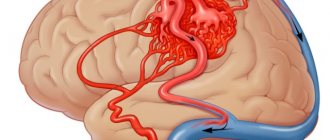
Ischemic stroke is a disorder of cerebral circulation, during which tissue is destroyed and blood vessels in the brain are clogged (without compromising their integrity). This phenomenon may be a consequence of difficulty or cessation of blood flow to one of the brain regions.
Mortality from this disease reaches 20% of the total number of cases, 50-60% become disabled for life, and only the remaining small percentage of people suffer ischemic stroke without consequences.
Theory
Ischemic stroke is also called “cerebral infarction.” This definition fully corresponds to the pathogenesis occurring in the organ during insufficient blood supply.
The word “ischemia” itself means a deficiency of blood supply to an organ or tissue due to a decrease or complete cessation of arterial blood flow to this part of the body.
The word “stroke” refers to a violation of the blood circulation in the brain, which is often accompanied by loss of consciousness or paralysis. If blood vessels burst simultaneously with this phenomenon, rapid death of brain cells occurs.
The process of tissue destruction does not stop even after normal blood flow has been restored. It is for this reason that it is extremely important that a person receives the necessary medical care in a timely manner. After suffering a cerebral infarction, the patient needs rehabilitation. It is an important part of general therapy, preventing possible complications.
Women are more susceptible to the occurrence of pathology.
What are the reasons
Stroke can be ischemic or hemorrhagic. In the first case, a blood clot blocks the artery that supplies blood to the right hemisphere of the brain. The ischemic form may be a consequence of severe vasospasm, which occurs due to atherosclerosis of the cerebral vessels, with hypertension.
A right-sided hemorrhagic stroke means that a vessel has ruptured, leading to hemorrhage in the corresponding hemisphere. This often occurs due to increased physical activity.
There are a number of factors that increase the risk of stroke:
- hereditary predisposition;
- endocrine disorders, including diabetes mellitus;
- arterial hypertension;
- increased cholesterol levels, leading to vascular atherosclerosis;
- obesity and lipid metabolism disorders;
- presence of chronic kidney disease;
- bad habits - alcohol abuse, smoking.
Important information: Consequences and treatment of lacunar ischemic stroke (infarction) of the brain
Right-sided stroke is less common in men than in women. However, the disease affects both sexes.
It is necessary to distinguish between diagnoses such as stroke and right hemisphere infarction. The first is a cerebrovascular accident caused by the reasons described above. The second is the softening of the tissues of the corresponding hemisphere.
Development rate and age
In older people with progressive sclerosis, ischemic stroke develops very slowly. Its symptoms may come and go intermittently over the course of a week. Impaired blood circulation can occur after a short period of initial symptoms, or completely suddenly.
In young people, the sudden onset of the disease may be associated with vascular embolism. Symptoms can be expressed during heavy physical exertion, during a severe coughing attack, during pulmonary operations under anesthesia, etc.
Diagnostics
A doctor can usually use a physical examination and family history to diagnose ischemic stroke. Based on the symptoms, they can also get an idea of where the blockage is.
If there are symptoms such as confusion and slurred speech, your doctor may perform a blood sugar test. This is because confusion and slurred speech are also symptoms of hypoglycemia (seriously low blood sugar).
Kinds
Based on the rate at which symptoms increase, the following types are distinguished:
- transient ischemic attack. Blood circulation in the brain tissue is disrupted for a day, accompanied by various symptoms, the nature of which directly depends on the location of the source of pathology.
- minor stroke. Manifests itself in the form of prolonged attacks of ischemia. To reduce neurological symptoms, drug therapy is used, the duration of which can vary from two days to three weeks.
- progressive ischemic stroke, the symptoms of which can gradually increase over several hours, sometimes days. After an illness, there is a risk of incomplete restoration of impaired body functions.
- total ischemic stroke - can lead to irreversible consequences. It is characterized by the death of the meninges and the most severe symptoms.
The vertebrobasilar circulatory system makes up only 30% of the main one. At the same time, heart attacks associated with it can permanently deprive a person of vision.
There is also an infarction of the spinal cord, which is called ischemic myelopathy.
The following phases are distinguished according to severity:
- Easy. Symptoms appear few and to an insignificant extent, the body’s recovery occurs quite quickly.
- Average. Signs appear depending on the focus of the disease, consciousness does not change.
- Heavy. Impaired consciousness, manifestation of a large number of neurological symptoms. After an attack, long-term inpatient treatment is necessary, aimed at restoring brain function and a subsequent rehabilitation course.
Based on their origin, subtypes are distinguished:
- Atherothrombotic. This type of stroke develops under the influence of chronic diseases of the central arteries. The blood supply to the brain is disrupted due to the detachment of a blood clot, which results in blockage of blood vessels. As a rule, the symptoms of a stroke increase gradually and appear while the person is asleep.
- Cardioembolic. It develops along with concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular system (heart disease, arrhythmia, myocardial infarction), and is usually localized near the middle cerebral artery. It can occur suddenly at any time of the day, the affected area is medium or large.
- Hemodynamic. Associated with a disruption in the movement of blood through the vessels: it occurs when blood pressure decreases. Among the diseases that precede this condition are stenosis, atherosclerosis, cerebrovascular disease and other vascular dysfunctions. It can occur both in a person at rest and in a state of physical activity.
- Lacunar. Usually appears in patients with hypertension and diabetes. Localized near small arteries that are located in the trunk, medulla oblongata or hemispheres of the brain. During a stroke, a space filled with cerebrospinal fluid is formed.
- Rheological. Occurs without any previously identified disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels.
The following periods of stroke are distinguished:
- The most acute period. Duration from 1 to 3 days. In the first three hours, the patient can be given an injection of thrombolytic drugs (during the “therapeutic window”). If with their help it was possible to suppress the development of a stroke, the doctor diagnoses a transient ischemic attack.
- Acute period. The duration of an acute stroke can range from 3 days to 4 weeks.
- Early recovery period. Duration up to 6 months.
- Late recovery period. Duration – up to 2 years.
- Residual effects. Duration for all time after the end of the previous period.
Ischemic stroke of the left hemisphere of the brain
ICD-10 code insultu-net.ru Ischemic stroke, or infarction of the left hemisphere of the brain (GM), ICD-10 code - I63 - a pathological condition in which an acute circulatory disorder (ACI) occurs within a few minutes or hours of the area in left hemisphere of the brain, manifested by the development of neurological symptoms of a focal (changes in speech, movements, vision, sensitivity, etc.) or general cerebral (changes in consciousness, headaches, persistent vomiting) character, persisting for more than a day or leading to death in the near future for reasons associated with cerebrovascular (changes in the vessels supplying the brain).
Among all strokes, ischemic stroke (IS) occurs in almost 85%.
Moreover, in the system of the carotid arteries (carotid), which supplies blood to the hemispheres, the brain is 6 times more likely than in the system of the vertebral arteries (vertebrobasilar), which supplies the posterior parts of the brain.
Causes
The “trigger” for an ischemic stroke is the cessation of blood flow to one or more areas of the brain. It is a consequence of impaired vascular patency or disruptions in the general hemodynamics of the body. Preceding factors include:
- coronary heart disease;
- diabetes;
- migraines in the temporal, parietal and occipital areas of the head;
- heart disease;
- hormonal contraception;
- excessive consumption of fatty foods,
- bad habits;
- increased blood viscosity;
- heredity.
The combination of two or more factors increases the risk of ischemic stroke.
8 out of 10 people who have suffered an ischemic stroke remain disabled for life.
What is ischemic stroke?
Ischemic stroke is one of three types of stroke. The disease is also called cerebral ischemia and cerebral ischemia.
This type of stroke is caused by a blockage in the artery that supplies blood to the brain. The blockage reduces the flow of blood and oxygen to the brain, leading to damage or death of brain cells. If circulation is not restored quickly, brain damage may be permanent.
Approximately 87 percent of all strokes are ischemic strokes.
Another type of serious stroke is a hemorrhagic stroke, in which a blood vessel in the brain ruptures and causes bleeding. Bleeding compresses brain tissue, damaging or killing it.
The third type of stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also known as a ministroke. This type of disease is caused by a temporary blockage or reduction in blood flow to the brain. Symptoms usually go away on their own.
Signs
Everyone needs to know the following signs so that if they are detected in a person (even a stranger), they can immediately take measures to quickly provide medical assistance.
Visible disturbances of consciousness. A person ceases to understand where he is and what surrounds him. His head begins to hurt badly. There may also be a visible decrease in the speed of reactions, loss of the ability to speak, fainting, and a coma.
Weakness and cramps
Decreased or complete loss of body sensitivity. A person suddenly stops feeling pain or touching any part of the body.
Paralysis of the body, decreased or complete loss of motor functions. It often manifests itself in disruption of the mechanisms of the facial muscles: a person cannot smile.
Additional symptoms may manifest differently, depending on the location of the pathology.
Signs of a right hemisphere stroke:
- sluggishness of movements, inhibited reactions;
- paralysis of the facial muscles on the left side;
- numbness of the limbs and paralysis of the body on the left side.
Signs of a left hemisphere stroke:
- speech disorder;
- loss of coordination and confusion of movements;
- dysfunction of the visual, olfactory and auditory organs.
Often, ischemic stroke may be preceded by transient ischemic attacks. Their difference from severe pathology is that MRI does not detect the focus of the infarction, and the duration of symptoms is no more than a day. The presence of a TIA is confirmed through an ECG, blood tests, and other laboratory tests.
The pathology has a different onset, depending on the degree of impairment of circulatory functions. The classification is as follows:
- Undulating onset. The manifestations of symptoms resemble outbreaks, which become more pronounced and longer lasting over time.
- Acute onset. The symptoms are pronounced and appear quickly.
- Tumor-like onset. Neurological symptoms increase gradually, and its result is a massive stroke that affects a large number of brain tissues.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke
The specific symptoms of an ischemic stroke depend on which area of the brain is affected. Some symptoms are common to most ischemic strokes, including:
- vision problems such as blindness in one eye or double vision (diplopia);
- weakness or paralysis in the limbs, which may be on one or both sides, depending on the artery affected;
- dizziness;
- confusion;
- loss of coordination;
- swallowing dysfunction;
- drooping facial skin on one side.
Once symptoms begin, it is very important to get treatment as quickly as possible. This reduces the chance of the damage becoming permanent. If you think someone is having a stroke, rate them using the FAST term:
- (F - face) Face . One side of the face is drooping and it is difficult to move.
- (A - arms) Hand . Ask the victim to raise both arms, see if one arm goes down, or if the person has significant difficulty raising his arm.
- (S - Speech) Speech . Is the speech intelligible (does it sound strange, can the person speak at all).
- (T - Time) Time . If the answer to any of the questions above is “yes,” it’s time to call your local emergency services (112 or 03).
Although a transient ischemic attack lasts for a short period of time and usually goes away on its own, it also requires calling a doctor. This may be a warning of a major ischemic stroke.
Consequences of the disease
The consequences are directly related to how extensive the area of brain tissue damage is and how quickly medical assistance was provided. Urgent consultation with a doctor plays an important role in maintaining and restoring circulatory functions. Among the main complications after an illness are:
- disturbance of urination and defecation;
- epilepsy;
- cerebral paralysis;
- thrombosis;
- infectious complications caused by long-term rehabilitation;
- cognitive impairment;
- dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system;
- paralysis of the limbs and the whole body;
- facial asymmetry.
The consequences of a cerebral infarction can be different, depending on the location of the pathology. Thus, among the complications after an ischemic stroke of the right lobe of the brain there are:
- impaired concentration;
- speech disorders;
- short-term memory loss.
Complications after a stroke of the left hemisphere:
- pronounced mental disorders;
- disorientation in time and space;
- memory loss.
An ischemic stroke can provoke cerebral edema, necrosis of the posterior and middle parts of the brain stem, and cause secondary hemorrhage in the brain, which, in turn, will cause death.
Treatment of ischemic stroke
The first goal of treatment is to restore normal breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. If necessary, the doctor will try to reduce the pressure in the brain with medications.
The main treatment for ischemic stroke is intravenous tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), which breaks up clots (thrombi).
Guidelines from the American Heart Association and American Stroke Association published in 2019 state that tPA is most effective when given within four and a half hours of stroke onset. It should not be given more than five hours after the onset of the stroke. Because tPA can cause serious bleeding, it should not be given if the patient has a history of:
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- bleeding in the brain;
- recent major surgery or head injury.
TPA should also not be prescribed to those taking anticoagulants (drugs that reduce the activity of the blood clotting system and prevent excessive blood clots).
If tissue plasminogen activator does not help, the clots may be removed with surgery. Mechanical removal of the clot can be performed 24 hours after the onset of symptoms.
Long-term treatment includes taking aspirin or anticoagulants to prevent further clots.
If an ischemic stroke is caused by a condition such as high blood pressure or atherosclerosis, treatment for those conditions is necessary. For example, your doctor may recommend placing a stent to open an artery narrowed by plaque or prescribing statins to lower your blood pressure.
After an ischemic stroke, the patient will have to remain in the hospital for observation for at least several days. If the disease has caused paralysis or severe weakness, the patient may also require rehabilitation to restore lost functions.
Diagnosis of the disease
Correct and timely diagnosis reveals the extent of the disease. Based on this, treatment is prescribed and further prognosis is made.
The most common diagnostic methods:
- Anamnesis of the patient's medical history, in order to identify the origin of cerebral circulatory dysfunction, as well as to determine the rate of development and sequence of symptoms.
- Taking into account all possible factors that could provoke an attack (cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, aneurysms and others).
- Conducting laboratory and instrumental studies, including coagulograms, biochemical blood tests and lipid profiles.
- Carrying out an ECG, MRI or CT scan of the brain to identify the source of the disease, determine its location, size and duration of appearance.
- Carrying out CT angiography if it is necessary to clarify the location of vessel occlusion.
How to quickly diagnose a condition in the field
Primary diagnosis of ischemic cerebral stroke
There is a simple procedure for diagnosing a stroke:
- Ask the person to smile - in conditions of developing brain pathology, the smile will be distorted due to the drooping corner of the mouth.
- If you ask a patient to give his name and date of birth, then when there is a threat of a stroke, the person begins to “mumble”, swallow words, and his speech becomes unintelligible, like that of a drunk.
- Ask the person to clench one hand into a fist, then the other, then slowly raise one arm and one leg in turn. During a stroke, the fingers are unable to clench tightly, they tremble, one limb is immobilized, or the patient has difficulty lifting it.
- In case of illness, the tip of the protruding tongue will deviate slightly to the side, whereas normally this does not happen.
- There is asymmetry of the face - possible drooping of one eyelid, unilateral sagging of the cheek tissue.
Important! If there is even one of these signs, you must immediately call an ambulance. It’s better to be wrong ten times, but not to miss the onset of necrosis in the brain tissue.
Treatment
After diagnosing the disease and confirming the diagnosis, the patient is hospitalized in the appropriate department of the hospital. If less than six hours have passed since the onset of the disease, the patient is sent to the intensive care unit. In the case when the patient is in a comatose state, he is placed in the intensive care unit.
When transporting the patient, it is necessary to keep his head elevated 30 degrees from the surface.
If an ischemic stroke was correctly recognized in the first hour, there is a chance to provide timely thrombolytic therapy, which can normalize blood supply to the brain and minimize the consequences of the pathology.
Standard treatment is a series of measures aimed at restoring and maintaining vital functions. It includes:
- stabilization of blood pressure;
- reduction of cerebral edema;
- relief of symptoms depending on their clinical manifestations;
- maintaining normal body temperature;
- prevention of various infections and diseases, which include urinary infections, pneumonia, bedsores, thrombosis, intestinal diseases, etc.
Thrombolytic therapy has many contraindications, since it carries a high risk of bleeding, including internal hemorrhages with the further development of hemorrhagic stroke.
One of the most common drugs for such therapy is the thrombolytic “Actilyse”.
The following groups of drugs are used to treat ischemic stroke:
- Blood thinners (Cardiomagnyl, Aspirin);
- Antiplatelet drugs (Tiklid, Plavix);
- Anticoagulants (Fragmin, Heparin, Nadroparin);
- Vasoactive substances (Trental, Vinpocetine, Pentoxifylline, Sermion);
- Neurotrophics (Nootropin, Cerebrolysin, Glycine, Piracetam);
- Angioprotectors (Prodectin, Etamzilat);
- Antioxidants (vitamins E and C, Mildronate).
Treatment methods do not depend on the area in which the disease is localized, but this does not exclude an individual approach to each patient depending on the characteristics of his body.
Paralysis of the right side of the body: treatment and rehabilitation
Patients who have suffered a left hemisphere ischemic stroke should be hospitalized in specialized angioneurological departments, where both general therapeutic measures (basic treatment) and specific therapy are prescribed.
Due to the long-term stay of the patient in a supine position, the risk of complications such as:
- thromboembolic complications (deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities, thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery and its branches),
- hypostatic pneumonia,
- bedsores,
- cardiac dysfunction and other serious conditions.
Therefore, it is important to ensure adequate pulmonary ventilation by performing tracheal intubation with further artificial ventilation (ALV), or timely sanitization (washing) of the respiratory tract and oxygen supply through nasal catheters.
Concomitant cardiovascular pathology is eliminated by a cardiologist by intravenous administration of blood replacement solutions or cardiotonics (dopamine) with reduced blood pressure (BP). High blood pressure is reduced with appropriate drugs (for example, sodium nitroprusside).
Of great importance is the treatment of cerebral edema, which threatens the development of compression of its various parts. For this purpose, osmotic diuretics (mannitol) are used.
Body temperature above 38°C is reduced with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). If it is caused by an infection, it is necessary to prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy.
In the presence of persistent vomiting, metoclopramide is used.
If psychomotor agitation or epileptic seizures occur, diazepam or sodium hydroxybutyrate is used.
The therapy carried out must ensure a normal water-electrolyte balance, as evidenced by the degree of moisture of the skin, tongue, tissue turgor, and hematocrit.
In addition, it is necessary to establish a balanced diet (in the absence of consciousness - parenteral or intravenous), proper care of the skin and mucous membranes. To prevent thrombosis, low molecular weight heparins (fraxiparin) are administered.
As a specific therapy, upon admission of the patient up to 3-6 hours from the onset of the disease, based on computed tomography data and the absence of contraindications (intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract or urinary tract in the last three weeks, the presence of blood diseases, blood pressure above 185/110 mmHg, state of stunning or coma, extinction of neurological symptoms) thrombolytic therapy is performed (administration of tissue plasminogen activator to dissolve the blood clot and restore blood flow).
In the future, the administration of antiplatelet agents (clopidogrel) is justified; after the acute period, the administration of neuroprotectors (piracetam), vasoactive drugs (nimotop), and vasodilators (pentoxifylline).
Extremely rarely, due to the high risk of complications, neurosurgical treatment methods are used for IS (removal of emboli or fatty plaques from blood vessels). In case of extensive ischemic stroke of the left hemisphere of the brain, when swelling of the brain substance increases rapidly and threatens the appearance of dislocation syndrome, it is possible to perform a neurosurgical operation to decompress the brain tissue.
If obstructive hydrocephalus occurs, an external drainage or ventricular shunt is applied.
In severe neurological disorders after stroke, movement disorders occupy a special place. Developed paralysis of the right side of the body requires specialized rehabilitation.
For contacts of rehabilitation centers in Russia and neighboring countries, see here.
Rehabilitation
A dense scar forms in place of the healed area of the brain.
The recovery process after an illness is quite long. It includes a set of various activities, the purpose of which is to return the patient to normal life. To achieve a positive result, the following may be prescribed:
- mandatory adherence to a diet and a certain diet;
- drugs aimed at restoring vascular function;
- exercise therapy;
- massage;
- radiation therapy;
- physiotherapy.
First of all, specialists in the field of neurological diseases, and then speech therapists, help restore the patient’s speech. The duration of rehabilitation and the methods used depend on the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient.
How to recover
After a stroke that paralyzes the right side, recovery is easier. When the left one is hit, everything becomes more complicated. However, recovery time is always individual. And the principles of rehabilitation will be the same in both cases.
Your doctor will tell you how to recover after a stroke. It should be remembered that early initiation of rehabilitation gives good results and increases the chances of full recovery.
The doctor prescribes further drug treatment and rehabilitation methods. But a lot depends on the patient’s condition. His limbs may become paralyzed, and then techniques such as passive gymnastics and massage are first used.
When they give results, you can move on to active exercises. Over time, this will be a whole complex of physical therapy. Some of the exercises will even be performed on simulators. The rehabilitation program also includes various physiotherapeutic procedures.
However, rehabilitation requires an integrated approach. In addition to purely physiological methods of restoring the sensitivity of the affected parts, correction is also needed in the psycho-emotional sphere. This often requires the help of a neuropsychologist. In left-handed people with a right-sided stroke, the speech center may be affected; they will need classes with a speech therapist.
Drug therapy
For drug therapy in the recovery period, nootropic drugs are more often used. They improve the higher integrative functions of the brain and help strengthen the nervous system, making it more resistant to damaging factors.
There are different groups of such drugs, they differ in their mechanism of action - for example, pyridoxine derivatives enhance cerebral cholinergic conductivity, other drugs accelerate the penetration of glucose through the blood-brain barrier into brain cells and improve its utilization.
For example, Piracetam improves memory and facilitates the rehabilitation process after a stroke. Can be taken in long courses. It is especially indicated for elderly patients.
Among the nootropics, Picamilon can also be distinguished, the action of which is based on the properties of nicotinic acid and GABA. The first plays an important role in the processes of tissue respiration. The drug is especially useful in cases of dysfunction of the optic nerve.
Phenibut and Pantogam have, in addition to nootropic, psychostimulating effects. They are recommended for people after a stroke, suffering from neurosis-like conditions and sleep disorders.
Important information: What kind of surgery is done after a cerebral stroke?
Lifestyle
A right-sided ischemic stroke often means that the patient has to learn to live again.
Family members should not do anything for the patient, only help him. It is necessary to arrange handrails in the house for movement, to fix some objects, but the patient must learn gradually, avoiding pain and fatigue, to take care of himself and even perform minor work.
You need to lie down less and sit more. When working with your hands, it is recommended to find solid support. Start exercises only from the stronger side, slowly, so that you are aware of the movements and without holding your breath, so that the pressure does not increase.
It's worth finding a hobby that involves your hands. This can be embroidery, knitting, drawing, modeling (ships, cars), spinning a yo-yo and a spinner. Hobbies return fine motor skills faster.
A special diet that limits fats is also needed. You will have to give up bad habits.
Folk recipes
Right-sided stroke cannot be treated with traditional methods. During the rehabilitation period, some of these remedies can be used, but only as additional therapy after consultation with a doctor.
For example, you can make a drink based on pine decoction (1 tablespoon of raw material per glass of boiling water) and finely chopped lemon. Half of the fruit must first be peeled, then mixed with the prepared decoction. This product is considered an antioxidant that improves blood circulation. It is given twice a day, an hour before meals, half a glass.
Among the non-traditional methods, one can highlight hirudotherapy - treatment with medicinal leeches, which is especially useful in the ischemic form, since these parasites secrete an enzyme that resolves blood clots.
Right side massage
A right-sided ischemic stroke often leaves the patient paralyzed in the left limbs, the corresponding side of the face, or the left half of the body. In this case, a special therapeutic massage is indicated, which will restore metabolism in the affected area. In addition, the procedure stimulates the development of connections between the remaining living neurons of the brain, so that they can take on the functions of the dead.
But recovery after a stroke involves massage not only for the purposes described above. If a person lies in bed for a long time, then his tissues not only atrophy, but bedsores appear. This can be prevented with proper care, but mechanical action (i.e. massage) will also be needed to improve local blood flow and tissue trophism.
For therapeutic massage, classical techniques are used - stroking, kneading, rubbing (they help remove stagnation), as well as vibration.
Prognosis for future life after illness
The main factors that play a role in making a prognosis are the area and degree of brain damage, the age of the patient, the causes of stroke and the form of its course. The final outcome will also be affected by the timeliness of medical care and placement of the patient in a hospital, correct diagnosis of the disease, the presence or absence of concomitant diseases, complications, and the duration of rehabilitation.
- Restoring vital functions after a cerebral infarction can be difficult due to complications:
- Having suffered extensive hemispheric or brainstem infarctions, accompanied by paralysis, paresis, disorders of motor, swallowing and speech functions;
- Severe state of the general hemodynamics of the body in diseases of the cardiovascular system in the stage of decompensation;
- Damage to both vascular systems, which results in limited collateral circulation.
Recovery after a stroke can be much easier and faster if:
- The ischemic stroke suffered was localized to a small, discrete area;
- The patient's age is less than 30 years;
- The general condition of the heart and blood vessels is satisfactory;
- During the disease process, only one extracranial vessel was affected.
The prognosis is largely influenced by the following factors:
- The area and location of the necrosis focus. If it is located in the area of vital centers of the brain and affects a large number of tissues, the likelihood of an unfavorable outcome (even death) increases greatly.
- Patient's age. The older the person, the more severe the disease and the greater the likelihood of complications.
- The severity of neurological disorders. The more acute the stroke, the less likely it is to restore body functions.
- The cause of the disease. For example, when the cause of a cerebral infarction is atherosclerosis or a blood clot, the prognosis becomes less favorable.
- The development of all kinds of complications. High mortality is recorded due to damage to the respiratory and cardiovascular centers, cerebral edema, the transition of ischemic stroke to hemorrhagic, etc.
Forecasts are divided into favorable, average and unfavorable.
- Favorable prognosis. It is given if, after suffering a pathology, one or more body functions were slightly impaired. As a rule, after high-quality rehabilitation and compliance with all medical recommendations, a crisis period of the disease begins, after which the patient completely returns to normal life.
- Average forecast. The course of the disease was accompanied by gastrointestinal dysfunction, diabetes mellitus, pneumonia and other pathologies.
- Poor prognosis. It is given if a large area of brain tissue is affected.
Features of prognosis depending on the affected parts of the brain
The brain stem contains a huge number of nerve bundles, a thermoregulation center, respiratory and vestibular centers. If during a cerebral infarction one of the departments that plays an important role in life support was affected, then the likelihood of further normalization of its work is very low. That is why with necrotic lesions of the trunk it is often very difficult to make any predictions.
The cerebellum is anatomically located close to the brainstem and is responsible for the coordination of movements. If this department has been affected, a person ceases to feel his body, he loses balance and orientation in space. With timely assistance, cerebellar function can be restored during the rehabilitation period.
The cerebral cortex is responsible for fixing and transforming information received through the optic nerves. When the right hemisphere is damaged, the patient loses the ability to see what is located in the left part of his visual field and vice versa. Changes in this part of the brain also affect the perception of visual images in general, including familiar people and everyday objects. After ischemia, complete restoration of vision can take up to six months, and poor recognition of rarely seen objects can persist until the end of the patient’s life.
If several parts of the brain organ are affected at once, a cerebral coma may occur. This is the most severe type of stroke, which is accompanied by extensive necrosis of soft tissues. Coma is often accompanied by loss of the ability to breathe independently (regular shortness of breath) and complete disruption of the cardiovascular system. The risk of death after a coma is very high, and with a favorable outcome, the chance of restoring previous body functions is less than 15%.
Left hemisphere ischemic stroke and its causes.
Among the main reasons are:
- Narrowing of the extracranial cervical arteries and arteries located at the base of the brain due to atherosclerosis (deposition of fatty plaques in the inner wall of blood vessels that calcify over time) - this cause occurs in 95% of cases;
- Embolism of intracranial arterial vessels, which occurs when they are blocked by detached parts of a blood clot, especially in the presence of heart disease (atrial fibrillation, cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction) - can be seen as the cause in 20%;
- Dissection of the walls of the main types of neck arteries - about 2%;
- Changes in the rheological properties (viscosity) of blood due to vasculitis (inflammation of the vascular wall) or coagulation (blood clotting) disorders due to diseases (leukemia, thrombocytosis) or when taking oral contraceptives.
- The occurrence of microangiopathies of small-caliber arteries due to lipohyalinosis, which leads to lacunar cerebral infarction - in 15-30%;
- Arterial hypertension (back in the 90s of the last century it was proven that with an increase in diastolic pressure (lower number) by 7.5 mm Hg, the risk of developing IS almost doubles));
- Smoking, hypercholesterolemia and diabetes mellitus;
AI on the right side of the body (development of paralysis or paresis)
Ischemic stroke in the occipital lobe (indicated by arrows)
Its development is typical within a few seconds or minutes from various focal disorders. In 75% of patients, an increase in blood pressure is observed in the first days of the disease, which then decreases spontaneously.
In ischemic stroke of the left hemisphere of the brain, its main cause lies in blockage of the main trunk of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) or internal carotid artery (ICA), the following appears:
- paralysis of the right side of the body (hemiplegia or hemiparesis)
- absence of all types of sensitivity (anesthesia)
- loss of half the visual field on the right (opposite) side of the body (right homonymous hemianopsia)
In addition, if the affected left hemisphere is dominant , then aphasia (lack of speech function) , agraphia (inability to write) and alexia (inability to read) develops, and if the left affected hemisphere is subdominant - violations of the body’s own circuitry and anosognosia (inability to give rational critical assessment of one’s physical condition). Such conditions are caused by extensive damage to the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes.
These symptoms are somewhat less pronounced with limited infarctions, which can occur when the branches of the middle, anterior cerebral and internal carotid arteries are blocked or narrowed.
If arterio-arterial embolism of the branches of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) on the left develops, combined with insufficiency of collateral (bypass) circulation, the so-called brachiofacial hemiparesis occurs (the presence of impaired movement in the right hand along with central paresis of the facial and hypoglossal nerves).
The combination of paresis of one right arm and the above symptoms is also characteristic of left hemisphere ischemic stroke of the brain. In the case when the blood clot spreads into the lumen of the ophthalmic artery (a. ophthalmica), in some cases it causes complete blindness.
Survival Statistics
Cerebral infarction ranks third in mortality in the world (after heart disease and malignant tumors). According to research, 12-25% of patients die in the first weeks of the disease. The main cause of death is cerebral edema. In second and third place are pneumonia, pulmonary artery blockage, followed by blood poisoning, respiratory tract dysfunction and kidney failure.
About 40% of deaths occurring in the first three days are associated with extensive necrosis of brain tissue. Among patients who survive the disease, about 70% become incapacitated and disabled due to neurological disorders. Over time, these disorders fade away, due to which six months after rehabilitation the disorders remain in 40% of patients, and after a year – in 25%.
Distinctive signs and symptoms
The main symptoms of the disease are determined by the importance of the affected area. A stroke on the right affects the centers of the brain, which are responsible for the orientation of the body in space and the analysis of information, and in left-handers the speech center is also located there.
Characteristic symptoms:
- paralysis of the left half of the body, which can be complete or partial;
- changed face - the nasolabial fold on the right is smoothed out, the corner of the mouth moves down;
- the patient's inability to assess the position of his own body;
- inability to concentrate.
There is a form of stroke associated with thrombosis or embolism of the carotid artery. It is dangerous because it is asymptomatic.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of pathology, you need to monitor your health and take into account the following rules:
- Monitor your blood pressure (especially for those people whose close relatives suffer from changes in blood pressure) and prevent critical deviations from the norm.
- Do not hesitate to consult a doctor if you experience unpleasant sensations from the cardiovascular system; undergo regular medical examinations.
- Do not overeat fatty foods.
- Following the basics of proper nutrition will help keep cholesterol levels under control (prevent the accumulation of plaques on the walls of blood vessels).
- Do not drink alcoholic beverages.
- Periodically take anise lofant tincture.
- No smoking.
- Get enough sleep regularly (sleep should last at least 8 hours).
- Do not use drugs containing high levels of hormones uncontrollably.
It is important to remember that a stroke can happen to anyone, especially in old age. Therefore, even minimal prevention can significantly reduce the risk of developing the disease.
Consequences and forecasts
A cerebral infarction causes various consequences, which can be either minor after minor attacks or extremely severe. Much in this case depends on the location and area of the affected area. Possible consequences of ischemic stroke:
- Mental disorders. Many patients who have suffered from this serious illness develop depression associated with the changes that have occurred to them. They worry that they will remain disabled for the rest of their lives, that they will not be able to lead their usual lifestyle, to live as before. Also, after a stroke, a person may become irritable and aggressive, his mood may change sharply and frequently for no apparent reason.
- Decreased sensitivity of part of the face or limbs. A fairly common consequence of a heart attack. The restoration of nerve fibers occurs quite slowly, so sensitivity can only partially return.
- Motor dysfunctions. This may require the use of a cane and make it difficult for the person to perform certain manual tasks.
- Cognitive impairment. They can relate to memory - a person forgets simple things - address, phone number, names. Patients also often underestimate difficulties, which is why their behavior may resemble that of a small child.
- Speech disorders. They appear infrequently. They consist of pronouncing incoherent phrases and sentences.
- Coordination problems. Frequent dizziness appears, and a person may fall when making sudden movements. It appears especially often if the patient has had a major ischemic stroke.
- Epilepsy. A fairly common consequence after a stroke - up to 10% of patients suffer from epilepsy attacks after suffering from the disease.
Ischemic stroke has a favorable prognosis with timely detection of the problem and adequate therapy, as well as proper rehabilitation. The sooner medical assistance is provided, the more favorable the outcome of the disease. The prognosis for life after ischemic strokes directly depends on the site of the lesion and its volume. Thus, with extensive cerebral infarction, death often occurs. A common cause of death after a heart attack is cerebral edema, less commonly pneumonia, heart disease, etc.
The prognosis for life after an extensive illness is as follows: about 40% of deaths occur in the first 48 hours. The patient's life expectancy depends on the degree of brain damage and the timeliness of therapy.
Motor functions are especially rapidly restored in the first 3 months after a stroke. If recovery does not occur within a year, the likelihood of this happening in the future is very unlikely.
The essence of pathology
So what is ischemic stroke? This is a severe violation of blood circulation in the brain, which is characterized by the death of cells and tissues. Another name for cerebral infarction or multifocal stroke.
Generally speaking, the diagnosis of ischemia is a lack of blood supply to a certain area or organ of the human body. In this case it is the brain. The process of tissue destruction occurs gradually (ischemic cascade). It does not stop even when blood circulation is restored. That is why timely first aid provides a chance for recovery and complete restoration of the body.
At each age, stroke has its own characteristics. In young people it develops suddenly and is often the result of blockage of blood vessels by foreign particles called emboli. The first symptoms of a cerebral infarction develop with excessive physical exertion, underwater work, coughing, or during surgery on the lungs.
Stroke in older people has a slow progression. Its manifestations wax and wane. And so on for a week or more. In some cases, this period is reduced to several days.
In pathological anatomy, an ischemic attack is classified as microscopic specimens. Along with it are hemorrhagic stroke and encephalopathy.
Classification of the disease: types, types
There are several types of cerebral infarction. It is classified according to the causes of its occurrence, the intensity of the increase in symptoms, and the periods of ischemic stroke.
Spicy
The acute stage of ischemic stroke is characterized by rapid recovery. It usually lasts less than a month. If the body recovers in less than 21 days, the pathology is called minor ischemic stroke.
Extensive
A major stroke is characterized by a long course. Symptoms last for a long period of time. And even after successful treatment, the patient continues to have neurological disorders.
Lacunar stroke
This type of cerebral infarction occurs in patients suffering from diabetes or arterial hypertension. Circulatory disorders occur in small areas of the brain. There is a possibility that a space will appear, which will subsequently be filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Right-handed
It is characterized by damage to the left side of the body and serious consequences. With timely assistance, almost complete recovery is possible.
Left-handed
It is much more dangerous than the previous type, since it leads to disruption of almost all body functions. Affects the right side of the body. Leads to the development of coma, epilepsy and paralysis. Often ends in death.
Stem
It is considered the most severe form of brain damage. It has rich symptoms and many consequences regarding the functioning of internal organs. This condition is characterized by paralysis, problems with balance, drooping eyelids on the side where the stroke occurred, difficulty with orientation in space, and other symptoms.
Trunk stroke is the most common cause of death.
Cerebellar
Less common than other forms. It is difficult to diagnose. Due to the proximity of the brain stem and important nerve centers, it requires prompt assistance. This type of stroke is characterized by incoordination, nausea, vomiting and dizziness. As the pathology develops, facial numbness and coma develop.
Atherothrombotic
It is a consequence of chronic diseases of the blood vessels, such as thrombosis. The cause of thrombotic ischemic stroke is a blood clot that breaks off and closes the lumen of the vessel.
Symptoms of pathology develop gradually. Most often they appear during night sleep.
Cardioembolic
The main factor provoking the development of this form of stroke is the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system. This includes various heart defects, heartbeat disorders, and myocardial infarction.
Most often, a stroke affects the middle cerebral artery, and the affected area can be medium in size or large. Symptoms develop suddenly regardless of the time of day.
Hemodynamic
Occurs when blood vessels narrow over a long period of time. The brain does not receive enough nutrients. The provoking factor in this case is hypotension. This also includes stenosis and atherosclerosis. Symptoms of such a stroke appear both at rest and while awake.
Hemorheological
Consequence of blood clotting disorders. The causes, factors and manifestations have not been thoroughly studied.
ICD 10 code
According to ICD 10, any form of cerebral vascular infarction is designated by code l63. At the end there must be a dot and a number, which shows the type of pathology. In addition to the code there is a letter A or B. The first indicates the presence of arterial hypertension, and the second indicates its absence.
Providing first aid (before the doctor arrives)
Before the specialist arrives, the patient must be given proper emergency care.
- Lay the patient down. The head should be in an elevated position (about 30 cm).
- Pillows should be placed under the shoulders and shoulder blades.
- Ensure a flow of fresh air into the room (open windows, vents).
- Unbutton your shirt and belt. Remove tight clothing.
- Blood pressure must be measured.
- During an attack, the patient may feel sick and vomit. To prevent him from choking on vomit, the patient's head is turned to the side.
Next, the emergency doctor will carry out all the necessary procedures to prevent brain swelling and normalize breathing and blood circulation. The patient must be hospitalized.
Already in the hospital, a differential diagnosis will be carried out with the appointment of an MRI or CRT, the indications of which will determine further treatment and the course of the pathology.
Price for treatment and rehabilitation after a stroke at the Yusupov Hospital
The Yusupov Hospital provides diagnostics, treatment and rehabilitation after a stroke. The examination is carried out using modern medical equipment. The drugs used meet European quality and safety standards. Surgical intervention is performed by experienced surgeons if there are strict indications. Qualified neurologists develop an individual treatment and rehabilitation plan for each patient. In this way, it is possible to achieve a positive effect in a minimum amount of time. Services are provided at an affordable price. Detailed information about the cost of treatment can be found by phone or on the official website of the Yusupov Hospital.
Make an appointment
Rehabilitation therapy
Neurologists have developed a scheme for how to recover from an ischemic stroke in the left MCA or in another area of the brain. It includes:
- Massage. Rubbing and kneading the muscles improves blood supply and helps restore damaged innervation.
- Physiotherapy. A magnet, laser and other hardware procedures are used to improve tissue microcirculation and restore the conductivity of nerve fibers.
- Exercise therapy. An individually selected set of exercises helps restore motor function. With the help of exercise therapy, treatment after stroke, if the side of the body is paralyzed, is carried out by making the patient passive flexion and extension movements in the immobilized limbs.
- Diet. The diet of patients should consist of foods that are easily digestible. You should exclude fatty meats, smoked and pickled foods, baked goods, and also limit the consumption of salt and sugar. It is recommended to include vegetables, vegetarian soups and cereals in the menu.
- Classes with a speech therapist. Necessary for restoration of speech functions.
Neurologists are positive if folk remedies are used in addition to the main treatment. It is recommended to drink tincture of fir cones or decoctions of chamomile, St. John's wort, and sage. Traditional medicine recipes help improve the functioning of internal organs and prevent possible inflammation associated with weakened immunity.
Forecast
The prognosis for ischemic stroke, especially before 50 years of age, is quite favorable if help was provided on time. This is how 80% of patients survive, and only 20% will die in cases of cerebral edema. But 80% of patients suffer from complications that remain with them for life; relapses occur in the first three weeks with every third patient.
Despite the favorable prognosis after a right-sided stroke, it is better to never experience an attack. And this can be done by visiting a doctor every six months and monitoring your condition, especially if you have risk factors. If an attack develops, immediately provide first aid and do not hesitate to call an ambulance, as the further quality of life of the victim depends on this.
ACVA – causes and risk factors
There are disorders in which an ischemic stroke is almost guaranteed to occur.
In most cases, acute stroke has the following causes:
- blood clots in blood vessels;
- atherosclerosis;
- cardiogenic embolism;
- arrhythmia;
- Takayasu's disease;
- infectious arteritis;
- Moyamoya syndrome;
- arterial hypertension;
- cardiac inactivity;
- hematological diseases and others.
Risk factors that make a stroke or cerebral infarction more likely:
- advanced age;
- high cholesterol concentration;
- smoking;
- heredity;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- arterial hypertension;
- diabetes;
- any heart pathologies;
- Fabry disease;
- abdominal obesity;
- vasculitis;
- addiction;
- chronic depression;
- insulin resistance;
- alcoholism;
- dyslipidemia;
- blood hypercoagulation and others.
Symptoms and causes of stroke
It is absolutely obvious that with a major stroke, the prognosis becomes more favorable if medical care is provided as soon as possible after the occurrence of a vascular accident, when serious disorders have not had time to develop. To do this, you need to promptly recognize the signs of ischemia. There are certain brain symptoms that can be used not only by doctors, but also by people without medical education. These include:
- impaired speaking. The victim pronounces words indistinctly and somewhat slowly;
- smile disorder. In this case, it is asymmetrical, one of the corners of the mouth is lowered;
- impaired motor activity, severe weakness in the limbs up to the inability to move them. If this symptom is not very pronounced, then you need to check it by comparing it with another healthy arm or leg; the limb on the opposite side of the lesion will drop.
Concomitant symptoms of the disease and disorders
Poor prognostic symptoms for stroke
There are symptoms that worsen the overall life prognosis of ischemic stroke:
- depression of consciousness;
- inability to move independently (the patient can only open and close his eyelids), lack of speech, although the patient’s understanding of what is happening may remain;
- pronounced cognitive and emotional-volitional disorders;
- dysphagia (difficulty swallowing);
- persistent hyperthermia - indicates damage to the thermoregulation center and aggravates ischemic damage to brain tissue. A decrease in body temperature by 1°C doubles the chances of a favorable outcome;
- muscle hypertonicity, throwing the head to one side, convulsive twitching or prolonged epileptic seizures, lack of coordination of movements, loss of control over the body;
- urinary incontinence;
- persistent gaze paralysis, eye movement disorder (pendulum-like oscillations or slow movements of the eyeballs, lack of synchrony of eye movements);
- violation of hemodynamic parameters (severe heart rhythm disturbances, high blood pressure);
- severe hemiparesis (weakening of the muscles on one side of the body);
- somatic diseases in the stage of decompensation, severe infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- pathological types of breathing: Kussmaul breathing (deep noisy inhalation and forced exhalation), Cheyne-Stokes breathing (alternating deep breaths and shallow respiratory movements, Biot breathing (long pauses between breaths);
- comatose state - the chances of recovery after four months of cerebral coma caused by ischemic brain damage remain only in 10% of patients.
Factors that aggravate the prognosis in acute cerebrovascular accidents include diseases of the cardiovascular system, the presence of concomitant diseases in the stage of decompensation, endocrine disorders, and a history of stroke.
Major stroke
If we are talking about an extensive right-sided stroke, then the general cerebral symptoms are most pronounced, and not focal ones, and the manifestations appear sharply and unexpectedly. The most common cause is blockage of blood vessels, plaques and poor circulation. The main manifestations are headache, vomiting, loss of consciousness, problems with swallowing, speech disorders, loss of sensation, paralysis and depression.
By the way, lacunar stroke is more common, which develops in 55% of cases due to blockage of blood vessels, poor elasticity of blood vessels and atherosclerosis.
Causes
Several conditions are considered to be the causes of left-sided ischemic stroke:
- atherosclerosis;
- blood clots;
- emboli;
- pressure of tumors on blood vessels;
- spasms.
Risk factors that provoke the development of a major stroke include high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, smoking, excessive drinking, old age, heart inflammation, high blood clotting, and taking hormonal contraceptives.
Complications after an attack
Almost 80% of patients after a right-sided stroke encounter complications, which can be completely eliminated in 70% after long-term rehabilitation. This is about:
- paralysis and loss of motor activity;
- numbness, loss of sensation on the left side;
- facial asymmetry;
- memory loss;
- speech impairment;
- loss of visual acuity and hearing;
- mental disorders;
- mental retardation;
- cerebral edema and coma.
Here you will learn about left-sided stroke
And in this article you will find information about hemorrhagic stroke on the right side https://insult-med.com/vidy/storona/pravostoronniy/gemorragicheskiy.html
If the stroke is hemorrhagic
The consequences of a hemorrhagic stroke on the right side of the brain are more severe than an ischemic stroke. This is due to the fact that, regardless of the size of the affected area of the brain, the recovery of nerve cells occurs slowly. The spilled blood compresses and impregnates the tissues, completely destroying them. This means that not all lost functions of the nervous system can be restored.
Minor hemorrhage
The prognosis for the life of people with a slight hemorrhage in the right hemisphere of the brain is ambiguous - 65–75% survive, but become disabled. The degree of disabling consequences is always higher than with the ischemic process, although the nature of the manifestations is the same - the left side is paralyzed, sensitivity is impaired, and there is a decrease in criticism, memory and vision in the left eye. This means that patients can:
- Recover completely (10–15%).
- Have a moderate neurological deficit - walk with a cane, capable of self-care, but limited (65–75%).
- Have a severe neurological deficit - move in a wheelchair or lie down, are not capable of self-care (15–20%).
The main distinctive features of the consequences after a hemorrhagic stroke in the right hemisphere:
- Increased sensitivity to loud noises and bright lights.
- Irritability, nervousness.
- Frequent headaches.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Frequent swallowing and sleep disturbances.
Massive bleeding (hematoma) or breakthrough of blood into the ventricles
Stroke-hematoma, a massive or large hemorrhage located in the right hemisphere, ends in early death in 95–99% of patients. If there is a breakthrough of blood into the ventricles of the brain, death occurs instantly or within the first day. No more than 10–15% of such patients can be saved by emergency surgery - removal of hemorrhage, drainage of the cranial cavity or ventricles. But the survivors will be severely disabled, comatose or disoriented, unable to care for themselves. Their life expectancy is short - from several days to several months.
Large hemorrhage in the right hemisphere of the brain can lead to coma
Classification
Cerebral arteries are divided into two vascular territories: vertebrobasilar and carotid. Stroke of the vertebrobasilar region includes lesions in the system of the posterior cerebral and basilar arteries. If there are disturbances in blood flow in the anterior or middle cerebral artery system, they speak of a carotid stroke.
On the affected side, ischemic stroke can be left-sided or right-sided.
There is a classification according to the lesion:
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA). A small area of the brain is affected. Symptoms disappear within 24 hours.
- Small – restoration of functions occurs within 21 days.
- Ischemic stroke is progressive - it is characterized by the gradual development of actual focal and cerebral symptoms, which can occur within a few hours or days. Restoration of functions after this occurs incompletely - the patient, as a rule, remains with some minimal neurological symptoms;
- Total (i.e. complete) ischemic stroke - implies a completed cerebral infarction with an actual incomplete or stable-regressive deficit.
The classification of ischemic stroke includes the following types of pathology:
- Atherothrombotic usually affects during night sleep. It can develop slowly and affects large and medium-sized vessels by blocking blood flow with cholesterol plaques.
- Cardioembolic form. It starts suddenly. Most often it occurs in the area of the blood supply to the middle artery of the brain. The size of the lesion can be medium or large.
- Lacunar form of ischemic stroke. Small perforating arteries are affected. A brain stem stroke does not develop immediately. The size of the lesions does not exceed 15 mm.
- The ischemic type caused by rare disorders is more difficult to diagnose. The cause of a cerebral infarction may be increased blood clotting, pathological changes in the walls of blood vessels, etc.
- Ischemic brain damage may have no cause. This condition is characterized by either the presence of several reasons for the development of ischemic brain damage or the inability to determine the cause of the pathology.
There are also several periods of ischemic stroke:
- The most acute period is the first 3 days. Of these, the first three hours were defined as a “therapeutic window”, when it is possible to use thrombolytic drugs for systemic administration. In case of regression of symptoms during the first day, a transient ischemic attack is diagnosed;
- acute period - up to 4 weeks;
- early recovery period - up to six months;
- late recovery period - up to 2 years;
- period of residual effects - after 2 years.
Types of stroke
Ischemic stroke is a pathological syndrome , the manifestations of which vary depending on the type of disease. If we consider the mechanism that led to the development of pathology, we can distinguish five types of stroke:
Atherothrombotic
Atherothrombotic stroke - its development is based on atherosclerosis, in which blockage of a vessel in large or medium arteries is caused by cholesterol “plaques”; This condition often develops at night during sleep.
Cardioembolic
Cardioembolic stroke - caused by a special type of blood clot - an embolus, which forms in various heart diseases (arrhythmia, endocarditis, heart disease) and blocks the arteries of the brain; the condition is sudden and develops during wakefulness.
Lacunar
Lacunar stroke - occurs when small vessels are damaged; most often develops in patients with hypertension or diabetes mellitus.
Hemodynamic
Hemodynamic stroke - caused by impaired blood movement through the vessels (for example, when pressure decreases), as a result of which the brain does not receive enough essential nutrients; most often develops in patients with concomitant vascular pathology.
Unknown origin
Stroke of unknown origin - it is not possible to identify the cause of the disease.
Rehabilitation and recovery
An increase in a favorable prognosis depends on the period at which rehabilitation measures are carried out. To do this, it is recommended to carry out restorative procedures after stabilizing the state of health and eliminating the threat to life. Rehabilitation is carried out by several specialists according to an individual plan. The main restoration measures of the early period include:
- Prevention of blood clots. Prolonged forced position leads to a decrease in the speed of blood flow in the arterial and venous beds. As a result, clots form that can travel to vital organs, including the lungs and brain. To prevent thrombosis, medications with an anticoagulant effect are prescribed to reduce blood clotting, and physical therapy is recommended in the early stages.
- Preventing pneumonia. Inflammation of the lung tissue is caused by a violation of respiratory excursion, which is manifested by the accumulation of pathogenic flora in the tissue of the organ. The proliferation of bacterial or viral agents leads to a decrease in the volume of the respiratory surface. After spontaneous breathing is restored, breathing exercises are prescribed.
- Prevention of urinary tract infection. Inflammation in the organs of the urinary system is provoked by prolonged leaving of the catheter necessary for urine removal. It acts as an entry point for infection. The recovery stage consists of early removal of the catheter with careful regular toileting of the genitals and a change of hygiene products.
- Anti-bedsore therapy. Impaired blood flow in compressed tissues provokes the appearance of trophic ulcers. When lying down for a long time, bedsores form on the surface of the skin, which can become infected. To prevent these formations, it is recommended to use anti-decubitus mattresses from the first days of hospitalization. Medical personnel or relatives need to massage the victim, which will restore blood flow. Particular attention should be paid to areas where increased pressure is applied. This is the area of the shoulder blades and hips.
- Reducing the risk of injury. A change in coordination of movements, if a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke develops on the left side of which is affected, leads to frequent falls and injuries. People in the rehabilitation phase need to use supporting devices, such as walkers or canes.
The duration of rehabilitation depends on:
- Speed of medical care.
- Patient's age.
- Volume of the affected area.
The average duration of rehabilitation is 3-6 months. In the long-term recovery period, the following is provided:
- Therapeutic physical culture and gymnastics. Regular exercise strengthens the tone of muscle fibers and increases motor activity. The set of classes is selected based on the level of physical fitness.
- Swimming. A visit to the pool, due to the even distribution of the load on the body, normalizes motor coordination and reduces hypertonicity.
- Speech therapy classes.
- Hirudotherapy. Hirudin entering the human body thins the blood and has a sclerosing effect.
Causes of ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere
The human brain is one of the organs in which metabolic processes occur most intensively, but the constant reserves of energy in it are not enough; under normal conditions, an adult has enough of them for about five minutes. That is why it is important to start cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the event of clinical death in this short period of time so that other disorders do not appear in the body.
The brain needs a regular supply of oxygen, but when, in the case of the above reasons, the blood supply is difficult, an ischemic zone may occur. If the vascular cause, be it a narrowing or blockage by a blood clot, is not eliminated in the next three hours, then this area becomes necrotic, secondary damage builds up around it, and the patient loses the functions for which this area of the brain is responsible forever. Further in more detail about extensive ischemic stroke (right side): consequences and treatment.
Development of stroke
Rehabilitation after stroke
An ischemic stroke of the brain can lead to consequences that will haunt the patient for a very long time or even his whole life.
The consequences of a heart attack require special rehabilitation, which is aimed at the patient’s social adaptation. During the entire period of rehabilitation measures, you should continue the prescribed drug treatment and strictly monitor the timely intake of necessary medications. After the end of the acute period of ischemic cerebral infarction, each patient is prescribed a special course of rehabilitation, which takes into account the characteristics of both the course of the disease and the patient himself (for example, concomitant diseases). Often rehabilitation activities include massages, physiotherapy, physical therapy, acupuncture and other procedures.
Many who hear the diagnosis of ischemic stroke for the first time have a question: what is it? This is a serious condition consisting of a sharp and significant reduction in blood supply to one of the areas of the brain, so ischemic stroke leads to consequences that are irreversible. It is extremely important to know the signs of this disease in order to help in a timely manner and call emergency medical services. To prevent the disease, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, normal sleep patterns, and giving up bad habits.