Hyperkeratoses are a group of diseases associated with thickening of the stratum corneum of the epidermis due to the high content of keratin or fibrillar protein, which makes our skin strong (it is second only to chitin in strength).
This protein consists of the cytoskeleton of epithelial cells (the upper layer of the skin and mucous membranes) and skin appendages (hair, nails). Therefore, they often talk about hyperkeratosis of the skin, hyperkeratosis of the squamous epithelium of the cervix, and hyperkeratosis of the nails. Thickening of the stratum corneum of the skin and appendages is treated by a dermatologist; with hyperkeratosis of the cervix, you need to go to a gynecologist.
General characteristics of the phenomenon
Hyperkeratosis of the feet is a phenomenon in which keratinization of the skin of the surfaces of a given area occurs and a scaly hard layer is formed. This does not affect the general well-being of a person, but it provokes disturbances in the skin tissues.
With hyperkeratosis, an unnatural growth of the stratum corneum of the skin occurs, the thickness of which reaches 1 centimeter or more. Such a violation is considered to be cosmetic, but it cannot be ignored, since in some cases it indicates disorders in the body.
The mechanism for the development of this phenomenon is as follows: skin cells divide too quickly, which is why their top layer does not have time to peel off. Normally, the latter constantly peel off and give way to newly formed ones. If this does not happen, then the epidermis of the feet thickens significantly.
Hyperkeratosis provokes complications such as the formation of painful calluses, which cause significant discomfort when walking, as well as ulcers and bruises, deep cracks, which are entry points for infection.
Reasons for appearance
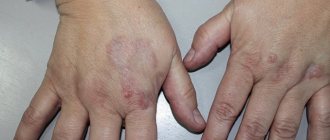
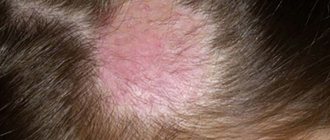
Follicular hyperkeratosis of the skin is formed when the process of replacement of epidermal cells is disrupted. With this pathology, the keratinized upper layer of the dermis does not exfoliate in time. It clogs the hair follicles, the sebaceous secretion does not come out, the hairs cannot come out, instead forming small elevations on the skin. They may be whitish or grayish. If inflammation occurs in the area of the hair follicle, the skin turns red, becomes rough, and rough.
Such negative changes form as an independent disease or act as a symptom of other pathologies.
“Goose bumps” most often occur against the background of:
Causes
Thickening and keratinization of the skin of the foot can be caused by external and internal factors.
External factors include the following:
- Features of a profession or lifestyle in which a person spends most of his time on his feet, that is, he walks a lot and for a long time. Keratinization is not uncommon for a person who runs or walks or walks barefoot.
- Wearing tight or too hard shoes, which put too much pressure on the feet and cause friction. With increased pressure, the body reacts by accelerating the division of skin cells.
- Wearing high-heeled shoes. In such shoes, the pressure is distributed unevenly: it is localized in the heels and toes of the lower extremities.
- Foot injury. Any wound or unhealed crack can cause roughening of the skin.
- Overweight. In this case, the foot area is subject to special stress.
- Foot deformities that are congenital or acquired (clubfoot, flatfoot). Under such conditions, the pressure on different parts of the foot is different, and areas of increased pressure arise. They are affected by hyperkeratosis.
Internal causes that provoke the development of hyperkeratosis include the following:
- diabetes mellitus, in which metabolic processes in the body are disrupted, which is expressed in poor circulation in the lower extremities and causes increased dryness of the skin, which becomes very vulnerable to various damaging factors;
- psoriasis;
- seborrhea;
- fungal infectious processes of the skin;
- erythroderma;
- lichen.
The combination of factors from different specified groups increases the risk of developing hyperkeratosis several times.
Causes of follicular hyperkeratosis
Dermatologists believe that keratosis pilaris is often not an independent problem of the body, but a concomitant symptom of other diseases:
- ichthyosis;
- psoriasis;
- endocrine disorders;
- diabetes mellitus;
- atopic dermatitis.
It happens that the disease manifests itself in healthy people - then the causes of follicular hyperkeratosis are:
- Lack of vitamins. A deficiency of vitamin C, which is responsible for the production of collagen, leads to peeling and irritation, and loss of skin elasticity. A lack of vitamins A and E makes the skin flabby, rough, and inflamed.
- Taking hormonal drugs. Hormones accelerate the process of cell renewal, keratinized scales do not have time to peel off, and the skin thickens.
- Poor nutrition. An unbalanced diet can lead to intestinal dysbiosis and cause irritation.
- Stress, emotional tension. Problems of the nervous system negatively affect the condition of the skin - dullness, dryness, and loss of moisture appear.
- Genetic predisposition. If the parents suffered from hyperkeratosis, then it is likely that the disease will be detected in the child.
- Cold. Low temperatures dry out, causing cracks and roughness.
- Treatment and symptoms of foot fungus
- Punctate keratolysis - causes and symptoms, treatment with drugs and folk remedies
- What is neurodermatitis: causes of the disease in children and adults
Symptoms of foot hyperkeratosis
Characteristic general symptoms that accompany the development of hyperkeratosis are:
- hardening of the epidermis along the entire surface of the foot or in several areas, the thickness of the layer can reach 1-3 cm;
- severe dry skin;
- the formation of deep cracks, which create a risk of infection;
- calluses and bumps on the surface of the skin.
Warts (spikes) may appear on the surface of the skin. The defeat is multiple. Warts have a yellow tint and are prone to ulceration, after which crusts form on their surface.
Types of cutaneous hyperkeratosis and symptoms
Skin hyperkeratosis is classified by origin (hereditary, acquired) and the nature of the clinical course . The last group is divided into the following types:
- diffuse;
- warty;
- follicular;
- lenticular;
- disseminated;
- multiform;
- seborrheic.
In this case, follicular hyperkeratosis comes in two varieties . They both develop due to a lack of vitamin, only in the first case - A, in the second - C.
Depending on the type of pathological process, the manifestations of the disease are characterized by such signs as excessive dryness, uneven surface of the epidermis, sometimes with the growth of dense crusts (“goose bumps”). also be present - large warts, nodules with a red or pinkish rim around them, protruding spines, keratinized plates and scales.
Hyperkeratosis of the feet is accompanied by the appearance of deep cracks, most often on the heels (you can read about their treatment in the article at the link), a burning sensation and pain when walking.
Photo of hyperkeratosis of the scalp, face and body:
Hyperkeratosis of the scalp
Hyperkeratosis of the skin of the legs and arms
Hyperkeratosis of the facial skin
Diffuse
This form of dermatological disorder affects very large areas of the body or the entire skin. There is severe peeling and noticeable dryness of the epidermis.
Diffuse skin hyperkeratosis can be either congenital or acquired, especially in old age.
The following reasons can cause it:
- Sjögren-Larrson syndrome;
- ichthyosis;
- senile changes in cell structure;
- polyneuropathy;
- celiac disease;
- leprosy;
- oncological diseases of the female reproductive system;
- sarcoidosis;
- lymphogranulomatosis.
Warty
This type of hyperkeratosis can also develop both under the influence of a genetic factor and cellular disorders acquired during life. This disease usually affects people whose professional activities involve prolonged constant contact of the skin with chemical compounds and radiation.
The hyperkeratosis in question is characterized by the presence of dense warty formations of a yellow-gray color ; small cracks periodically appear on the surface of the warts.
Rescue balm copes well with various skin damage. You can read instructions for use in this article.
Follicular
As the name suggests, this type of disease affects the follicles : due to the cessation of exfoliation of the stratum corneum of the epidermis, they become clogged, and the follicular duct is completely blocked by skin scales.
The likelihood of getting sick increases if immediate family members suffer from this problem.
In addition, risk factors include poor personal hygiene, constant friction against rough textures (for example, work clothes), exposure to hard or cold water, and wind. The main cause of the development of pathology is a deficiency of vitamins A and C in the body.
There are few clinical manifestations of follicular hyperkeratosis of the skin - dry surface of the epidermis, peeling, red small tubercles or pimples near the hair follicles . With mechanical damage, extrusion, a red rim forms around the keratolytic formations, as they become infected.
Different approaches to the treatment of hyperkeratosis of the feet
Treatment of foot hyperkeratosis can be carried out using different methods. In this case, medications can be used, hardware procedures can be performed, or traditional recipes can be used.
Drug therapy
For hyperkeratosis, the following medications are prescribed:
- Solkokerasal. The drug contains salicylic acid, which has a pronounced antiseptic effect. The ointment softens the skin and prevents the formation of cracks. The stratum corneum gradually softens, the skin is saturated with moisture. The product should be rubbed into problem areas 1-2 times a day.
- Hydrocortisone ointment. Hormonal ointment reduces the severity of irritation and inflammation and normalizes the process of exfoliation of cells of the stratum corneum. This product should be applied 2 times a day to the affected area.
- Doctor. This cream contains urea, which fills the skin with moisture and prevents its loss in the future. This product also helps soften the stratum corneum and nourish the epidermis, heals cracks and disinfects wounds, and eliminates pain in the feet. It is recommended to apply the Healer cream to the feet affected by hyperkeratosis once a day, but in severe cases the procedure must be repeated twice - in the morning and in the evening.
- Calcipotriol. The drug is available in the form of ointment, solution and cream. The product stimulates the restoration of damaged cellular elements and suppresses the uncontrolled process of cell division. The ointment should be applied twice a day.
- Tigazon. This product contains vitamin A. It normalizes the processes of epithelization and keratinization of the skin. The drug is available in capsule form. The dosage is determined by the doctor on an individual basis.
Cosmetic keratolytics for pedicures and special socks with a peeling effect also have a good effect.
Hardware techniques
Hardware procedures are performed by a specialist podiatrist. They are as follows:
- Softening of the hard layer. For these purposes, special chemical solutions are used that prepare the skin for further manipulation.
- Removing the coarsened layer. To do this, use a scalpel with special removable blades of different sizes, which allow you to effectively remove areas of keratinization in different areas. The roughened areas are removed down to the young layer of the epidermis.
- Grinding. This is done using files or a special apparatus with disposable attachments.
Folk recipes
Traditional medicine can also help in the fight against hyperkeratosis. This method in itself is auxiliary: it should complement the use of medications and hardware procedures. But if the form of the disease is not too advanced, then folk remedies can have a sufficient effect.
Folk remedies for hyperkaratosis of the feet include the following:
- Baths with sea salt. To prepare for the procedure, you should fill a basin with warm water and add 100 g of natural salt without flavorings, as well as a tablespoon of soda. Place your feet in the basin and hold for 15 minutes, then wipe dry and lubricate with nourishing cream.
- Compress with oatmeal and vegetable oil. Prepare oatmeal (3 tablespoons) by pouring boiling water over it. Leave for 15 minutes. Pour 3 tablespoons of any vegetable oil into warm porridge and stir. Place oatmeal in plastic bags and place your feet in them, secure with bandages. Cover with a blanket and wait 2 hours. After the specified period, remove the compress, wash your feet and lubricate the treated areas with a rich cream.
- Beeswax ointment. You need to pour 130 ml of vegetable oil into a frying pan and fry a head of onion, previously chopped, in it. After the onions are ready, strain the remaining oil through a strainer and add 60 g of beeswax. Place the container with the mixture on the fire, heat over low heat, and bring to a boil. Cool. Lubricate your feet with the resulting ointment before going to bed, secure the top with cellophane and put on warm socks.
- Compresses with oil. You can use any vegetable oil. Lightly heat 3 tablespoons of oil. Steam your feet. Soak cotton socks in heated oil and put them on, secure with cling film on top.
Treatment should be comprehensive in order to prevent complications and infection.
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease
If characteristic skin problems appear, you should consult a dermatologist as soon as possible. The specialist examines the skin and collects the patient’s complaints. It is important to differentiate hyperkeratosis from other skin diseases, for example, psoriasis or lichen, which also cause peeling of the skin. If the diagnosis is in doubt, a biopsy of suspicious skin areas may be performed.
To treat the disease, ointments with topical corticosteroids are used to treat the damaged areas. This may include prednisolone or hydrocortisone ointment, fluacinolone-based formulations, or clobetasol. In addition, glucocorticoid drugs are prescribed, which have an exfoliating and anti-inflammatory effect, thoroughly cleansing and disinfecting the skin.
Patients with hyperkeratosis of any form are advised to take warm baths with the addition of salt, baking soda or starch and further moisturizing with cosmetic creams.
If hyperkeratosis is detected, mechanical peeling is contraindicated, as it can aggravate the patient’s condition. Only acid (chemical) peeling based on creams with a mild effect is allowed. These are products consisting of salicylic, lactic, citric and other acids. Vitamins A and C are also prescribed orally.
Plantar hyperkeratosis is treated with antifungal ointments, and also requires the elimination of all pathological factors of the disease. It is necessary to replace shoes with more comfortable ones, as well as receive orthopedic help in case of flat feet or club feet. In addition, salt baths, mechanical grinding using a hard sponge and pumice at home are useful. After this, the feet are lubricated with a moisturizing and nourishing cream.
As for possible complications of the disease, they can be observed with plantar hyperkeratosis, when cracks, corns appear, and a secondary fungal infection begins to develop. Follicular hyperkeratosis in some cases causes pyoderma. Formations with a warty form sometimes develop into a malignant tumor. The prognosis for timely and high-quality treatment of hyperkeratosis is favorable, although in some cases the fight against the disease can last a lifetime with alternating stages of exacerbation and remission.
Prevention measures
To prevent the risk of developing hyperkeratosis, it is necessary to pay attention to such preventive measures as:
- wearing comfortable, not tight, appropriately sized shoes that do not create excessive friction or pressure on the foot;
- weight control, timely getting rid of extra pounds;
- performing regular foot skin care procedures, timely removal of the stratum corneum;
- avoidance of traumatic factors;
- proper nutrition, maintaining a balance of nutrients and consuming vitamins and microelements necessary for the body;
- timely treatment of foot fungus;
- constant control over chronic diseases of internal organs, which can provoke the development of hyperkeratosis.
Treatment with medications
In the treatment of hyperkeratosis of the feet, drugs of the retinoid group, as well as products containing vitamin D, are used.
These medications accelerate the rejection of dead epidermal scales and ensure timely renewal of the skin at the cellular level. Let us describe in more detail some popular drugs.
Tigazon
Belongs to the group of retinoids, contains vitamin A. Designed to normalize the regeneration processes of epidermal cells.
Tigazon should not be used by people with kidney or liver failure, allergies to medications, excess vitamin A in the body, or pregnant women.
You need to take the drug correctly. The course of taking tigazon is 2-3 months, 0.5-1 mg per kilogram of weight daily.
An overdose is fraught with side effects such as:
- dryness, inflammation of the lips or mucous membranes;
- constant thirst;
- hair loss (stops after stopping the medication);
- inflammation of the cuticle.
In patients with diabetes, obesity, alcoholism, and some other pathologies, the level of cholesterol in the blood may increase.
Calcipotriol
This is a synthetic analogue of vitamin D. Slows down the synthesis of keratinocytes. Designed to treat nails and areas of the foot affected by hyperkeratosis.
The drug is used externally, twice a day. The maximum daily dose should not exceed 15 g, weekly - 100 g. The duration of treatment is from six to eight weeks. The result is noticeable after 14 days of therapy.
Attention: an overdose is fraught with the development of hypercalcemia!
Calcipotriol is not recommended for treatment of pregnant women and children under 18 years of age. In some cases, dermatological irritation in the area of application is possible.
Lipamide
The drug belongs to the category of drugs prescribed to normalize metabolism. Its main active ingredient is thioctic acid. Its properties are similar to lipoic acid. The substance restores the balance of fats and carbohydrates.
Hyperkeratosis cannot be treated with lipamide if you have the following diseases:
- allergy to the components of the drug;
- convulsions;
- stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- diabetes;
- gastritis.
The medicine is not used to treat pregnant and lactating women, as well as children under six years of age.
An overdose can lead to side effects such as:
- nausea;
- rash;
- change in taste sensations;
- vomit;
- itching;
- headache;
- diarrhea;
- shock;
- dyspnea;
- eczema;
- hemolysis;
- pain in the abdominal area.
In combination with alcohol it can cause severe intoxication. During treatment with lipamide, the patient needs constant monitoring of blood sugar levels. Taking the drug helps reduce it, which creates a risk of developing hypoglycemia.
The duration of the course and dosage are selected by the doctor individually, depending on the characteristics of each specific case.
Hyperkeratosis of the feet: what is it?
Hyperkeratosis of the feet is a pathological condition of the plantar zone of the skin, which manifests itself in the appearance of scaly formations. When the form is advanced, the disorder leads to deep and bleeding cracks. Most people do not attach importance to the onset of a cosmetic defect that has arisen on the skin of the feet, which can lead to an extreme complication when the skin begins to crack and bleed.
The dead cells continue to grow, creating new seals. The skin becomes extremely dry and sensitive to mechanical stress. Often, due to the disorder, the sensitivity of certain areas of the skin is lost. The disease covers both the entire plantar surface and local, individual zones.
Disturbances settle on the heels, phalanges of the fingers and the lateral surfaces of the feet. In the first case of damage, it is called “diffuse hyperkeratosis.” The second option is classified as a “limited” type of violation. Hyperkeratosis of the feet, photos of which show signs of disorders, is treated in two ways - medications and traditional medicine.
Note. A neglected condition not only leads to cracks and rough skin, but also triggers an inflammatory process throughout the body.
There is a risk of “catching” an infection, which will worsen a person’s general well-being.
What is hyperkeratosis
Cutaneous hyperkeratosis is a disease that occurs when the upper stratum corneum of the epidermis thickens excessively. Epidermal cells rapidly divide, which, combined with disturbances in the desquamation process and the appearance of keratin, immediately leads to thickening. Signs of the disease are the formation of nodules of varying sizes, protrusions, spines, and keratinized plates. The skin becomes dry, rough, and there is a significant decrease in sweating. Hyperkeratosis often appears during puberty and weakens with age, but there are cases of the disease in adults.
Symptoms
The onset of the disease is often attributed to harmless signs of shoe rubbing, without paying attention to it. However, if you notice the following symptoms, you should be wary:
- the plantar skin has become extremely dry and flaky;
- the plantar zone has become very rough;
- loss of sensitivity is detected in some areas of the feet;
- compactions and painful calluses appear;
- the skin is affected by cracks.
Further, the picture becomes more dangerous, the number of affected areas increases, and the cracks begin to bleed. Doctors urge not to wait for the acute form to occur, but to contact them without delay.
Diagnostics
- When the disease occurs, the flaking keratin clogs the follicles;
- many nodules appear on the skin, which can cover a very large area;
- in the normal state, the bubbles are 1-3 millimeters, and with inflammation they increase in size to 5 millimeters; the tubercles rise slightly above the skin;
- sometimes the tips of a hair peek out from under the goose bumps;
- infrequently, skin hyperemia can be observed on the affected area;
- the inflammatory process appears and disappears suddenly and causes discomfort; pimples have a reddish color and do not look aesthetically pleasing.
“Goose bumps” are most often localized on the abdomen, thighs, arms and buttocks, less often on the interscapular region, chest, legs and shoulders. Yellow-brown papules may appear in the armpits, face, and scalp. The rash can also affect the palms, soles of the feet and mucous membranes.
The papules itch and the patient feels uncomfortable. You cannot self-medicate, since treatment is strictly individual. The course of treatment is prescribed by a dermatologist.
The diagnosis of the disease is carried out by a dermatologist, who makes a conclusion after a thorough examination of the skin, without using special laboratory diagnostics. To distinguish follicular hyperkeratosis from acne on the face, you should carefully examine the rashes - with keratosis they are rough and dry, small and of the same size.
External reasons
- Overweight. Doctors agree that the disorder is “activated” due to increased pressure on the feet. This leads to the expert conclusion that excess weight provokes the occurrence of this disease.
- Uncomfortable shoes. The “provocateur” of dermatological pathology is compressive shoes that disrupt the normal blood circulation of the legs and feet. Excessive load on this area manifests itself in the development of hyperkeratosis.
- Natural features and injuries. Common flat feet, clubfoot and other defects disrupt the correct distribution of the load on the feet, as a result of which they provoke the development of pathology.
Types and methods of treatment
Follicular hyperkeratosis
It develops as a result of blockage of the mouth of the follicle by keratinized epidermal cells. In this case, signs of aseptic inflammation appear. The main provoking factors for the development of this type of hyperkeratosis are a lack of vitamins A, K, ascorbic acid, as well as errors in personal hygiene.
It most often occurs in children, adolescents and people prone to allergic reactions. Moreover, if there are already cases of hyperkeratosis in the family history, the risk of its development increases significantly.
There are two types:
- Type I occurs due to a lack of vitamin A. It affects the skin of the buttocks, extensor surfaces of the arms and legs, as well as areas on the elbows and knees. It becomes dry and rough, feeling like sandpaper to the touch.
- Type II is the result of vitamin C deficiency. Changes affect the skin of the abdomen and thighs. Very often, especially if there is also a lack of vitamin K, the rash becomes hemorrhagic in nature.
The rashes look like small dense pinkish nodules located near the follicle. Externally, this skin resembles “goose” skin. In addition, patients are constantly bothered by mild itching, but they seek help from a doctor most often because of cosmetic discomfort.
The diagnosis is made based on examination data. No special diagnostic methods are used.
Follicular hyperkeratosis photo
Treatment of follicular hyperkeratosis
Follicular hyperkeratosis is a chronic process. It is impossible to completely cure it. If it occurs against the background of a certain disease, then the first priority is to consult related specialists - a therapist, an endocrinologist, a rheumatologist.
You can temporarily improve the condition of the skin with the help of creams and lotions containing lactic or any fruit acid, which help moisturize and soften it. Cosmetics containing emollients also have a good effect. They are used mainly in winter, when it is necessary to protect the skin from low temperatures and prevent irritation.
Your doctor may prescribe short courses of topical steroid medications. They relieve itching and inflammation. However, you cannot use them all the time. Preparations for internal and external use containing vitamins A and C can also correct the processes of regeneration and exfoliation.
In some cases, the rash may regress on its own once the patient reaches adulthood.
Lenticular hyperkeratosis
Photo: Lenticular
The pathological changes are based on a disruption of the process of keratin formation. The etiology of this failure has not yet been clarified, but experts believe that the reason lies in some transformations of the human genome.
The disease is chronic, exacerbations often occur after excessive sun exposure. Clinically, the rash looks like hard papules 1-5 mm in diameter. They may be reddish-brown or yellow-orange in color. The favorite localization is the dorsum of the feet, legs and thighs; the skin of the arms, body, palms and ears is less commonly affected. Isolated cases of rashes on the oral mucosa have been reported. Papules are evenly scattered over the skin, do not tend to merge and do not cause discomfort. When squeezed out, a kind of plug comes out of the nodule, leaving a small, slightly bleeding depression.
Disseminated hyperkeratosis
Photo: Disseminated
Like lenticular, the etiology of the process is not clearly defined. The clinical picture is the appearance of short, stiff hairs on the skin on the body and limbs. Sometimes they form small groups of 5-6 hairs, resembling brushes.
For differential diagnosis from other dermatological problems, material is collected followed by histological examination.
Treatment of disseminated hyperkeratosis
Treatment of lenticular and disseminated hyperkeratoses is the use of drugs in the form of ointments containing corticosteroids and retinoids. Regular chemical peels and moisturizing treatments can also solve the problem and temporarily eliminate a cosmetic defect. However, they should only be performed by specialists - dermatocosmetologists. It is not recommended to scrub the skin yourself. This can lead to its damage and the appearance of pyoderma as a result of secondary infection of microtraumas.
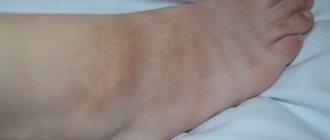
Hyperkeratosis of the feet
Photo: Stop
Provoking factors are excess weight, flat feet, wearing uncomfortable shoes, which increase the load on the foot. Irregular foot care makes the situation worse.
The localization of areas of hyperkeratosis may indicate specific causes.
Rough skin on the heels indicates a fungal disease or problems with the endocrine system.
For example, hyperkeratosis of the feet often develops against the background of diabetes mellitus.
If the skin thickens along the outer edge of the heel, this indicates a previous injury to the musculoskeletal system or clubfoot, both congenital and acquired. And coarsening of the middle part of the foot occurs with longitudinal flatfoot.
Excessive keratinization of the inner edge of the foot indicates weakness of the ligamentous apparatus of the ankle joint and calf muscles. In this case, the formation of areas of hyperkeratosis is facilitated by excess weight, flat feet and any other factors that place excessive stress on the ankle joint.
Whatever the etiology of plantar hyperkeratosis, the stratum corneum gradually reaches a significant thickness. Dry skin often cracks. Deep and painful fissures can bleed and often become infected.
Hyperkeratosis of the feet treatment
Hyperkeratosis of the palms and feet photo
Treatment of the pathology is complex. It is necessary not only to put the feet in order, but also to eliminate the very cause of the disorders. Symptomatic therapy is carried out by a podiatrist. It removes keratinized epidermis using hardware methods.
If the cause is orthopedic problems, consultation with an orthopedic doctor is necessary. And when the appearance of hyperkeratosis is caused by shoes, in this case it will be enough to simply choose a comfortable pair for daily wear in order to evenly distribute the load on the foot.
A dermatologist will help you get rid of fungal diseases by prescribing the necessary medications. And in case of endocrine disorders, you should definitely visit a specialist in this profile.
To treat painful cracks, the doctor prescribes applications with synthomycin ointment and treatment of dry areas of skin with retinol. After healing, it is necessary to completely remove the stratum corneum. At home, all you need to do is steam the skin of your feet, then use a pumice stone to carefully remove the rough crust. Treatment of cracks also includes the use of keratolytic (regenerating) drugs and emollient cosmetics.
In a cosmetology salon, you can get rid of the disease faster than with home procedures. However, in any case, you should then regularly take care of your feet, prevent fungal diseases and wear comfortable shoes.
Warty hyperkeratosis
Grayish or yellowish nodules form on the skin.
Subungual hyperkeratosis
One of the symptoms of onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nail plate. Such hyperkeratosis manifests itself by thickening and changing its shape. It rises somewhat, and grayish-yellowish growths become visible from under its edge.
Seborrheic hyrekeratosis
Photo: Seborrheic
In terms of symptoms, it is somewhat similar to follicular. Only the favorite localization of the rash is the face, neck and scalp. Keratomas are small yellow or pink formations.
In the initial stage, dandruff appears, the hair becomes dry and brittle. Gradually, they begin to fall out, and in the follicle clogged with epithelial cells, new hair no longer grows. If diagnosed untimely or not treated regularly, the patient may experience partial or complete baldness.
The scalp is constantly itchy. It is very dry and thin, so it is easily injured even when combing. Moreover, these scratches can easily become infected, which will require additional treatment.
Hyperkeratosis of squamous epithelium of the cervix
Another name for this pathological process is leukoplakia. The mechanism of development is based on thickening of the epithelium as a result of chronic inflammation. The cause of the phenomenon may be:
- cervical cancer;
- presence of papillomavirus;
- gynecological examinations and manipulations (abortion, installation of an intrauterine device);
- frequent stress and overwork;
- endocrine pathologies;
- inflammatory diseases of the genital organs.
Also, hyperkeratosis of the squamous epithelium of the vagina and vulva - the external genitalia - accompanies some sexually transmitted infections.
Suspicion of pathology arises already at the appointment during a gynecological examination. The final diagnosis is made based on colposcopy data in combination with cytological and histological examination.
Internal reasons
If external causes are somehow dealt with by eliminating, for example, “harmful” shoes, or trying to reduce body weight, then internal factors are much more difficult to destroy. The internal reasons here are as follows:
- Endocrine diseases, such as diabetes. Such diseases affect the development of hyperkeratosis because they disrupt all body functions.
- Fungal pathologies. In advanced cases, a common fungal infection brings with it a more serious dermatological disease. This happens when the fungal infection continues to spread without treatment. That is why it is important to pay attention to your health even with minor symptoms.
- Metabolic problems. The human body is an integral system, so the failure of one component leads to a disruption in the functioning of another. Problems with the absorption of substances and their breakdown affect the body as a whole, hence pathological conditions of a dermatological nature arise.
- Atherosclerotic lesion of the vascular system. Atherosclerosis disrupts the normal functioning of blood vessels, including those localized in the feet. This leads to disruption of natural circulation, problems with blood circulation and increased stress in the legs.
- Seborrheic or psoriasis manifestations. All skin lesions are “provocateurs” that cause hyperkeratosis. An advanced degree of dermatological pathology, infection in combination with a weakened immune system are a worthy basis for the occurrence of the disease.
An effective preventive measure that reduces the risk of pathology includes the use of regular pumice stones when bathing, as well as the use of moisturizing creams.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional medicine methods help alleviate the condition with such a diagnosis as hyperkeratosis of the skin of the legs.
Healing compositions are very easy to prepare. They do not directly fight the cause of the pathology, but they are good at relieving unpleasant symptoms such as itching, soreness and others.
Potato compresses
Peeled tubers need to be grated on a fine grater. Distribute the resulting pulp over gauze and apply to the affected area.
After an hour, replace the compress with a fresh one. After another 60 minutes, repeat the manipulation a third (last) time. To achieve the effect, procedures must be carried out daily.
Onion tincture
To prepare the solution you need:
- Take a glass of dry onion peel.
- Pour in 150 ml of vinegar.
- Leave in the dark for 14 days.
- Strain.
Soak gauze in the tincture, apply to problem areas, and leave for 30 minutes to an hour. If your feet have cracks, this method cannot be used.
Aloe juice
Agave helps get rid of many health problems, including restoring the skin of the feet.
For hyperkeratosis, the plant should be used as follows:
- Cut off the lower leaves.
- Wrap in cotton cloth.
- Place in the refrigerator for three days.
- Cut into thin plastics.
- Cover your legs with a bandage overnight.
- In the morning, remove the compress.
- Lubricate your feet with a weak solution of salicylic alcohol.
Another effective way: combine aloe juice, castor and eucalyptus oils in equal parts. Apply the mixture to the foot, wrap it in cling film, and put clean socks on top.
Diagnostic methods
A dermatologist can diagnose hyperkeratosis. There is also such a narrow specialist as a podiatrist, who directly deals with foot problems. Diagnosis and subsequent treatment takes a comprehensive approach, so a dermatologist often prescribes a consultation with an orthopedist or endocrinologist if endocrine or musculoskeletal causes are suspected.
Only a complete study of possible factors guarantees getting rid of hyperkeratosis forever. At the first stage, the doctor examines the patient and then prescribes a study in the form of tests. If necessary, recommends consultations with other specialists. To confirm the diagnosis, it is possible to take material (biopsy) of the upper layer of skin and use a histological approach.
Features of various types of skin hyperkeratosis
Follicular hyperkeratosis (goose bumps) manifests itself in the form of small red tubercles that appear at the site of the mouths of the hair follicles - the hair root and the surrounding root sheath - clogged with keratinized scales. The disease is accompanied by dry skin and itching, most often affecting the forearms, thighs, buttocks, legs, as well as the skin in the areas of the elbow and knee joints. For patients suffering from follicular hyperkeratosis, treatment is prescribed after examination by several specialists at once, at least a dermatologist and endocrinologist.
Warty hyperkeratosis can be hereditary or acquired. The disease is characterized by yellow, wart-like rashes that crack and crust over. It can degenerate into a malignant form.
Lenticular hyperkeratosis is characterized by large yellow-brown formations up to 5 mm in diameter. This type of skin hyperkeratosis often affects the ears and oral mucosa.
Seborrheic hyperkeratosis of the head is characterized by small spots of yellow and sometimes pink color, dense to the touch and covered with an easily detachable greasy crust. As the disease progresses, the spots begin to rise above the skin and increase in size.
Diffuse hyperkeratosis of the skin is characterized by the ability to completely cover the skin, causing dryness and flaking of the skin.
Disseminated hyperkeratosis - characterized by formations resembling short thickened hairs, located singly or in “tassels” of 3-6 elements.
Actinic (senile hyperkeratosis) appears in older people who spend a lot of time in the sun, which provokes the appearance of small, rough and at the same time very sensitive brown spots.
How to treat
If the diagnosis has determined hyperkeratosis of the feet, treatment is prescribed depending on the cause and nature of the pathological condition. To eliminate hyperkeratotic manifestations, it is important to adhere to the following treatment method:
- moisturizing and softening the surface of the skin - achieved through the use of special medicinal products recommended by the doctor;
- destruction of dead horny compaction - removal of the keratinized layer of the upper layer of the epidermis is carried out by a podiatrist using a special scalpel. Essentially, this is a professional blade with attachments;
- grinding the upper skin - done independently, for example, with a pumice stone or a special brush with attachments, sold in a pharmacy. A more effective method is a procedure performed in a salon using a laser or radio waves. This method is called hardware.
Skin hyperkeratosis: treatment and prevention
To treat hyperkeratosis (we are talking about external manifestations), medications and cosmetic procedures are used; the choice of methods is determined by the cause of the disease, the location on the patient’s body, as well as the severity of the disease.
Cosmetic procedures are used to soften the skin and free its surface from keratinized scales. The hyperkeratosis treatment program includes laser peeling, microdermabrasion, mesotherapy with vitamin cocktails, as well as various types of peelings. To combat hyperkeratosis, acid peels containing salicylic, glycolic, citric, lactic, tartaric and malic acids are best suited. In addition, cryotherapy (cold treatment) is actively used for seborrheic keratosis.
Drug treatment. Any type of hyperkeratosis is accompanied by dry skin, so experts consider it advisable to use medications containing retinoids (natural and synthetic analogs of vitamin A), as well as ointments containing vitamin D. Ointments containing corticosteroids temporarily but quickly relieve irritation and normalize the exfoliation of keratinized scales.
Ointments and creams for external use. If small areas of the skin are affected by hyperkeratosis and the disease is relatively mild, a good result is achieved by using creams and ointments rich in fats, which soften the skin and help retain moisture in it. When choosing cosmetic preparations, you should give preference to products with Shea butter (Shea butter), since the fatty acids composing it are close to those contained in the stratum corneum of the epidermis. In addition, for skin affected by hyperkeratosis, components such as panthenol (relieves irritation and softens the skin), salicylic acid (2%, facilitates the removal of scales), urea (20%, restores the elasticity of the stratum corneum and moisturizes the skin), and also lactic and glycolic acids.
Prevention
Preventive measures include the following main points:
- avoid uncomfortable and uncomfortable shoes that squeeze your feet;
- use emollients and moisturizers;
- use pumice to help the skin get rid of unnecessary particles;
- eat healthy and natural food filled with vitamins.
Remember that it is easier to try to prevent the occurrence of pathology than to treat it later. If you notice damage to the skin of your feet, visit a dermatologist and take care of your health in advance.
- 1. Hyperkeratosis of the feet
- 2. Manifestations
- 3. Reasons
- 4. Symptoms
- 5. Treatment of foot hyperkeratosis
- 5.1. Drug treatment
- 5.2. Treatment of hyperkeratosis of the feet in a podiatrist's office
- 6. Prevention
Hyperkeratosis of the feet is a keratinization of the skin on the surface of the feet, in which the epidermis layer seems to “grow”, forming a rough, scaly layer. As a rule, people do not attach due importance to this, periodically cleaning off the overgrown skin with a pumice stone. However, very often such procedures have a temporary effect: neither pumice nor nourishing foot cream helps for a long time, and soon new growths appear on the feet.
So, what is hyperkeratosis? Translated from Greek, this term means “excess keratin.” This refers to severe keratinization of the skin on the sole. In fact, this defect can be considered cosmetic, but under certain conditions it is necessary to treat it with due attention. It can be a reflector of certain processes in the human body.
Treatment of keratosis pilaris
If you experience symptoms of goose bumps, you should seek help from a medical facility. A dermatologist, endocrinologist and cosmetologist will conduct a thorough diagnosis of your skin and prescribe an appropriate course of treatment for keratosis pilaris. Do not try to get rid of the disease at home - this can only worsen the situation. The disease cannot be completely cured, but it is possible to reduce the inflammatory process and return the skin to a healthy appearance by adhering to the following recommendations:
- Do not perform unprofessional mechanical facial cleansing. Use soft masks and surface peels based on acids - lactic, glycolic, salicylic.
- To prevent the localization of keratosis from increasing, take baths with the addition of milk or decoctions of medicinal herbs.
- Avoid sun exposure, as tanning makes the layers of the epidermis dry and thin.
- Choose care cosmetics carefully - soaps and gels with a drying effect will only aggravate the disease. Give preference to gentle moisturizers.
- Do not squeeze out the rash - this can lead to inflammation, infection, and scarring.
- Prevent hypothermia and overheating of the skin.
- Try to wear loose clothing and shoes that fit properly.
- Eat right, eat more vegetables and fruits, which will saturate your body with the missing vitamins.
Treatment of follicular hyperkeratosis with drugs
When treating follicular hyperkeratosis with drugs, patients are prescribed tretionin, ascorbic acid, vitamin A, drugs based on salicylic acid, and sometimes topical corticosteroids. Often, a dermatologist prescribes LacHydrin, a cream-lotion containing lactic acid that helps moisturize the skin. To soften it is recommended to use:
- Castor oil;
- glycerol;
- baby cream;
- fish fat.
Ointment for follicular hyperkeratosis
Treatment of hyperkeratosis often occurs with the use of ointments containing isotretinoin. "Uroderm" is an ointment for follicular hyperkeratosis, consisting of 30% urea. This element effectively breaks down the protein bonds that hold together the keratinized particles of the epidermis, creating additional conditions for exfoliation of horny layers in keratosis. Urea retains moisture in the intercellular space, preventing the skin from drying out. Using the drug for two weeks reduces dryness and keratinization.
Hyperkeratosis of the feet
This flaw is diagnosed in the office of a specialist (orthopedist or dermatologist) during a visual examination, on the recommendation of which sometimes a histological analysis of the epidermal material is not superfluous.
The problem is that the described disease sometimes leads to the appearance of ulcers or calluses of various types on the skin of the feet, and small hemorrhages. All this can be corrected with the help of some procedures. Although not dangerous to the human body as a whole, hyperkeratosis causes significant discomfort during movement.
It should be clarified that along with the listed complications, there may also be calluses, both under the nails and between the toes, and hard root calluses, the cause of which is excessive load on the foot.
Diagnosis of skin hyperkeratosis
An examination of the epithelial surface, which has obvious signs of hyperkeratosis, can be carried out in a public hospital or in a private clinic. A patient who has an appointment with a doctor will need to undergo an external examination by a specialist, and then undergo the following types of tests, including diagnostic procedures:
- blood from a vein - infection of the body with bacterial infections and viruses is excluded (a biochemical study of the selected biological material for the concentration of hormones is also performed);
- morning urine - the general indicators of urine are determined, the glucose level is determined, the presence or absence of an inflammatory process in the body);
- blood from the ring finger - a clinical analysis is carried out to determine the concentration of red blood cells, platelets, phagocytes, lymphocytes and other vital components;
- scraping — sowing feces for the presence of helminth eggs and larvae;
- Ultrasound diagnostics - tissues of the thyroid and pancreas, appendages in women, adrenal glands are subject to examination;
- a smear from the surface of the diseased skin - a sterile cotton swab is used to collect the microflora of an area of the epithelium that has signs of hyperkeratosis, as well as small scales, which are studied in the laboratory, the possible presence of fungal infections and parasitic microorganisms is determined;
- epithelial biopsy - performed if the disease has become complicated and there are signs of changes in the cellular structure of the epidermis.
If necessary, the attending physician may decide to prescribe an additional examination of the liver, as well as the gastrointestinal tract. The health of skin cells, as well as the full performance of their functions, depends on the condition of these organs.
Manifestations
As mentioned above, the term itself in translation means excessive formation of keratin and looks like a strong keratinization of the epithelium, which slowly exfoliates. It has been established that in this case, new layers of skin on the soles grow faster than the previous ones die off. Since the disease affects different people differently, podiatrists classify it according to the principle “manifestation - type of hyperkeratosis.”
The most common case is the formation of dry calluses, which, like corns, create pain and difficulty during movement. Bruises in the form of dark red spots are called unsafe, since a trophic ulcer can form in this place. Therefore, as a rule, a specialist recommends removing this area. Also fraught with bad consequences are very deep cracks through which infection can penetrate.
Callus is the next manifestation of the disease. It appears between the second and fifth fingers, has an internal core and causes quite strong pain.
Next in the classification is interdigital soft callus. Under the influence of moisture, erosion forms on damaged skin, and there is the potential for fungus to appear.
The next type is nail hyperkeratosis. There are two options here. Under the influence of a fungal infection, the pad under the nail thickens, or the plate itself thickens (onychogryphosis).
The last type is fibrous callus, a type of dry callus. An unpleasant feature is that it compresses the nerve endings. Therefore, it causes severe pain and forms a keratinized area in the form of a honeycomb.
Treatment methods for skin hyperkeratosis
The modern pharmaceutical industry offers a wide selection of drugs that improve the trophism of epithelial tissues, ensure their sufficient moisture and prevent further progression of the keratinization process. Listed below are all the treatments for skin hyperkeratosis.
Medications
The main part of the medications used for the treatment of skin hyperkeratosis is aimed at restoring the normal functions of the diseased area of the skin, as well as its hydration.
The following are the medications that are most often prescribed by dermatologists and are highly effective:
- Petrolatum - mineral oil, which is used to treat an area of the body with keratinized epithelial cells (the drug is applied 2 times a day until the symptoms of the disease completely disappear, and the average cost of 1 tube of medication is 25 rubles);
- Salicylic acid - apply an even layer to the surface of the skin once a day, and then cover it with a piece of sterile gauze bandage (course of treatment is 12-15 days, and the average price for a jar of medicine is 90 rubles);
- Retinol acetate - taken 1 time per day orally, 12 drops after eating, and a small amount of oily liquid is applied to the affected area of the skin, spreading the medication in an even layer (the therapeutic course is 7 days, and the cost of the drug is 50 rubles);
- Carboderm is a cream with a pleasant smell that contains propylene glycol, which provides skin hydration, has an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect (applied to keratinized skin in an even layer 2 times a day, the general course of treatment is 2 weeks, and the average price of the medication is 230 rubles. ).
It is very important that treatment of a dermatological disease begins only after the cause of hyperkeratosis has been identified and eliminated. This will allow you to quickly get rid of the disease and prevent its relapse.
Traditional methods
In addition to drug therapy, there are alternative ways to treat keratinization of the upper layer of skin.
To quickly get rid of hyperkeratosis at home, it is recommended to use the following folk recipes:
- decoction from the string - take 1 tbsp. l. dried stems and leaves of this plant, pour into a metal container, pour 1 liter of running water, put on low heat and boil for 15 minutes. (after cooling, use the healing decoction as a skin wash, doing this procedure 2 times a day for 15 days);
- beetroot applications - select a medium-sized root vegetable, wash it, peel it, cut off a round slice and apply to the affected area of the skin for 2 hours (conduct treatment daily for 10 days);
- homemade ointment - you will need to take 1 raw chicken egg, 3 tbsp. l. honey collected from herbs, 1 tsp. sunflower oil, mix all components until a thick, uniform mass is obtained, and then apply to the surface of the skin affected by hyperkeratosis in the morning and evening for 15 days;
- aloe juice - pick a small piece of the leaf of this indoor plant, cut off the outer skin and treat the stratum corneum of the epithelium with the juicy pulp (the therapeutic procedure is performed 2 times a day for 14 days, it allows you to relieve the inflammatory process, moisturizes the skin, and also prevents the formation of new scales) .
The effectiveness of the above traditional medicines has not been confirmed by laboratory studies.
Before using medicinal plants, you should consult a dermatologist.
Other methods
In addition to the use of drug therapy, as well as folk remedies for the treatment of skin hyperkeratosis, laser removal of the keratinized layer of the epithelium is actively used.
This procedure is carried out in private clinics and public hospitals with good material and technical resources. Using a laser, a dermatologist removes the upper, diseased layer of the epidermis without violating the integrity of the skin.
After 1-2 weeks, complete renewal of epithelial cells occurs without traces of keratinization. The average cost of the procedure ranges from 4 to 8 thousand rubles. depending on the area of skin damage, as well as the complexity of the clinical case.
Symptoms
This pathology has the following signs: along the entire surface of the foot or in several areas, the dermis layer becomes thicker, sometimes reaching three centimeters; the skin is characterized as too dry, cracks and various types of calluses are possible.
All types of hyperkeratosis are characterized by common symptoms, such as thickened and sometimes lumpy epithelium of quite considerable thickness, which does not look very attractive, and is also fraught with various complications.
Products with acids and urea
Urea is an excellent moisturizer. When choosing any product for the body, it is advisable to ensure that the composition contains not only oils rich in fatty acids, but also urea. But, as for urea, there is a nuance: at a small percentage (usually up to 10%), it works as a humectant. At high levels, from 20% to 50%, urea becomes a keratolytic (exfoliating ingredient). For example, in Ameliorate body cream, lactic acid acts as an exfoliant, and urea acts as a moisturizer. Pharmacy Uriage Kératosane 30 and SVR Xerial 30 contain 30% urea, that is, in these products the ingredient functions as a keratolytic. By the way, SVR has Xeriale Extreme with a record urea content of 50%. This remedy is more suitable for combating calluses and corns. It should not be applied to rough areas.
- 01
- /
- 05
Treatment of foot hyperkeratosis
First of all, it is necessary to establish and eliminate the cause of the disease. First, you need to choose comfortable shoes, lose extra pounds, and try not to overstrain your legs by excessive walking or standing for long periods of time. Next, if any, cure fungal infections of the nails and feet. Here is a list of the most common methods of treating the disease.
The use of keratolytic drugs that have the ability to make the skin softer. These include some acids, such as lactic and salicylic. For several decades, urea has been effectively used in dermatology, which in small concentrations very well moisturizes and then exfoliates dead skin. A more saturated solution can even dissolve the nail, so it can be useful in the treatment of fungal infections.
In podiatry offices, the patient periodically undergoes certain manipulations, the essence of which is the medical “grinding” of keratinized and thickened areas using high-speed burs and cutters.
If cracks or ulcers have formed on the foot, they are treated in a targeted manner, irradiating the desired areas. This procedure is called photodynamic therapy, which has an antimicrobial effect on the dermis. Unlike the similar effects of a course of antibiotics, this technology almost completely avoids side effects.
Various orthopedic techniques are considered quite effective, namely the use of special insoles made for a specific patient. They make it possible to evenly distribute body weight over the surface of the entire foot.
Drug treatment
1. For several months, even up to a year, retinoids are prescribed with a gradual reduction in dose, taking into account the individual effect on the body.
2. Several courses of taking vitamins A, B, C and biotin.
3. It is advisable to use medications prescribed by your doctor to improve fat metabolism.
4. If the disease is congenital, a combination of short-term steroid hormones with anabolic ones is recommended for significant relief and complete elimination of symptoms.
Treatment of hyperkeratosis of the feet in a podiatrist's office
Podologists who graduated from higher medical educational institutions are specialists in this field. The treatment algorithm was developed over many years of research and practical experience and consists of several components. Namely, softening the keratinized and hard layer, removing it and further processing the skin by grinding.
Medicine knows a variety of techniques that lead to softening of the skin. Here are some of them.
The most popular is the classic version using water in which salt and aromatic substances are dissolved. This is a fairly pleasant and painless method.
To enhance the effect, modern medicine offers various chemical compositions that have the ability to soften the skin (foams, gels, solutions). They significantly speed up the process, disinfect well and are very inexpensive.
To remove the affected areas, use disposable equipment, such as a scalpel, etc. Often the lesions affected by this disease are localized between the fingers or on the joints of the phalanges and look like grains or narrow ribbons. In this case, it is convenient to remove all these formations with hollow blades.
For a doctor performing such a manipulation, it is important to take special care - after all, he must remove the hard stratum corneum down to the young dermis. If the specialist’s technical skills, as well as visual self-control, are of a sufficient level, then the affected areas will disappear completely, and healthy soft tissues will not be affected.
The last point of such an operation will be the actual smoothing of the skin. For these purposes, ordinary nail files are used, which are used for manual sanding. Hardware technologies that provide benefits in efficiency, time and hygiene. In this case, special disposable ceramic devices work.
In comparison with foreign countries, where this disease is cured by podiatrists or podiatrists, who identify and eliminate orthopedic disorders and infectious pathologies on the skin of the feet, in Russia, as in other CIS countries, this branch of medicine is developing quite slowly. There are a small number of private institutions in large cities only at the expense of patients, since there is no proper licensing of such an industry from the state yet. But they still have the necessary equipment in the form of equipment for therapeutic pedicure, high-speed cutters and burs, with the help of which the areas affected by the disease are removed. In some of these clinics, in addition to everything, they produce custom-made corrective insoles and prostheses to correct the incorrect distribution of weight on the surface of the foot, which is a fairly significant factor in the healing process.
Clinical picture
Follicular hyperkeratosis
This form of pathology occurs with a lack of vitamins A and C, as well as with non-compliance with personal hygiene rules. Genetic predisposition also plays a significant role in the development of this pathology.
Due to a violation of the detachment of keratinized epithelium, the ducts of the hair follicles become clogged and take on the appearance of tubercles or pimples. Most often, those areas of the skin that are prone to dryness are affected - these are the area of the elbows, knees, buttocks and outer thighs.
If the disease is not treated and the influence of unfavorable factors (low temperatures, uncomfortable clothing) is not eliminated, hyperkeratosis covers an increasingly larger area. Gradually, a rim of hyperemic skin forms around the follicles, which can become inflamed.
Constant mechanical impact provokes a violation of the integrity of the epithelial layer and leads to infection of the follicles and the development of large areas of pyoderma.
Follicular hyperkeratosis
Lenticular and disseminated hyperkeratosis
This disease is more common in older men; in women, the pathology is very rare. The cause of this type of hyperkeratosis is still not clear, but most experts agree with the version of a genetic mutation, as a result of which excess keratin is formed in epithelial cells.
Lenticular hyperkeratosis of the skin has a chronic course, exacerbations occur after prolonged sun exposure. In the area where the follicles are located, horny papules with a diameter of 1 to 5 mm, yellow-orange or reddish-brown, are formed. Most often, the skin is affected in the area of the back of the feet, legs, thighs, and rarely - areas of the torso, arms or ears. There are known cases of localization of this pathology on the oral mucosa.
If you remove the scale, you will find a small, moist depression underneath with a drop of blood in the center. The papules do not merge and there is no pain when pressed.
Disseminated hyperkeratosis looks like short and thick hairs, which are localized mainly on the skin of the limbs and torso. The elements do not tend to merge, but are sometimes arranged in groups in the form of tassels.
Hyperkeratosis of the feet
This type of disease is often classified as a cosmetic defect and not given due attention to the treatment of the pathology. But if you let the disease take its course, the patient will soon experience all the delights of complications, which include bleeding fissures, pain when walking, and a feeling of stiffness.
The causes of foot hyperkeratosis are quite common - uncomfortable shoes, lack of foot care, excess weight, lack of vitamins, various vascular pathologies. The onset of the disease occurs at a young age - 20-30 years, with age the manifestations become more pronounced and are less amenable to therapy.
If the stratum corneum is evenly thickened over the entire surface of the heel, it is worth suspecting the fungal nature of the disease or a disorder in the endocrine system. Hyperkeratosis in the area of the outer edge of the foot indicates flaws in a person’s gait.
Hyperkeratosis of the feet
Follicular hyperkeratosis and hyperkeratosis of the feet
Subungual hyperkeratosis
This type of hyperkeratosis is detected in onychomycosis - damage to the nail plate by various filamentous fungi. The main clinical symptom of the disease is thickening of the nail plate, changes in its structure (compaction or, conversely, looseness) and color.
There are 2 degrees of severity of subungual hyperkeratosis:
- Moderate – nail thickness 1-2 mm.
- Pronounced - the nail is thicker than 2 mm.
Prevention
A very significant factor influencing the prevention and treatment of hyperkratosis is the proper care of the feet of the lower extremities. It should consist of several important procedures. This is, firstly, abundant moisturizing of the skin with the help of softening baths, both purely water and with the addition of herbal decoctions, soda, essential oils or chemical solutions intended for this. After this, your feet should not be dried too thoroughly, but should remain slightly damp. Next, we perform mechanical removal of the keratinized layers using pumice, which has different hardness, or a double-sided nail file.
The next important point will be to lubricate cleansed feet with vegetable oils (tea tree, jojoba, almond), which will not only moisturize and make the skin soft, but also heal small cracks and wounds at the same time.
In particularly advanced cases, overnight compresses made from aloe, propolis and other plants have a good effect. It is important to do this in a timely manner and not to start the process of coarsening the dermis.
Stages and degrees of skin hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis is a disease that has identical stages of development regardless of its location on the human body. The only difference is the intensity of the pathological process.
Thus, the skin surface of the face is more delicate and sensitive, which causes rapid progression of the disease. Damage to the feet can become chronic and ongoing, due to constant mechanical impact on the epithelium and involuntary separation of keratinized particles from the foot.
The following stages of hyperkeratosis of the skin surface are distinguished:
- Stage 1 - slight dryness of the epithelium appears, which is determined visually as a whiter area of skin, and during palpation it is rough;
- Stage 2 - the skin surface is covered with small particles, which are easily removed during cosmetic procedures, but appear again after 1-2 days;
- Stage 3 - the number of keratinized cells reaches its maximum, the skin becomes rough, loses its elasticity and shine; Stages of foot hyperkeratosis
- Stage 4 - the epithelium affected by hyperkeratosis partially stops performing its functions; due to the lack of a sufficient amount of moisture, cracks and ulcers constantly appear, from which ichor is released, the skin itches, and an infection may develop.
Without the organization of effective therapy, the disease reaches stage 4 of development, after which secondary diseases and complications arise. The latter are capable of affecting organs and tissues located in close proximity to the site of dermatological pathology.
Types of keratotic disease
Modern medical science classifies keratosis pilaris into 3 types. According to the specific symptoms and after identifying the causes of the disorders, the doctor determines the type of lesion and selects the appropriate treatment for it.
There are papular keratoses, these include: ringworm, especially dangerous is the one that affects the scalp; Morrow-Brook syndrome is a type of hyperkeratosis similar to acne, more often diagnosed in children.
Persistent lenticular type is a hereditary pathology, it is very rare, and its first signs appear only after 40 years. Monilectrix is an incurable disease that develops due to atrophy of hair follicles and hair loss.
Atrophying keratoses, which include:
- Superciliary cicatricial erythema is a chronic form of keratosis in which atrophy of the eyebrows develops, leaving small scars;
- Keratoderma spinosa - the formation of nodules in the hair follicles that look like spikes, resulting in partial hair loss;
- Siemens keratosis pilaris - develops in boys in the first months after birth, the symptoms are similar to erythema of infants;
- Atrophoderma vermiformis - most often appears on the cheeks, with the formation of small rashes that become tiny scars over time.
- There are also keratoses vegetans:
- Darier's disease is a genetic pathology with a chronic course, when the skin is covered with a large number of cone-shaped nodules.
- Porokeratosis of Mibelli is also a hereditary pathology in which there are single formations on the skin, usually on the legs and arms.
- Disseminated superficial keratosis of Reschigi - occurs mainly in children and is characterized by generalized lesions of the skin.
- Perforating elastoma is a hereditary pathology that provokes connective tissue pathologies.
Hyperkeratosis of the skin of the face and head
With the development of follicular hyperkeratosis on the skin of the face and head, the following signs appear:
- dryness, roughness and unevenness of the surface;
- brittle and dull hair;
- dandruff;
- burgundy bumps;
- severe hair loss.
In the absence of timely diagnosis, partial or even complete baldness occurs. Often this disease is associated with hyperkeratosis in other areas throughout the body. On the face, follicular hyperkeratosis is clearly visible - the affected area of the skin becomes dry, uneven, and scales and small spines do not form. In severe cases, the face becomes covered with a characteristic crust.
Hyperkeratosis on the legs
This form of pathology is often classified as a cosmetic defect, so it is not given importance and is not given due attention during treatment. But when the disease starts, the patient will soon feel all its complications - bleeding cracks, stiffness and pain while walking.
Causes of foot hyperkeratosis include:
- wearing uncomfortable shoes;
- improper care;
- excess weight;
- lack of vitamins;
- vascular diseases.
Usually the disease begins at another 20–30 years of age, but with age it manifests itself much more strongly and is less amenable to correction.
When the stratum corneum is thickened over the entire surface of the heels, there is a risk of fungal infection and disruption of the endocrine system. Damage to the outer edges of the foot indicates an irregular gait.
On elbows and shoulders
With elbow hyperkeratosis, rough patches of skin form on the elbows and the skin becomes very dry and rough. This violation can be found quite often, but not all people give it due importance. Goose bumps also often form on the shoulders and upper back.
Classification and causes of development of follicular hyperkeratosis
Most skin diseases from this group are hereditary in nature and begin to manifest themselves under the influence of unfavorable factors. The second type of follicular keratoses is acquired. It is divided into:
- Primary. Occurs against the background of metabolic or endocrine disorders.
- Secondary. Accompanies other dermatological disorders.
Depending on the clinical manifestations and changes in the skin, the pathology is divided into several types. Hyperkeratoses accompanied by the appearance of nodules are called papular. These include:
- Jeveri's disease. Accompanied by spiky rashes of a pinkish or orange hue. The keratinized formations can merge with each other. In 50% of cases it affects the phalanges of the fingers.
- Lenticular hyperkeratosis. It is characterized by the appearance of small, rough papules that are not prone to fusion. When the formation is removed, a bleeding depression remains. This pathology most often occurs in older men and is a rare type of keratosis.
"Goose bumps" or follicular hyperkeratosis
Oh - guys always wrapped me up in jackets in the summer - they said - oh, you're cold, but I just also have goose bumps since childhood.
1) it never bothered me at all because... not very noticeable, only rough skin to the touch.
2) at the age of 20 I rubbed with pumice. At first, the goose bumps rubbed off until they bled - but you can’t rub so hard because... first blood, then a crust, then all over again. But if you rub your hands with a pumice stone 1-3 times every day and then apply a softening cream, you can easily maintain a well-groomed appearance of your hands - and not worry - I’ve been wearing short sleeves all my life and it doesn’t bother anyone.
what does it look like?
My daughter started having a small rash on her arms and legs when she was five months old.
looks like small pimples. there's something white inside
In general, the doctors tell me that this is a diathesis
but nothing helps
neither sea nor diet
although at sea. I agree
skin becomes better
Lina, I wouldn’t be shaking either if it weren’t so noticeable... My skin, on the contrary, is quite smooth to the touch, but it looks terrible, solid red dots, sometimes with inflammation, in short, short sleeves are contraindicated for me(
Yes, the sea is perhaps the only thing that makes the skin more or less normal, but as soon as the tan goes away, everything is new. The dermatologist is of no use, she said it will go away with age (my mother is 43 and it still hasn’t gone away for her) she says use a scrub and moisturizers. But I know this even without her. By the way, coffee scrub also helps me very well, it softens perfectly and after it the skin looks much better, but this is only for a while(
I have a little on my forearms.
The cosmetologist recommended a very good scrub to me. just thermonuclear, the skin is then smooth and smooth.
salt + baking soda. in equal proportions, fine salt.
then a nourishing cream - for children or just very oily. Do this once every three days - and you practically don’t feel anything to the touch.
I have Differin lying around the house, although I bought it for pimples, but it didn’t help. There is also dalacin and baziron (though I’m allergic to it). Do you think I can try it? I really don’t know if they can be applied to large cavities.. As for vitamin A, I used retinoic ointment, the effect was minimal.
Alice, did Differin help you get rid of it for good?
Yes, pozaluisto, napiwite nazvanie krema
Ammonium Lactate Cream, 12%
some comments are funny to read)) goose bumps are not scary and it happens from birth. You can only be sure that you have goose bumps if Comrade Doctor himself tells you about it. I say this so confidently because at the age of 11 my mother took me by the hand to the doctor to show me my shoulders. He reassured my mother and gave me some advice, but I had nothing to worry about, I’m 11, what difference does it make to me what I have)) After 14, as you understand, everything changed. Now I’m 23, I don’t suffer, I don’t have complexes, I don’t suffer from this goose bump. because I almost don’t have it anymore. The advice is the same that the doctor gave her - BATH. And there is nothing better, and it helps one hundred percent. You need to visit the bathhouse regularly, at least once a month, the temperature should be at least 80 degrees, and after the steam room use a scrub and moisturizer. I’m so lucky, my mom, dad, grandma, aunt are fans of the bathhouse, so for me, the bathhouse is first and foremost a pleasure, and secondly, it’s medicine. Now and for the last three years I have no goose bumps on my thighs and mild goose bumps on my shoulders. This doesn't mean she doesn't appear anymore. It appears, but now it takes three to four months, and then I go to the bathhouse again. AND NO CREAM WILL HELP YOU LIKE THIS! Although I won’t lie and I never tried it... I didn’t have the need. And I’m not the only one, several friends and acquaintances of my parents got rid of this problem in the same way.
Hyperkeratosis of squamous epithelium
Hyperkeratosis of the squamous epithelium of the cervix is detected only during a gynecological examination. It usually does not cause any symptoms or discomfort; a small number of patients may have copious clear discharge.
To confirm the diagnosis, a scraping of epithelial cells is taken and sent for cytological examination.
Hormonal drugs
Follicular hyperkeratosis often appears after the use of hormonal drugs or hormonal contraceptives. In women, under the influence of hormonal drugs, the process of cell renewal can accelerate, which can cause keratosis, including follicular keratosis.
Stress and poor nutrition affect the condition of the entire body and disrupt the balance of group I vitamins, which affect the condition of the skin. The skin becomes dull, dry and wrinkled.
Lenticular and disseminated hyperkeratosis
The causes of these types of skin diseases of the face and body have not been fully studied. The basis of the disease is a disruption of the process of keratin formation in the cells of the epidermis. It has an unclear origin, but most scientists adhere to the version of a gene mutation in cells, accompanied by the formation of excess keratin.
The disease occurs in a chronic form, there is no tendency to regression, and the period of exacerbation is replaced by insolation. The clinical picture of lenticular hyperkeratosis is as follows: horny papules appear around the follicles - the main symptom of the disease. They are red-brown or yellow-orange in color and can reach 5 mm in diameter. If you remove the horny scale, a small wet depression appears with a drop of blood in the center. Most often, such hyperkeratoses affect the thighs, legs, back of the feet, and less often the follicles of the torso, arms and ears. In rare cases, the lenticular form of the disease can be detected on the oral mucosa. The papules are scattered, they do not merge together and do not cause pain.
With disseminated hyperkeratosis, patients develop elements on the skin that resemble thick, short hair. They are located in isolation, but sometimes papules can accumulate in groups of 3-6 affected follicles and resemble a brush. To differentiate lenticular or disseminated hyperkeratoses from warts, papillomas and ichthyosis, a histological examination is performed.
In all cases when lenticular or disseminated hyperkeratosis is diagnosed, its treatment consists of the use of special ointments and chemical peels. They are aimed at softening and moisturizing the skin, improving its condition and clinical picture, and with regular use they can solve the problem of hyperkeratosis. The use of scrubs and pumice, as in the case of hyperkeratosis of the follicles, is undesirable.
Causes of hyperkeratosis
The congenital disease is inherited from parents in a so-called autosomal dominant pattern. This means that the disease occurs in representatives of every generation, regardless of the gender of the child. The disease can be triggered by a lack of vitamin A in the body, the use of hormonal drugs, and hypothermia.
Acquired keratosis pilaris usually occurs in the following cases:
- If a person has vitamin deficiency. Vitamin A deficiency especially affects the condition of the skin (additional signs include brittle hair and blurred vision due to dry cornea). Lack of vitamins B, C, D and E contributes to the development of hyperkeratosis.
- Often, such a skin disease occurs in people infected with HIV, as well as against the background of diabetes, hypothyroidism (lack of thyroid hormones), tuberculosis, and syphilis.
- Follicular hyperkeratosis can develop as a result of skin allergies, lupus erythematosus (an autoimmune disease that affects not only the skin, but also the heart, lungs, and joints), scleroderma (damage to the skin, blood vessels, and musculoskeletal system due to pathological compaction of connective tissue) .
- Provoking factors for the occurrence of keratosis pilaris can be exposure of the skin to harmful industrial dust, chemicals, and some medicinal ointments. Sometimes the disease manifests itself after radiation and chemotherapy.
The cause of exacerbation of the disease can be the stress experienced, as well as the consumption of spicy, salty, fatty foods, and strong coffee.
Video: Causes of follicular hyperkeratosis in children. Prevention measures
Complications and prognosis
Complications caused by follicular hyperkeratosis have not yet been identified in adults. The disease manifests itself as an unpleasant cosmetic defect, does not pose a threat to life and health, but can signal the presence of internal dysfunctions and pathologies.
Ignoring the signs of follicular hyperkeratosis in a child can provoke the development of an inflammatory process, which will lead to the spread of sores throughout the body (if the disease does not go away after puberty).
With properly selected therapy, the acquired anomaly can be easily eliminated. The congenital form is incurable.
Treatment of goose bumps or follicular hyperkeratosis
One of the most characteristic signs of keratosis pilaris is considered to be roughness, which is most often localized on the skin of the upper and lower extremities on the back side. Most typical location:
It also occurs on the head, face and other parts of the body, but much less frequently. Hyperkeratosis does not affect the mucous membranes. A small rash is clearly visible on the affected areas, the color of which varies from white to pink. The brown tint of plaques is characteristic of keratosis in older people. The size of the dots is 1–2 mm.
Plaques are localized in one area or affect a fairly large area. Many patients have a symmetrical location, for example, on the right and left shoulder. Scars due to congenital hyperkeratosis are rare. Scarring is characteristic of some acquired forms of pathology.
The hairs located under the scales curl because they cannot penetrate the stratum corneum. Some people develop inflammation against this background, manifested by:
Sometimes excessive keratinization is complicated by suppuration resulting from infection of scratched pimples.
Follicular keratosis is often combined with other dermatological pathologies that require fundamentally different treatment. If you have skin problems, you should visit a dermatologist or dermatovenerologist.
Diagnosis of follicular keratosis is carried out visually
Recommendations and advice from specialist dermatologists
In order for the treatment to be successful and to avoid exacerbation of keratosis pilaris, it is recommended to avoid consuming foods that provoke skin allergies. It is necessary to strengthen the immune system, as well as the nervous system.
You should be careful when choosing clothes and wear only things made from natural materials. They should not restrict movement or rub the skin.
People suffering from skin diseases are advised to stay out of the sun as little as possible. Do not allow the skin to dry out.
How is the disease classified?
Hyperkeratosis can be hereditary or acquired. In addition to this classification, other forms of the disease are distinguished.
What skin hyperkeratosis can be like:
- follicular – expressed by the appearance of compactions and reddish pimples on the body;
- seborrheic (damage to the scalp);
- diffuse;
- warty - the formations are similar to yellowish warts, prone to cracking and crusting;
- lenticular - based on incompletely studied gene mutations, more common in men over 30 years of age, and is a chronic form;
- disseminated (scattered) – covers large areas of skin;
- polymorphic.
In turn, the follicular form also differs by species, and depends on the lack of a specific vitamin.
Follicular hyperkeratosis
This type of disease bears this name because due to a disruption in the process of exfoliation of dead epidermal cells, follicles become clogged, leading to the accumulation of sebum. On the skin, this process manifests itself in the form of redness and pimples. The disease is also called “goose bumps”.
Remember! Skin prone to dryness is most susceptible to the manifestations of the disease. This is the buttocks area and the outer surface of the thighs, knees. Sometimes rashes are confused with cellulite.
What are the reasons for:
- Bad cosmetics, violation of personal hygiene procedures, hard water, uncomfortable clothes.
- Lack of vitamin C, which is responsible for the production of collagen, which gives elasticity to blood vessels and skin. If it is not enough, the vessels become fragile, collapse, the skin becomes covered with bruises, bruises, early skin aging (wrinkles) begins, and the skin flakes off.
- Deficiency of vitamin D, which nourishes bones and skin, is responsible for the proper functioning of the thyroid gland, strengthening the immune system and removing waste and toxins. Its deficiency affects the increase in the rate of reproduction of epidermal cells, which prevents the old layer from peeling off.
- A lack of vitamin A inhibits the production of new skin cells, causing the skin to lose its smoothness, become flabby, and become inflamed.
- Taking hormonal drugs. It is observed in young girls taking contraceptives. Hormones can accelerate the formation of new cells, leading to hyperkeratosis.
- A state of stress, nervous overstrain, and increased irritability provoke disturbances in the body's functioning, which leads to excessive consumption of vitamin B. The consequence of this is aging of the skin, it becomes dry, gray in color, and flaky.
- Failure to comply with nutritional rules. Improper nutrition leads to a deficiency of vitamins necessary for the body, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, intestinal dysbiosis and, as a consequence, follicular hyperkeratosis.
Experts in the field of cosmetology and dermatology argue that the disease remains not completely cured, and the skin must be carefully cared for.
Important! Protect your skin from exposure to the sun, cold, aggressive effects on the skin of various peelings and mechanical cleansing of the skin.
Hyperkeratosis of the feet
The disease is caused by 2 groups of reasons. One of them is internal causes - various kinds of diseases, circulatory disorders, lack of vitamins and hereditary predisposition. Other reasons are external, which specifically affect the legs.
External factors:
- uncomfortable, tight or large shoes;
- excess weight;
- constant load when walking;
- foot deformity: hallux valgus, flatfoot, clubfoot, etc.;
- poor level of hygiene.
Hyperkeratosis of the feet appears in the form of thickening, affecting the entire surface of the foot. The most pronounced thickening is on the heel and big toes. The skin becomes drier, flakes, noticeably whitens and thickens. Areas of thickening are prone to cracking.
Attention! The cracks that form can be very deep and cause severe pain and bleeding. Walking becomes very difficult due to pain.
Subungual
This type of disease is caused by the activity of a fungal infection, and is the body’s protective reaction to the penetration of foreign microorganisms.
The nail plate may thicken or, conversely, become loose and change color. The disease can be expressed in a moderate form: the nail is no thicker than 1-2 mm, or it can have a pronounced form, in which the nail thickens by more than 2 mm.
People visiting public places are at greatest risk: baths, swimming pools, gyms. To protect yourself from fungus, it is important to maintain foot hygiene. Older people are more susceptible to fungal infections than younger people due to a lack of body defenses.
Important! Delaying treatment can lead to complete destruction of the nail plate.
Hyperkeratosis of the facial skin
If hyperkeratosis of the feet or surface of the body can be hidden under clothes and shoes, then hyperkeratosis of the facial skin becomes a tangible problem for its owner.
How it manifests itself:
- certain areas of the skin thicken;
- dryness, redness, peeling are noted;
- crusts form;
- the process is accompanied by pain;
- the affected area is covered with nodules and small pimples;
- active facial expressions lead to bleeding wounds and cracks;
- a whitish-gray scaly stripe forms above the lip.
Successful treatment involves the use of a whole range of measures. First, the initial cause of the development of disorders in the body is determined, then the doctor prescribes drug therapy, and various creams, ointments, masks, scrubs for care and moisturizing are prescribed for skin care.
Seborrheic
Hyperkeratosis of the scalp often remains hidden for a long time. A person complains of dandruff, split ends, brittle, dull hair, dry scalp. Sometimes there may be purple pimples and bumps, and the skin becomes like sandpaper. Often this form is combined with hyperkeratosis affecting other parts of the body.
Attention! Lack of treatment leads to hair loss, i.e. complete or partial baldness. The hair follicles die forever.
If you suspect seborrheic hyperkeratosis, you should contact a dermatologist, trichologist, hematologist, neurologist, or immunologist. They will help you understand the causes of the disease and determine the correct course of treatment. Often the cause cannot be determined precisely, and then treatment is aimed at stopping a process that cannot be completely stopped.
Cervical hyperkeratosis
The pathological condition of the cervix, in which keratinization of the epithelial layer occurs, is called leukoplakia. This condition is precancerous and requires careful diagnosis and prompt treatment. The group most susceptible to this condition are women over 40 years of age who are in the active phase of hormonal and physiological changes. Every year the disease gets younger.
What causes hyperkeratosis of squamous epithelium:
- venereal diseases in the chronic phase;
- early onset of sexual activity, variety of partners, frequent change of sexual partner;
- viruses, bacteria, fungus, candidiasis;
- unsuccessful operations, abortions;
- multiple births;
- contraceptive devices (coils, etc.), unsuitable contraceptives, poor personal hygiene;
- smoking (even passive smoking).
Careless handling of tampons, medications, and other objects inserted into the vagina.
Important! The disease is characterized by the absence of symptoms. No pain, discomfort, etc. Detection is possible only during a gynecological examination.
Hyperkeratosis presents as well-defined white patches that may protrude above the surface of the epithelial tissue.
Treatment is selected individually, based on the patient’s age, number of births (perhaps the woman has not given birth yet). Women may be offered options for radiosurgery, laser intervention, cryodestruction, and cauterization.
Treatment
It is necessary to treat not only the external signs of dermatitis, but also the diseases that led to its appearance. In order to get rid of the disease, they resort to drug therapy and the use of unconventional methods.
In order for the treatment of keratosis pilaris to be effective, the patient is prescribed physical therapy, strict adherence to a diet, and the elimination of external provoking factors, if any.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have a problem with hyperkeratosis, you should consult a dermatologist. Additionally, you may need to consult an endocrinologist or infectious disease specialist.
Drug treatment
Includes the use of ointments and gels for external application. They soften, moisturize the skin, and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Vitamin complexes and preparations based on fish oil are widely used for internal use.
For follicular hyperkeratosis the following are prescribed:
- castor oil;
- glycerol;
- "Decamine ointment";
- "Lachydrine";
- "Uroderm";
- "Davonex";
- "Tazarotene";
- "Elidel";
- "Protopic".
- The last two medications are immunomodulators and are prescribed for severe forms and complications of the disease.
Do not apply scrubs to the affected surface or rub it with a hard brush or pumice stone: there is a risk of damaging the top layer and causing infection. The skin should be cleansed using gentle cleansers.
In a child, treatment of manifestations of keratosis pilaris is carried out using:
- salicylic ointment;
- medications that contain urea;
- water-soluble petroleum jelly.
- Often childhood hyperkeratosis disappears on its own as the baby gets older.
Traditional medicine methods
To treat follicular hyperkeratosis, it is recommended to use folk remedies. In order for their use at home to be safe and bring tangible benefits, they should be used only with the permission of a doctor and under his direct supervision.
Propolis
Cover the areas affected by the rash with a thin layer of the product, apply a film on top, and wrap it with a bandage. Wear the bandage for several days.
Beet
Before use, the vegetable is thoroughly washed and the skin is removed. Then it is crushed into a paste, and the resulting mass is applied to the lesions. After three hours, wash off the compress and apply moisturizing cream to the affected areas.
Potato
The grated potato mass is applied to a cloth (gauze or bandage) and applied to the affected area. The compress is removed after 1-2 hours, the skin is washed and lubricated with cream.
Yeast
The dough is prepared with milk. After the yeast swells, add flour and make a flat cake. It is bandaged to the sprinkled areas and kept in place for several hours.
Aloe
Cut a leaf of the plant, pour boiling water over it, keep it in hot water until the liquid cools. Then the aloe is placed in the freezer, after three days it is taken out, cut into thin strips, which are then applied to the sore skin. Leave the compress on all night, remove it the next morning, and smear the painful papules with salicylic alcohol and Vaseline. Repeat the procedure until the rash disappears.
Onion peel
Take four tablespoons of onion peel, after washing it, drying and crushing it, pour in a glass of vinegar (250 ml), leave for 14 days without access to daylight. The liquid is filtered, the resulting sediment is applied to the sores, and left for no more than half an hour. After each procedure, the time can be gradually increased.
Physiotherapy methods
To make the hyperkeratotic rash disappear, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed:
- photodynamic therapy: papules are treated with a special composition, and then they are exposed to laser beams until they are completely removed from the surface of the epidermis;
- laser hair removal - helps prevent the risk of hair ingrown into the skin and reduce the number of sores.
Skin care
To provide complete care for problematic skin on which traces of hyperkeratosis have appeared, to get rid of them and to prevent further spread of rashes throughout the body, cosmetologists advise their patients:
- take medicinal baths with the addition of milk and herbal infusions;
- after water procedures, smear the body with anti-inflammatory cream;
- make herbal masks;
- use enzyme cosmetics and peeling creams.
The course of the disease in childhood
In childhood, follicular hyperkeratosis manifests itself as nodular rashes. Multiple dense nodules are noticeable on the skin; they are rough to the touch. During remission, they do not cause any inconvenience, if you do not take into account the appearance. But during exacerbation, these elements turn red and itch. When such rashes appear along with dry feet and palms, the doctor diagnoses hereditary keratosis. Most often, lesions in a child are located on the buttocks, hips, shoulders, face and head. The nodules form symmetrically and are best visible during puberty, when treatment is required.
Principles of treatment for children
In children, keratosis pilaris often requires no treatment at all. But the doctor strongly recommends sufficiently moisturizing the skin, exfoliating and relieving itching when it occurs. For this, pharmacies have many different creams, ointments and rubs that are suitable for a child at any age.
Treatment with folk remedies
Goose bumps can also be treated using traditional medicine recipes:
- Compress with aloe - to prepare it, take the leaves of a plant that is less than five years old, wash it thoroughly, freeze it for several days, cut it into thin slices and apply it to the affected areas. A film and bandage are applied on top for fixation. The compress should be left overnight and repeated every other day.
- Compress with propolis. A thin layer of propolis is spread on the skin, a film and a bandage are placed on top for fixation.
- Compress with potatoes - raw potatoes are finely rubbed on a track along with the skin, the paste is placed in gauze and applied to the affected area for 1 - 2 hours.
Diet
People who are prone to developing the disease are advised to strictly review their diet, start eating smaller meals and adjust their drinking regime. The diet should include:
- fruits and vegetables;
- red fish and seafood;
- lean meats;
- cottage cheese, milk, natural yogurt;
- eggs;
- unrefined vegetable oils;
- nuts and dried fruits;
- wholemeal bread;
- cereals
It is important to drink enough liquid - 30 ml per 1 kg of weight.
Prevention measures
It will not be possible to prevent the manifestation of follicular hyperkeratosis, but you can try to reduce the intensity of its exacerbations. To do this you need:
- with the onset of cold weather, lubricate the skin with a rich cream every day;
- eat right, take a course of multivitamin complexes in the fall and spring;
- wear clothes made from natural fabrics;
- try not to come into contact with allergens;
- use gentle detergents.
To prevent keratosis pilaris from causing severe discomfort, you must strictly follow all the rules, listen to the advice of a dermatologist or cosmetologist, and monitor the condition of the skin and the entire body as a whole. We recommend watching an informational video on the topic of the article.
Causes of hyperkeratosis
Skin hyperkeratosis is not an independent disease. Disruption of keratinization processes and thickening of the epidermis occurs with erythroderma, lichen, ichthyosis and other diseases. For a number of reasons, the disease can develop on the body of a healthy person.
Hyperkeratosis most often occurs, as mentioned above, due to excessive and prolonged compression of areas of the skin of the body or feet. The body “turns on” a defensive reaction to external aggression, carrying out increased cell division and the formation of new ones. As a result, a violation of keratinization and thickening of the epidermis, or skin hyperkeratosis, occurs. Most of the load falls on the feet, which is where the disease manifests itself most often.
The cause of impaired keratinization and thickening of the skin can be not only narrow, tight and, conversely, larger shoes, but also a person’s excess weight in combination with his high stature. Very often, hyperkeratosis of the foot occurs in people with flat feet. With this disease, the shock-absorbing properties of the spine are disrupted, causing special problems associated with the development of hyperkeratosis.
Diabetes mellitus is one of the main causes of skin hyperkeratosis. With this disease, metabolic disorders occur, sensitivity is dulled, and the skin receives insufficient nutrition. All this leads to the formation of hyperkeratosis of the foot.
The cause of this disease can be ichthyosis and psoriasis, which cause disturbances in the production of keratin and the condition of the epidermis. Poor circulation in the lower extremities can also lead to the disease.
A little about the disease
In a healthy person, the epidermis is constantly renewed, and the death of cells goes unnoticed. With pathology, changes occur in the structure of the skin, which is reflected in their appearance. The dermis on the face and body becomes denser and becomes covered with scales or dots. The reason is accelerated cell division, disrupted desquamation and the occurrence of keratosis. In simple words, we can say this: dead particles do not exfoliate, but remain on the surface and clog the hair follicles. Having examined the integument, it is possible to notice various rashes, nodules and small tubercles. Dryness and roughness are noted, and sweating in the affected areas is increased. The problem is localized in the following areas:
- legs – feet, calves and knees;
- arms - shoulders, elbows and palms;
- back.
Follicular hyperkeratosis is most often diagnosed in children, adolescents and people with weakened immune systems. The disease is not considered dangerous, but it must be treated. Untimely therapy spreads over large areas, causes severe itching and looks very unpleasant. If you scratch the inflamed areas, a bacterial infection may occur.
Drug treatment
The course of using drugs to regulate the division and desquamation of horny scales may vary. It consists of both preparations for oral administration and ointments or creams for topical use. The right remedy allows you to completely get rid of the problem. The following types of drugs are used:
- Corticosteroids. Necessary for advanced forms of the disease, which is accompanied by an inflammatory process. Effective products in the form of ointments, according to reviews from many patients: Prednisolone, Flucinar, Dermovate, Hydrocortisone or Beloderm.
- Retinoids. Derivatives and synthetic analogues of vitamin A, necessary for the regeneration of skin cells. In addition, the drugs suppress the keratinization process, preventing growths on the dermis. Available in different forms: creams and ointments, oral tablets and solutions for injections. Videstim, Lokatsid, Retin-A, Neotigazon and Tigazon have the best results.
- Products based on salicylic acid. Solutions and ointments help fight the stratum corneum, removing cells and preventing recurrence. It is recommended to use ointments with a concentration of 1 to 10%, as well as solutions (no more than 2%). Depending on the problem, apply it directly to the rash or treat large affected areas.
It is necessary to use vitamins not only for external, but also for internal use. Patients are often prescribed vitamin complexes with a high content of vitamins A and C. Therapy is sometimes delayed for a long time, but it cannot be interrupted. A break can provoke focal hyperkeratosis on the body or face.
Clinical manifestations of some keratoses
Hyperkeratosis is a skin disease that is considered a pathology; its occurrence is evidenced by the proliferation of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. If we talk about the natural processes that occur on the skin of a healthy person, then this is the regular exfoliation of the upper layer of the epidermis and the growth of new skin cells instead of old ones.
Pityriasis pilaris
Being widespread, it begins to appear in children of 2–3 years of age, reaches maximum development (usually in girls and young women) by 15–20 years, after which its activity gradually decreases and “fades out” by adulthood.
The disease is characterized by rashes localized on the arms and legs (outer surface), on the skin of the buttocks and, less commonly, on the face, on the skin of the scalp, elbows and knee joints. The elements are reddish small dense nodules, pierced in the center with a twisted, spiral-like vellus hair. The affected areas resemble "goose bumps" that occur with chills or a sudden feeling of fear.
The rashes are accompanied by slight itching, increased dryness of the affected areas and mild peeling, especially in the area of the outer surface of the upper and lower extremities. These phenomena intensify at low environmental humidity.
Pityriasis pilaris
Devergie's disease
Or pityriasis versicolor pilaris Devergie - a rare chronic inflammatory dermatosis with a gradual, less often acute, onset with satisfactory general health. There are two clinical variants of the disease:
- Classical.
- Juvenile Limited.
This keratosis is represented by eruptions of papular follicular elements of a conical shape with characteristic spines of the horny epithelium, called “Beignet cones”. The follicles, in the center of which the hair is located, are surrounded by an erythematous zone. When palpating the surface of the skin in the area of the nodule rash, a typical roughness is felt (the “grater” symptom). An orange-red or brick-red color of the rash is also typical.
At the initial stage, the rashes are grouped into one plaque or erythematous spots localized on the upper half of the body. Subsequently, they gradually spread to the lower half of the body, to the face and scalp. On the face they look like erythematous spots with moderate peeling, and on the head they are accompanied by itching of varying intensity and pityriasis-like peeling, reminiscent of seborrheic dermatitis.
Over time, the clinical symptoms gradually change. Individual scaly erythematous plaques merge, resulting in the spread of skin lesions, and the process takes the form of diffuse erythroderma. In this case, the most important differential diagnostic symptom is individual round (coin-shaped) areas, the diameter of which is about 10 mm, of visually healthy skin.
They are randomly scattered on any part of the body and are located against the background of diffuse erythroderma. Peeling in the area of the lesions is heterogeneous. It is small-plate in nature on the upper half of the body and, predominantly, large-plate in nature on the lower.
Half of the cases of the disease are accompanied by Bignet's sign, which is hyperkeratosis of the dorsal surface of the digital phalanges of the hand. In 80% of cases, at the beginning of the disease or a little later, hyperkeratosis of a yellowish-red color develops on the palmar and plantar surfaces.
But often the elements of the rash in Devergie’s disease may be similar to those of psoriasis, and diffuse erythroderma may be similar to toxicoderma. In addition, there is frequent damage to the nails, manifested in pronounced subungual hyperkeratosis, yellowish coloration and longitudinal or transverse striations of the nail plates, and their deformation like a “bird’s claw” (onychogryphosis).
It appears as small scattered yellowish-orange or reddish-brownish horny papules with a diameter of up to 5 mm. Sometimes papules may be surrounded by a ridge of the same color. Under the horny masses (after their removal) a depression is exposed with a somewhat moist surface and pinpoint bleeding.
It usually begins in childhood with dry skin on the palms and feet, which gradually spreads to the scalp and torso. As a result of severe keratoderma, deep folds and cracks form on the palms and soles. In addition, thickening and deformation of the nail plates gradually develop, and longitudinal grooves appear on them.
Against the background of dry skin, scattered follicular dry nodules of dense consistency and round shape appear, in the center of some of them a horny spine or a fragment of hair is visible. The elements have a grayish color, are located, as a rule, symmetrically and are localized mainly on the buttocks, the lateral surface of the arms and legs, and very rarely on the face (mainly in children). In some cases, skin hyperemia occurs in the areas of the rash. The process worsens during the cold season of the year.
It is more common among men and begins in adolescence. There are descriptions of family cases of this pathology. Characteristic elements are isolated, densely located follicular papules. The inflammatory reaction is not expressed. In the central section of the follicular opening of the pathological element there is a thin grayish scale, after removal of which black dots are exposed. After the elements of the rash resolve, a depigmented atrophic scar remains in their place.
As a rule, it manifests itself in childhood or adolescence (sometimes at birth) with erythema, closely spaced follicular hyperkeratic nodules, creating the impression of a granular relief, and atrophic changes of varying severity.
The rashes are symmetrical in nature and are initially localized on the skin of the outer eyebrow area, after which they can spread to the skin of the forehead, cheeks, chin and, in very rare cases, the shoulder area, buttocks and thighs. After some time, the formation of superficial follicular scars occurs, combined with excessive keratinization, which gives the lesions a mesh appearance.
On the skin of the cheeks, redness (erythema) with mildly expressed keratosis and almost imperceptible atrophy predominates. Atrophic processes lead to hair loss (sometimes significant) in the eyebrow area. Sometimes pityriasis-like peeling and bluishness of the nail phalanges, redness of the skin in the area of the palms and soles may develop.
There have been cases of combination of keratosis with congenital malformations, with a slowdown in physical and mental development.
Or Darier's follicular dyskeratosis vegetans, is a relatively rare pathology characterized by multiple isolated follicular hyperkeratic rashes up to 5 mm in diameter on “seborrheic” areas of the skin.
The disease develops in children and adolescents. The elements of the rash are initially flesh-colored. Then they become covered with small grayish-brown crusts, merging into growing (vegetative) warty lesions, accompanied by weeping in the skin folds. Initially, the rash appears on the skin of the face and scalp, behind the ears, spreads to the interscapular area, sternum area, skin folds and sometimes throughout the body.
One of the characteristic symptoms of the disease is hyperkeratosis under the nails. Splitting and uneven breaking of the nail plates occur at the free edge. Cracks appear on them in the form of the letter “V” and longitudinal, alternating reddish-brown and whitish lines.
On the dorsum of the hands and feet, the rashes resemble warts. Sometimes it is possible to damage the palmar and plantar surfaces in the form of mildly expressed pinpoint hyperkeratosis, widespread or resembling broken lines. Isolated cases of a combination of skin lesions with small whitish-bluish papular rashes on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, esophagus and larynx, rectum and vagina have been described.
Complications of the disease are possible as a result of infection with a skin bacterial-viral infection, as well as exacerbation in the spring and summer, due to increased sensitivity to ultraviolet rays.
Pityriasis versicolor pilaris Devergie
Salon and home treatments for follicular hyperkeratosis
So, we have established that the affected areas should not be subjected to harsh mechanical stress. This means that chemical peels (using salicylic, glycolic and lactic acid) are more suitable for us. After such peeling, the cosmetologist usually applies moisturizing and softening cosmetics to avoid drying out the skin.
In addition, laser facial resurfacing will be effective for follicular hyperkeratosis. For skin care at home, baths with the addition of a decoction of thyme, celandine, horse chestnut, chamomile or nettle are recommended. After taking a bath, you need to apply a nourishing cream or body milk that will help relieve inflammation. In addition, masks (compresses) with aloe, propolis, and grated potatoes will be useful.
Treatment and prevention of the disease will be more effective if you normalize your sleep and rest patterns, adjust your diet, and lead a healthy lifestyle. In addition, special attention should be paid to the choice of face and body skin care products, giving preference to gels, foams and tonics that will soften and moisturize the skin.
You may be interested in: Acne. Development mechanisms and predisposing factors
Goose bumps, or keratosis pilaris
Goose bumps most often appear on the arms, cheeks and legs, but can occur on any other part of the body. Follicular keratosis is excessive keratinization of the skin. This condition does not harm the body, although sometimes the bumps can be painful. But more often this dermatological disease is regarded as a cosmetic defect. Of course, you can put up with this, but you really want to have smooth skin, wear open tops, short dresses. Therefore, it is better not to put up, but to declare battle on the unpleasant “goose bumps”!
The nasty little bumps can be white, pink, red or even purple. They can appear in a small area, or, conversely, occupy a large part of the body. For some, they become inflamed, and then redness appears in the affected area. In the winter season, the affected skin dries out, begins to itch, and the bumps become pronounced. In any case, you need to consult a dermatologist to make an accurate diagnosis.
Where does this less than aesthetic phenomenon come from? Keratin plugs are to blame for everything - keratinized keratin, which normally should be easily removed from the skin. In case of disease, dead epithelium is not removed, but accumulates in the area of the follicles where hairs grow on the skin. Sebum attaches to keratin, causing inflammation in the form of pimples and bumps. It is not known exactly why this happens; experts are inclined to believe that genetics is to blame. Keratosis is more pronounced in those people who have thicker body hair. In youth, the phenomena of keratosis are more noticeable; with age they may disappear.
To treat keratosis pilaris, dermatologists prescribe medications, ointments, creams containing salicylic, lactic, glycolic acid, and urea. Treatment cannot be neglected if you want to have smooth, beautiful skin. If keratosis is not too pronounced, regular use of moisturizers, a balanced diet, and the predominance of natural fabrics in clothing are sufficient. Also, use soft scrubs, gommages and natural body peels 1-2 times a week to remove dead skin cells. Take vitamins A and E and omega acids internally.
We advise you to supplement your treatment with simple but effective methods!
1. Sea salt. Add it to body scrubs, mixing it with honey. Apply and rub the scrub very carefully without causing pain. leave on the body for 15 minutes, then rinse with warm water.
2. Brush with natural bristles. This method can only be used if the pimples are not inflamed or painful. Gently massage the affected areas with a brush, removing dried keratinized tubercles. After dry brushing, take a warm shower and apply a moisturizing body oil such as coconut. Instead of a brush, you can use pumice, but then cleaning should not be dry - clean the skin using soap foam.
3. Moisturizing body mask. Take 2 teaspoons of avocado pulp, mix with honey, olive oil and kefir. There should be one teaspoon of each product. Apply the mixture to the affected areas of the body, rinse after 15 minutes under a warm shower.
4. Enrich your diet with leafy greens, beets, berries, and fatty fish. Drink more water.
5. Try to be in a dry, cold room less often, and expose goose bumps to the sun’s rays more often.
Important!
Don’t take on all the methods at once, try them one at a time - carefully and without fanaticism. If any unwanted effects occur, stop using this method immediately.
Good luck in your fight for soft and healthy skin!
Was the article helpful? Like and don't forget to subscribe to the channel!
Hyperkeratosis of the foot or plantar hyperkeratosis
Signs of foot hyperkeratosis:
Dry callus - most often located in places that are the supporting points of the bones: the heels, the space under the toes in the area of the metatarsophalangeal joints (where the foot connects to the toes).
The skin in these places experiences increased pressure, being squeezed between the supporting surface and the bone. As a result, a formation with a clear boundary is formed, consisting of compressed keratinized scales.
Calluses are characterized by uniform thickness and yellow color, and may be accompanied by painful sensations, especially when pressure on the affected area increases and cracks form.
Core callus is a dry callus, in the center of which a translucent dense core consisting of horny masses is formed.
The edges of the callus are smooth, the boundaries are clear. It is characterized by sharp pain when pressed vertically, which is caused by the impact of the horny rod on the nerve endings inside the skin.
The areas of the sole in the area of the metatarsophalangeal joints, the so-called “ball of the foot”, the lateral areas of 1-5 toes, the skin of the toes on the back of the foot above the joints between the phalanges, especially with a “hammer-shaped” deformity of these toes, are susceptible to the formation of core calluses.
The soft callus is localized between the fingers, where there is increased humidity, so areas of ulceration (maceration) appear on it, causing constant severe pain and burning.
It is often complicated by the addition of infection and the development of inflammation.
Fissures are a complication of common hyperkeratosis of the foot and usually develop around the heel. Cracks can bleed, become wet, become infected, and cause significant pain and discomfort.
The squamous form of mycosis of the feet is observed in diabetes mellitus. With this form, flat, dry plaques and thickened spots (papules) appear on the skin of the arch of the foot, blue-red in color and covered with gray scales.
Along the edge of the plaques, you can identify a kind of “border” of exfoliated cells. These rashes can unite and occupy a large area, and sometimes the entire sole, back and sides of the foot. Along with such manifestations, patients may have dry yellow calluses with cracks.
With subungual hyperkeratosis, the most common cause is fungal infection of the nails. It is also observed with injuries and dystrophy of the nail plate. A sign of a pathological process will be a gradual thickening of the nail, starting from its edge.
In response to the proliferation of fungal flora, keratinocytes begin to rapidly divide and form a mass of horny epithelium of gray-yellow color, which accumulates under the nail plate, lifting the latter and creating a visible thickening of the nail.
Subungual hyperkeratosis can occur not only on the feet, but also on the hands.
General information
Hyperkeratosis is understood as a pathological change in the epidermis due to excessive thickening of its upper stratum corneum. Superficial horny scales of the epidermis normally contain a certain amount of keratin protein and are exfoliated from the surface of the skin. Delayed desquamation of the horny plates or increased formation of keratin in them (as a result of constant irritation or poor nutrition of the skin) lead to the development of hyperkeratosis. With follicular hyperkeratosis, the mouths of hair follicles are involved in the pathological process with the development of their aseptic inflammation. Follicular hyperkeratosis, or “goose bumps,” is not only an aesthetic, but also a dermatological problem that requires a comprehensive cosmetic and medical solution.