Many people, regardless of gender and place of residence, have encountered a disease such as B12 deficiency anemia. In some medical sources it is referred to as Addison-Biermer disease. It appears due to a lack of vital vitamin B12 in the body.
Most of it is contained in the bone marrow and tissues of the nervous system, so a lack of the substance leads to disruption of the functioning of almost all organs.
Symptoms of the disease vary from person to person. For example, one person may feel severe weakness, while another patient may not notice the progression of the disease. In both cases, surgical treatment is necessary, since ignoring its signs leads to dangerous consequences, including disability or death.
Absolutely anyone can get anemia, so you need to know what preventative measures and treatment methods exist.
Diagnosis of anemia
Diagnostics includes a whole range of measures. A mandatory item is a blood test, as a clinical one. and so general. If the disease has already begun to progress, the analysis will reveal an insufficient number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Possibly insufficient hemoglobin levels.
In order for a blood test to give the correct result, you must take it on an empty stomach, do not smoke for several hours beforehand, do not take medications, and avoid heavy physical activity.
B12 deficiency anemia is also characterized by various disorders that a blood test can help identify. Red blood cells can vary greatly in shape and size. At the same time, they will have a rich scarlet color due to the high content of hemoglobin in them. Modern laboratories can indicate the exact amount of hemoglobin in red blood cells.
A biochemical blood test will help determine the exact level of vitamin B12 in the blood.
However, this does not mean that the indicator will necessarily be low. In some cases, the norm is even exceeded if anemia is caused by metabolic disorders. Therefore, when making a diagnosis, the doctor takes into account other signs of the disease and also collects anamnesis.
Iron levels in the blood may be higher than normal. When red blood cells break down and release iron, it is used to make new red blood cells. With a deficiency of vitamin B12, this becomes difficult, so the concentration of iron in the blood increases.
More information about anemia can be found in the video.
One of the methods for diagnosing this disease is bone marrow puncture. At the moment, this is the most reliable analysis that can completely confirm or refute suspicions of B12 deficiency anemia. This procedure is performed before the doctor prescribes treatment to ensure the results are accurate.
Bone marrow puncture is performed under sterile conditions. A small amount of bone marrow is removed through a puncture in the chest and sent for analysis. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the substance will reveal enlarged cells with a large amount of hemoglobin, as well as impaired maturation of blood cells. If the doctor suspects B12 deficiency anemia caused by insufficient production of the gastric enzyme, he will prescribe an EGD to examine the gastric mucosa. The doctor will also evaluate your diet and may prescribe an ultrasound of the liver and a blood test for thyroid hormones.
Causes of anemia due to lack of vitamin B12
There are many reasons that can trigger the appearance of the disease. The etiological factors of the disease can manifest themselves in a deficiency of cyanocobalamin or folic acid, which is caused by:
- vegetarianism;
- low absorption capacity of the gastrointestinal tract;
- gastrectomy;
- neuropsychiatric disorders;
- many diseases and viral infections;
- improper, unbalanced diet;
- atrophic processes in the intestines and stomach.
Only a specialist in laboratory conditions can identify the true cause of vitamin deficiency. A blood test provides a complete clinical picture of the disease and allows for an accurate diagnosis. If you notice symptoms of B12 deficiency anemia, seek medical help immediately.
Chronic alcoholism and other bad habits can cause vitamin B12 deficiency, as they significantly weaken the human immune system and worsen a person’s health. Prevention of the disease is a balanced diet, a healthy lifestyle, and adherence to personal hygiene rules.
A deficiency of vitamin B12 is normal during pregnancy, so there is no need to panic when symptoms are detected. In this case, you need to visit your local gynecologist, who will prescribe a complex of vitamins or a drug that contains the maximum amount of the deficient substance.
There are two main reasons that cause anemia. These include insufficient intake of the required amount of vitamin B12 from food and disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, which lead to a decrease in absorption and absorption capacity.
Diagnostics
If the doctor suspects that you have B12 deficiency anemia, you will be asked to take a general blood test, they may also take a spinal tap (due to some similarities between anemia and leukemia) and undergo an FGS to see the condition of the stomach.
In case of anemia, a blood test reveals a low number of red blood cells and low hemoglobin, and after puncture the presence of hypertrophied erythropoiesis cells is revealed. If the cause of this type of anemia lies in a lack of enzymes, then this will be determined as a result of FGS (swallowing a special probe).
At the next stage of diagnosis, doctors will try to find out what the body is missing: only vitamin B12 or also folic acid. To do this, you will need to submit your urine for testing. It will look at the level of methylmalonic acid. If it rises, then you are only lacking B12.
For B12 anemia, take medications and injections
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of B12 deficiency anemia, you need to follow a number of rules. The basis of preventive measures is maintaining a proper balanced diet.
The usual diet must be balanced and must include products of animal origin. If a person refuses meat and fish, then he must consume at least eggs and milk. As a substitute, you can cook dishes with soy.
To prevent anemia, it is also recommended to use special vitamin complexes in tablet form. It is especially important to take these medications after surgery on the digestive organs.
B12 deficiency anemia is a slow progressing disease, but despite its apparent harmlessness, it has very serious consequences. To avoid the occurrence of dangerous neurological symptoms, you need to consult a doctor at the first signs of anemia.
Diagnosis of B12 deficiency anemia
An informative and easy-to-use method for diagnosing B12-folate deficiency anemia is a complete blood test. With B12-deficiency anemia, characteristic changes in the composition of the peripheral blood are formed in the form of disturbances in the shape and size of erythrocytes (macrocytosis, poikilocytosis), the appearance of nuclear substance residues in erythrocytes (Jolly bodies, Cabot rings), as well as an increased color index.
Typical manifestations of the megaloblastic type of anemia, which distinguish it from other forms of anemia, are the combination of an anemic symptom complex with moderate leukopenia and the appearance of giant neutrophils with a hypersegmented nucleus. B12-folate deficiency anemia is not characterized by reticulocytosis, even taking into account the decrease in the absolute numbers of reticulocytes.
In a situation where it is difficult to diagnose the megaloblastic type of hematopoiesis, the patient is recommended to perform a sternal puncture and examine the puncture for red line hyperplasia and the presence of megaloblasts.
In order to distinguish between deficiency of cyanocobalamin and folic acid, it is recommended to study blood serum using microbiological and radioimmunological methods to determine the quantitative and qualitative content of vitamin B12. The criterion for reducing the level of cyanocobalamin in the body is the detection of methylmalonic acid in a urine test.
A biochemical blood test is accompanied only by an increased level of bilirubin due to its indirect fraction.
Administration of injections
Treatment of B12 deficiency anemia is carried out by administering vitamin B12 injections. The injection form allows you to achieve quick results. You can give injections intramuscularly, subcutaneously or intravenously.
Adults are advised to administer 100-200 mcg of the drug every other day. In case of particularly severe pathology, the dosage is 400-500 mcg per day for a week. When blood counts are normalized, the dosage of cyanocobalamin is reduced to 100 mcg.
For B12 deficiency anemia, clinical recommendations include maintenance therapy with injections. It is prescribed during the period of remission. For children, injections are administered subcutaneously in dosages of 30 mcg. Daily use of the medicine will help normalize the level of vitamin in the body after 15 days. In addition, doctors prescribe folic acid.
Symptoms
Pernicious anemia has a number of characteristic features due to the fact that the reserves of cyanocobalamin in the human body are so large that it is almost impossible to identify the developing disease at an early stage. The first manifestations of the disease become noticeable several years after its onset.
The negative effect on all organs and systems affects primarily hematopoiesis, but manifests itself at the very beginning of the disease in the form of rapid fatigue and weakness. Later, increased sweating and dizziness occur due to impaired functionality of the digestive system.
A malfunction of the hematopoietic system with B 12 deficiency anemia manifests itself in the form of a decrease in the level of red blood cells in the blood. The quality of oxygen transportation decreases and hypoxia of organs and tissues develops. The following are recognized symptoms of hematopoietic disorders:
- Changes in the color of the skin and mucous membranes. The lack of hemoglobin that occurs with anemia leads to the fact that the skin and mucous membranes acquire a jaundiced tint. The patient's face becomes pale, the pink color of the mucous membranes disappears, and they become light gray or slightly yellow. This color change is an indication that bilirubin levels in the blood are rising due to the destruction of red blood cells that occurs in the bone marrow and spleen cells.
- Hypoxia (lack of oxygen) leads to rapid heartbeat. An increased heart rate is one of the body's defense reactions to anemia. A rapid heartbeat is necessary to increase the amount of blood passing through all organs and tissues, filling them with oxygen.
- Increased blood supply causes a disruption in the usual rhythm of the heart muscle and an increase in load. All this leads to severe pain in the heart area, radiating to the left shoulder, and in some cases to the stomach.
- Megaloblastic anemia manifests itself as a slight enlargement of the spleen, which occurs due to increased load on this organ. Red blood cells, which are significantly larger in size, clog the passages in the organ's channels, causing blood to accumulate and change in size.
- Pernicious anemia or anemia causes vision impairment, and the appearance of spots before the eyes occurs as a result of a disruption in the adequate blood supply to the retina and its vitreous body. Hypoxia leads to a decrease in the quality of vision, disruption of the supply of nutrients to the cells of the visual organs, which is why the patient complains of constant flashing of dark or shiny dots, strings or circles before the eyes.
- One of the symptoms indicating the presence of a disease such as megaloblastic anemia is dizziness and frequent fainting. They arise due to the fact that the brain experiences oxygen starvation.
No less indicative symptoms of B12 deficiency anemia are disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system, manifested in the form of loss of appetite and weight.
Feature of the disease
B12 deficiency anemia is a pathology characterized by a lack of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood. It occurs as a result of a disruption in the metabolism of this vitamin in the body or insufficient intake.
This leads to a deterioration in the production of red blood cells. Without this compound, red blood cells cannot divide normally. In addition, pathological cells - megaloblasts - are formed.
Diet
B12 deficiency anemia will be treated more successfully if you properly develop a nutritional plan. If you notice the signs of the disease in time and consult a doctor, you can get by with just a diet without long-term treatment (of course, in cases not aggravated by other diseases and pathologies). After all, the same American doctors who proved the curability of this type of anemia simply introduced raw liver into the diet of the test patients and got a positive result.
The diet of patients involves a large amount of meat and dairy products, as well as vegetables that help blood formation. It will not be possible to correct the condition by eating only vegetables - they do not contain vitamin B12 in its pure form, they only provide “raw materials” for subsequent processing in the digestive organs and the production of cyanocobalamin, which a weakened body cannot do.
Products containing B12
In descending order, their list is as follows:
- cattle liver – from 30 to 60 mcg;
- liver of small cattle and pigs – up to 30 mcg;
- poultry liver – 10 – 15 mcg;
- sea fish – from 1.5 to 12 mcg;
- rabbit and hare meat – 4.3 mcg;
- cattle meat – 2.5 mcg;
- sheep meat and pork – 2 mcg;
- eggs – 0.5 mcg;
- sour cream – 1 – 1.5 mcg.
Other useful products
If therapy uses drugs that compensate for iron deficiency, then it is necessary to introduce into the diet foods that promote its absorption (sometimes the body has difficulty accepting this element, nausea and an unpleasant taste in the mouth may appear):
- plums and honey;
- baby cereals and dry milk formulas for babies.
Hematopoietic vegetables:
- beet;
- all legumes;
- tomatoes.
Fresh fruits and vegetables in any form, especially grapes and apples.
Harmful products
You will have to exclude some things from your diet. At least until the vitamin balance is restored:
- alcohol;
- coffee;
- Pepsi and Coke;
- pickles and anything that contains marinade and vinegar.
It is better to avoid coffee if you have B12 anemia.
Table No. 11
We bring to your attention a daily diet for a patient with B12-deficiency and B12-folate deficiency anemia.
Meals will be five times a day, satisfying, with a noticeable increase in the amount of protein food. So:
- 1st breakfast: chopped apple with cabbage and sour cream for dressing, scrambled eggs, oatmeal with milk, weakly brewed tea;
- 2nd breakfast: sandwich with white bread and a slice of cheese, apple juice (preferably freshly squeezed, diluted by a third with water);
- lunch: soup cooked with beef, beef meat with crumbly rice porridge, compote;
- afternoon snack: rosehip decoction;
- dinner: cutlets, boiled egg, boiled beet salad, cottage cheese casserole;
- before bed: a glass of kefir or Varents.
Cooking
- Bread of any kind, both for sandwiches and additions to dishes, and in the form of sweet confectionery.
- The first courses are prepared in meat broths.
- Meat, fish, liver can be fried, boiled, baked, and smoked. It is advisable only to separate the pulp from the fat - its amount is supposed to be slightly reduced in the diet.
- Milk and fermented milk products can be eaten and drunk in all their variety. All types of cheese and sour cream are required.
- Eggs – boiled and fried.
- Fat-containing products: oils are acceptable - butter, sunflower, olive. It is better to avoid cakes with rich thick cream.
- Cereals: porridge and pasta can be eaten salty and sweet, with milk, with meat, etc.
- Legumes: cook thoroughly (for speed, you can add a little soda on the tip of a knife while boiling). As a rule, they are added to soups, but can be eaten separately or prepared in salads.
- Vegetables, fruits, berries are best eaten fresh, but you can also cook compotes, mousses, jellies, or squeeze juice.
- Spices – add a little to improve the taste, but in moderation.
- Confitures and honey - with tea, buns, as usual.
- Drinks - thick milkshakes, juices, rosehip infusion - everything except alcoholic drinks.
With B12 deficiency anemia, the main guarantee of successful treatment is the speed of detection of the disease. Do not let it lead to serious complications; visit a doctor when you discover the first symptoms.
Metabolism of vitamin B12 in the body
Participation of vitamin B 12 in hematopoiesis
Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) is one of the most important components of bioorganic reactions for the construction of DNA strands, as well as the synthesis and regeneration of myelin in the body.
There are two factors that contribute to the performance of specified functions by cyanocobalamin. The role of the external factor is performed by vitamin B12 itself as a component of food, the internal factor (Casla) is synthesized by the parietal cells of the stomach. Entering the stomach with food proteins, which are cleaved from the vitamin by gastric juice pepsin, the external factor binds to the carrier protein and is transported to the final section of the duodenum. Here both factors meet, form a complex and are absorbed in the final ileum with the participation of receptors on cells of the intestinal mucosa. Once in the blood, cobalamin forms a complex with another transport protein and is delivered to organs and tissues, where it is used in synthesis processes.
Diagnosis methods
A blood test can determine whether a person has anemia, which is characterized by a lack of vitamin B12. It can help identify the following signs:
- decrease in the level of red blood cells, hemoglobin;
- increased color index, which exceeds 1.05 units;
- the presence of macrocytosis, characteristic of the group of macrocytic type anemias;
- leukopenia;
- decrease in blood cells such as reticulocytes, monocytes;
- thrombocytopenia.
If these indicators are identified, the attending physician can prescribe effective treatment, which is based on drug therapy, diet and additional procedures. In addition, an increased level of bilirubin in the blood may indicate the presence of anemia.
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient may be prescribed a bone marrow puncture. It is necessary to do this in order to exclude the occurrence of other diseases that have similar symptoms. If this procedure showed hyperchromia, then there is no doubt about the diagnosis, since it is characteristic of B12 deficiency anemia. Diagnosis of the disease is carried out both in a paid clinic and in a public clinic.
In order to know whether there is a risk of developing the disease, it is necessary to conduct a routine examination and take a blood test once a year. This will allow you to promptly identify the signs and symptoms of anemia and take the necessary measures to eliminate it.
Symptoms
Symptoms may vary for each person. The main symptoms of anemia include:
- Weak muscles;
- numbness or tingling in the arms and legs;
- Problems with walking;
- Nausea;
- Decreased appetite;
- Weight loss;
- Irritability;
- Lack of energy or getting tired quickly (fatigue);
- Diarrhea;
- Smooth and swollen tongue;
- Fast heart rate.
If anemia caused by a lack of vitamin B12 is present, then in addition to the above, adults and children may also have symptoms such as:
- pale yellow tint to your skin;
- sore and red tongue (glossitis);
- mouth ulcers;
- paresthesia;
- impaired vision;
- irritability;
- depression;
- a decline in your mental abilities such as memory, understanding and judgment (dementia).
Additional symptoms in people with anemia caused by folate deficiency may include:
- symptoms associated with anemia;
- decreased sense of taste;
- diarrhea;
- numbness and tingling in the legs and arms;
- muscle weakness;
- depression.
As you can see, all of the above symptoms can look like symptoms of any other health problem. Therefore, always consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
How is deficiency diagnosed?
This type of anemia is usually detected during a health screening using a routine blood test. If the level of B12 in the blood is low, then a deficiency is detected. Your healthcare provider will review your medical history and perform a physical examination.
You may also need other blood tests. In some cases, other evaluation procedures, such as a bone marrow biopsy, may be performed.
Dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract and nervous system
The development of anemia leads to disruption of the production of juices that ensure proper digestion. Food that has not undergone high-quality processing is not fully absorbed in the stomach and intestines, and there is no complete absorption of vitamins and microelements into the mucous membrane.
All this causes the appearance of unstable and unstable stools. Patients complain of diarrhea or constipation for unknown reasons, bloating, heartburn and nausea.
Disruption of the normal functions of the gastric mucosa causes pain in the stomach itself and in the intestinal area. Patients talk about bitterness in the mouth and inflammation of the oral mucosa.
There is a danger of frequent infections due to the presence of pathogenic microflora. Pernicious anemia forces patients to consult specialists with suspected gingivitis, glossitis, stomatitis or other infectious inflammatory processes in the mouth.
All this leads to a taste disturbance, and patients have difficulty distinguishing sour from salty, and the altered taste causes an aversion to certain foods, especially those rich in nutrients and vitamins.
Megaloblastic anemia differs from B12 folate deficiency anemia in that it is characterized by impaired functionality of the nervous system. The main component of all nerve fibers in the human body is myelin sheaths, the formation of which is impossible without the participation of cobalamin.
In cases where nerve fibers are replaced by scar tissue, neurological disorders occur. The described process affecting the brain is especially dangerous.
Symptoms characteristic of a disease such as Addison-Birmer disease or pernicious anemia:
- impaired mobility of the hands and gait;
- feeling of pins and needles in the feet and hands;
- difficulty breathing and dizziness;
- weakness and fatigue.
One of the most complex diseases, b12 deficiency anemia, is characterized by such symptoms as changes in the blood picture and enlargement of the spleen, a pronounced and rapidly developing inflammatory process in the oral cavity, but most importantly, disorders related to neurological pathologies.
Unlike the symptoms of pernicious anemia, the symptoms of an illness caused by a lack of folic acid are not associated with impaired functionality of the nervous system and do not include neurological disorders.
Consequences of not following the diet
If you do not follow a diet and let everything take its course, a low level of hemoglobin can lead to atrophy of the genital organs, disruption of the respiratory system and digestive tract. Also, due to the low hemoglobin content in the blood, the entire cardiovascular system suffers, which leads to the development of various pathologies.
Proper nutrition for anemia will help cope with unpleasant symptoms much faster than conventional drug treatment. The most important thing is a properly composed menu and compliance with the rules.
Share the article on social media. networks:
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Drug treatment
Anemia due to vitamin B12 deficiency is quickly and easily treated. Its symptoms are eliminated quickly and without the use of complex manipulations. In most cases, the disease is treated with medications that compensate for the lack of vitamins and microelements. Replacement therapy is intended to eliminate not only the manifestations and first signs, but also the source of the disease.
Preparations containing vitamin B12
Today, there are 3 types of medications that treat anemia. These include drugs such as:
- Adenosylcobalamin;
- Cyano-cobalamin;
- Oxycobalamin.
The drug Cyano-cobalamin is administered by intramuscular injection every day for 14 days. Oxycobalamin, which has a stronger bond with proteins, is administered once every 2 days. But the drug Adenosylcobalamin has a more effective effect. It has an active effect on funicular myelosis, but has no effect on erythropoiesis.
The results of the injections are noticeable after just a few procedures. At the same time, the patient feels improved health, vigor and increased physical and mental performance. Moreover, blood counts improve and megaloblasts, which are concentrated in the bone marrow, disappear. After administration of the medicine, the level of reticulocytes increases after 5-6 days. Treatment continues for at least 4 weeks. The average dosage of the drug varies from 150-200 mcg per day.
If the patient has funicular myelosis, the dose is increased to 1000 mcg. The effectiveness of treatment is indicated by persistent remission. If it is absent, then this phenomenon indicates that the diagnosis is incorrect and the treatment is ineffective.
Consolidating therapy is prescribed after the main course of treatment. For two months it is necessary to administer Cyanocobalamin 1-2 times a week. After which, a drug containing vitamin B12 is administered for 6 months. Injections should be done 2 times a month, and the dose of the drug is 500 mcg.
People who suffer from chronic anemia due to a lack of vitamin B12 can alleviate their condition by completely curing the disease. In most cases, Epogen injections are recommended. Epogen is a hormone that stimulates the production of cells such as red blood cells. If anemia is caused by renal failure, then dialysis and Epogen procedures are prescribed. In extreme cases, a kidney transplant is necessary.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies is allowed only after consulting a doctor. Improper treatment at home can lead to serious consequences, which will require a lot of time and expense to eliminate. First of all, folk remedies are aimed at the causes of the disease, which include atrophic gastritis and helminthiasis.
To eliminate anemia due to B12 deficiency, you need to eat animal products. Diet is the most effective way to improve the patient’s condition and return the hematopoietic process to normal functioning.
Foods rich in vitamin B12 include:
- meat fish;
- seafood;
- fermented milk products, cheese, cottage cheese;
- liver;
- dried fruits.
Plant products practically do not contain this vitamin. But to compensate for the lack of folic acid, you need to eat leafy greens, cereals, beans, cauliflower, and mushrooms. A healthy diet based on animal products can help eliminate symptoms of the disease and reduce vitamin deficiency. After a 2-week diet, a person will feel relief and return to normal health. But this is only possible at the initial stage of anemia.
In addition, folk remedies include taking various decoctions, infusions of medicinal herbs and natural preparations. So, decoctions of meadow clover and rosehip help well. Freshly squeezed juice from beets, carrots, and radishes also helps improve your condition. Treatment of the disease must be comprehensive, so it is necessary to combine both drug therapy and diet.
Recipes
The diet during pregnancy can have a very varied menu, thanks to the large list of permitted products.
Roast
To prepare you will need half a kilogram of beef, the same amount of potatoes, 2 onions, one carrot, 2 tablespoons of olive oil, parsley, dill, salt.
Actions:
- Peel vegetables.
- Chop the onion into smaller pieces and grate the carrots on a coarse grater.
- Fry them in a heated frying pan for 1-2 minutes, add a little water and simmer for another 5 minutes.
- Cut the potatoes into small pieces and place them in a baking dish. Pour vegetable mixture on top.
- Cut the beef into small pieces and add to the vegetables. Add a glass of water and salt to taste.
- Cover with foil.
- Bake in the oven at 180 degrees for 30 minutes.
Spaghetti with cutlets
To prepare you will need 200 grams of spaghetti, the same amount of minced beef, a boiled egg, an onion, 3 tablespoons of tomato paste, a tablespoon of vegetable oil, salt.
Actions:
- Peel the onion and grate it on a fine grater. Do the same with the boiled egg.
- Add onion and egg to the minced meat, add salt.
- Roll the minced meat into cutlets and cook them in a double boiler until cooked.
- At this time, cook the spaghetti and add a tablespoon of vegetable oil to it.
- Add tomato paste before use.
Vegetable salad
To prepare you will need bell peppers, zucchini, onions, celery, olives, tomatoes, 50 grams of hard cheese, a tablespoon of olive oil, parsley, dill, pepper, salt.
Actions:
- Peel the zucchini and onion. Cut the vegetables into small pieces.
- Mix them in a deep plate. Grate the cheese over them on a fine grater.
- Add herbs, pepper, salt and olive oil. Mix thoroughly.
Treatment and prevention
Treatment should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor. Self-medication or treatment with folk remedies is undesirable and extremely life-threatening with progressive anemia. Treatment for B12 deficiency anemia involves increasing the level of this vitamin in the blood and also eliminating the cause of the anemia.
The doctor can adjust the diet, advise eating more meat, and vegetarians - more milk and soy products. Intramuscular injections and multivitamin complexes will help increase the vitamin content. Vitamin B12 is administered intramuscularly in courses of a month and a half.
The dosage is determined by the doctor depending on the severity of the patient's condition. In case of thrombosis, it is recommended to avoid injections. The vitamin should not be administered intramuscularly during pregnancy. Pregnant women are prescribed vitamins in tablets and their diet is adjusted. Diet is also a method of prevention.
The largest amount of vitamin B12 is found in liver (especially beef), fish, rabbit, beef, pork, chicken eggs, and natural sour cream.
It is necessary to completely eliminate alcohol both during treatment and prevention. For severe anemia, a blood or red blood cell transfusion is possible. This is a last resort method, used only if there is a threat to the patient's life. If the established cause of anemia is worms, it is necessary to take drugs that destroy parasites, as well as various enzymes that support intestinal function.
For stomach diseases, it is necessary to take medications that restore and protect the mucous membrane, as well as follow a diet so as not to overload the stomach
It is important to reduce the load on the liver during treatment, since it is in the liver that the supply of vitamin B12 is deposited. A damaged liver is unable to store vitamins
The doctor may prescribe hepatoprotectors or clarify which foods are beneficial or harmful to the liver. The effectiveness of treatment can be assessed by a blood test. Blood is donated regularly during treatment.
In continuation of the article
Complete blood count - platelets: diagnosis and interpretation
The norm of leukocytes in the blood of pregnant women by trimester
Complete blood count - leukocytes: normal for age
Leukocytosis: increased levels of white blood cells in the blood
Proper preparation for a general blood test
What are red blood cells responsible for and what is their norm in the blood?
Features of treatment
After diagnosing B12-deficiency anemia, treatment is prescribed immediately, as this helps prevent the risk of developing various types of complications. Therapy is carried out medicinally - by injecting vitamin B12 in increased dosages to completely eliminate the signs of pathology. Patients must always adhere to supportive treatment.
When carrying out therapy, it is important to take certain measures to normalize the functioning of the digestive, hematopoietic, and nervous systems. During treatment with medications, the patient must be under the supervision of specialists and donate blood at least 2 times a week.
In particularly severe cases, blood transfusions are performed. In addition, vitamin B12 is administered in increased quantities until the risks of complications are completely eliminated. The patient's nutrition is of particular importance. You definitely need to diversify your menu and add foods with a high content of vitamin B12 to your usual diet. Patients are advised to have a nutritious and varied diet.
Which doctor should I contact?
Symptoms of the disease appear very slowly and do not cause any particular inconvenience in the early stages. But with its development, B12 deficiency anemia causes serious complications that can threaten the patient’s life
Therefore, it is important to detect the disease as early as possible. Diagnosis of this disease involves:
Unfortunately, the disease can only be diagnosed using hardware methods. But first, the doctor, conducting an initial survey and examination, finds out:
- What symptoms are noticed?
- Are there any congenital pathologies?
- Are there external signs of illness?
- Has the patient's stool changed?
- What health complaints have appeared recently?
Having drawn up an overall picture and assessed the patient’s condition, he will direct him to:
- blood test to detect megaloblasts;
- bone marrow puncture;
- irrigoscopy, esophagogastroduodenoscopy;
- Ultrasound;
- computer or magnetic resonance imaging.
In most cases, these instrumental research methods are sufficient to diagnose the disease. Having studied all the data obtained, the doctor can determine the cause of the disease and prescribe effective therapy. His choice is based on the patient’s age, the severity of the disease and the characteristics of the body. For example, some medications made in the form of alcohol tinctures are strictly contraindicated for children.
The best hematologists in Moscow
Causes and treatment of anemia due to folic acid deficiency
Anemia develops as a result of a lack of folic acid in the body or if its absorption is impaired.
The form of anemia is much less common than the previously described forms of the disease. What can cause folic acid deficiency:
- Poor and unbalanced diet;
- Alcohol poisoning and chronic form of alcoholism;
- Pregnancy;
- Worm infestations;
- Liver diseases requiring dialysis;
- Oncology;
- Taking certain forms of medications that interfere with the absorption of folic acid.
Taking medications containing folic acid in tablet form, but only after establishing an accurate diagnosis.
The daily dose is no more than 1 mg.
In severe forms of the disease, the dosage is revised and prescribed in increased quantities.
Prevention of folate deficiency anemia is carried out during pregnancy and in patients with severe symptoms of a deficiency of this vitamin, which cause increased metabolism.
Treatment
According to ICD-10, treatment of B12-deficiency anemia should pursue three goals:
- Replenish the deficiency of cyanocobalamin as soon as possible to prevent disruption of the most important vital functions.
- If possible, eliminate the causes of anemia or carry out regular maintenance therapy to maintain vitamin B12 balance.
- Prevent irreparable changes in the bone marrow and nervous system.
For this purpose, first of all, injections with B12 are prescribed, the dosage of which depends on the degree of development of anemia, and Oxycobalamin, which restores the functions of the nervous system. Then tableted “Adenosylcobalamin” is added to normalize metabolic processes.
Anemia in children
Among the main causes of the development of the disease in childhood are the following:
- changes in intestinal microflora;
- the presence of worms in the body;
- not enough vitamin in the child’s body;
- congenital pathologies.
Symptoms of B12 deficiency anemia are similar to those in adults. However, there are also characteristic signs of the pathology, in particular such as:
- severe caries;
- persistent stomatitis;
- changes in the nail plate;
- changes in the eyeball;
- decreased intelligence and concentration.
To make a diagnosis, you need to take blood tests, and, if necessary, undergo a comprehensive diagnosis, which includes:
- gastroendoscopy;
- irrigoscopy;
- ultrasound diagnostics of the liver and kidneys;
- colonoscopy.
Treatment of B12-deficiency anemia in a child consists of saturating the body with the required vitamins. The medicinal course of vitamins is 15 days. A low-calorie diet, which contains foods containing B12, is also additionally prescribed.
What is B12 deficiency anemia
The disease to which this article is devoted has many synonymous names. It is also known as:
- megaloblastic or pernicious (from the Latin “disastrous”) anemia;
- Addison-Beermer disease.
With B-12 deficiency anemia, pathological processes in the body are caused by a deterioration in DNA synthesis. The division of all cells that must be regularly renewed slows down. This refers to cells of the skin, tissues of the nervous system, bone marrow, mucous membranes of organs (in particular, the gastrointestinal tract) and blood.
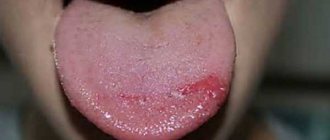
The disease creeps up slowly, unnoticeably. Its typical early signs - weakness, fatigue, dizziness, periodic shortness of breath, pallor - are very easy to mistake for symptoms of other ailments. A more characteristic feature is a red and glossy, as if varnished tongue.
In the absence of adequate treatment, a patient with megaloblastic anemia gradually develops gastric achylia (a pathological condition in which there is no hydrochloric acid and pepsin in the gastric juice).
Prevention and treatment
To avoid illness, you must follow some rules.
Firstly, you should strictly monitor the variety of your diet. Think twice before getting carried away with the idea of vegetarianism.
An unbalanced diet is quite capable of becoming an independent cause of anemia (albeit of a different type), especially in older people and children.
Secondly, you should completely give up alcohol.
Thirdly, in autumn, winter and spring it is advisable to take additional B vitamins. The development of Addison-Birmer disease is prevented by folic acid and cyanocobalamin (aka B12).
Cyanocobalamin is found in liver, eggs, and milk. It can also be administered into the body through injections.
Tablets are made from folic acid - they are freely sold in almost every pharmacy and are inexpensive. Natural sources of an important substance can be:
- fruits;
- liver;
- kidneys;
- greenery;
- soybeans
Proper treatment of B-12 deficiency anemia ensures improvement in blood counts within a couple of months, and elimination of neurological pathologies requires at least six months. In addition to vitamin therapy, enzyme and fixative drugs are prescribed.
Lack of treatment leads to serious consequences, such as nerve degeneration, gastric malignancy, heart failure, etc.
How is deficiency treated?
B12 deficiency anemia and folate deficiency often occur together and are difficult to distinguish from each other.
Most cases can be easily treated with injections or tablets to replace missing vitamins. Treatment may include vitamin B12 injections or taking folic acid tablets.
Vitamin B12 supplements are usually given by injection first. Then, depending on whether your deficiency is related to your diet, you will need B12 tablets between meals or regular injections. These procedures can last for the rest of your life.
Folic acid tablets are used to restore folate levels. They usually need to be taken for four months.
In some cases, adjusting your diet can help and even prevent the anemia from recurring.
Foods that are rich in folic acid include:
- Orange juice;
- oranges;
- romaine lettuce;
- Spinach;
- Liver;
- Rice;
- Barley;
- Sprouts;
- Wheat germ;
- Soya beans;
- Leafy vegetables;
- Beans;
- Peanut;
- Broccoli;
- Asparagus;
- Peas;
- Lentils;
- Chickpeas (garbanzo beans).
Foods rich in folic acid and vitamin B-12 include:
- Eggs;
- Meat;
- Domestic bird;
- Milk;
- Mollusk;
- Enriched cereals.
Taking oral folic acid is better than eating foods rich in folic acid. Vitamin B-12 is not absorbed as well as with injections.
Causes
According to the International Classification of Diseases ICD-10, the disease is assigned code D51.
Causes of B12 deficiency anemia:
A meager diet, devoid of animal products. A person who is inclined to eat exclusively plant foods must understand that he runs the risk of getting sick, since vitamin B12 is found in liver, milk, and eggs. Congenital weakness of the gastric glands and, as a result, lack of enzymes for the absorption of B12
That is, in this case, the vitamin enters, but is not absorbed into the blood. Worms that absorb vitamin B12 and doom the donor organism to a deficiency of an important element. Some other diseases that affect the supply of vitamin B12 to the blood: pancreatic disorder, enteritis, Crohn's disease, etc. Previous operations on the gastrointestinal tract. Consequences of cancer. Advanced age. Appetite disorder due to systematic drinking and constant hangover.
Pregnancy and increased need for vitamins.
Vitamin B12 deficiency may develop during pregnancy
Diet food
People suffering from B12 deficiency anemia must follow dietary recommendations very strictly, as this promotes faster recovery. The diet must include dishes prepared from:
- whole grains;
- rabbit meat, lamb, beef;
- beans and peas;
- sea fish;
- chicken and beef liver.
A balanced diet is especially required during the period of intrauterine development of a child, since the formation of the fetus largely depends on the intake of vitamins in the pregnant woman’s body. You can prepare dishes in the usual way. You need to consume food 5 times a day. Be sure to drink enough water.
Mechanism of development of B12 deficiency anemia
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) enters the body of a living being, including humans, through food of animal origin, since the body itself is not able to synthesize this vitamin. With a normal, balanced diet, the average person absorbs 30 to 50 micrograms of vitamin B12 daily into the intestines, while the body's daily requirement is 3 to 5 micrograms. When absorbed, cobalamin is deposited in the liver, which can contain up to 5 mg of the vitamin in an adult. That is, it is not at all surprising that the first symptoms of malignant anemia appear several years after the start of cobalamin intake in insufficient quantities.
Vitamin B12 deficiency provokes a violation of DNA synthesis in all cells of the body
Vitamin B12 deficiency provokes a disruption of DNA synthesis in all cells of the body. And first of all, this becomes noticeable in the mucous membranes and hematopoietic tissues, the processes of cell division in which occur more intensively. After the vitamin enters the cell, it takes on one of the following forms:
- deoxyadenosylcobalamin. It takes part in the formation of fatty acids, the deficiency of which leads to damage to the nervous system;
- Methyl-B12. Actively participates in the synthesis of DNA components, in particular thymidine. And the lack of cobalamin in the body leads to a stop in the synthesis of this nucleoside, resulting in the formation of a DNA molecule with an inferior structure. This molecule is prone to rapid destruction, which prevents normal cell division.
Lack of vitamin B12 leads to disruption of DNA synthesis during the process of hematopoiesis at the initial stage of red blood cell development, which makes their further development impossible.
What is also very important, cobalamin deficiency leads to disruption of the formation of not only red blood cells, but also platelets and leukocytes. This disruption process is expressed much weaker than the disruption of red blood cell formation
But if this phenomenon occurs over a long period of time, then there is a high probability of developing a syndrome characterized by a lack of all important blood components.
Possible complications
If emergency measures are not taken to treat anemia, serious complications can occur that pose a threat to human life. Among them it is necessary to note the following:
- coma;
- severe illness;
- destruction of cells of internal organs;
- myelosis.
A comatose state is characterized by the fact that the affected person does not respond to external stimuli. Coma occurs when the brain is hypoxic and can lead to the death of the patient.
A severe degree of the disease significantly worsens a person’s well-being and triggers irreversible consequences in the body. This degree occurs when the hemoglobin index is below 70 g/l. Funicular myelosis refers to damage to the cells of the spinal cord, as well as nerve endings. At the same time, the sensitivity of the limbs deteriorates, and unsteadiness of gait appears. As the pathology progresses, sensitivity completely disappears, and the person cannot move independently.
Over time, the cells of internal organs are completely destroyed, which provokes a disruption in their functioning. If the treatment process began very late, then complications simply cannot be prevented.
Risk groups for developing vitamin B12 deficiency
The majority of people suffering from vitamin deficiency are vegetarians. They refuse to consume animal products, thereby leading to a deficiency of the necessary substance. The risk group also includes children of vegetarians, since during intrauterine development they do not receive the vitamin in the proper amount. There are also risks:
- persons who have undergone severe surgery to remove a section of the intestine in which vitamin absorption occurs;
- having autoimmune pathologies, Crohn's disease, hyperthyroidism;
- teenagers during a period of active growth and development;
- elderly citizens;
- pregnant women;
- people with tumor diseases.
Important! Taking glucose-lowering and antacid medications also leads to the risk of developing vitamin deficiency.
Interesting facts about vitamin B12
- The intestinal microflora synthesizes vitamin B12. As a result, the consumption of fermented milk products and preparations of live bacteria contribute to the normal content of intestinal microflora, although the amount of vitamin they produce does not cover the body's needs.
- If a person has a harmless passion for sweets, then the own microflora of the intestinal tract changes, putrefactive bacteria, fungi, and parasites appear, which begin to lay claim to vitamin B12, which comes with food.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of megaloblastic anemia involves a number of complex measures:
- At the initial visit, it is necessary to interview the patient in detail. It is necessary to ask about all the complaints that the person has. How long ago did he begin to notice a deterioration in his health and well-being? It is also important for the doctor to know whether there is a hereditary predisposition to diseases of the stomach and intestines. The patient's living and working conditions are of no small importance.
- During the examination, the patient’s pale skin and bright varnished tongue cannot escape the doctor. When measuring blood pressure, hypotension (decrease in values) is noted. The heartbeat is rapid, this can be determined by palpating the pulse or auscultating the heart area.
- Laboratory blood test. Megaloblastic anemia is characterized by a decrease in the number of platelets, red blood cells and reticulocytes. The hemoglobin level decreases, but the color index increases. Normally, its values should range from 0.85 to 1.05. When diagnosing megaloblastic anemia, the color index is 1.06 or more.
- Biochemical blood test. This study is carried out to identify concomitant pathologies. In Addison-Birmer disease, high levels of iron, bilirubin and lactate dehydrogenase are found.
- The level of cyanocobalamin in the blood serum is determined. It is sharply reduced.
- Laboratory examination of urine. This analysis will help identify primary and concomitant diseases.
- Laboratory diagnostics of bone marrow. The formation of red blood cells in large quantities is detected.
- To identify pathologies of cardiac activity, electrocardiography is performed. Tachycardia, arrhythmias and signs of myocardial nutritional deficiency can be detected.
Forecast
The earlier the presence of B12-deficiency anemia was detected and comprehensive treatment was carried out, the better the prognosis will be. If you visit a doctor late or have a hereditary form of anemia, the prognosis will be quite unfavorable. Damage to the nervous system is especially dangerous. In this case, patients have to be treated throughout their lives. It is worth noting that severe B12 deficiency anemia can lead to the death of the patient.
This is a rather complex disease. However, with timely consultation with a doctor and complex therapy, this condition is completely harmless. The greatest danger is oxygen starvation, anemic coma, and loss of consciousness. In this case, treatment involves a blood transfusion.
When the disease occurs during pregnancy, it is important to support the body of the woman and child. Therefore, the daily dosage of vitamin B12 should be doubled. Cobalamin reserves in the body are significantly reduced during liver disease and frequent pregnancy. Women are also prescribed a special diet.
Stages of anemia development
The main symptoms of the disease directly depend on the stage of its development. The severity of a patient’s condition is usually determined based on the number of erythrocytes (red blood cells) in the blood. Depending on this indicator, three stages of the disease are distinguished:
- In mild forms of anemia, the number of red blood cells ranges from 90 to 110 g/l.
- The moderate form of severity is characterized by a more significant decrease in the number of red blood cells - from 90 to 70 g/l.
- If the patient’s red blood cell count is 70 g/l or less, then we are talking about a severe form of B120 deficiency anemia, which is extremely dangerous to health and even life.
Therapy for B12 deficiency anemia
Therapy for B12 deficiency anemia begins with treatment of the root cause of this deficiency - this is therapeutic therapy to destroy helminths, normal and balanced nutrition, as well as surgical methods for treating malignant neoplasms.
For the complex treatment of anemia, the drug B12 is administered into the body at a dosage of 200.0 mcg - 250.0 mcg per day. The drug is injected into muscle tissue, or injected under the skin of the human body.
If anemia has affected the centers of the nervous system, then the drug therapy regimen is as follows: for the first 3 calendar days, a vitamin dosage of 1000.0 mcg per day, and subsequent treatment according to the prescribed regimen. The treatment regimen, as well as the dosage of B12, is prescribed by the attending doctor and depends on the degree of deficiency in the body of vitamin B12, which caused anemia.
After stabilization of this vitamin in the body, to maintain it at a normal level, B12 preparation is used in treatment at 100.0 mcg - 200.0 mcg 1 time per calendar month.
Clinical recommendations for rapid replenishment of red blood cells in the blood include intravenous administration of red blood cells, which can restore the destroyed balance in the composition of the blood plasma of the human body.
Features of the disease
The human body must maintain a balance of vitamins, micro- and macroelements. With a deficiency of vitamin B12, anemia develops. Lack of B12 provokes disturbances in the synthesis of DNA and RNA, which is a direct threat to the performance of vital functions by organs. That is why this type of anemia is considered fatal.
It will also be useful for you to learn about what aplastic anemia is on our website.
We also recommend studying this topic:
Iron deficiency anemia in adults
Symptoms and types
In order to prevent the disastrous consequences of the disease, it is important to identify the lack of necessary substances as early as possible. To do this, you need to know how B12-deficiency anemia manifests itself. Symptoms of the disease are similar to traditional signs of anemia:
- dizziness;
- flashing before the eyes;
- muscle weakness;
- drowsiness or insomnia;
- deterioration of the condition of the skin, nails, hair;
- dyspnea;
- irregular heartbeat and chest pain;
- numbness of certain parts of the body;
- pallor;
- digestive disorders;
- fainting.
We recommend studying the article on a similar topic “Symptoms and consequences of anemia during pregnancy” within the framework of this material.
The most characteristic sign is pale skin, a painful tint, as well as changes in the oral cavity. The patient has a feeling of dryness and burning in the mouth, atrophy of the papillae of the tongue. The tongue itself takes on a bright red or crimson color, and its surface becomes “varnished” in appearance.
A characteristic symptom is glossitis
In addition, there is a decrease in hemoglobin levels, which leads to intense oxygen starvation of tissues, including the brain . This affects not only the patient’s well-being, but also his mental activity. The changes affect the bone marrow, where red blood cell synthesis occurs.
Erythromegaloblasts are found in the bone marrow structure
Depending on the observed hemoglobin concentration and the number of red blood cells, anemia can be of three degrees of severity:
- light;
- moderate;
- heavy.
Important: men have higher hemoglobin levels, so if the level is 110 g/l you should be wary, while in women this is the norm.
There are also congenital and acquired forms of the disease. Congenital is observed in children born from a mother with anemia, when the woman is a vegetarian, as well as in the presence of pathologies of the systems responsible for the absorption of vitamin B12 and hematopoiesis.
Causes and consequences
Vitamin B12 is very important for the body, as it is involved in the process of RNA synthesis. If this process is disrupted, the negative impact will spread throughout the entire body, and some organs may stop working properly.
| Indicators | Iron-deficient | Hemolytic | Hypoplastic | B12-deficient |
| Hemoglobin | ↓ | ↓↓ | ↓↓ | ↓↓↓ |
| Red blood cells | ↓ | ↓ | ↓↓ | ↓↓ |
| Color indicator | ↓ | Norm | Norm | ↑ |
| Red blood cell diameter | ↓ | ↓ | Norm | ↑↑ |
| Average erythrocyte volume (AER) (MCV) | Norm, ↓ | ↑ | Norm | ↑↑↑ |
| Average hemoglobin content in erythrocytes (MSHE) (MSN) | ↓ | ↑ | Norm | ↑↑↑ |
| Average hemoglobin concentration in erythrocytes (MSHC) | ↓ | Norm | Norm | ↑ |
| Reticulocytes | Norm | ↑↑↑ | ↓↓↓ | ↓ |
Table: Main indicators of deviations from the norm for different forms of anemia, including B12 (highlighted)
The main cause is a lack of vitamin B12, but it can be caused by various factors.
To understand what direction to move in when fighting this type of anemia, it is important to know what factors lead to a lack of such an important vitamin:
- Unbalanced diet . This is especially true for vegetarianism. A person gets B12 from food, so you need to choose the optimal composition of your daily diet.
- Impaired functioning of the digestive organs . Problems with the gastrointestinal tract disrupt the process of processing and absorption of nutrients. This is especially true for chronic pathologies, tumors and surgical interventions.
- Violation of the synthesis of necessary enzymes . With a sufficient amount of cobalamin substances in food, the vitamin may not be absorbed by the body due to the lack of necessary enzymes (Castle factor).
- Helminthic infestations . Parasites in the gastrointestinal tract reduce the level of nutrients entering the blood from the intestines.
- Medications. Some medications can reduce gastric secretion, and consequently the absorption of the vitamin.
- Pregnancy . B12 deficiency anemia can be combined with iron or folate deficiency, since the woman’s body experiences additional consumption of nutrients, which is associated with fetal development.
If you do not begin to treat anemia, the consequences can be extremely dangerous, because it is not for nothing that this disease is called malignant. The following complications are possible:
- tissue hypoxia and disruption of internal organs;
- bone marrow changes;
- irreversible neurological disorders, particularly in the brain, for example, funicular myelosis;
- pernicious coma.
We previously wrote about the causes of hemorrhagic anemia and recommended adding it to your bookmarks.
We also recommend studying this topic:
Anemia in children: symptoms and treatment, disease prevention
Why is this form of anemia dangerous? Possible complications
Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia can be extremely dangerous if not treated promptly. As already mentioned, first of all, the lack of this substance affects the state of the nervous system. Complications of this type of anemia include damage to the spinal cord and peripheral nerves. In turn, such disorders are accompanied by discomfort and tingling in the limbs, complete or partial loss of sensation, and fecal or urinary incontinence.
Against the background of a chronic deficiency of cyanocobalamin, the functioning of the entire body deteriorates - various diseases of the kidneys, heart and other organs may appear. Sometimes, against the background of a sharp decrease in the number of red blood cells, brain hypoxia develops, which leads to pernicious coma.
If you start treatment in the early stages, then all of the above complications can be avoided. Late therapy can eliminate vitamin deficiency, but, alas, changes in the nervous system are already irreversible.
Diet for this form of anemia
A balanced diet is especially necessary during the period of intrauterine development of a child, since the formation of the baby, as well as the occurrence of intrauterine pathologies that are revealed after birth, depend on the intake of vitamins in the body of a pregnant woman.
During pregnancy, the need for vitamin B12 increases by 50.0%.
| products | amount of B12 in mcg |
| · calf liver | · 60,0 |
| liver of a young piglet | · 30,0 |
| chicken liver | · 16,0 |
| · mackerel fish | · 12,0 |
| · rabbit meat | · 4,30 |
| · veal | · 2,60 |
| · perch fish | · 2,40 |
| · pork | · 2,0 |
| · eggs | · 0,40 |
| · fat sour cream |
For B12 deficiency anemia, a diet is used - table No. 11. This diet should increase the content of protein and vitamin B12 in the body. The food preparation method is standard. You need to eat 5 times a day.
Energy value of diet No. 11:
- Proteins - 110.0 grams - 130.0 grams (60.0% animal origin, 40.0% plant origin);
- Fats - 100.0 grams - 120.0 grams (80.0% animal and only 20.0% vegetable);
- Carbohydrates - 400.0 grams - 450.0 grams;
- Salt - no more than 15.0 grams;
- Purified water 1.5 liters.
| foods useful for B12 deficiency anemia | prohibited products |
| · veal, pork, chicken liver | · milk |
| · salo | · baking |
| · butter | · confectionery sweet products |
| · mackerel fish | · tea |
| · meat: veal, rabbit, pork | caffeinated drinks |
| · eggs | · Coca Cola |
| · fat sour cream | · alcoholic drinks |
| · low-fat cottage cheese | Do not use vinegar in cooking |
| · hard cheese | sweet carbonated drinks |
| · soft cheese | |
| Legumes: peas, lentils | |
| vegetables: carrots, potatoes, cabbage, beets, tomatoes | |
| · fruits of all varieties | |
| · berries of all types | |
| Green vegetables are rich in iron | |
| · garden greens | |
| mineral water |
Vitamin B12 deficiency and medications
Many medications are known to significantly interfere with the absorption of vitamin B12, so some patients often also suffer from vitamin B12 deficiency. Interactions may also occur with other substances and medications. A list of some of them can be found in the table below.
- Alcohol and drugs
- Heavy smoking
- High coffee consumption
- High doses of vitamin C
- High sugar intake
- Eating food that is too hot (stomach and intestinal irritation)
- High absorption of synthetic vitamin B12
- Taking acid blockers/ulcer medications
- Taking diabetes medications
- Various drugs (antibiotics, psychotropic drugs, aspirin, chemotherapy, estrogen-based birth control and hormonal drugs (proton pump inhibitors), diabetes drugs (metformin), antihypertensive drugs), drugs for heart problems (beta blockers, nitrate sprays , nitroglycerin), cholesterol-lowering drugs (statins), treatment of impotence.
Fertility problems
Very often, the reproductive functions of women and men deteriorate due to vitamin deficiency. Cyanocobalamin plays an important role in this process.
A woman’s fertility lies in her ability to conceive a baby, carry it to term and reproduce normally. Poor fertility means that a woman can conceive, but finds it difficult to carry a child to term. In other cases, the child is born normally, but problems arise during labor.
Male fertility depends on how a man's sperm fertilizes a woman's egg. This ability is best manifested from 15 to 50 years. Due to a lack of vitamin B12, there is a noticeable decrease in fertility, which causes difficulties in conceiving a child.
In recent years, cases of serious problems with male and female fertility have become more frequent.
Diagnosis of deficiency
Determining vitamin B12 deficiency in men, women and children is done in the same way: using an analysis. The indicators depend on age, the norm for adults is 148-729 pmol/l, and for schoolchildren 9-12 years old - 135-803 pmol/l.
The doctor interprets the test results. If cobalamin deficiency is diagnosed, treatment will require dietary adjustments and supplementation.
Before the analysis, you should not eat anything, drink alcoholic beverages, or play sports. Blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach.
The significance of the internal factor
Cyanocobalamin from food products entering the gastrointestinal tract is absorbed using the so-called intrinsic factor (IF) . Here's how it happens:
- In the stomach, B12 is absorbed with the internal factor, as was previously thought, in no hurry; it finds protein-R and combines with it in order to be sent to the duodenum in the form of a complex “Vit B12 + protein-R” and there, under the influence of proteolytic enzymes, break down;
- In the duodenum, cyanocobalamin is freed from protein-R and, in a free state, meets the internal factor that has arrived there, interacts with it and forms another complex - “Vit B12 + VF”;
- The “Vit B12 + VF” complex is sent to the jejunum, finds receptors intended for internal factor, connects with them and is absorbed;
- After absorption, cyanocobalamin “sits” on the transport protein transcobalamin II, which delivers it to the sites of primary activity or to a depot to create a reserve (bone marrow, liver).
It is obvious why such great importance is given to the internal factor, because if everything is in order with it, then almost all of the cyanocobalamin supplied with food will safely reach its destination. Otherwise (in the absence of VF), only 1% of vitamin B12 will leak through the intestinal wall by diffusion, and then the person will not receive the amount of such an important vitamin he needs.
The body's daily need for cyanocobalamin is from 3 to 5 mcg, and its reserve is from 4 to 5 grams, therefore, it can be calculated that if the supply of vitamin B12 is completely excluded (for example, during a gastrectomy), then the reserves will dry up in 3- 4 years. In general, the supply of vitamin B12 is designed for 4-6 years, while folic acid, in the absence of supply, will disappear in 3-4 months. From this we can conclude that B12 deficiency during pregnancy does not threaten if its level was normal before, but folic acid, if the woman did not consume raw fruits and vegetables, is quite capable of falling below the permissible limit and creating a deficiency state (the development of folate deficiency anemia ).
Vitamin B12 is found in products of animal origin, folic acid is found in almost all food products, however, cyanocobalamin tolerates heat treatment remarkably well for a long time and is preserved for entry into the body, which cannot be said about folic acid - after 15 minutes of boiling, this vitamin does not there will be no trace...
Other treatments
In mild cases of the disease, treatment is carried out with drugs in tablet form. Depending on the main cause that provoked the disease, treatment methods are selected separately. If there are worms in the body, antihelminthic drugs are required. Neoplasms are eliminated through surgery, as well as the use of radiation therapy techniques.
If the functioning of the intestines and stomach deteriorates, the doctor prescribes medications that help eliminate inflammation in this area. If anemia was caused only by a lack of vitamin B12 in the body, then drugs are prescribed that contain cyanocobalamin. Unlike injections, taking the vitamin in this form does not cause pain, and it is also convenient for the patient.
If the absorption of the active substance is somewhat difficult due to increased acidity of the stomach, then vitamins B5 and B9, as well as preparations containing calcium, will help improve this process. In addition, you can use folk remedies that stimulate the process of hematopoiesis and help the absorption of vitamin B12.
Stinging nettle increases the number of red blood cells in the blood. An infusion of the leaves of this plant should be consumed 0.5 cups 3 times a day before meals. For malignant anemia, an infusion of common pikulnik helps. It is also recommended to use rosehip infusion or decoction.
What are the similarities and what are the differences?
As noted above, B12-deficiency and B12-folate deficiency anemias belong to the group of megaloblastic anemias, which are characterized by a decrease in DNA production, which, in turn, impairs the proliferation of cells capable of rapid division. These are the cells:
- Bone marrow;
- Skin;
- Mucous membranes;
- Gastrointestinal tract.
Among all rapidly proliferating cells, hematopoietic (blood-forming) cells show the greatest tendency to accelerate proliferation, therefore symptoms of anemia are among the first clinical manifestations of these megaloblastic anemias. There are often cases when, in addition to anemia (decrease in the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin), other signs of hematological pathology are observed, for example, a decrease in the number of blood platelets - platelets (thrombocytopenia), neutrophilic leukocytes (neutropenia, agranulocytosis), as well as monocytes and reticulocytes.
blood for B12 deficiency anemia
Why are these types of anemia so interrelated and what is their difference? The fact is that:
- The presence and direct participation of vitamin B12 is very necessary for the formation of the active form of folic acid, which, in turn, is very necessary for the production of thymidine, an important component of DNA. This biochemical interaction with the participation of all necessary factors allows us to fully ensure the normal formation of blood cells and gastrointestinal tract cells (gastrointestinal tract);
- Vitamin B12 is also assigned other tasks - with its participation, individual fatty acids (FAs) are broken down and synthesized. If the content of cyanocobalamin is insufficient, this process is disrupted, and harmful, neuron-killing methylmalonic acid begins to accumulate in the body, and at the same time the production of myelin, a substance that forms the myelin sheath, which has an electrically insulating function for nerve cells, decreases.
As for folic acid, the breakdown of FA does not require its participation, and with its deficiency the nervous system does not suffer. Moreover, if a patient with B12 deficiency is prescribed folic acid as a treatment, then for a short time it will stimulate erythropoiesis, but only until it is in excess. An excessive amount of the drug will force all the B12 present in the body to work, that is, even the one that was intended to ensure the breakdown of fatty acids. Of course, this situation does not lead to good - nervous tissues are even more affected, deep degenerative changes in the spinal cord develop with loss of motor and sensory functions (combined sclerosis, funicular myelosis).
Thus, a deficiency of vitamin B12, along with impaired proliferation of hematopoietic cells and the development of anemia, has a negative effect on the nervous system (NS), while a deficiency of folic acid only affects the division of hematopoietic cells, but does not affect the health of the nervous system.
What is the disease?
In fact, B12-deficiency anemia is known by various terms - percynous or megabloblastic anemia, pernicious anemia, and Addison-Biermer disease. This disease is accompanied by a decrease in the number of red blood cells, which is associated with a deficiency of vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin). It is worth noting that not only bone marrow structures, but also nervous tissues are especially sensitive to the lack of this substance, which, in fact, makes the disease extremely dangerous.
In most cases, patients are diagnosed with B12-folate deficiency anemia, in which there is also a lack of folic acid. The symptoms of the disease were first described relatively recently - in 1855, the English doctor T. Addison was researching an unknown disease. And already in 1926, researchers W. Murphy, J. Will and J. Minot noted in their studies that the symptoms of the disease go away if raw liver is introduced into the patient’s diet.
Deficiency in women
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a very dangerous phenomenon for the fair sex. Women over 40 years of age and older are especially susceptible to this.
Women need B12 for the following processes in the body:
- for preventive purposes and for the treatment of rickets, osteoporosis, etc.;
- as an auxiliary and protective agent for problems with the mucous membrane, for example, from stomatitis;
- for good general well-being.
B12 has a positive effect on the quality of hair and skin. When it is deficient, the hair loses its shine, becomes brittle, the skin flakes, and pigment spots appear on it.
Vitamin B12 deficiency in women is determined by the following signs:
- a woman complains of frequent dizziness;
- her hands tingle and go numb;
- the skin acquires pale shades;
- memory deteriorates;
- bothered by the feeling of constant fatigue;
- vision is impaired;
- weakness appears in the muscles;
- taste becomes weaker, the tongue burns, discomfort appears in it;
- mood changes frequently;
- there are problems with the functioning of the heart;
- shortness of breath appears;
- coordination of movements is impaired;
- the temperature rises.