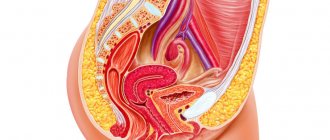
A disease such as gastric erosion is considered by gastroenterologists to be the most common gastroduodenal ailment in humans. This disease is detected in every tenth patient examined with an endoscope. What is gastric erosion? Symptoms, causes, treatment of this disease - these are the points that will be discussed in detail in this article.
Gastric erosion - what is it?
Pathological changes in the mucous membrane have its own histological features.
Gastric erosion is damage to organ tissue, which is characterized by the appearance of superficial ulcers without destruction of the muscle layer. Defects can be single or multiple. In 10% of people suffering from this disease, ulcerative elements are diagnosed in the lower third of the antrum and on the wall of the duodenum, causing bulbitis, which aggravates the course of the disease.
Types of gastric erosions
The erosive process can develop in several directions. There are various modifications of classifications by which pathology is divided. The authors offer these options.
- According to the type of occurrence of erosion, there are: primary - as an independently arising form;
- secondary - due to another disease;
- malignant - in the form of the initial stage of cancer.
- single - up to 3 lesions;
- acute - lasting from 10 days to 2 months;
- hemorrhagic;
The topographic location of gastric erosion is also determined:
- in the antrum;
- at the bottom of the organ;
- in the area of the pylorus.
Forms of the disease
Like any other disease, gastric erosion, its symptoms, the treatment of which may depend on the form of its occurrence, is divided into:
- Acute, the location of which is most often observed in that part of the organ that is commonly called the “bottom”. The main external signs of the acute form are the absence of epithelial layering on the body of the erosion, a weak degree of infiltration by lymphocyte cells and the almost complete absence of fibrin deposits at its base. Symptoms of acute gastric erosion are always very vivid and painful, their intensity and strength are much higher than those observed with peptic ulcer disease. Treatment of acute forms of the disease in most cases lasts no more than 2 weeks.
- Chronic, which is most often localized in the antrum of the stomach and consists mainly of so-called granulation tissue. The edges of erosion in this form are surrounded by layers of hyperplastic epithelium, and at the bottom there are dilated capillaries and degeneration of the ventricular glands. Chronic erosion of the antrum of the stomach, the symptoms of which are somewhat milder than those of the acute form, requires longer treatment for 2-6 months or longer. The duration of therapy may depend on the degree of damage to the gastric mucosa and the body's susceptibility to drugs.
Causes of gastric erosion
Signs of pathology appear suddenly or develop gradually. The causes of gastric erosion play an important role in the pathogenesis. These include:
- bacterial infection by Helicobacter pylori;
- low quality food;
- frequent intake of spicy, cold, hot foods, food additives and dyes;
- drug therapy over a long period of time, especially the use of antibacterial and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs of the sulfonamide group;
- regular psycho-emotional stress, stressful situations;
- chronic concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine system;
- occupational hazard;
- bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol in large doses;
- unfavorable heredity.
Attention! Identification of several risk factors at the same time increases the likelihood of erosion of the gastric mucosa.
Causes
Erosion of the gastric mucosa can occur not only in an adult, but also in a child, and the main predisposing factor is considered to be the aggressive effect of the acidic environment of the stomach on the protective mucous layer. Common reasons why a violation occurs are:
- Abuse of heavy drugs, which first cause superficial erosions, and then become the root cause of stomach ulcers.
- Poor nutrition and the predominance of spicy and fatty dishes in the menu, under the influence of which multiple erosions form on the mucous epithelium of the stomach and duodenum.
- Frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages and cigarettes.
- Liver pathologies, for example, cirrhosis, under the influence of which the blood vessels of the stomach spasm, causing erosive formation to appear on the tissues.
- Stomach cancer in the early stages, irritating and corroding the mucous layer.
- Complications after operations or severe injuries.
- Diabetes mellitus, in which a disorder of carbohydrate metabolism provokes damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive organ.
It is extremely rare, but still occurs, erosion of the stomach walls in children with leukemia. However, such a disorder is secondary, as a result of damage to the mucous membrane due to the progression of pathology with multiple lesions of the lymph nodes and their partial or complete destruction. In order to treat such a pathology correctly, it is important to first find out what the cause triggered the development. Attempts to self-medicate and use folk remedies are vitally dangerous.
Symptoms of gastric erosion
The pathological process manifests itself in different ways, depending on the nature of the disease, location, and type of lesions.
In most cases, symptoms of gastric erosion in adults are represented by the following options:
- The presence of discomfort and pain in the upper half of the anterior abdominal wall, sometimes in the left hypochondrium. Characteristic signs of the syndrome are at night and “hunger” pain. In the presence of acute erosion, there is paroxysmal pain.
- Dyspeptic symptoms in the form of heartburn, belching, nausea, vomiting, unstable stool.
- Attachment of hemorrhagic syndrome with bleeding from erosions in the form of an admixture of “coffee grounds” in the vomit, dark brown stool.
- In chronic pathology, iron deficiency anemia occurs, nails become brittle, hair may fall out, and back pain may occur. Asthenia appears, which is characterized by decreased performance, weakness, and irritability.
Against the background of a long course of pathology, an exacerbation often occurs, which is characterized by a sudden onset and disruption of the patient’s condition.
Are stomach erosions dangerous?
If there are areas of modified mucous membrane, symptoms may not be detected for a long time. Therefore, patients are interested in why gastric erosion is dangerous and what consequences of the pathology arise. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, there is a possibility of degeneration of the morphological substrate, which manifests itself as complications or the formation of a malignant process.
Types of erosion
Gastric erosion (symptoms, photos presented in this article) can be of several types:
- Hemorrhagic deep or superficial, which is characterized by the presence of blood plaque on the surface and is surrounded by a pale edematous membrane.
- Superficial flat, which is distinguished by a hyperemic rim around the body and a clean bottom, sometimes with a whitish coating on it.
- Complete or hyperplastic inflammatory, the main symptom of which is considered to be a polyp-like form of the body of erosion, located at the highest point of the fold of the stomach with the presence of slight edema.
Diagnostics
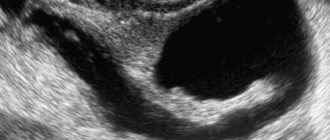
An examination for suspected pathology includes anamnesis, objective data and auxiliary studies. The specialist first clarifies the patient’s complaints and determines the possible causes of the disease. Then he orders an additional examination.
Endoscopic photo of multiple gastric erosions
Gastric erosion is diagnosed using the following methods:
- general clinical and biochemical tests of blood, urine and feces;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy with biopsy from an erosive lesion;
- chromogastroscopy;
- intragastric pH-metry;
- detection of Helicobacter pylori by the activity of the enzyme urease;
- morphological study of mucosal biopsies in chronic patients;
- ultrasound method of examining the abdominal cavity.
Important! Ancillary activities help determine the diagnostic criteria with which the gastroenterologist makes the final diagnosis.
Prevention
Measures to prevent gastric erosion are associated with maintaining a healthy lifestyle. The patient needs to limit the risk of stressful situations that can complicate the course of the disease. In any case, erosion should be treated in a timely manner, which will allow achieving a positive result.
Periodic examinations allow therapy to be carried out in the early stages of the disease. If a patient has diabetes mellitus, then he needs to undergo periodic preventive examinations. The doctor prescribes taking vitamin complexes, especially in winter. A preventive diet should be agreed with a doctor, as should the use of folk remedies.
Project consultant, co-author of the article: Ovchinnikova Natalya Ivanovna | Gastroenterologist, Hepatologist, Infectious disease specialist 30 years of experience / Doctor of the highest category, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Education:
Diploma in General Medicine, Novosibirsk State Medical Institute (1988), Residency in Gastroenterology, Russian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education (1997)
Gastric erosion: treatment
An integrated approach to disease treatment is the main factor for a successful outcome. Treatment of gastric erosion includes drugs and a regimen presented in the following table.
Table 1. Treatment of gastric erosion
| Drugs | Reception scheme | |
| 1. | Antibiotics:
| Up to 7-14 days |
| 2. | Antacids (Maalox, Gaviscon, phosphalugel) | Up to 10 days |
| 3. | Proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole) | Up to 10 days - in acute form, up to 8-12 weeks in chronic form |
| 4. | Histamine receptor blockers (ranitidine, famotidine) | Up to 10-14 days |
| 5. | Bismuth preparations (De-Nol) | Up to 4-8 weeks |
| 6. | Prostaglandins | Up to 4-8 weeks |
| 7. | Regenerative agents (actovegin) | Up to 4-8 weeks |
Treatment of gastric erosion with medications differs in acute and chronic pathology. In the first case, therapy takes up to 2 weeks. In addition to the main regimen, short-course painkillers are included. With a long course of the disease, it takes from 4 to 8 weeks, in some cases longer.
Therapeutic measures for various defects have some differences, presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Symptoms and treatment of certain types of gastric erosions
| Type of erosion | Characteristic | Symptoms | How to treat |
| Acute erosions of the body of the stomach | Flat polymorphic defects with fibrinoid and hematinic plaque located in the antrum or fundus of the stomach | Signs of acute gastric erosion are sharply expressed due to the symptom in the form of pain in the upper abdomen, which is difficult to relieve with medications, often accompanied by hemorrhagic syndrome in the form of vomiting mixed with blood or melena | Acute erosion is treated with the following medications:
|
| Chronic gastric erosion | Mature or immature lesions with a halo of hyperemia, desquamation and tissue necrosis | Symptoms of chronic erosions are manifested by discomfort and pain of a less pronounced nature, there are signs of dyspeptic disorder | Treatment of the condition includes the use of:
|
| Multiple hemorrhagic erosions of the stomach | There are more than 4 lesions | Periodically there are signs of gastric bleeding and symptoms of melena | The solution to the problem of how to treat multiple hemorrhagic erosions lies in stopping the bleeding and restoring the mucous membrane with medications and laser therapy. The main groups of drugs are:
|
| Hemorrhagic erosions | Point hemorrhagic erosions of the stomach are characterized by the deposition of hematin and isolated hemorrhages, prone to the formation of ulcerative process and malignancy | Hemorrhagic single erosions of the body of the stomach rarely have an acute onset; a latent course of the pathology is noted with the formation of anemia and manifestations of asthenia; blood corpuscles are determined in stool tests | Treatment of hemorrhagic erosions consists of restoring the gastric mucosa and eliminating anemia |
| Hyperplastic erosion | Endoscopic and X-ray signs of the disease reveal immature elements with pronounced regenerative cell hyperplasia on the walls of the stomach; signs of hyperplastic erosion develop reversely in 30% of cases | The course of the disease is chronic with periodic exacerbation of symptoms due to the influence of unfavorable factors | Treatment of hyperplastic erosion of the stomach includes drugs that can be taken as for the chronic version. Treatment must be long-term, for 5-7 years. |
| Complete erosion | A chronic variant of the course in the form of raised areas of the mucous membrane of the full type with an umbilical depression in the center, similar to smallpox elements | Complete erosion of the prepyloric part of the stomach is characterized by a chronic course with periodic exacerbation of symptoms and a high probability of the formation of ulcerative elements | Treatment according to the chronic erosion protocol |
Conservative treatment of erosions: medications, surgery
The main goal of treating gastric erosion is to heal it, eliminate pain and prevent bleeding. Secondary erosion also involves treatment of the underlying disease, which resulted in complications with the stomach. Gastroenterologists offer patients a list of medications from the following groups:
- Gastroprotectors, which include Cytotec, Simaldrate and Gelusil.
- Anticholinergic drugs - the drug "Scopolamine" or "Atropine".
- Histamine blockers - medications Gastrozol, Omeprazole, Cimetidine, Ranitidine, Omez and Metronidazole.
- Antacids - calcium carbonate, drugs "Almagel", "Maalox" and others.
- Preparations with an enveloping effect - aluminum hydroxide, bismuth or white clay.
If there is bleeding hemorrhagic erosion of the stomach, the symptoms of which are quite pronounced, treatment is primarily aimed at stopping the bleeding and includes gastric lavage with cold water and intravenous infusion of blood or its components. In addition, it is necessary to administer aminocaproic acid, vikasol and fibrinogen by injection, which increases blood clotting and prevents large blood losses.
To reduce the risk of developing polyp erosions at the site, laser or electrocoagulation is used, carried out in a hospital setting. In particularly severe cases of systematic bleeding, the patient may undergo endoscopic or abdominal surgery, during which the part of the stomach affected by erosion is removed.
Nutrition
One of the main stages of treatment is a special diet. Nutrition for gastric erosion must be of high quality and varied in order to provide the body with microelements, vitamins and energy components. The frequency of meals increases to 5-6 times a day. The temperature of the food should be comfortable to avoid irritation of the mucous membranes.
Diet for erosive gastritis with a sample menu for a week
What can you eat if you have stomach erosion and what can’t you eat?
The diet must meet the requirements presented in Table 3.
Table 3. Nutrition for gastric erosion
| You can eat | Can't eat |
| I eat it boiled, steamed, stewed | Food with a rough texture |
| Lean meat and fish - chicken, beef, rabbit, pike perch | Fatty meat with elements of connective tissue and skin; offal |
| Stewed vegetables (pumpkin, beets), neutral-tasting fruits - apples, pears, peaches | Raw plant foods, sour vegetables and fruits, citrus fruits, walnuts, seeds |
| You can drink jelly, sweet fruit infusions, weak tea | Juices, fresh drinks, sparkling drinks, coffee, cocoa |
| Porridge - buckwheat, rice, oatmeal | Yeast baked goods, products made from low-grade flour |
| Baked goods made from premium flour, vegetable oil | Butter, margarine |
| Honey, marshmallow | Chocolate |
| Milk porridges, puddings, low-sour cottage cheese | Fermented milk products, kefir |
| Boiled eggs, omelet | Legumes, celery, turnips, radishes |
| Alcoholic drinks, including beer |
Symptoms of gastritis
The symptoms of the pathology in question are quite easy to notice. Having felt them, the sick person cannot help but pay attention to them. The main symptom characteristic of this pathology is the intensity of the pain syndrome.
The signs of the disease are very similar to the clinical picture of peptic ulcer disease. But pain during erosion is persistent. The pain syndrome is so severe that even with treatment of the disease, it is not always possible to stop it immediately. So, in some patients, pain continues even in the first or second month of therapy.
Symptoms similar to peptic ulcers include:
- constant severe pain;
- dyskinesia (impaired functioning of the biliary system);
- hungry night pain;
- dyspepsia (digestion problems).
Patients also exhibit symptoms of the disease such as:
- bleeding. With erosion, blood can be observed in feces and vomit. With such an alarming sign of illness, it is better to visit a doctor. The color of vomit is usually dark brown. If there is internal bleeding, surgery (removal of part of the stomach) may be required;
- low hemoglobin;
- nausea, vomiting;
- anemia;
- heartburn;
- violation of the excretion of bile from the body;
- brittle hair, nails, dry epidermis. These signs indicate the development of anemia, which is provoked by erosion. Such symptoms are especially striking in the presence of internal bleeding. A bluish tint of the epidermis is also observed.
At the initial stage, gastric erosion does not manifest itself in any way, but the manifestation of multiple ulcers noticeably worsens general well-being and provokes hunger pain. Signs of the disease should be alarming, since they only intensify over time. If a person does not understand how a characteristic illness manifests itself, pay attention to the following symptoms of gastric erosion:
- nausea, prolonged vomiting;
- sour belching;
- epigastric pain in the abdomen after the next meal;
- heartburn;
- internal bleeding;
- the presence of blood impurities in the stool;
- decrease in hemoglobin;
- increased fragility of nail plates;
- general weakness, increased fatigue;
- indigestion;
- impaired flow of bile from the body;
- anemia due to erosion;
- instability of blood pressure.
With acute erosive gastritis, there may be signs such as a feeling of tension and heaviness after eating and increasing dull pain. The patient will experience heartburn and nausea, and may vomit blood. The latter may still be in the feces; the stool will vary in consistency. Erosive acute gastritis often appears unexpectedly, then the disease will develop quickly. There may be phenomena such as flatulence and loss of appetite.
Depending on the accompanying changes and signs, erosion is divided into three groups:
- Primary – we are talking about a self-occurring disease in which the remaining organs of the gastrointestinal tract are not affected.
- Secondary – negative changes are observed in the functioning of the heart, blood vessels, and other systems.
- Malignant – characterized by the development of Crohn’s disease or the formation of oncological structures.
Another classification involves division based on the severity of the process, the presence or absence of polyps, bleeding (hemorrhagic) surfaces. Often the inflammation spreads to the duodenum and esophagus, due to the improper functioning of the pylorus connecting them to the stomach.
The pathology can be acute or chronic.
Acute
A peculiarity is the presence of both single and multiple inflamed areas, shaped like an oval or circle. The location is the bottom of the digestive organ or its central proximal section. The size of the redness does not exceed 2–4 mm. Provided the disease is at a mild stage, the right diet and an appropriate treatment regimen, the disease can be cured quickly - complete epithelization occurs in 10 days. If serious atrophy is detected, recovery is delayed for a period of up to two months.
Chronic
They are always present in large numbers and only in the antrum. The occurrence of such erosion in the stomach is often accompanied by the formation of a peculiar visual chain of foci in the form of suction cups with a diameter of no more than 0.5 cm. However, another scenario with a chaotic localization of pathogenic structures is not excluded. It takes more than one year to treat the disorder.
The course of erosion of the gastric mucosa is similar to an ulcer. The main difference concerns the intensity of the pain syndrome. In the situation under consideration, the maximum severity of discomfort and its persistence over a long period of time are noted. Often, even medications taken for one or two months are unable to cope with spasms.
Other signs include:
- Presence of pain on an empty stomach.
- Dysfunction of the biliary system with the development of dyskinesia.
- General malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract with symptoms of dyspepsia - belching, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, flatulence due to improper digestion of food.
- Presence of occult blood in stool tests.
- Decreased hemoglobin.
Erosion is dangerous due to gastric bleeding, but their symptoms in the form of darkening of the stool, general weakness, and dizziness are present when the duodenum is affected simultaneously with the digestive organ.
Erosion of the gastric mucosa is accompanied by very pronounced symptoms. A distinctive feature is that painful sensations cannot be completely eliminated even within several months from the start of treatment for the pathology.
Clinical manifestations of pathology should be considered:
- spasms in the abdominal area, which become much more intense due to eating or at night;
- belching and burning sensation in the throat;
- nausea, which ends with productive vomiting, bringing serious relief;
- the presence of bloody impurities in the stool, indicating an internal form of bleeding;
- digestive disorders.
Other symptoms indicating that it is necessary to treat gastric erosion include an increased degree of fragility of the nail plates, as well as dry skin, general weakness and fatigue of the body. In addition, experts pay attention to the likelihood of problematic bile excretion, a decrease in hemoglobin levels and destabilization of the sense of smell. Most rarely, the disease occurs without any symptoms, which occurs with the secondary appearance of erosion.
Stomach erosion: treatment with folk remedies
Along with drug therapy, alternative methods are used. Many patients are interested in how to treat gastric erosion with folk remedies. The following are the most effective natural products that can be used at home. Recipes from them are presented in the table.
Table 4. The most effective folk remedies for treating gastric erosion
| Potato juice | The juice obtained by rubbing 2-3 potato tubers is diluted with a small amount of water. Drink up to 3 times a day half an hour before meals for 14 days |
| Sea buckthorn oil | Consume warm, 5 ml 2-3 times a day before meals. |
| Flax seed | Boil one tablespoon of seeds for 5 minutes. They insist for two hours. Take the mucous mass 3-4 times a day before meals |
| Aloe honey | Aloe juice is mixed with honey. Take daily in the morning on an empty stomach for a month |
| Calamus root | Pour one teaspoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water and cook for another 15 minutes over low heat. Drink 50 ml of the decoction before meals for 14 days. |
Symptoms of acute and chronic erosive lesions
According to the form of formation, the clinical course of the disease can be classified as acute and chronic gastric erosion. The acute form is characterized by a sharp change in well-being and pain of varying intensity. Timely treatment of acute gastric erosions with medications or folk remedies ensures recovery within 1-2 weeks. Chronic pathology of the gastric tract is accompanied by sharp outbreaks of pain activity and their sudden disappearance. The duration of therapeutic drug treatment that eliminates pain symptoms, in this case, ranges from two months. The main clinical symptoms of acute or chronic forms of erosive lesions of the stomach are characterized by the following features:
- abdominal cramping, worsening at night or worsening after eating;
- constant burning sensation in the esophagus;
- constant gag reflex and nausea;
- indigestion, in the form of loose stools;
- violation of bile excretion;
- sour belching and heartburn;
- dizziness and general weakness of the body.
It should be noted that in some cases, especially with repeated manifestations, the erosive lesion is asymptomatic. The primary signs of the disease can be easily eliminated with a diet specially prescribed by the doctor and a set of therapeutic measures.
Prognosis for treatment and recovery
Symptoms of the disease may be mild, but increase over time. With a long-term course of the pathological condition, patients are concerned about the question of whether gastric erosion can be cured forever. Complete restoration of the mucous membrane occurs with timely intervention in the acute phase of the process. The positive result of treatment of the chronic form depends on the morphological type of erosive defects and the degree of influence of provoking factors.
Preventive recommendations
To prevent erosive damage to the stomach and possible complications, it is first of all important to monitor your diet and exclude from the menu dishes that irritate the mucous tissues of the digestive organ. It is also worth monitoring the intake of heavy medications and regularly monitoring the condition of the stomach. If you are predisposed to the formation of erosions and ulcers, it is important to completely get rid of bad habits; if you have characteristic symptoms, do not self-medicate, but immediately consult a doctor for help. By following these simple rules, you will be able to maintain your health and prevent the development of dangerous complications.
Diagnostic measures
The diagnosis can be confirmed using fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
Erosion and papules of the antrum of the stomach can be suspected in the acute period based on the characteristic complaints of the patient. To visually detect ulcers on the gastric mucosa, fibrogastroduodenoscopy, ultrasound diagnostics and radiography with the introduction of a contrast agent are used. It is important to conduct a breath test for Helicobacter pylori contamination. A stool test for occult blood is also indicated. In severe cases, magnetic resonance imaging is performed.
Main groups of medications in the treatment of gastritis
Investigating the causes of the development of the disease, scientists concluded that the overwhelming percentage of gastritis is the result of activation of Helicobacter pylori . Consequently, the treatment regimen for erosive antral gastritis consists of the following points:
- combating pathogenic microflora with antibiotics and bismuth salts;
- decreased acidity of gastric juice;
- protection of the gastric mucosa;
- relieving muscle spasms;
- anesthesia;
- aids digestion;
- replenishing the lack of vitamins and minerals.
Against the backdrop of a massive drug attack, it is imperative to follow a diet and nutrition regimen to guarantee a successful recovery. In the acute form of the disease, the effect of the toxic substance is first eliminated, then treatment begins.
Antibiotics
In the drug treatment of erosive gastritis, the leading role belongs to antibiotics. Given the high adaptive ability of microbes, a tandem of penicillin drugs and a group of macrolides is used to achieve optimal results.
Penicillin antibiotics
The very first antimicrobial drugs, the honor of discovery of which belongs to Alexander Fleming in 1928. Penicillins have low toxicity and a wide spectrum of action on pathogenic microflora. To treat stomach diseases, acid-resistant synthetic drugs such as Amoxicillin are used. It is not destroyed in an acidic environment, is quickly absorbed in the intestines, and penetrates well into the gastric tissue through the bloodstream. Penicillins kill gastric invaders by preventing the formation of bacterial cell walls.
Amoxicillin is prescribed 2 times a day, 1,000 mg, with an interval of 12 hours (for example, at 8:00 - the first tablet, and at 20:00 - the second).
Antibiotics of the macrolide group
This group of drugs has little toxicity, is well tolerated by patients, and has mild, rare side effects. The semisynthetic antibiotic Clarithromycin exhibits the greatest resistance to hydrochloric acid. It disrupts microbial protein synthesis, exhibiting a bacteriostatic effect.
Take Clarithromycin 500 mg together with Amoxicillin also twice a day, every 12 hours according to the following regimen:
- 8:00 - Amoxicillin;
- 10:00 - Clarithromycin;
- 20:00 - Amoxicillin;
- 22:00 — Clarithromycin.
The course of treatment with antibiotics is 7 days, but if there is a strong bacterial contamination, it can last up to 10-14 days.
Bismuth salts
To cure erosive gastritis, bismuth salts are best suited. They form a protective film in the acidic environment of the stomach, which helps scarring of ulcers and erosions by protecting the mucous membrane from aggressive factors. Bismuth preparations stimulate the synthesis of mucus and bicarbonates and inhibit the secretion of pepsin. They kill microbes directly at the site of erosion, where antibiotics do not penetrate.
The following bismuth-containing products are used: Vikair, Vikalin, De-Nol, Ventrisol, Tribamol, Bismafalk. Price range: from 20 rubles for domestic Vikair to 1,200 rubles for imported De-Nol. Take 3-4 times a day after meals with warm water. The course of treatment is 14 days.
Through the joint efforts of two Novosibirsk scientific institutes, a new drug based on bismuth tripotassium dicitrate was synthesized. Preclinical trials of the drug have proven its safety and antimicrobial activity. According to the inventors, the drug will be available in pharmacy chains in 2019.
Proton pump inhibitors
This is the name of a group of drugs that block the movement of chlorine and hydrogen atoms in the gastric mucosa. The synthesis of hydrochloric acid with a lack of H+ and Cl- is inhibited, and the acidity of gastric juice decreases. The first drug of this group (Omeprazole) was synthesized in 1979 by Swedish chemists. The invention of drugs that suppress high stomach acidity has significantly reduced the percentage of surgical interventions in the treatment of ulcers.
One of the drugs (at the discretion of the gastroenterologist) is prescribed in the following doses: Omeprazole, Esomeprazole, Rabeprazole - 20 mg, Lansoprazole - 30 mg, Pantoprozole - 40 mg 2 times a day for a week.
Gastroprotectors
They exhibit an effect similar to bismuth salts - they form a thin film on the mucous membrane, which is not absorbed or dissolved, but slowly slides into the intestines. There it adsorbs excess liquid, toxins, and irritants. Used for diarrhea associated with the disease. Does not affect microbes. The active substance of the drugs Neointestopan, Kaopectate is magnesium salts.
Rebagit, Rebamipide, Rebamipide-Makledoz contain rebamipide. It protects the cells of the gastric mucosa, enhances the secretion of mucous secretions, and increases blood circulation. The tablets are recommended to be taken for gastritis caused by alcohol and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Venter, Sukrat, Sucralfat, Ulgastran, Ankrusal contain a complex of aluminum salts. Once in the stomach, the active substance is fixed on the necrotic masses of the ulcerative lesion, forming a protective film. Well protects the mucous membrane from the action of pepsin and bile acids. Used for a form of gastritis caused by reverse bile reflux, as well as for patients on hemodialysis.
Relieving muscle spasms
The presence of symptoms such as painful spasms of the stomach muscles impairs the quality of life. This group of drugs is especially relevant for chronic diseases during exacerbation.
Papaverine hydrochloride is a reliable antispasmodic. It reduces smooth muscle tone and relaxes painful contractions of the stomach. Has a calming and hypotensive effect. The medication is not prescribed as a course, but symptomatically, that is, when spastic pain occurs. It is used both in tablets and in injections, rectal suppositories.
Analgesics
The inflamed, eroded gastric mucosa reacts painfully to any irritating substance. Metamethasone sodium, better known as Analgin, suppresses the synthesis of compounds that cause pain and has a weak anti-inflammatory effect. For gastrointestinal diseases, injections of the drug intramuscularly from 250 to 500 mg three times a day are indicated. Analgesics do not treat gastritis, they are just painkillers.
Digestion Aid
Suppression of enzyme synthesis reduces the digestive ability of the stomach; it requires outside help. Drugs such as Festal, Mezim, Cholenzym, Allochol, contain extracts of ox bile, pancreatin, promote the digestion and absorption of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
It should be noted that enzyme preparations increase the activity of antibiotics. Simultaneous administration with bismuth salts reduces the effect of enzyme agents.
Vitamins and iron supplements
Impaired digestion of food causes a lack of vitamins and minerals. Of particular importance for erosive gastritis with bleeding are iron supplements and vitamin B12. The development of anemia can be prevented by injections of Ferrum-Lek, Venofer, Ferkoven, Ferbitol. Such treatment is prescribed with great caution when there is a threat of severe anemia, since there is a high risk of overdose and the formation of infiltrate at the injection site with subsequent abscess formation.
Cyanocobalomin stimulates hematopoiesis and is administered subcutaneously, intramuscularly, or intravenously. The dosage and method of introducing drugs into the body is calculated by the doctor based on the data of a blood test for hemoglobin and a stool test for occult blood.
Treatment
Therapy can be either outpatient or inpatient. It depends on the symptoms, form of the disease, and the degree of damage to the mucous layer. In addition, hospitalization is indicated if bleeding is detected.
To the question of how long it takes to treat the disease, we can answer the following: wound healing usually occurs within 7 days. If there are signs of a chronic process, then complete recovery may take several years. The choice of drugs directly depends on the cause of this pathology .
Treatment of gastric erosion has a number of main directions:
- Prescribing appropriate medications to eliminate the primary disease and consequences.
- Special gentle diet.
- The use of traditional methods as an auxiliary therapy.
Drug treatment
If the patient has increased acidity, then medication treatment includes taking drugs that protect the mucous membranes from the negative effects of gastric juice. Medicines that reduce the production of hydrochloric acid are also prescribed.
- Antacids - Almagel, Phosphalugel, Rennie, Maalox. These remedies quickly reduce acidity levels and protect the walls of the stomach.
- Proton pump inhibitors - Pantoprazole, Omeprazole, Rabeprazole. They help reduce the amount of acid produced.
- H2-histamine receptor blockers - Famotidine, Ranitidine. These tablets protect the walls of the organ from negative effects.
Motor function correctors are indicated for people with digestive disorders. It is manifested by the presence of constant nausea and fullness of the stomach. The most effective means are Motilium, Motorix, Nausilium.
If the cause of the disease is the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, then the treatment complex includes antibiotics, for example, Clarithromycin, Amoxicillin and drugs to reduce the production of hydrochloric acid.
When bleeding begins, instrumental treatment is performed. If the lesion is minor, you can use an endoscope . With its help, very cold water is injected into the organ, after which small lesions are coagulated. This can be either electrocoagulation or a laser procedure that helps avoid the appearance of polyps.
The administration of blood clotting drugs, for example, aminocaproic acid, fibrinogen or vikasol, is considered mandatory. Severe bleeding is eliminated by surgery with partial resection of the stomach.
The role of diet in the treatment of erosion
To maximize the benefits of treatment, it is important to remember how to eat properly during erosion. To do this, you need to exclude the following foods from your diet:
- Carbonated drinks and coffee.
- Fatty meats, smoked meats.
- Spices, salty and sweet foods.
- A number of vegetables, for example, turnips, radishes.
- All citrus fruits.
- Alcoholic drinks.
You can diversify your diet:
- Kissel.
- Eggs.
- Low fat dairy products.
- Oatmeal and semolina.
- Low-fat hard cheeses.
It is better to steam or boil food. Meals should be taken at least 5 times a day, and portions should be small. You should not eat cold or hot foods; preference should be given to moderately warm and fresh food.
Now about what fruits can be eaten during erosion. It should be noted that their selection is small. Bananas, plums, peeled and grated pears and apples are useful.
What else is needed?
The doctor decides how to treat erosive gastritis. He assesses the patient's condition and prescribes medications. Some patients, in addition to basic medications, are prescribed additional medications if there are indications for this:
- painkillers and antispasmodics - No-shpa, Papaverine, Riabal and others;
- agents that suppress active acid production - H2 receptor inhibitors: Ranitidine, Quamatel, Famotidine; PPI inhibitors: Omez, Controloc, Omeprazole, Lansoprazole;
- drugs that help restore the damaged stomach wall - Sucralfate, Methyluracil, Venter and others;
- sedatives – Bulgarian valerian, motherwort tincture, Relaxil;
- complex of vitamins: first of all – B 12 to prevent anemia.
Sometimes it is necessary to go to hospital to avoid complications.
Important! Since erosive gastritis is dangerous due to bleeding, treatment in the acute phase is often carried out in hospitals. With adequate and timely treatment, the patient has every chance to restore health. In addition, first of all, it is necessary to strictly follow all the recommendations of the gastroenterologist, incl. and regarding the prevention of erosive gastritis.
Types of erosive gastritis
Before starting therapy, it is necessary to identify the type of disease. There are several forms and types of the disease:
- Spicy. The development of inflammation occurs very quickly over the entire surface of the gastric walls.
- Hemorrhagic. The inflammatory process becomes chronic.
- Erythematous gastritis. It develops in the antral region of the organ - where the duodenum begins.
- Reflux gastritis. It is characterized by the reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus, which causes erosion on the mucous membrane.
Among stomach diseases, the most common is the chronic form. Medicines for the stomach and intestines for erosive gastritis are prescribed by a doctor after examination, medical history and diagnosis. Their purpose depends on the characteristics of the diagnosis and the age of the patient.
Physiotherapy
Purpose of therapeutic exercises:
- improve general blood circulation, including in the abdominal cavity;
- normalize the motor activity of the stomach and intestines, eliminate nausea, belching, constipation;
- increase the overall tone and protective properties of the body.
Exercise therapy is prescribed not only for the period of exacerbation; exercises must be performed daily thereafter to prevent exacerbation of the disease. In the acute stage of the disease, exercises are performed in the ward while sitting or lying down, including breathing movements, in the joints of the limbs, gentle turns and bends of the torso.
After the acute symptoms subside, the patient is sent to the exercise therapy room, where an instructor works with him. Step-by-step sets of exercises are prescribed with a gradual increase in load: lying on your back, stomach, side, sitting and standing. Great importance is given to diaphragmatic breathing, which is a kind of massage of the abdominal cavity, improves blood circulation and organ function.
A contraindication for therapeutic exercises is gastric bleeding from erosions, even minor, when the patient is prescribed bed rest.
Symptoms
The painful symptoms that patients complain about depend on the location of the erosion - if it is located in the body of the stomach, then the complaints will be pain in the hypochondrium; with damage to the antrum, the discomfort is localized in the center of the abdomen.
Pain in pathology is divided into 2 main groups:
- hemorrhagic;
- ulcerative.
Those suffering from erosion of the body of the stomach complain of:
- discomfort and pain after eating;
- sometimes pain occurs when there is no food in the stomach (hunger pain);
- nausea;
- belching air;
- constantly recurring attacks of heartburn;
- pain on the right under the ribs;
- attacks of hunger pain radiating in the spine.
Signs of gastric erosion, similar to gastritis or peptic ulcer, are observed in 4 out of 5 patients. Additional symptoms in older people will be pressure surges against the background of hunger pain, paroxysmal pain in the chest, yellowing of the skin, and severe fatigue.
The presence of bleeding and complaints of weakness will be observed in 1 person out of 5. Such a patient complains of:
- heartburn;
- black chair;
- constant weakness and anemia;
- low ability to work;
- vomiting with traces of blood.
Bleeding erosions are dangerous because subtle, minor, but constant bleeding causes anemia due to the constant loss of hemoglobin. The difference between bleeding erosions and superficial ones is the absence of pain - if with minor bleeding the patient complains of pain, then with large bleeding the pain practically disappears. This can be explained by the destruction by the pathological process, first of the endings of the nerve fibers approaching the mucosa, then of the blood vessels. If pathologies are noted over large areas, and during exacerbations massive bleeding and a sharp deterioration in condition are recorded, the patient should be taken to a doctor as quickly as possible.
Classification of pathological changes
There are some types of pathological defects in the inner wall of the organ. There are erosions:
- Primary;
- Secondary – accompanying the underlying disease;
- Malignant - as one of the symptoms, a manifestation of a malignant process in the gastric lining (cancer, lymphoma);
- Benign.
1. Acute (most often complicated by bleeding, the duration of defects does not exceed seven days)
2. Chronic (existing for a long time and not epithelializing within a month)
Preventive actions
The main preventive measures are proper nutrition, work and rest patterns, and a healthy lifestyle:
- proper sleep and rest;
- stress resistance;
- walks in the open air;
- a varied diet, including fruits, vegetables, boiled or baked foods;
- minimum alcohol;
- to give up smoking;
- taking vitamins;
- limiting intake of fatty, fried, spicy, smoked foods;
- compliance with hygiene rules (wash hands with soap, wash fruits and vegetables with soap and boiling water);
- treatment of chronic inflammation (sinusitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, caries and other infections);
- chew food thoroughly;
- Avoid eating very hot, cold or rough foods.
Physiotherapeutic methods
Dry celandine grass. Take a tablespoon of raw material and pour a glass of boiling water into a thermos. The product is infused for at least 1.5 hours. It should be strained before use. Use half an hour before meals, 2 tablespoons three times a day is enough.
Stomach erosion is treated with great success with folk remedies based on chamomile (anti-inflammatory effect), St. John's wort and yarrow. Take St. John's wort and yarrow herbs, chamomile flowers in equal quantities (2 parts each), add one part of dry celandine herb to them. Grind the resulting mixture and pour 20 grams with one glass of boiling water. It is enough for the product to infuse for half an hour. Drink only fresh infusion, 100 grams, three times a day. Take before meals.
Aloe is used in almost all areas of traditional medicine. Stomach erosions can also be treated with products based on it. Treatment with a remedy prepared from leaves that are no more than 3 years old is effective. Take 5 leaves of the plant and freeze, this will make it easier to mince. After grinding, squeeze out the aloe juice through gauze or a wide bandage and mix with 5 tablespoons of honey. The drug is taken in the morning before breakfast. Treatment will take 3 weeks.
Vegetable oils have an enveloping and wound-healing effect. Treatment with folk remedies based on olive oil and sea buckthorn oils is the most popular. Olive oil and sea buckthorn juice are taken in equal quantities. You can take 5 tablespoons. Mix the ingredients and leave for 3 days. The product is drunk in the morning before breakfast. Continue treatment for 2 weeks.
Often treatment with folk remedies involves the use of alcohol tinctures. For erosions, propolis tincture is used. 15 grams of the product are filled with 96% alcohol in a volume of 100 ml. It is necessary to tightly close the jar and put it in a dark place for 2 weeks. Before use, dilute 50 drops of the medicine in a glass of milk. Drink before meals 3 times a day.
Electrotherapy and phototherapy play a stimulating role in the healing process - it improves blood flow and increases the reparative properties of tissues. Physiotherapy procedures include UHF, infrared irradiation, magnetic therapy, and iontophoresis with biostimulants (peloidin).
If signs of bleeding appear, the patient is hospitalized in the surgical department, where he undergoes a diagnostic gastroscopy. As a rule, bleeding from erosions is capillary in nature and is not severe. To stop them, the method of laser coagulation through a video probe is used; it is less traumatic than previously used methods of radiofrequency thermocoagulation. If necessary, the patient is given hemostatic drugs and given a blood or red blood cell transfusion.
In cases where it is not possible to reduce the level of stomach acid, and the erosion does not heal for a long period, a vagotomy operation gives a good effect - the intersection of the branches of the vagus nerve in the stomach, as a result, acid production is reduced. This operation is performed using a minimally invasive method without a large incision, through several punctures on the abdominal wall.
The optimal solution to the question of how to best and quickly cure gastric erosion will be selected by a gastroenterologist, and after treatment he will give recommendations on how to prevent exacerbation.
Erosive - what is it?
Erosion occurs as a response to constant inflammation of the gastric mucosa in a chronic form, or as a response to severe stress. The gastric mucosa is damaged in the form of erosions - cracks, ulcerations. The disease can be acute and develop rapidly in a dangerous form. Or it proceeds hidden and leads to multiple erosive damage. It also happens that erosion of the mucous membrane is also found in the duodenum. If measures are not taken, incl.
and special medications, damage to the mucous membrane can take on an ulcerative form. The drug treatment and additional traditional medicine used, as a rule, provide a good chance of a favorable outcome.
The treatment regimen for erosive gastritis is similar to that used for stomach ulcers. Both diseases have approximately the same symptoms and a fine line between one condition and the other. First of all, treatment will be aimed at eliminating the very cause of the disease. For example, if it turns out that bacteria are to blame, antibacterial drugs will be used. Then the acidity of the stomach is adjusted, finding out whether it is low or high. And, of course, treatment is provided aimed at relieving symptoms: pain, dyspeptic symptoms (nausea, vomiting, etc.). Drug treatment is usually combined with traditional methods and strict nutritional rules.
Features of treatment
Treatment of gastric erosion is complex and necessarily includes diet therapy, cessation of smoking and alcohol, and the fight against stress factors. If necessary, pharmacological drugs, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed, and in case of severe disease, endoscopic coagulation of bleeding vessels and even removal of part of the stomach in the classical way.
Complex treatment of gastric erosion necessarily includes:
- lifestyle correction;
- special strict diet;
- taking medications.
Drug treatment
For gastric erosion, taking into account the nature of the disease, medications are prescribed:
- reducing the acidity of gastric juice and the production of hydrochloric acid - antacids (Rennie, Almagel), proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole), H2-blockers of histamine receptors (Kvamatel);
- agents that have a healing and restorative effect (bismuth preparations - De-Nol, Vikalin, synthetic prostaglandins - Misoprostol, if there is no pregnancy);
- antispasmodics (No-shpa);
- if Helicobacter pylori is present, antibiotics (watch the video);
- in case of bleeding - hemostatic drugs, hemostatics.
In addition, drugs that improve gastric motility (Motilium), vitamins, iron supplements in case of low hemoglobin, etc. can be used.
If Helicobacter pylori was detected during the examination, then a course of antibiotic therapy is necessarily prescribed, which is selected taking into account the sensitivity of the bacteria or empirically based on data on previous treatment, the presence of concomitant diseases and drug tolerance.
In situations where the treatment is chosen correctly, and the patient strictly follows the doctor’s recommendations regarding lifestyle and nutrition, the existing mucosal defects quickly heal and disappear, leaving no trace.
Folk remedies for stomach erosion
Traditional medicine by itself does not cure erosion, but helps relieve symptoms and improve general condition. All of them should not replace classical treatment, and they can only be used with the permission of a doctor.
The following are considered the most effective:
- Sea buckthorn oil. Taken on an empty stomach, half an hour before meals. Accelerates the healing of erosions.
- Propolis infusion with milk.
- Infusion of celandine.
- Decoctions of calendula, chamomile, flax seed.
Diet therapy
For erosions during an exacerbation, table No. 1 is prescribed, as recovery progresses, table No. 5 is prescribed, and for low acidity, table No. 2 is prescribed. In all cases, difficult-to-digest foods that cause inflammation of the mucous membranes, too fatty foods, and alcohol are excluded.
During an exacerbation, when creating a menu, it is important to observe the following principles:
- Coffee, carbonated drinks, chocolate, kvass, coarse fiber, cabbage, everything fatty, fried, salty, spicy, sour fruits, legumes, canned food, marinades, millet, barley, rich broths are excluded.
- The consumption of simple carbohydrates, baked goods, and white bread is limited.
- Puréed vegetable soups, semi-liquid porridges, including those made with milk, lean boiled meat, fish, poultry, omelettes, jelly, and non-sour fruits are allowed.
- All food is served warm and should not be too hot or cold.
- In the first days of illness, everything must be consumed in pureed or semi-mashed form, and vegetables and fruits are served mainly after heat treatment, for example, apples are not fresh, but baked.
Traditional dishes are soft-boiled eggs, oatmeal, steamed cutlets, slimy rice soup, jelly.
With chronic erosions, the diet has to be followed for quite a long time, since the disease can last for several years. And in case of unsuccessful conservative therapy, their removal with a special loop for polypectomy during FGDS is indicated.
The next important step is to eliminate the diseases and causes that caused erosion:
- combating neuropsychic tension and stress factors;
- complete cessation of smoking, since nicotine contained in tobacco smoke impairs local blood circulation and the healing of erosive surfaces;
- treatment of underlying diseases that contribute to the onset of the disease.
At this stage, in addition to the gastroenterologist, other specialists may be involved in treatment, for example, a pulmonologist, endocrinologist, therapist, cardiologist, etc.
Causes
Erosive antral gastritis is provoked by several factors:
- Long-term use of a number of medications.
- Alcohol and drug use.
- Smoking.
- Physical inactivity.
- Mechanical injury and burns.
- Infectious and parasitic pathogens.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Unhealthy eating, overeating.
- Prolonged stress.
- Kidney and liver pathology.
- Tissue ischemia.
- Radiation exposure.
- Duodeno-gastric reflux.
In most cases, acute erosive gastritis is provoked by toxic substances. For example, the effects of NSAIDs (Movalis, Ketonal, Diclofenac), cocaine, alcohol, diphosphonates and cardiac glycosides. The inflammatory process and damage to mucous tissues can be caused by bacterial and viral pathogens or parasites:
- bacteria Helicobacter pylori;
- cytomegaloviruses;
- streptococci;
- clostridia;
- helminths (for example, anisakiasis).
In some cases, the inflammatory process develops when the functions of the pyloric sphincter are impaired, when the contents of the small intestine, along with bile and pancreatic secretions, are thrown into the stomach and irritate the mucous membrane.
Erosive antral gastritis can be primary or secondary. Secondary is caused by another disease:
- Hyperparathyroidism.
- Crohn's disease.
- Uremia.
- Diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2.
- Stomach cancer.
- Sepsis.
Features of the disease
Erosive gastritis of the stomach, unfortunately, is quite common among gastrointestinal diseases. The reason for this is stress, disturbed ecology, and eating on the run. irregularity of food intake. And when problems with digestion arise, people, as a rule, try to cure themselves. They take medications that they have prescribed for themselves, obtaining temporary relief or, possibly, worsening. This transforms the disease into a chronic form or, even worse, accelerates the onset of complications. If symptoms such as:
- burning sensation in the pit of the stomach;
- heartburn, nausea, vomiting;
- discomfort and bloating;
- increased previously tolerable pain that appears after eating;
- the appearance of a white coating on the tongue and pain in the stomach area upon examination;
- the presence of blood in the vomit and the black color of the stool indicate the presence of bleeding erosions.
There is no way to put off a visit to a gastroenterologist.
Features of localization of pain
Signs of erosive processes in the intestines and stomach have the same symptoms. In order to more accurately find out about erosions of the stomach and duodenum, you need to conduct an endoscopic examination. In the intestine, during erosion, damage can form on the surface of the walls. Erosion of the duodenum differs from the way erosion of the antrum manifests itself. With erosion in the intestines, a person may complain of constipation, which occurs quite often.
Pain is localized in the lower abdomen or in the middle of the abdominal cavity. Alternating constipation and diarrhea often occur. There is a feeling of bloating. Blood clots will also be released along with the stool. There may be some mucus. This is due to the fact that bleeding opens in the intestines. When such symptoms are noticeable, it is better not to wait a week to go to the hospital, because... bleeding may only get worse. In this case, changing the menu will no longer help; full-fledged treatment will be needed. The patient's appetite may deteriorate. The person becomes distracted, nervous, irritable. Apathy appears, there is no desire to do anything, you constantly feel weak, lethargic and tired. This negatively affects a person's performance.
In order to determine the diagnosis, it is necessary to use fibrogastroduodenoscopy and irrigoscopy. Feces must be examined for the presence of various impurities, and their composition and other characteristics are taken into account. Only after these studies is a special diet prescribed for gastric erosion. In addition, the treating doctor may prescribe a sigmoidoscopy to confirm the diagnosis.
ethnoscience
- A decoction of calamus root. It doesn't take long to prepare - it only takes 15 minutes. To do this, you need to grind the dry root and pour boiling water over it, put it on the fire and cook for about 15 minutes. Allow the liquid to cool and take 50 ml before meals.
- Wounds heal well if you take 1 tsp half an hour before lunch and dinner. sea buckthorn oil.
- An infusion of immortelle will also be useful. Dried leaves of the plant should not be boiled; just add hot water and let it brew (the same way as regular tea). You need to take the liquid half an hour before meals.
An effective folk remedy for stomach erosion is also an infusion of a mixture of St. John's wort, yarrow, celandine and chamomile flowers, taken in proportions 2:2:1:2. 20g of the medicinal mixture should be infused for half an hour with a glass of boiling water, and then drink 100g 3 times a day half an hour before meals.
A folk remedy that successfully copes with stomach erosion is the collection of St. John's wort (4 parts), knotweed (2), dried grass (4), celandine (2), sage (2), calamus root (0.5), peppermint leaves (0. 5) and yarrow flowers (1 part). 20 grams of the dry mixture of this folk remedy for stomach erosion is poured with 200 grams of boiling water and left in a thermos for 8-10 hours. You need to drink the prepared infusion 3-4 times a day, 200g, an hour after meals.
A tasty folk remedy for stomach erosion is a teaspoon of honey every morning on an empty stomach. For severe pain, propolis is more effective.
It is recommended to combine all folk remedies for gastric erosion with traditional medications and diet for gastric erosion.