the organ we are talking about works.
So, that part of the cervix that is located in the vagina and which the doctor sees during a gynecological examination in the speculum is quite logically called the vaginal part of the cervix. Inside the cervix is the cervical, or cervical, canal, which opens into the uterine cavity. There are two physiological narrowings in the cervical canal - the external and internal pharynx. The external os opens into the vagina. In nulliparous women, it is round in shape, and after childbirth it takes on the appearance of a transverse slit. The internal os opens into the uterine cavity. The cervical canal contains mucus, the main function of which is to prevent infection from entering the uterine cavity from the vagina.
The structure of the cervix.
The outside of the vaginal part of the cervix is covered by stratified squamous epithelium. The word “multilayered” itself suggests that it consists of several layers of cells. Thus, it has a significant (of course, by microscopic standards) thickness and performs a protective function. The mucous membrane of the cervix, covered with stratified epithelium, has a pale pink color.
Inside the cervical canal there is a cylindrical, or glandular, epithelium. It is thinner and more delicate, consists of a single row of cells, and the blood vessels shining through it give it a red color.
The columnar epithelium has a completely different function - to produce mucus. Columnar epithelium is hormone-dependent: when there are a lot of female sex hormones, it produces liquid mucus, when there is little, thick mucus. This invention was invented by nature for conception: through liquid mucus, sperm very easily penetrate the uterine cavity, meet the egg, and fertilization occurs. This quality of mucus is observed during the period of ovulation. The rest of the time, cervical mucus is thick, viscous, its function is protective - no infectious agent can penetrate the uterine cavity and cause inflammation.
The zone where two types of epithelium meet is called the transition zone, or transformation zone. At different age periods of a woman, this zone is located at different levels, which depends on the stage of development of the female reproductive system.
Thus, in newborn girls and virgins, the junction zone is located on the outer cervical surface. In this case, they talk about congenital erosion.
Histological structure of different types of cervical epithelium (in women of reproductive age and during menopause).
During puberty or during pregnancy, when a high level of sex hormones is noted in the female body, the cylindrical epithelium begins to quickly “crawl” out of the cervical canal and is located around the external pharynx, resulting in the formation of a red spot in this place. The same can happen if a woman takes hormonal contraceptives.
As a girl grows up, the level of sex hormones decreases, the stratified squamous epithelium begins to displace the cylindrical epithelium into its place - into the cervical canal, and the junction zone moves closer to the external pharynx.
With age, the border of the two epithelia completely hides deep into the cervical canal, which is why it becomes invisible. Therefore, ectopia no longer occurs in women of the older age group.
It is also useful to read: Using suppositories to treat cervical erosion
Solutions and ointments for tampons
If you do not resort to drug removal of cervical erosion, you can treat it using traditional medicine methods. One of the effective ways to treat this problem is tampons with various healing impregnations:
- Propolis. It is considered one of the best remedies for treating many ailments and erosion is no exception. All preparations of bee origin have antibacterial, antimicrobial, antioxidant and wound-healing effects. To prepare a medicinal solution, you need to melt 25 grams. Vaseline and add 5 g. crushed propolis. Heat everything together over the fire, but do not bring to a boil. Then the mixture must be filtered and soaked in a cloth swab. Insert a tampon into the vagina every day for 10-12 hours for two weeks;
- Mumiyo. To do this, you need to soak a clean rag swab with mumiyo (4%) and leave it overnight for 10 days. Then you can take a break for a week and repeat the course of treatment. During the treatment period, it is necessary to exclude taking a hot bath, physical activity and intimate life;
- Celandine in dry form must be ground and sifted. Mix the resulting flour with Vaseline. Insert tampons with the resulting impregnation every day 4 times for 2 hours. The course of treatment is a week. At the same time, you can take herbal decoctions - chamomile, string, calendula, which have a calming and anti-inflammatory effect on the female body.
There are many impregnations for tampons that have wound healing and regenerating effects. The most popular ones are given as an example.
Ectopia – is it dangerous or not?
Today, medicine has firmly established that ectopia, especially small ones, is a natural stage in the development of the female reproductive system. The spot of columnar epithelium at different periods of life against the background of hormonal surges can either appear or disappear, sometimes be very small, sometimes more extensive. And with age, the body completely eliminates this area, moving the transformation zone deeper into the cervical canal.
Quite often , ectopia occurs in young nulliparous women, and is a physiological condition that does not require treatment and does not pose a health hazard.
Need to know
If you have been diagnosed with ectopia of the cervix, but a cytological examination does not reveal pathological cells and there is no human papillomavirus, then your erosion is not dangerous, nothing needs to be done about it, it will go away on its own over time. The only thing that should not be ignored is annual gynecological examinations.
If HPV is still detected, and there are no atypical cells in the Pap test, then nothing needs to be done about your erosion. Just see a gynecologist twice as often (every six months).
Let's take a look at the medical history...
So, we have already mentioned that ectopia (we will get used to speaking correctly) is a common condition in which a gynecologist sees a red spot around the external os of the cervix. Previously, due to imperfect research methods, it was believed that this was a defect in the cervical tissue, which could turn into cancer if left untreated. Therefore, in order to prevent cervical cancer, they tried to eliminate this defect by cauterization. Moreover, cauterization was performed on almost all women in 100% of cases.
But science moved forward. It became clear that the doctor’s eye cannot examine the cervix and its defect in detail: after all, it is necessary to evaluate the quality and structure of the cells. But it is almost impossible to do this with the naked eye. And in the daily practice of gynecologists, colposcopes began to appear - microscopes for a detailed study of the condition of the cervix.
The procedure of colposcopy, examination of the cervix in mirrors under microscope magnification, allows you to assess the condition of the epithelium and the presence of pathological changes.
Diagnostics have become more advanced. It was established that “erosion” is not an area devoid of epithelium at all, but a displacement of the intracervical columnar epithelium onto the vaginal part of the cervix. It is the columnar epithelium on the surface of the cervix that looks like a red spot.
When should erosion be treated?
In most cases, erosion does not need to be treated. But for this there are two conditions that should be remembered:
- There should be no inflammatory process;
- There should be no atypical or cancer cells in the smear for oncocytology.
When we talk about ectopia, we mean that the cylindrical epithelium of the cervical canal is not in its place, that is, not inside the cervix, but outside - on its vaginal part. The columnar epithelium is very thin and easily injured. The vaginal environment is not entirely natural for him. In addition, microbes can enter the vagina during sexual intercourse or from the rectum and harm the delicate epithelium.
Therefore, to prevent ectopia from developing into a complicated form, you need to keep the vagina clean, follow the rules of intimate hygiene and use condoms or spermicides during sex. This is especially true for women who are in sexual search and do not have a permanent sexual partner.
Chronic cervicitis during colposcopy (presence of hyperemia and discharge from the cervical canal).
Infusions and decoctions for oral administration
In addition to external effects on pathology, decoctions and infusions based on natural ingredients will help speed up the healing process. Their advantage is that many vitamins and minerals enter the body at the same time, which strengthen the immune system.
They have an antibacterial effect, relieve inflammation, and some improve blood circulation, which promotes metabolism. At the same time, the process of cell regeneration is accelerated, and the affected tissues are renewed.
For drinking, you can use the following recipes:
- Calendula decoction. Crushed flowers and leaves of calendula (commonly known as marigolds) need to be boiled for 5-7 minutes in a liter of water. Strain the resulting broth and leave for at least 20 minutes. Take orally daily before meals 15 minutes;
- Pumpkin seeds. They must be ground in a blender or meat grinder and pour boiling water over them. Leave for 10-12 hours. Then strain and take 100 ml daily;
- Yarrow inflorescences need to be boiled for 20 minutes in a liter of water. You can drink it like regular tea throughout the day.
Such decoctions strengthen the body's protective functions and help destroy pathogenic microflora. In addition, plants are rich in antioxidants, which are necessary to combat the negative effects of free radicals.
Inflammation of the appendages in women: symptoms and treatment at home.
Details about bartholinitis: causes, symptoms, treatment.
What should a woman do with mastitis? Find out in this article.
How long does it take to treat using different methods?
The duration of treatment depends on the nature of the erosion and the degree of neglect of the pathology. Surgical methods require several weeks for healing and tissue restoration (4-6). If conservative therapy is used, the time period increases as several courses of treatment are required.
Erosion is an unpleasant disease, but curable . Some people are helped by medicines and pills, others have to resort to more radical methods. The main thing is not to neglect and follow the doctor’s recommendations, and in the future, regularly visit a gynecologist and monitor your health more carefully.
What is erosion
The content of the article
Pathology is a defect in the mucous membrane, which can occur against the background of infections, injuries or hormonal disorders and have varying severity, which will determine the method of treatment.
There are true erosion, pseudo-erosion and ectropion. With all these pathologies, a bright red area of damaged or modified epithelium appears on the cervix around its pharynx - this is what the upper layer of cells is called in medicine.
This disease affects women of any age. Most cases occur during the reproductive period and later; about 12% of patients are teenage girls. Gynecologists state that during routine examinations one of the types of erosion is detected in every second patient.
How is ectopia diagnosed?
There is no diagnosis of cervical erosion worldwide. However, although today most practitioners do not consider cervical erosion a disease and claim that there is no such diagnosis, in the international classification of diseases of the 10th revision (ICD-10) under the heading “Non-inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs” it is assigned code N86. Allow me a small clarification: this section refers only to a case of ectopia with complications, that is, a pathology variant that requires treatment.
Ectopia is a condition that has no symptoms. And only a gynecologist can detect it during an examination. Very rarely (when the ectopia reaches a large size), there may be complaints of spotting after intimacy, or copious white or mucous discharge from the vagina may appear. There is never pain during erosion. And it cannot be seen on an ultrasound.
So, what does a doctor do if he discovers an unclear red spot on the patient’s cervix during a gynecological examination?
Firstly, the doctor will definitely take smears from the cervix for atypical cells. A smear for cancer cells in gynecology is called a Pap test. This is a very important analysis. Even if a woman is gynecologically healthy, she must undergo it without fail once a year.
The process of collecting material for a Pap test.
On a note
Cervical Papanicolaou smear examination (PAP test) is the main method for identifying precancerous conditions of the cervix. Material for cytology is collected from three areas: from the outer part of the cervix, from the junction of stratified squamous and columnar epithelium, and from the lower third of the cervical canal. To take material for examination, special brushes are used.
Reviews about the treatment
“I have not yet been pregnant or given birth, but I began to be sexually active at the age of 16. Recently I was diagnosed with erosion and the doctors said that I needed to burn it out. But at home I was advised to douche with salt and soda and use homemade tampons with propolis at night. You know, it helped a lot. I took three courses of 10 days each, and the doctor at the appointment was surprised - the erosion disappeared.”
Alenka, 19 years old
“A year after giving birth, problems began on the female side. It hurts, it bleeds, it itches. Doctors diagnosed “cervical erosion.” I was afraid to cauterize and remembered the nurse from the maternity hospital who said that you need to wash yourself with walnut decoction and drink mumiyo. I decided to try it. After a week and a half, I felt relief and the discomfort disappeared. I stuck to douching, didn’t take hot baths, and eliminated sex for a while. Everything is fine. The erosion hasn’t disappeared yet, but it has become much smaller in size.”
Yulia, 27 years old
"Dear ladies! The best remedy for erosion are tampons based on propolis and mumiyo. It’s just a magical method and doesn’t require any surgery!”
Oksana, 38 years old
Which cauterization method is preferable for cervical dysplasia and cancer?
Often, mild dysplasia detected may simply be a consequence of inflammation. And after anti-inflammatory therapy at the control oncocytology, not a trace will remain of it.
But if dysplasia really needs to be treated, it is important to choose the right cauterization method. When a doctor decides on the method of surgical treatment of dysplasia, the key factors are the following:
- Severity of dysplasia;
- Woman's age;
- Does her plans include motherhood in the future?
Of course, gentle surgical methods are indicated for young women with mild to moderate dysplasia who are planning to give birth after cervical treatment. For this, cauterization with laser, radio waves, argon or freezing with liquid nitrogen can be used. In case of deep lesions of the cervix in women who do not plan to give birth, diathermoelectrocoagulation or electroexcision may be justified.
Extent of spread of cervical cancer.
With advanced forms of cancer, it happens that it is not possible to save the cervix, and due to the deep germination of the tumor process, it is necessary to completely remove not only the cervix, but also the body of the uterus.
Is there actually erosion?
Translated from Latin, “erosio” means “corrosion.” For many years, it was believed that erosion was a defect in the cervical tissue (ulcer) that could develop into cervical cancer if not treated. And cauterization was carried out on all women in a row. This is how it was in the time of our grandmothers and mothers.
As time passed, gynecology developed progressively, and the following became clear:
- There is virtually no cervical cancer without infection with the human papillomavirus;
- The presence of erosion in itself does not increase or decrease the likelihood of developing cancer;
- Often erosion is not erosion at all, but ectopia;
- Ectopy is the migration of cervical epithelial cells from the inner part of the cervix to the outer surface;
- Ectopia is not a disease, but a physiological condition of the cervix that does not need to be treated: over time it goes away on its own.
This is what large cervical erosion on the anterior and posterior lips looks like during colposcopy.
On a note
Cervical erosion is not a female disease that needs to be treated. This is the norm. In other words, cells turn from the inside out (in medical parlance, this condition may be called ectropion). No matter how paradoxical it may sound, if you do nothing about such erosion, it will go away on its own.
Therefore, if you are informed that you have been diagnosed with erosion, do not panic, do not rush to remove it and spend money on treatment, the cost of which is often quite high.
We repeat once again that the concept of erosion is outdated, and it is more correct to say ectopia (false erosion or pseudo-erosion). But this term has become so firmly established in our everyday life that it continues to be used not only by patients, but, oddly enough, even by doctors. This is probably due to a lack of information among women. If the patient is told that she has “erosion,” then no additional questions arise, because she heard this name from her friends, mother or grandmother. But if you tell a woman that she has ectopia or ectropion, then she is unlikely to immediately understand what the doctor is talking about; she will also decide that something terrible and dangerous has been discovered in her.
This is what a large cervical ectopia looks like during colposcopy.
Therefore, doctors still have a long way to go to eliminate illiteracy among the female population.
On a note
The term “erosion” is currently used exclusively for true erosions that arise as a result of an infectious process, trauma or radiation.
Frequently asked questions for women with cervical erosion (ectopia)
Is it possible to install a spiral if there is erosion?
Can. But only on the condition that there are no signs of inflammation in microflora smears, and there are no atypical cells in oncocytology smears.
It is important to know
Uncomplicated cervical erosion is not a contraindication for the installation of an intrauterine device.
Is it possible to have sex if there is erosion?
Can. But you need to remember that small erosion does not give any symptoms and does not interfere with sexual activity, but large ectopia (more than 1-1.5 cm) can cause bleeding after sexual intercourse. In this case, you will need to see a doctor for examination.
Is it possible to use tampons for cervical erosion?
Yes, you can.
Can erosion affect the conception of a child and the pregnancy in the future?
Erosion itself does not affect conception and does not cause obstetric complications. The problem is different. It happens that the tactics for managing and treating erosion are chosen incorrectly. An unjustified desire to cauterize uncomplicated ectopia can lead to narrowing of the cervical canal, which often causes infertility.
Why does menstruation delay due to erosion?
Cervical erosion does not affect the menstrual cycle, and delayed menstruation is associated with concomitant pathology.
What are the psychosomatic causes of erosion?
According to the theory of psychosomatics, erosion occurs in women who do not accept their feminine essence, are dissatisfied with their relationship with their partner, and experience certain difficulties in their sexual life. Official medicine does not focus on psychosomatics, so a practicing gynecologist is unlikely to recommend that his patient accept herself as a woman in terms of treating erosion (although this is exactly the advice that is given on numerous forums).
We think that from the above you understand: it is very important to decide whether your erosion is normal or pathological. The tactics of further management and treatment will depend on this. Knowing in which cases ectopia can be observed and in which it needs to be treated, you will not part with “your blood” in vain, because the cauterization offered in many clinics is paid, and the price for services is far from symbolic.
Useful video about cervical erosion
Douching solutions
To increase the effectiveness of treatment, in parallel with tampons, it is advisable to douche with healing solutions prepared at home:
- Nutshell. To prepare the decoction, you need to boil the walnut shell until brown. Then strain the resulting liquid and mix in a 1/1 ratio with clean warm water. Douche in the morning and evening, as well as between changing a tampon;
- Dilute 2 tablespoons of soda and salt into half a liter of water. Boil the resulting solution and, after it has cooled, douche. This remedy reduces the inflammatory process and promotes the regeneration of tissue cells of the cervical mucosa. Carry out the procedure daily in the morning and evening. During the treatment period it is better to refuse sex;
- Salt solution. In a liter of warm boiled water you need to dissolve 10 ml of salt. You need to douche with this remedy for 10 days, 2 times a day. Then take a week break and continue treatment.
Douching is only relevant with an integrated approach to getting rid of erosion. When a tampon is in place, all the dead cells collect inside and douching is necessary to cleanse the vagina.
Types of surgical intervention
Cauterization of cervical erosion, the price of which varies from 300 to 10,000 rubles, is carried out in various ways using various means. The most common options are:
- Diathermocoagulation. The procedure is carried out using electric current. As a rule, this method is recommended for patients who have given birth and who have not been planning a pregnancy for at least a year.
- Cryotherapy. Cauterization is carried out with liquid nitrogen. During the procedure, the so-called “freezing” of the tissue occurs. This method is considered more gentle than the previous one. However, cervical erosion after cauterization with nitrogen may recur.
- Laser therapy. This method is considered one of the most effective of all used to treat cervical erosion. Feedback from patients indicates that healing is much faster than in other cases. During the procedure, a laser beam of minimal power is used. After such exposure there are no scars left.
- Radio wave treatment of cervical erosion. As a rule, such an effect is recommended for those planning a second pregnancy. This procedure is also prescribed for nulliparous patients. The process uses the Surgitron apparatus. Radio wave treatment of cervical erosion is a virtually painless method. However, this procedure is considered one of the most expensive. The price can reach 10 thousand rubles. There are no scars left after the procedure. There is also no bleeding. However, there may be vaginal discharge and nagging pain in the lower abdomen for 2-3 days. After cauterization in this way, it is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse for at least ten days. Anesthesia is not required for the procedure. However, if the patient wishes, a lidocaine injection can be given.
What should I do if my Pap test reveals cancer cells?
If cancer cells are found in a cytological study, then this condition will no longer be called erosion. This is dysplasia (precancer) or even cervical cancer. In this case, you need to take a targeted biopsy from the suspicious area under the control of a colposcope.
The biopsy results are sent to the laboratory for histological examination, and only a histologist can make a final verdict, based on which the following actions are taken:
- If, according to the results of the biopsy, there is no cervical cancer, but a precancerous process is confirmed, then in this case treatment is indicated (most often by cauterization of the cervix);
- If cancer is confirmed, then the method of choice is wide conization - excision of the cervix, in which the focus of the affected tissue is removed in the form of a cone with an apex extending deep into the cervical canal.