As women age, changes occur in their bodies that cause health problems and significantly worsen their quality of life. One of the diseases that is especially common among the fair sex is osteoporosis, or decreased bone density. In advanced cases, it can lead to disability, and therefore requires timely diagnosis and therapy. How to recognize the symptoms of osteoporosis and get rid of the pathology?
Treatment of osteoporosis in older women
What is osteoporosis?
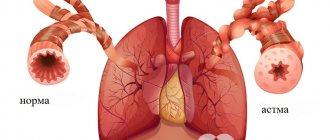
Osteoporosis is a condition in which bone density decreases, causing it to become brittle and prone to pathological fractures. In other words, osteoporosis is increased “porosity” of the skeleton.
Human bones contain calcium and phosphorus, which make them hard and strong. Normally, bone density increases up to 25-30 years of age, reaching a maximum at 35 years of age, then gradually begins to decrease. When the disease occurs, excessive leaching of minerals from bone tissue occurs, bones become porous, resembling a sponge in structure, and a decrease in bone density occurs - osteopenia.
This disease affects all the bones of the skeleton at the same time, which leads to the risk of fractures in the simplest life situations, under the most ordinary loads.
The risk group for osteoporosis primarily includes women over 55 years of age who are going through menopause.
In addition, patients with reduced levels of sex hormones, people with increased levels of sweating, low weight, hereditary predisposition, as well as those who lead a sedentary lifestyle are susceptible to osteoporosis.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you suspect the development of osteoporosis, you should contact an orthopedist or osteopath and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis.
At an appointment with a specialist
To identify the disease, the doctor collects the patient’s medical history and complaints, and then sends her for a comprehensive examination, which includes laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods.
- X-ray of the spine . It is carried out to identify changes and damage to the spinal column.
- Densitometry . One of the most informative methods for diagnosing osteoporosis, which allows you to determine bone density and its decrease using an X-ray or ultrasound machine.
- Blood tests . If the development of pathology is suspected, tests are prescribed for thyroid and ovarian hormones, the level of calcium, phosphorus and other substances.
X-ray of the spine
In addition, women with symptoms of osteoporosis may need to consult a gynecologist, endocrinologist and vertebrologist.
Attention: densitometry can be X-ray, computed tomography or ultrasound, and the procedure, which is carried out using an ultrasound or CT machine, is considered more accurate and informative (X-ray densitometers sometimes overestimate indicators, which leads to incorrect diagnosis and treatment).
Densitometry
Causes
The cause of osteoporosis may be a long history of smoking, alcohol abuse, digestive problems, metabolic failures, or the disease is inherited. In old age, osteoporosis often occurs due to poor absorption of calcium and nutrients into the intestines.
The consequences of the development of osteoporosis, in the form of fractures of the vertebral bodies and long bones, cause a significant increase in morbidity and mortality among the elderly. The main reasons that can lead to the development of osteoporosis are:
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- insufficient physical activity and sedentary lifestyle;
- poor nutrition and abuse of restrictive diets;
- use of medications (usually hormonal);
- disorders of digestion, thyroid and pancreas functions;
- hormonal changes that occur during menopause;
- dysfunction of the ovaries (or their removal) and adrenal glands, as well as other diseases of the endocrine glands.
Risk factors in women
The main cause of osteoporosis is a lack of calcium in the bones. At the age of 25-30, girls experience the so-called peak of “bone activity”, when bone density is at its highest level. After 30 years, closer to 40, the supply of calcium in the bones of our skeleton begins to decrease, but we practically do not notice this until menopause occurs.
During menopause in women, the body stops producing a hormone called estrogen, which controls the presence of calcium in the bones. After this, nothing holds back the destructive cells, and they begin to mercilessly destroy our bones.
The risk of developing osteoporosis in women increases in the following cases:
- early menopause (up to 44 years);
- removal of the uterus and/or ovaries;
- absence of menstruation for more than six months, caused by following a strict diet (hunger strike) or intense physical activity.
In men
The risk of developing osteoporosis in men, according to some scientists, is triggered by a decrease in testosterone levels in the blood. This condition can be caused by the following unfavorable factors:
- taking glucocorticoids;
- alcoholism;
- smoking;
- hypogonadism (a pathology in which testosterone levels drop below a critical level).
Causes and risk factors
The cause of the development of the disease can be a long history of tobacco smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, metabolic disorders, digestive disorders and others. In old age, osteoporosis occurs due to the fact that calcium and some nutrients begin to be poorly absorbed.
The most common cause of osteoporosis is hormonal imbalance. Osteoporosis is most often observed in women during menopause. And the point here is not so much a lack of calcium in the body (there is just enough calcium), but a disruption in the functioning of bone building cells. And these phenomena occur due to hormonal imbalance, so in this case the woman should consult a gynecologist and, if necessary, undergo hormonal treatment.
The fact that bones become more fragile with age is a natural physiological phenomenon. However, for some people these processes occur at an accelerated pace. Several factors contribute to this, including:
- smoking;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- disorders of the digestive system;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- being female;
- Caucasoid or Mongoloid race;
- thinned bones;
- old age (over 65 years);
- hereditary predisposition;
- vitamin D deficiency;
- frequent use of certain medications (such as corticosteroids and anticonvulsants);
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hormonal changes that occur during menopause;
- disorders of the adrenal glands;
- other diseases of the endocrine glands.
As for osteoporosis of the senile type, it develops due to calcium deficiency - when the rate of destruction of bone tissue prevails over the rate of formation of new bone tissue. As a rule, this form of osteoporosis is typical for people over 70 years of age. According to statistics, senile osteoporosis is almost twice as common in women, and in more than 95% of cases it is associated with the postmenopausal period.
In less than 5% of cases, osteoporosis is associated with other diseases or certain medications. This is the so-called secondary form of osteoporosis, which develops against the background of diseases of the kidneys, endocrine glands and other disorders leading to structural and functional disorders of bone tissue.
There is also an idiopathic form of osteoporosis (mainly in young people). This is a fairly rare type of disease, the cause of which remains unclear. Idiopathic osteoporosis can develop in infants, children and young adults whose hormones are normal. Moreover, such people do not have diseases that could cause the development of osteoporosis.
Classification
Primary osteoporosis
Primary (involutional, postmenopausal, senile or senile) osteoporosis. It usually develops in old age (after 50 years). Risk factors for primary osteoporosis include:
- elderly age;
- fragile physique;
- small height;
- indications of fractures in the family history;
- late onset of menstruation (after 15 years);
- early cessation of menstruation (before 50 years);
- scanty and infrequent menstruation;
- infertility;
- long-term lactation (more than 6 months).
Primary osteoporosis develops in women 4-5 times more often than in men.
Secondary osteoporosis
What it is? Secondary osteoporosis develops when processes develop in the human body that change the metabolism of bone tissue (decreasing its mass). The causes of secondary osteoporosis include the following hormonal imbalances:
- increased activity of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism), diabetes mellitus, hyperparathyroidism, hypercortisolism (develops due to long-term use of corticosteroids, or as a consequence of chronic diseases).
- In addition, the causes of development can be: leukemia (leukemia), multiple myeloma, metastatic lesions of bone tissue, thalassemia
Senile osteoporosis (senile) or other forms of this disease are also divided depending on the location of the pathological changes:
- Osteoporosis of the spine. The destruction of the vertebrae occurs, which is manifested by severe pain in the lower back.
- Hip. Characterized by destruction of the femoral neck. Without proper treatment, it can even lead to death. There is a high chance of bone fractures or displacement.
- Osteoporosis of the feet. At the first symptoms of this pathology, the appearance of cramps in the calf muscles is observed.
- Knee. In the absence of proper treatment, it can provoke serious consequences, including disability of the patient.
- Periarticular osteoporosis, affecting only the large joints.
Prevention
Prevention of osteoporosis includes regular monitoring by specialists upon reaching a certain age and the presence of provoking factors. To do this, examinations are carried out to determine the level of calcium and bone density - densitometry.
- It is useful to enrich food with foods that contain calcium and promote its absorption: legumes, dairy products, nuts.
- In addition, it is important to maintain a balanced diet to maintain optimal weight, avoiding sudden changes.
- It is also worth giving up bad habits: alcohol, smoking, excessive consumption of caffeinated drinks.
- Physical activity also reduces the risk of osteoporosis because it increases stress on the bones, which stimulates their strengthening.
Important! As an additional source of calcium, it is also necessary to take medications containing calcium and vitamin D.
For women over 50 years of age, the question is raised about the need for hormone replacement therapy to reduce the risk of developing osteoporosis. For this, it is recommended to consult an endocrinologist.
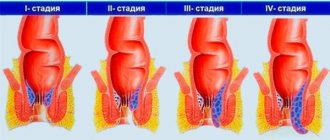
Degrees
There are 4 stages of osteoporosis, each of which is accompanied by its own symptoms and treatment.
| Stages of osteoporosis | Symptoms in adults |
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
Because bone health is dependent on estrogen production, the incidence of osteoporosis increases sharply after menopause. Women aged 50-55 years suffer from fractures due to osteoporosis 4-7 times more often than men. By the age of 70, fractures occur in every second woman.
Stages
There are 4 stages of development of osteoporosis:
- the first (I) stage has no symptoms, there is a gradual decrease in bone density;
- second (II) stage: bone tissue becomes thinner, but the integrity is not yet compromised;
- third (III) stage: the disease affects several parts of the spinal column, bone density is further reduced, the shape of the vertebrae is changed;
- fourth (IV) stage: the shape of the bones changes, radiological areas of clearing are detected.
First signs
Now about the signs. Many of you are probably thinking: what is the difference between the symptoms of osteoporosis and the signs. Symptoms are what we feel and can assume about the presence of a disease, and signs are what we observe, that is, what already indicates the onset of the disease.
The primary symptoms of osteoporosis are difficult to identify, which is why the disease is often called the “silent killer.” A person learns that bone tissue has become brittle and brittle after a broken limb. The question arises: how to check the condition of bones for osteoporosis? It is worth addressing the secondary signs:
- stoop, senile hunchback;
- decrease in height by 3-5 cm per year;
- aches in the body and joints.
To avoid fractures, you should be examined by a doctor if early signs of osteoporosis appear, such as worsening posture, pain in the thoracic or lumbar spine, or its curvature.
Urgent consultation with an orthopedic traumatologist, rheumatologist and endocrinologist is required if two fractures have occurred in a short period of time, bone pain is present, or if height has decreased by 1.5 cm or more.
Types of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis can be an independent disease or a symptom of another pathology or disorder in the body.
Depending on the cause of bone thinning, the disease is divided into primary and secondary forms.
Primary
This type includes conditions that arise against the background of natural aging of the human body.
Primary osteoporosis occurs:
- senile (senile);
- postmenopausal.
An independent pathology also includes idiopathic osteoporosis, which develops at a young age (occurs even in infants). The mechanisms of its development are unknown. Sick children or adolescents may not have any objective reasons for thinning bone tissue.
Young patients have stable hormonal levels, sufficient saturation of the body with essential vitamins and microelements, but at the same time there is destruction of the bone structure. Fortunately, this form of disorder is quite rare.
Secondary
Secondary osteoporosis is diagnosed if it occurs against the background of pathological conditions of other organs and systems, as well as as a result of taking medications. It is worth noting that less than 5% of the total number of patients suffer from the secondary form of the disease.
Osteoporosis can be caused by the following diseases:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- kidney and adrenal diseases;
- rheumatism;
- digestive disorders;
- Bekhterev's disease;
- pathologies of the hematopoietic system;
- systemic lupus erythematosus.
A decrease in bone mineral density can also be due to other reasons. Only a qualified specialist can determine the presence of osteoporosis and the factor that provokes it.
Symptoms of osteoporosis
The disease can be completely asymptomatic for a long time. The first symptoms of osteoporosis often appear already at the stage of severe osteopenia and are expressed in the occurrence of bone fractures. Typically, fractures are detected in the chest (ribs), vertebral bodies, femoral neck, and tubular bones.
However, there are still several symptoms of osteoporosis in women that can warn a person of impending danger:
- There is a slight decrease in human height (by 3 cm) relative to the value of 25 years;
- Excessive slouching. It may indicate the presence of vertebral fractures;
- Severe pain in the lower back may also indicate fractures in the corresponding part of the spine;
- Periodic bone fractures due to falls from a height equal to a person’s height. The vertebrae, femoral neck and wrist bone are most often damaged.
- The first symptoms of osteoporosis can manifest themselves as pain in the thoracic and lumbar regions; this pain occurs as a result of prolonged static loads (that is, during sedentary work, etc.).
- Leg cramps may also occur at night.
- Nails become brittle and become split.
In addition, some people diagnosed with osteoporosis suddenly begin to turn gray and experience rapid heartbeat - these symptoms are rare, but do occur. There are a number of signs of osteoporosis that simply cannot be ignored. These include:
- constant feeling of heaviness in the area between the shoulder blades;
- curvature of the spinal column;
- frequent fractures of large and small bones;
- general muscle weakness;
- growth decreases.
The above signs indicate that osteoporosis is severe and is an irreversible process. In this case, the patient can only be helped by stabilizing the general state of health and stopping the progression of the disease.
With this disease, a fracture can occur under the influence of a very weak load, for example, when trying to lift a saucepan of water, a fracture of the radius bone occurs in the wrist area. To avoid this, it is necessary to diagnose osteoporosis long before it causes trouble.
According to statistics, symptoms of osteoporosis in women over 50 years of age, expressed to varying degrees, are detected in 30%, which is mainly due to a decrease in estrogen synthesis in the body.
The danger of the disease lies in its slow asymptomatic development or the appearance of minor symptoms, which even doctors attribute to manifestations of metabolic arthritis. Despite the fact that arthritis and osteoporosis develop simultaneously, they are different diseases: osteoporosis is a systemic disease.
First signs and symptoms
Symptoms of osteoporosis most often do not appear; people can live for many years without suspecting that such processes are taking place in their body. But still, scientists note a decrease in bone tissue as the main symptoms of osteoporosis in women; aching pain in the lower back and frequent fractures can sometimes be disturbing.
Ordinary doctors most often cannot determine the cause of frequent fractures, only such narrow specialists as orthopedists or surgeons can suspect this disease, after which they send them for x-rays of bones, etc., women are sent to a gynecologist. With osteoporosis, the patient may decrease in size due to a decrease in bone tissue, even becoming 10–15 cm shorter in height.
Symptoms of osteoporosis include:
- The appearance of cramps in the lower extremities at night - they are in no way related to physical fatigue or uncomfortable posture during sleep.
- Lower back pain – it is never constant, it is characterized by periodicity and varying degrees of intensity.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract - this occurs due to severe deformations of the vertebrae, which literally “press” on the internal organs, compressing them.
- Constant fatigue - this indicates a violation of metabolic processes, a decrease in the rate of recovery of the body's strength.
- The development of diabetes mellitus - with the primary signs of this disease, it is necessary to consult a specialist about identifying early signs of osteoporosis.
- Problems with oral health – too much plaque forms on the teeth, stomatitis and periodontitis may periodically flare up.
- Allergic reactions to previously familiar foods/irritants appear.
- The nail plates on the hands and feet become brittle and delaminate.
It is impossible not to pay attention to such serious symptoms as:
- bone tissue fractures;
- feeling of heaviness in the area between the shoulder blades;
- general muscle weakness;
- downward change in height;
- rachiocampsis.
They, in turn, are evidence that the disease is at a later stage. Often osteoporosis at this stage is already irreversible; it is only possible to stop its progression or slow down its entire effect on the body.
Complications
- The most common fractures are the vertebral bodies, femoral neck, and radius. According to WHO, hip fractures place osteoporosis in 4th place among all causes of disability and mortality. Osteoporosis reduces life expectancy by 12–20%.
- The first spinal fracture increases the risk of repeated spinal fractures by 4 times and the risk of hip fractures by 2 times.
- Prolonged bed rest contributes to the development of pneumonia, bedsores, and thromboembolism.
Slowing down the development of osteoporosis and preventing complications is possible with timely consultation with a doctor, laboratory and instrumental diagnostics, and receipt of recommendations for treatment and corrective therapy. Everyone should remember this, especially middle-aged women.
Forecast
With timely detection of the pathological process, its correction and exclusion of risk factors, the prognosis is favorable. However, in some cases, the ability to work is reduced; if necessary, such patients are recommended to work that does not require physical labor.
The main complication of osteoporosis is fractures and their consequences.
Sometimes they cannot be avoided. This especially applies to diseases in older people. For example, with a hip fracture, there is a high risk of disability and death. That is why it is very important to pay special attention to the prevention of this serious disease. Menopause in women Arthrosis of the knee joint Crohn's disease Urolithiasis Hepatitis C: first signs and treatment regimen Hypertension
Diagnostics
Osteoporosis is a disease that lies at the intersection of many medical disciplines. The search for its causes most often begins in the office of a gynecologist, endocrinologist or therapist. Sometimes, in the case when the manifestation of the disease manifests itself as a pathological fracture, it may be a traumatologist - an orthopedist.
The following conditions are taken into account as indications for the densitometry procedure:
- early onset of menopause;
- anorexia;
- secondary amenorrhea (long-term course);
- renal failure (chronic);
- hypogonadism (primary);
- hyperparathyroidism;
- low testosterone (relevant in particular for men);
- malnutrition;
- estrogen deficiency;
- the presence of diseases that may be associated with osteoporosis (spondyloarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteochondrosis, etc.);
- therapy with corticosteroids.
Diagnosis of osteoporosis includes:
- An X-ray examination, in which an X-ray image of the bone is taken and the color saturation in the image is used to judge the condition of the bone and its density. The lighter the frame, the stronger the violation.
- Absorptiometry is the diagnosis of a disease using two beams, and not one, as with a densitometer. The more the bone absorbs radiation, the more serious and extensive the destruction.
- Ultrasound. In this case, the absorption rate of ultrasound is taken into account; the higher it is, the more obvious the disturbances in the structure of bone tissue are.
- Single-photon densinometry. This method is based on determining the density of bone tissue and takes no more than 15 minutes. Computed tomography.
- Blood chemistry. Using it, you can determine the exact content of calcium, alkaline photophase, vitamin D, parathyroid hormone and phosphorus in the blood.
Features of the disease and causes of osteoporosis in women
Osteoporosis is a chronic progressive disease of the musculoskeletal system. It is caused by a decrease in bone density due to metabolic disorders.
Bone consists of two components. It is covered on top with a dense compact fabric of a homogeneous structure. There is a spongy porous substance inside. In a healthy person, it consists of clearly defined plates with small gaps between them, located in the direction of the probable maximum load.
In patients with osteoporosis, bone tissue does not receive enough minerals to maintain the necessary structure. The plates become thinner, and over time they are completely destroyed, the “sponge” thins out and takes on a chaotic appearance. This leads to the fact that the skeleton loses its tolerance to stress. Bones break from external influences that are not dangerous to a healthy person.
In women, symptoms of osteoporosis in most cases appear after 45 years of age (during menopause). This is explained by a decrease in the level of estrogen in the body, a hormone that regulates intraosseous metabolism. Due to a decrease in its synthesis, the balance in the activity of cells “responsible” for the renewal of skeletal tissues - osteoclasts and osteoblasts - is disrupted. The former destroy the “waste” material, the latter form new bone cells.
Against the background of a lack of estrogen, osteoclasts begin to prevail over osteoblasts. Tissue renewal is slower than tissue destruction. The bone structure is disrupted, becomes thinner, becomes brittle and brittle.
Attention: according to research, over 10 years of menopause, bone mass decreases by 30%.
Osteoporosis also develops against the background of artificial menopause. After surgical removal of the ovaries or long-term use of hormonal drugs that suppress estrogen synthesis. A number of external or internal reasons can accelerate the approach of the disease.
Treatment of osteoporosis
How to treat osteoporosis in women? Osteoporosis is treated with medication; people with endocrine system disorders are prescribed medications that will help restore hormonal levels. Older people are prescribed nutritional supplements rich in calcium and vitamin D. Women during menopause are prescribed hormone replacement therapy, as well as bisphosphonates.
Doctors will prescribe a special diet, physical therapy, and massages to absolutely all patients. Of course, any force loads should be minimal - only a specialist will be able to select an adequate training program taking into account the degree of bone fragility.
The main goal in the treatment of osteoporosis is to reduce bone loss while simultaneously intensifying the process of its restoration. Comprehensive treatment of osteoporosis includes hormonal therapy (estrogens, androgens, gestagens), vitamin D, bisphosphonates, calcitonin.
Drugs used in the treatment of osteoporosis:
- Drugs that stimulate bone formation: bioflavonoids, vitamin D3; salts of strontium, calcium and fluorine
- Drugs to suppress bone resorption: bisphosphonates (zoledronic acid, risedronate, ibandronate, alendronate, pamidronate), calcitonin, natural estrogens
- Hormonal drugs for osteoporosis are selected depending on gender, age and risk factors. When choosing drugs for women, the phase of menopause, the presence of the uterus and the woman’s desire to have menstrual-like reactions in the postmenstrual period are taken into account.
Unfortunately, today it is impossible to completely cure osteoporosis, however, with the help of drugs that affect the absorption and subsequent absorption of calcium, the condition of the skeletal system can be significantly improved.
Physiotherapy
A healthy lifestyle is a big and sure step in the treatment of osteoporosis. The concept of a healthy lifestyle in this case means therapeutic exercises, massage and sunbathing.
Regular gymnastics (at least 3 times a week for 30 minutes) will allow you to achieve bone tissue growth by 3-5% in just a couple of months.
It is advisable that the set of exercises be selected by a specialist - only he will be able to calculate the load required on the body, taking into account the characteristics and capabilities of the patient being treated.
Exercise (workouts)
Exercise is an important part of an osteoporosis treatment program. Physical activity is necessary to build and maintain bone throughout adult life, and complete bed rest leads to severe bone loss. Evidence suggests that the most beneficial physical activities for bone health include strength or resistance training.
Exercise can help maintain or even slightly increase bone density in adulthood, and together with adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, can help minimize age-related bone loss in older adults. Using different types has other important benefits for people with osteoporosis. It can reduce the risk of falling by increasing muscle mass and strength and improving coordination and balance. In older people, exercise also improves function and increases the time until they can get by without assistance.
If you have osteoporosis, you should avoid jerking exercises. To help protect you from fractures, a physical therapist or physical rehabilitation specialist can recommend specific exercises to strengthen and support your back, teach you how to move around and perform daily activities safely, and create an exercise program that meets your limitations.
Nutrition
When treating osteoprosis, great attention should be paid to nutrition: food must contain calcium, phosphorus, vitamins D, K, C, E, and magnesium.
What foods are most beneficial for maintaining bone density? The diet should be varied and sufficient in energy value. It is recommended to include the following products in your diet:
- Milk. In first place, of course, we need to put dairy products - the main source of calcium in nature. It is permissible to consume milk in any form. A large amount of calcium is found in cheese and cottage cheese.
- Fresh vegetables and herbs. Eating cabbage, carrots, pumpkin, vegetable seeds, beans, peppers, and any greens is good for bones.
- Fish products contain trace elements in large quantities.
- Seeds, bananas, oatmeal, buckwheat. The products listed contain magnesium. It is this mineral that is involved in creating the mineral support of bone in addition to calcium.
- Products containing phosphorus: chicken, beef, liver, eggs, bread.
- Sunflower and olive oils: contain copper, which is also needed by bones.
In addition to vitamin D3, the body also needs vitamins C, A, K and group B, especially B, in the fight against osteoporosis. They also take part in the absorption of calcium and its penetration into bone tissue. Products containing these vitamins are mainly of plant origin.
These include:
- White cabbage;
- citrus;
- bell pepper;
- black currant;
- sea buckthorn;
- tomatoes;
- carrot;
- strawberries;
- papaya;
- pineapples;
- bananas;
- legumes;
- buckwheat grain;
- oats;
- leafy vegetables and more.
One of the founders of juice therapy, Norman Walker, proposed his course of therapeutic nutrition for osteoporosis, which is based on 21-30 day cycles twice a year, during which, against the background of a balanced diet, the patient is recommended to consume 0.5 liters of freshly squeezed juice from celery, carrots and turnips daily in equal proportions.
A diet for osteoporosis is based not only on including foods containing a lot of calcium in the diet, but also on excluding from it foods that enhance the excretion of calcium from the body and disrupt its absorption processes. These products include:
- refractory animals and freeze-dried fats (lamb fat, lard, margarine, mayonnaise), sausages, sweets, coffee and caffeine-containing drinks, chocolate and cocoa;
- fatty meats, sauces, canned, pickled and salted foods;
- unrefined vegetable oils, snacks (salty crackers, chips), salt, baked goods;
- alcoholic and carbonated drinks;
- melted butter;
- foods high in oxalic acid (rhubarb, sorrel), and limit the consumption of table salt to 5 g/day.
Elderly people suffering from osteoporosis should prefer a diet that includes many plant foods. A dairy diet is not recommended for them, firstly, with age, milk is less absorbed in the body, and, secondly, dairy products contain a lot of fat, and, consequently, cholesterol, which provokes the development of atherosclerosis.
Doctors to see
Osteoporosis in old age is not a death sentence, but you need to consult a doctor in time. Since the causes of the disease relate to many areas of medicine, they start by visiting a therapist. After the initial diagnosis, it will become clear which specialist to contact – a gynecologist or an endocrinologist.
If the disease manifests itself as a pathological fracture, the examination begins with a traumatologist or orthopedist.
How to treat osteoporosis with folk remedies?
Before using any folk remedies, be sure to consult your doctor.
- Licorice is naked. Grind the root of the plant, pour a tablespoon of raw material into 0.45 liters of hot water, soak in a water sauna for half an hour, leave for 90 minutes, filter. Take ½ glass four times a day before meals.
- You need to mix 100 g of propolis and 50 g of buckwheat honey. Then add 100 g of crushed and pre-dried eggshells in the oven. It is recommended to take the resulting mixture two teaspoons once a day.
- Eggshells for bone osteoporosis. Egg shells are crushed into powder (using a blender), and then mixed with lemon juice in a 1:1 ratio. The product is taken orally at ¼ or ½ teaspoon for two weeks, after which a break is taken for a week.
- Fresh juice of young nettle helps with fractures in the femoral neck. It is recommended to rub it into the affected area twice a day.
- Infusions of various herbs are very effective. To prepare them, you can use St. John's wort, dandelion roots and others. You need to pour a tablespoon of herb into 220 ml of boiling water. The cooled liquid is drunk throughout the day.
- Mumiyo is taken orally. To do this, you need to make a small ball of 2-4 grams and dissolve it in 100 g of warm water. The drug is taken for 3-4 weeks, after which a break is taken. It has been proven that mumiyo is the best folk remedy for treating osteoporosis in women and men.
The list of beneficial herbs and medicinal plants is wide, but you must understand that not all of them can be used to treat bone disease. For example, natural foods that contain oxalic acid will only worsen the course of the disease.
Forms of osteoporosis
According to localization, osteoporosis is:
- Systemic, with general bone damage;
- Local, in which one or more bones are affected.
For reasons of occurrence:
- Primary, if the causes are menopause, aging, heredity or other internal processes of the body;
- Secondary, if the cause is another disease, for example, ovarian apoplexy or treatment of an unrelated disease with hormonal drugs, for example, bronchial asthma or pyelonephritis.
According to the structure of the lesion, they are distinguished:
- Cortical osteoporosis, occurring in the upper layers of the bone;
- Trabecular, in which the structure of the spongy substance inside the bone is disrupted;
- Mixed.
By age period of occurrence:
- Menopausal, occurring directly during menopause;
- Senile, which is diagnosed after the age of seventy.
Senile osteoporosis is the stage of the disease at which it has reached its full development. At this stage, all preventive treatment options are lost, so the main focus must be on preventing the possibility of fractures.
Symptoms
At the initial stage of development, the disease is simply impossible to detect, since it is caused by invisible signs that can be attributed to ordinary malaise or fatigue. With a sudden change in weather, aching pain in the bones, fatigue appears, at a young age - gray hair, increased heart rate, periodontal disease.
The most severe complication of such a disease is a pathological fracture . Bones break under minimal stress, such as sneezing, coughing, or awkward movement. They grow together rather poorly and incorrectly, since the structure of the bone tissue is damaged. Over time, cramps appear in the limbs (especially at night), nails split, and legs become deformed.
A broken femoral neck causes disability in older people. This is the thinnest bone connecting the head to the body, and it is most susceptible to breakage when a person falls. Often people do not even realize that a bone is broken and suffer pain that radiates to the groin. After a fracture, the affected leg becomes shorter than the healthy leg by as much as four centimeters.
Treatment is very labor-intensive and lengthy, and the disease only recedes if the blood vessels are not damaged. Otherwise, the femoral head dies.
If a person’s posture has changed (noticeable stoop, decreased height, spinal immobility), this indicates vertebral fractures. Around the world, 700 thousand people get sick every year.
Osteoporosis is also widespread in joint diseases. They swell, become deformed, hurt, crunch, and become immobile.
Diagnostic methods
Even with obvious manifestations, symptoms are not enough to make a diagnosis. They occur in various diseases of the skeletal system, so all patients are referred for x-ray diagnostics. Plain x-rays will show changes only after a quarter of the bone mass has been lost. Therefore, it is used mainly for fractures. We can talk about severe osteoporosis if:
- reduced height of the vertebrae, changes in their shape - wedge-shaped;
- the spongy substance (loose part of the bone) has become porous;
- the cortical layer (the dense part under the periosteum) is thinned;
- bone pattern with enlightenment (spotted) or the bones look like glass, and their outline seems to be drawn with a pencil.
Densitometry
For early detection of the disease, a densitometry method is required. It is based on the fact that low density bones transmit X-rays well. Their absorption is recorded and compared with that of healthy people. Instead of X-rays, ultrasound and tomography are used to assess the condition of the skeletal system.
If osteoporosis or osteopenia is detected (calcium leaching, initial stage), then before prescribing therapy you need to undergo tests for indicators of mineral metabolism.
They will be needed during treatment to assess its effectiveness. The most important studies:
- calcium in the blood (ions) and urine;
- osteocalcin, alkaline phosphatase, blood phosphorus and magnesium;
- deoxypyridinoline and hydroxyproline urine.
Calcium in urine
If it is difficult to make a diagnosis, the doctor may recommend a radionuclide scan with strontium (usually if a tumor is suspected), or an iliac bone biopsy (a piece of tissue is taken for analysis). To identify the cause of the pathology, a comprehensive examination of the kidneys, intestines, thyroid and parathyroid glands, genitals, and adrenal glands is carried out.
Principles of nutrition for osteoporosis in senile and elderly people
Daily calcium intake:
- Dairy products;
- Fish;
- Eggs;
- Green vegetables;
- Pumpkin;
- Carrot.
Phosphorus-containing products:
- Beef or veal;
- Poultry meat;
- Beef or poultry liver;
- Nuts.
You should not eat foods rich in calcium together with those containing phosphorus, since calcium is poorly absorbed.
Increasing the consumption of vegetables and fruits to generally strengthen the body through vitamins and microelements.
Avoid foods that neutralize calcium:
- Coffee, tea, drinks based on coca leaves;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Margarine, lamb and lard;
- Salt and products containing large amounts of it - pickles, sausages, smoked meats.
Treatment
Osteoporosis is a disease closely associated with fractures. The main therapy is aimed at their prevention. Secondary symptoms in women are relieved by systematic treatment in the form of multivitamin complexes and physical exercises.
Drug therapy
Treatment is carried out with medications that normalize metabolic processes in the body, restoring the content of phosphorus and calcium. Medications are taken continuously over a long period of time. If changes in hormonal balance are detected, patients are prescribed hormone replacement medications - strictly according to indications.
Physiotherapy
Prescribed by the attending physician, the patient undergoes a course under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor. After learning the basic exercises, the patient is allowed to perform them at home. Training is carried out to the best of the body's capabilities - any excessive load can lead to habitual fractures and a deterioration in general condition.
Traditional medicine methods
Alternative therapy raises doubts among medical practitioners. The problem of osteoporosis is associated with low absorption of calcium by the body and gradual destruction of bones.
Traditional recipes suggest replacing medications with the following:
- 200 g of parsley and dill are crushed, pour 0.5 liters of fresh boiling water, leave for 3 hours. The cooled drink is filtered, take 300 ml/day. Treatment is carried out for 3 months.
- 50 g of walnut leaves are poured into 1 liter of boiling water, the dishes are covered with a lid, and kept for 10 minutes. After straining, use 1 tbsp. before each meal - up to 4 times a day.
- Take shells from chicken eggs, wash them thoroughly and dry them. Grind into powder, pour into a glass container, and add lemon juice. After the shell is completely dissolved, the composition is taken on an empty stomach, 1 tsp.
Before using homemade medicines, you must do an allergy test. A small amount of the substance is spread on the inner surface of the elbow, wait 20 minutes. If there are no blisters, itching, or redness, you can begin therapy.
Correction of physical activity and lifestyle
Physical activity and lifestyle are an integral part of the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis.
Patients, especially the elderly, need to seek help from a doctor so that a specialist can select a physical activity that matches their level of training, as well as the presence of concomitant pathologies. The basic rules include:
- Incorporating physical activity into your lifestyle every day. Exercises should not cause discomfort or pain to the patient. It is forbidden to perform heavy exercises that can lead to injury.
- Regularly relieve back tension. To do this, the patient needs to take a supine position for 30 minutes with cushions placed under the neck and lower back.
- Preference should be given to swimming and walking, as well as breathing exercises.
Recommendations for older women
Selecting physical exercises for older women can be difficult due to poor health.
For patients who cannot move independently, it is sufficient to perform flexion and extension of the limbs in intact joints. In case of dizziness, headache, or difficulty moving, it is necessary to use objects that serve as support for it. In order to prevent complications, it is possible to perform a massage aimed at improving blood circulation and maintaining the tone of muscle fibers.
Prevention of osteoporosis in older people Preventive measures recommended to patients can reduce the risk of developing the disease. Among them are:
- Nutrition rules with a daily intake of sufficient amounts of calcium, phosphates and vitamins.
- Physical activity necessary to maintain muscle tone and metabolic processes.
- Timely examination in the presence of risk factors.
- Elimination of smoking and bad habits.
The dangers of osteoporosis for older women
Every second patient over 65 years of age with a bone fracture is diagnosed with osteoporosis. The older she is, the more severe her injuries. Research shows that 50% of women over 80 years old show signs of fractured ribs and vertebrae. Compression injuries develop primarily due to osteoporosis.
Frequent fractures of the femoral neck, ankle, radius, shoulder joint, the vertebrae also suffer; they often sag, the formation of a Schmorl’s hernia is quite possible.
Displaced fractures are especially dangerous. Moreover, injuries occur not only after a fall, but also due to the efforts made. For example, when trying to pull out a stuck plug from a bathtub or open a tightly closed door.
The consequences of fractures do not go away without leaving a trace, they bring life problems:
- Physical : acute and chronic pain, increased fatigue and bone deformation.
- Psychological : decreased self-esteem, depression, deterioration in general well-being. Many women develop a persistent fear of falling.
- Economic : expenses for treatment.
- Social: isolation from society, lack of independence, loss of the usual social role.
Frequent fracture sites
Pain is the main symptom of osteoporosis
Back pain is the very first sign of osteoporosis and haunts on an ongoing basis. As soon as a woman stands without moving for 20 minutes, her back begins to ache and ache. When you move, it becomes easier, and if you lie down, everything goes away without a trace. But it’s not for nothing that osteoporosis was given a “nickname” - the silent killer. It may well develop without pain or be disguised as osteochondrosis.
With age, pathology leads to deformation of the spine, it shrinks, which negatively affects the condition of the internal organs of the lungs and heart. A woman develops breathing problems and chest pain similar to heart pain. Read how to distinguish them here.
A vertebral compression fracture is always accompanied by intense, constant pain. Painkillers can help you cope with it. The condition will improve with bed rest. But a minimally invasive operation to restore the vertebral body may be required, only then painkillers will not be required.
Forms of the disease
Doctors have identified two large groups of osteoporosis:
- Primary (95% of all incidence cases):
- senile (most common, people get sick after 70 years);
- postmenopausal (with the onset of menopause, estrogen levels drop, which leads to a significant decrease in bone density);
- idiopathic (rare, develops at a young age).
- Secondary - caused by other diseases accompanied by increased bone fragility.
Stages
There are conditionally four stages of osteoporosis, differing in the depth of destruction of bone tissue.
- In the initial phase, the patient experiences brittle nails and dry skin; changes in the bones can only be seen during medical examination.
- At the second stage of the disease, discomfort in the spine increases, pain occurs in the area of the shoulder blades, and the heartbeat quickens. The x-ray shows bone lesions.
- In the third stage, x-rays show strong changes in the spinal column, the bone marrow canal is enlarged, and “fish vertebrae” appear—as experts have dubbed the characteristic flattening of the vertebral elements. Pain in grade 3 osteoporosis becomes more frequent and severe, and the risk of fractures increases.
- In the last stage, demineralization of the bones motivates a change in their shape, the cavity in which the bone marrow is located becomes twice as wide, the woman’s height “sits” by 8-10 cm. A small physical action, even shaking while sneezing, can cause a fracture.
The trouble of age
Osteoporosis of the hip joint is a loosening of the bone tissue in one of the most mobile parts of the body. A hip fracture is one of the most common injuries in older patients. The slightest load, awkward body rotation or bending can cause a fracture in the part of the skeleton where the bone thins the most over the years.
Basic principles of the diet
You can improve your health, prolong youth, and preserve beauty with the help of a proper diet. Nutrition for osteoporosis in women compensates for the lack of calcium in the body, which ensures the strength of bones and joints.
The patient receives about 1.5 g of active alkaline earth metal per day. The secret of health is that food must contain a full range of vitamins, minerals, and microelements. The basis of a complete diet is vegetables and fruits rich in B vitamins.
A proper diet and walks in the fresh air improve the absorption of calcium in the body. Restricting salt affects blood estrogen levels, preventing osteoporosis.
Reducing the consumption of animal proteins in food avoids intoxication.
Poor nutrition can be a real test for the body. If the patient eats poorly, signs of metabolic disorders, weight gain, pain in the sacrum, and discomfort in the back muscles appear.
A sharp decrease in body weight or prolonged fasting do not promise anything good for a woman after 50 years of age. Excess calories lead to weight gain and the appearance of fat on the abdomen, thighs, and buttocks. Estrogen deficiency and unbalanced diet are the main factors in the development of osteoporosis in women.
Healthy foods are often replaced by meals containing preservatives, stabilizers and dyes. Poor calcium metabolism in the body is often caused by the development of the following diseases:
- renal pathology;
- pancreatitis;
- malignant tumor;
- vitamin deficiency
The term osteoporosis itself (translated from Latin “osteo” means bone, and “porosis” means the formation of a cavity, porosity) already contains a definition of pathology associated with a violation of metabolic processes in the body, namely the predominance of transformation (destruction) of bone tissue over the process of its formation.
As a result, human bones become fragile, their density decreases and their structure changes, and the likelihood of fractures increases.
In this regard, one of the important methods of treating the disease is diet, which helps, along with drug therapy, to replenish the missing elements.
Treatment of osteoporosis in older women necessarily includes proper nutrition. The essence of diet therapy is to provide the body with substances that are necessary to build normal bone tissue.
On the one hand, they are also involved in the formation and strengthening of bones, like calcium, and on the other hand, without them, the full absorption of calcium by the body is impossible.
Recommended daily intake of calcium:
- children (11-18 years old) – 1200 mg;
- premenopausal women – 800 mg;
- postmenopausal women – 1500 mg;
- men (over 18 years old) – 800 mg.
In addition, other microelements are also needed:
- magnesium – 400-800 mg;
- phosphorus 800-1000 mg;
- copper – 3 mg.
And also vitamins: vitamin D (400 IU), C, A, K, group B and folic acid.
The diet is normal, 4 times a day. The only rule that applies to all diets is to have breakfast, lunch and dinner at the same time.
Food processing and temperature conditions
With a lack of calcium in the body, bones become so fragile that an awkward movement or twist can cause a fracture. In addition, the diet for osteoporosis contains many plant foods rich in vitamins.
Vitamins A, C, group B have antioxidant properties, improve appearance, make skin elastic and smooth, nails strong, and hair shiny.
Other publications:
Osteopenia: causes of pathology, signs, diagnosis and treatment, The benefits and harms of an elliptical trainer - everything is not as simple as it seems, How to treat osteoporosis of the hip joint - one of the most dangerous types of osteoporosis,
What to drink instead of hormones?
What to do if you are afraid to take HRT or they are contraindicated? Numerous advertisements, friends, and experienced colleagues offer their medications that help in this matter. I don’t have time to go to the doctor, I know from experience, but the pharmacists at the pharmacy will help you choose a dietary supplement by asking the right questions.
Phytoestrogens are taken for non-aggressive symptoms, when they are annoying but can be tolerated. Dietary supplements do not act immediately, but have a cumulative effect from 2 weeks to 1 month.
The most famous:
- Qi-klim - a series from Evalar.
- Estrovel.
- Klimalanin.
- Mense.
Qi-Klim line of drugs
We take pills for hot flashes and strengthen our bones
By the way, the majority of women, as already mentioned, do not even think about osteoporosis. And the appearance of the first signs of menopause makes one look for a medicine to prevent or get rid of hot flashes, depression, and insomnia.
So hot flashes, to some extent, force us to replenish the production of estrogen, thereby preventing osteoporosis, even if we do not yet realize it. It’s worse for those who have very mild or completely absent hot flashes. Few people are aware and take dietary supplements. My friends with medical education are absolutely not touched by the topic of possible fractures and the prevention of osteoporosis. And conversations with random women about menopause and the question: “What are you taking?” - I often hear a proud answer - “Nothing!”
Distracted
Vitamin D in the fight against osteoporosis
The body needs little calcium; the main task is to absorb it. Without vitamin D, calcium will be useless. The daily requirement for vitamin D for humans is 400 IU (according to the recommendations of the Food and Drug Administration). This norm is suitable for healthy, young people. For the rest, a dose of 800 to 5000 IU is recommended, according to indications.
To get a dose of vitamin D, you need to be in the sun, but tanning in our case can be dangerous, causing melanoma skin cancer. Moreover, as we now understand, estrogen protectors are not produced. And what should poor women do now during this period, wear a burqa? It's a vicious circle - you need the sun vitamin to absorb calcium, but the bright sun is harmful.
Of course, I’m exaggerating, you shouldn’t sunbathe and work outside for a long time in hot hours, but choose the time for classes and procedures - morning, evening, shade. Maybe not enough, but still at least something. And don’t forget about anti-tanning cream, especially in the spring, otherwise age spots will come out and remain throughout the summer.
Then there is only one way out - take additional vitamin D as a supplement. Fortunately, it is fat-soluble and accumulates in the body. There are also foods that contain nutrients - eggs, liver, fatty sea fish. But as observations show, from products, only a few reach the norm. Therefore, it is necessary to use vitamin complexes. Aquadetrim from a pharmacy, 2-3 drops per day, is an excellent option. Or a convenient option - Now Foods, Vitamin D-3, 1000 IU, 360 softgels from the online store.
Important: Vitamin D in large doses is toxic to the body, so first you need to get tested and monitored after 3-6 months.
Drink Aquadetrim in drops or soft tablets in courses
. Another important detail is the amount of magnesium, which is absorbed less and less with age. And it, like K2 (MK7), activates vitamin D so that it is useful.
Bisphosphonates
Synonym: disphosphonates. These are synthetic analogues of pyrophosphates contained in bone tissue and ensuring its mineralization. The structure of bisphosphonate molecules is such that they capture hydroxyapatites and deposit them in the intercellular space of bone tissue, the matrix.
Bisphosphonates inhibit the resorptive effect of osteoclasts. On the contrary, they help osteoblasts that restore bone. Injecting or ingesting these medications increases bone strength and reduces the risk of fractures. The most effective are the latest generation of bisphosphonates - Ibandronate and Zoledronate under the commercial names Boniva, Rezoklastin, Rezorba.
Therapeutic exercises for osteoporosis
People suffering from osteoporosis are advised to walk and jog more often: walking and running put stress on the bones and strengthens them.
The following classes will be useful:
- dancing and aerobics;
- horse riding;
- cycling;
- tennis;
- jump rope.
There are also special exercises to strengthen bones, develop flexibility and coordination.
Please note that swimming, despite its enormous benefits, does not affect the skeletal system, since the body in water is in a weightless state and does not put stress on the bones.
But before starting classes, you definitely need to consult with your doctor.
The effect of menopause on bone health
Hormonal deficiency during postmenopause leads to bone tissue undergoing serious changes. It is impossible not to notice them, since the main sign of the lesion is the characteristic hunching of older women. Fragile vertebrae are injured in the form of spinal deformation (kyphosis) and decreased height.
Menopause is considered the main cause of the development of osteoporosis, since with the end of menstruation, the ovaries stop producing estrogen after 5-7 years. This hormone is responsible for retaining calcium in the bones throughout a woman’s life.
Early menopause and osteoporosis
Unfortunately, in many women, ovarian function fades early, before the age of 40. Changes occur in the body as during menopause at 48-50 years of age. Why menopause begins so early against the background of complete health is unknown. A woman is plagued by: hot flashes, increased anxiety, sleep disturbances, malfunctions of the genitourinary system, increased blood pressure. And all these symptoms are in the prime of life, it’s a shame.
This is where the proverb comes from: “All illnesses begin after 40,” which is quite true, especially for women with premature menopause. The less estrogen produced in the body, the higher the risk of developing atherosclerosis, hypertension and, as a consequence, heart attacks and strokes. At the same time, the skeletal system suffers, the woman develops osteoporosis, and the likelihood of fractures increases.
Natural early menopause develops according to natural laws. Its exact causes are being studied, but 50-80% of cases remain unclear. There is confirmed data on the influence of heredity; you can’t argue with genes. But acquired life risk factors are:
- Heavy physical activity.
- The absence of childbirth during a woman’s life, as an immune and inflammatory lesion of the ovaries causing infertility.
- Stress, poor quality nutrition, frequent viral infections.
Osteoporosis is a companion of women with temporary amenorrhea (lack of menstruation) caused by pathological reasons. This problem often occurs among professional athletes who exhaust their bodies with hard training.
Serious eating disorders lead to amenorrhea, especially in those concerned about their figure. In this regard, anorexia nervosa and bulimia are dangerous. You cannot ignore the absence of menstruation; you need to consult a gynecologist. Unfortunately, young women rarely pay attention to this fact; they don’t have periods, but oh well. But this is only due to ignorance of entire generations along the female line. Where are they talking about the consequences?
You cannot avoid early menopause with a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus). After the operation, the ovaries continue to work producing estrogen, but not for long.
Delayed puberty and osteoporosis
Mineralization of bone tissue is completed in girls by 14-16 years, and in boys by 17-18. This process is ensured by the influence of hormones on the body. If puberty occurs on time and proceeds without any disturbances, then bone mass will gain peak values during this period.
Constitutional delay in growth and sexual development entails insufficiency of the function of the sex glands and, accordingly, problems in the production of sex hormones. In girls, this disease - hypogonadism - affects bone tissue, its mineral density will be reduced. Research confirms that late first menstruation increases the risk of osteopenia.
Diagnosis of early menopause
Which doctor should a woman consult to diagnose osteoporosis? The first visit should be made to a gynecologist. The examination will take more than one day, so consultations with doctors - an endocrinologist, rheumatologist, or orthopedist - may well be necessary.
To understand that a woman is actually developing early menopause, a laboratory examination is necessary, namely screening (osteoporosis). It can be done independently for money, for example, the DNAOM laboratory provides services (dnkom.ru/analizy-i-tseny/kompleksnye-resheniya-dlya-vzroslykh/osteoporoz-screening/), . Also in the clinic, with the direction of a doctor, it is possible to undergo diagnostic procedures:
- Determination of the level of the hormone estradiol - its decrease.
- A pelvic ultrasound evaluates the structure of the ovaries, as well as the growth rate of the uterine mucosa (it slows down in menopausal women).
- Biochemistry - a blood test to determine the level of follicle-stimulating hormone. With the early onset of menopause, its rate increases sharply. Thus, the body tries to stimulate the activity of weakened ovaries.
Treatment for early menopause
Contacting a gynecologist for help in a timely manner will help eliminate the negative consequences of early postmenopausal osteoporosis as much as possible. Treatment for hot flashes is based on replenishing the missing hormones: estrogen and progesterone. Hormones are prescribed as a last resort when severe symptoms of menopause are bothersome.
Therefore, they start with non-hormonal replacement therapy. The main efforts are directed towards combating the symptoms of menopause and maintaining normal vaginal microflora. Drugs are prescribed to prevent the development of rapid osteoporosis and atherosclerosis.
Drugs
Vitamin-mineral complexes and bisphosphonates should be selected by the attending physician. Bisphosphonates (diphosphonates) are substances obtained artificially and consisting of two phosphonates. Preparations based on them help stop the destruction of bone tissue. When they enter the body, they bind to calcium and retain it in bone tissue. For the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis, the patient may be prescribed:
- “Bonefos”, “Clobir”, “Sindronate”, “Clodron” (based on clodronic acid) Reduce the concentration of calcium in plasma and prevent the development of hypercalcemia.
- "Skelid" (based on tiludronic acid). The drug is intended to increase bone density.
- "Didronel", "Xidifon", "Pleostat" (based on etidronic acid). Drugs with a wide spectrum of action.
- “Fosamax”, “Alendronate”, “Forosa”, “Alental” (based on alendronic acid). The drugs are prescribed for pathologies of bone and cartilage tissue.
- "Rizofos", "Gemfos", "Actonel", "Atelvia" (based on risedronic acid). Prescribed for all types of osteoporosis.
Calcium preparations
Calcium itself does not mean anything for osteochondrosis. To achieve results, calcium-containing drugs are taken with bisphosphonates. There are many preparations containing calcium. But their benefits for bone pathology are not the same. So, in inorganic forms it is zero. Therefore, you should not take calcium chloride or calcium carbonate. Calcium in chelated compounds is absorbed better. But chelated calcium is present only in dietary supplements.
Osteogenon is the drug of choice for osteoporosis in women. Here calcium is present in the form of hydroxyapatites. It is these salts that represent the inorganic part of the matrix. Oteogenon tablets not only saturate the bone with calcium.
The drug has a complex positive effect on the condition of bones. It contains organic matrix components. Osteogenon stimulates collagen synthesis and increases the activity of osteoblasts. Vitamin D preparations (Ergocalciferol, Cholecalciferol) improve the absorption of dietary and medicinal calcium.
Necessary and contraindicated drugs
There are many different dietary supplements and complex preparations in pharmacies that can be used to balance the presence of necessary substances in the body. Osteoporin, which contains polysaccharide fibers and fructooligosaccharide fibers, is considered one of the complex drugs for the prevention of the disease.
With this composition, the drug helps the body absorb calcium better. The drug also contains vitamins such as D3, K1, C, B6.
It is not able to replace full-fledged treatment, but has two main functions: it participates in immune processes, forcing dormant cells to turn into leukocytes and store information about infections, and also ensures normal bone formation by participating in calcium metabolism processes.
For adults, the daily intake is 15 mcg. after reaching the age of 70 years, this norm increases to 20 mcg.
Foods rich in vitamin D:
- Especially important are fish oil and cod liver, which contain beneficial fatty acids that help regulate hormonal levels in women;
- Sea fish and seafood;
- Liver of animals and birds;
- Milk and dairy products;
- Egg yolk.
List of drugs for treatment
Osteoporosis (symptoms in women are controlled by medications) requires a thorough diagnostic examination before using drug therapy. Its use is unacceptable without a doctor's prescription.
Bisphosphonates
The drugs are pyrophosphate analogues that stop bone resolution. With their help, new bone tissue is formed. Popular biosphosphonates are represented by Risedronate, Bonviva, Alendronate - in tablets and Zoledronate - in injections.
Calcitonin preparations
The medications are responsible for regulating the hormone of the same name, which helps in the formation and maintenance of bone strength.
Treatment is carried out:
- Miacalc - made from salmon fish;
- Ostever;
- Alostin;
- Boar.
Selective estrogen receptor modulators
The drugs have a specific effect similar to the effect of estrogens on bone structure. Therapy and prevention of osteoporosis is carried out: Raloxifene, Tamoxifen. Both drugs are often used as substitutes for biosphosphonates in cases of intolerance to the latter. Therapy with this group of drugs is long-term; if taken daily, it can last up to 4 years.
Denosumab (Prolia)
Medicines based on Denosumab are human monocellular bodies that help restore large loss of bone mass and prevent possible fractures. The advantages of use include the possibility of introducing 1 r. In 3-6 months, but the high price is not always available to patients. In advanced cases, treatment of osteoporosis is carried out by Exzhivoy, Prolia.
Means of versatile action
Vitamin D metabolites are approved for use in patients of the older age subgroup. They are allowed for use by patients with renal failure - the drugs are not processed in the kidneys. Treatment can reduce the rate of bone loss and prevent fractures that develop due to primary osteoporosis or associated with the use of glucocorticosteroids.
Osteoporosis (symptoms in women disappear when using a number of medications) cannot be cured with medications, however, it can be transferred to a stage of stable remission.
This is done using:
- Calcitriol;
- Alphacalciferol;
- Osteogenon - recommended for accelerating the healing of fractures, not suitable for the treatment of systemic disease;
- Bivalos - accelerates the recovery processes in the bones, reduces gaps in them, the general course of therapy is 2-4 months.
Types of osteoporosis
- postmenopausal – manifests itself during menopause, when female sex hormones are produced in insufficient quantities;
- senile – occurs after 65 years as a result of aging and wear and tear of the body, decrease in body weight and bone strength;
- corticosteroid – caused by long-term use of hormones;
- secondary - develops as a result of complications after diabetes mellitus, cancer, chronic renal failure, lung diseases, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, chronic hepatitis, Crohn's disease, long-term use of aluminum preparations.
At-risk groups
Most susceptible to the disease:
- women during menopause;
- aged people;
- people leading a sedentary lifestyle;
- women with menstrual irregularities;
- people with short stature;
- people with low weight;
- people with thin bones;
- people taking corticosteroid hormones, anticonvulsants, heparin, thyroxine, products containing aluminum;
- people with a genetic predisposition.
Classification of joint pathology
The disease has several stages. Often the problem is discovered in the second stage. Stage 2 osteoporosis is characterized by certain symptoms. You can suspect a diagnosis if the following factors are present:
- Low patient stature;
- Frequent fractures of small joints;
- Long-term absence of conception;
- Age-related changes;
- Stooping and low weight of a person;
- Lack of menstrual cycle;
- Long lactation;
- Heavy bleeding during menstruation.
Experts have found that the disease is often found in people who are short. Normally, people grow until they reach puberty. Correct growth is more than three centimeters per year. With low growth, the patient exhibits improper absorption of microelements entering the body. This entails a violation of the structure of the skeleton, muscle frame and hormonal imbalance. If a doctor observes a person with short stature, he prescribes an additional blood test to check the level of calcium salts.
Various degrees of porosis are found in people with a history of frequent fractures of small bones. A tendency to fractures occurs due to poor absorption of minerals.
People whose relatives have problems with brittle bones should also be more careful. If several fractures occur within a short period of time, an examination for calcium salts is necessary.
Osteoporosis of varying degrees is also detected in patients with long-term infertility. Lack of conception indicates abnormal activity of the gonads. The disease can be stopped only after undergoing a thorough examination by an endocrinologist and gynecologist. The risk group also includes men with poor sperm count. They should visit an andrologist every six months.
The majority of patients are elderly people. In old age, the work of all systems and organs slows down. There is a gradual decrease in hormonal and mineral levels. For this reason, older people need to undergo an annual medical examination. It will detect the disease at any stage.
Patients with low weight also cause concern. If a person does not gain weight for a long time with proper nutrition, he needs a medical examination. You should also visit a surgeon if you have severe stoop. This problem is observed against the background of weakness of the spinal column. The disease develops when the absorption of microelements into the bloodstream is impaired.
During the examination, several stages of the disease are established. The second stage is common. At this stage, individual areas of the bone shell become loose. The advantage of this stage is the rapid stopping of bone destruction. During an X-ray examination, the doctor detects small echogenic areas on the membrane.
There is also a faint glow of the joints. The edges of the frame are blurred in some photographs.
The third stage is characterized by a stronger glow of the entire shell. Individual bones change their shape. Also in the third stage, pain occurs. Pain in osteoporosis is reduced only with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory substances. Analgesic drugs provide relief for a short period of time.
At the fourth stage, frequent decompression fractures of the joints are detected. In a certain group of people, the joints are completely destroyed. External changes also appear. Joints and bones become deformed. The person loses the ability to move.
A feature of osteoporosis is considered to be low diagnosability. The problem can only be detected through examination by a specialist.
Main symptoms of pathology
The disease may not have clinical manifestations for a long time. Most patients seek medical help in advanced stages of the disease.
Osteoporosis (symptoms in women begin with fractures, prolonged bone healing and repeated violations of the integrity of bone tissue in the same areas) is quite difficult to diagnose in the early stages.
Upper and lower limbs
The development of pathology is accompanied by fractures:
- radius - a large load on the arms or emphasis on them when falling during icy conditions;
- fibula - for injuries, bruises.
Femoral necks
The defeat begins with an altered gait accompanied by unpleasant sensations during movement. Fractures in the femoral neck are associated with peculiarities of the anatomical structure - constant increased load, tissue wear and household injuries provoke fractures.
Spine
Signs of spinal column destruction include:
- decrease in height – up to 3 cm;
- prolonged, statistical pain in the spine;
- hump formation;
- slouch.
Changes in the structure of the organ negatively affect all internal organs. With sudden movements in the back area, painful sensations occur.
Joints
Damage to the joints is accompanied by:
- aches and pain syndrome;
- weather dependence – the body’s reactions to weather changes;
- rapid fatigue during physical activity.
The disease can cause tooth loss, massive graying, and deformation of nails.
Exercises to fight osteoporosis
The American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons recommends performing a set of simple exercises to prevent osteoporosis. To get results you need to exercise regularly, at least 3 times a week.
Be sure to walk at a fast pace and ride an exercise bike. If possible, you should go dancing and swimming. Weight-bearing exercises can help combat bone loss.
According to Dr. Rebecca Jackson, a professor at The Ohio State University in Columbus, to prevent osteoporosis, you need to do exercises that put alternating pressure on the bone.
Important: if osteoporosis has already begun to develop, then before starting training, you need to consult a doctor and choose a safe sport.
Why does regular exercise strengthen bone tissue?
Many studies have been conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of exercise in preventing osteoporosis. According to data provided by Texas Woman's University in Denton, bone density in the lumbar vertebrae increased by 1.3% in young women. This happened thanks to a training program that was implemented over 27 weeks.
Another group of women did these exercises for 10 years. During this period of time, their bone tissue density increased by 8-10%. The comparison was made with women who did not engage in sports.
Rebecca Jackson and colleagues evaluated the effects of exercise in 14 older women. In their lives, they moved little and led a predominantly sedentary lifestyle. The experiment lasted 8 months. 7 patients exercised on exercise bikes for half an hour 3 times a week. A control group of women did not do this. In exercising patients, there was an increase in bone density.
Based on the data obtained, it was possible to calculate that over 3 years of regular training this figure can increase by 5-10%.
Loading the bones is a mandatory part of physical exercise.
How to avoid fractures with osteoporosis?
In 1994, an article was published in the New England Medical Journal. It says older people can avoid falls and fractures by keeping their blood pressure under control by taking prescribed medications. According to Mary Tinetti of Yale University, women should increase their physical activity levels and do exercises to improve their flexibility. and maintaining balance.
Other recommendations for creating a safe environment for an elderly person include the presence of:
- handrails and rugs in the bathroom;
- lighting;
- stable crutch;
- comfortable shoes.
Causes of osteoporosis
Basically, the disease develops due to a lack of calcium caused by various reasons.
Osteoporosis occurs as a result of:
- smoking for a long time;
- alcohol abuse;
- digestive problems;
- metabolic disorders;
- hereditary disease;
- hormonal imbalance (especially during menopause);
- taking synthetic corticosteroids;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- poor muscle development;
- lack of calcium or vitamin D;
- excessive consumption of meat - it contains substances that wash away calcium from the body;
- excessive consumption of coarse fiber foods (cabbage, bran, rye bread, potatoes) - reduces calcium absorption;
- abuse of caffeine contained in coffee, tea, Coca-Cola, chocolate – increases the excretion of calcium from the body.
Provoking factors
By itself, age can already be considered a fairly strong cause of osteoporosis. But there are also factors that help increase the likelihood of such a violation of the bone structure in the body:
- Smoking. Smoking leads to intoxication of the body, which means that almost all cells and tissues are clogged with combustion products. This has an extremely negative effect on metabolism in bone structures.
- Lack of calcium intake from food. A poor diet is generally one of the most common provoking factors. High-calorie, delicacy foods with a minimum of vitamins and minerals lead to the depletion of all tissues of the body. Eating refined foods won't bring healthy bones.
- Excessive consumption of coffee and tea. Love for coffee and tea cannot be called bad habits. Moreover, according to the latest data, these drinks protect the vascular system from many pathologies. But coffee and tea wash away much-needed microelements from the body. By the way, it is especially harmful to drink coffee and tea during meals, especially if the dishes contain foods high in calcium, which a person consumes to help his bones. The active components of coffee and tea (in particular, tannin) bind to calcium and make this trace element unavailable for absorption. In addition, tea and coffee are drinks that have a diuretic effect, and this quality negatively affects mineral balance.
- Long-term use of anticoagulants. Such drugs help thin the blood, but at the same time the opposite effect is observed when there is a decrease in the accumulation of nutrients and other components in the blood.
- Physical inactivity. The bone structure is strengthened under loads, and in their absence its blood supply is reduced. The quality of both bones and all surrounding tissues deteriorates.
- Metabolic diseases. Hypo- and hyperthyroidism are frequent companions and causes of osteoporosis. By the way, these diseases are also more common in older women.
Coffee and tea are drinks that interfere with the absorption of many vitamins and microelements, and therefore they should be drunk separately from meals.
And, of course, heredity plays an important role. If close relatives have been diagnosed with this disease, the likelihood of its occurrence increases significantly.
Contraindications
Increased levels of calcium (hypercalciuria) and vitamin D in the body, immobilization due to osteoporosis or limb fractures, renal failure.
There are a number of diseases for which it is not recommended to take medications containing vitamin D.
These include:
- hypercalcemia (increased calcium levels in the blood),
- active form of pulmonary tuberculosis,
- stomach and duodenal ulcers,
- acute renal or liver failure,
- chronic kidney and liver diseases,
- some heart diseases (congenital defects, coronary artery disease, myocarditis, myocardiopathy).
Prevention of osteoporosis
To prevent osteoporosis, you need to eat right and lead an active lifestyle.
You can also periodically take supplements containing calcium and vitamin D.
But it is best to use fish oil as a source of vitamin D, and ground eggshells for calcium: they are perfectly absorbed by the body, unlike drugs.
Main directions of prevention
The health of a woman who has reached the age of 50 largely depends on the lifestyle she led in childhood and youth. The skeleton is formed before the age of 25, and this process occurs in parallel with an increase in bone density. Women with a hereditary predisposition to osteoporosis should know that exercise, swimming, walking and any moderate physical activity helps strengthen bones.
Also, you should pay attention to the quality of food. The daily diet should consist of foods rich in vitamin D, calcium and phosphorus
To eliminate risk factors, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle!
Prevention of osteoporosis during menopause
Women who have crossed the forty-year mark are required to visit a gynecologist and therapist at least once a year. It’s better to visit these specialists once every six months. This rule is also relevant if menstruation has already stopped completely or the period between the dates of menstruation has increased.
Hormonal levels in women who have entered menopause change in any case, even if the menopausal symptoms are mild. After 50 years, it is recommended to do X-ray or, preferably, ultrasound densitometry once a year. Almost all parts of the body where there are bones are subject to scanning.
Particular attention is paid to: spine, radius and femoral neck
With the onset of menopause, a woman will have to reconsider her lifestyle, which implies not only the exclusion of unwanted foods and drinks from the diet.
For example, drinking four or more cups of coffee per day leads to increased calcium excretion. But if you drink it with milk, this will partially offset the harm from caffeine. If the habit of drinking coffee cannot be eradicated, then you can find a worthy alternative in the form of barley drink or chicory. Prevention of osteoporosis also includes:
- Maintaining a normal weight for your age and height. Excessively thin women are at greater risk of becoming victims of osteoporosis than overweight women. But doctors recommend finding a “golden mean”.
- To give up smoking. According to medical statistics, bone density in smokers is 10% less than in non-smokers.
- Refusal of alcoholic drinks. Alcohol negatively affects bone metabolism and reduces calcium absorption.
- Moderate physical activity. Physical activity should be optimal. Each human body has its own maximum capabilities. Therefore, the intensity of physical activity should be determined individually.
- Taking special medications that control metabolic processes, ensuring high absorption of calcium in the gastrointestinal tract, guaranteeing the deposition of this mineral in the bones.
- Eating fish oil and flaxseed oil. These are Omega-3, 6, 9 acids of natural origin. For ease of use, they are sold in the pharmacy in the form of capsules. Fish oil and flaxseed oil contain large amounts of vitamin D, which increases calcium absorption.
Why is it dangerous for humans?
If the bone substance loses strength, then a fracture can occur when falling from a height of one’s own height, and in severe cases, even during an awkward movement, a sharp turn, or lifting a heavy object. Since there is not enough calcium supplied, or its integration into the bones is impaired, their damage takes a long time to recover. There may be malunions and curvatures. This causes further difficulties in movement, which becomes a cause of disability.
For a young person, this threatens loss of ability to work, restrictions on social contacts, and problems in family life.
This disease is called the silent killer because it occurs latently for a very long time. The resulting fractures are often the first sign of advanced bone destruction.
If osteoporosis is not detected in time, damage to the spine and femoral neck can cause death.