The mucous membrane of the uterus is covered with a thin layer, medically called the endometrium. During menstruation, the layer is naturally renewed. Under certain unfavorable conditions, extensive covering of the walls of the uterus and cervical canal with foreign formations - endometrial polyps - is possible. The phenomenon often occurs in women of childbearing age, so when identifying a problem, you need to know what to do when planning and how to behave during an already formed pregnancy. In any case, the woman will need a mandatory consultation with a specialist and an explanation of the nuances arising from the pathology.
The presence of a polyp does not exclude conception. A pregnant woman needs serious examinations at various stages, including assessment of the condition of the uterus and genital tract. Since the concepts of polyp and pregnancy are compatible, careful monitoring and constant supervision of a specialist over all processes occurring in the body is necessary. The appearance of a growth during pregnancy usually does not affect the mother and child. Doctors usually do not take any measures to eliminate it, but only monitor it throughout the entire period.
If there is no pregnancy, but it is planned and polyps are identified, it is imperative to remove the formations, undergo a full examination and get the results, and only then return to conceiving a baby.
Definition of a polyp
The functioning of the female body, in particular its reproductive component, is directly dependent on the level of natural sex hormones. Deviations in indicators become the reason for the formation of growths called polyps. Neoplasms can be actively growing and have a large scale both in the uterine cavity and outside it - in the cervical canal. This most often occurs when:
- prolonged hormonal imbalance;
- after childbirth;
- frequent abortions.
The growth of a polyp can be affected by disruptions in the body and hormonal imbalance between progesterone and estrogen. This becomes the beginning of hyperplasia - the process of the appearance and intensive growth of tissue cells that form growths in the uterine cavity. The formation has the shape of a flat growth or mushroom with a small stalk. There are single polyps or groups ranging in size from 1-2 mm to 2 cm or more.
Detection of pathology of the internal uterine layer interferes with the process of conception and often becomes a reason for infertility. The formed polyp clogs the fallopian tubes, which reduces the patency of the genital tract and prevents the fertilized egg from reaching the uterus and attaching to its walls. Conception is also impossible due to hormonal imbalances, which lead to a shortage of mature eggs. The endometrial layer is damaged, which during conception can inhibit the development of the fetus or lead to artificial termination of pregnancy.
How does endometrial polyp affect pregnancy? Removal of the polyp will need to be postponed and surgery performed after childbirth so that the patient can carry the child to term normally.
Why do polyps appear in the uterus?
There may be several reasons why growths form inside an organ. You can never predict why and when this disease will manifest itself. But some categories of women are at particular risk.
- With hormonal disorders. If there are surges in sex hormones, including during menopause, then the risk of developing such a disease increases.
- With blockage of blood vessels. If the vessels, of which there are a huge number, become clogged, then epithelial cells join them. A mushroom-shaped growth appears.
- With inflammatory processes in the form of endometriosis, cervicitis. In tissues, during inflammation, the number of leukocytes increases, which simultaneously reduce the attack of infection, but contribute to the increase in endometrial cells.
- With injuries to the uterine cavity, abortions are a thing of the past. At the site of cleaning, scarring occurs in the form of a scar, which over time becomes overgrown with endometrial cells.
- With diabetes and excess weight, which often accompanies each other.
- With ovarian dysfunction. With ovarian dysfunction, an increased amount of estrogen in the blood is observed not only during the first period of the menstrual cycle (normal), but throughout the entire month, without stopping. Some parts of the endometrium do not exfoliate, remaining in the uterine cavity and growing further.
In some women, taking a drug based on tamoxifen provokes the formation of polyps.
Reasons for appearance
The causes of polyps are not fully understood. But some circumstances have been identified under which their origin and growth occur. These include:
- hormonal imbalance;
- vascular pathology;
- frequent diagnostic scrapings;
- inflammation of the genital organs;
- abnormalities in the functioning of the immune system;
- traumatic injuries;
- unsuccessful births and abortions.
They are provoked by:
- endocrinology diseases;
- bad heredity;
- high sugar;
- high blood pressure;
- excessive production of estrogen with excess weight;
- with inactivity, stagnation forms in the pelvic area;
- frequent use of pharmaceuticals;
- failures in exchange processes;
- presence of infection in the body;
- incomplete detachment of the placenta during labor;
- venereology diseases;
- abortion caused by pharmacological drugs;
- incorrect use of the spiral.
Signs
A polyp during pregnancy is characterized by certain symptoms. If they appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Otherwise, the symptoms threaten the health of both the woman herself and, in pregnancy situations, the fetus in the womb. Doctors indicate the following symptoms:
- cycle failures;
- bleeding after menopause;
- infertility;
- failed IVF;
- discharge between periods.
The manifestation of growths in the early stages of pregnancy is accompanied by:
- spasmodic pain in the sacrum;
- discharge with blood after examination by a gynecologist;
- the appearance of white mucous discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- spotting and bleeding after exercise;
- aching and nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
Can it bleed?
A polyp may bleed during pregnancy. This symptom appears due to injury caused by medical equipment during examination or during sexual intercourse. The condition is very serious, because through damage in the walls of the growth, an infection enters the body, threatening health. If bleeding occurs due to a polyp of significant parameters or it is located in the cervical canal, then a mandatory consultation with a doctor is necessary. Bloody discharge is inconsistent; it can appear or disappear, be intense or moderate.
How does a polyp get eliminated?
Most often, polyps do not interfere with childbirth; they come out on their own during delivery, together with lochia and the inner lining of the uterus.
Surgical removal of a polyp of the cervical canal during pregnancy is a radical option in cases of severe inflammation, necrosis of the polyp, and heavy bleeding.
Women during pregnancy are prescribed gentle techniques:
- laser polypectomy with the introduction of an endoscope to monitor the process of cauterization of damaged vessels;
- thermocoagulation;
- targeted hysteroscopy – a painless, low-traumatic option for polyp removal during gestation;
- cryodestruction with burning of the polyp with liquid nitrogen;
- constriction in the case of localization of the tumor near the external pharynx by throwing a cord over the leg of the polyp and twisting it for subsequent tissue necrosis.
Curettage of the cervical canal in women during pregnancy is not performed.
If a polyp bleeds during pregnancy, what should you do? Doctors prescribe gentle removal methods at any trimester: cauterization with electric current, laser, radio loop.
After removal, the doctor redirects the tissue sample for histology to exclude or confirm the malignancy of the formation, and redirect the woman for consultation with an oncologist.
Diagnostic measures
An integrated approach is required to diagnose and detect tumors in the uterus. It is formed from the data collected by the doctor during the examination of patients and the results of examinations. For this:
- examination is performed using gynecological speculum. The procedure identifies tumors in the cervix or uterine prolapse;
- To identify polyps in the body of the uterus, an ultrasound is necessary. Inspection and palpation are not able to determine the appearance of neoplasms. During the examination, the doctor pays attention to the parameters of the uterus, expansion, thickness of the endometrial layer, which necessarily increases when a polyp forms;
- hysteroscopy is performed. The technique is considered the most informative and is performed by introducing a microscopic device with a video camera into the cavity. The procedure allows you to accurately recognize the location, quantity, configuration and color of growths;
- lab tests. When performing hysteroscopy, the body of the polyp is pinched off and a histological examination of its cells is performed;
- diagnostic curettage is performed for subsequent laboratory analysis of cells;
- metrography. Necessary x-ray examination of the cavity and body of the uterus. Contrast is used to help detect uneven endometrial layer and small foreign growths.
All diagnostic techniques require modern equipment and appropriate knowledge of doctors. Modern clinics have the ability and the necessary resources to guarantee an accurate and timely diagnosis of a polyp at an early stage, referring to the detected slight thickenings and formations in the endometrium.
Types of decidual polyps
Gynecologists distinguish several types of benign formations in order to subsequently recognize their structure and nature during histology analysis.
Worth knowing! Polyps can be true or false. Pseudopolyps are not dangerous and often disappear without a trace in women giving birth after the birth of a child. True polyps are a reason for a biopsy with the removal of a piece of tissue from the cervical canal and subsequent study in order to timely detect cancer.
Based on their structure, polyps are divided into 3 types:
- glandular – safe with a loose structure, formed as a result of hormonal imbalance;
- fibrous (dense neoplasms) prone to malignancy, more often observed in women during menopause or serious hormonal abnormalities;
- glandular-fibrous, consisting of glandular cells and connective tissue, requiring excision;
- adenomatous - the most dangerous (precancerous) requiring immediate removal and observation by an oncologist.
Possible complications
The appearance of formations during pregnancy can be characterized by serious complications and consequences. Among them:
- dysfunction of the ovaries;
- inflammation of the endometrium;
- the appearance of cancer cells;
- pathologies of fetal development;
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- placental abruption;
- inflammation;
- uterine rupture;
- heavy bleeding;
- sepsis;
- problems during childbirth caused by weak uterine contractions;
- freezing of the child.
If the endometrial polyp is small in size and there is no growth or transformation during pregnancy, then it is not dangerous for the unborn baby. Exceptions occur only in situations where:
- malignant growths. Their mandatory removal is necessary;
- the polyp becomes inflamed and becomes a source of infection. Measures are taken to eliminate inflammation;
- leads to dilatation of the cervix, causing early labor and miscarriage. A pessary is used (a ring to hold the body of the uterus or suturing is performed, the sutures from which are removed before childbirth).
Pregnancy and the occurrence of polyps
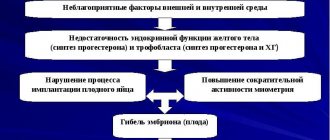
At different phases of the menstrual cycle, a woman’s body produces either progesterone or estrogen.
As a rule, the body reacts to the fertilization of an egg with rapid hormonal changes. However, it happens that the balance of hormones is disturbed. As a result, the cells begin to grow excessively - hyperplasia is formed. As a consequence of this, a growth forms on the walls of the cervical canal or on the cervix. When the endometrium grows, conception is difficult. Often it is the uterine growth that causes infertility. The neoplasm leads to blockage of the fallopian tubes, reducing their patency. The fertilized egg cannot enter the uterine cavity. Even if a fertilized egg manages to penetrate the uterus, it cannot attach to its wall as a result of the altered structure of the endometrium. The likelihood of miscarriage increases.
In some cases, endometrial growth interferes with ovulation.
When planning the birth of a baby, you need to get rid of the growth and only then make attempts to conceive.
How to treat
If, as a result of research, polyps are found in the uterus during pregnancy, then there is no need to worry. Doctors believe that growths are dangerous only if they tend to grow rapidly. To control the process, frequent and systematic visits to the gynecologist will be required; special attention should be paid when particularly dangerous indicators are detected. There are cases when there is no need to treat a polyp, since the polyp disappears on its own or is removed after childbirth. In any case, medical supervision is necessary and includes prescribing and taking certain medications. As a rule, this is a progesterone substitute - Duphaston. Antibacterial treatment is possible if the cause of growth is inflammation of the genital organs. To avoid miscarriage or premature birth, doctors do not perform surgery during pregnancy. In this case, patients are prescribed regular ultrasound, which allows them to monitor indicators of transformation, changes in parameters, and are also recommended to maintain sexual rest and avoid excessive stress.
Types of uterine polyps
Types of polyps in the uterus
- Neoplasm in the cervical canal. This type of outgrowth does not interfere with fruiting, so such pathologies are rarely removed. With hormonal changes in the body due to a new condition, they often disappear on their own without medical intervention.
- Polyp in the gallbladder. Gallbladder polyposis does not threaten the mother and child, provided the function of this organ is preserved.
- Decidual polyp is a consequence of pregnancy. Against the background of hormonal changes, the structure of the endometrium changes, a decidual growth appears, which is easily confused with a number of other varieties. After childbirth, the structure of the uterine endometrium normalizes - it disappears.
Polyp during early pregnancy
If a formation on the walls of the uterus or in the cervical canal was not detected before conception, and the fertilization of the egg occurred successfully, the embryo is fixed and develops normally, then there is a possibility that everything will go well and will not cause problems for the woman and the developing embryo. You will need to be under the supervision of a gynecologist throughout your pregnancy. If inflammation appears, the parameters of the polyp increase, bleeding or spotting and other processes that threaten the woman’s health are observed, then doctors prescribe surgical removal of the formation at 12-14 weeks of pregnancy. If a polyp appears in the cervical canal and to exclude the development of infections in the short term, it will be enough to use antibacterial therapy.
Consequences for the fetus
An uncomplicated polyp of the cervical canal does not pose a danger to the course of pregnancy, especially when it comes to the growth of decidual tissue. This formation exists until childbirth and usually comes out safely along with the placenta.
A polyp, accompanied by frequent bleeding, disrupts the normal rhythm of life of the expectant mother. Hospitalizations and examinations, worry about the baby - all this plunges a woman into a state of chronic stress. And even the belief that the polyp itself is not dangerous does not always help to cope with natural fears. In such a situation, the only method of solving the problem may be to remove the polyp.
An infected polyp that arises against the background of chronic cervicitis threatens intrauterine infection of the fetus. The risk is small, but the expectant mother should not ignore the symptoms of inflammation and postpone a visit to the doctor. In case of infection, local anti-inflammatory treatment is indicated, taking into account the duration of pregnancy, or removal of the polyp.
A polyp with suspected malignancy is a serious problem, and wait-and-see tactics are not justified here. After the biopsy, the question of surgery is decided. Such a complication may become an indication for termination of pregnancy. Childbirth with polyps of the cervical canal is carried out through the natural birth canal, if the formation does not block the exit from the pelvis. Otherwise, preliminary removal of the formation will be required. For large polyps, a caesarean section is performed.
Is it possible to get pregnant with uterine polyps?
Will it be possible to get pregnant with an endometrial polyp? A question that often worries nulliparous women does not have a clear answer. According to statistics, there are many cases of successful conception in the presence of a polyp in the uterus. If the endometrium grows unnaturally, pregnancy is possible; the polyp does not interfere with conception. If the pregnancy is planned in advance, you will first need to undergo an ultrasound, visit a gynecologist, and undergo tests. If a polyp is detected, you need to undergo a course of treatment, and, if necessary, remove the polyp. If conception occurred in the presence of minor foreign bodies in the uterus, then regular visits to the doctor will not hurt you. The problem must be kept under control, since the growth can lead to placental abruption, which can lead to a decrease in the flow of blood into it. It’s hard to imagine, but development may stop, nutrition and oxygen supply to the embryo may be disrupted, hypoxia will appear and there will be a threat of miscarriage.
Treatment tactics for cervical canal polyp
Outside of pregnancy, all polyps found in the lumen of the cervix must be removed. An exception is made for small formations - up to 5 mm. If the polyp does not bother you and does not interfere with the conception of a child, you can leave it alone. The growth of education, the appearance of bloody discharge or infertility are reasons for a polypectomy.
Polyp removal methods:
- Traditional polypectomy using a conchotome.
- Laser polypectomy - the operation is performed with a high-precision laser.
- Loop excision - excision of the polyp along with the tissues of the cervix using a thin loop.
- Cone-shaped excision of the cervix (conization) is performed for large polyps, as well as suspected malignant degeneration of the formation.
The removed polyp is sent to the laboratory for histological examination. The bed of the formation is cauterized with a laser, radio waves or other available method.
During pregnancy, expectant management is indicated. If the polyp does not bleed or bother you, do not touch it. Removing the formation by any, even the most gentle, method can provoke a miscarriage or premature birth. Most cervical polyps come out on their own during childbirth. If the polyp remains, its removal after the birth of the child is indicated.
Indications for polypectomy during pregnancy:
- Frequent bleeding due to a polyp.
- Suspicion of malignancy.
- Polyp infection.
- Impossibility of childbirth through the natural birth canal.
Polypectomy can be performed at any stage of pregnancy, but is usually performed after 16 weeks. The procedure takes place under local anesthesia. After the polyp is removed, the cervix will bleed for 1-2 weeks. This is a normal condition that does not require special treatment.
Complete healing of the cervical mucosa occurs in 4-6 weeks. During this period it is recommended:
- Avoid intimacy until the postoperative wound has completely healed.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Do not take a bath, limit yourself to a daily shower.
- Do not lift heavy objects, avoid physical activity.
- Do not douche.
According to indications, after removal of the polyp, conservation therapy is carried out. Antispasmodics and tocolytics, magnesium preparations and other drugs are prescribed, taking into account the duration of pregnancy. If there is a threat of miscarriage or premature birth, hospitalization is carried out in a hospital.
A polyp of the cervical canal is a condition that can significantly disrupt the course of pregnancy and childbirth. If a pathology is detected, it is necessary to undergo a full examination by a doctor to make sure that the formation does not pose a danger to the fetus. If the polyp persists after childbirth, you definitely need to get rid of it as soon as possible.
The nuances of removing growths during pregnancy
Surgery to remove a growth on the endometrium or cervical canal at any stage of pregnancy is not recommended, as there is a risk of harm to the fetus. But there are cases when there is an urgent need for it. There are factors and prerequisites that require immediate surgery, despite pregnancy. These include:
- growths over 1 cm;
- polyp growth by 2 mm per month;
- intense bleeding, with threat of miscarriage;
- the appearance of additional processes;
- danger of developing infection and contamination of the fetus.
To eliminate the problem, several methods of surgical intervention are used, the most effective of which are hysteroresectoscopy or hysteroscopy.
In other cases, removal of polyps in the uterus during pregnancy is excluded. The only possible operation is to cut off the growth in the cervical canal. Anesthesia is required to provide pain relief. It must be selected personally, taking into account the characteristics of each patient. The genital organs are disinfected, the cervical canal is spread apart and the growth is cut off using a hysteroscope.
How is polyposis treated in pregnant women?
If the mother and fetus are not in danger, doctors prefer a wait-and-see approach: careful hygiene, sexual rest, avoidance of heavy physical activity, hormonal therapy, which minimizes the risk of miscarriage and stops the growth of the polyp.
Surgical intervention on a polyp during pregnancy is highly undesirable, as it can lead to spontaneous abortion. The exceptions are the following cases:
- growths larger than 1 cm, continuing to grow by more than 2 mm per month;
- heavy bleeding;
- high risk of fetal infection.
For safe and effective removal of polyps, we recommend the radio wave method using the Surgitron device. Its undeniable advantage is its bloodlessness and prevention of re-formations.
Pregnancy after removal
If conception is impossible due to a growth in the uterine cavity, then pregnancy occurs very quickly after hysteroscopy of the polyp. After receiving the histology results, the doctor prescribes hormonal therapy aimed at reducing the development of relapse. Treatment with drugs lasts from 3 to 6 months, after which pregnancy planning can begin.
Pregnancy after surgery to remove an endometrial polyp, despite rumors and risks, is possible for most women. The work of doctors and the desire of a woman will bring the happiness of motherhood closer.
Polyps in the uterus and pregnancy – a death sentence for infertility?
The growth inside the uterus in the form of a tubercle of tissue is not felt by the patient herself, but is a complex obstacle in the path of the sperm.
Depending on the degree of the disease, there is a possibility of pregnancy, but for this you must undergo a course of treatment and diagnosis. Often, in order to become a mother, surgery is necessary.
A polyp is considered a benign formation, prone to recurrence and growth, but does not pose a threat to a woman’s life. However, sometimes such growth can turn into malignant tumors, so removal of the polyp and hormonal therapy is the best option for preventing complications
Can a polyp be confused with pregnancy?
In unclear situations, a knowledgeable and experienced doctor will be able to distinguish a polyp from pregnancy. To do this, it is enough to have basic knowledge and have the results of tests and diagnostics. Establishing the correct diagnosis is not difficult, since endometrial growths differ from the fetus in shape and shade. The fertilized egg is round and dark in color, while the polyp is lighter. Misdiagnosis in such cases is extremely rare. But, if you still want to be sure, then contact another specialist to re-confirm.