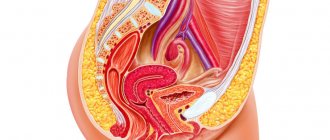
Colpitis (vaginitis) is suppuration of the vaginal mucosa with possible damage to the vulva, which is infectious or non-infectious in nature.
It is also called “vaginitis”.
What it is, the consequences, symptoms and treatment of this disease are explained in this article.
Vaginitis is often encountered in gynecological routine work.
60% of women aged 18 to 45 have indications of such a disease at least once. However, the disease does not escape girls either.
The incidence peaks among children under 6 years of age due to poor personal hygiene.
Post-menopausal women also suffer from colpitis, although it is also explained by the aging of the body. It is clear that with aging, the body’s defenses weaken and decrease, which means the success of attacks by microbes and viruses increases, which leads to numerous diseases, including women’s diseases.
The disease can have both specific and nonspecific occurrence, which is explained by etiological factors.
The occurrence of colpitis is promoted by:
- gonococci,
- mycoplasma,
- Trichomonas,
- chlamydia,
- candida and microbes.
A nonspecific disease is caused by intestinal and pseudomonas bacillus, streptococcus and staphylococcus.
Can colpitis disappear without consequences?
Believing colpitis to be a non-serious disease, almost all ladies believe that the disease can go away on its own.
Cases of healing are very rare and only when the body’s defenses are not weakened in any way and the disease is nonspecific.
Any carelessness and frivolity in relation to this disease leads to serious consequences for the body, which women should not forget.
It usually happens that women find out after some time that the signs that bother them have disappeared. But this does not mean that the disease has passed, it has passed into a sluggish existence. Under certain conditions, colpitis is activated again after some time. At the beginning of the disease, you need to see a doctor and start treatment.
Causative agents of colpitis
Specific and nonspecific colpitis develops due to exposure to different types of bacteria. Specific colpitis is provoked by those bacteria that should not be found in the vaginal mucosa of a healthy woman. In this case we are talking about gonococcus gonorrheal vaginitis develops ; trichomonas colpitis provokes trichomonas ; chlamydia causes chlamydial vaginitis ; under the influence of Treponema pallidum, syphilitic vaginitis develops ; Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes tuberculous vaginitis ; mycoplasma and ureaplasma provoke mycoplasma or ureaplasma vaginitis .
Sometimes a mixed nature of pathogenic flora is noted in the female vagina, that is, viruses, fungi or other bacteria are also present. But if they are combined with the pathogens described above, we are still talking about specific vaginitis.
The development of nonspecific vaginitis is the result of exposure to so-called opportunistic pathogens. In a woman's normal health, such microorganisms are part of the normal vaginal microflora. However, under certain conditions, such bacteria become pathogenic.
Depending on the nature of the pathogen, nonspecific vaginitis is divided into bacterial vaginitis (they are provoked by streptococcus, Proteus, Escherichia coli , staphylococcus, gardnerella, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ); fungal vaginitis , viral vaginitis (they are provoked by the herpes simplex virus, human papillomavirus ); mixed vaginitis .
It should be noted that if a woman has nonspecific vaginitis, its symptoms are similar to specific vaginitis. However, the treatment tactics are different, since for a specific form of the disease it is very important to examine and treat all its sexual partners.
atrophic vaginitis is also distinguished , which is a unique set of symptoms in older women, as well as in those patients who have undergone certain surgical operations that have caused premature menopause .
Signs of colpitis in women
Photo of discharge from colpitis.
Signs of the disease are mainly as follows:
- Discharges that depend on the etiology of the disease and its level. They increase compared to the period when the woman was not sick. The leucorrhoea becomes liquid, foamy, cheesy, and sometimes purulent with an unpleasant odor. Bloody clots appear in them, with atrophic colpitis;
- Swelling of the genital organs and their redness;
- A burning sensation that increases during a long walk, and also at night and in the 2nd half of the day;
- Irritability, insomnia, and neuroses that the disease causes constantly bother the lady;
- Occasional pain in the pelvis. They increase during the act of defecation or sexual intercourse;
- Frequent urge to urinate, urinary incontinence in women;
- Raising body temperature.
The peak of the disease will be accompanied by an increase in symptoms, which will vary depending on the prerequisites for colpitis.
When the disease takes a permanent, chronic form, its effect becomes mild.
However, the most persistent symptom that worries a woman is considered to be incessant itching in an intimate place, even against the background of light discharge.
Candles for restoration of biocenosis
Many medications, especially antibacterial ones, disrupt the natural microflora in the vagina. Therefore, after completing a course of treatment for vaginitis, it needs to be restored. This will also help eliminate unpleasant symptoms such as dryness and irritation. What means can restore the vaginal microflora?
Atsilak
A probiotic that is used in the treatment of gynecological diseases. The acidophilic bacteria it contains suppress pathogenic microorganisms and help restore the natural environment in the vagina.
Bifidumbacterin
The drug contains live bufidobacteria and is available in different forms. In gynecology, vaginal suppositories are used. Used to balance microflora in the vagina. Can be used in combination with antibacterial, antiviral and other drugs.
Vagilak
Vaginal suppositories that promote the growth of beneficial lactobacilli and improve the microflora of the internal genital organs.
Increases mucosal resistance to pathogenic microorganisms. Most drugs intended to restore the internal environment have no contraindications and can be used in people, regardless of age. In rare cases, an allergic reaction may occur. The only thing you need to remember is strict adherence to storage temperature conditions. Otherwise, the bacteria will die and treatment will be pointless.
Causes of colpitis in women
Activation of the disease at different ages has the following prerequisites:
- In children, the disease develops to a greater extent as a result of microflora entering the vagina. The disease is provoked by streptococci, staphylococci, including pinworms;
- In adulthood, women are more often diagnosed with special colpitis of an infectious nature. Trichomonas, a sexually transmitted disease, dominates. Candida colpitis is detected less frequently, the prerequisite for which is, to a greater extent, a hormonal disorder during pregnancy;
- Women after menopause more often develop nonspecific colpitis caused by staphylococci and streptococci. But candidiasis, atrophic, and other types of colpitis have the opportunity to exist and are diagnosed.
At any age, the factors in the development of the disease are either personal pathogenic microflora, or infectious tiny organisms belonging to the group of fungi, microbes or microbes.
Diagnostics
Often the complaints described by the patient are enough for the gynecologist to suggest the presence of colpitis. But to confirm the alleged diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct certain studies. First of all, the doctor will definitely conduct a gynecological examination. The insertion of a gynecological speculum into the vagina causes pain in a patient with colpitis. When examining the mucous membrane, the doctor is able to detect its swelling, redness, and the presence of purulent or serous deposits.
After a gynecological examination, a bacterioscopic and bacteriological examination of a smear from the vagina and urethra is carried out. This is necessary to identify the pathogen and select the most effective therapy.
A bacterioscopic examination of a smear from the cervical canal reveals an increased number of leukocytes, the presence of bacteria, a smear from the urethra - 15-20 leukocytes in the field of view. To determine the causative agent of colpitis, a bacteriological study of vaginal discharge is carried out.
Types of colpitis
They are recognized due to the fact that they were a prerequisite for inflammation of the mucous membrane. Any type of disease manifests itself in specific clinical manifestations and differences, and in specific healing.
The most popular types are:
- Trichomonas colpitis. Suppuration appears due to the activity of Trichomonas, flagellated parasitic microorganisms. The most well-known way of their penetration is sexual, but infection is also possible through personal belongings. The disease is easily diagnosed and has no problems in curing. The discharge is usually foamy and large, with a nasty odor and purulent manifestations. The main remedy used for healing is flagyl along with local effects;
- Candidiasis colpitis. Suppuration is caused by the proliferation of fungi, which eventually begin to exhibit a pathological effect on the body. Clinical signs are curdled discharge and itching. Infection can occur both sexually and when immunity declines. Antimycotic agents are used together with local effects;
- Atrophic colpitis. The suppuration is probably caused by a decrease in estrogen in the body. A woman feels dryness and burning in the genital area. Healing occurs thanks to hormone replacement therapy.
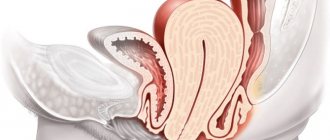
Colpitis, what is it?
Colpitis in women is an inflammatory process that develops on the vaginal mucosa. Only in isolated cases is colpitis a single isolated inflammatory process. In most cases, this pathological condition occurs simultaneously with inflammation of the mucous membranes of the external genitalia (with vulvitis), the canal of the uterine cervix (with endocervicitis) and/or the upper membranes of the urethra (with urethritis). In fact, colpitis can be considered one global problem consisting of many smaller problems. Colpitis includes not only the notorious vaginal candidiasis (typical thrush), but also more dangerous STDs (which are sexually transmitted) that affect the mucous layers of the vagina, thereby provoking the development of inflammatory processes of various sizes in them.
Causes of colpitis
The causes of the malaise are specific tiny organisms that are ready to seep into the vaginal mucosa and begin to multiply there.
Among the causes of the disease are:
- Non-compliance or incomplete compliance with intimate hygiene;
- Lack of a permanent man, refusal to use condoms;
- Endocrine system diseases: diabetes, hypothyroidism;
- Damage to the genital organs: chemical, mechanical, thermal. They can occur as a result of rupture during childbirth, long-term use of an intrauterine device, rough sexual intercourse, etc.;
- Poor underwear made from low-grade artificial synthetics;
- Scarlet fever and measles, pathogens that reach the girl’s genitals by hemolytic means;
- Menstruation, pregnancy, breastfeeding, menopause and other hormonal changes;
- The disease is caused by hormone-containing substances, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and broad-spectrum antibiotics;
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for oncology;
- Decrease in estrogen in a woman’s body;
- Decreased immunity or immunodeficiency due to HIV infection;
- Vitamin deficiency;
- Diseases of the stomach and intestines, allergies;
- Abortion.
Prevention of colpitis
Both specific and nonspecific methods are used as preventive measures aimed at preventing vaginitis. From a young age, a girl should pay special attention to observing all the rules of personal hygiene. Washing must be carried out using soft hygiene products.
A girl should be taught from childhood to wash herself correctly: movements should be directed from front to back, so that infection does not spread to the genitals. Hygiene measures need to be significantly strengthened during menstruation. If a woman suspects a vaginal infection, she should immediately stop using tampons during menstruation.
Without a doubt, a necessary preventive measure is the absence of casual sex and the mandatory use of a condom.
To prevent weakening of the immune system, chronic diseases of internal organs and inflammation of the genital organs should be treated in a timely manner.
stress for a long time , or undergoes a long course of antibiotic treatment, she should definitely take lactobacilli preparations for some time to prevent changes in the vaginal microflora towards pathology.
An important preventative measure is hardening, as well as preventing a lack of vitamins in the body.
Consequences and results of colpitis
The lack of current drug treatment for any type of colpitis threatens with severe consequences for a woman’s body.
Among the probable and not very favorable results, the following are especially dangerous:
- Diseases in acute form can change into chronic, sluggish ones. Constant inflammation in the vagina is difficult to treat with medication, and worries the woman about relapses;
- The disease affects the genitourinary system. Colpitis has the ability to activate urethritis and cystitis;
- Erosion of the cervix, endometritis, cervicitis, salpingoophoritis;
- All special colpitis, when left untreated, has every chance of resulting in infertility or difficulties in conceiving and bearing a baby. Chronic colpitis is often considered a factor in ectopic pregnancy;
- Synechia in girls, which is expressed in the fusion of the labia with each other;
- The appearance of bleeding areas on the vaginal walls, through which various infections spread;
- An infection that can appear after visits to the gynecologist and operations.
Complications
Colpitis is not as scary as its complications. The whole danger is that if colpitis is not treated, the infection can spread to other genitourinary organs. The infection spreads upward, gradually involving the cervix, the uterus itself, the fallopian tubes, and the ovaries in the inflammatory process. This can lead to disruption of the menstrual cycle, as well as problems with conception. In addition, the infection can spread through the urethra and provoke the development of urethritis and cystitis. The presence of long-term colpitis can serve as a favorable background for the development of cervical erosion.
Colpitis can seriously complicate the course of pregnancy. The progression of the infection can lead to its spread to the amniotic fluid and premature birth. In addition, directly during childbirth, while passing through the birth canal, the newborn can become infected.
How and how to treat colpitis in women
How to reduce the effect of this disease on the body before a diagnosis is made?
Important! It is usually not recommended to treat it before taking tests to determine the disease, because this can make the results of laboratory tests questionable and unreliable.
Only one drug should be taken to relieve the symptoms of the disease, which is extremely troubling for women, and this is Fluomizin.
The product does not affect test results and is capable of eliminating the harmful and unpleasant effects of the disease on the female body in a short time.
Treatment of the disease is carried out and monitored by a specialist.
Independent treatment of colpitis with suspicious means and methods can lead to bad consequences.
Before choosing one or another medicine or treatment method, the doctor will carry out specific diagnostic steps that will allow you to find the factor in the onset of the disease.
In accordance with this, a healing technique will be developed.
First of all, etiotropic treatment is used, which consists of acting on a specific causative agent of the disease.
The doctor has bactericidal and antimycotic drugs. hormonal and antiviral agents. From time to time, the use of pharmaceutical agents in combination will be required.
To heal from colpitis use:
- Ketoconazole as a cream. Treatment course up to 5 days;
- Nystatin in the form of vaginal suppositories. Treatment 2 weeks;
- Diflucan in tablet form. Taken once;
- Flagyl, period 10 days;
- Ampicillin, course 7 days;
- Cephalexin, 7 days.
Local treatment consists of using various antiseptics, vaginal suppositories are prescribed, for example, Iodoxide or Betadine, as well as washing and douching with solutions of boric acid, potassium permanganate, soda. The procedures must be completed for at least 14 days.
In addition to local healing, therapy for concomitant diseases is needed.
Without eliminating the cause of the disease, the disease will recur.
Ovestin and Estrocad are used as hormone replacement agents.
If you have diabetes, you need to constantly monitor the percentage of glucose in the blood and monitor your weight.
In case of an inflammatory process in children caused by scarlet fever or measles, bactericidal treatment is needed.
When doctors manage to destroy the initiating cause, then the hope of a complete cure for colpitis is considered quite feasible.
Before healing, you must adhere to the following:
- Refusal to have sex while undergoing therapy. Proof of inflammation destruction must be confirmed by laboratory testing;
- Since a sexual partner can also have a specific disease, there is a risk of re-infection after the restoration of sexual activity, he also needs to undergo a course of treatment;
- Hygienic treatment twice a day with antiseptic agents;
- During the healing period, you must follow a diet. Avoid salty and spicy foods. It is important to use fermented milk drinks in the menu;
- Some medications require avoiding strong drinks, for example, Flagyl.
When the course of treatment is completed, the woman needs to restore the normal microflora of the vagina by reproducing the natural biocenosis in the mucous skin.
Various substances are used for this purpose, including:
- Acylak;
- Vagilak;
- Bificol;
- Bifidumabacterin;
- Lactobacterin.
Particular attention should be paid to the treatment of colpitis in pregnant women.
Treatment regimen for colpitis
Specific treatment
Etiotropic treatment depends on the pathogen that caused colpitis. Drugs and treatment regimens for colpitis are presented in the table.
| The causative agent of the disease | Drugs and treatment regimen |
| Nonspecific bacterial colpitis | • polygynax 1-2 vaginal capsules per day for 7-12 days; • terzhinan 1 suppository at night for 10 days; • meratin-combi 1 vaginal tablet at night for 10 days; • mikozhinaks 1-2 vaginal capsules for 7-12 days; • betadine, vocadine (iodine-polyvinylpyrrolidone) 1-2 vaginal capsules for 7-12 days. |
| Gardnerella colpitis | •Ung. Dalacini 2% is administered using an applicator into the vagina once a day for 7 days or ointment tampons 2 times a day in the morning and evening for 2-3 hours, for 7-10 days; • ginalgin, 1 vaginal suppository at night, for 10 days; • terzhinan (meratin-combi, mikozhinaks) 1-2 vaginal capsules for 12 days; • metronidazole 0.5 g 2 tablets 2 times a day for 10 days; • Klion-D 100 is administered deep into the vagina at night, 1 tablet for 10 days. |
| Trichomoniasis colpitis | The course of treatment is 10 days during 3 menstrual cycles. • metronidazole (ginalgin, Klion, Efloran, Trichopolum, Flagyl, Pitrid) in the morning and evening, 1 vaginal suppository for 10 days; • tinidazole (Fazizhin) 1 suppository at night for 10 days; • makmiror complex 1 vaginal suppository at night for 8 days; • terzhinan (meratin-combi, mycozhinax) 1 vaginal suppository at night for 10 days; • trichomonacid vaginal suppositories 0.05 g for 10 days; • nitazol (trichocide) 2 times a day, suppositories in the vagina or 2.5% aerosol foam 2 times a day; • Neo-Penotran 1 suppository at night and in the morning for 7-14 days; • hexicon 1 vaginal suppository 3-4 times a day for 7-20 days. |
| Candidiasis colpitis | • nystatin 1 vaginal suppository at night for 7-14 days; • natamycin 1 vaginal suppository at night for 6 days or a cream that is applied to the surface of the mucous membranes and skin in a thin layer 2-3 times a day; • pimafucort 2-4 times a day in the form of cream or ointment for 14 days; • clotrimazole - 1 vaginal tablet at night for 6 days; • canesten 500 mg once in the form of a vaginal tablet; • miconazole 2-3 times a day vaginal cream for 6 days. |
| Genital herpes | drugs with direct antiviral action: • acyclovir (ciclovir, Zovirax, Vivorax, Virolex, Acic, Herpevir) - cream for application to the affected area 4-5 times a day for 5-10 days; • bonafton - 0.5% ointment, topically 4-6 times a day for 10 days; • epigen (aerosol) - 4-5 times a day for 5 days; interferons and their inducers: • a-interferon in suppositories - vaginally for 7 days; • Viferon - suppositories, 1-2 times a day, 5-7 days; • Poludan - 200 mcg topically 2-3 times a day for 5-7 days; • Gepon - 2-6 mg diluted in 5-10 ml of saline, in the form of douches or vaginal tampons 1 time per day for 10 days. antiviral drugs of plant origin: • alpizarin - 2% ointment topically 3-4 times a day; • megosin - 3% ointment for application to the cervix after douching, apply for 12 hours 3-4 times a week. |
Treatment of vaginal dysbiosis
After specific treatment, it is necessary to restore the normal microflora of the vagina, for this purpose the following drugs are used:
- bifidumbacterin
(lyophilisate of living bifidobacteria) vaginally 5-6 doses diluted with boiled water, 1 time a day for 5-8 days or 1 vaginal suppository 2 times a day for 5-10 days;
- bificol
(lyophilized microbial mass of active strains of bifidobacteria and Escherichia coli) - vaginally 5-6 doses 1 time per day for 7-10 days;
— lactobacterin
(lyophilisate of live lactobacilli) - vaginally 5-6 doses, diluted with boiled water 1 time per day, 5-10 days;
— colibacterin dry
(lyophilisate of living bacteria) - vaginally 5-6 doses 1 time per day for 5-10 days;
- vagilak
(Lactobacillus acidofilus - 18 mg, Lactobacillus bifidus - 10 mg, yogurt culture - 40 mg, whey powder - 230 mg, lactose - 153.15 mg) - 1 capsule in the vagina 2 times a day for 10 days;
- acylac
- 1 vaginal suppository at night for 10 days;
— “Simbiter-2”
(one dose contains 1000 billion living cells of microorganisms of a 25-strain probiotic culture) - the contents of the bottle, previously diluted with boiled water (1:2), are administered intravaginally for 10-15 days.
Vitamin therapy for colpitis
— multivitamins in courses (Vitrum, Centrum, Uni-cap, Multitabs);
- riboflavin 0.005 g 2 times a day;
- ascorbic acid 200 mg with tocopherol acetate 100 mg 3 times a day.
Prevention of vaginitis
Prevention of colpitis is no less important, because it helps eliminate the causes of the inflammatory process and often together with a therapeutic effect.
Therefore, it is important to take the following preventive actions:
- You need to visit your local gynecologist at least once a year. Innovative doctors advise attending preventive examinations every 6 months. This will help to detect the disease in time and begin healing immediately. When the symptoms of the disease began to appear during pregnancy, then there is no need to wait for the next date of visit to the doctor; it is better to immediately come to the consultation and talk about your own observations and concerns;
- It is necessary to carefully monitor intimate hygiene associated with washing, with the introduction of high-quality hypoallergenic disinfectants. Particular attention should be paid to the appearance of microflora in the vagina, which often occurs due to the incorrect use of toilet paper. It is important that its movements are oriented forward and backward. It is imperative to keep an eye on the constant change of underwear. It should be made from natural fabrics, since synthetics create a wet and warm environment favorable for microbes;
- All kinds of medicinal substances must be prescribed only by a doctor. In particular, this probably applies to the use of bactericidal agents, which are often taken independently;
- You need to come to a doctor at the very beginning of the disease with colpitis. This is probably explained by the fact that at the beginning of the disease it is eliminated much easier and faster. The measures taken will not allow the disease to become chronic, when the disease leads to sad consequences for the woman’s health;
- We should not forget about measures to increase the body's defenses. This will not only prevent the formation of the disease, but also speed up recovery from it. To do this, you need to give up those actions that cause harm to the body, eat right, and do not give up regular walks and exercise.
To free yourself from the consequences of the disease, you need to go through physical therapy. It will dramatically improve your situation with chronic colpitis.
Of all the methods, iontophoresis with zinc and ultraviolet irradiation with the introduction of short wavelengths enjoy a special reputation.
To recover from this disease, you must first change your lifestyle, which can be the most difficult thing for many representatives of the fair sex.
Follow the rules and routines proposed by doctors and science, be constant and calm in your preferences and desires, maintain cleanliness and hygiene both at home and at work.
It is better to try to avoid health problems than to undergo long and painful treatment later.
Treatment
It should be comprehensive and aimed both at the causative agent of colpitis and at eliminating related problems. For etiotropic purposes the following are used:
- antifungal agents - Nystatin, Fluconazole (Candizol), Itraconazole (Funit), etc.;
- antibiotics - Doxycycline, Azithromycin, Josamycin, Clindamycin, Ornidazole, etc.;
- antiprotozoal drugs for the treatment of colpitis caused by Trichomonas - Metronidazole (Metrogyl, Flagyl, Klion);
- antiviral - Acyclovir, Valacyclovir and others.
Combination drugs with antifungal, microbial and protozoal activity have shown high effectiveness:
- Polygynax;
- Terzhinan;
- McMiror;
- Neo-Penotran;
- Ginalgin.
These products can be used in the form of ointments, gels, vaginal tablets or suppositories. After completing antibacterial therapy, it is very important to prescribe drugs that normalize the natural acidity and microflora of the vagina:
- Lactobacterin;
- Biovestin;
- Bifidumbacterin;
- Zhmelik et al.
For the treatment of senile colpitis, it is advisable to use estrogens that increase the biological protection of the epithelium, for example, Ovestin in suppositories or ointments.
For antiseptic purposes in the form of douching (washing the vagina with an enema or syringe), the following may be prescribed:
- Chlorhexidine;
- Dioxidine;
- Chlorophyllipt;
- Miramistin.
Douching for more than three to four days is not recommended, as it interferes with the process of restoring the natural biocenosis of the vagina.
You should also pay attention to treating your sexual partner if infections transmitted through sexual contact are discovered. We should not forget about concomitant pathologies that affect the condition of the vaginal mucosa, such as ovarian hypofunction, diabetes mellitus and thyroid diseases. For vaginitis, you should adhere to a very light diet, which limits sweet and flour products. The following will be useful:
- fermented milk products (kefir, cottage cheese);
- grains, vegetables and fruits;
- foods high in polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamins A, B, E - fish oil, tuna, cod, caviar, shrimp, spinach, carrots.
From traditional medicine, douching with infusion of calendula or St. John's wort will be useful; tampons soaked in sea buckthorn oil; mumiyo.
Traditional methods of treatment
Folk remedies can be used as an addition to drug therapy, but only with the permission of a doctor. Many products based on medicinal herbs have antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties and are used for douching and vaginal irrigation.
To eliminate symptoms and speed up recovery, it is recommended to use the following recipes:
- Infusion of celandine. The product is chosen for sitz baths, adding it to the water. To prepare the infusion:
- 2 tbsp. l. place dry celandine in a thermos and pour 1 liter of boiling water;
- leave for several hours.
- A decoction of horsetail, chamomile or calendula. Used as a solution for douching.
- 2 tbsp. l. pour 0.5 liters of boiling water over the selected dry plant;
- leave for 3 hours.
- Sea buckthorn oil. A tampon is soaked in this product and inserted into the vagina at night. It is recommended for use in the atrophic form of colpitis.
- A decoction of medicinal plants for douching. To prepare it you need:
- Mix sage, mallow flowers, oak bark and chamomile flowers in equal parts;
- 2 tbsp. l. pour 2 cups of boiling water over the collection;
- leave for several hours.
- Douching with soda solution. This treatment is effective for heavy discharge. To prepare the product, 1 tbsp. l. soda is dissolved in a liter of boiling water.
- Propolis with honey. A tampon is soaked in the product and inserted into the vagina for 2 hours. The duration of treatment is 14 days. How to cook:
- take a piece of natural propolis (no larger than a hazelnut), chop;
- add 50 g of water, place in a water bath;
- After dissolving the propolis, strain the product and cool;
- add 1 tsp. honey.
Folk remedies for chronic colpitis - gallery
Celandine is used for sitz baths
Horsetail is used for douching
Sea buckthorn oil is recommended for use in atrophic colpitis
Herbal decoction relieves inflammation
Baking soda helps with heavy discharge
Propolis relieves inflammation
General symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of colpitis can be distinguished by the type of bacteria, degree, severity and nature of the disease. The group of nonspecific colpitis has the following characteristics:
- excessive discharge that has a bad odor. The structure can be mucous or mucopurulent, sometimes with the presence of blood;
- severe hyperemia and swelling of external organs and mucous membranes of the genitals;
- pain during urination;
- the appearance of a burning sensation;
- formation of petechiae on mucous membranes;
- prolonged itching;
- the appearance of individual areas with erosion;
- decreased sexual desire;
- pain in the lower abdomen.
During non-acute colpitis, the symptoms temporarily subside and patients experience:
- reduction of swelling and redness of the mucous membranes;
- reduction in the amount of discharge;
- the pain goes away.
Chronic form
Colpitis, which has become chronic, is characterized by the following symptoms:
- slight swelling of the genitals;
- periodic discharge.
For many women, the chronic disease occurs without significant symptoms. Sometimes they feel nagging pain in the lower abdomen and observe discharge. Examination reveals degenerative changes in the epithelium. If a chronic form is detected, doctors recommend an ultrasound scan.
This makes it possible to identify complications resulting from colpitis. Treatment follows the traditional scheme. The patient is prescribed vaginal ointments and suppositories. Douching is required. At the same time, treatment of concomitant diseases is carried out.
Treatment of atrophic colpitis
In most cases, suppositories for colpitis, the names of which were listed above, are used to treat all types of diseases, except atrophic ones. To cure the latter, the suppository must include an estrogen component. These most effective and popular means include:
- "Ovestin" - contains estriol. Full analogues of this drug: “Estrovagin”, “Estriol”.
- "Gynoflor E" - in addition to estriol, this medication contains lactobacilli, which allows you to achieve maximum therapeutic effect.
How to treat pathology?
Chronic specific vaginitis can be caused by one or more types of microorganisms. To treat this form of the disease, antiviral, antiseptic, and antibiotics are used.
Sometimes it is very difficult to cope with colpitis, since many microorganisms can hide inside other pathogens. They can also become resistant to the drugs used. For example, chlamydia often lives inside trichomonas, making them very difficult to destroy. In this case, Trichomonas colpitis must first be cured, and then a course of antibiotics must be prescribed. But such therapy is not always effective due to the fact that pathogens can quickly get used to antibacterial drugs. Therefore, the body is “shaken” with the help of certain medical agents that activate the pathogen and aggravate the chronic process. And the disease in the acute stage is easier to treat.
Systemic medications for chronic nonspecific colpitis are not always needed. Typically, treatment of mild forms is carried out using combined topical drugs.
If chronic vaginitis occurs against the background of another pathology (diabetes mellitus, hormonal imbalance, etc.), its treatment is carried out first.
Drugs used in the treatment of chronic vaginitis - table
| Group of drugs | Name | Description |
| Antibacterial drugs |
| Necessary for a specific form of vaginitis. They act directly on the causative agent of the disease. It is recommended to first determine sensitivity to antibiotics. |
| Antifungal drugs |
| Used for fungal infections. |
| Vaginal suppositories or tablets |
| Effective against bacterial and fungal infections, have anti-inflammatory properties. They work directly at the source of inflammation, relieve the symptoms of the disease, gently affecting the mucous membrane. |
| Hormonal agents |
| They are used if the disease occurs during menopause and is associated with a decrease in estrogen levels. |
| Vaginal creams and gels |
| Effective agents that have a long-term effect on the source of inflammation. A positive effect is noted after the first use. |
| Probiotics |
| After a course of antibiotics, it is necessary to take medications that restore the vaginal microflora. |
Drugs for the treatment of chronic colpitis - gallery
Amoxiclav is used for a specific form of colpitis
Fluconazole is necessary for vaginitis caused by fungus
Hexicon acts directly at the site of inflammation
Klimonorm is used during menopause
Fenistil eliminates inflammation and itching
Lactonorm restores vaginal microflora
Causes
As a result of a decrease in the number of lactobacilli, lactic acid becomes insufficient to protect the mucous membrane (these bacteria synthesize it). This condition occurs for the following reasons:
1) Acute phase vaginitis often manifests itself in girls due to the unformed vaginal epithelium, which during this period is thin, with unformed local immunity. Moreover, it has an alkaline reaction environment.
2) Nonspecific vaginitis in older women is associated with an atrophic nature, when the mucous membrane becomes dry and thinned. This occurs as a result of a decrease in the production of lubrication by the vaginal glands, which directly depends on the level of estrogen. Such an environment is favorable for the proliferation of microorganisms of the opportunistic group (present in small quantities on the genitals).
3) Improper personal hygiene often provokes the development of colpitis. Women who do not perform daily procedures are at risk for developing vaginitis. After all, microorganisms that should normally be removed begin to multiply diligently on the genitals. Often the protective forces of local immunity become insufficient, which leads to illness.
Girls who, on the contrary, try too hard to take care of genital hygiene and, in addition to water procedures, use douching with antiseptics (potassium permanganate, furatsilin) more often than others suffer from exacerbations of colpitis. This is due to the mechanical washing out of not only pathogenic flora, but also lactobacilli. Their numbers become insufficient to create local immunity.
4) Therapeutic and diagnostic procedures (curettage of the uterine cavity, abortion, probing, hysterosalpingoscopy, installation or removal of an intrauterine device) have a mechanical effect on the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity, which provokes a decrease in the redox potential. In addition, it is also possible that an infection may be introduced onto gloves or instruments from the outside when performing procedures, while reduced immunity will not be able to fight it.
5) The introduction of various foreign bodies into the vagina for therapeutic purposes or specifically (for sexual satisfaction, contraception, hygienic tampons) is a favorable background for the proliferation of pathogenic flora. In addition to mechanical trauma to the vaginal mucosa, prolonged irritation by objects occurs. Subsequently, an inflammatory process and the addition of an infection are observed, causing nonspecific vaginitis.
6) Promiscuous sexual intercourse causes the colonization of the epithelium by microorganisms, leading to an infectious process. Most often, it is treated by women on their own. Incorrectly selected drugs cause a decrease in the protection of the vaginal mucosa and the development of acute nonspecific vaginitis.
7) Use of low-quality products for intimate hygiene, which are an aggressive environment for the epithelium. As a result, burns and microcracks occur, into which pathogenic flora penetrates.
 A long course of taking antibiotics or self-medication with them leads to vaginal dysbiosis with the death of lactobacilli and a change from an acidic to an alkaline environment. These conditions are most favorable for the predominance of opportunistic flora.
A long course of taking antibiotics or self-medication with them leads to vaginal dysbiosis with the death of lactobacilli and a change from an acidic to an alkaline environment. These conditions are most favorable for the predominance of opportunistic flora.
9) Inflammatory diseases of the uterus and cervical canal (endometritis, endocervicitis), in the absence of adequate treatment or in an advanced form, contribute to the spread of infection into the vagina and the proliferation of its agents.
10) Malnutrition of the vaginal epithelium is associated with massive bleeding after childbirth or in case of a lack of vitamin A in the diet. It is an important component for the normal functioning of the genital organs as a protective barrier. With its deficiency, nonspecific colpitis or other inflammatory diseases occur.
The main risk groups are:
· pregnant women;
· patients with ovarian hypofunction;
· women suffering from diabetes.
In expectant mothers and people with diabetes, the microflora often changes with a predominance of pathogenic ones, which is associated with increased exudation processes (transition of the liquid part of the blood from the capillaries to the vagina). Glycogen (carbohydrate) falling on the epithelium becomes a good background for nonspecific vaginitis. Women with ovarian hypofunction suffer from low levels of sex hormones, which leads to high acidity of the environment and, accordingly, colpitis.
Vaginitis during pregnancy
Vaginitis is a side effect of infections such as chlamydia, trichomoniasis, ureoplasmosis, candidiasis, etc. Pathogenic bacteria displace healthy flora, causing inflammation of the mucous membranes. If the inflammation is not treated in time, it can spread to the uterus and appendages, which is especially dangerous during pregnancy.
Penetrating into the uterus, the infection affects the placenta, making it more vulnerable. The result is premature birth, miscarriages in the early stages and miscarriage in later stages. Sometimes the infection that develops along with vaginitis penetrates the placenta to the fetus. In this case, the child (if it is a girl) may become infected and various developmental pathologies may occur.
Treating the disease during pregnancy is quite difficult. Strong drugs are prohibited, and weak ones do not always give results. Therefore, traditional medicine methods will be effective.
Do not forget about proper and balanced nutrition, a complex of multivitamins and stimulation of the immune system. You should also lead a healthy lifestyle and avoid stressful situations.
Vaginitis in pregnant women can be identified by general symptoms - itching, discharge with an odor, pain in the lower abdomen. Of course, such signs can indicate many different diseases that gynecology deals with. Colpitis, however, is the most common. Therefore, any abnormal discharge should always alert a woman.
Diet
To improve the effectiveness of treatment, it is necessary to maintain proper nutrition. The consumption of spicy, starchy, sweet and salty foods should be excluded from the diet. Preference is given to fresh vegetables, fruits and protein-rich foods. The speed of recovery is positively influenced by foods containing polyunsaturated acids: tuna, fish oil, flaxseed oil, cod, etc.
Indications
Topical medication is necessary for infection with various pathogenic microorganisms. Vaginal tablets are used if the disease is provoked by streptococci, staphylococci (nonspecific vaginitis). And also if Trichomonas, Gardella, Candida Albicans, Candida glabrata or Candida parapsilosis fungi have entered the body.
Vaginitis is very dangerous during pregnancy. The pathological condition can provoke infection of the fetus or even miscarriage. Pregnant women are contraindicated from using most medications. But there are still vaginal tablets that can be prescribed by a gynecologist during pregnancy.
Before using any medication for treatment, consultation with a specialist is necessary. All medications have contraindications and side effects. Which suppositories will not harm your body and will give an effective result can only be determined by a doctor after conducting all the necessary diagnostic examinations.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Colpitis develops against the background of disturbances in metabolic processes occurring in the body. Experts identify several reasons for this situation:
- Injury to the vaginal mucosa. This can happen during an abortion, the introduction of a contraceptive IUD, non-compliance with douching technology, and so on.
- Allergic reaction to exposure to chemicals. Often the female body reacts this way to the use of lubricants or the use of condoms.
- Hypothermia.
- Prolonged exposure to high temperatures. This happens when visiting a bathhouse or sauna.
- Experienced stress, psychological or mental stress.
- Diseases of the endocrine system: diabetes, obesity, and so on.
- Wearing underwear that is too tight and made from synthetic fabrics. It creates a favorable atmosphere for the life of pathogenic bacteria.
- Pathologies of the genital organs that are congenital in nature.
- Hormonal imbalances. Related to this is the fact that women during menopause more often suffer from this disease.
- Long-term treatment with antibacterial drugs.
- Failure to comply with individual hygiene standards.
- Atrophic processes occurring on the vaginal lining.
The above factors provoke the death of beneficial microorganisms and the active reproduction of harmful ones. The causative agents of colpitis include: staphylococcus, streptococcus, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, fungi such as Candida and some others.
The natural microflora of the vagina is suppressed as a result of overly active sexual activity. Therefore, it is worth abandoning promiscuity.
Senile colpitis
The disease occurs during menopause. During this period, the functions of the female organs fade away, and the acidity of the vagina decreases significantly. The mucous membrane undergoes atrophy. All this contributes to the development of pathogenic flora.
During this period, the functions of the female organs fade away, the acidity of the vagina decreases significantly
Senile colpitis is characterized by a sluggish process. Women usually complain of vaginal dryness. Pain and burning rarely occur.
Severe dryness causes itching. If the patient is bothered by purulent discharge mixed with blood, then doctors will prescribe an examination to identify malignant tumors in the uterus.
Prevention measures
To avoid this disease, every woman should adhere to preventive measures, which include:
- maintaining intimate hygiene;
- use of contraceptives during sexual intercourse;
- conducting sexual relations only with a regular partner;
- taking hormonal and antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor;
- exclusion of injuries to the vaginal mucosa.
By following preventive instructions, you can not only avoid the manifestation of colpitis, but also increase the body’s resistance to the effects of pathogenic factors influencing the woman’s body.
Treatment of colpitis with folk remedies helps to quickly get rid of the disease and return to full functioning.
Classification
According to the pathological process, colpitis is divided into the following types:
- spicy;
- chronic.
According to the type of pathogens that cause the development of this disease, there are:
- specific colpitis that develops when infections enter the body that are transmitted through sexual intercourse (for example, Trichomonas colpitis);
- nonspecific, occurring when opportunistic microorganisms enter the body (for example, candidal colpitis).
Based on the age periods in which the inflammatory process occurs, the following are distinguished:
- colpitis in adolescence;
- colpitis in women of reproductive age;
- senile colpitis;
- atrophic colpitis, which occurs due to increased vaginal dryness.
Kinds
According to the ICD classification, the disease refers to inflammatory diseases of the female pelvic organs. There are several forms, each of which differs in the causative agent, certain symptoms and an individual approach in choosing a treatment technique. It can be primary (the pathological process develops directly in the vagina) or secondary (the pathogen penetrates from the uterus or vulva). There are 3 types of colpitis:
- Candidiasis (thrush). It is observed when the mucous membrane is infected with yeast fungi. Often occurs during pregnancy, as well as when taking antibiotics.
- Atrophic. Caused by a violation of the production of sex hormones - estrogens. It develops with the use of certain medications, in old age and in women who have had the uterus or ovaries removed.
- Trichomonas. The most common type of disease. The causative agents are various types of Trichomonas.
If treated incorrectly, the acute form becomes chronic, which is characterized by a sluggish course with periodic relapses and mild symptoms. With this type of disease, inflammation gradually spreads to the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries, causing adnexitis and endometritis over time, which significantly increases the risk of infertility.
Diagnostic measures
The first examination, which is carried out by a gynecologist, is an examination of the woman in a special chair using mirrors. The doctor will see diffuse redness, note tissue looseness, swelling and pinpoint hemorrhages. In advanced forms of the disease, minor erosions are possible. Some of the clinical signs can be seen in the photo.
The doctor will take a smear for analysis to determine the composition of the microflora and the presence of pathogenic microorganisms. Then he will palpate the uterus to determine its position, the degree of tension for the development of complications.
- carrying out polymerase chain reaction;
- colposcopy;
- general blood and urine analysis;
- blood test for sexually transmitted infections.
After receiving all the data, the doctor will be able to assess the patient’s condition and issue a prescription with the most effective drugs.
Review of tablets for vaginal administration
Suppositories for the treatment of the disease are selected by a gynecologist based on the form of the pathological condition. The specialist determines the methodology using the diagnostics performed. As a rule, suppositories should be used to treat vaginitis as part of complex therapy (tablets, cream, gel, etc.).
Suppositories for the treatment of the disease are selected by a gynecologist
- Suppositories for colpitis Polygynax;
- Terzhinan;
- Meratin-combi;
- Mikozhinax;
- Nystatin, Miconazole, etc.
List of medications for trichomonas form of the disease:
- Metronidazole, Klion, Efloran;
- Macmiror complex (with these suppositories you can treat a large number of sexual diseases);
- Hexicon.
This is not a complete list of remedies that can be recommended to eliminate infections in the genitals of women.
Livarol and Clotrimazole are analogues
Livarol and Clotrimazole are analogues. They are intended to treat pathologies that are fungal in origin. The advantage of these drugs is that they have only a local effect, without harming other organs and systems of the body.
The active element is active against fungi that cause thrush, staphylococci, streptococci. During the period of gestation (II, III trimesters), the drug is prescribed with caution by a doctor. Only if the effectiveness of treatment is higher than the risk of negative effects on the fetus. The same applies to women during lactation.
As a rule, the duration of therapeutic measures is 10 days. Administration of 1 piece before bedtime is prescribed. If itching, dryness, pinkish discharge, as well as feelings of nausea and dizziness occur, you should cancel the course and consult a doctor.
Terzhinan suppositories for colpitis contain the following active components:
- Neomycytin sulfate (antibiotic with antibactericidal effect);
- Ternidazole (leads to the death of fungi);
- Nystatin (has an antifungal effect);
- Prednisolone (has an anti-inflammatory effect).
Terzhinan suppositories for colpitis
are contraindicated for use in pregnant women (first trimester). With the consent of the attending physician, it can be used with caution in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters. The following side effects may occur:
- Pain, itching, burning;
- Dryness of the genitals;
- Redness and hives on the external genitalia;
- With prolonged use, atrophy of the vaginal mucosa may occur.
The duration of therapy is 1-3 weeks. Insert 1 piece before bedtime. You can pre-moisten it with water for easy insertion.
Chlorhexidine is prescribed for the treatment of vaginal inflammation of various etiologies. It is not absorbed into the circulatory system and remains only in the vaginal mucosa. The therapeutic result is observed within 4 hours.
Chlorhexidine is prescribed for the treatment of vaginal inflammation
The medicine has contraindications such as intolerance to the components of the drug and childhood. For pathologies of the genital organs in women, 2 pieces per day are prescribed. The duration of therapeutic measures is 7-10 days. If necessary, treatment measures can be extended up to 20 days.
Like Chlorhexidine, Vocadine is an antiseptic and is recommended for various forms of the disease. The drug is not prescribed for an allergic reaction to its constituent elements, for severe diseases of the thyroid gland, or hyperthyroidism. And also during the period of gestation and lactation. In some cases, a gynecologist may prescribe medication in the first trimester of pregnancy when other methods do not give the desired result. The exact dosage and duration of therapy is determined by the attending physician.
Polygynax is prescribed for the treatment of bacterial and fungal vaginitis.
These drugs are prescribed for the treatment of bacterial and fungal vaginitis. Not able to destroy staphylococci and aerobic microbes. Not prescribed in case of immunity to active substances, in the first trimester of pregnancy and during lactation.
As a rule, vaginal tablets must be administered 2 times a day. The minimum course of therapeutic measures is 6 days. If necessary, it can be extended by a gynecologist to 10-20 days. The first few days of treatment, itching and irritation may occur in the vagina. If these phenomena do not go away, it is necessary to cancel the course of therapy and contact a medical institution for help. The gynecologist will replace Polygynax and Nystatin with other drugs.
Do not self-medicate under any circumstances. All medications can be used only after the permission of the attending physician. Otherwise, you can cause irreparable harm to your body.