What do you mean by frequent urination?
Normally, 75% of the fluid consumed per day is eliminated from the body during urination. Urine accumulates in the bladder, whose volume is about 300 milliliters. As soon as an organ becomes full, a signal is sent to the nervous system to empty it.
In a healthy man, this happens about 5-6 times a day, while in a person with pathology, the urge to empty the bladder occurs up to 10-15 times a day, sometimes the impulses arrive immediately after going to the toilet.
Risk factors for this pathology are:
- Age – after 50 years, the risk of this symptom increases.
- Diet - people who mainly eat meat have a predisposition.
- Place of residence - most often, problems with emptying the bladder occur in people living in areas with an unfavorable environmental situation and increased background radiation.
- Genetic predisposition - if there are men in your family who suffer from kidney or prostate diseases, then the risk of developing an unpleasant symptom is higher.
The sensitivity of nerve receptors can increase for various reasons - from hypothermia to high emotionality. A pathology is considered to be a condition when a man is unable to hold urination for 10-15 minutes.
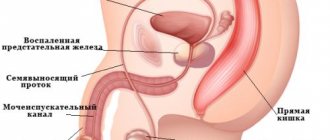
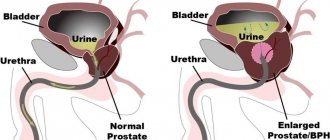
But frequent urination in men occurs not only due to irritation of the receptors - the function of urine secretion is affected by the prostate gland. In this case, urgent therapy is required. The prostate can increase in size and delay the excretion of urine or, on the contrary, contribute to more frequent emptying of the organ.
Frequent urination without pain in men: features of the condition
The term “urinary disorders” summarizes all manifestations of changes or disorders in bladder emptying. The amount of daily urine is also important. The reasons for deviations are varied. They can be caused by inflammatory, mechanical, neurogenic or psychogenic etiological factors.
The release of urine is usually a physiological phenomenon. Examination of urine is one of the oldest diagnostic procedures in medicine. General criteria for urination:
- the amount of urine excreted daily;
- color;
- frequency.
It is necessary to pay attention to the amount of urine excreted. Daily urine production depends on fluid intake. It varies on average from 1000 to 1500 ml per day.
Deviations from a medical point of view:
- Anuria: less than 100 ml per day.
- Oliguria: less than 500 ml is excreted per day.
- Polyuria: the daily amount of urine exceeds 4 liters.
If urine output increases, the first cause may be excess fluid. It is possible that the patient consumes too much water or teas. The disorder often occurs in young people. Sometimes they unknowingly take in large amounts of water because they become thirsty during physical activity.
Normal urination
Normally, a person excretes approximately 800 ml of urine per visit to the toilet. Healthy urination is about 1.5 liters per day. The frequency depends on several factors.
It is important to know! If urine output per day is extremely low and visits are limited to 3-4 times per day, this indicates oliguria. With pathologically frequent urination, the patient excretes up to 4-5 liters per day.
Natural causes
Polyuria is present when the daily urine output exceeds two and a half to three liters. The most common cause of frequent urination without pain in men is an increase in fluid and alcohol intake.
Many people believe that they need to drink a lot. However, this also leads to increased urine output. Polyuria may occur because renal function is impaired. Thus, kidney disease is a common cause of increased fluid excretion. Polyuria is one of the first symptoms of various pathologies of the endocrine system, including diabetes mellitus and adrenal insufficiency.
The most common reasons:
- Diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2. In the early stages of the disease, thirst, fatigue, and increased frequency of urination are common. The latter can be explained by an increase in sugar content in the urine.
- Chronic renal failure.
- BPH.
- Testicular diseases.
- Prostatitis.
- Palpitations (tachycardia) caused by heart disease or hormonal disorders.
- Low potassium levels (hypokalemia). A decrease in the content of this element in the blood often occurs in connection with treatment with diuretics and after severe vomiting. Other symptoms of hypokalemia may include fatigue, muscle pain and weakness.
Increased fluid intake is the main reason for increased urine output. Excessive use of water is also found in mental illness (eg, obsessive-compulsive disorder).
Rare reasons:
- Diabetes insipidus. The disease is associated with a violation of the regulation of fluid balance by hormones in the body. The production of an antidiuretic substance, which counteracts excessive excretion of water, is reduced. This leads to the excretion of up to 5-10 liters of urine per day. The result is pathological thirst.
- Addison's disease, or adrenal insufficiency. Typical clinical findings include fatigue, loss of appetite, weight loss, dizziness, increased skin pigmentation, low blood pressure and fever.
It is important to know! A common cause of urinary disorders in men is usually the lifestyle - beer, as well as a psychological disorder (psychogenic polydipsia) associated with compulsive drinking of liquid. Some patients may experience water poisoning.
Nocturnal polyuria in men is a condition in which the volume of urine produced at night exceeds (depending on age) 20-33% of the total 24-hour urine. The disease is one of the most common symptoms of nocturia.
Alarming symptoms of frequent urination without pain
If the patient experiences sudden changes in the amount of urine (more than 2-3 liters per day) without increased fluid intake, it is recommended to consult a doctor. Even if there are other symptoms such as fever, weakness, dizziness or general malaise, you should visit a doctor.
Risk of consequences
If you urinate more frequently, your risk of developing electrolyte disturbances increases. In a normal person, the urine excretion function maintains an optimal water-salt balance. In patients with diabetes insipidus, it quickly becomes unbalanced. Patients develop cardiac arrhythmias, muscle twitching, dizziness and headaches. Women suffer from pain in the urinary tract and experience discomfort in everyday life.
Causes of the symptom
There are several reasons for frequent urination in men of any age; non-drug treatment or pills are used depending on the disease that led to the appearance of symptoms. In extreme cases, even surgery can be used. Conventionally, the root causes can be divided into groups.
- Physiological reasons. These include drinking large amounts of fluids, choosing drinks with a diuretic effect, and hypothermia. If there is no illness that affects the functioning of the bladder, then urination becomes more frequent for 1-2 days. This condition does not bring additional discomfort.
- Pathological causes are ailments that affect the excitability of nerve receptors located on the walls of the bladder, the functioning of the kidneys and prostate gland.
Most often problems arise when:
- inflammatory processes;
- benign or cancerous tumors;
- infectious lesions of the urethra or bladder;
- diabetes;
- use of diuretics;
- stress, hypothermia, severe cold;
- overactive bladder.
Before prescribing medications for frequent urination in men, the doctor collects an anamnesis. It is important for him to understand when the problems began and what events preceded them.
For example, suspicion of infectious organ damage will be in those men who had unprotected sexual intercourse several days before the appearance of signs of pathology.
If physiological reasons lead to frequent urination, then treatment is not prescribed.
Frequent and painless urination
Frequent urination without pain is a symptom of a huge number of diseases. Let's try to consider some of them.
Physiological causes in adults and children
Urination may become more frequent when:
- taking large amounts of spicy, sour and salty foods, alcohol. There will be no pain, an increased volume of light urine is released, more than 200 ml at a time. Other symptoms include only mild tickling in the urethra during urination;
- stress, tension, excitement: a large daily amount of urine of normal color is released, while the single volume of urination is not increased. There may be a feeling that you need to urinate more, although the person has just gone to the toilet;
- pregnancy: in this case, other signs indicating this condition will be observed;
- along with menstruation;
- after freezing - for several hours.
Pathological causes
They can be roughly divided into those that cause predominantly nighttime and increased urination around the clock.
Frequent urination at night can be caused by:
- Cardiovascular failure. In this case, swelling will be noted in the legs, sometimes even higher (on the abdomen), interruptions in the functioning of the heart or pain in it, and shortness of breath.
- Diabetes. Increased thirst and dry mouth are also noted; the skin becomes dry, wounds and cracks easily appear on it, which do not heal well.
- Adenoma and carcinoma of the prostate. Symptoms other than nighttime urination may not be noticed. During the day, a man can feel quite well, only urinate in small portions. You can get more information about these and other male diseases that lead to frequent urination from the article: The main reasons for increased frequency of urination in men.
A person will urinate equally often both during the day and at night when:
- diabetes insipidus. At the same time, he is constantly tormented by thirst and drinks a lot, but, unlike his sugar “brother,” there is no dry mouth, dry and itchy skin;
- cystocele (prolapsed bladder): more common in women who have given birth. In addition to painless frequent urination, urinary incontinence will also be noted: when coughing, lifting heavy objects, laughing, and later during sexual intercourse;
- spinal cord injuries and tumors;
- weakness of the muscles that make up the wall of the bladder. The disease begins in childhood and is characterized by no changes in the general condition, but only frequent urination in small portions of urine, as well as a strong urge to urinate;
- uterine fibroids. In this case, painful periods, intermenstrual bleeding, and a large volume of monthly blood loss will also be noted;
- taking diuretics.
What additional symptoms may appear?
During the appointment, the urologist always asks the patient about additional signs of disease. They can be used to make a diagnosis.
- There is no discomfort with an overactive bladder. This disease is caused by brain tumors or trauma to this area, age-related changes or obstruction of the urinary tract.
- If the symptom manifests itself mainly at night, then in most cases a diagnosis of prostate adenoma is made. The tumor causes the urine stream to become weak or intermittent, and there is a delay in urine output. If the pathology is not treated, it will lead to involuntary emptying of the bladder at night.
- A rich drinking regime and an abundance of plant foods in the diet irritate the receptors of the bladder; due to the abundance of fluid, it quickly becomes overfilled. Physiological characteristics lead to the fact that a man empties his bladder more often in the first half of the day. In both situations there are no other symptoms.
- Acute pain in the back and groin - signals stones or sand in the kidneys. This disease is characterized by a false urge to urinate.
- Urogenital infections and sexually transmitted pathologies lead to painful urination, burning and discharge from the urethra.
- In diabetes mellitus, blood glucose levels increase. This symptom can only be noticed through a blood test; it is always prescribed by a urologist. Additionally, a man is recommended to write down the amount of fluid consumed over the previous 2-3 days before taking it.
These are just some of the symptoms that accompany a man’s main problem. Additionally, weakness, chills, fever and other signs of inflammatory processes may be observed. Immediate treatment for frequent urination is required if pus or urine is released along with urine.
Important! You should not put off visiting a doctor if you have incontinence, as this is a clear symptom of tumor formation.
Treatment with folk remedies at home
Traditional methods for the treatment of frequent urination are considered by modern medicine as a possible addition to the main therapy, which can be introduced only after preliminary approval of all prescriptions with a urologist, andrologist and other specialized specialists. It is impossible to completely replace doctor’s orders with them!
- Medicinal tea from St. John's wort and centaury. Take 1 teaspoon of dried and crushed St. John's wort and centaury in equal proportions, mix them and brew like classic tea, strain and drink hot 3-4 times a day for 1 month;
- Wonderful vegetables. Take 1 small bunch of fresh, just picked parsley and regular carrot tops. Finely chop these greens and mix. Pour boiling water over 1 tablespoon of the mix and let it brew until it cools, then strain and consume within 24 hours in 4 doses. The procedure can be repeated daily for 2 weeks;
- Infusion of medicinal herbs. Take 1 teaspoon each of chamomile, bearberry and corn silk in equal proportions. Mix them and pour 1 liter of boiling water, letting it brew for 15 minutes. Strain and drink half a glass 3 times a day for 3 weeks.
Diagnosis of urinary disorder
To determine the cause of a symptom, it is not enough to interview the patient. It is possible to determine how to treat frequent urination in men only after diagnostic procedures. It includes:
- biochemical and detailed blood tests;
- study of urine composition;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, pelvic organs, prostate;
- bacterial culture of a smear from the urethral mucosa;
- computed tomography of the kidneys (prescribed for acute pain, blood in urine).
Urinalysis can be more than just general. For differential diagnosis, a study using the Zimnitsky method is more useful. With it, all urine per day is collected for analysis - each portion in its own container. The method allows you to get an idea of the total volume of urine. Additionally, it is necessary to record each urination, which helps to know the interval.
The patient may also be deprived of fluid for a period of 4 to 18 hours, while urine is taken every hour for analysis to determine osmolarity. The last diagnostic method is used to determine what led to frequent emptying of the bladder - diabetes insipidus or nervous strain. So it is used as a clarifying method in case of poor general analysis.
Diagnostics
The frequent urge to urinate in men creates a certain discomfort, because a person has to be close to the toilet, which is not always possible. Due to constant trips to the toilet at night, there is a high risk of insomnia, irritability, decreased performance, decreased overall tone and chronic fatigue.
In addition, the lack of timely treatment for this pathology causes the underlying disease to worsen and become chronic. Therefore, at the first sign of increased frequency of trips to the restroom, you should consult a doctor and undergo the necessary tests.
When going to see a doctor, you need to know as much as possible about the nature of your problem. He may ask questions to determine the cause of the disease. It will be necessary to answer the following questions:
- When did the frequent urination start?
- What could be the reasons, was anything unusual noticed?
- What is the basis of nutrition, are there any bad habits?
- What is the number of sexual partners, are contraception used?
- Are there hereditary diseases?
In addition, an appointment may be issued for the following studies: blood test, blood biochemistry, urine test. Additionally, an instrumental study must be performed if the analysis shows an unclear picture of the underlying disease.
Features of treatment of infections
For diseases of an infectious nature, doctors recommend using medications for frequent urination in men. They will be the safest way to treat urinary excretion disorders in a child. Drugs are prescribed based on diagnostic data.
The most common infectious diseases include:
- cystitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- prostatitis.
They are characterized by the proliferation of infectious agents in the urethra. Any of these pathologies can occur acutely or chronically. In the second case, the symptoms will be subtle and more effort will be required for diagnosis and treatment.
For infections, antibiotics, uroseptics and immunomodulators are prescribed. Diagnosis helps in choosing the right antibacterial tablets for frequent urination: urethral smear culture and urine analysis.
If a patient needs help urgently, doctors choose broad-spectrum antibiotics. For specific inflammation, they are used extremely rarely, since pathogens (gonococci, chlamydia and other microorganisms) are not sensitive to them. Most often, men are prescribed a whole list of remedies to ensure a comprehensive approach. First of all, it contains antibiotics:
- "Ciprofloxacin";
- "Acyclovir";
- "Monural";
- "Furadonin";
- "Erythromycin";
- "Ceftriaxone";
- "Doxycycline."
Among uroseptics, the most commonly used are preparations of plant origin or synthetic products made on their basis. The most commonly used medications are with the following names:
- "Urolesan";
- "Phytolysin";
- "Canephron."
You can buy any of these medicines - they practically do not differ in their effect on the body. They received great reviews.
Immunity stimulants help increase the resistance of the body's defenses to infectious pathogens and prevent diseases from becoming chronic:
- "Timalin";
- "Gelon";
- "Polyoxidonium";
- "Ribomunil".
Many doctors recommend giving patients warm baths for the lower torso and limbs with the addition of:
- potassium permanganate solution;
- decoctions of chamomile flowers, string;
- infusions of sage and calendula.
As an additional method of treatment, you can ingest infusions and decoctions from plants called natural antibiotics:
- cranberries;
- lingonberries;
- wormwood;
- bearberry.
These herbal remedies improve well-being, but using them alone is not enough. Additionally, you can take multivitamin complexes and plant extracts of aloe, eleutherococcus, and ginseng.
The use of combinations of the listed agents allows for treatment of infectious pathology at several levels, preventing it from becoming chronic. The recommendations given can be applied when treating at home. In hospitals, only pharmacological therapy is most often used.
Similar drugs are used to treat cystitis in women.
Treatment
Features of treatment for frequent urination depend on the diagnosis. In most cases, a conservative approach is used, which is a complex of drug therapy, physiotherapy, diet, exercise and traditional medicine recipes.
Drug therapy
Taking medications should be started only after the diagnosis has been clarified. The attending physician should prescribe medications. Depending on the cause of frequent urination, the following medications may be used:
- Antibiotics. Such treatment is required if the disease is infectious. The antibiotic is selected after identifying the pathogen and its susceptibility to the drug. Until such information is received, broad-spectrum drugs may be used. More often they resort to cephalosporins, penicillins, and fluoroquinolones. Outside the period of exacerbation, drugs of the nitrofuran series are used - most often Nitrofurantoin.
- α-blockers. Such drugs are actively used in urology for the treatment of urinary disorders, prostatitis, and prostate adenoma. This could be Doxazosin, Tamsulosin.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Such drugs are prescribed to relieve inflammation and pain. This could be Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Nimesulide.
- If NSAIDs are ineffective, glucocorticosteroids are used. These medications are steroid hormones and are used in short courses.
- Antiprotozoal agents. Such drugs are prescribed in the presence of infection. Metronidazole is often used.
- Canephron N. This drug is a diuretic. It is prescribed for chronic infections of the genitourinary system and kidney inflammation.
- Carbamazepine. This drug is an antiepileptic, but it also reduces the production and excretion of urine. It is prescribed for diabetes insipidus.
- Vesicare. This drug is an antispasmodic and is prescribed for overactive bladder.
- Minirin. The drug is used for diabetes insipidus, it reduces the volume of urine excreted and the frequency of urination.
- Nativa. The drug is prescribed for nocturnal polyuria, primary nocturnal enuresis in children over 5 years of age, and diabetes insipidus (central origin).
- For atrophic changes in the bladder due to age, Desmopresin is prescribed.
- Vitamins. Vitamin therapy is needed to strengthen the immune system, fight infection or inflammation, normalize blood circulation and metabolic processes. With frequent urination, they resort to B vitamins, ascorbic acid, vitamin E, carotene, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Antiseptic solutions. Such products are usually used to rinse the bladder. The procedure is performed using a catheter through which the drug is injected and then released. This is done until a clear liquid is obtained.
All medications must be prescribed by a specialist. It is necessary to strictly follow all its instructions, especially the medication regimen and its duration. Treatment should be continued even after the disappearance of unpleasant symptoms, unless otherwise recommended by the doctor.
Physiotherapy
Complex treatment for frequent urination often includes physical therapy. The prescribed procedures depend on the cause of the pathology and may include the following areas:
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- balneotherapy;
- hydrotherapy, medicinal baths;
- magnetic therapy;
- amplipulse therapy;
- ultrasound;
- laser therapy;
- UHF therapy.
Visiotherapeutic procedures are appropriate only after a diagnosis has been made. Many techniques have contraindications, including the presence of kidney or bladder stones, acute inflammatory process.
ethnoscience
Alternative medicine can help with frequent urination. It should be used as an additional direction in treatment, but not replacing it. For frequent urination, the following recipes are effective:
- Take equal parts cherry stems and corn silks, steam with boiling water and leave for half an hour. Take chilled several times a day.
- Grind the dried pomegranate peel into powder. Take a pinch of the product three times a day, adding it to a teaspoon of water. Treatment lasts 5 days.
- Grate fresh onions and place the resulting pulp on cheesecloth. Apply this compress to the lower abdomen and hold for several hours. Repeat the procedure every day until recovery.
- Steam 20 g of crushed dried mint with 1.5 liters of boiling water and boil for 10 minutes. Then leave until cool. Take a glass three times a day.
Diet
If you experience frequent urination, you should make some changes to your diet:
- Avoid red meat, chocolate, caffeine and baked tomatoes. These products irritate the bladder.
- Enrich your diet with apples, bananas, cherries, raspberries, sweet potatoes, beans, and brown rice.
- Maintain drinking regime. Most of the liquid should be drunk in the first half of the day.
- Limit salt intake.
- Avoid fried, spicy, smoked foods, marinades, herbs and spices.
How is adenoma treated?
Prostate adenoma develops over a period of one to 10 years. It undergoes three stages. Conservative treatment can be used at the initial stage of the disease. It should be started when there is an urge to empty the bladder, a feeling of an incompletely emptied bladder, and a weak stream of urine.
Pharmacological drugs will not be able to completely remove benign. The tumor, which is called an adenoma, they will only stop its growth. The drugs must be used for life.
With a benign tumor, the tone of smooth muscle structures increases, so patients are prescribed antispasmodics from the group of alpha-blockers for life:
- "Tamsulosin";
- "Doxazosin";
- "Silodosin";
- "Terazosin".
After 2-3 weeks you can see an improvement, but if you stop taking it, the positive effect will disappear. During therapy, side effects from the drugs used are observed: low blood pressure, headaches, dizziness.
For the best result and quick relief from an unpleasant symptom, doctors supplement treatment with agents that reduce the sensitivity of nerve receptors to testosterone production.
This group includes: “Prostamol”, “Permixon” and “Flutamide”. Additionally, you need to take medications from the hormonal group. They regulate the production of testosterone, which prevents the growth of the organ and reduces its weight. Today the following are used for therapy:
- "Cyproterone";
- "Duprasteride";
- "Finasteride".
Most patients need to take drugs from each group simultaneously to achieve results. A combined approach provides the best results.
The disadvantage of all of these remedies is the high cost of treatment due to the fact that a long course or constant treatment is required. Therefore, many men agree to undergo surgery to remove the tumor at an early stage in order to cure the disease immediately.
Preventing frequent urination
By eating a balanced diet and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you can moderate the amount of urine you produce.
Habit adjustments may include limiting your intake of alcohol and caffeine, and avoiding foods that irritate the bladder or act as diuretics, such as chocolate, spicy foods, or artificial sweeteners.
Fiber-rich foods relieve constipation, which can indirectly improve the passage of urine through the urethra, since constipation often causes the rectum to put pressure on the bladder and urethra.
Drug treatment of other pathologies
Adenoma and infections are the most common pathologies of the excretory system, causing frequent urination in men. Doctors choose non-drug therapy or tablets from another group for other ailments - hormonal imbalances, pathologies of the nervous system. For diagnosed urolithiasis, a combined approach includes:
- Following a special salt-free diet.
- Lysis procedure - stones are dissolved directly in the bladder, and then they are excreted along with urine.
- Taking medications: “Urodan”, “Etamide”, “Blenmaren”, “Allozyme”, “Uralit”. The selection of drugs is carried out based on the salt composition of the conglomerates.
Pathologies of the nervous system can also lead to increased urine output or the appearance of false urges. In this case, the symptom cannot be eliminated without treating the underlying disease.
If pathology of the nervous system has led to the development of bladder overactivity, then the doctor may advise taking cheap and relatively safe drugs with an antispasmodic effect - “No-shpu” or “Papaverine”. For stress, antidepressants are used - Duloxetine or its analogues.
Any type of diabetes and age-related bladder dysfunction require lifelong prescription of hormonal medications. Their selection is carried out only after a blood test.
The dosage is also prescribed individually. In elderly patients over 50 years of age, hormonal drugs should stop the development of tissue degeneration characteristic of menopause; an example of such a drug is Desmopresin.
Causes of frequent urination in men
Frequent urination can be a sign of various pathologies. The following reasons for this violation are possible:
- Pathologies of the urinary system (the bladder and kidneys are most often affected):
- urolithiasis disease;
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- renal failure;
- kidney stone disease.
- Urogenital infections (mycoplasmosis, chlamydia).
- Overactive bladder.
- Endocrine system disorders:
- diabetes;
- hormonal imbalance;
- natural aging of the body and wear and tear of the endocrine system.
- Pathologies of the prostate gland:
- prostatitis;
- adenoma (benign hyperplasia);
- carcinoma (malignant neoplasm).
- Congestive heart failure.
- Nervous system disorders:
- neurosis;
- chronic stress.
- Spinal cord damage and nerve conduction disorders.
- Taking medications with a diuretic effect or urinary disorders are among the adverse reactions.
The causes of frequent urination may not be pathological. This is often associated with products that have a diuretic effect:
- tea (especially green) and coffee;
- lemons;
- cranberry juice;
- ginger;
- watermelon;
- melon;
- eggplant;
- parsley;
- celery;
- beer.
Urination may become more frequent when a man consumes any of the listed foods or drinks constantly and in large quantities. The reason may also lie in the peculiarities of the drinking regime.
Other therapies
Other types of therapy can be used as auxiliary types of therapy and in the absence of effect from the use of tablets for frequent urination. Alternative remedies include: traditional medicine, physiotherapy and surgery. You cannot prescribe procedures for yourself.
All prescriptions should be made only by a doctor. You should not contact centers that promise to use warming instead of drugs for frequent urination in men.
Before any therapy, diagnostics must be carried out, only then the prescribed method will help and not harm.
Important! During infectious processes, it is forbidden to apply heating pads or hot compresses to the groin area - microbes multiply more actively in warmth.
Prevention
Prevention measures are as follows:
- timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases (genitourinary, endocrine, cardiovascular and others);
- maintaining an adequate drinking regime;
- conducting gymnastic exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles (if they are weak);
- maximum avoidance of hypothermia of the body, being in a draft;
- carrying out activities for general hardening of the body, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, etc.
Operation
In advanced cases and in the absence of effect from traditional therapy, surgical intervention is used. It helps to get rid of frequent urination in men, which develops against the background of:
- the appearance of cancerous tumors;
- adenoma;
- the formation of large stones in the bladder.
Before the operation, the patient undergoes a more detailed examination. It determines the size and shape of neoplasms and accurately indicates their location. The patient requires preparation before and after the intervention.
Some manipulations, for example, crushing stones, are carried out using the endoscopic method - it is less traumatic. When choosing it, the recovery period is reduced several times.
Symptoms
Frequent urination caused by natural phenomena is not characterized by the presence of other signs of illness.
This is a natural reaction of the body and is not a pathological condition.
If frequent urges occur due to illness, they are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain and discomfort during urination occur due to inflammation and swelling;
- false urges are a sign of complete blockage of the urethra with a stone or compression by an enlarged prostate gland;
- discharge indicates the presence of infection;
- renal colic occurs when stones pass through the urinary tract;
- elevated body temperature, weakness and malaise are common symptoms of inflammation;
- blood, mucus, pus in the urine indicate the addition of bacterial flora or damage to the walls of the organs of the urinary system;
- Erectile dysfunction occurs when the prostate is damaged.
Clinical picture
In order for a doctor to make a diagnosis as accurately as possible, it is important for him to evaluate the clinical picture of the disease.
In the case of frequent urination, the clinical picture consists of the following factors:
- At what time of day is the problem most acute? If the patient often goes to urinate exclusively during the day, he is diagnosed with “pollakiuria”, if at night - “nocturia”. In the second case, most of the daily urine is excreted at night.
- Is there any pain, discomfort or any unpleasant sensations?
- How often do the urges occur? With some pathologies, a person goes to urinate literally every ten minutes.
- How much urine is released each time you go to the toilet?
- Are there any additional symptoms: fever, discharge, itching, burning, thirst, weight loss, increased fatigue, etc.?
- Has the urine changed color or does it contain impurities?
Try to answer these questions at home, the day before your doctor's appointment. To ensure you don't forget anything, use a notepad and pen and write down your observations. It can be difficult to remember every detail in a limited amount of time.
Diagnosis and treatment
Frequent urination that occurs due to natural causes (drinking too much, caffeine) does not require treatment. Also, a similar symptom occurs during pregnancy due to pressure on the pelvic organs. In pregnant women, this phenomenon goes away on its own; you need to see a doctor if it is accompanied by a burning sensation. If the cause is mental stress, a psychotherapist solves the problem.
All other cases require examination and testing. Therapy will consist of highly targeted drugs (antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodics, etc.). Surgery is needed extremely rarely, as a rule, for adenoma and in severe cases of overactive bladder.
Due to the fact that this symptom is unpleasant, most patients strive to get rid of it as quickly as possible. But, as in the case of other diseases, there is a proportion of sufferers who rely on traditional medicine and self-medication. Doing this is dangerous, as you risk aggravating the disease. Most of the diseases leading to pollakiuria and nocturia can be treated within a few weeks and disappear without a trace with proper treatment.
Urinary system in women
Urinary system in women
Although the process of going to the toilet is considered an intimate thing, it is necessary to tell your doctor about the changes occurring in the body. You can’t think that the doctor will shame you or even won’t understand. Forget this nonsense and feel free to contact your doctor.
A person should consume 2 to 2.5 liters of water per day during normal physical activity. This includes water in the form of free liquid and in the form of food. In total, an adult woman's body contains about 54% water, and a man's body contains 61%. It is difficult to overestimate its importance for the human body.
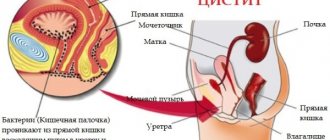
- The main organs of the urinary system are the kidneys. They not only remove water from the body, but also help filter and remove toxins. The kidneys are located on the sides of the spine, in the pelvis.
- The renal pelvis collects urine from the kidneys and discharges it into the ureters.
- The ureters are tubes that carry urine into the bladder.
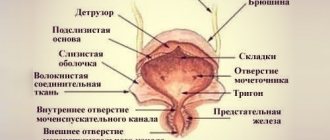
- The bladder stores urine and is located in the lower abdomen.
- The urethra, in fact, secretes urine out. It has the appearance of a tube, much shorter than that of men. In men, the length of the urethra is 23 cm, in women it is only about 5 cm. In most cases, this is due to a large number of diseases of the urinary system in women.
This is interesting: How and with what to treat thrush in women and men at home: symptoms, medications, prices
Nature of treatment
How to overcome this disease is decided by the doctor in accordance with the examination results.
The nature of the treatment of the pathology is determined by its main cause. For a disease such as diabetes, the goal of treatment will be to control the acceptable level of blood sugar. Antibacterial therapy is used to treat inflammation of the urinary organs.
Bladder disorders are treated with special physiotherapeutic procedures (therapeutic gymnastics).
Cystitis and urethritis are treated on an outpatient basis - the patient undergoes rehabilitation at home, under the supervision of a specialist.
Pathologies in the form of acute pyelonephritis or newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus often require hospital treatment.
Frequent urination is successfully treated in the women's and men's health clinic. Our doctors have earned the trust of patients and gained experience in solving this problem.
What to do if you experience frequent urination?
The lower abdomen and lower back hurt, a burning sensation appeared in the urethra during and after intercourse, the color of the urine has changed (cloudy, with blood, with pus) - immediately consult a urologist. Body temperature elevated to 38-39 degrees and dark urine are common signs of pyelonephritis.
If the color of your urine is lighter than usual, there is no pain or burning, and your overall health is normal: check your diet. If you are taking medications, carefully read the “side effects” and “contraindications” sections in the instructions.
When to see a doctor
We have come to the conclusion that in all cases, except pregnancy, frequent urination is either a symptom of a disease or indicates that lifestyle changes are needed in life.
You should see a doctor if:
- Pain appeared in the lower abdomen, albeit minor;
- Weakness appeared in the body;
- Blood appeared in the urine;
- For nocturia (the need to empty the bladder at night);
- If the urine is darkened or purulent discharge is observed in it;
- The temperature rose to 38°;
- Discharge appeared.
The doctor will examine you, conduct a survey, take a smear for analysis, and then make a final diagnosis.
Possible associated symptoms
The presence of accompanying symptoms depends on the cause of frequent diuresis. In a physiological state, the color of urine and its composition may change slightly. For pathological causes, disease-specific symptoms are present. It is rational to consider the symptoms accompanying frequent urine output, depending on the pathology that caused it:
- Prostatitis: discomfort and/or pain in the perineum, at the root of the penis, without irradiation (spread) to other areas, decreased potency, up to loss, rarely - bloody or cloudy discharge from the penis;
- Prostate adenoma: the presence of severe discomfort, pain in the perineum, the root of the penis, in the sacral or pubic area, decreased sexual function, changes in the composition of sperm, urine, pathological discharge;
- Prostate cancer: discomfort and pain in the groin, perineum, at the base of the penis; in advanced stages, severe pain. There is a violation of sexual function, changes in the composition of sperm, urine, stool retention, pathological discharge from the penis, a steady decrease in body weight, progressive weakness;
- Diabetes mellitus: increased appetite and increased thirst, decreased tolerance to physical and mental stress, deterioration of general condition when eating foods rich in carbohydrates, visual impairment. Infections that are difficult to treat often develop;
- Diabetes insipidus causes severe disturbances in mineral balance, severe thirst, and changes in the nervous system. Patients are prone to convulsions, loss of consciousness, diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- Pyelonephritis: severe intoxication (fever, chills, weakness), changes in the composition of urine, the presence of bacteria in it, pain;
- Glomerulonephritis: protein metabolism disorders, edema, decreased appetite, decreased performance, weakness, changes in urine composition, progressive increase in blood pressure, development of renal failure;
- Cystitis: discomfort and pain in the bladder area, weakness, moderate or slight increase in temperature, pain when urinating. In severe cases, blood appears in the urine;
- Urethritis: pain and pain when passing urine, a moderate or slight increase in temperature, possible redness of the penis (especially the head), the composition of urine changes, there may be pathological discharge;
- ICD: pain along the urinary tract (up to unbearable), slight increase in temperature, changes in the composition of urine, pathological discharge from the penis is possible;
- Chronic renal failure: severe disturbances in the metabolism of minerals and proteins, swelling, disruption of the nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular systems, pain and discomfort in the lumbar region;
- Urogenital infections - the main sign of a sexually transmitted infection is a change in general condition, the presence of pathological discharge from the penis.
Diseases affecting urination
The main reasons for increased diuresis are the presence of diseases listed in respectively. section. They affect the urinary system differently, have different pathogenesis (mechanism of development) and lead to different consequences. To better understand the physiology of frequent urination, it is necessary to consider these diseases.
Urolithiasis disease
Urolithiasis means a disease characterized by impaired kidney function, changes in the composition of urine and the formation of stones in the organs of the urinary system. It is worth knowing that stones can form not only in the kidneys, but also in the bladder. The disease can be asymptomatic for a long time, which is why it is often diagnosed at advanced stages.
Pathological symptoms appear when stone(s) migrate through the urinary tract or are blocked. In 1 case, the main symptom is a strong pain syndrome, in 2 – a violation of urination, up to a complete stop. In most situations, there is an increase in diuresis, but with a decrease in its volume.
Diabetes
The disease develops due to insufficient production of insulin in the cells of the pancreas or due to its inability to be absorbed by the body. In 1 case, the leading cause is a decrease in the population of specific insulin-producing cells of the gland. In 2 – a decrease in the number of specific receptors for the hormone on cell membranes. Regardless of the cause, severe metabolic disorders and progressive development of pathological symptoms are observed.
Urogenital infections
A number of urogenital (genitourinary system) infections can cause urinary disturbances, either in the direction of increased or decreased frequency. They often cause prostatitis, cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis and other diseases. With isolated damage to the genital organs, specific symptoms come to the fore, and not diuresis disturbances.
Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is a nonspecific inflammation of the kidneys, with a predominant localization of the pathological process in the tubules of the organ. The main cause of the disease is a bacterial infection. The renal pelvis, calyces, and interstitial tissue are often affected. In addition to urination problems, there are signs of inflammation
Glomerulonephritis
It is an inflammation of the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys, often of autoimmune origin. An increase in diuresis is rarely observed, since the dominant symptoms are metabolic disorders and kidney function.
Chronic renal failure
At an advanced stage, the disease is characterized by an increase in urine output. This is due to severe dysfunction of the organ, when water and salts dissolved in it are not absorbed by the body and “fly” through the kidneys. The condition is accompanied by severe concomitant symptoms.
Urethritis
The male urethra is a very thin and long canal. If in women infections immediately enter the bladder, then the special structure of the urethra in men allows infections to spread to the urethra without reaching the bladder.
Many factors can lead to urethral disease:
- Viral infections;
- Bacterial infections;
- STD;
- Candidiasis caused by taking antibiotics;
- Narrowing of the canal lumen due to congestion in the pelvis;
- Irritation to chemicals (soap, spermicidal lubricants);
- Mechanical damage to the penis (trauma, masturbation, rough sexual intercourse).
An increased urge to urinate is accompanied by sensitivity and pain in the penis, and it may even become swollen. Itching and unpleasant odor occur in the genitals.
After laboratory results of urine and a smear from the urethra, the doctor prescribes broad-spectrum antibiotics or local treatment with ointments and solutions.
Prostatitis
A purely male disease , inflammation of the prostate tissue, can occur in acute or chronic form. Prostatitis begins with frequent trips to the toilet, which do not bring relief. Sharp, sudden urges to “urinate” resemble those that occur when drinking large amounts of liquid. In this case, diuresis does not differ in increased volume, but on the contrary, there is a reduction in the portion of urine.
to frequent urination : a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, sexual dysfunction, pain in the perineum and scrotum, and pain during urination.
Treatment is carried out with complex therapy: antibiotics, immunomodulators, physiotherapy, prostate massage and radical lifestyle changes.
Diagnostic methods
At the first stage, the attending physician collects a detailed history of the patient’s life and illness to establish risk factors. After which he conducts an external examination to identify other signs of a particular disease.
To detect the nature of the pathology, the urologist may prescribe the following laboratory and instrumental examination methods:
- a general and biochemical blood test allows you to identify markers of inflammation - increased leukocytes, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, dysproteinemia, fibrinogen;
- in a general urine analysis, the level of leukocytes, erythrocytes and the presence of pathogenic flora are of leading importance;
- the level of antidiuretic and adrenocorticotropic hormone allows one to detect pituitary pathology;
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography of the brain is performed to detect tumor processes that can cause such a clinic;
- the levels of potassium, calcium, sodium and chlorine make it possible to assess the filtration function of the kidneys, disturbances of which occur when the glomerular apparatus is damaged;
- bacteriological culture helps not only to identify the causative agent of the disease, but also to select the correct treatment, since its sensitivity to antibiotics is determined;
- PCR is carried out to detect the DNA of the pathogen and its antibodies;
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys and pelvic organs shows anatomical changes that occur during diseases;
- Digital rectal examination of the prostate gland allows you to detect malignant, benign tumors and prostatitis.
Which doctor should I contact?
First, you need to figure out how many times you need to go to the toilet for such trips to be considered frequent. We found out that a person drinks up to 2.5 liters of liquid per day. For such a norm, he will empty the bladder 3-7 times. Why does the number of hikes vary so much? Because how often you empty your bladder depends on many factors. Increasing your fluid intake and eating foods that have a diuretic effect will significantly increase the amount of urine excreted and the frequency of going to the toilet.
If the rhythm of life is normal, the amount of fluid you drink has not increased, then visiting the toilet more than 10 times will be considered a pathology. Also, a single amount should not exceed 200-300 ml. At the same time, it became noticeable that such frequent urination interferes with normal functioning and sleep at night, which means it’s time to visit a doctor.
First you need to visit a therapist. The doctor will conduct a detailed examination, feel the bladder, and check the condition of the kidneys. Why should you visit it first? The fact is that frequent urination can be a symptom of a gynecological disease, or maybe a urological one. Next, a competent therapist refers the patient to a highly specialized specialist based on his analyzes and research.
Many women are simply embarrassed to visit a urologist, considering him a specialized male doctor. This is a deep misconception. There should be no embarrassment when it comes to health! A urologist deals not only with male diseases, but with diseases of the urinary and genitourinary system as a whole.
Don't hesitate to contact a urologist
If kidney disease is detected, the therapist may refer you to another specialist - a nephrologist. This is a doctor who deals directly with kidney diseases. If the problem is in the woman’s reproductive system, then she is referred to a gynecologist for further treatment.
It should be remembered that you need to contact at the first symptoms of frequent urination, because the sooner you see a doctor, the faster he will solve this problem.
Causes of pathology
The emptying mechanism is triggered by irritation of the receptors of the bladder and urethra. The muscles of the bladder stretch when filled, which leads to receptors transmitting a signal to the brain about the need to go to the toilet.
When the urinary system is inflamed, receptors transmit signals to the brain much more often, regardless of the fullness of the bladder, so when a man empties, only a few drops of urine may be released.
There are different causes of the disease. Frequent urination may be a symptom of the following diseases:
- inflammation of the prostate gland (prostatitis);
- inflammatory kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis);
- inflammation of the bladder (cystitis);
- BPH;
- stones in the ureters and bladder;
- genitourinary infections;
- infection in the urethra (urethritis);
- diabetes.
Prostatitis
One of the common causes of frequent urination is inflammation of the prostate gland. The desire to urinate with this disease is unbearable and occurs suddenly. As a result of attempts to go to the toilet, only a few drops of urine come out. With prostatitis, problems with potency may appear, emptying the bladder becomes difficult, the lower abdomen hurts, and the urge almost never stops, although the bladder is empty. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by cramps in the groin area and pain, general poor health, and fatigue.
To prescribe the correct treatment, you need to visit a urologist. After identifying the causes and type of inflammation of the prostate gland, he can recommend physiotherapeutic procedures, diet, massage and drug treatment. It is quite possible to get rid of the disease in a few weeks if it has not entered the chronic phase.
Inflammatory kidney diseases
Urination becomes more frequent with pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis - inflammatory processes in the kidneys. These pathologies can also be the causes of this problem in children. Pyelonephritis is accompanied by weakness, high fever, lower back pain and chills. Characteristic symptoms of glomerulonephritis are high blood pressure, blood in the urine, and swelling.
Both diseases are very dangerous if there is no treatment. As a rule, a patient with kidney disease is sent to a hospital, where he is prescribed a set of restorative procedures and a course of antibiotics.
Inflammation of the bladder (cystitis)
The disease is more common in women and children, but also occurs in men. Inflammation may result from hypothermia or infection. Attempts are accompanied by pain, increased body temperature, and weakness. The lower abdomen feels tight and painful, especially after sex. Urine is usually cloudy, with purulent impurities.
To diagnose cystitis, it is necessary to undergo tests, based on the results of which the doctor prescribes treatment. Depending on the nature of the disease and its neglect, methods such as physiotherapy, herbal medicine, antibiotics, etc. can be used.
Prostate adenoma
In this case, a benign prostate tumor occurs. Due to this, the organ enlarges and begins to put pressure on the urethra. Adenoma is more common in older men than in young men.
The initial symptoms of this disease include frequent urge to go to the toilet at night.
If the adenoma is at an advanced stage, difficulties arise in emptying, since urine does not pass well through the urethra.
To prevent the disease from progressing, you need to consult a doctor when the first symptoms appear and begin treatment.
Stones in the ureters and bladder
A constant urge to go to the toilet, as a symptom of urolithiasis, is caused by irritation of the mucous membrane of the urethra and bladder by stones.
Almost always with this disease, bowel movement is accompanied by severe pain. The reason for this is the movement of stones through the genitourinary system.
Before prescribing treatment, the patient undergoes an examination, after which the doctor chooses a method that helps eliminate stones.
Urogenital infections
This symptom is also present if a sexually transmitted disease progresses in the genitourinary system. In patients with gonorrhea, trichomoniasis and chlamydia, the infected genitals and urinary tract are affected. Irritation of the mucous membrane leads to frequent urge to go to the toilet, especially in the morning. Evacuation occurs with pain and burning. The lower abdomen often feels tight. Urine contains impurities in the form of white mucus and blood streaks.
If these symptoms occur, you should immediately seek medical help and undergo a course of comprehensive treatment.
Urethritis
Urethritis occurs due to infection of the urethra. The consequence of this is inflammation of the urethra, leading to frequent urge. The disease can be recognized by acute pain when emptying the bladder, burning and stinging.
If urethritis is left untreated, symptoms may disappear for a while, but then return with complications. The pathology worsens with prolonged exposure to the cold, alcohol abuse, and sexual arousal.
Diabetes
Men suffering from diabetes, in addition to frequent urination, experience symptoms such as:
- strong thirst;
- dry mouth;
- weakness, fatigue for no reason;
- reproductive system disorders;
- constipation;
- inability to have children.
It is difficult to diagnose this disease based on the last three symptoms, since they are similar to the signs of many other pathologies. The main signs to suspect diabetes should be severe thirst and dry mouth.
When the body tries to remove excess sugar, it takes a large amount of water from organs and tissues. This is where thirst, dry mouth and constipation appear.
Diagnosis of the disease
A urologist diagnoses and treats urinary problems. Even though this doctor is considered a men's doctor, this does not mean that women cannot visit him. A urologist can collaborate with a gynecologist when making a final diagnosis, but this is not always necessary.
What examinations need to be completed:
- blood and urine tests (general + biochemistry);
- bacteriological tests of blood and urine;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic/abdominal organs;
- extended examination of the urethra (urethrography);
- kidney urography;
- a study of bladder function, which includes several stages and can only be carried out in a hospital setting;
- Additionally, X-rays, CT or MRI may be prescribed for areas that need to be examined to clarify the diagnosis.
It is not always the urologist who deals with the problem. If there is chronic stress, the patient is sent to a neurologist, in case of hormonal imbalances - to an endocrinologist, in case of heart problems - to a cardiologist.
A urinary diary is very informative. In this case, the patient records the approximate volume of fluid drunk and excreted over a certain amount of time.
Video on the topic
How to get rid of frequent urination? Answers in the video:
If something in the body begins to function incorrectly, a person loses calm, good mood and well-being. Do not expect that frequent urination will stop bothering you on its own - consult a doctor so that the disease does not become a latent form.
Frequent urination is a temporary symptom that can appear against the background of pathologies. This phenomenon is referred to as pollakiuria, and is sometimes accompanied by pain and burning, severe discomfort and a feeling of incomplete emptying. Frequent urination can also be caused by external factors, in which case the symptom goes away on its own in a short time. It is important to distinguish pathology and the normal process of frequent bowel movements from each other.
When the state is natural
A physiological (natural) painless increase in urine output is often observed. It is associated with an increase in its formation and removal from the body. This condition is not accompanied by any pathological symptoms or discomfort. There is also no change in the stream of urine, and no impurities appear in it. In some situations, the color of urine may change.
The physiological increase in urine formation is temporary and quickly normalizes after the provoking factor is eliminated. A natural increase in diuresis (urination) is observed in the following situations:
- Consumption of food and drinks that have diuretic properties;
- The use of medications with a diuretic effect;
- Excessive fluid intake;
- Unhealthy addiction to alcohol (especially beer);
- Stress;
- Mental fatigue;
- Strong negative emotions;
- General hypothermia of the body;
- Consumption of caffeine-containing products in large quantities.
Frequent urination is a normal reaction of the body
The average size of a man's bladder is 250-300 ml. It is considered normal to have 4-5 episodes of urination during the day and one at night.
In some situations, frequent urination is a normal physiological reaction of the body due to:
- hypothermia;
- drinking large amounts of liquids;
- stress, anxiety, chronic fatigue;
- use of diuretic medications (as well as drinks, foods);
- age-related changes after 40 years: in adulthood, more urine is produced at night, which leads to multiple visits to the toilet.
Pathological conditions that cause increased urination
In addition to the diseases listed above, increased frequency of urination can be observed in the following cases:
- Excessive fear;
- Presence of uncompensated injuries;
- Development of withdrawal syndrome – withdrawal syndrome of drugs or drug use;
- For the period of bladder recovery after injury;
- Frequent loss of consciousness;
- Development of status epilepticus – epileptic seizures are repeated one after another. Involuntary release of urine is observed after almost every seizure;
- Impaired urinary control during or shortly after treatment of malignant neoplasms.