A gastric ulcer is a frequently recurrent pathology of a chronic nature, in which ulcerative defects form on the mucous membrane of the organ. The course of the disease is characterized by alternating periods of exacerbation and remission.
The main cause of the development of the disease is considered to be an imbalance in the interaction of the protective mechanisms of the gastrointestinal tract and the influence of aggressive environmental factors. Having discovered the manifestations of symptoms of a stomach ulcer, it is necessary to seek medical help, since this pathology can threaten not only health, but also human life.
Causes of peptic ulcer
The main and main cause of the development of stomach ulcers is considered to be Helicobacter pylori infection. The acid-fast bacterium Helicobacter can destroy the mucous membranes of the stomach, and the duodenum is also affected.
The transmission of the bacterium to each other can occur through household contact with an infected person (through saliva during a kiss, through shared utensils and hygiene items). Men are more prone to the disease than women.
Other common causes of ulcers include:
- Poor nutrition
- Constant stress and anxiety, shock
- Hereditary predisposition
- Chronic diseases of the digestive system
- Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages
- Taking certain groups of medications
- Development of the disease against the background of hepatitis, cirrhosis, pancreatitis, tuberculosis, Crohn's disease
- First blood group
Coffee, cocoa, water with gases, too cold or too hot food, baked goods - all this can be classified as dangerous factors that can provoke peptic ulcers. People who smoke also belong to the risk group.
Causes
Bacteria Helicobacter pylori
For many years, the bacteria Helicobacter pylori was considered the only “culprit” of stomach ulcers. These are unique microorganisms: hydrochloric acid, which is the basis of gastric juice, in combination with caustic pancreatic enzymes, is a highly toxic environment for most living organisms. Up to 99% of all microorganisms accidentally swallowed or ingested with food die in the stomach. This is why a healthy person can eat a small amount of obviously stale food without consequences - harmful bacteria will be destroyed and digested.
The exception is the strains of the genus Helicobacter, which not only withstand this acidic environment, but are also capable of changing it. By actively multiplying, they alkalize the stomach, reducing the efficiency of food digestion and causing symptoms of gastritis with low acidity. As a result, an imbalance occurs, leading to uncontrolled proliferation of Helicobacter, inflammation and ulcers.
This theory has now been refuted, since bacteria have been found in the stomach of almost all people in the world. They live in an acidic environment, but do no harm.
Thus, Helicobacter pylori is called only one of the factors in the development of stomach ulcers, among others the following:
- Inadequate immune response to the presence of microorganisms. The body, trying to fight the invading agents, “eats” itself.
- Gastritis with high acidity as a predisposing factor - in this case, the content of Helicobacter may be acceptable or low.
- Abuse of alcohol, spicy foods, caffeinated drinks.
- Anomalies of the autonomic system associated with the central nervous system and mental disorders - attacks of ulcers sometimes occur against the background of neuroses, depression, and severe stress.
- Infections that weaken the body - tuberculosis, HIV.
- A separate provoking factor is smoking. Nicotinic acid in combination with resins inevitably enters the esophagus and stomach, corroding it.
- Abuse of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - ordinary aspirin is often the culprit of gastric bleeding.
In young people, stomach ulcers usually develop due to poor nutrition. Eating fast “on the run,” abuse of coffee and energy drinks, fast food and other junk foods interfere with the normal functions of gastric juice secretion.
The impact of Helicobacter is considered by modern medicine to be secondary, although 38% of patients with gastric and duodenal ulcers actually find abundant contamination with these microorganisms.
What are the symptoms of a peptic ulcer?
Stomach ulcer is considered a rather complex and dangerous disease. If its signs are not recognized in time and proper treatment is not started, the disease can lead to the death of the patient. The difficulty is that gastritis and ulcers have similar symptoms, which is why the diagnosis can be made incorrectly.
How to recognize a stomach ulcer? The first characteristic symptoms:
- Pain in the central region of the upper half of the peritoneum. This symptom is typical for most patients. At the same time, patients often note that the pain intensifies after physical activity, eating “bad” food, alcohol and smoking cigarettes. The pain may radiate to the heart area.
- High acidity of gastric juice.
- Almost 90% of patients suffer from heartburn due to an ulcer an hour to an hour and a half after eating.
- Vomiting and nausea after overeating.
- Loss of appetite (on a subconscious level, the patient is afraid of experiencing pain after eating, and deliberately avoids eating).
- Patients suffer from sour belching, which has a bitter taste.
- Feeling of heaviness after eating, flatulence.
- A feeling of satiety occurs after eating a small amount of food.
- Patients may lose weight rapidly.
- Problems with going to the toilet (constipation or diarrhea).
- Pain is felt when palpating the stomach.
- A dense white coating forms on the upper part of the tongue.
- Patients may experience sweaty palms (this is a fairly rare symptom).
The main manifestation of the disease
Most often, the disease manifests itself in severe unbearable pain. A stomach ulcer is characterized by the presence of wounds of various sizes, which can be localized in different places on the mucous membrane of the organ. It is clear that these damage to the walls of the stomach, no matter how small they are, can cause pain.
Pain from a stomach ulcer can be either constant or paroxysmal. Most often they appear after eating (in a couple of minutes or after half an hour). They may disturb the patient at night or on an empty stomach, and increase after smoking or drinking alcoholic beverages.
Quite often it occurs that the pain radiates to the back or behind the sternum; as a result, a person complains about the heart or lower back, not realizing the true pathology. Such radiating pain makes it difficult to diagnose and detect the real problem.
Signs of exacerbation of a stomach ulcer
A stomach ulcer has a wave-like course - a period of remission is replaced by a stage of exacerbation. The manifestation of signs of exacerbation of a stomach ulcer directly depends on the severity of the disease.
The most common symptom is heaviness and pain in the area between the navel and sternum. The pain can last up to several hours. Therefore, it is difficult not to notice the exacerbation of the ulcer. In the acute form of the disease they say “an ulcer has opened.”
What are the main signs of exacerbation of an ulcer:
- Sharp, severe pain that is difficult to bear.
- The chair is black. This color “indicates” that gastric bleeding has begun.
- Vomiting blood.
Where pain can usually be felt (pain location):
- The cardinal section of the stomach, not far from the esophagus - aching pain, a feeling of heaviness in the pit of the stomach. Pain occurs immediately after eating. In this case, the pain can “transition” to the heart area. Accompanied by heartburn and belching.
- The middle section or bottom of the stomach - dull pain. Occurs on an empty stomach, or 30 minutes after eating. There is no belching or heartburn. But the tongue becomes covered with a white coating.
- Pyloric part of the stomach - pain can be felt three hours after eating. The pain also occurs at night. Eating food can dull the pain. There is heartburn and belching.
An exacerbation of a peptic ulcer is very dangerous and can lead to the formation of scar tissue, which will become an obstacle to the passage of gastric contents into the small intestine.
If signs of an aggravated ulcer are detected, you should immediately seek medical help.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease and their intensity vary and depend on:
- places where the ulcer is located;
- size of the ulcer;
- general state of human health, his age;
- presence of other diseases;
- acidity level.
The main symptom of the disease is abdominal pain, which appears in the epigastric region and spreads to the thoracic region, then under the left shoulder blade or to the lumbar region, can be localized between the shoulder blades or spread throughout the body.
Video on the topic:
How does an ulcer manifest itself at an early stage?
A slight aching pain is felt, which intensifies when eating spicy foods, drinking alcohol, or with a long interval between meals. Painful sensations can intensify with physical activity. As the disease develops, a traceable connection appears between food intake and the occurrence of pain. By observing the time that passes after eating and before the onset of the first manifestations of pain, you can find out the area of damage to the mucous membrane.
| Area affected by ulcers | Characteristics of pain |
| Cardiac, subcardial | The pain is mild, appears within 20 minutes after eating, is concentrated in the upper part of the stomach, and can radiate to the heart. There is no connection with physical activity; it directly depends on food intake. Plain milk and taking antacids help reduce pain. |
| Lesser curvature of the stomach | Mild, aching pain occurs in the epigastric region. About an hour passes from the start of eating until the first pain appears. The pain subsides when the stomach contents pass into the intestines. As the ulcer develops, painful sensations often begin to occur at night, in the evenings, and during long intervals between meals. |
| Greater curvature of the stomach | The pain is not intense, of a vague nature. There is no clear connection between food intake and the occurrence of pain. In this area of the stomach, ulcerative lesions are very rare, but in half of the cases these formations can turn out to be malignant. |
| Antrum | The pain is localized most often in the epigastric region, quite strong, aching in nature. Usually occurs in the evening or at night. May be accompanied by sour belching, heartburn, and in severe cases, vomiting and bleeding are possible. |
| Pyloric canal | The pain often occurs in attacks throughout the day, is intense and can last about half an hour. In some cases, the pain has an increasing character with a quiet attenuation. It usually occurs at night and with long intervals between meals. Localization - right side of the thoracic region. |
In addition to pain localized in various areas of the stomach, the patient also experiences other symptoms:
- heartburn. This symptom is often the only manifestation of gastric ulceration for a long time. A burning sensation in the esophagus and epigastric region occurs in 80% of patients. Heartburn appears after eating one and a half to two hours before the onset of pain or can alternate with them;
- belching. This symptom occurs in half of patients with peptic ulcer disease. Usually this is a sour belch, but in some cases there is also a bitter belch;
- nausea or vomiting. These signs indicate an exacerbation of the disease. Nausea may occur several hours after eating along with pain, vomiting occurs at the maximum of pain syndromes and brings relief;
- constipation Can occur in almost half of cases of the disease. Often constipation is caused by a decrease in physical activity, the absence of foods with coarse fiber in the menu and reflex intestinal dyskinesia. Exacerbation of the ulcer increases constipation, often causing more suffering to the patient than the existing pain in the stomach. Constipation causes irritation in the colon and in this case it alternates with diarrhea.
Additional symptoms
Other symptoms of a stomach ulcer may include:
- increased gas formation;
- thick coating on the tongue;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating;
- increased sweating of the palms;
- painful sensations on palpation in the epigastric zone.
Separately, any of these signs may indicate other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, but if 2-3 of the above symptoms occur simultaneously, the presence of an ulcer may be present.
A characteristic manifestation of gastric ulcers is periodicity - alternation of exacerbations and remissions. If there are no other diseases besides a stomach ulcer, the exacerbation stage can last from 6 to 12 weeks, then the symptoms completely disappear and the ulcerative defects are scarred. The remission stage ranges from several months to several years, until the first provoking factor. In later stages of the disease, relapses become more frequent and can occur almost every autumn or spring.
Complications of peptic ulcer
A stomach ulcer can cause the following unpleasant and very serious complications:
- Perforation or perforation. With this complication, the wall of the mucous membrane is depleted and a through hole is formed. Through this opening, the contents of the stomach enter the abdominal cavity. As a result, the patient is diagnosed with peritonitis, which is extremely life-threatening.
- In approximately 80% of patients, ulcerative bleeding occurs, the intensity of which depends on the location and extent of the lesion.
- An ulcer that is not cured in time quickly becomes chronic. Patients with chronic ulcers have to undergo a therapeutic course twice a year to stop the next attack of exacerbation.
- Adhesion of neighboring organs to the stomach. With chronic peptic ulcer disease, the walls of the stomach are gradually destroyed, neighboring organs (for example, the liver) can stick to the stomach and the disease can spread further.
See also on the blog: Alternative treatment of the pancreas at home
Characteristics of the disease
Before examining in detail the symptoms of stomach ulcers in adults, it is necessary to find out what kind of disease it is and what its features are.
In short, this is a painful pathological condition characterized by damage to the internal mucous tissue of the stomach. Small wounds are corroded by gastric juice, which provokes a deterioration of the condition. Deeper lesions appear, similar to ulcers.
According to reviews, stomach ulcers are a recurrent chronic disease. That is, it is characterized by a constant sluggish course and regular exacerbations. Most often, the condition worsens in autumn and/or spring.
Sometimes the disease manifests itself in the form of a single wound on the wall of the stomach. However, more often than not, multiple lesion sites are observed.
According to experts, ulcers occur more often in young men than in girls. On the other hand, women during menopause are more susceptible to the disease than middle-aged men.
Signs of a perforated stomach ulcer
Perforation is the formation of a through hole in the walls of the stomach. The reasons for this phenomenon may be the following:
- Exacerbation of chronic ulcers
- Overeating, excessive filling of the stomach with food
- Diet violations (eating spicy, salty foods)
- Increased gastric acidity
- Sudden physical activity
A perforated ulcer begins with a mild form and gradually progresses to a severe stage. The main symptom is severe pain, which is accompanied by various symptoms at all stages.
Signs of a perforated stomach ulcer:
- Constant feeling of nausea and frequent vomiting
- Skin becomes pale
- The patient produces cold sweat
- Increased heart rate and shortness of breath appear
- Pain spreads to the entire abdomen and upper limbs
- The body temperature rises sharply and significantly, and a fever may even begin
- The abdominal muscles tense, causing unbearable pain when touched
In the early stages of perforation of the ulcer, the patient experiences severe pain, but it can be alleviated by taking a special position (lying on the right side and pressing the legs bent at the knees as close to the body as possible).
At the next stage of perforation, the patient feels relief and almost no pain is felt. But a day after perforation, all signs of a perforated ulcer worsen and the patient’s condition greatly deteriorates.
What is a stomach ulcer and its causes?
A gastric ulcer is a pathology that is characterized by the formation of small defects (ulcers) in the gastric mucosa. The causes of this disease are considered to be:
- bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- negative effects of bile, hydrochloric acid;
- long-term use of anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs, hormone-based drugs;
- other factors.
Peptic ulcer disease is an irreversible pathology; scars form at the sites where ulcerative defects occur.
This disease is classified as a chronic disease and has a cyclical course of the disease. Stages of remission alternate with exacerbations, which most often occur in the autumn and spring months. Peptic ulcers are among the most common diseases, along with cardiovascular and oncological diseases.
According to statistics, gastric ulcers are found in 10% of the population, about a third of this number did not even suspect the existence of this disease before. The first signs of the disease are quite mild and are often mistaken for stomach colic, indigestion and other digestive problems; sometimes the onset of the disease is asymptomatic.
Diagnosis and treatment
To diagnose a gastric ulcer, a FEGDS procedure and radiography are performed. Urine, feces and blood are also given for analysis and an ultrasound examination of the stomach and abdominal organs is performed. A biopsy is necessary to detect Helicobacter bacteria.
Unfortunately, there is no medicine yet that can cure ulcers. Treatment should be carried out comprehensively and aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease.
If the ulcer is caused by Helicobacter bacteria, then the infection is first eliminated and the acidity of the gastric juice decreases.
Further treatment is aimed at restoring the damaged mucous membrane.
Treatment of ulcers takes from two weeks to two months. Patients are usually prescribed medications Omeprazole and Amoxicillin. Clarithromycin. However, the course, duration and methods of treatment are determined by the doctor individually, depending on the severity of the disease.
If medications cause complications and if certain indicators are present, surgery may be performed.
See also on the blog: Diet for gastritis of the stomach: menu for the day
Indicators for surgery:
- Perforation of the ulcer
- Heavy bleeding
- Malignant neoplasms
Scheme of disease development
In order to promptly identify the disease and prevent the occurrence of complications, you need to know what an ulcer is, what symptoms the disease manifests, what types of stomach ulcers there are and the causes that provoke the progression of pathological processes.
The inner walls of the stomach are covered with a mucous membrane formed by the organ itself. This is a kind of protective layer that blocks the influence of various types of “foreign” microorganisms and gastric juice, as well as preventing mechanical defects from rough food or foreign objects accidentally entering the stomach. If an organ, due to certain reasons, does not produce a sufficient amount of mucus, sensitive places appear in the protective shell, where ulcerative defects are formed under the active influence of irritating factors.
Depending on the characteristics of development, the following classification of types of ulcers has been compiled:
According to the clinical picture:
- acute;
- chronic.
According to the nature of the damage localization:
- cardinal part of the stomach;
- antrum;
- subcardinal section;
- pyloric canal;
- body of the stomach (along the anterior or posterior wall, along the lesser or greater curvature).
By number of affected areas:
- multiple defects;
- single ulcers.
According to the size of the ulcerative defect:
- small (up to 0.5 cm);
- medium (from 0.5 to 1 cm);
- large (from 1.1 to 3 cm);
- gigantic (more than 3 cm).
By degree and stage of development:
- active stage;
- healing;
- scarring;
- remission stage.
By phase:
- relapse (exacerbation);
- incomplete remission;
- complete remission.
According to the course of the disease:
- hidden;
- mild form with rare relapses;
- moderate severity (relapses up to 2 times a year)
- severe form (complications and frequent relapses).
Regardless of the type of peptic ulcer, patients experience inflammation of the mucous membrane, disruption of the digestive process, general weakness and pain in the abdominal area. At the first signs of a stomach ulcer, you should consult a gastroenterologist who can accurately diagnose the presence and type of disease, the stage of its development and possible complications. The doctor also determines the causes of the pathology and determines whether a stomach ulcer can be cured in each individual case.
Traditional treatment
Folk remedies for stomach ulcers can be used at home to relieve pain only in the absence of exacerbations.
- Potato juice. Grate the potatoes and extract potato juice by squeezing. Dilute the juice with boiled water in a 1:1 ratio. Drink on an empty stomach 30 minutes before breakfast.
- Plantain. This plant has a healing effect. Plantain leaves should be brewed and drunk instead of tea.
- To make the taste more pleasant, you can add a little honey.
- Sea buckthorn oil helps a lot. It should be taken 2-3 weeks one hour before meals.
- Taking a glass of kefir at night with the addition of 1 tbsp will help relieve the symptoms of ulcers. salted butter.
Treatment methods
Gastric ulcer is a chronic disease that requires constant maintenance therapy in combination with proper nutrition. Treatment begins with a thorough diagnosis, since the symptoms of ulcers, gastritis and other diseases of the digestive system are largely similar.
Therapy for stomach ulcers consists of several components - drug treatment, surgery, diet, and traditional recipes.
Medicines
To destroy Helicobacter bacteria, antibiotics of the following groups are used:
- macrolides – Erythromycin, Clarithromycin;
- antibacterial agents of the penicillin group - Amoxicillin;
- nitroimidazoles – Metronidazole.
Important! You can learn about the treatment of stomach and duodenal ulcers here.
To reduce the acidity of gastric juice, Omeprazole, Ranitidine, Almagel, Maalox are used. De-nol is an effective drug that not only has an astringent effect, but also destroys Helibacter infection.
Solcoseryl is used for intravenous injections - the drug promotes the rapid restoration of the epithelium on the surface of the stomach.
Important! In therapy, 3–4 components are used simultaneously; the doctor selects them individually. Duration of treatment – 2 weeks.
Diet
A diet for ulcers involves a complete abstinence from alcohol, strong coffee, and all unhealthy, hot and cold foods. You should not eat foods that are designed to increase appetite - onions, garlic, radishes.
You can only eat steamed and boiled food in a liquid or pureed state. You should eat 5-6 times a day, drink 250 ml of milk for breakfast every day, eat cereal, prepare dishes from seasonal vegetables, non-acidic fruits and berries.
Surgery is necessary when the ulcer is perforated - otherwise the cells may degenerate into neoplasms that are similar to malignant tumors.
Important! How to treat stomach ulcers at home? Read our article.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods can be used only during periods of remission of peptic ulcer disease. Juice therapy helps cope with stomach ulcers. Healthy juices - cabbage, potato, blackcurrant, birch, sea buckthorn.
Important! Find out more about treating ulcers with folk remedies on our website.
Honey will help reduce the manifestation of peptic ulcers. Mix 300 ml of liquid honey with 300 g of chopped walnuts and unsalted butter. Place the mixture in a fireproof dish and bake in the oven for 20 minutes at 100 degrees. Take 15 g of medication three times a day 30 minutes before meals, do not drink it.
Stomach ulcers are an incurable disease, so they are easier to prevent. Stress, alcohol and smoking, junk food, and poor diet have a negative impact on the functioning of the digestive system. The diet should contain a minimum amount of foods that irritate the gastric mucosa and increase acidity. Hands should be washed frequently and thoroughly to avoid Helicobacter pylori infection entering the body.
Nutrition for stomach ulcers
Diet for stomach ulcers is extremely important. It is very important to eat foods that will not destroy the walls of the stomach. It is better for the food to be ground. You should eat food that does not need to be chewed for a long time (to reduce the production of gastric juice).
Foods that will worsen the condition of peptic ulcers:
- Salt
- Fatty meat, lard
- Fried food
- Spices and seasonings
- Sausages, smoked meats, preserves
- Bakery products
- Strong tea and coffee
- Soda
What to eat:
- Eggs, steamed omelet
- White bread
- Dairy and vegetable soups
- Boiled vegetables
- Dairy
- Boiled meat and boiled fish
- Porridge, pasta
- Weak tea, compote
- Rose hip decoction
- Non-acidic juices
- Water without gas
Nutrition for an ulcer patient
Treatment of peptic ulcer is impossible without following a special diet. Otherwise, relapses or complications occur. The patient is allowed to eat lean meats, jelly, porridge cooked in water, low-fat dairy products, and boiled eggs.
Coffee, alcoholic beverages, fried, fatty, spicy, smoked foods are strictly prohibited; many types of fresh fruits and vegetables, cocoa, flour products.
Food requirements:
► food should not be too hot or too cold (icy);
► should be boiled, baked or steamed;
► exclude foods that irritate the walls of the stomach;
► serve small portions;
► eat seven times a day.
Preventive measures
Following simple rules of prevention will help avoid stomach ulcers and their complications:
- Stressful situations and emotional disorders should be avoided
- It is recommended to sleep at least 8 hours a day
- It is better to refuse or at least reduce the consumption of fatty, salty and smoked foods
- You should eat often, but in small portions (the principle of fractional meals)
- Quitting smoking and alcohol
A stomach ulcer is a serious illness that can become life-threatening. It is impossible to diagnose it yourself. If primary symptoms are detected, you should consult a doctor for diagnosis and proper treatment.
Prevention
The question of how to treat a stomach ulcer should be replaced by another: how to prevent the disease. This pathology almost never occurs immediately; it is preceded by the stage of gastritis and erosive gastritis. The stomach has an excellent ability to regenerate, so if local inflammation of the mucous membrane appears, it is enough to take measures to restore full health.
Smoking and alcohol are the main causes of stomach ulcers.
Prevention methods include:
- regular meals - without hunger strikes and subsequent overload of the stomach;
- correct selection of foods - it is undesirable to constantly eat spicy, smoked, fatty and fried foods; such food should appear in the diet of healthy people only occasionally;
- at the first signs of gastritis, do not ignore it, but carry out appropriate treatment;
- avoid stress if possible;
- remember that alcohol and smoking are one of the main factors in the development of ulcers.
It is recommended to be examined by a gastroenterologist from time to time if discomfort is noticed in the epigastric region. The decision to destroy Helicobacter is made by the doctor; they may not interfere with the body’s vital functions, but if there is a risk of developing an ulcer, specific therapy is used against these microorganisms.
Main features
To understand the causes of the disease, it is necessary to dwell in more detail on the symptoms of stomach damage. Pain in the epigastric zone can be associated with food intake or not, they appear periodically or constantly. The pain may be:
- blunt;
- bursting;
- suddenly appeared dagger.
Loss of appetite may be complete, which is typical for cancer or acute catarrh of the stomach. Also, decreased appetite occurs with chronic gastritis, deterioration of gastric peristalsis, and due to pyloric stenosis. Sometimes the patient retains his appetite, but with some restrictions. It is present in stomach ulcers. Sometimes there is a perversion of appetite, selectivity to certain products.
Stomach problems can be signaled by:
- White mucus on the tongue, which appears due to excessive desquamation of the epithelium of the tongue. This sign is one of the first manifestations of gastrointestinal damage.
- Belching, which appears due to contraction of the stomach muscles when the cardiac passage is open. It may be with air, which is the result of the formation of gases in the organ due to abnormal fermentation of the stomach contents. This process occurs against the background of delayed gastric emptying. Gases are most often odorless. There is belching with the smell of a rotten egg. The symptom is characteristic of gastritis with reduced secretion, chronic atrophic gastritis and delayed evacuation of gastric contents. If the discomfort has a bitter aftertaste, then the problem lies in the reflux of bile from the duodenum into the organ. Gastritis with high acidity is characterized by belching with a sour taste.
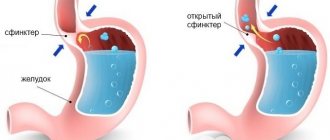
- Heartburn appears against the background of a violation of the tone of the lower part of the esophagus and the cardiac zone of the stomach. This leads to incomplete closure of the sphincter, causing the acidic contents of the stomach to reflux into the lumen of the esophagus.
- Nausea is associated with antiperistaltic movements of the organ. The mechanism for the development of such discomfort is due to stimulation of the vomiting center, the extent of which has not yet been fully studied. Occurs with lesions of the digestive tract and intoxication.
- Vomit. Typically, such a symptom occurs due to irritation of the stomach receptors by bad food and their inflammation in cases of stomach pathologies or organic narrowing of the outlet of the stomach. As a result, antiperistaltic movements are observed. This discomfort is called gastric vomiting. After this, the patient feels relief. Vomiting may be accompanied by large amounts of acidic food being thrown out. It often appears at night or in the evening. Similar discomfort is experienced when the outlet of the stomach narrows. With profuse vomiting with an unpleasant odor, gastric atony or atrophic gastritis can be judged. When the vomit is acidic in nature, the symptom occurs periodically - this is evidence of pyloric stenosis or hyperacid gastritis. If vomiting accompanies the process of eating food, or occurs a couple of hours after a meal, it indicates gastritis, a gastric ulcer or oncology. Vomiting that begins after a meal 6 hours later is characteristic of ulcerative lesions of the duodenum or final gastric tract. If there is blood, bile, pus or mucus in the vomit, one can judge an inflammatory chronic disease. If a bleeding stomach ulcer is present, the vomit will resemble coffee grounds.
- Constipation. This condition often accompanies gastritis with high acidity or gastric ulceration. In this case, stool retention is periodic. Their development mechanism is associated with deterioration of peristalsis due to the prolonged passage of acidic gastric contents into the duodenum.
- Diarrhea. Loose stools accompany gastritis with low acidity. In such a situation, the mechanism of development of pathology is opposite to that observed with constipation.
- Losing weight. It occurs in situations where, due to atrophic or inflammatory processes, there is dysfunction in the digestion of foods.
- Pale skin, fatigue, weakness and dizziness. Such symptoms accompany severe gastritis with low acidity. Signs appear due to poor absorption of vitamin B12 by the stomach. Because of this, internal bleeding may occur, then the stool becomes black.
- Temperature increase. It can be observed during an acute attack of inflammation of the stomach. If a low-grade fever is observed for a long time, this is a symptom of organ cancer.
Despite the fact that gastric diseases can differ significantly from each other, their symptoms can be differentiated, that is, indicating several diseases at the same time. However, there is a persistent list of symptoms, the combination of which should immediately contact a therapist to receive a referral for diagnosis. If a person feels and notices two or more of the signs listed below, you should not hesitate to get examined:
- Constant feeling of thirst.
- A sharp decrease in body weight.
- Regular pain in the abdominal area, in any projection.
- Fatigue, sweetness, inability to perform previously feasible work and activity.
- Appetite disturbances (in any direction – both absence and causeless increase).
- Gastrointestinal dysfunction of any nature (diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, heartburn, flatulence, belching, bad breath).
Gastrointestinal dysfunction is one of the symptoms of stomach problems
Possible complications
This serious disease can cause the following complications:
- Penetration . This term describes the destructive process of the stomach wall, in which the organ located below suffers, and usually this is the pancreas. During penetration, a person experiences acute pain and a significant increase in temperature. The pain is regular.
- Perforation . The contents of the stomach penetrate the peritoneum. All signs of intoxication and poisoning of the body, severe pain and weakness are observed. 10 hours after the onset of the disease, a person develops peritonitis - inflammation of the peritoneum.
- Bleeding . A very dangerous complication. The person vomits masses the color of coffee grounds, the feces turn black, and sweating increases.
- Stomach cancer. Regeneration of the ulcer is rare, but it is possible. The most dangerous in this case are callous ulcers. When malignant tumors appear, a person begins to lose weight and appetite decreases.
Stomach cancer
- Pyloric stenosis . The most dangerous complication, and its risk increases with frequently recurring ulcers. With stenosis, food cannot move into the intestines. For stenosis, the symptoms are nausea and vomiting, belching, weight loss.
Types of disease
Peptic ulcer disease is often classified depending on which part of the stomach it affects - the cardia, the central part of the stomach (body), antrum or pylorus. Also, in the stomach there may be either one single ulceration or several. The size of a stomach ulcer can vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters. A small ulcer is considered to be a formation having a diameter of less than 5 mm, a medium one - 5-20 mm, a large one - 20-30 mm, a giant one - more than 30 mm.
PUD is predominantly a chronic disease that may have periods of exacerbation and longer periods of remission. During remissions, the size of the stomach ulcer decreases, and during exacerbation, it increases.
Diagnostics
The following tests are used to diagnose gastric ulcers:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Stool analysis (general and occult blood).
- FEGDS with biopsy sampling.
- Ultrasound of the digestive organs.
- X-ray with contrast agent.
- pH-metry.
If necessary, endoscopic ultrasonography, X-ray examination, and CT are performed. Special testing is carried out to determine the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori:
- serological method (antibodies are detected in the blood);
- stool test;
- radionuclide urease test (exhaled air is examined);
- rapid urease test (tests the gastric mucosa after FEGDS);
- PCR analysis. Detects the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in saliva and feces. It is considered one of the most accurate tests that detects bacteria in the early stages of the disease. In addition, this test is performed to monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
Treatment of the disease
It is strictly forbidden to treat a stomach ulcer on your own. At the initial stage, it is very important to make a correct diagnosis. This cannot be done without medical assistance. Treatment of ulcers should only be carried out under the supervision of a physician.
To fight the Helicobacter pylori bacterium, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics. In addition, it is necessary to take medications that reduce the acidity of gastric juice. The doctor will recommend coating medications to maintain the stomach's protective mechanism. For this purpose, you can take decoctions of flax seed, which has enveloping, anti-inflammatory and healing properties.
To treat gastric ulcers, vitamin preparations containing vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) and vitamin U (methylmethionine sulfonium chloride) are used. Pantothenic acid helps the mucous membrane recover faster. Vitamin B5 deficiency leads to excess hydrochloric acid in the stomach. Increased portions of pantothenic acid, on the contrary, inhibit gastric secretion. Vitamin B5 improves intestinal motility.
Vitamin U also reduces the secretory function of the stomach and at the same time has an analgesic effect.
Dosages, medication schedule and course of treatment are determined only by the attending physician.
If multiple, recurrent ulcers are observed, as well as if complications arise, surgical treatment may be prescribed - gastric resection and vagotomy.
Gastric resection is an operation to remove the diseased part of the stomach. It is used quite rarely, when diagnosing very large lesions or ulcers complicated by severe cicatricial stenosis of the stomach.
Vagotomy is a surgical procedure that cuts the nerves that stimulate the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the prognosis for the disease is favorable.
Risk factors
No person is immune from the disease. As a rule, stomach ulcers most often occur under certain conditions in people at risk. Factors causing the disease are:
- frequent stressful conditions, chronic stress;
- disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, mental and nervous exhaustion;
- psychological breakdowns, depression, chronic fatigue syndrome;
- advanced oral diseases, such as caries;
- genetic predisposition and abnormal development of the gastrointestinal tract;
- frequent use of medicinal non-steroidal drugs - Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Ketoprofen;
- use of hormonal steroids;
- prolonged uncontrolled use of antibiotics;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- poor nutrition, lack of a balanced diet and daily routine;
- stomach injuries;
- frequent consumption of energy drinks and soda, baked goods;
- abuse of too hot and cold foods.
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Due to overstrain of the nervous system, all internal organs suffer. This leads to an imbalance in the body. The production of enzymes in the digestive system is disrupted, and endocrine pathology occurs. The human body ceases to resist infections. Taken together, an internal stress state arises, leading to various dysfunctions, including stomach ulcers.
Caries
It is necessary to regularly visit the dentist to protect the gastrointestinal tract from infection from pathogenic microorganisms accumulated on diseased teeth
Caries, like other diseases of the oral cavity, can cause gastric ulcers. The process of gastritis and stomach ulcers is simple: bacteria that cause diseases of the gastrointestinal tract enter the stomach from the oral cavity, where they live and multiply on carious teeth.
Heredity
In 50% of cases of gastric ulcers, hereditary mechanisms are involved. Many negative factors affecting metabolism and enzyme production are passed on from generation to generation. Thus, the body’s secretion of gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin, histamine and serotonin, which affect the acidity of gastric juice, has a genetic relationship.
The predisposition to the formation of stomach ulcers is transmitted predominantly through the male line. It is believed that the risk of developing the disease in first-degree heirs is 3 times higher than the incidence of ulcers in people with unburdened heredity.
It should be understood that heredity is only a factor, and not a certain inevitability of the occurrence of the disease.
Smoking
Smoking negatively affects human health in general, including the digestive system.
Nicotine contained in tobacco causes vascular spasms, leading to a lack of blood supply to the gastric mucosa. All this leads to a loss of the ability to restore and heal the surfaces of the stomach and its mucous membrane. This phenomenon contributes to complications and exacerbations of peptic ulcer disease.
Poor nutrition
Caffeine, alcohol, soda, spicy and rough foods - all this injures the gastric mucosa, irritating and deforming it. At the same time, there is an increase in the secretion of gastric juice. Swelling of the walls of the organ and its inflammation develop. Enzymes entering the damaged stomach aggravate the situation, leading to the formation of ulcers. And irregular nutrition worsens health.
Very hot and cold foods have a similar effect on the stomach, irritating the mucous membrane and damaging the walls of the organ.
Frequently eating large quantities of baked goods can lead not only to extra pounds, but also to peptic ulcers. This is due to the use of yeast in the preparation of dough for buns and pies. Yeast increases the acidity of gastric juice. Regular increase in acidity destroys the gastric mucosa, gradually leading to the occurrence of peptic ulcers.
The influence of drugs on the development of the disease
Everyone knows that the difference between medicine and poison is the dosage of the drug. But not every person follows exactly all the doctor’s instructions. By exceeding the dose, a person poisons his body with drugs that should serve for good. The price to pay for arrogance and self-medication is often a stomach ulcer. Improper use of medications increases the acidity of digestive juice, reduces the activity of enzymes, which leads to erosions and stomach ulcers.
Medicines of the ulcerogenic group lead to this disease. It includes:
- painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs that irritate the gastric mucosa;
- antimicrobial and antiparasitic drugs that negatively affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- food enzymes used for other purposes and in violation of the regimen;
- hormonal agents that suppress the immune system and stimulate increased enzyme release;
- anticoagulants that affect blood clotting.
Only by following the instructions of the attending physician, observing the dosage and rate of use of medications, can you avoid the occurrence of peptic ulcers.
Psychosomatics
There is an opinion among scientists, confirmed by a number of studies, that stomach ulcers are often psychosomatic in nature. The human psyche provokes the occurrence and development of gastric ulcers. A connection has been discovered between human emotions and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. An example is the fact that many people, when worried or anxious, “eat up” problems, and some, on the contrary, refuse food. The result is a violation of the diet and balance of nutrition, which results in peptic ulcer disease.
Melancholy, fear, uncertainty, disappointment are factors in the occurrence of stomach ulcers
The psychosomatic cause of stomach ulcers is lack of support, lack of communication and understanding, spiritual emptiness. But at the same time, opposite emotions arise: a desire for independence and outbursts of anger.
Uncertainty and lack of prospects against the backdrop of pent-up emotions lead to muscle spasms in various organs, including the stomach. Internal experiences lead to health problems. A stomach ulcer is the result of “digestion” of unresolved problems, including:
- envy;
- jealousy;
- inferiority complex;
- increased excitability;
- perfectionism;
- anxiety states;
- mental contradictions.
If the above conditions are present, and there is also a persistent feeling of discomfort, spasms and pain in the abdominal area for no apparent reason, then the help of a psychotherapist is required. Normalization of mental state accelerates healing, stabilizes a person’s physical health and protects against the development of complications of peptic ulcer disease.
Guidelines for the treatment of gastric ulcers
This very unpleasant disease is always treated according to a certain scheme, which is developed very well and allows you to normalize the disturbed balance and accelerate the remission phase in 21-30 days.
- Treatment with drugs. To destroy Helicobacter pylori, they have not yet come up with anything more reliable than antibacterial agents. The standard plan involves using two types of antibiotics. Antibiotics and dosage are selected by the doctor individually. The medications should be taken in full for 14 days.
- Drugs that suppress the production of hydrochloric acid. Among the proven effective drugs, omeprazole or its modern analogues can be noted.
- Medicines containing the substance bismuth (for example, De-nol), which promote the regeneration of stomach tissue after inflammation. In addition, bismuth-based products can destroy the microorganism Helicobacter pylori and coat the walls of the stomach. Natural enveloping agents are substances that form a thick emulsion in the microenvironment of the stomach that covers the gastric cavity with a protective film, thereby protecting it from mechanical and chemical influences. Among the folk remedies that have such properties are a decoction of flax seeds, fresh potato juice, a decoction of licorice root, liquid porridge from whole oats, corn starch, herbs: marshmallow rhizomes and Icelandic moss.
An alternative to flaxseed decoction can be flaxseed flour diluted in warm water, which is taken according to the instructions. This is the main therapy. In addition to the main treatment, the doctor may, if necessary, prescribe:
- gastroprotectors (to accelerate the recovery and protection of the gastric mucosa), - anticholinergics (drugs that eliminate digestive disorders), - antispasmodics (to relieve and block pain), - prokinetics (drugs that normalize the evacuation process of the stomach (its motility)).
Diet is necessary, important and one of the main conditions for effectively combating stomach and duodenal ulcers. All foods after which the patient feels a deterioration in health are excluded from the menu. It is important to follow all instructions and instructions regarding diet and nutrition. So,
- frequent meals in small quantities: at least 5 times a day;
- exclusion of rough, fibrous foods;
- exclusion of foods that irritate the walls of the stomach: hot, cold, sour, spicy, fatty, fried and canned foods are prohibited;
- limiting sweet, carbohydrate foods;
- refusal of alcohol-containing drinks and tobacco mixtures;
- steaming, boiling and stewing. Frying, grilling, smoking is unacceptable;
- limiting vegetables and fruits with coarse fiber during the exacerbation season;
- Food that lingers in the stomach for a long time and is difficult to digest is prohibited.
What foods contribute to the epithelization of ulcers?
Lactic acid products with lactoflora or bifidobacteria reliably heal ulcerative defects. It is by drinking a glass of fermented milk mixture at night that you can improve and stabilize the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract and, accordingly, strengthen local immunity. During an exacerbation, a strict diet is necessary, which, as the patient’s condition improves, is gradually expanded by adding some dishes to the menu. Preference in the diet is given to viscous, liquid and semi-liquid porridges, slimy soups, puree soups and cream soup. Porridge is seasoned with butter. Steam omelettes, meat and vegetable patties and soufflés, steamed meatballs, jelly, pumpkin porridge are examples of dishes for exacerbation of ulcers.
Reasons for development
Peptic ulcer disease occurs for the following reasons:
- Increased acidity of gastric juice. This phenomenon may be caused by organ dysfunction or infectious diseases. The acidity of gastric juice is increased by spicy, salty, sour, fried, flour and sweet foods. Those who like food that is too hot are also at risk.
- Chronic gastritis. These are inflammatory or inflammatory-dystrophic changes in the mucous membrane of the organ.
- Acute and chronic forms of vascular diseases, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus.
- Constant stress, depression and depression, psycho-emotional stress.
- Violation of the diet, abuse of fast food, semi-finished products, snacks on the go, dry food.
- Alcohol abuse, smoking.
- Long-term use of certain medications, such as acetylsalicylic acid, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or iron supplements.
- Closed skull injury, which led to disruption of hormonal regulation of gastric juice secretion.
- Infection of the stomach with campylobacter and fungal microorganisms of the genus Candida.
People with blood group 0(I), with a burdened heredity, with a congenital increased number of cells that produce hydrochloric acid, as well as with a congenital deficiency of the organ's protective factors are predisposed to the development of gastric ulcer.
When stomach diseases develop, their symptoms are similar.
Frequent use of certain medications can cause ulcers
Stomach ulcers can occur due to the use of certain groups of medications. Such an ulcer, due to its causal origin, is called a drug-induced gastric ulcer.
The cause of drug ulcers is ulcerogenic drugs - drugs whose side effects are expressed in the formation of a defect in the mucous membranes of the digestive organs.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, the well-known aspirin, which is included in this group, have a pronounced ulcerogenic effect. The risk of ulcers occurs with large doses and prolonged use.
Often such ulcers are asymptomatic and are discovered by bleeding or perforation (perforation). They are identified by endoscopic examination and examination of the patient’s medical history.
Treatment consists of stopping the use of the drug, which is suspected of causing the ulcer, and other general means (lowering acidity, increasing mucosal protection).
Approximately 40% of side effects associated with the use of medications are caused by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and more than 80% of the impact from them is taken by the stomach.
Drug ulcers are a fairly common phenomenon. This is due to the impossibility of replacing these medications in patients due to the high likelihood of complications of the underlying disease.
Destructive effects of NSAIDs in the stomach:
- Once in the stomach, these drugs penetrate the epithelium (the protective layer of the stomach cavity), damaging it. The result is a weakening of the protective properties of the stomach cavity, and the risk of damage.
- NSAIDs reduce the synthesis of prostaglandins, which are involved in lowering acidity levels, the formation of protective mucus and other important processes in the stomach and the body as a whole.
If the patient has had stomach problems in the past (gastritis, ulcers) or is present in the present, then the use of these drugs should be treated with particular caution, as they can cause a relapse or exacerbation.
But work has already been developed and is underway on a new generation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with reduced side effects. In particular, the use of NSAIDs in parallel with proton pump inhibitors (substances that reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach) is practiced.
The first signs of the chronic form
It is important to know! Symptoms of stomach ulcers and the initial part of the rectum (duodenal) are very similar, but there are some exceptions. Therefore, accurate diagnosis occurs only with the help of medical equipment and tests.
As a rule, signs of an ulcer of the initial part of the rectum (duodenum) in the early stages are:
- rapid, sharp or chronic pain in the abdomen, below the thoracic region.
- fatigue, accompanied by a constant feeling of hunger;
- bloating and flatulence;
- nausea, vomiting.
However, you should know that an asymptomatic course of the disease at the initial stage is also possible.
In later stages there is:
- vomiting blood;
- sharp night pains;
- bloody stool.
Causative agents of the pathological process:
- Helicobacter bacterium;
- stress;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- hereditary predisposition;
- poor nutrition.
They have a cause-and-effect relationship with each other: gastritis causes ulcers in the stomach and in the initial part of the small intestine.
As a result of Ph imbalance, the patient suffers from:
- regular heartburn before/after meals;
- flatulence and bloating;
- unhealthy breath;
- heaviness in the stomach.
It is important to understand that treatment at an early stage of stomach diseases, like any other ailment, can prevent serious consequences and the possible occurrence of more severe forms of disease.
Take care of yourself and be healthy!
- Pain in the stomach area;
- Attacks of heartburn and nausea (usually after eating);
- Frequent belching with a sour taste;
- Diarrhea or constipation;
- Loss of body weight;
- Flatulence and bloating.
- Chills;
- Increased body temperature;
- Dry mouth;
- Change in skin color (pallor);
- Rapid pulse.
Often pain sensations that arise in the stomach radiate to other internal organs. They can be of varying intensity. This depends on the depth and size of the lesion, as well as the patient’s sensitivity threshold. If such unpleasant sensations in the epigastric region bother a person for a long time, then he may notice their cyclical nature. As a rule, attacks of exacerbation of ulcers occur in the off-season.
What are the first signs of a stomach ulcer? Knowing about this is very important, because thanks to this you can diagnose the disease in its early stages. So what conditions indicate an incipient problem?
- Frequent nausea. May occur regardless of food intake, sometimes occurring in the morning.
- The body can react to food with a gag reflex. In this case, vomiting will be very profuse.
- The patient will gradually lose appetite. After all, pain will be associated with the process of eating.
- There will also be weight loss. And all because the patient will try to eat as little as possible so that pain does not appear.
However, it is worth saying that these symptoms are often signs of a thyroid dysfunction. That is why, at the first doubts and suspicions about this problem, you should seek doctor’s help and undergo a specialized examination that will help you accurately determine the diagnosis.
What are the signs of a stomach ulcer? So, first of all, the patient should pay attention to the nature of the pain.
- The pain is localized in the epigastric region. Atypical localization of pain: lower back, thoracic region, area under the left shoulder blade.
- Hunger pains. They occur at night or three or sometimes four hours after eating. Disappears within half an hour after the stomach is full of food.
- Late pain. Occurs approximately 2 hours after eating. They begin when processed food leaves the stomach. Occur if the patient has a pyloric stomach ulcer.
- If the body of the stomach is affected, the patient is likely to experience early pain. So, they will appear approximately half an hour to an hour after eating. Over the course of a couple of hours, the pain will intensify and then begin to subside.
Considering the various signs of a stomach ulcer, it is worth noting that the pain can be combined. Those. If several parts of the stomach are affected by ulcers, both early and late pain may occur.
What other signs of a stomach ulcer exist? So, the following symptoms can tell about this disease:
- Sudden belching. It may occur after eating, i.e. meal, and independently of it.
- Nausea.
- Heartburn.
- Feeling of heaviness in the stomach.
It is also important to say that vomiting often brings relief to the patient’s condition. That is why patients can initiate this process themselves. As a result, weight loss also occurs - another important symptom for this problem.
Having examined the various signs of stomach ulcers and gastritis, it is worth saying that the disease should be diagnosed as early as possible. After all, only in this case the treatment will bring the desired results. If you do not start the process of getting rid of the problem in time, various complications may arise.
What are the signs of a perforated stomach ulcer? So, initially it must be said that perforation itself, or perforation, is the destruction of all layers of the stomach at the site of the wound. As a result, everything that is in this organ, i.e. the food that gets there begins to fall out into the abdominal cavity. As a result, very severe pain occurs in the upper abdomen.
It is also important to say that even turning the body and deep breathing can lead to pain. So, these symptoms do not go away even after taking medications. After a while, the pain affects the entire surface of the abdomen, and the peritoneum becomes inflamed. So-called peritonitis occurs. And this is a very dangerous problem that can even threaten the patient’s life. Immediate hospitalization and surgery will be required.
Other signs of stomach and intestinal ulcers that indicate complications of this disease:
- Bleeding in the stomach.
- Penetration, i.e. spread of the problem beyond the boundaries of this body.
- Stenosis, i.e. narrowing of the lumen, which is located between the stomach and duodenum. He is called the gatekeeper.
Every person must know what signs of a stomach ulcer are dangerous and when to seek medical help. After all, these are the diseases that can eventually lead to stomach cancer. There are no early symptoms of this disease, and the patient only feels a sign of an ulcer or gastritis.
A stomach ulcer has a wave-like course - a period of remission is replaced by a stage of exacerbation. The manifestation of signs of exacerbation of a stomach ulcer directly depends on the severity of the disease.
The most common symptom is heaviness and pain in the area between the navel and sternum. The pain can last up to several hours. Therefore, it is difficult not to notice the exacerbation of the ulcer. In the acute form of the disease they say “an ulcer has opened.”
What are the main signs of exacerbation of an ulcer:
- Sharp, severe pain that is difficult to bear.
- The chair is black. This color “indicates” that gastric bleeding has begun.
- Vomiting blood.
Where pain can usually be felt (pain location):
- The cardinal section of the stomach, not far from the esophagus - aching pain, a feeling of heaviness in the pit of the stomach. Pain occurs immediately after eating. In this case, the pain can “transition” to the heart area. Accompanied by heartburn and belching.
- The middle section or bottom of the stomach - dull pain. Occurs on an empty stomach, or 30 minutes after eating. There is no belching or heartburn. But the tongue becomes covered with a white coating.
- Pyloric part of the stomach - pain can be felt three hours after eating. The pain also occurs at night. Eating food can dull the pain. There is heartburn and belching.
An exacerbation of a peptic ulcer is very dangerous and can lead to the formation of scar tissue, which will become an obstacle to the passage of gastric contents into the small intestine.
Perforation is the formation of a through hole in the walls of the stomach. The reasons for this phenomenon may be the following:
- Exacerbation of chronic ulcers
- Overeating, excessive filling of the stomach with food
- Diet violations (eating spicy, salty foods)
- Increased gastric acidity
- Sudden physical activity
A perforated ulcer begins with a mild form and gradually progresses to a severe stage. The main symptom is severe pain, which is accompanied by various symptoms at all stages.
Signs of a perforated stomach ulcer:
- Constant feeling of nausea and frequent vomiting
- Skin becomes pale
- The patient produces cold sweat
- Increased heart rate and shortness of breath appear
- Pain spreads to the entire abdomen and upper limbs
- The body temperature rises sharply and significantly, and a fever may even begin
- The abdominal muscles tense, causing unbearable pain when touched
In the early stages of perforation of the ulcer, the patient experiences severe pain, but it can be alleviated by taking a special position (lying on the right side and pressing the legs bent at the knees as close to the body as possible).
At the next stage of perforation, the patient feels relief and almost no pain is felt. But a day after perforation, all signs of a perforated ulcer worsen and the patient’s condition greatly deteriorates.
The first symptoms of a stomach ulcer are the same in both women and men. These include:
- pain in the upper abdomen associated with eating;
- other manifestations of gastric dyspepsia;
- change in food preferences;
- weight loss.
Pain syndrome
- Feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating.
- Heartburn is a burning sensation that occurs when stomach acid enters the esophagus. It is a consequence of the effect of acid on the esophageal mucosa.
- Vomit. Usually the urge occurs immediately after eating, preceded by heartburn and severe nausea. If this was preceded by pain, then relief comes after it.
- Belching: sour, bitter, putrid.
- Bad breath.
- White coating on the tongue.
- Constipation, increased gas formation.
- Decreased appetite, weight loss.
Stages and degrees of stomach ulcers
A stomach ulcer, the symptoms and manifestation of which is expressed in spasms of acute pain, develops in several stages of damage to the gastric mucosa.
In this regard, gastroenterologists distinguish the following stages of the disease:
- Stage 1 – local inflammation of the mucous membrane forms, which during primary gastroscopy can be identified as gastritis or a pre-ulcerative condition;
- Stage 2 - the first signs of erosion of the mucous membrane appear, which affect only the superficial layer of the digestive organ, the patient experiences aching pain, cramps in the stomach;
- Stage 3 – a trophic ulcer is formed with a recurrent form of the course, which can be in both acute and chronic forms of development, requiring complex treatment with a long course of medications or surgical intervention;
- Stage 4 - the trophic process covers not only the mucous layer, but also the deeper tissues of the stomach, the function of the muscles of the organ is disrupted, perforated formations are formed, periodic or constant bleeding begins, there is a real threat of death.
The stage of peptic ulcer, as well as its type, which are established in the process of comprehensive diagnosis of the gastrointestinal tract, influence the scheme and duration of the therapeutic course. The presence of stages 3 and 4 of the disease may require emergency surgery.
Additional symptoms
However, pain does not always occur and can be short-term. How to determine a stomach ulcer in this case?
Usually the disease is accompanied by other symptoms, which primarily include discomfort in the abdominal area associated with eating. In this case, on an empty stomach or after eating, a person may experience heaviness in the stomach, heartburn, a feeling of fullness, and so on. The patient may also experience sour belching with a bitter aftertaste.
Very often, patients are bothered by attacks of nausea, which appear an hour and a half after eating and end with profuse vomiting, which brings a feeling of relief. The vomit contains all the food eaten and even bile.
Abnormal bowel movements are another manifestation of gastric ulcers in adults. Symptoms of the disease in this case are regular severe constipation.
Description of the disease
The stomach is the main organ of the human digestive system, where food received from the oral cavity undergoes primary chemical processing and is prepared for the process of absorption of substances necessary for the body - proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the small intestine.
The task of processing the food bolus is taken on by an extremely caustic liquid - gastric juice. It consists of several enzymes, but its main component is hydrochloric acid. The main reason that gastric juice does not begin to digest the stomach itself is the protective properties of the gastric mucosa lining the walls of this organ. However, if the integrity of the mucous membrane is compromised for any reason, then the acid begins to corrode the underlying layer of the stomach walls - the muscle layer.
This process leads to a violation of the integrity of the wall and the appearance of a formation called an ulcer. However, in this case, it is necessary to clearly distinguish between gastric ulcers and erosions, which can also occur on the surface of the stomach walls. Although in most cases the precursors of ulcers are erosions.
With erosions, damage to the gastric mucosa is observed, but the muscular layer of the walls itself is not affected. Erosion usually heals on its own within a few days and does not lead to damage to the walls of the organ. The ulcer can also heal, but in this case a scar remains on the surface of the walls. If this does not happen, the ulcer becomes chronic. In other cases, an ulcer can lead to the destruction of a section of the stomach wall.
PUD, unlike gastritis, is not accompanied by significant variations in such a parameter as the acidity of gastric juice. In most cases, acidity in ulcers is within normal limits or slightly increased. With low acidity, gastric ulcers cannot form, unlike gastritis, which can also occur in similar conditions.
Treatment
When treating stomach ulcers, complex therapy is prescribed. The first priority is to neutralize the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
Next, the level of stomach acidity decreases, which eliminates a number of unpleasant symptoms (belching, heartburn, nausea) and prevents the development of complications. The duration of treatment for ulcer depends on the degree of development of the pathology and the size of the ulcer (from two weeks to two months).
Complex of drug treatment:
| Group of drugs | Name |
| Antibacterial agents |
|
| Mucosal protection products |
|
| Antacids |
|
| Proton pump blockers |
|
| H2-histamine receptor blockers |
|
| Synthetic analogs of prostaglandin E1 |
|
| M-cholinergic receptor blockers |
|
| Antispasmodics |
|
| Prokinetics. |
|
| Probiotics |
|
| Sedatives |
|
| Antidepressants |
|
When is surgery indicated?
In some cases, peptic ulcer cannot be cured with conservative therapy alone. Then surgery is necessary. The operation is performed when there are specific indications.
Absolute indications for surgery:
- Perforation.
- Bleeding.
- Third degree stenosis.
- Transformation of ulcers into oncology.
Relative readings:
- penetration;
- deformation of the stomach with scars;
- too frequent relapses;
- second degree of stenosis;
- callous ulcer;
- the ulcer does not heal for a long time.
If surgery is indicated, there is no need to avoid or delay surgery. It should be borne in mind that any elective operation has much lower risks than an emergency operation. In addition, emergency surgery is often ineffective, and complications threaten life and health.
Types of surgical operations for stomach ulcers:
- Resection. Part or all of the organ is removed. The ulcer is excised along with the adjacent portion of the gastric wall. Several types of such operations are used.
- Vagotomy. The nerve endings that are responsible for the production of gastrin are removed. The integrity of the stomach is not compromised.
- Endoscopy. This operation is performed without an incision in the peritoneum. Holes are made into which the equipment for the operation is installed.
Diet
The purpose of a therapeutic diet for stomach ulcers is to eliminate pain, dyspepsia and create conditions for the healing of the ulcer. With the help of diet, the level of acidity in gastric juice is reduced and regeneration processes are stimulated. The diet excludes the use of strong stimulants of gastric secretion and irritants to the mucous membrane. The diet should include foods that are quickly digested: liquid and mushy foods.
Video on the topic:
Therapeutic nutrition for peptic ulcer must meet certain requirements:
- food should remain in the stomach for a short time;
- food should not stimulate an increase in acidity in gastric juice;
- fractional meals in small portions, with an interval of 3–3.5 hours;
- avoiding overly hot or cold foods;
- Limiting salt intake to 10 grams. in a day;
- the diet must be balanced and contain all the necessary substances.
What you can and cannot eat when you have ulcerative stomach:
| Can | It is forbidden |
| Stale wheat bread, crackers, dry biscuits | Brown bread, any pastry made from butter dough |
| Boiled lean meat and fish, chicken, steamed cutlets | Fatty meat, rich meat broth, canned food |
| Dairy products (not sour and with a small percentage of fat content) | Raw vegetables and fruits |
| Slimy soup with added cereal and milk | Carbonated drinks, coffee |
| Boiled vegetables and fruits (not sour, low in fiber, without rough crust) | |
| Potato and cabbage juice, decoctions of rosehip, flaxseed, oats, herbal tea, jelly, compote, still mineral water | Spices, sauces, mayonnaise |
Folk remedies
Stomach ulcers can be effectively treated with traditional medicine recipes. Before using folk remedies, you should consult a gastroenterologist, as there may be contraindications.
Several effective folk remedies that are available for use at home:
- Sea buckthorn oil. Take 1 teaspoon before meals three times a day. You can mix sea buckthorn oil with propolis tincture.
- Fresh carrot juice. Drink 1–1.5 liters during the day. Duration of treatment is from two to four months. At this time, it is necessary to exclude sugar, wheat flour and starch from the diet.
- Propolis. Mix 5 g of propolis and 100 g of butter. Let simmer in a water bath for 45 minutes. Cool, strain and store in the refrigerator. Take 1 tsp before meals. 2 times a day (you can add honey).
- Dilute fresh potato juice 1:1 with boiled water. Take 1/2 glass in the morning on an empty stomach an hour before meals.
- Medicinal herbs (celandine, St. John's wort, plantain, calendula) can be used individually or as a collection. You need to brew the herbs like tea. You need to drink medicinal tea regularly - 2-3 times a day.
Video on the topic:
Treatment of stomach ulcers: treatment regimen
To cure a peptic ulcer, it is first necessary to eliminate the causes of the ulcer. Based on the results of the studies performed, treatment is prescribed depending on the specific case, the presence of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the patient’s age, and other factors.
Directions for treating stomach ulcers:
- eliminate Helicobacter Pylori;
- reduce the secretion of gastric juice to cause faster scarring and promote
- eliminating the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, since the optimal condition for its existence is an acidic environment;
- relieve inflammation, stimulate tissue regeneration, raising the protective functions of the mucous membrane to the proper level.
Medications
- Groups of antibiotics used for Helicobacter pylori infection:
- Macrolides (Erythromycin, Clarithromycin). Clarithromycin tablets are used 500 mg, morning and evening;
- Penicillins: Amoxicillin is prescribed 500 mg 4 times a day, after meals;
- Nitroimidazoles: Metronidazole, taken 500 mg 3 times a day, after meals.
- Antacid medications - reduce the acidity of gastric juice, which protect the gastric walls - Maalox. This function is partly characterized by activated carbon and Polysorb.
- Drugs that block the endings of histamine receptors: Ranitidine, Nizatidine, Famotidine
- Medicines that suppress the proton pump - Omeprazole in the process of stomach ulcers.
- Medicines involved in tissue repair - for example, Actovegin, Solcoseryl.
- Medicines that help relieve inflammation and pain - gastroprotectors: Venter, De-Nol, Solcoseryl, Misoprostol. Myotropic antispasmodics, used to relieve pain, true analgesics.
- Drugs that reduce secretion inside the stomach - anticholinergic blockers and ganglion blockers.
Operation
Indications for surgery for stomach ulcers:
- Perforation of an ulcer (the occurrence of a through defect in the wall of the stomach or duodenum).
- Bleeding from an ulcer that cannot be stopped with hemostatic agents and endoscopic hemostasis.
- Cicatricial narrowing of the outlet of the stomach, making it difficult for food to pass through.
- Long-term non-healing ulcers suspicious for malignancy.
- Often recurrent (more than 3-4 times a year) ulcers.
- Combination of an ulcer with diffuse polyposis.
| Types of surgery | Description |
| Resection | removal of part of the stomach or complete resection. The ulcerative lesion is surgically removed along with part of the organ. There are several varieties of such interventions; |
| Vagotomy | vagotomy is very popular today. The essence of this operation is that the organ itself remains unharmed, and the nerve endings that are responsible for the production of gastrin are removed. As a result, stomach ulcers heal on their own after some time; |
| Endoscopy | endoscopic technique for the treatment of peptic ulcer. The advantage of this operation is that it does not require large incisions in the peritoneum. With this technique, holes are made where special equipment is installed to perform the operation. |
Resection
Vagotomy
Possible complications after surgery:
- Recurrence of ulcers. An ulcer can occur both in the remaining part of the stomach and (more often) in the area of the anastomosis.
- Dumping syndrome. This is a symptom complex of autonomic reactions in response to the rapid entry of undigested food into the small intestine after gastric resection. Manifested by severe weakness, palpitations, sweating, dizziness after eating.
- Adductor loop syndrome. It manifests itself as bursting pain in the right hypochondrium after eating, bloating, nausea and vomiting with bile.
- Iron deficiency and B-12 deficiency anemia.
- Intestinal dyspepsia syndrome (bloating, rumbling in the abdomen, frequent loose stools or constipation).
- Development of secondary pancreatitis.
- Adhesive disease.
- Postoperative hernias.
Diet plays a very important role in the recovery of patients during the post-rehabilitation period. Patients should eat according to a set schedule, many times a day, little by little. This is a special therapeutic nutrition, the goal of which is to quickly improve the patient’s condition and the functionality of the gastrointestinal organs. During the postoperative period, the patient's diet includes grated, pureed and liquid dishes. IN
Nervous tension and stress are completely contraindicated for patients. As soon as a person finds himself in a stressful situation, the stomach begins to work intensively and produce more enzymes. Gastric juice becomes aggressive.
If the disease is diagnosed in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. A course of drug treatment is required. If necessary, surgical intervention. If complications such as gastric bleeding, perforation of the organ wall or stenosis are detected, death is possible if the necessary medical assistance does not arrive on time.
Harsh Turn: Complications
PUD is dangerous not in itself and not because of the digestive disorders that it causes, but because of its complications. Complications can be fatal in many cases. The most dangerous complications include:
- massive bleeding,
- perforation of the ulcer,
- malignancy (transformation of an ulcer into a malignant tumor).
Massive bleeding is one of the main factors responsible for the death of people suffering from the disease. They occur in 20% of patients with peptic ulcer. When bleeding, patients experience signs of anemia, vomiting blood, and black stools. The drop in blood pressure caused by exsanguination can lead to collapse, shock and death. Therefore, if there are signs of internal bleeding, the patient must be immediately taken to the hospital.
Another dangerous complication is wall destruction. A relatively successful option in this case may be when some other organ appears behind the wall of the stomach. Most often this is the pancreas. Hydrochloric acid will begin to corrode this organ, resulting in acute pancreatitis.
Also, when ulcerative formations are perforated, the intestines, gallbladder, lesser omentum, and liver may be affected
However, it often happens that the contents of the stomach are simply poured into the peritoneum and a person develops acute peritonitis, accompanied by severe pain and fever. The reason for this development of events may be physical stress or alcohol consumption. Peritonitis also threatens the patient with death, and without immediate medical attention it is inevitable.
Another dangerous complication is pyloric stenosis. This is the name of the sphincter that separates the stomach from the first section of the small intestine - the duodenum. Pyloric stenosis is always a complication of a pyloric ulcer. Narrowing of the pylorus leads to stagnation of food in the stomach, and ultimately to obstruction of the pyloric canal. Treatment for severe stenosis is always surgical.
Malignant tumors are also dangerous complications. However, a tumor at the site of the ulcer develops less often than is commonly believed - in only 3% of cases. However, the risk of oncological tumors in patients with peptic ulcer is several times increased compared to the rest of the population.
Patients with peptic ulcer require lifelong monitoring. They should be tested for Helicobacter pylori approximately every six months.
A stomach ulcer can cause the following unpleasant and very serious complications:
- Perforation or perforation. With this complication, the wall of the mucous membrane is depleted and a through hole is formed. Through this opening, the contents of the stomach enter the abdominal cavity. As a result, the patient is diagnosed with peritonitis, which is extremely life-threatening.
- In approximately 80% of patients, ulcerative bleeding occurs, the intensity of which depends on the location and extent of the lesion.
- An ulcer that is not cured in time quickly becomes chronic. Patients with chronic ulcers have to undergo a therapeutic course twice a year to stop the next attack of exacerbation.
- Adhesion of neighboring organs to the stomach. With chronic peptic ulcer disease, the walls of the stomach are gradually destroyed, neighboring organs (for example, the liver) can stick to the stomach and the disease can spread further.
As I said at the beginning of the article, very often people do not pay attention to stomach problems. And if they do, they are afraid of diagnosis. For example, gastroscopy is a rather unpleasant procedure, but without it an accurate diagnosis cannot be made.
How such irresponsibility can result:
- Bleeding
- Stenosis of the gastroesophageal sphincter (the opening between the stomach and intestines). In this case, food cannot move from the stomach further into the intestines. And I have to have surgery.
- Perforation of the wall of the stomach or duodenum. In other words, a hole is formed through which everything we eat enters the abdominal cavity or even into a neighboring organ (pancreas). There it all rots and peritonitis develops. And a person has no more than a day to sound the alarm. And here only emergency surgery can save you.
- Cancer.
Factors leading to stomach ulcers
As already noted, 60% of the population are carriers of Helicobacter, but not everyone develops the disease. Why do some people get stomach ulcers and others not? The risk group includes those who regularly experience the effects of adverse factors.
Long-term use of certain medications
The condition of the mucous membrane is affected by taking Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid), Indomethacin, Butadione, Atophan, Reserpine, caffeine and corticosteroids. Their effect is called ulcerogenic, that is, it disrupts the balance of the protective forces of the stomach walls and aggressive factors (gastric juice, Helicobacter). To form a defect, it is necessary to use large doses or a long course of treatment, since drugs cannot quickly cause stomach ulcers.
The ulcerogenic effect of drugs is realized in different ways. One of the mechanisms is an increase in the aggressiveness of hydrochloric acid and pepsin (components of gastric juice), which develops due to stimulation of secretory cells. Another option is that the drug releases biologically active compounds that stimulate the release of hydrochloric acid.
Stress
The digestive process occurs under the control of the nervous system. When a person experiences emotional stress, a redistribution of its activity occurs: skeletal muscles and sensory organs become toned, attention increases, breathing and heartbeat increase. Blood flow to the digestive organs decreases.
This condition of the central nervous system leads to increased secretion of hormones that harm the stomach and intestines. One of them is corticotropin-releasing hormone. Its main function is to stimulate the adrenal glands to increase the production of adrenaline and steroid hormones. Their combination activates the body's reserves to combat stress.
But another effect of corticotropin-releasing is that it reduces appetite, and the person does not want to eat, even when the stomach is completely empty. Or another effect is observed due to the action of steroids: ravenous hunger appears, cravings for high-calorie and flavorful foods, overeating. As a result of such dietary disturbances, the secretion of hydrochloric acid, pepsin, and bile increases, and the susceptibility of the walls to microbes that cause stomach ulcers increases.
Character traits, internal conflicts
Gastric and duodenal ulcers are included in the “big psychosomatic seven”, that is, this is a disease, one of the reasons for the appearance and development of which is personality traits, conflicts, and emotional experiences. Research has revealed that people with internal conflicts, those who have suffered psychological trauma, and those living in socially unfavorable conditions (quarrels in the family, at work, pressure, humiliation) are susceptible to peptic ulcer disease.
Disturbances in the digestive system are provoked by such traits as resentment, suspicion, depression, anxiety, feelings of despair, loneliness, fear and anger. What causes a stomach ulcer in these cases? At the physiological level, this is explained by the neurohumoral (nervous system, hormones) connection between human experiences and the work of internal organs.
Hereditary predisposition
Research has identified genetic markers, the detection of which indicates an increased risk of the disease. People with blood type I are 1.4 times more likely to develop stomach ulcers. In this case, there is a tendency to complications and a severe course. About 42% of the European population are in this risk group.
The mechanism of the disease is associated with the lack of the body’s ability to produce antigens that are responsible for the synthesis of glycoproteins in the mucous membrane. As a result, it turns out to be insufficiently protected from the influence of aggressors.
Smoking
Tobacco smoke contains nicotine, tar and other toxic gases. When smoking, the secretion of saliva increases, it absorbs all harmful compounds and enters the stomach, irritating its mucous membrane and provoking an increased secretion of hydrochloric acid. This is the direct effect of cigarettes on the stomach.
In addition, smoking provokes vasospasm in the walls of the organ and the accumulation of mucus on them. The transmission of impulses to the brain is disrupted, and the person does not feel hungry. Increased acidity and an empty stomach inevitably lead to ulcers.
Alcohol consumption
Ethyl alcohol, entering the stomach, provokes an increase in its acidity. In addition, it affects the functioning of the nervous system, as a result of which the transmission of impulses and the contraction of the smooth muscles of the organ are disrupted.
Eating disorder, improper diet
Rare meals, fast food, overeating, frequent consumption of spicy, sour, salty, fatty foods lead to disruption of the digestive process. Gastric juice is secreted intensely, increased acidity leads to irritation of the mucous membrane and is a favorable condition for the activation of Helicobacter.
These are the main causes of stomach ulcers and gastritis - a previous disease in which the mucous membrane is inflamed, irritated for a long time, and acidity is impaired. Other pathologies can also lead to damage to the walls: duodenogastric reflux, diabetes, infectious foci in the body, disorders of the kidneys, heart, blood vessels, iron deficiency. The causes of stomach ulcers in middle-aged women can be changes in the hormonal system.
There are 2 reasons for the development of stomach ulcers: increased acidity and activation of Helicobacter Pylori bacteria. Most often both components are present. There are many factors that can lead to increased secretion of gastric juice and the spread of bacteria: uncontrolled use of drugs, smoking, alcohol consumption, poor diet, stress, emotional problems, concomitant diseases (most often gastroduodenal reflux and chronic gastritis).
Author: Olga Khanova, doctor, especially for Zhkt.ru
Causes and characteristics of symptoms of stomach ulcers in men and women
Although women are statistically less predisposed to developing peptic ulcers, when ulcers appear, the symptoms are similar in men and women.
It is believed that women have a higher pain threshold, the body is less sensitive to pain and is capable of self-healing during pregnancy (when all body systems are activated). An important factor that provokes the appearance of ulcers in women is “dieting” (due to the desire to lose weight), as well as a more impulsive and emotional character (this leads to the fact that women more often suffer from antral ulcers, a common harbinger of stomach cancer).
In men, the most common causes of stomach ulcers are:
- smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- stress.
They are more likely to have ulcers of the greater curvature of the stomach.
Ulcers are quite often diagnosed in children and adolescents, especially during puberty. The main cause of ulcers in children is considered to be the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Although this bacterium is present in the body of 90% of the population, it begins its destructive activity only in a weakened body and under the influence of other negative factors:
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- stress;
- improper diet and diet;
- infection with pathogenic bacteria due to non-compliance with hygiene rules.