What is this
By food allergy we mean the body’s response to any food ingredient found in the gastrointestinal tract. At the same time, the immune system actively combats incoming allergens, provoking the formation of large amounts of histamine, a substance that increases vascular permeability. As a result, a clinical picture arises that is typical for a pathology such as allergies.
The disease is often confused with a concept such as food intolerance, mainly due to the similarity of symptoms. However, the mechanisms of formation and progression of these pathologies are completely different. The fundamental difference between food allergies is the participation of the immune system in the genesis of the disease, which is not the case with intolerance to food components.
In addition, there is a difference depending on the amount of allergen ingested and the strength of the body's reaction to it. In the case of allergies, severe symptoms are observed even with a small amount of the provoking product eaten. With food intolerance, the strength of the reaction directly depends on the amount of allergen entering the body: the more there is, the more pronounced the symptoms appear. An allergen product consumed in a small dose may not cause any reaction at all.
Helpful: Causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck in children
Basics of catering for allergy sufferers
Don't be intimidated by the vastness of the lists above. Having an allergy does not mean that you have to eliminate ALL of these foods from your diet. As a rule, each person is allergic to only one, or at most several, foods. The main task is to find them. Special tests - allergen tests - can help with this. However, you can go the other way: just gradually introduce each of the above-mentioned products into your diet in small quantities, and watch your body. If a rash or any other manifestation of an allergy appears, remember what you should not eat in the future. No reaction - congratulations, you can safely eat this product. Thus, find all your “dangerous” points and further formulate your diet, excluding them from the composition of your dishes.
What happens
Types of allergies are determined by the occurrence of typical symptoms to various groups of protein-containing products or to multiple food additives contained in food components.
For milk
An allergic reaction to cow's milk is one of the most common, especially in children. The allergens in this case are milk proteins: casein, beta-lactoglobulin, alpha-lactalbumin, lactoferin, bovine serum albumin. Allergies usually manifest themselves to several proteins at the same time. Please note that milk proteins are resistant to high temperatures. Therefore, this product is contraindicated for dairy allergy sufferers, even when boiled.
Children with allergies may have a typical reaction to beef proteins. In this case, they talk about cross-allergic manifestations to similar components.
For meat products
Foreign pathogenic agents in meat are also proteins: gammaglobulin, serum albumin. However, unlike dairy analogues, meat proteins are susceptible to destruction during heat treatment, so allergies to meat are quite rare. Allergenic representatives of this group are: pork, beef, poultry. But typical manifestations of sausage and sausage products cannot be called rare. Symptoms, in this case, arise as a reaction to various food additives contained in products: preservatives, dyes, spices, nuts, etc. The method of preparation is also important. When consuming raw-dried and raw-smoked sausages, the risk of allergy symptoms increases several times.
On eggs
Egg white is a foodborne pathogen that is widespread among allergy sufferers. The yolk is not so toxic, but is also prohibited for consumption if you are prone to a reaction to eggs. Moreover, we are talking not only about eggs in their natural form, but also about products where it is contained as an ingredient.
For fish
Fish proteins are also strong allergens, causing rapid and rather severe characteristic symptoms. The reaction is usually permanent, lasting throughout life. Particularly strong symptoms are observed when consuming fatty (sea) fish, fish with red meat, as well as crustaceans and other seafood.
For nuts
Almost all types of nuts can cause allergies. Even with a small amount of the product eaten, people prone to the disease experience a strong reaction, characterized by rapid manifestations. This allergy is most dangerous for children, as it leads to severe intoxication.
For strawberries
Hypersensitivity to this berry is due to the content of salicylic acid, as well as other components: flavonoids, pectins, essential oils. In addition, a pathological attack can be provoked by chemicals that are used to treat berries to protect them from spoilage and to speed up ripening. A food reaction to strawberries is one of the most common manifestations of allergies.
Food allergies to a specific product are highly individual, but the symptoms of the disease are generally similar. Thus, children often have a reaction to chocolate and products that contain cocoa, cereals, and citrus fruits. In adults, typical symptoms can be observed when consuming exotic fruits, spices, cheeses, etc.
What is food allergy
According to the definition given by the European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology, food allergy refers to adverse reactions to food .
A food allergy manifests itself as a reaction of the body to the intake of certain categories of non-toxic food products (not associated with the consumption of spoiled or contaminated food products).
Like all allergies, a reaction to food is caused by an error in the immune system , which identifies one or more proteins contained in certain foods (allergens) as an enemy and “protects” the body by specifically destroying the perceived enemy.
Products that most often cause allergic reactions:
|
The mechanisms by which such reactions develop can be divided into 2 main types:
- IgE mediated reactions, which are caused by the action of IgE antibodies produced by the immune system, which bind to the receptors of certain immune cells, such as mast cells and basophils, and cause a process known as mast cell degranulation), which leads to the release of chemical mediators, causing a “typical allergic inflammation".
- Non-IgE reactions develop in the absence of IgE antibodies and occur over a long period (about 72 hours) after ingestion. The late response occurs some time later (several hours or a day), after the “arrival on site” of cells such as neutrophils, eosinophils, macrophages and lymphocytes.
Epidemiology of food allergies
There is no exact data on the prevalence of food allergies. In addition, existing data may be significantly distorted by a large number of misdiagnoses.
According to more or less reliable studies conducted within the European Union, the incidence among adults (over 10 years of age) ranged from 1 to 2%. of food allergies was higher in the population of children under 3 years of age, for whom the data is close to 8%.
Pathogenesis – the mechanisms by which the disease develops.
The disease is localized in the intestines and lymphatic tissue.
In the gastrointestinal tract, food products, under the influence of appropriate reactions, are decomposed into simpler compounds that are absorbed by the mucous membranes, and then, through participation in appropriate metabolic reactions, are converted into energy for cell growth and life.
The gastrointestinal tract is protected by a gastroenteric barrier, which, at the same time, ensures the passage of nutrients and prevents the passage of components harmful to the body.
Under normal conditions, this complex interaction between nutrients and the gastrointestinal barrier is regulated by the process of oral tolerance, which allows the intestines and lymphatic system to bind and absorb nutrients, and induce protective responses against antigens.
The mechanisms that determine the action of oral tolerance are not entirely understood today. It is assumed that it interacts with the mechanism of hyposensitization to antigens. If the mechanism does not work against specific antigens or microorganisms, then an immune reaction develops.
The reasons that violate the integrity of the mechanism are unknown; it is assumed that the effect is caused by an increase in the permeability of the mucous membrane or the lack of breakdown of food proteins.
The “fault” of the gastrointestinal barrier is proven by the higher incidence of food allergies in children under three years of age. In fact, their gastroenterological barrier is not yet fully formed.
Causes
There are many factors that can lead to food allergies. Children are more susceptible to it, starting from a very early age, since the developing body, which has not yet strengthened its immune system, is very susceptible to all kinds of allergens, including food ones.
In children
The main causes of the disease in childhood are:
- genetic predisposition (in a child, the risk of developing the disease increases several times if at least one of the parents suffers from this pathology). The reaction, by the way, may also be to another allergen, different from the hereditary one;
- consumption by a pregnant woman of an excessive amount of potentially allergenic foods, for example, fish, smoked meats, etc.;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and biliary system;
- malfunction of the thyroid gland;
- early transition of the baby to artificial feeding;
- irrational, unbalanced diet;
- frequent treatment with antibiotics.
In adults
Food allergies in adults may have slightly different causes. Among them are:
- inflammatory pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, characterized by a histamine effect;
- improper, irregular nutrition;
- insufficient production of enzymes by the pancreas, dyskinesia of the bile ducts;
- deviations in the acidity of gastric juice.
Useful: How to treat a nail wound on a leg?
Causes of allergic reactions in adults
Factors influencing the appearance of allergies in an adult are direct contact of adults with hyperallergenic substances or the adult’s predisposition to allergies.
Allergens, affecting the body of an adult, contribute to allergies. Often the cause of allergies in adults is a hereditary factor.
Classification of irritating antigens:
- Fungus or mold;
- Medicines of the penicillin and aspirin series;
- Allergy to fur, saliva, waste products of domestic animals;
- Poisoning with salts and vapors of heavy metals;
- Allergy to food due to individual intolerance to animal and plant substances;
- Alcohol containing dyes and flavors;
- Allergies that appear when exposed to low air temperatures, ultraviolet rays, water mixed with chlorine and salt;
- Low-quality cosmetics, interaction with household toxic and chemical substances - mainly detergents;
- Stinging insect bites.
Allergy to washing powder photo
The accumulation of pollen grains also provokes an allergy manifested by a runny nose, lacrimation, photophobia and cough. Often, allergies occur in adults during the flowering season of plants with a high concentration of allergens - poplar fluff, ragweed, wormwood, pine needles lead to allergies.
Allergies are exacerbated by:
- weakened immune system;
- genetic factor;
- alcohol and tobacco abuse;
- increased humidity and air pollution;
- parasitic diseases.
The manifestation of signs of food allergies in an adult is often due to a lack of the necessary enzymes involved in the digestion of food - thus the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, as a result of which lactose and sucrose intolerance appears.
In women, allergies often intensify due to hormonal changes in the body: during adolescence, pregnancy, and menopause.
Photo of allergies on the face
Symptoms
The signs of food allergies are quite numerous, but in each individual case their manifestation is absolutely individual and depends on the degree of the body’s predisposition to the disease.
In children
The first signs of the disease can be noticed at a very early age. The infant has:
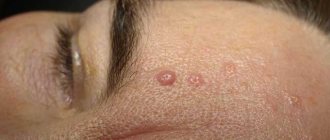
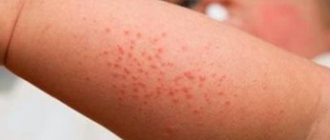
- the appearance of a rash all over the body or in local areas (pictured);
- itching;
- peeling of the skin on the face (cheeks);
- persistent diaper rash, even with continuous care;
- the appearance of scales on the head and eyebrows;
- hives;
- itchy rash near the anus.
In addition to the above symptoms, children 1 year of age experience a deterioration in their overall health, weakness, fatigue, and apathy. Skin manifestations of the disease may include:
- nausea, vomiting;
- itching in the mouth;
- stomach pain;
- lack of appetite;
- constipation;
- diarrhea.
Symptoms of food allergies in children can appear within 20-30 minutes after the allergen enters the body. At this moment, it is important to help the baby cope with an allergic attack, so as not to provoke possible complications.
It happens that in a baby at the first attack of the disease the allergen is not identified. With the introduction of complementary foods, the situation may worsen, since an unknown allergen will be in the baby’s diet. It will be much more difficult to identify it, so it is extremely important for mothers to notice any changes in the child’s condition after meals, especially in the 1st and 2nd year of life.
As the child gets older, the symptoms will weaken somewhat as the immune system strengthens and the gastrointestinal tract matures.
In adults
An allergic reaction to food in adults can manifest itself with the same signs as in children. However, the severity is usually not so high, and the number of symptoms in most cases is less. An adult can register:
- rash;
- itching in areas of rashes and in the mouth;
- Gastrointestinal disorders (diarrhea, nausea, colic);
- allergic rhinitis (rare with such allergies);
- atopic dermatitis.
Causes of pathology
Heredity is a factor that provokes the appearance of an allergic reaction to consumed foods.
The presence of increased sensitivity guarantees an immediate response. Almost instantly after consuming a “dangerous” product.
Sometimes the time interval for reacting to a food allergen stretches for 10-12 hours, sometimes up to a day.
Considering the above, changes to the diet should be made in the morning so that it is possible to control the child’s reaction to the product consumed.
Possible food allergens:
- honey
- milk
- chocolate
- chicken eggs
- rye
- wheat
- beet
- nuts
- tomatoes
- oranges
- grenades
- strawberry
- raspberries
- chicken meat
A reaction to food additives included in the composition is possible: preservatives, dyes.
The list is extensive, all of them, to a large extent, contribute to food allergization. It is advisable to make every effort to ensure that the diet consists exclusively of natural products. GMOs can cause considerable harm, causing a significant blow to the immune system. Modified products are “unrecognizable” by liver and stomach enzymes. Refusing to accept them, they do not digest such food, which provokes allergization of the body.
Such problems created by modified products are “fixed” at the genetic level, and the disorders are inherited.
Complications
Symptoms of the disease are periodic in nature, since they appear only when the allergen comes into contact with the body. However, the disease will progress to a more severe form if left untreated.
Gastrointestinal disorders due to allergies can cause such pathologies as:
- allergic enterocolitis - inflammation of the intestinal mucous membranes. Often occurs against the background of allergies to milk and soy;
- allergic esophagitis - inflammation of the esophagus;
- allergic gastroenteritis - inflammation of the gastric mucosa.
The most severe complications of the disease are:
- angioedema (Quincke's edema). Manifests itself in the form of severe dense swelling both in different areas of the skin and on the mucous membranes of internal organs;
- anaphylactic shock, in which the general condition sharply worsens, loss of consciousness, convulsions, and respiratory arrest are possible;
- swelling of the larynx, which can lead to suffocation.
In children, food allergies can lead to arterial hypertension, nervous system disorders, and the development of anemia. Therefore, it is so important to know how the disease manifests itself and why it is dangerous.
Food allergy therapy
The only treatment for food allergies is to eliminate foods that cause an allergic reaction from the diet. However, often removing the allergen is quite problematic, especially in children, as it can lead to a deterioration in the diet.
Symptomatic treatment involves taking antihistamines.
If the allergic reactions are very severe and you are afraid of anaphylactic shock, then treatment includes adrenaline injections and immediate hospitalization. Those who suffer from food allergies with violent reactions should always carry a dose of epinephrine placed in an automatic injector with them to quickly administer the dose into the thigh muscle. It is recommended to wear a bracelet on your wrist with information about the allergies you suffer from.
Further treatment consists of therapy and desensitization to the allergen. Treatment consists of administering under the tongue, under the supervision of a physician, a dose of allergens that increases over time. In this way, gradual desensitization to food that causes allergies is formed.
Diagnostics
The manifestation of a food allergy is a reason to consult a doctor. It is necessary to determine the food pathogen causing the reaction and undergo a treatment course aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease and restoring the body.
The diagnostic complex includes:
- a description of the signs of the disease, the time of their appearance, as well as the patient’s diet before the symptoms appeared;
- examination of the patient;
- taking urine and stool tests;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- skin test (contact of an allergic solution with the skin for several hours before the onset/absence of symptoms). The procedure is prescribed for adults and children over 5 years of age;
- abdominal endoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract.
Allergy to cow's milk
This is the name given to the reaction to the main protein components of milk, which are whey or casein. Children suffer more often from this type of allergy: approximately 2.5% of children cannot drink milk. Caution should be exercised by parents whose families have cases of the disease among their immediate relatives. The best way to protect your baby from milk allergies in the first years of life is breastfeeding.
How does a food allergy to milk manifest in a child? The most well-known symptoms are vomiting after feeding, colic, gas, and restlessness of the baby. Sometimes dry skin, itching, rash, and atopic dermatitis may appear.
Typically, children with a cow's milk allergy are also sensitive to milk from other animals, so it should be offered with caution.
In 85% of children, the disease goes away by the age of 5. But you should remember that a baby who has a reaction to milk may also have other types of allergies. In addition, there is a risk of developing allergic rhinitis in the future.
Since dairy products contain calcium, which is necessary for bones and teeth, without which the normal functioning of many body systems is impossible, you need to look for other sources. Eating dark green leafy vegetables, canned fish, orange juice, dried figs and prunes is beneficial.
Treatment
The question of how to treat food allergies is of fundamental importance especially for children, since they suffer attacks of the disease more severely than adults. Treatment is carried out comprehensively, using different methods.
Diet
One of the most important methods of antiallergic therapy is a special hypoallergenic diet. It allows you to prevent allergens from entering the body and restore normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
In cases where the allergen is not identified, use a nonspecific (basic) diet containing foods that do not cause a pathological reaction. These include:
- beef, lamb (lean);
- turkey meat, chicken (fillet);
- goat milk;
- low-fat cottage cheese, kefir;
- pasta from durum wheat;
- oatmeal, buckwheat, rice;
- white cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli, cucumbers, spinach, lettuce, asparagus, sorrel, peas, beans;
- squash, zucchini;
- dill, cilantro, parsley;
- onions, garlic (with caution);
- pumpkin;
- non-red fruits and berries;
- vegetable oil;
- green tea, dried fruit compote, mineral water.
All dishes are prepared in a gentle manner, i.e. by boiling, baking, stewing or steaming. Limit the consumption of salt and sugar. The diet includes 4-5 meals a day in small portions until the symptoms of the disease disappear.
For food allergies, the following are prohibited:
- pork, veal (fatty);
- any sausages;
- goose, duck;
- eggs;
- milk and dairy products with a high percentage of fat;
- fish (sea) and seafood (crustaceans, mussels, etc.);
- tomatoes, beets, eggplant, carrots, peppers;
- red fruits and berries;
- citrus;
- nuts;
- honey;
- baked goods, ice cream;
- food containing cocoa beans;
- mushrooms;
- sauces, vinegar, seasonings;
- alcohol;
- coffee;
- foods and drinks containing flavorings, preservatives, dyes, etc.
If the pathology is diagnosed in an infant, then the nursing mother must adhere to a basic diet throughout the entire period of breastfeeding. If the child is on artificial nutrition, with the help of a doctor, an adapted milk formula is selected that does not contain components that can cause allergies. Complementary foods are introduced with caution, starting with half a teaspoon per day, and the response is assessed. If it is absent (there are no characteristic symptoms), then the dose is gradually increased and switched to a new product.
If an allergen is identified, a specific (elimination) diet is used, excluding provoking foods, as well as those foods in which they are partially present. So, in case of an allergy to milk, any products containing it are contraindicated: cheese, cottage cheese, butter, yogurt, ice cream, etc. However, it should be noted that milk is a rich source of calcium and avoiding it in case of allergies should be justified by consuming other foods that contain this mineral in sufficient quantities for the body: fish, legumes, vegetables.
A diet for a reaction to eggs involves avoiding any food containing egg whites. Therefore, when making gastronomic choices, you should pay attention to the composition of products and avoid eating those that contain allergens.
The dietary regimen can be followed from one week to several months, and in the case of severe pathology - for life. The strong reaction in children weakens with age, however, it does not go away completely. In any case, the manifestation of food allergies obliges the patient, first of all, to follow a diet.
Drugs
Taking medications helps remove allergens from the body and quickly alleviate unpleasant symptoms. It is proposed to use drugs from the following drug groups:
- Sorbents whose task is to bind and remove food irritants from the body. Enterosgel is most preferable in this regard. It is prescribed to children from 1 year of age, dissolving the permitted dose in boiled water. Take 2-3 times a day. Other drugs in this group: Phosphalugel, White Coal, Lactofiltrum.
- Antihistamines. They have a pronounced anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory effect, reduce active symptoms. Examples are: Cetirizine, Desloratadine, Suprastinex, Loratadine. The drugs are taken in courses in the dosage prescribed by the doctor.
- Hormonal drugs. Prescribed in case of severe form of the disease, accompanied by swelling of the respiratory tract and suffocation. Examples: Prednisolone, Dexamethasone. Administered intravenously or intramuscularly.
- Hormonal ointments (Elocom, Fluorocort). They are used only as prescribed by a doctor, as they have side effects that can harm the body. Indicated for moderate to severe skin symptoms.
- Non-hormonal ointments (Fenistil, Bipanten). Effective against skin manifestations of allergies of mild to moderate severity.
All medications are prescribed by the attending physician and taken within the time period specified by him. In case of severe manifestations of allergies (Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock), it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance and take the patient to the hospital.
Folk remedies
Taking herbal decoctions, infusions, and lotions on the affected skin also helps eliminate unpleasant symptoms and cleanse the body. The most effective for these purposes:
- Nettle (Crystal nettle). Prepare an infusion of a tablespoon of dried flowers and a glass of boiling water for half an hour. Take a glass three times a day.
- Celery is fragrant. Take 2 tsp of freshly squeezed juice. three times a day half an hour before meals.
- Duckweed is small. Prepare an alcohol tincture from 50 ml of vodka and 1 tsp. crushed raw materials. Take 15 drops, dissolved in water, 3 times a day.
In a similar way, medicinal products are made from centaury, St. John's wort, and chamomile. Solutions based on these herbs have blood purifying, anti-inflammatory, diuretic, immunostrengthening and other properties. Before use, consult a doctor.
Food diary for allergies
Main article: Sample of a food diary for allergies and rules for keeping it
The form of such a diary is arbitrary, the main thing is to write down everything that a person eats, even if it is one cracker or one berry. Punctuality is the most important rule. Two points must be observed: what was eaten and what reaction appeared to it.
It is convenient to divide a sheet of paper into 3 columns: meal time, food composition and reaction. Descriptions of food should be as detailed as possible.
| Meal time | What was eaten | Reaction |
| 19:00 | Milk (brand name), yesterday's milk, in the refrigerator, 1 glass | After 5 minutes the eyes turned red, Loratadine was taken, the redness went away after 1 hour |
If you keep a scrupulous diary, after 1-2 weeks the picture will become clear. Of course, you need to be honest with yourself and don’t forget to bring in a pie eaten on the street or a piece of cake you were treated to at work.
When a suspicious product is detected, it is completely abandoned for 2 weeks, and then a small portion is eaten and the body’s response is closely monitored. This way you can set the tolerance threshold. For example, after eating a slice of orange, nothing happens, but half of it already causes a reaction.
Prerequisites
There are many prerequisites for the development of an aggressive immune response to food. The patient does not always eat the allergen. In some cases, it is enough just to touch the causative agent of the process or come into tactile contact with it. For adults, there are two types of food allergies : hidden and actively expressed.
The latent variety refers to the flaccid form. If the patient regularly consumes the allergen and is in no hurry to give it up, the malaise gradually turns into a chronic form. It is enough to exclude the pathogen from the diet for the patient’s body to enter the resting stage.
In addition to year-round food allergies, there are spasmodic and temperature types. With an abrupt reaction, the patient suffers mainly from headaches. They occur when a particular product is consumed. We are talking about food that does not act as an allergen for a specific person.
In the case of temperature allergies , symptoms make themselves felt even with slight hypothermia of the body.
Allergy to citrus fruits
Symptoms appear in early childhood, but adults are not immune to this disease. An allergy to tangerines, oranges, lemons and other citrus fruits can have symptoms such as enterocolitis, runny nose, watery eyes and redness of the eyes, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, swelling of the bronchi, urticaria and itching.
Allergy to tangerines and other citrus fruits is especially difficult for children, in whom it manifests itself as enterocolitis and dermatitis. The child suffers from unbearable itching, scratches his skin, loses appetite and sleep.
Types of allergies
As the immune response manifests itself, the following types of reactions are distinguished:
- hidden: an allergy to food is not determined immediately, but after a sufficiently long period of time, due to the accumulation of the allergen in the body;
- pronounced: negative consequences appear immediately after consuming the allergen.
According to the nature of the manifestations, a hidden allergy can be:
- year-round: the reaction is observed constantly, even when consuming a small amount of the allergen;
- spasmodic: the immune system negatively perceives foods that were previously perceived normally;
- temperature: symptoms increase significantly even with the slightest hypothermia of the body;
- mixed: pathology is provoked not only by consuming the product, but also by its smell (oral), or by contact with it (contact).
In most cases, there is an immediate response to a product that irritates the immune system.
The first signs of the disease are:
- slight swelling of the mucous membranes, nasal discharge, lacrimation;
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, colic;
- skin rashes, itching;
- headache, general weakness, increased body temperature;
- Quincke's edema;
- anaphylactic shock.
During the course of the reaction, the symptoms intensify, and if immediate assistance is not provided, death is possible.
Peanut allergy
This form of food allergy affects approximately 0.6% of people of different ages. The disease can be severe, even life-threatening. Only 20% of children can outgrow it, which is why it is most common in adults. Those who are allergic to peanuts should carefully study the composition of products and, just in case, always have a syringe tube with adrenaline with them.
Prevention
Prevention of all types of allergic reactions is based on preventing any contact with the product that causes the allergy. Of course, if a reaction to a food product occurs, it is very difficult to control the course of the allergy, so in case of any undesirable manifestations, you must contact an allergist-nutritionist.
You should be clear about what you are consuming in your diet. The menu should contain only well-known and proven food products. You should avoid canned, pickled or dried ingredients. The best preventative measure for most people with allergy symptoms is to follow a special therapeutic diet. The important point here is to get rid of woolen household items, down pillows and maintain cleanliness.
List of products allowed for allergies in adults
These foods can be eaten, but in small doses:
- Chicken and beef
- Cereals – oats, corn, rice, buckwheat
- Some vegetables - green peppers, beets, potatoes and turnips
- Apricots, peaches
- Legumes – peas, soybeans, beans
- Berries – rose hips, lingonberries, cranberries, black currants
- Semolina
- Milk, butter, sour cream, cottage cheese, yogurt
- Lamb meat
- Pasta
- Berries – blackberries, black and white currants, cherries, cranberries and rose hips
- Fruits – bananas
- Vegetables – beets, carrots, turnips, onions and garlic
What foods are good for allergies?
The following products are useful for allergy sufferers:
- From fermented milk products only kefir, thermostatic yogurt, fermented baked milk
- Boiled fish - perch
- Boiled meat, but not fatty. You can have chicken breast, beef and pork tenderloin
- By-products - heart, kidneys, liver, tongue
- Cereals – buckwheat, corn, oatmeal, pearl barley, rice
- Lenten olive and sunflower oil
- Some fruits - white cherries and white currants, green apples, pears
- Dried – prunes, apples, pears
- Vegetables – zucchini, cucumbers, cabbage
- Greenery
- Mineral water without gases
- Compotes
- Herbal infusions
What does it come from?
Research into the mechanisms of the body's reactions to allergens is still ongoing. However, today medicine confidently declares that the development of possible manifestations of allergies begins immediately after birth. The most common causes of food allergies in children are:
- Improper nutrition of a pregnant woman.
- Pathologies of intrauterine development.
- Poor nutrition during lactation (transmission of antibodies with milk).
The development of allergies can be triggered by short-term breastfeeding, during which incorrectly selected infant formula and dairy products were introduced as complementary foods. The fact is that the protein present in cow's milk often causes a negative response from the body.
Another risk factor is the large volume and variety of first foods. The introduction of a new diet is a decisive moment for a small organism, so any food should be introduced one type at a time, starting with small portions. At this stage, it is important to monitor the reaction of the child’s body: the condition of the skin, stool, and the appearance of a runny nose or cough.
Food allergies (photos of various forms of the pathological process are usually presented on informational posters and booklets for young mothers) require mandatory treatment and control. This is a fairly serious pathology that can cause significant harm to the body both in infancy and in adulthood.
Medications
It is impossible to completely recover from unwanted manifestations with the help of medications alone. Drug therapy is effective only in treating the symptoms of food allergies and improving the general condition of the patient. Influences exclusively with drugs are used only when the body reacts to a large number of allergens or in cases where doctors cannot determine the true culprit of the pathology. In these cases, medications of various types are used.
It can be extremely difficult to recognize the disease, so the diagnosis and treatment of such manifestations in adults should be carried out by an allergist, and in children - by a pediatrician. Only these specialists can not only make a correct diagnosis, but also help cope with the disease. A comprehensive examination of the patient helps select the correct treatment. Here it is important to identify other concomitant diseases, including chronic ones.
After conducting a survey, the specialist prescribes the necessary symptomatic treatment and refers the patient to the necessary examination. Special tests included in the examination plan will allow you to determine the presence of food allergies with high accuracy and reliability.
List of allergen products
Scientists have conducted many studies, on the basis of which they have compiled a list of possible allergens. Clients with excessive sensitization of the body will have to exclude irritants from the menu one hundred percent.
High risk of allergic reactions:
- whole milk;
- chocolate;
- eggs;
- honey;
- soy;
- crustaceans;
- wheat;
- peanut;
- sea fish;
- nuts.
Often cause acute symptoms:
- citrus;
- red, orange berries, vegetables and fruits;
- poultry meat;
- mushrooms;
- melons
Average degree of allergic activity:
- pork;
- potato;
- rice;
- corn;
- peaches;
- peas;
- buckwheat.
Low risk of allergic manifestations:
- apples;
- zucchini;
- plums;
- mutton.
Often the body reacts sharply not to the components of one or another product, but to emulsifiers, flavors, dyes, sweeteners contained in canned food and concentrates. It is no coincidence that almost all patients note that stewed fish does not cause allergies, while canned or smoked products quickly lead to negative symptoms.
Risk factors
Food allergies are common among all age groups. The risk of developing pathology is highest with the following factors.
- Heredity. Allergic reactions are easily transmitted from parents to children at the genetic level. If the mother or father has any form of allergies (food, skin, etc.), there is a chance that the child will develop food allergies.
- Enzyme deficiency. In order for food to be digested and absorbed by the stomach and intestines, special enzymes are produced in the gastrointestinal tract. In the absence or insufficient production of these substances, digestion processes are disrupted and food intolerance develops. Thus, when there is a lack of lactase enzyme in the intestines, an allergy to dairy products occurs in adults and children. It manifests itself as a digestive disorder, in which lactose causes irritation of the mucous membrane and provokes fermentation processes.
- Age. Most often, food allergies occur in young children. This is due to the fact that the child’s immunity is at the stage of formation and is easily susceptible to allergens. The situation is especially difficult for infants who are gradually switching to regular nutrition. Each new product is a new test for the baby’s digestive system and immunity. If parents do not know what foods they may be allergic to, and when preparing the child’s diet they are not guided by the pediatrician’s recommendations, there is a high probability that the body will develop a response to such aggressive changes.
Wheat allergy
Wheat can provoke various reactions in both children and adults. There are two types of reactions. In the first case, immediately after eating food, a food allergy occurs, the symptoms of which manifest themselves in the form of hives or difficulty breathing.
The second type of reaction is called celiac disease, or intolerance to gluten (a protein found in grains). For some time the disease proceeds hidden. Abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nervousness may occur. Children gain weight poorly and grow slowly. The disease usually begins to appear after the introduction of cereals into the diet, but sometimes the signs are so insignificant that the diagnosis is confirmed only in adolescence.
Allergies or food intolerances?
Food intolerance, which can be congenital, must be distinguished from allergies. Intolerance is the inability to break down and absorb a food product because the body does not have the necessary enzymes and other substances. Intolerance is detected in infancy and accompanies a person throughout his life. The most striking example is intolerance to cow's milk, when consumption of any amount causes severe digestive upset. No antibodies are produced in this case.
It is impossible to distinguish “by eye” an allergy from an intolerance, especially if the condition has arisen for the first time. Therefore, if a food allergy is suspected, a thorough examination is performed.
Methods for detecting and diagnosing allergies
There are 3 effective methods for detecting allergies: anamnestic, skin test and laboratory diagnostics.
Anamnestic method
With the anamnestic method, the doctor, together with the patient, analyzes the period of life during which the allergy occurred. Over time, an adult begins to understand which foods and their combinations cause an undesirable reaction.
If you cannot immediately identify such a product, then you will have to keep a food diary for some time. It is troublesome and time-consuming, but very reliable.
The point of keeping a food diary is to first eat foods that definitely do not cause any reaction, and then introduce one new food every 10-12 days and carefully monitor the body’s reaction.
By examining your entire diet, you can identify those foods that trigger the onset of an allergic reaction. This method is used in cases where skin tests cannot be performed due to the risk of developing anaphylactic shock.
Skin test
This is a quick and easy way to detect an irritating product. Notches are applied to the disinfected skin of the forearm with a scarifier, and an extract from suspicious products is applied to scratches. Sometimes ready-made diagnostic kits are used, in which the allergen is applied directly to the scarifier.
Swelling and redness develop on scratches where the allergen has entered. The severity of the allergy is judged by the diameter of the redness.
Laboratory diagnostics
Includes the following tests:
- general clinical blood test - an increased number of a special form of leukocytes or eosinophils is detected;
- determination of IgE concentration in the blood - abnormally high in food allergies;
- determination of the amount of IgE and IgG - increase in response to a certain product.
The combination of these methods provides every basis for establishing an accurate diagnosis.
Disease prevention
To summarize, the following preventive measures can be distinguished:
- 1 - 2 times a year, completely cleanse your body of debris, which in 95% of cases causes any manifestations of allergies.
- timely examination by an allergist
- eliminating or minimizing hazardous foods
- strengthening the immune system through sports, contrast showers or taking vitamin complexes
- refusal of fried, smoked or spicy foods; replacing them with steamed dishes
- timely treatment of infectious diseases, especially in the spring-autumn period
- -partial or complete refusal of antibiotics; It is antibiotics that reduce the number of beneficial bacteria in the body, thereby lowering the level of immunity
By following the above recommendations, you will not only be able to easily cure an emerging allergy, but also prevent it in advance.
General recommendations and treatment methods
Your doctor will tell you how to get rid of food allergies. First of all, the specialist will prescribe tests that will help identify the allergen. Effective therapy is possible only after the dangerous product is eliminated from the diet.
Drug therapy
Treatment of food allergies in adults is based on taking antihistamines or corticosteroids.
Methods of therapy:
- One of the new treatment methods is immunotherapy. The essence of the procedure is to introduce the allergen in a diluted form under the epidermis. This provokes an immune response with the corresponding synthesis of antibodies. This procedure has a positive effect on the immune system. The manipulation is performed 4 times a week in a clinical setting. The disadvantage of the technique is the long period of therapy, which takes more than two years;
- The most popular way to treat skin allergies of various kinds is to take antihistamine medications. Doctors usually prescribe Loratadine. This drug does not have side effects on the nervous system and does not cause liver problems. The product quickly relieves signs of an allergic reaction. Another advantage is the affordable price. 20 tablets cost approximately 20 rubles. Specialists also prescribe Desloratadine. Unlike most antihistamines, this drug does not cause drowsiness, so it can be taken by people of any profession. Doctors also prescribe Suprastin, Claritin and other similar drugs;
- Experts prescribe not only antihistamines, but also corticosteroids, not for oral administration, but for external use. Such drugs are prescribed for severe forms of pathology. Most often, doctors advise using Fluorocort, Lorinden, Flucinar and others. Corticosteroids are used only as prescribed by a doctor to avoid complications. The duration of use of some of them is five days;
- For allergic rhinitis, nasal drops or sprays are prescribed. Depending on the severity of symptoms, antihistamines, corticosteroids, vasoconstrictors, and nasal rinses are prescribed. In mild cases of pathology, antihistamines and nasal rinses are prescribed. Vasoconstrictor and corticosteroid drops and sprays are prescribed only if other medications have proven ineffective. Such drugs give an immediate effect, but they can be used for a short time. Most often, antihistamines are prescribed for allergic rhinitis - Fenistil, Zyrtec, Allergodil and others.
The safest medications are considered to be nasal rinses consisting of sea salt and water. They relieve nasal congestion and improve the condition of the mucous membranes.
Alternative medicine
Folk remedies and recipes are often used to treat food allergies. Their use is also permissible after consultation with a specialist.
Alternative medicine:
- Infusions of chamomile and calendula have proven their effectiveness. To prepare them, take a small spoon of each herb and pour a glass of boiling water. The product is infused for a quarter of an hour, after which it is filtered and used for oral administration and for wiping the affected areas of the epidermis;
- To relieve external symptoms, it is also recommended to take baths, to which are added decoctions prepared from oats, string, yarrow and chamomile. The duration of water procedures is 15 minutes. This bath helps relieve itching and swelling of soft tissues;
- Eggshells will help get rid of the manifestations of pathology. To do this, it is crushed into powder, which is recommended to be consumed about a quarter of a small spoon, washed down with plenty of water, three times a day. Duration of therapy is fourteen days.
Allergenic products
All products have varying degrees of impact on the body.
Product allergenicity table
| Degree | Products |
| highly allergenic | chocolate, milk, honey, peanuts, citrus fruits: lemon, orange, grapefruit, tangerine, fish, berries, fruits, vegetables that are red or orange in color: raspberries, currants, strawberries, carrots, tomatoes |
| average allergenicity | legumes, cereals, peaches, potatoes, pork |
| low-allergenic | apples, zucchini, gooseberries, lamb |
It is a fate that sometimes negative signs are caused not by the product itself, but by the dyes, flavors, and stabilizers in its composition.