Today in our article we continue the women's theme and talk about inflammation of the ovaries, or as it is professionally called oophoritis. To find out initially whether you have inflammation, you need to answer a simple question - do you have pain in the lower abdomen more often than once a month during the period of regulation? If the answer is yes, then we strongly recommend contacting a gynecologist.
Read more about our current illness. Oophoritis belongs to the group of pelvic inflammatory diseases. And, unfortunately, it occurs quite often in young girls and women from 18 to 25-30 years old.
Classification and causes
In gynecology, the term “appendages” is used to collectively refer to the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
Adnexit
Inflammatory processes in the ovaries and tubes proceed in the same way and very rarely develop in isolation, so the disease has received a mixed name - salpingoophoritis (adnexitis).
The lesion begins from the inner layer of the tubes, covers the middle and outer membranes, then flows to the integumentary epithelium of the ovaries. In this case, pathological processes can affect both ovaries (both tubes) or be localized only on one side.
Inflammatory processes in the ovaries and fallopian tubes are caused by infectious pathogens, including sexually transmitted ones. These include:
- chlamydia, gonococci, myco- and ureaplasma;
- staphylococcus, streptococcus, Escherichia coli,
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other pathogenic viruses and bacteria, as well as non-spore-forming anaerobes.
As a rule, these infectious pathogens come from the lower genital tract (ascending infection), so advanced inflammation of the vaginal mucosa (vaginitis, colpitis) and/or external genitalia (vulvitis) will inevitably lead to inflammation of the appendages.
Less commonly, inflammatory pathogens can enter from:
- peritoneum;
- rectum or appendix;
- spread through the bloodstream.
Based on the localization of the inflammatory process, it can be assumed with 90% probability which of the infections caused adnexitis:
- bilateral inflammation is a consequence of damage by chlamydia, gonococci or tubercle bacilli;
- unilateral (right or left) – a manifestation of “activation” of E. coli, staphylococci, streptococci or enterococci.
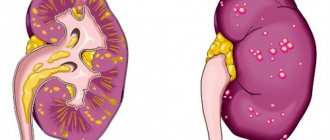
Ovarian cyst
Of the inflammatory diseases that affect only the ovaries, a cyst is the most common type of pathology. An ovarian cyst is a benign neoplasm in the form of a thin-walled “sac” filled with semi-liquid contents, which can occur outside or inside the organ itself.
There are the following types of cysts:
- follicular (functional);
- luteal (corpus luteum);
- hemorrhagic;
- dermoid;
- endometriosis (“chocolate”);
- cystadenoma;
- polycystic syndrome.
In 70% of cases, the cyst arises as a functional feature of “defective” maturation of the egg and goes away by the next menstruation. In other cases, it can not only reach enormous sizes, but also degenerate into a malignant tumor. With early diagnosis and treatment, situations where surgical intervention is required are quite rare.
An ovarian cyst can be a consequence of surgical interventions, inflammatory diseases or hormonal imbalance, including the resulting imbalance of hormones in the body of a pregnant woman.
The cause of the formation of a cyst in the left ovary may be chronic colitis. The causes of a cyst in the right ovary include not only colitis, but also surgery to remove the appendix.
How to treat ovarian inflammation
The sooner a woman begins treatment, the higher the chance of overcoming the disease without complications. You need to take care of prevention and go to the gynecologist as soon as the first symptoms of oophoritis, salpingitis, and adnexitis appear. He will prescribe an ultrasound for the woman, look at the results in the photo, and conduct tests, including culture for bacteria from the vagina. Features of treatment depend on what stage the inflammation is at, what causes it, and how it proceeds. It is extremely dangerous if the disease is detected in a pregnant woman. This is a threat to the life of the woman and the fetus.
Chronic
Treatment of the disease comes down to pain relief, restoration of reproductive function and the formation of beneficial microflora of the woman’s genital organs, which has an anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effect. The doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators, physiotherapy - mud therapy, mineral baths, gynecological massage, acupuncture. Treatment of chronic ovarian inflammation takes a long time and sometimes requires surgical intervention.
- Causes of chronic endometritis - signs, diagnosis, treatment regimen with antibiotics and hormones
- Varicose veins of the pelvis - symptoms and treatment
- Vaginitis - causes, symptoms, diagnosis in women and girls, treatment methods
Acute
Exacerbations of adnexitis and oophoritis are treated in a hospital. It is important to suppress the pathogen as quickly as possible before the disease enters the chronic stage, so antibiotics (based on the results of flora culture) and anti-inflammatory are prescribed. Droppers are used against intoxication, and general strengthening agents are administered - vitamins, antioxidants. To restore sexual microflora, a probiotic is given. Therapy necessarily includes painkillers.
"Provocateurs"
The most common and first cause of inflammation of the appendages is considered to be hypothermia of the body - wearing clothes and shoes that are not in season, ignoring drafts, frequently getting wet feet, prolonged swimming in cold water.
Other predisposing factors that weaken the immune system and trigger the development of the disease include:
- regular large blood losses during menstruation;
- chronic diseases of internal organs and untreated infectious diseases;
- overwork, stress and depression;
- excessive enthusiasm for diets;
- practicing “male” sports or work associated with increased physical exertion.
Women need to pay special attention to the treatment of mechanical tissue damage received during an abortion or during labor. The same warning applies to women who have undergone gynecological surgery.
Provoking factors contributing to the occurrence of ovarian cysts include:
- the appearance of menstruation before the age of 11 years;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- taking the oncological drug Tamoxifen;
- diseases caused by hormonal disorders;
- complications after gynecological operations;
- obesity;
- smoking.
For the formation of an ovarian cyst, which can degenerate into a malignant tumor, the provoking factor is considered to be a female age threshold over 40 years.
Prevention
Due to the fact that sexually transmitted infections are a common and main cause of oophoritis, it is very important to use barrier (condoms) and local (suppositories, vaginal tablets) contraception methods that reduce the threat of sexually transmitted diseases. Indeed, for the development of most sexually transmitted infectious diseases, even a single unprotected sexual intercourse is enough.
Preventive measures include:
- visiting a gynecologist at least twice a year;
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- timely diagnosis of infectious diseases of the genital tract;
- treatment of non-genital chronic infections;
- fortified food;
- refusal of alcohol, nicotine;
- strengthening the immune system.
In case of chronic oophoritis, sanatorium-resort treatment will help to avoid exacerbation of the disease, which has an anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic effect and prevents the formation of adhesions. Timely preventive measures have a general health-improving effect, avoid disability, antibiotic therapy and improve the quality of life.
Thus, ovarian inflammation is a disease leading to reproductive impairment in women. It requires complex and long-term therapy. But drug treatment alone is not enough. To eliminate oophoritis forever, you need to take a different look at your lifestyle, start sticking to a daily routine and eat well.
Generalized characteristics of signs of adnexitis
Common signs of ovarian inflammation are disruption of the menstrual cycle, decreased libido, pain in the lower body, irritation, itching and vaginal discharge.
Pain in the lower abdomen can be acute, paroxysmal or almost continuous, dull and aching. Often women complain of pain in the lumbar or sacral area. All types of pain intensify after cooling, before menstruation (dysmenorrhea). Women receive particular complaints about pain during sexual intercourse.
Symptoms of ovarian inflammation that cause particular discomfort are purulent or serous discharge (leucorrhoea). The released liquids can be colorless, white, gray. In purulent cases they have a dirty yellow or swamp-greenish tint, and are accompanied by an extremely unpleasant odor.
As a result, heavy discharge causes irritation of the mucous membranes of the vagina and severe annoying itching of the external genitalia.
Complications
If ovarian inflammation is diagnosed in women, then treatment must be started as early as possible, that is, if a woman feels symptoms of ovarian inflammation, she must immediately consult a doctor. If the disease becomes chronic or the treatment is carried out poorly or incompletely, there is a risk of complications, which include:
- inflammatory adhesions (blockage of the fallopian tubes, which will lead to the inability to conceive or the risk of ectopic pregnancy);
- cysts;
- cancerous tumors;
- tubo-ovarian abscess (the cavity is filled with pus);
- twisting (rotation) of the ovaries.
You should not think that the inflammatory process will affect only one organ specifically, because the fallopian tubes can gradually become inflamed, the infection will spread to the uterine cavity, which will then lead to the disease adnexitis (if both the ovaries and fallopian tubes are inflamed), salpingoophoritis and endometriosis.
Many people are concerned about the question: Is it possible to get pregnant with inflammation of the ovaries? Yes, it is possible, but the child will become infected in utero, which can lead to complications with his health in the future.
Symptoms of acute adnexitis
Acute inflammation of the appendages is accompanied by:
- fever above 38°C, chills and fever;
- nausea, general lethargy and sharp cutting pain in the solar plexus;
- purulent discharge;
- the appendages increase in size and upon palpation respond with acute unbearable pain, and when the uterus is displaced, painful sensations occur.
The duration of the acute course is 1-2 weeks, after which the disease becomes subacute and then chronic and will require significant efforts from the woman for a complete cure.
The likelihood of pregnancy with inflammation of the right ovary
If the process is chronic and causes complications, the probability of pregnancy is 20-25%.
When the disease is acute, the pathological process has been successfully stopped, the probability of a successful pregnancy is 70-80%.
Manifestations of chronic adnexitis
The chronic course is dangerous due to the absence of pronounced symptoms. In most cases, a diagnosis is made only after a woman consults a gynecologist with the problem of being unable to get pregnant for a long time.
During a gynecological examination, the doctor feels “heaviness” when palpating the appendages; during such manipulation, women complain of moderate pain.
As a result of a chronic purulent inflammatory process, not only the appendages themselves are affected, but also the inner lining of the abdominal cavity - adhesive connections between the layers of the peritoneum occur, which are manifested by constant constipation or diarrhea.
In addition to stool disorder, chronic adnexitis is always accompanied by a faint, blurred pain in the area below the stomach.
Diagnosis of oophoritis
It is not always possible to establish the presence of oophoritis only on the basis of symptoms, since a similar picture is observed in diseases such as appendicitis, ectopic pregnancy, peritonitis, tumor diseases of the uterus and ovaries. To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to know about the presence and methods of treatment of previous diseases, the nature and time of occurrence of ailments, the presence of complications in a woman during childbirth, abortions, and intrauterine procedures. The localization of pain, the nature of the discharge, and the existence of other signs of inflammation are clarified.
A gynecological examination reveals the presence of swelling and tenderness of the ovaries, changes in the mobility of the appendages.
Laboratory tests of blood, urine and vaginal smears can determine the presence of an inflammatory process by the increased content of leukocytes.
An ultrasound of the pelvic organs is done to clarify the nature of the disease.
Bacteriological smear analysis. Allows you to determine the type of opportunistic microorganisms and their sensitivity to various antibiotics.
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) - determination of the type of infection by the presence of antibodies corresponding to it in the blood. The method allows you to roughly assess the nature of the infection. Used to detect chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis and other hidden infections.
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is a method that allows you to determine with 100% accuracy the type of viruses that caused inflammation by their DNA (including detecting human papillomavirus, herpes, the causative agent of tuberculosis, chlamydia and others).
Hysterosalpingoscopy. The method is used to detect structural changes resulting from inflammation. The organs are filled with a special liquid, and then, using ultrasound, they monitor its progress through the pipes and determine their patency.
Laparoscopy. Allows you to examine the uterus, tubes, ovaries. The most effective diagnostic method. An optical device with a camera is inserted through a small hole in the abdominal wall.
Symptoms of an ovarian cyst
As a rule, a functional ovarian cyst does not manifest itself in any way and is diagnosed accidentally during an ultrasound examination of another disease.
Other types of ovarian cysts are characterized by the following symptoms:
- pallor, attacks of dizziness (up to loss of consciousness);
- heartburn and constipation;
- increased hair growth on the body and face;
- painful sensations during sexual intercourse;
- nagging dull pain from the affected ovary during menstruation;
- pain in the lower abdomen that appears after physical activity;
- frequent false urge to urinate and/or defecate;
- intermenstrual bleeding or slight spotting;
- delay or severe disruption of the menstrual cycle;
- sudden loss of body weight;
- an increase in the volume of the abdominal circumference and palpation of the compaction;
- unsuccessful attempts to get pregnant.
In cases of cyst rupture, women complain of nausea and uncontrollable vomiting, spotting appears, body temperature rises sharply and pain appears characteristic of an “acute abdomen”. If such symptoms occur, urgent hospitalization is required.
Causes
The ovaries can become inflamed if they are penetrated by:
- pathogens that cause sexually transmitted infections (eg, gonorrhea agents);
- opportunistic microorganisms (streptococci, staphylococci, candida).
The development of adnexitis is also provoked by:
- childbirth;
- abortion;
- intrauterine devices;
- genital surgery;
- careless performance of diagnostic procedures.
If a woman has a cold in her ovaries, then there is a high probability that an inflammatory process will break out in the glands.
Adnexitis is not the root cause, but a consequence of infectious processes occurring in the uterus and fallopian tubes . Occasionally, pathogens enter the ovaries with blood or lymph if a woman is sick with tuberculosis, tonsillitis, or has carious teeth.
The infectious and inflammatory process moves from the uterus to the tubes. Purulent exudate appears in the fallopian tubes and adhesions form. Their walls become denser, and the lumen narrows.
If treatment is not started at this stage, the gonads are drawn into the inflammatory process. The tube is soldered to the ovary. In severe cases, the peritoneal tissues undergo destructive changes. Ultimately, it all ends with rupture of the fallopian tube and peritonitis.
Adnexitis in pregnant women
Women who were able to become pregnant against the background of a chronic inflammatory process in the appendages should prepare for the inevitable process of exacerbation.
Manifestations of adnexitis will depend on the type of infectious agent. The “first signs of return” of inflammation will be the appearance of leucorrhoea and causeless pain in the lower part of the body.
Particularly noteworthy are cases of not repeated inflammation of the appendages during pregnancy, but direct infection during it.
It is recommended to terminate pregnancy if adnexitis is caused by syphilis or gonorrhea. In other cases, the woman has to make a difficult choice between maintaining the pregnancy and terminating it, since antibacterial treatment of inflammation of the appendages threatens the normal development of the fetus, and at the same time, the pregnancy is very difficult to maintain due to the constant threat of miscarriages.
How to treat ovarian inflammation in women
Drug treatment includes drugs of several groups - anti-inflammatory, to increase immunity, painkillers, antiviral (antimicrobial), physiotherapy. An antibiotic for inflammation of the ovaries in women is prescribed selectively, based on culture results. During the treatment period, a woman should avoid sexual intercourse and alcohol. The woman undergoes the examination together with her sexual partner, and if necessary, he is also prescribed treatment.
Pills
To relieve inflammation of the tissue of the fallopian tube or ovary, drugs are prescribed according to one of the following regimens: Ceftriaxone or Cefotaxime with Metronidazole plus inhibitors, or Ofloxacin or Ciprofloxacin with Metronidazole plus Doxycycline. It is advised to take vitamins E and C, painkillers - Tempalgin, Pentalgin, Analgin, Spazmalgon, Aspirin. Gynecologists use other pills for ovarian inflammation:
- Amoxiclav;
- Azithromycin or Sumamed;
- Biseptol;
- Urotropin;
- Trichopolum;
- Clindamycin;
- Gentamicin;
- Negroes;
Candles
If necessary, the doctor can prescribe topical medications to the woman - suppositories. Depending on the situation, two types are used - anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial (antiviral). Suppositories are characterized by an almost complete absence of side effects, only sometimes patients complain of itching or burning. Chronic inflammation cannot be cured with suppositories alone.
The following types of suppositories have a strong therapeutic effect for oophoritis:
- Hexicon - inhibits the causative agents of oophoritis, is a prophylactic against thrush;
- Betadine is an antimicrobial, antiviral, bactericidal agent, characterized by a gentle effect on the mucous membrane of the genital organs due to the base - gelatin, water;
- any suppositories with indomethacin, propolis, oak bark or walnut - soothe, relieve inflammation, pain and other discomfort from oophoritis.
Folk remedies
Alternative methods of therapy are not recommended as the primary treatment for inflammation of the uterine appendages or ovaries in women. They are effective as an aid to improve the general condition of a woman, reduce inflammation and pain. Folk remedies for women are sitz baths, douching, herbal decoctions (clover, St. John's wort, walnut, coltsfoot, immortelle, etc.). Fees apply:
- Collection against inflammation: immortelle, yarrow, leaves of birch, strawberry, coltsfoot, mint, corn silk and bean leaves - 2 parts each, knotweed, nettle, string, rowan and rose hips - 3 parts. Grind everything in a coffee grinder, take 2 tbsp. l. mixture, pour 0.5 l. boiling water and leave overnight in a thermos. Drink a quarter glass before meals 4 times a day, in courses, for 2-3 months.
- Ingredients for douching: yarrow, sage, rosemary and oak bark in a ratio of 1:1:1:2. Pour 100 g of the mixture into 3 liters of water and heat in a water bath for about half an hour. Strain. Use warm, doing 2 vaginal douches - morning and evening. Or another recipe popular among women: pour a pinch of calendula into a glass of boiling water and leave for 1 hour. Douche daily.
Ovarian cyst in pregnant women
The follicular type of neoplasm and corpus luteum cyst are asymptomatic, do not require treatment and disappear before the 20th week of pregnancy.
A danger to the health of a pregnant woman and to the normal development of the fetus are “asymptomatic” ovarian cysts that are too large (over 6-8 cm) or external forms in the form of a “hat on a stem”. Such neoplasms must be removed between 14 and 16 weeks of pregnancy.
Constant and severe pain in the lower abdomen is caused to a pregnant woman by “chocolate” (endometriotic) types of ovarian cysts. They are dangerous due to possible growth (up to 30 cm) and subsequent rupture.
During early pregnancy, characteristic symptoms that are caused by an increase in the volume of the cyst above 5 cm include:
- pain in the ovaries and pelvic area;
- swelling;
- bloating;
- frequent urination.
An immediate call to the ambulance is necessary in the following cases: severe nausea, vomiting, fever, severe pain in the lower body.
Treatment of oophoritis
The treatment method depends on the form of the disease and the type of infection that causes it.
In the acute form, treatment is carried out in a hospital setting. The woman must remain on bed rest. Cold compresses are applied to the lower abdomen. Antibacterial, painkillers, antipyretics, and restorative drugs are used. Antibiotics for treatment are selected depending on the sensitivity of the infectious agent.
In the subacute form of the disease, quartz irradiation of the area of inflammation is used. For chronic inflammation, drug treatment is used, as well as physiotherapy and medicinal baths.
The following methods are used:
- Hirudotherapy is treatment with leeches to remove adhesions, relieve swelling and inflammation.
- Electrophoresis is the administration of drugs through the skin using a weak direct electric current.
- Gynecological massage. Allows you to eliminate adhesions, increase the tone of the uterus, and restore its normal location.
- Magnetotherapy is treatment with a low frequency magnetic field. Has an anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect.
- Laser therapy, IR, UV irradiation are optical methods for eliminating microorganisms.
Note: If inflammation of the ovaries occurs as a result of a sexually transmitted infection, then both sexual partners should be treated at the same time. Sexual contact should be avoided at this time.
When treating advanced chronic diseases, one has to deal with the presence of complications requiring surgical intervention.
Video: Complications of ovarian inflammation
To prevent oophoritis, it is necessary to promptly treat any inflammatory processes in the body, strengthen the immune system, lead a healthy lifestyle, use condoms, and undergo regular gynecological examinations.
Inflammatory processes often occur in the female genital organs. They are dangerous because they can harm the entire body as a whole. As a result, the normal state of the appendages and uterus is disrupted. Very often, an ectopic pregnancy is provoked or it does not occur at all.
It is possible to prevent dangerous consequences only through early diagnosis and modern treatment. It is the symptoms of inflammation of the ovaries and appendages that will be discussed in this article.
Interrupted tubal pregnancy
Pain in the ovaries is often triggered by pregnancy.
The main reasons include:
- threat of interruption of pregnancy;
- presence of a cyst;
- cyst rupture.
If there is continuous dull pain, a tubal pregnancy is diagnosed. The fetus grows and the risk of pipe rupture increases.
If there is continuous dull pain, a tubal pregnancy is diagnosed. The fetus grows and the risk of pipe rupture increases. A pipe rupture is indicated by pain that spreads to the lower back.
In addition to pain in the ovarian area, discomfort occurs in the anus. A woman feels pressure before defecation. Bloody discharge occurs when blood comes out of the tube. They are distinguished by their smearing character. Usually the discharge is scarlet in color.
There is an opinion among women that if the ovary pricks during pregnancy, then this is normal. But statistics show that pain during pregnancy does not occur without an obvious reason. When the uterus significantly increases in size, the ovaries, along with the fallopian tubes, move above their normal location.
Often, women experience pain in their ovaries during early pregnancy due to overstretching of the ligaments that support the uterus, ovaries and tubes. Tension arises in them as they suffer from increased stress. You can get rid of this symptom by normalizing your diet and sleep patterns. Get plenty of rest and do gymnastics and breathing exercises.
Every gynecologist will tell you that during pregnancy the function of the paired glands is almost completely turned off. Therefore, pain cannot arise in them. It’s another matter if the discomfort began even before pregnancy, and only intensified during this period. A pregnant woman may suffer from inflammation as well as ovarian tumors.
The best option is to take preventive measures before pregnancy. If you notice pain in the ovaries in the early stages of pregnancy, contact your gynecologist. Otherwise, complications such as abortion, hypoxia, placental abruption and others may occur.
We recommend you learn: How to recognize
ovarian cyst pain
What are appendages and how do they become inflamed?
A woman's appendages are the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
They are located in the pubic area, above the pubic bone. These organs are responsible for the growth and development of the egg, as well as its release into the uterine cavity. The maturation of female germ cells occurs inside the ovary. In the middle of the cycle, a mature egg leaves it into the cavity of the fallopian tube and goes to the uterus. At this point, the egg can be fertilized by a male reproductive cell (sperm). Then, when it gets on the uterine mucosa, it will attach to its surface, and pregnancy will begin. If the egg remains unfertilized, then it leaves the uterine cavity along with the mucous epithelium. This is how menstrual bleeding occurs.
All internal hollow organs of a person are lined with mucous epithelium. Inflammation of the appendages is expressed in redness and swelling of their mucous surface. Most often, inflammation affects the fallopian tubes, but can also spread to the ovarian mucosa.
The action of the inflammatory response is aimed at limiting the spread of infection.
With redness and swelling, a number of biochemical processes are triggered that stop the further spread of the pathogen and cause its death. Thus, inflammation of the uterine appendages is a response to the penetration of bacteria or viruses inside. _
Local inflammation of the ovaries and appendages in women is called adnexitis in medical terminology.
Factors and causes of adnexitis
The cause of adnexitis is infection. Inflammation is caused by pathogenic organisms (so-called bacteria) or pathogenic particles (viruses). Moreover, they can enter the appendages in different ways, during sexual intercourse or during medical procedures (installation of a spiral, curettage of the uterus during an abortion). Internal infection is also possible - with the bloodstream from another inflamed organ. More often than others (in 80% of cases), the causative agents of inflammation are cocci and chlamydia.
In order for pathogens to enter the appendages from the outside, they must overcome the protective barrier of the vaginal mucosa. Healthy vaginal flora protects the epididymis from pathogens. If the vaginal microflora is disturbed for some reason, then infection becomes possible.
The following factors lead to a decrease in immunity, disruption of the vaginal flora, and the appearance of inflammation:
- Hypothermia – banal situations such as “I caught a cold”, “I dressed poorly”, “I got my feet wet”, “I sat in the cold”.
- Stress – forms general muscle and vascular spasm, disrupts blood circulation, and causes congestion. Therefore, against the background of constant stress, various infections often appear.
- Unsatisfied sexuality (forms stagnant processes).
- Hormonal disorders - most often hormonal imbalance occurs while taking contraceptives.
- Sexual life with several sexual partners often causes the transmission of sexually transmitted infections to each other, the appearance of acute and chronic inflammation.
Note: the human bacterial flora contains pathogenic microorganisms in certain quantities. At the same time, their vital activity is controlled by the immune system. With a persistent decrease in protective reactions (due to particular psychoses, stress, poor nutrition, and other reasons), inflammation of the internal organs can form on its own, without the presence of a source of infection.
How to determine the presence of inflammation in the adnexal organs? What are the signs of inflammation of the appendages in women if the process has acquired a sluggish chronic form?
Symptoms of inflammation of the appendages in women
The main symptom of inflammation is pain. With adnexitis, it occurs in the lower abdomen, lower back and may be accompanied by additional symptoms - unpleasant mucous discharge (leucorrhoea), failure of menstruation.
In acute adnexitis, the pain is severe. They are accompanied by painful urination and pain. They can also hit the leg. Acute adnexitis is often accompanied by fever. Possible indigestion.
The chronic form, sluggish inflammation of the appendages in women does not cause an increase in temperature. The pain is felt as mild, moderate, or may be absent altogether. The appearance of mild pain in chronic adnexitis can be felt against the background of an increase in temperature during a cold infection. Pain during sexual intercourse is also possible, especially with deep penetration.
_
Note: often pain during sexual intercourse is the only sign of sluggish chronic adnexitis.
In an acute process, mucous discharge from the vagina (leucorrhoea) may have a strong unpleasant odor, yellow or green tints. They can also be abundant and create some discomfort throughout the day for a woman. With chronic adnexitis, the discharge is weak or absent altogether.
Also, the presence of chronic inflammation in the appendages may be accompanied by menstrual irregularities. The reason for this is the ovaries perform the function of producing sex hormones - estrogens, progestins. In inflamed tissues, hormonal synthesis is disrupted, which causes deviations in the timing of menstruation, their abundance, duration, and other cycle disorders.
Often chronic adnexitis occurs unnoticed. However, it needs to be treated. A long-term chronic process is dangerous due to complications.
Consequences of inflammation of the appendages: adhesions and infertility
What does adnexitis threaten a woman with? Why is a sluggish inflammatory process harmful if it does not create pain or a source of discomfort? Why is it important to know about the presence of inflammation?
Let us list what processes occur in the appendages during a long-term, sluggish inflammatory process:
- The mucous membrane of the fallopian tubes swells, increases in size, the lumen in the tubes narrows, they become impassable for eggs. This condition is called “tubal” infertility.
- The consequence of a long-term inflammatory disease is adhesions. They are rope-like growths of connective tissue on the inflamed mucosa. This is a kind of “bridge” that fences off the inflammation zone from healthy cells. In the future, the presence of adhesions may cause the fertilized egg to stop moving towards the uterus. Which means it causes infertility, the inability of a woman to become pregnant. Also, the cause of adhesions can be the use of antibiotics.
- If the passage of the egg through the fallopian tube is difficult or impossible, the fertilized zygote may linger in it or go in the other direction - to the abdominal cavity. This is how an ectopic pregnancy forms.
- The process of synthesis of female sex hormones is disrupted. Which leads to menstrual irregularities and unstable egg maturation.
_
Conclusion: chronic inflammation of the appendages often causes disruption of a woman’s reproductive function, disruption of the reproductive processes, which can be defined in a more understandable word - infertility.
Why does the disease occur?
Inflammation of the right ovary develops due to infection from nearby organs:
- appendix;
- intestines.
There is another way of spreading pathogenic microorganisms - hematogenous. This is a descending infection, which most often provokes the development of an inflammatory process in the right ovary. When talking about the susceptibility of the gland to various diseases, doctors often associate the pathological process with the anatomical features of the organ. This primarily concerns more active blood flow and increased size.
The development of oophoritis on the right side can be caused by pathogenic microflora that penetrates the body under certain conditions. These pathogens include:
- gonococci;
- mycoplasma;
- trichomanas;
- chlamydia.
We must not forget about pathogenic microorganisms that are constantly present in the body:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- mushrooms.
Since initially in women the right ovary is slightly larger in size than the left, it is more actively supplied with blood and therefore there is a higher probability of infection entering here through the hematogenous route.
The main danger of right-sided oophoritis is that the infection spreads rapidly and in a short time affects the paired left ovary. Bilateral inflammation can cause disruption of the functionality of the gonads and the development of infertility. Among other reasons for the occurrence of the disease, its development is facilitated by:
- constant hypothermia;
- long-term use of an intrauterine contraceptive device (coil in the uterine cavity);
- violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes as a result of complex surgical interventions;
- the disease occurs against a background of weakened immunity in the presence of other infectious diseases;
- Chronic infectious diseases provoke the development of the disease due to a decrease in the quality of the body's protective functions.
Doctors recognize pregnancy as a dangerous period. It is at this time that women experience a significant change in hormonal balance. No less dangerous are the days of menstruation, when the epithelium is rejected and the inner surface of the uterus becomes open to various types of infections. Infection is possible on the days of ovulation. The place where the egg is detached from the ovary is also a gateway for the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms, as a result of which the ovary can become inflamed.
Classification
The inflammatory process localized in the ovaries can occur in several forms:
- acute - duration varies from 5 to 15 days, and the main clinical sign is pain in the lower abdomen;
- subacute;
- chronic - when there is no treatment for the acute version, inflammation will continue for many years with alternating phases of exacerbation and resolution of symptoms.
Symptoms of the chronic form are often hidden, which greatly complicates the process of establishing the correct diagnosis. It is extremely rare that chronic inflammation develops immediately, without going through an acute or subacute stage.
Depending on the location, inflammation occurs:
- unilateral - inflammation of the right or left ovary occurs;
- bilateral - both segments are involved in the pathological process.
Contraindications for use
Contraindications to the use of suppositories are divided into general and individual.
General injuries include traumatic injuries to the mucous membranes.
- Allergic reaction to the active substance;
- Diseases of the lower digestive tract (for rectal suppositories);
- Cervical erosions;
- Oncological diseases of the genital tract and rectum;
- Uterine bleeding.
Most suppositories are prohibited for use by pregnant women and children. Certain situations when taking a suppository is contraindicated are indicated in the instructions for use.
IMPORTANT! Suppositories contain the same medications as tablet and injection forms. If the patient has had an unsuccessful experience with a certain remedy, it is not recommended to use it as a suppository.
Diagnostics
In order to determine the presence of an inflammatory process in a woman’s appendages, it is necessary to contact a medical institution and undergo the following types of examination.
Scroll:
- donate capillary blood from the ring finger to establish the qualitative and quantitative composition of vital cells;
- undergo an ultrasound scan of the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes in order to promptly determine the possible presence of foreign tumors, as well as structural changes in epithelial tissues;
- collect smears from the mucous membrane of the vagina and uterus, which are sent to the laboratory to determine the bacterial microflora of the internal genital organs;
- donate venous blood, which is examined for the level of female sex hormones, the presence of dangerous strains of infectious microorganisms, as well as cancer cells;
- undergo transvaginal echography, which reflects the health status of the tissues of the internal genital organs;
- donate urine for biochemical testing.
If necessary, the attending physician may prescribe the patient to undergo MRI diagnostics. The average cost of an examination in a private clinic ranges from 3000-3500 rubles. In a public hospital, this diagnosis is carried out free of charge.
Treatment of pain in the ovaries
If the tingling in the lower abdomen is caused by ovulatory syndrome, you can cope with it yourself - apply a warm heating pad, No-Spa will help relieve cramps, bed rest and avoidance of intense physical activity are indicated. With constant, sharp and intense pain, drug treatment cannot be avoided; sometimes surgery is required.
Medicines
Since discomfort in the ovarian area may indicate various diseases, therapy is aimed at eliminating the main cause of discomfort. In treatment, medications are most often used in the form of vaginal suppositories and tablets.
Main groups of drugs:
- antibiotics – Ampicillin, Cefazolin, Trichopolum;
- anti-inflammatory suppositories - Indomethacin, Diclofenac, Movalis, Terzhinan;
- antiviral drugs – Cycloferon, Acyclovir;
- hormonal medications - Duphaston, Danazol;
- anti-adhesion agents – Longidaza.
Vitamin complexes are prescribed as an additional medicinal and anti-inflammatory method of therapy; Magnesium B6 is considered the best for women’s health.
Duphaston hormonal drug
How do candles work and how to use them?
Suppositories for inflammation of the ovaries and appendages are mainly used vaginally, but there are also rectal preparations. Their action begins within a few minutes, since the pelvic organs are penetrated by an extensive network of blood vessels, and the active ingredients of the drug very quickly enter the bloodstream and reach the source of inflammation.
Another advantage of treatment with suppositories is the fact that they bypass the gastric mucosa, thereby not causing irritation (unlike tablets).
Treatment with suppositories is carried out taking into account the following rules:
- The suppository is inserted while lying on your back (vaginal preparations) or on your side (rectal preparations).
- All types of candles are used at night, before bed, after observing hygiene rules, unless use twice a day is indicated. Rectal medications are administered after a bowel movement.
- You should lie down for half an hour after administration so that the drug has time to melt and distribute throughout the mucous membranes.
- Panty liners must be used throughout the entire course of treatment.
Diagnostic measures
The doctor makes a diagnosis based on a comprehensive examination.
Oophoritis has a similar clinical picture to the following diseases:
- appendicitis;
- peritonitis;
- uterine tumor.
To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to identify all concomitant diseases. Sometimes inflammation of the ovaries is observed in women who have had abortions, as well as in those who have inserted intrauterine devices.
To make a diagnosis, the doctor clarifies the location of the pain and finds out the nature of the discharge. A gynecological examination is performed. It allows you to identify swelling, abnormal location of the ovaries in women, pain in the organs of the genitourinary system.
Blood and urine tests are needed to check for the presence of an inflammatory process. The doctor pays attention to the number of leukocytes. To clarify the nature of the disease, it is necessary to perform a pelvic ultrasound . PCR diagnostics allows you to determine what type of virus it is. Laparoscopy is a progressive examination method. To perform the procedure, the doctor inserts a tube with a camera into an opening in the abdominal wall.
Names and descriptions of popular drugs
Suppositories for the treatment of oophoritis are divided into 4 groups. The doctor selects the most suitable drug depending on the type of inflammation and the patient’s complaints.
Antibiotics
This group is used to suppress the proliferation of microbes.
Improvement occurs within the first day after the start of therapy.
Antibiotics are used for the full course (until negative results of microscopic examination).
The most common of them:
- "Chlorhexidine" (Hexicon) is an antiseptic and disinfectant drug that is effective against most bacteria and fungi. It has a high activity profile and is safe for pregnant women. The treatment period is 10-14 days;
- "Polygynax" is a combination drug that includes 2 antibiotics (neomycin, polymyxin) and an antifungal component (nystatin). The effect develops during the first day. The drug is used for the treatment and prevention of acute and chronic oophoritis for 1-2 weeks. "Polygynax" is not used during pregnancy and lactation;
- "Dalacin" (Clindamycin) is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial drug. Highly effective from the first day against bacterial and fungal flora. For Dalatsin, the shortest treatment period has been developed - 3 days. Not for use under 18 years of age, during pregnancy and lactation. Sold with an applicator for easy administration;
- Povidone-Iodine (Betadine) is an antiseptic that is effective against bacteria, protozoa and fungi. Microorganisms do not develop resistance to this drug. The course of treatment is 10 days. Use with caution during pregnancy. Contraindicated in case of allergy to iodine;
- Vagisept is a combination drug containing metronidazole and fluconazole. Effective in the treatment and prevention of oophoritis caused by fungi, protozoa, and intracellular microorganisms. The course of treatment is 10 days. The product is not used in the 1st trimester.
IMPORTANT! If you are allergic to an antibiotic in the form of tablets or injections, taking it in the form of suppositories is prohibited.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
This group of drugs is used to reduce the manifestations of the disease.
The drugs effectively relieve swelling and muscle spasm, reduce the local temperature in the lesion and eliminate pain.
Common anti-inflammatory drugs:
- "Indomethacin Sopharma" is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. It is used for severe symptoms of inflammation and pain. The effect develops within 20 minutes after administration. Contraindicated for pregnant women and lactation;
- Voltaren is an anti-inflammatory drug that is most effective for spasms in the pelvic area, swelling and pain. The effect develops within half an hour after administration. Voltaren is contraindicated in children under 6 years of age and women in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy;
- Meloxicam is an extended-release drug. It has not only local analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, but also a general antipyretic. Contraindicated in girls under 12 years of age, during pregnancy and lactation.
Anti-inflammatory suppositories are rectal. The course of treatment with drugs of this group is 5-7 days.
To restore flora
Suppositories for restoring microflora are divided into prebiotics and probiotics.
Prebiotics are food components of lactobacilli, probiotics are live bacteria.
The drugs are used to suppress the proliferation of opportunistic bacteria and increase the number of beneficial bacteria.
Doctors most often prescribe the following:
- "Bifidumbacterin" . Contains bacteria of the genus Bifidum. Allowed at any age, during pregnancy and lactation. No side effects were found. The course of treatment can last up to 3 weeks. Administration is rectal or vaginal;
- "Acilact" . The product for vaginal administration contains lactic acid bacteria (lactobacillus). Suppresses the proliferation of opportunistic flora and restores the level of lactobacilli in the body. Has no contraindications;
- "Vagikal" is a herbal preparation based on calendula. Effectively restores hormonal and microbial levels in the genital tract, relieves acute and chronic inflammation. Contraindicated in case of allergic reactions.
REFERENCE. Antimicrobials promote the development of microbial imbalances. For this reason, suppositories are also used after antibiotic therapy to restore the composition of the flora.
From adhesions
Suppositories that are effective against adhesions contain enzyme preparations. Enzymes have a resolving effect. This group of drugs is used after the main course of therapy:
- “Distreptase” is a drug that not only prevents the formation, but also promotes the dissolution of adhesions. The course of treatment is 10-21 days. "Distreptase" is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation;
- "Longidase" is a highly active enzyme agent containing hyaluronidase and cocoa butter. It has pronounced absorbable and anti-inflammatory effects. Contraindicated under 12 years of age, during pregnancy and lactation;
- "ASD-2" is a complex drug for rectal administration. Improves tissue trophism and blood circulation, increases the level of its own enzymes. Has a moderate antimicrobial effect. Contraindicated during pregnancy.
Candles against adhesions can be used for a long time. If the course is exceeded for 21 days, a short break is taken, after which the course is repeated if necessary.
What to do?
- Track the pattern of pain (does it depend on the menstrual cycle)
- Make an appointment with a gynecologist and ultrasound
- In case of acute pain, put cold on the lower abdomen and call an ambulance.
If you experience pain in the ovaries during menstruation, you can take a painkiller; antispasmodics are not recommended, as they can increase bleeding. In all other cases, painful sensations require consultation with a doctor. Depending on the cause of the occurrence, treatment may vary:
Ectopic pregnancy - if the pathology is diagnosed at an early stage, the woman is given pills with an abortifacient effect or undergoes laparoscopy, during which the fertilized egg is carefully removed. If an ectopic pregnancy leads to a rupture of the tube, then as an emergency the woman undergoes abdominal surgery, during which both the fertilized egg and the tube itself are removed.
Inflammatory processes - a course of antibiotic therapy is selected individually, after the acute process has stopped, additional physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed.
Cysts - depending on the cause of the neoplasm, its growth and effect on the menstrual cycle, treatment is selected. For some women, hormonal therapy (oral contraceptives) is selected; in case of multiple cysts, as well as the threat of torsion of the leg, a planned operation is performed through punctures in the anterior abdominal wall - laparoscopy.
Ovarian tumors of a malignant nature - the stage of cancer and the presence of complications in the form of metastases are assessed, depending on this, chemotherapy, radiation therapy or radical surgery are prescribed.
In order to promptly recognize ovarian pathologies, women of reproductive age and menopausal women should undergo an annual routine examination by a gynecologist and undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Dull, increasing pain on the right or left during pregnancy signals a possible improper attachment of the fertilized egg in the fallopian tube. An ectopic pregnancy, if diagnosed in a timely manner, allows one to avoid rupture and removal of the tube, while a progressive pregnancy can lead to complications, massive internal bleeding and even the death of the woman.
Antifungal agents
Such tablets have a detrimental effect only on fungal infections, while they have no therapeutic effect on other pathogens. Antifungal agents are prescribed as additional therapy for ovarian inflammation. This can be explained by the fact that taking massive doses of antibacterial drugs can cause thrush and the development of other fungal infections.
Antifungal drugs used in the treatment of oophoritis (inflammation of the ovaries) include:
- Nystatin (daily dosage - 2,500,000 units, 6-8 times a day for 10 days);
- Amphotericin (daily dosage – 200 mg twice a day for 3 days);
- Nizoral (daily dosage – 200 mg once a day for 3 days).
Side effects of such medications include nausea and vomiting, general malaise, diarrhea, allergic reaction, and dizziness.
Effective Treatments
Therapy for adnexitis must be carried out necessarily. It is good if treatment begins in the acute stage. However, medical practice shows that inflammation emanating from the vagina and affecting the appendages is already chronic.
Treating ovarian inflammation at home can be done with over-the-counter medications or alternative medicine. Often, patients are able to buy effective medications prescribed by doctors without a prescription. When taking such drugs on your own, you must be aware of responsibility for your own health, evaluate the consequences of treatment and strictly follow the instructions for use. Good results, according to reviews from women, are shown by an integrated approach when therapy is carried out with the help of medications and traditional recipes.
Treatment with medications
Inflammation of the tissues of the ovaries and fallopian tubes is caused in 90% by chlamydia. Microorganisms cannot be classified as bacteria or viruses. For this reason, it can be very difficult to find an effective medicine for chlamydia. It is necessary to use antiprotozoal agents to which the infectious agent will be sensitive. For self-treatment of adnexitis, women use antibiotics.
They will be effective if the disease is caused by bacteria: streptococci, gonococci, E. coli, peptococci and other pathogens.
- Metronidazole and drugs based on it have been used for many years to treat adnexitis. The medicine is prescribed in the form of tablets for a course of treatment. If necessary, you can use suppositories or vaginal gel. Combining several forms of antiprotozoal antibiotic will achieve the best effect. Metronidazole appears to be effective even when other antibacterial drugs do not show good results.
- Azithromycin (Sumamed, Aditrus) is used in a short course of 3-5 days. The medicine is used in tablet form. Despite the fact that it is included in the list of prescription products, you can buy it yourself if you wish. The drug has a wide spectrum of action and is effective against gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms.
- Doxycycline (Unidox, Vibramycin) is widely used in venereology. The drug is effective against most bacteria that cause inflammation in women. In severe cases, an injection form can be used, but at home patients prefer to take tablets.
- Ceftriaxone (injectable drug) is used to treat the appendages and uterus. The use of this antibiotic shows good results. It is effective against many pathogens, with the exception of viruses.
Ovarian apoplexy
Pain in the ovarian area is caused by apoplexy - rupture of the ovary. The pathology can also occur in adolescence, but is more often diagnosed in women over 25 years of age.
Apoplexy is a hemorrhage in the ovary caused by damage to the vascular walls.
The state is called:
- the presence of a cyst;
- physical activity;
- sexual intercourse during ovulation.
The pathology causes sudden, acute pain.
Signs of the disease include:
- asthenia;
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- loss of consciousness;
- pain in the area of the sacrum of the coccyx and lower back.
The severity of the pathology depends on the volume of blood lost. Treatment of the disease is carried out in a hospital setting. In extreme cases, surgery is indicated. Often there is a disturbance in the morphological structure of the corpus luteum due to pathologies in the vessels against the background of inflammation. The process occurs during ovulation.
There are several forms of pathology:
- Painful. There are acute pains.
- Anemic. Accompanied by fainting and asthenia.
- Mixed. Includes features of previous types.