An increase in the weight of the spleen up to 200 g indicates the presence of splenomegaly. The disease is characterized by the appearance of pain in the left hypochondrium, an increase in body temperature sometimes up to +40°C, nausea, and vomiting. During palpation, the disease manifests itself as unpleasant sensations. In order to understand in detail the causes of the disease, you should familiarize yourself with its types. This information will allow patients to make every effort to avoid the causes and prevent the disease.
Spleen in the human body
What is the disease
Splenomegaly or enlargement of the spleen is inherently not an independent disease, but a consequence of a number of other ailments. The pathological process involves an increase in the mass of the organ over 600 g, and it can be clearly palpated in the area of the left hypochondrium.
The spleen is located in the left hypochondrium
Splenomegaly has varying degrees of severity - from moderate (mild or insignificant), which can be observed temporarily, to pronounced, when the organ occupies half of the abdominal space. The most severe forms of splenomegaly are observed with oncological lesions of the blood.
Enlargement of the spleen can reach gigantic proportions
An enlarged spleen, in turn, disrupts the normal process of hematopoiesis, i.e., the production of blood elements that accumulate and die in the diseased organ, provoking a condition dangerous to the health and life of the patient, called hypersplenism.
How to treat splenomegaly?
Question - what is splenomegaly and how to treat it? — first of all arises in a person when he hears such a “strange” diagnosis for the first time. Since this condition develops against the background of some pathology, therapy should be carried out aimed at eliminating the root cause.
In case of an infectious process provoked by bacteria, antibiotics are indicated, and if the disease has a viral etiology, antiviral drugs are indicated.
Mycoses are treated with antifungal agents, and helminthic infestations are treated with anthelmintics. In case of echinococcosis, when cysts with larval forms of the pathogen grow into the spleen, only surgical removal is possible.
Against the background of anemia, especially caused by vitamin B12 deficiency, vitamin therapy is indicated. Oncological diseases of the blood are treated with antitumor drugs. To relieve severe inflammation of the spleen and suppress an overly activated immune system, hormonal drugs are used.
Unfortunately, drug treatment for splenomegaly does not always produce results. If there is no positive dynamics and the spleen continues to grow in size, a malfunction in its functioning leads to excessive destruction of blood cells (hypersplenism) - surgical removal of the organ is indicated.
- The same tactics are followed when a malignant tumor is detected.
Splenomegaly requires careful attention from the patient and regular monitoring by the attending physician, especially if it develops against the background of a chronic infection. The most dangerous complication of an enlarged spleen is its rupture. It can be triggered by increased physical activity, bruises, and injuries received, including while playing contact sports.
In addition, splenomegaly is characterized by hypersplenism - increased filtration of blood cells with subsequent destruction. Against this background, a deficiency of erythrocytes, platelets and leukocytes develops, and hyperplasia (overdevelopment) of the bone marrow is formed compensatory to restore the normal concentration of blood cells.
It happens that when examining patients with an enlarged spleen and without any clinical manifestations, the causes of this pathological condition are not found. This result is not a reason to stop diagnosing. The examination should be repeated after 6-12 months.
The spleen is an organ of the hematopoietic and immune systems, so if splenomegaly develops, you should visit a hematologist and immunologist. However, the initial examination can be carried out by a therapist. This specialist will palpate the organ and, if necessary, prescribe ultrasound diagnostics and laboratory tests.
With the results obtained, the patient may be referred to a specialist. In addition to a hematologist and immunologist, this could be an infectious disease specialist, an oncologist or a surgeon.
I hope I explained what splenomegaly is and it became clear that an enlarged spleen in a child or adult is not a reason to panic. Pathology in children under 3 years of age in the absence of disease is a variant of the norm. For adults, if the cause of organ enlargement has not been found, they should undergo regular diagnostic tests. This way you will be able to protect yourself from complications of splenomegaly itself and identify dangerous ailments in time.
Splenomegaly is a pathological condition characterized by an enlarged spleen. This is not an independent disease, but an important symptom of another disease. It is also worth noting that an enlarged spleen can be diagnosed in 5% of completely healthy people.
Sometimes splenomegaly can occur simultaneously with liver enlargement. In this case, they talk about progression.
This pathological condition can occur in people from different age groups, including young children. The spleen is an unpaired organ that is located in the abdominal cavity on the left side. This is a kind of anatomical “filter” that has the ability to retain pathogenic microorganisms, as well as damaged blood cells, and prevent them from spreading further throughout the human body.
An increase in non-oncological origin is eliminated by treating concomitant pathology. The therapeutic direction is selected depending on the diagnosis of the primary disease.
Conservative treatment consists of prescribing various drugs aimed at the cause of the pathology.
Medicinal groups:
- antibacterial;
- antiviral;
- hormonal;
- antifungal;
- antiprotozoal;
- antitumor (in the early stages of neoplasms).
Bone marrow transplantation or transfusion of blood components is required for hematological diseases.
Surgical treatment is primarily indicated for malignant neoplasms and splenic abscess.
Splenectomy is necessarily prescribed for:
- thrombosis of the splenic vein;
- congenital spherocytosis;
- autoimmune thrombocytopenia;
- villous cell leukemia;
- Gaucher's disease.
Previously, Hodgkin's lymphoma was an indication for organ removal. Now, thanks to the improvement of staging methods, this measure is rarely resorted to. There is evidence that in adults the risk of developing other tumors increases sharply after splenectomy.
Splenomegaly is caused by an abnormal enlargement of the spleen, can occur in people of all ages and affects females and males equally.
The spleen is an important organ that performs a number of functions in the body:
- Participates in the formation of immune defense. The spleen filters out pathogenic microflora and creates antibodies that are necessary to protect the body from various ailments.
- Destroys old red blood cells and platelets by absorbing them from the bloodstream.
- Accumulates a reserve of red blood cells. In emergency situations, it is the spleen that provides the body with the necessary blood reserve. In case of significant blood loss, this organ saturates the blood with red blood cells and platelets, preventing oxygen starvation.
- Accumulates iron, released during the destruction of red blood cells.
Splenomegaly is characterized by abnormal enlargement of the spleen. This syndrome occurs secondarily, without acting as an independent nosological unit.
In a healthy person, the spleen is relatively small and weighs no more than 150 grams. The organ is hidden behind the rib frame, which significantly complicates its palpation or makes it completely impossible.
It is possible to feel the spleen when it is enlarged. With splenomegaly, the organ grows two or even three times in size. And such an increase may be a consequence of the development of a number of serious ailments in the body.
Splenomegaly is often confused with splenic hypertrophy. The latter pathology is observed in approximately 10% of healthy children against the background of imperfect development of the immune system.
Splenomegaly can affect all ages, occurring with equal frequency in men and women.
Due to the fact that the spleen is an important part of the human immune system, an increase in its size indicates the development of various diseases of an infectious or non-infectious nature in the body. The main causes of splenomegaly are:
- Autoimmune diseases. These include periarteritis nodosa, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc. In this case, the development of hyperplasia occurs against the background of increased phagocytic function of the spleen.
- Infectious diseases. When the immune load on an organ increases, its size increases. This is possible with viral, fungal, bacterial, parasitic and protozoal infections of both acute and chronic types. Thus, HIV infection, tuberculosis, syphilis, schistosomiasis, blastomycosis, etc. can lead to the development of splenomegaly.
- Myeloproliferative diseases. The cause of splenomegaly can be malignant degeneration of spinal cord cells. Myeloid leukemia, polycythemia, and myeloid metaplasia have such a development mechanism.
- Impaired immune processes. Due to metabolic disorders of a hereditary or acquired nature, infiltration of the parenchyma with lipids, macrophages and other metabolites occurs. This leads to the development of splenomegaly against the background of diseases such as Zolweger syndrome and phenylketonuria.
- Hematological disorders. They develop due to increased load on the spleen due to acquired or hereditary blood diseases.
- Circulatory problems. When stagnation occurs, a disruption of blood outflow through the venous bed occurs. As a result, the pressure in the portal vein system increases, and the spleen undergoes hypertrophic changes. A similar condition can be caused by thrombosis of the splenic vein or twisting of the vascular pedicle of the organ.
- Various injuries of the abdominal cavity of a traumatic nature.
- Diseases of oncohematological nature, such as Hodgkin's lymphoma and leukemia.
If the cause of splenomegaly is an autoimmune disease or a pathology of hematopoiesis, then an enlarged spleen manifests itself in the early stages of the development of these ailments.
The organ is characterized by rapid growth, as a result of which it can be easily detected by the patient himself during palpation.
ICD-10 disease code: D73.
Symptoms
Severe intestinal upset (diarrhea) is one of the symptoms of splenomegaly
The main symptom of splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen several times its normal size. It should be understood that such a state of the organ does not always indicate a disorder. In some cases, the increase occurs against the background of active activity of the spleen caused by an infectious lesion of the body.
The clinical picture is determined by the manifestations of the initial pathology, against which the spleen enlarged. If splenomegaly is inflammatory in nature, then it is characterized by the following symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased body temperature;
- severe weakness;
- diarrhea;
- pain, often acute, localized in the left hypochondrium.
If the disease is non-inflammatory in nature, then its symptoms will be as follows:
- Normal or subfebrile body temperature remains.
- You may experience a dull pain in the left hypochondrium. Usually these are sensations of a pressing or aching nature that are of low intensity.
- Symptoms of intoxication of the body may be completely absent or mildly expressed.
- The skin turns pale and may take on a bluish tint.
- Performance decreases.
- Appetite worsens.
Characteristic signs of the disease
Moderate splenomegaly may be asymptomatic . When the organ reaches a significant size, the patient may experience:
- bloating;
- feeling of pain and discomfort in the left hypochondrium;
- lack of appetite;
- feeling of quick satiety;
- weight loss;
- weakness, dizziness.
These signs develop due to pressure from the enlarged spleen on the organs of the digestive system. The patient may also have symptoms related to the underlying disease that caused the splenomegaly.
As the organ enlarges, the patient develops sensations of pain and discomfort in the left hypochondrium
All about the spleen - video
Symptoms of an enlarged spleen
As noted above, an enlarged spleen can compress and disrupt the functioning of neighboring organs, in particular the stomach. Therefore, patients often complain of a full stomach, despite eating little food.
Pain is often felt in the abdomen, or in the back on the left, and it can radiate to the left shoulder. All complaints arise against the background of insufficient blood supply to certain areas of the spleen, which are gradually being destroyed.
Other signs of splenomegaly
► Paleness of the skin.
► Depending on the reason that provokes a change in the size of the organ, symptoms characteristic of one or another disease appear: change in skin color, increase in body temperature, digestive disorders, aversion to food.
► Pain on the left side of the body when inhaling, radiating to the lower abdomen, shoulder or arm.
► Frequently recurring colds, viral (flu, ARVI), fungal, and other infectious diseases indicate dysfunction of the spleen.
► Bloating, feeling of fullness in the stomach. Children and adults suffering from an enlarged spleen quickly become satisfied with small meals.
► Abdominal colic, prolonged nausea, frequent tendency to vomit.
► Excessive sweating, especially at night.
► General weakness.
► Anemia (low hemoglobin content), pinpoint bleeding not associated with injury.
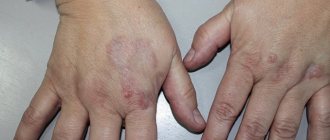
► The appearance of bruises, hematomas, ulcers on the skin, feet, tongue, and inner surface of the cheeks.
► Tachycardia (fast pulse), low blood pressure.
► Jaundice discoloration of the skin.
► Halitosis.
► Consolidation, tension inside the abdominal cavity during palpation.
Diagnosis methods, including ultrasound
First of all, the doctor will analyze the patient’s complaints, conduct an external examination and palpate the spleen area.
A doctor palpates the spleen
To clarify the diagnosis and determine the cause of the disease, the following laboratory tests are performed:
- clinical and biochemical analysis make it possible to judge the balance and condition of blood elements (with splenomegaly, changes are necessarily present in the blood test, for example, the number of leukocytes decreases);
- a blood test for the presence of bacteria allows us to judge the infectious nature of the disease;
- a coagulogram reveals changes in blood clotting processes;
- urine analysis allows us to identify pathological abnormalities - the presence of protein, sugar, bacteria;
- stool analysis reveals the presence of parasitic infestation;
- Ultrasound examination allows you to determine the size and density of the organ.
Ultrasound determines the size and density of the spleen.
Further, depending on the suspicion of pathologies causing splenomegaly, clarifying studies may be carried out:
- tumor marker tests;
- tests for autoimmune markers;
- spleen puncture;
- CT or MRI provides information about the condition of the organ and the anatomical structures surrounding it;
- radioisotope research provides accurate information about the state of the spleen cells.
Diagnostic methods
Splenomegaly requires serious treatment, therefore, if signs are present, it is better to identify the disease as early as possible and prevent its further development. First of all, the doctor examines the patient himself, performs palpation, and then prescribes examination methods. Usually this is a combination of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods.
The main diagnostic methods are: CT, ultrasound, radiography. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages. The ultrasound method is used more often, since thanks to its data it is possible to obtain a complete picture of the deviation and data on possible consequences. Ultrasound is performed not only in the area of probable deviation, but also in relation to the rest of the abdominal organs.
If it is necessary to determine blood circulation in the spleen, the doctor recommends undergoing a magnetic resonance imaging procedure, since in complex cases this diagnostic method is considered the most informative.
In case of emergency, the patient undergoes a puncture of the organ, and material is taken from it for analysis. This method is used extremely rarely, but is used if abnormalities in the functioning of blood vessels are suspected.
There is a possibility of conducting a study if there is a suspicion that the disease was inherited from the parents. In this case, genetic examination is necessary in order to make it possible to cure the pathology and increase the likelihood that the genes will not be passed on to future generations.
The next step in the examination is taking blood and urine tests. The blood and urine diagnostic method is a laboratory research method.
Methods of treating the disease
When symptoms of splenomegaly appear, the patient first needs to contact a therapist, who will analyze his condition and refer him to a specialist - hematologist, endocrinologist, oncologist, etc.
Treatment of pathology is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease that causes it. Conservative therapy serves to eliminate infection, reduce pressure in the corresponding veins, fight the oncological process, etc.
In some cases, it is necessary to resort to splenectomy - removal of the spleen. Surgical treatment is used in the following situations:
- gigantic size of the spleen;
- hemolytic anemia, leading to the death of red blood cells;
- hypersplenism;
- abscesses and large cysts;
- splenic infarction due to vessel thrombosis;
- rupture of the spleen with hemorrhage into the organ;
- hairy cell leukemia;
Gaucher disease (congenital pathology).
Gaucher disease is a hereditary metabolic pathology
Traditional medicine
As already mentioned, splenomegaly is not an independent disease and therefore effective treatment can only be one that can eliminate the underlying cause of the pathology. Of course, folk recipes will not help cope with such serious diseases as blood cancer, etc. Moreover, they can be used in parallel with the main treatment to maintain the functioning of the spleen and only after consultation with a doctor. Here are some useful recipes:
- Infusion of shepherd's purse . Brew 15 g of herb with a glass of boiling water, let it brew, strain. Drink a tablespoon 4-5 times a day.
- Tincture of hop cones . Pour three large cones or five small ones with a glass of alcohol or strong vodka and let it brew for 10 days in a dark, cool place. Take 40 drops three times a day in a small amount of water.
- Infusion of nettle leaves, strawberries, string and violet flowers . Mix the raw materials in equal proportions, then pour two tablespoons of the mixture into 0.5 liters of boiling water, cover and let it brew until it cools, then strain and take a glass in the morning and evening. People prone to irritation of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract should exclude nettle from this recipe.
Dietary recommendations
A special diet for splenomegaly is usually not recommended, but it is advisable for the patient to slightly adjust the diet to make it easier for the body to function . To activate the function of hematopoiesis, iron, copper, and vitamin C are needed. Considering the fact that excess sugar has a negative effect on the functioning of the spleen, its consumption should be limited. In addition, the patient is recommended to eat foods rich in pectin to regulate glucose levels in the body.
So, the patient’s diet should contain:
- dietary meats;
- sea fish, seafood;
- porridge, primarily buckwheat;
- vegetables - cabbage, beets, pumpkin, tomatoes, paprika, etc.;
- fruits and berries, primarily pomegranate, citrus fruits, currants, apples;
- honey (if you are not allergic to it);
- ginger;
- fruit and vegetable juices, berry fruit drinks;
- rosehip decoction;
- green tea.
Foods that are best excluded from the diet, or at least reduce their consumption:
- alcoholic drinks;
- canned food, smoked meats;
- fatty foods;
- fast food restaurant products;
- confectionery;
- fresh white bread;
- carbonated drinks;
- strong coffee and black tea.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention of splenomegaly. Preventive measures consist of preventing diseases that can cause this pathological syndrome. In general, general measures to prevent the syndrome should be highlighted:
- strengthening the immune system;
- absence of bad habits;
- proper and rational nutrition;
- sufficient supply of vitamins and minerals;
- timely treatment of any diseases, especially infectious and inflammatory ones;
- sanitary and thermal processing of products;
- moderate physical activity;
- regular preventive medical examinations (at least once a year).
Splenomegaly is a pathological syndrome that can occur against the background of various diseases. The formation of the clinical picture is based on the primary disease and its nature (inflammatory, non-inflammatory). Treatment tactics also depend on the underlying cause of splenomegaly.
Features of pathology during pregnancy and in children, including infants and newborns
Women diagnosed with severe splenomegaly are advised to abstain from childbearing until the cause of this condition is eliminated. If the disease is detected in the early stages of pregnancy, doctors may decide to terminate it, and in later stages, deliver it by cesarean section.
Splenomegaly in children is caused by the same reasons as in adults. The peculiarity is that such a diagnosis for a child can be made erroneously. 35% of newborns, 15% of six-month-old babies and 3–5% of primary schoolchildren may have an enlarged spleen. This fact is not a sign of disease.
Possible causes of pathology, including giardiasis and blood diseases
Depending on the reasons that caused splenomegaly, the pathology is conventionally divided into the following types:
- Functional enlargement of the spleen in response to the impact of infections on the body - viral, bacterial, fungal, parasitic. This type of splenomegaly can be caused by:
- mononucleosis;
- hepatitis;
Inflammation of the liver can lead to splenomegaly
- tuberculosis;
- sexually transmitted infections, in particular syphilis;
- toxoplasmosis;
- giardiasis;
- malaria;
Malaria is a parasitic infection of red blood cells
- cytomegalovirus infection;
- Enlargement of the organ due to stagnation of venous blood. This type of pathology develops against the background of increased growth of vascular tissue and an increase in the number of red blood cells. Stagnation of blood can be caused by the formation of clots or compression, for example, by a neoplasm, of large veins, such as the portal, hepatic or splenic;
- Hypertrophy of the spleen as a result of the accumulation and destruction of blood elements in it. In this case, the development of pathology can be caused by the following reasons:
- hemolytic autoimmune anemia;
- sickle cell anemia;
Sickle cell anemia is a hereditary hematopoietic disease
- neutropenia and thrombocytopenia, also caused by autoimmune factors;
- continuous hemodialysis, during which the cell membranes of blood elements are destroyed;
- Enlargement of the spleen, which is a consequence of the activation of the synthesis of altered blood elements during tumor lesions of the hematopoietic system. In this case, the cause of the development of pathology may be the following diseases:
- myeloid leukemia;
- myelosis;
- lymphocytic leukemia;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- polycythemia vera;
- essential thrombocythemia;
- lymphoblastoma;
- Hodgkin's lymphoma;
- myeloma;
- Enlargement of an organ caused by mixed reasons, usually associated with the accumulation of various kinds of substances in it and mechanical damage. This category of reasons includes:
- spleen cysts of various etiologies, including parasitic ones;
- amyloidosis;
- Gaucher disease;
- histiocytosis;
- rupture of the spleen with bleeding within the organ;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
Systemic lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune generalized lesion of the skin and internal organs.
- thyrotoxicosis.
Causes of splenomegaly
The spleen is an important component of the immune system. An increase in functional activity, an increase in blood flow speed and organ size accompanies a large number of diseases of both infectious and non-infectious nature. The main reasons for the development of this pathology include:
- Infectious diseases
. An increase in size occurs as a result of increased immune load on the organ due to bacterial (syphilis, tuberculosis), viral (HIV, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus), fungal (blastomycosis, histoplasmosis), parasitic (schistosomiasis, echinococcosis), protozoal (malaria, leishmaniasis) acute and chronic infections. - Autoimmune diseases
. Hyperplasia develops with an increase in the phagocytic function of the spleen, activation of the reticuloendothelial system against the background of autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, periarteritis nodosa). - Myeloproliferative diseases
. Splenomegaly is formed during malignant transformation of bone marrow cells, which is accompanied by their excessive proliferation and impaired hematopoiesis, including in the spleen. These conditions include polycythemia vera, myeloid leukemia, and myeloid metaplasia. - Neoplasms of various etiologies
. Enlargement of the organ may be associated with benign and malignant formations of the spleen, tumors of the hematopoietic system (lymphoma, acute and chronic leukemia) and with metastasis from other foci (lung cancer, liver cancer). - Hematological disorders
. The syndrome develops against the background of increased functional load on the spleen due to hereditary and acquired blood diseases (hemolytic anemia, thalassemia, cyclic agranulocytosis, etc.). - Metabolic disorders
. Splenomegaly occurs as a result of infiltration of the parenchyma by macrophages, lipids or other metabolites in acquired and hereditary metabolic disorders (phenylketonuria, Wilson's disease, Zolweger's syndrome, glycogenosis, etc.). - Circulatory disorders
. When the outflow of blood through the venous channel is disrupted as a result of stagnation, vascular tissue grows, the number of red blood cells increases, pressure in the portal system increases, and organ hypertrophy develops. This condition can be caused by thrombosis of the splenic vein, torsion of the vascular pedicle of the spleen.
Reasons for the increase
An enlarged spleen can occur due to various reasons. This pathology is called splenomegaly. The change in the size of the spleen is affected by stagnation of venous blood. Due to impaired blood flow, vascular tissue and the number of red blood cells grow, which leads to the development of Banti disease.
Congestion can occur when pressure in large veins increases due to a blood clot or severe heart failure.
The main reasons for an enlarged spleen are:
- Bacterial and viral infections
- Parasitic infections
- Neoplasms
- Liver diseases
- Blood diseases
- Hemolytic anemia
- Presence of cysts
In many cases, splenomegaly occurs as a result of various infections (hepatitis, rubella, measles, mononucleosis, etc.). The spleen is affected when helminths and arthropods enter the body.
The cause of an increase in the size of the spleen can be autoimmune diseases such as lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and periarteritis.
In case of damage to the spleen and the resulting tumors, ulcers, cysts or infarctions also affect the functioning of this organ. Formed elements in blood diseases are destroyed, and this entails an enlargement of the spleen. This is usually observed with hemolytic anemia, congenital spherocytosis, neutropenia, thrombocythemia, etc.
Symptoms
With an enlarged spleen, no special signs are observed. Many may not know about this, and then discover the pathology during a medical examination.
Most often, clinical manifestations are observed with a significant size of the spleen, due to which surrounding organs are compressed.
Clear signs of an enlarged spleen:
- Pain in the left hypochondrium
- Bloating
- Constipation
- Heartburn
Pain on the left side may intensify when you sigh and radiate to the shoulder. If compression of the stomach occurs due to an enlarged spleen, the patient may have a lack of appetite or a feeling of fullness in the stomach.
A slight increase in body temperature, night sweats, weight loss, drowsiness, fatigue, and weakness may also occur.
In later stages, the temperature can rise to 40 degrees. Nonspecific symptoms of splenomegaly include poorly localized abdominal pain and bloating. If you have these symptoms, you can contact a hematologist, oncologist or gastroenterologist.
Diagnostics
To diagnose splenomegaly, your doctor will do a visual examination. Upon palpation, an enlarged spleen can be detected. To identify the cause of the disease, a series of laboratory tests are performed.
The doctor prescribes a complete blood count, as well as a blood smear to assess the number and composition of white blood cells and other formed elements.
It is also necessary to take a biochemical blood test, which can be used to determine possible pathologies of the liver or pancreas. In addition, you can determine the content of trace elements in the blood. To monitor the condition of the urinary tract and kidneys, a general urine test is performed. To evaluate the functioning of the digestive system, a coprogram is performed. A stool test is also taken to check for the presence of worm eggs and protozoa. To identify the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics, blood cultures are prescribed.
In addition to laboratory tests, instrumental diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- Ultrasound
- Computed tomography
- Sternal puncture
- Biochemical markers
More information about the functions of the spleen can be found in the video.
Thanks to an ultrasound examination, you can check the condition of all organs of the abdominal cavity.
Computed tomography allows you to assess the condition of the spleen in detail and identify a tumor or damage.
If a disease of the circulatory system is suspected, a sternal puncture is performed, during which a puncture is made in the anterior wall of the sternum. It is possible to conduct a genetic study in case of suspected hereditary diseases, which led to an enlarged spleen. After the results of the study and diagnosis, treatment is prescribed.
Classification
In gastroenterology, the syndrome is classified depending on its etiology and pathogenesis. There are two forms of splenomegaly, which have different nature and clinical manifestations:
- Inflammatory
. Occurs against the background of a bacterial, viral, protozoal, fungal infection (acute viral hepatitis, rubella, tuberculosis, salmonellosis, malaria, etc.). It manifests itself with a clear clinical picture and general intoxication of the body. - Non-inflammatory
. Develops as a result of various diseases of a non-infectious nature (anemia, amyloidosis, cirrhosis of the liver, leukemia). In this case, the symptoms of the underlying disease are more pronounced, the clinical manifestations of the spleen are blurred.
Forecast
As a rule, the prognosis does not depend on the patient's age or previous splenectomy , but is determined by the underlying disease . Accordingly, survival and mortality vary widely depending on the pathological process causing the enlarged spleen, the presence of internal bleeding and organ failure.
Death directly from splenomegaly occurs extremely rarely, but may result from an unsuccessful postoperative period.
An enlarged spleen can be damaged by trauma, such as a blow to the abdomen, as its lining is thinned.
In this case, conservative treatment (without surgery) is usually offered, which is selected depending on the condition of the spleen, its membranes and hemostatic function.
Video on the topic: Infectious mononucleosis. What it is?
Symptoms of splenomegaly
The clinical picture depends on the initial pathology, causes and degree of organ enlargement. In most cases, the symptoms of the primary disease come to the fore. Inflammatory splenomegaly is accompanied by an increase in body temperature to febrile levels, nausea, vomiting, loose stools, and severe weakness. Painful sensations are often sharp and cutting in nature and are localized in the left hypochondrium.
With a non-inflammatory etiology of the disease, the body temperature is normal or subfebrile. There is a dull aching or pressing pain in the left hypochondrium of low intensity. General symptoms of intoxication are absent or mild. Splenomegaly syndrome is accompanied by the appearance of pale skin with a bluish tint, decreased appetite, and decreased performance. There is often a simultaneous increase in the size of the spleen and liver - hepatosplenomegaly. In this case, the main symptoms are accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the hypochondrium on the right.
Types of splenomegaly
In the vast majority of cases, this syndrome is not independent; an increase in size or atrophy of the spleen tissue occurs as a consequence of various diseases. The genesis of splenomegaly can be different.
Inflammatory
Splenomegaly
May occur after bacterial and viral infections. Intoxication of the body occurs with toxic waste products of protozoa, microorganisms and parasites. Purulent processes can lead to changes.
Another reason is acute circulatory disorders in the tissues of the spleen or mechanical damage caused by injuries of various types. During such violations, not only do punctate hemorrhages appear, but nearby tissues are also damaged. An abscess may begin and, as a result, acute inflammatory processes. The disease is manifested by a sharp increase in body temperature, pain in the spleen, loose stools and nausea. There are several forms of the disease.
Photo of the removed spleen, greatly enlarged in size
1. Non-inflammatory
The first cause of the disease is anemia of the spleen tissue. As a result of various diseases, hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood sharply decrease. Due to insufficient oxygen, tissues die, as a protective reaction, increased division of surviving cells begins, and the size of the organ increases significantly.
The second reason is systemic dysfunction of vital organs. Including the circulatory system, heart, lungs, etc. During this splenomegaly, the temperature rarely exceeds +37°C, and there is no pain when palpated at the first stage of the disease. The pain is weak and aching.
Symptoms of splenomegaly
2. Mixed
It has the most complex clinical manifestations, is difficult to treat, and requires great effort from the doctor and the patient. The impetus for the occurrence of splenomegaly is simultaneously several reasons, including hereditary ones at the gene level. Symptoms vary depending on the course of the disease.
Complications
The most serious complications of splenomegaly include splenic rupture. This condition is accompanied by massive bleeding and leads to the development of hemorrhagic shock, and in the absence of emergency measures, to death. Dysfunction of the spleen can be combined with intraorgan destruction of blood cells, the occurrence of hypersplenism, which is accompanied by leukopenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia. As a result, blood clotting is impaired, the immune function of the body decreases, and hypoxia develops. This condition can lead to life-threatening consequences (shock, bleeding).
Splenectomy
Congenital absence or surgical removal (splenectomy) does not have a profound effect on the viability and growth of the organism.
Removing an organ increases susceptibility to bacterial infections, especially in young children.
Removal surgery is indicated for excessively active destruction of red blood cells and the development of anemia, a decrease in the level of leukocytes and platelets. If the size is too large, which interferes with the functioning of other internal organs. In case of bleeding or partial destruction of an organ.
Diagnostics
Primary diagnosis consists of consulting a gastroenterologist. During a physical examination, a specialist palpates a pathologically enlarged organ and percussion identifies altered splenic dullness. By studying the history of life and illness, the doctor can suggest the cause that led to the development of splenomegaly. To confirm the diagnosis and carry out differential diagnosis, the following instrumental studies are prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the spleen
. Allows you to determine the size and shape of the organ. Detects injuries, inflammatory processes, neoplasms and abnormalities of the spleen. - Plain radiography of the abdominal cavity
. The images reveal an enlarged spleen and displacement of nearby anatomical structures (stomach, intestines). With fluoroscopy, the spleen is mobile and participates in the act of breathing. - MSCT of the abdominal cavity
. A modern research method that allows you to obtain a detailed image of the organ. When the primary disease is localized in the abdominal cavity (tumor, hydatid cyst), this method helps determine the cause of splenomegaly. - Spleen scintigraphy
. Using radioisotope research, it is possible to determine the functional state and focal changes in the splenic parenchyma. At the same time, liver scintigraphy is often performed, which can help in finding the cause of the disease.
In case of a pronounced clinical picture with symptoms of intoxication, OAC, biochemical blood test, and OAM are prescribed. Splenomegaly is differentiated from benign and malignant formations, abscess, and splenic cyst.
Diagnosis of an enlarged spleen
► First degree: there is an enlargement of the spleen upon palpation one finger from under the costal arch.
► Second degree: the spleen is palpated to the middle of the border between the hypochondrium and the navel.
► Third degree: the enlarged spleen reaches the midline.
► Fourth degree: the huge spleen penetrates the right abdomen or pelvis.
The attending physician begins complex treatment only after a detailed diagnosis that determines the causes of the enlarged spleen. In addition to palpation of the organ, computed tomography and radiographic examination of the abdominal organs are used.
A blood test determines a decrease in the number of blood cells: platelets, red blood cells and white blood cells. In some cases, the doctor determines the cause of the enlarged spleen by the size and shape of the blood cells.
Treatment of splenomegaly
Treatment tactics are based on finding and eliminating the causative disease. In case of infectious processes, therapy is carried out taking into account the causative agent of the disease (antibacterial, antiviral, antiprotozoal drugs, etc.). For autoimmune pathology, hormonal drugs are prescribed. For hematological diseases and neoplasms, antitumor drugs, radiation and chemotherapy, and bone marrow transplantation are used. Inflammatory splenomegaly with severe symptoms of intoxication require detoxification and anti-inflammatory therapy. Vitamins and mineral complexes and painkillers are prescribed symptomatically.
If the spleen is large, some storage diseases (amyloidosis, Gaucher disease, etc.), hypersplenism, thrombosis of the portal and splenic veins, the organ is removed (splenectomy). A diet for splenomegaly involves avoiding fried, smoked, canned foods, and alcoholic beverages. It is recommended to reduce the consumption of baked goods, mushrooms, coffee, chocolate, and carbonated drinks. Preference should be given to lean meats (rabbit, beef), vegetables (peppers, cabbage, beets), cereals, fruits and berries (citrus fruits, bananas, apples, raspberries, etc.). For drinks, it is recommended to drink weak tea, fruit drinks and homemade compotes.
Prevention of splenomegaly
No one can give a 100% guarantee that it will be possible to avoid the disease, even following all the rules. First of all, you should reconsider your lifestyle, and you need to start with nutrition and physical activity. The main rule of physical activity is the moderate use of one’s strength. With frequent reboots, the spleen may not be able to withstand it and rupture. It is important to stop smoking and drinking alcohol. Physical education and sports and bad habits are incompatible.
You should strengthen your immune system as much as possible, get vaccinated and take vitamins. It is recommended to protect the abdomen and chest area from strong and medium impacts. It is important to undergo examinations by doctors at least once every 12 months; you should avoid serious illnesses and advanced stages of influenza, colds and similar ailments.
Like many pathologies, this disease often develops due to neglect of one’s health. It is easier to avoid the manifestation of a disease than to later be treated for it and go on diets all your life. But if something unpleasant has already happened, you must follow the instructions of your doctor. You should not hope that the disease will go away on its own.
In advanced cases, the disease cannot be cured, and even after the spleen is removed, the person will not be able to live a full life. Therefore, it is better not to delay treatment and, at the first manifestations of the disease, go for tests and undergo an examination.
What is splenomegaly
Splenomegaly is an abnormal enlargement of the spleen associated with the occurrence of any pathological process in the body and is not an independent disease. In simple words, this is a symptom of an enlarged spleen. The symptom itself is not dangerous, but in any case, an in-depth diagnosis aimed at identifying the causes is required.
Normally, the spleen cannot be felt during palpation. In an adult, the functions of the spleen are as follows:
- Participation in the formation of immunity is filtering out harmful bacteria and viruses, retaining blood antigens and creating antibodies that are so important for protecting the body from diseases.
- Removal from the general bloodstream, absorption and neutralization of old red blood cells.
- Accumulation of spare blood and saturation of the body with it in emergency situations. With significant blood loss, the spleen releases a supply of platelets and red blood cells into the general blood stream, thus saturating the body with the necessary oxygen.
Splenomegaly in children, features
If an enlarged spleen in adults is a possible signal about the development of a pathological process in the body, then splenomegaly in children is not always a cause for concern.
Normally, the spleen of some babies may slightly exceed the maximum threshold values taking into account age. Thus, in a newborn, a deviation in the length of this organ of up to 30% is considered acceptable. By six months of age, the spleen can exceed the maximum threshold length by 15%, and by three years it can differ from the norm by only 3%.
If a baby is diagnosed with splenomegaly, he is required to undergo a full range of diagnostic procedures. It is necessary to take general and biochemical blood tests, examine urine, and conduct a stool examination - a coprogram.
Since helminthic infestations and infections are a common cause of spleen enlargement in children, examination of stool for worm eggs, immunological analysis for the presence of protozoa and bacteriological blood testing to identify the infectious agent and its drug resistance are indicated.
The doctor receives basic data on the degree of enlargement of the organ, its structure, the presence or absence of neoplasms in it after an ultrasound scan of the spleen. Treatment will be required if any pathologies that trigger the development of splenomegaly are identified.
However, there are situations when an enlarged spleen in a child is not a sign of pathology. This symptom is just a reason for a serious examination, but not necessarily a warning about the danger of a serious illness.
Causes of splenomegaly
As already mentioned, splenomegaly is caused by another disease in the body - from cancer to common inflammatory infections. In 70% of cases, the cause of an enlarged spleen is cirrhosis of the liver. Other possible causes of an enlarged spleen:
- Viral infections, such as mononucleosis.
- Bacterial infections, in particular syphilis, as well as bacterial endocarditis.
- Parasitic infections, such as malaria.
- Chronic hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis C, cirrhosis and other liver diseases.
- Injuries to the spleen due to injuries to the abdominal cavity.
- Various hemolytic anemias are conditions in which premature breakdown of red blood cells occurs.
- Oncohematological diseases - leukemia and Hodgkin's lymphoma.
- Metabolic diseases.
- Increased pressure in the veins passing through the liver or spleen, as well as thrombosis of these veins.
- One of the causes of splenomegaly is stagnation of venous blood in the spleen. The venous network is well developed in the spleen. Therefore, when the outflow of venous blood from it is disrupted, it increases. When blood accumulates in this organ, vascular tissue begins to grow and the number of red blood cells increases.
It is worth noting that in hematopoietic pathologies and autoimmune diseases, characteristic splenomegaly occurs in the early stages of the disease. The organ quickly and greatly increases in size and is easily detected even when independently palpating the epigastric region.
- Children and young people infected with viral mononucleosis.
- Residents and visitors to areas where malaria is endemic.
- Suffering from Gaucher disease, Niemann-Pick disease and some other hereditary metabolic diseases affecting the condition of the liver and spleen.
Symptoms
The overall clinical picture, in this case, is quite ambiguous, since the nature of the symptoms will mainly depend on the underlying factor. However, in general, it is possible to identify signs that are characteristic of a certain form of the pathological process. So, with the inflammatory nature of the enlargement of the spleen, the symptoms may be as follows:
- pain in the left side of the abdominal cavity;
- a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the stomach, as the spleen, enlarging, puts pressure on the walls of the organ;
- increased body temperature;
- intoxication;
- nausea, rarely with vomiting;
- pale skin, bruises under the eyes;
- increased night sweats;
- weight loss.
The non-inflammatory form has a rather sparse clinical picture - occasionally the patient may be bothered by nagging pain in the left area of the abdominal cavity, the temperature rarely rises to low-grade fever.
Enlargement of the liver and spleen can be caused by viral hepatitis, which manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- ARVI symptoms;
- headache;
- increased fatigue and weakness, which is caused by intoxication of the body;
- yellowing of the skin;
- disruption of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- nausea, often with vomiting, vomiting does not bring relief;
- sleep disturbance.
Since this clinical picture is similar to influenza or ARVI, most patients do not seek medical help in a timely manner. Organ enlargement can be diagnosed only in the advanced stages of viral hepatitis.
In case of pathologies of the genitourinary system, the clinical picture can be characterized by the following signs:
- a feeling of discomfort and aching pain in the left region of the abdominal cavity;
- a feeling of fullness in the stomach even with a minimal amount of food consumed;
- frequent urge to urinate, burning and itching after bowel movement;
- Women may experience menstrual irregularities;
- decreased desire for a sexual partner, discomfort during sexual intercourse.
The reason that the spleen is enlarged may be tuberculosis of this organ. However, the clinical picture in this case, until a certain stage of development, has practically no specific signs. In the later stages of the development of this disease, the clinical picture may be supplemented by the following manifestations, which can be determined by laboratory and instrumental methods:
- a sharp decrease in the number of leukocytes, platelets;
- poor blood clotting, which can lead to hemorrhage;
- the organ itself has a densely elastic consistency, with places of softening in the area of caseous decay.
In some cases, splenic tuberculosis is a complication of liver cirrhosis.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
The spleen may become enlarged while performing its normal functions in response to another disease. Some infections and diseases that affect blood cells increase blood flow to the spleen. Additionally, diseases affecting the spleen are common causes of enlargement. Splenomegaly is not always an abnormal condition, and the size of the spleen does not necessarily indicate a dysfunction.
Since splenomegaly is a consequence of many different diseases, there are no specific symptoms.
Possible symptoms of splenomegaly:
- Infectious and inflammatory splenomegaly can be manifested by fever, pain in the left hypochondrium, as well as nausea, vomiting and stool disorder.
- As for non-inflammatory forms of splenomegaly, they can be manifested by a slight increase in temperature, mild pain in the left hypochondrium and slight pain when palpating the left hypochondrium.
- Other clinical signs, as a rule, depend on the manifestations of the underlying disease; sometimes pain is observed on the left side of the spleen.
Unfortunately, splenomegaly can be asymptomatic for a long time. If an enlarged spleen is detected, it is necessary to identify and eliminate the causative disease against which the spleen enlarges.
Enlarged spleen
This condition is medically called splenomegaly. An enlarged spleen, as a rule, can be easily palpated (palpated). It is well known that in a healthy person the spleen cannot be palpated. However, in certain unforeseen cases, the organ is capable of more than doubling its size.
As noted above, the weight of a healthy spleen is 150 g. Its dimensions are 10-11 cm in length and 3-4 cm in width. The diagnosis of splenomegaly is usually made when the spleen is enlarged more than 200 g.
Other cases, when the enlargement of the organ does not exceed acceptable limits and are diagnosed by “light percussion”, echography or tomography, are not considered a violation.
Why does the spleen increase in size?
An enlarged spleen can increase the uptake of blood cells, but this situation has the other side of the coin - in the process of extracting a large number of pathogenic cells from the circulatory system, the filtering ability of the spleen deteriorates. This is another reason for the large increase in the size of the spleen.
Gradually, the pathological process can go so far that an unacceptable number of cells begin to be removed from the circulatory system. This phenomenon is called hypersplenism - the pathological destruction of blood cells, causing a decrease in platelets, red blood cells or white blood cells.
Thus, a decrease in the number of red blood cells leads to anemia. In turn, a decrease in the number of leukocytes provokes the development of infectious diseases. A decrease in the number of platelets has a detrimental effect on hemostatic functions.
If the causes of spleen enlargement are not determined in a timely manner and appropriate comprehensive treatment is not started, the spleen will destroy completely healthy cells along with pathological ones.
The spleen tends to increase in size with concomitant not only somatic, but also oncological diseases.
List of the most common causes of an enlarged spleen
- Leukemia, granulomatosis.
- Liver diseases - cysts, tumors, cirrhosis.
- Hematological pathology - leukemia, immunoleukemia, anemia.
- Severe chronic and acute infectious diseases - syphilis, malaria, brucellosis.
- Pathological changes in blood circulation.
- Opisthorchiasis.
How is splenomegaly diagnosed in adults?
- When diagnosing a disease, information is initially collected from the patient’s words. It is necessary to find out what disease led to the enlargement of the spleen and what the patient’s complaints are. The doctor usually finds out how long these symptoms have been bothering the person and what he associates with their occurrence. The doctor also needs to know whether the patient visited exotic countries before the onset of the disease, whether there were changes in the general condition, whether the patient smokes or abuses alcohol.
- Laboratory research methods include clinical and biochemical blood tests, coagulogram, general urine test, coprogram, stool test for the presence of helminths, as well as bacterial blood culture.
- Ultrasound of the spleen. The purpose of an ultrasound examination is to confirm or refute the presence of injuries to the organ being examined, neoplasms, inflammatory processes and developmental anomalies
- If it is necessary to confirm splenomegaly in cases of questionable results after a preliminary examination, ultrasound is the method of choice due to its high accuracy and low cost. CT and MRI can provide more detailed images of the organ. MRI is particularly useful in identifying portal thrombosis or splenic vein thrombosis. Radioisotope testing is a highly accurate diagnostic method that can identify additional details of splenic tissue, but the method is very expensive and difficult to perform.
If the patient does not feel ill, has no symptoms of illness other than those due to splenomegaly, and there is no risk of infection, there is no need for a wide range of tests other than a complete blood count, peripheral blood smear, liver function tests, abdominal CT scan cavity and ultrasound of the spleen.
The role of the spleen in the body
The organ is located in the upper part of the abdominal cavity under the ribs on the left. The spleen has a slightly elongated oval shape. The main task of this organ is to properly regulate the process of hematopoiesis. At the same time, the blood is filtered from harmful organisms, bacteria and toxins.
This feature makes the system one of the most important centers of the lymph nodes. After purification, pathogenic particles completely disappear, in particular we are talking about dead red blood cells, which can cause cancer. At the slightest attempt to penetrate the body of viruses and infections, the tissues of the spleen will begin to work in an enhanced mode, also sending signals to other parts of the lymphatic system.
Attention! Thanks to the presence of the spleen, it is also possible to regulate the coagulation of blood cells, which protects our vessels from thrombosis and dangerous bleeding. The organ directly responds to changes in other systems, which leads to its rapid increase.
Role of the spleen
Treatment
Treatment of splenomegaly, as a rule, comes down to eliminating the causative disease that caused the enlargement of the spleen. Therapy can be carried out using antibacterial drugs (if splenomegaly has a bacterial etiology). Treatment of tumors and diseases of the hematopoietic system consists of the use of antitumor drugs. Hormonal drugs and vitamin therapy are widely used.
- leukocyte transfusion;
- platelet transfusion;
- treatment of the patient with glucocorticoids (prednisolone is prescribed in the amount of 20-40 milligrams per day for 4-6 months);
- removal of an enlarged organ or splenectomy (prescribed if conservative treatment does not bring results).
Causes of enlarged spleen and liver: which spleen should be normal?
Spleen
Liver is the body’s protective filter. The spleen is also responsible for processing and filtering harmful substances in the human body.
What kind of spleen should be normal? Here is the answer:
- Normal sizes: length - 12-16 cm, width - 6-8 cm, thickness - 2-4 cm, weight - 100-200 g.
The liver has its own indicators:
- The width of the gland is from 23 to 27 cm, length is 14-20 cm, transverse size is 200-225 mm, the edges of the organ are clear and even.
If the liver is enlarged:
- This could be a warning sign.
- It is necessary to conduct an examination of the entire body, and especially of this gland.
- Normally, the liver is not enlarged. If after an ultrasound the doctor reports that the liver is enlarged, then treatment is needed.
- Normally, the liver should not protrude from under the costal arch and there should be no pain.
- If the liver is enlarged, it is necessary to exclude a tumor or infection with the help of additional studies.
Cause of liver enlargement:
- May be hidden in hepatitis, cirrhosis, alcohol intoxication.
- The liver enlarges during intoxication due to the use of antibiotics and hormonal drugs.
Liver treatment:
- It depends on its size and on what diagnosis the doctor makes.
- Medicines are prescribed.
- To this it should be added that diet is important. You need to eat often, in small portions. You need to eat about six times a day. The interval between meals should be about 4 hours. Dinner should preferably be held no later than 19.00.
- Animal fats should be avoided.
- Treat foods, including vegetables, thermally.
- Diet No. 5 according to Pevzner is shown.
- It is also necessary to add more plant fibers, foods rich in antioxidants and amino acids to the diet.
If the spleen is enlarged:
- If this organ begins to grow and a person feels severe heaviness in its area, you need to consult a therapist.
- The initial examination helps the doctor make a preliminary diagnosis.
- Then the patient is referred to a specialist.
- If you have heartburn, aching sensations in the left hypochondrium, bloating, gas, weakness and sweating, you need to consult a doctor, these are signs of a diseased spleen.
- It is possible that this is an infection or toxins that have entered the body.
The reasons for an enlarged spleen can be different. Perhaps the following pathologies develop in the body:
- Mononucleosis
- Hepatitis
- Tularemia
- Typhoid
- Purulent reactions to some problems in the body
- Endocarditis
- Problems are most often associated with infections
- There may also be congestion in the spleen
Treatment for an enlarged spleen:
- Therapy in the field of spleen diseases is aimed at reducing the activity of the underlying disease.
- It is important to stop the growth of the organ.
- There are many specific and highly specialized medications, but only a doctor should prescribe them.
Remember: Self-medication is dangerous!
- If doctors have diagnosed cancer, chemotherapy will be needed.
- Autoimmune diseases cannot be cured, but they can be stopped.
- In some cases, surgery is performed to remove the spleen.
Currently, many people prefer to be treated at home on their own, without going to the doctor. But it's not right. The doctor must make a diagnosis, prescribe treatment, and only then can you begin to make healthy healing herbal decoctions.
Spleen size in moderate splenomegaly
If palpation reveals an enlarged spleen, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound. The method reveals the exact location, weight, length, width of the organ. Splenomegaly occurs:
- moderate, which manifests itself temporarily;
- pronounced, observed in individuals with various diseases.
The doctor identifies the type of condition to determine the cause and prescribe treatment. Splenomegaly comes in different sizes in adults and children. For each age, doctors determine the normal size of the spleen.
When palpating, the exact dimensions cannot be determined; the parameters are assessed during ultrasound. An image of the spleen is displayed on the screen, the doctor calculates the length, width, and weight.
In adults
Moderate splenomegaly includes parameters for an adult:
- length from 13 to 20 cm;
- weight from 350 to 500 g.
If the measurement parameters exceed these numbers, the doctor writes in the medical history about a severe form of splenomegaly. In this case, the spleen is enlarged so much that it will stand out from under the ribs (visible to the naked eye). With moderate enlargement of the organ, it can be slightly felt under the left ribs; exceeding the parameters is a temporary phenomenon.
This is interesting: Enlarged liver in an infant: causes and treatment of hepatomegaly in a newborn
In children
Splenomegaly in a child is most often physiological. Therefore, the diagnosis of moderate splenomegaly may be made erroneously. This condition is observed in schoolchildren, but this does not indicate a disease.
If splenomegaly is caused by a disease, then in children it is most often helminthic and parasitic infestations, since children spend a lot of time in the sand and do not always wash their hands.
Diet food
An enlarged spleen (the causes and treatment of this pathology are related to diet) needs menu adjustments. Without reducing the load on the organ, it is impossible to achieve a sustainable positive result, therefore, when treating the spleen, it is necessary to exclude harmful foods.
Table of foods for an enlarged spleen:
| Category | List of products |
| Allowed |
|
| Limited |
|
| Prohibited |
|
Medicinal infusions
An enlarged spleen (the causes and treatment of this disease can be different) needs a reduced load and appropriate therapy. Before you begin traditional methods of treatment, you should ask your doctor about the advisability of using certain components.
The most effective recipes for infusions:
- Hop cones . Pour 1 part of the herbal component into 4 parts of alcohol with a strength of 40%. After this, leave in the dark for 10 days, shaking the container occasionally. At the end of the period, clean the infusion from impurities. You need to drink 40 drops daily until it runs out.
- Shepherd's purse . Steam 250 ml of boiling water with 10 g of plant collection, leave for 20 minutes. Subsequently remove impurities. Drink the product 5 times during the day, drinking 30 ml of infusion.
- Healing collection of herbs No. 1 . Combine the greens of nettles, strawberries, strings, and tricolor violet flowers in equal quantities. Steam 1 liter of boiling water with 100 g of the resulting herbal mixture. After 60 min. clean the infusion. You need to drink the product daily, drinking 200 ml of infusion three times a day
- Healing collection of herbs No. 2 . Combine chamomile inflorescences, nettle herbs, St. John's wort, fennel, immortelle and angelica rhizome in the same volume. After 3 hours, clear the infusion. You need to take it three times a day, drinking 200 ml of the drink at one time.
- Common agrimony . Pour 15 g of the plant collection into 250 ml of boiling water and leave for 1 hour. Then clean the product from impurities. Take 30 minutes before your main meal. For 1 day you need to drink 1 tbsp. infusion.
- Rose hip . Pour 60 g of plant fruits into a thermos and pour 1 liter of boiling water. Leave it overnight. Drink the entire product the next day in equal parts, taking the drink after meals.
- St. John's wort . Steam 10 g of herb with boiling water in a volume of 250 ml. Leave for half an hour, clean. Take ¼ tbsp. 3 times a day.
- Strawberry . Grind the leaves and berries of the plant separately and take 15 g of each component. Pour the mixture into a thermos and pour boiling water (800 ml). Leave for 3 hours. You should drink 250 ml of the drink at a time in the form of tea three times a day.
- Field bindweed . Pour 30 g of herbs into 200 ml of 3% vinegar. Infuse the product for 1 day in the dark. At the end of the period, clean it. For oral administration, dissolve 1 tsp. the resulting product in 100 ml of water. This procedure should be carried out 2 times a day: morning and evening.
- Lesser periwinkle . 1 tsp. Infuse the collection of the plant in 1 tbsp. boiling water 20 min. When the time is up, clear the drink. Take the medicine three times in equal parts during the day, regardless of the main meal.
- Rosehip, dandelion, sorrel . This product must be prepared separately. 1 tbsp. l. Steam rosehip root with boiling water (250 ml). Infuse 2 hours of 15 g of dandelion root in boiling water (200 ml) in a thermos for 4 hours. Steam sorrel leaves (30 g) with boiling water (200 ml), leave for half an hour. At the end of time, clean all healing infusions. Take: in the morning - rosehip infusion, in the afternoon - dandelion, in the evening - sorrel, drinking the entire drink in one dose. Therapy is carried out for 60 days, and if necessary, repeat after 3 months.
Symptoms of pathology and what it means
The clinical picture of splenomegaly is ambiguous, because it depends on what exactly triggered its development. In general, there are such general signs of the inflammatory form of pathology as:
- pain in the left side of the peritoneum;
- heaviness and overcrowding in the stomach area, developing due to the fact that the spleen enlarges and begins to put pressure on the walls of the neighboring organ;
- increase in body temperature;
- intoxication;
- nausea, rarely with productive vomiting.
Pallor of the skin, bruises under the eyes, as well as an increase or occurrence of night sweats, and a sharp and unmotivated decrease in body weight are likely to occur.
The non-inflammatory form is characterized by a rather poor clinical picture. So, the patient is rarely, but still bothered by nagging painful sensations in the left side of the peritoneum. Temperatures may increase, but only to low-grade fever.
At the same time, for example, with pathologies of the genitourinary system, the symptoms are as follows:
- discomfort and painful aching sensations in the left side of the peritoneum;
- overcrowding in the stomach even with the minimum ratio of food consumed;
- constant urge to urinate, severe burning and itching after each productive urge.
Thus, we can say with confidence that the characteristics of the symptoms can be used to judge the form of the disease and the reasons for its development. Given the criticality of the symptoms, it is very important to cure the spleen if it is enlarged, and how exactly to do this will be discussed below.
Treatment methods
Treatment of splenomegaly is carried out only in inpatient conditions. Treatment with folk remedies at home is prohibited, as this can lead to a worsening of the patient’s condition, as well as the development of complications.
The first thing that medical specialists need to do is to find out the true reason for the progression of the pathological condition in the patient. It is important to accurately establish the disease that caused the splenomegaly, since first of all it is necessary to cure it.
Treatment of splenomegaly in children and adults includes the use of:
- hormonal agents. Prescribed to slow down the development of the inflammatory process;
- antibacterial therapy. Indicated if it has been accurately established that splenomegaly has developed under the influence of viruses and bacteria;
- antitumor drugs. Prescribed in the presence of blood and liver ailments, as well as in the detection of tumor-like formations;
- vitamin therapy.
In severe clinical situations, they resort to surgical treatment - the organ is removed.
Decoctions
An enlarged spleen (the causes and treatment of inflammation of the organ must be determined by a doctor) can return to normal if medicinal decoctions are used that reduce the load on the organ.
Decoction recipes:
- Lovage . Pour 15 g of crushed rhizomes of the plant into a container and add 400 ml of water. Boil the product for 15 minutes. At the end of time, wrap the container with the broth. After 1 hour, clean. The medicine must be taken within 10 minutes. before eating, drinking a decoction of 80 ml at a time.
- Common pikulnik . Pour 400 ml of water into 100 g of plant collection. As soon as the product boils, remove from heat. Leave for 30 minutes and then clean. You should drink the healing decoction in small portions for 1 day.
- Silver wormwood . Steam 15 g of herb with 550 ml of boiling water, and then boil for another 15 minutes. When the broth has cooled, it must be cleaned and then pour in honey (30 ml). Drink a decoction of wormwood 40 minutes before. before meals, drinking 80 ml of healing drink at a time.
- Creeping wheatgrass . Pour 50 g of plant root with water (500 ml). Infuse the product cold for 3 hours, and after the time has elapsed, boil for 10 minutes. You should drink 70 ml of wheatgrass decoction before meals, after clearing it of impurities.
- Madder tincture . Add 400 ml of water to 15 g of plant root. Cook for 10 minutes, then cool and peel. Drink ½ tbsp. madder decoction twice a day before meals.
- Herbal decoction . Pre-grind the healing ingredients. And then mix in the following proportions: St. John's wort (1 tbsp), hop cone (1 pc.), rose hips (5 fruits), calendula flowers (1.5 tbsp), dill stem (1 tbsp. ). Place all components in one container and add 500 ml of water. Boil the product for 5 minutes, and then leave until it cools, wrapping the container in a warm scarf. Subsequently, the plant decoction should be cleared of impurities. During the day, drink the medicine 3 times, 80 ml before meals. The entire course is 14 days, then interrupt for 5 days, then repeat the therapy.
- Oak bark and soapwort root . Take 2 tbsp of each component. l. in crushed form. Fill the mixture with water in a volume of 1 liter. Boil for 5 minutes, without letting it boil too much. Allow the broth to cool and then peel. Drink the drink three times a day, mixing it in equal proportions with water. The entire course is 30 days, if necessary, repeat after a 2-week break.
- Dandelion officinalis . Grind the root of the plant. Pour 15 g of the mixture with water (250 ml). Boil for 20 minutes, without letting the mixture boil too much. Strain and take for tumors in the spleen, drinking hot medicine before going to bed at night.
- Pine buds . Grind the component. Steam the resulting mixture (1 tbsp) with boiling water (250 ml). Let stand for 30 minutes, and then cook for another 10 minutes, without letting the product boil too much. Clean and drink in case of severe pain, drinking 200 ml of the decoction at a time, warm.
Symptoms of the disease
An increase in the size of the spleen is considered a secondary pathological syndrome.
The non-inflammatory form of the disease is accompanied by aching pain from the left hypochondrium, as well as a feeling that the organ is “bursting.” The spleen is well palpated.
The inflammatory (infectious) form is accompanied by fever, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, general weakness, as well as subcostal pain on the left side of the body. And:
- heart rate increases;
- hemoglobin level decreases;
- body temperature rises;
- the oral cavity becomes “overgrown” with ulcers;
- the risk of bleeding increases.
Complications
Important! The most serious complication of the disease is considered to be organ rupture, accompanied by severe bleeding. Rupture of the spleen leads to hemorrhagic shock, and if emergency measures are not taken, the consequence is death.
Treatment of an enlarged spleen at home
The infectious form is treated comprehensively, using antibiotics, modulators and stimulants of the immune system. Gastroenterologists hospitalize the patient only in exceptional cases of acute manifestations of splenomegaly. If necessary, surgical intervention is indicated.
The non-inflammatory form is amenable to successful therapy with a favorable prognosis. Splenomegaly of non-infectious etiology is treated with gentle, proven phytotherapeutic agents. Herbal infusions and decoctions, applications and compresses are popular.
Folk recipes
Treatment of an enlarged spleen in an adult begins immediately after identifying the causes of the painful condition. The action of these folk remedies is aimed at reducing the size of the organ. To relieve the inflammatory process, ointments, tinctures and casseroles are prepared.
Honey ointment
A healing, highly effective, very ancient medicine based on butter, ginger root and bee honey.
- Melt 2 tbsp. l. butter in a water bath.
- Rub melted butter into 50 g of ginger on a fine grater.
- Pour the mixture into 2 tbsp. l. thin honey, and thoroughly grind to a cream-like state.
Rub honey ointment into the area of the affected organ before going to bed until it runs out. It turns out to be effective not only for splenomegaly, but also in the treatment of other internal organs, for example, kidney cysts. No special storage conditions are required for the ointment.
Raisin tincture
Getting ready before bedtime.
- Wash 50 g of dried grapes, add grape vinegar (200 ml) and leave overnight.
- In the morning, eat 5-6 berries on an empty stomach with 2 tbsp. l. vinegar tincture.
The course of treatment is 25-30 days.
Radish casserole with horseradish root
One large radish (any kind, but preferably black) is washed and the core is cut out of the root vegetable.
- Mix 3 tbsp. l. finely chopped horseradish root with 2 tbsp. l. honey
- Place the honey and horseradish mixture into the drained radish.
- Bake in the oven until done.
For 10 days, eat 2 tbsp in the morning. l., and before bedtime - 1 tbsp. l. casseroles. Keep refrigerated. Do not cook in advance, but bake one radish at a time. This remedy is also successfully used in the treatment of symptoms of pyelonephritis in women. To prevent the development of neoplasms, porridges, tinctures and decoctions are prepared.
Pea porridge
- Rinse and soak for 7-8 hours 7 tbsp. l. regular peas.
- Boil 250 ml of water and cook the peas until tender without adding salt.
- Cool and visually divide into 4-5 parts.
- Eat the first portion before 6 a.m., and the last portion no later than 3 hours before bedtime.
Herbal remedy against hemangioma and lymphoma
- Boil the kettle and measure out 125 ml of boiling water.
- Pour boiling water over 20 g of finely chopped chicory root.
- Cover the mixture for three quarters of an hour, then strain into a separate container.
Take 2 tbsp. l. three times a day for 21 days.
Useful tips
To relieve inflammatory processes in the human body, chicory is considered an effective remedy. Moreover, all parts of the plant are used.
- Steamed leaves are used as applications, applied to the body in the area of the diseased organ.
- Chicory flowers are brewed as tea and drunk several times a day. This is a very effective measure in the treatment of erectile dysfunction.
- Ready-made chicory extract (sold as a paste in small jars) also has a healing effect if used regularly as a daily drink.
- Tincture of hop cones is used as a natural analgesic and sedative.
- Rosehip decoction is very useful. It is prescribed to raise tone, and as a perfect fortification and strengthening of the body's immune system.
- A rosehip decoction with the addition of rapeseed and angelica root in a 1:1:1 ratio should be drunk, especially by men who experience rapid ejaculation.
Treatment with wormwood
A decoction based on wormwood will help quickly cure the spleen. Homemade medicine can cause allergies, so during the course of treatment, monitor your general health - if irritation appears on the skin, stop taking it and consult a doctor.
Preparation:
- Place 20 grams in a small container. wormwood.
- Bring water (220 ml) to a boil and brew the plant material.
- Infuse under the lid; to obtain a rich decoction, wrap the container with a towel.
- Filter, use gauze cloth folded in 3 layers.
- Add 25 gr. honey, mix.
Take the product three times a day, it is recommended to take it half an hour before meals. Dosage for one time – 100 ml. The duration of the course of treatment is two weeks.
Functions of the spleen:
- production of antibodies that fight pathogenic bacteria;
- blood purification;
- production of phagocytes and lymphocytes;
- control of red blood cells and platelets - destruction and disposal of non-viable cells (transportation to the liver for excretion along with bile);
- transportation and maintenance of fluid balance;
- platelet accumulation;
- removal of waste from muscle and joint tissues;
- participation in metabolism;
- in the prenatal period, the organ is responsible for the process of hematopoiesis.
Useful tips
Regardless of whether the operation was performed or the doctor limited himself to drug treatment, it is important to follow several tips:
- Start eating healthy, so you need to give up fatty, fried and smoked foods. You also need to avoid alcohol.
- The patient should eat 5-6 times a day, but in small portions.
- Avoid fast and sudden movements. Falls and even minor injuries can be dangerous for people in this condition.
- Spend as much time as possible outdoors.
Other folk remedies
Enlarged spleen (the causes and treatment of the pathology can vary significantly, but folk remedies will help relieve inflammation, regardless of the provoking factor) for maximum effect in treatment requires careful adherence to the dosage of the prescription components.
Effective recipes for healing remedies:
- Heat 60 ml of honey to a liquid consistency. Pour 30 ml of warm olive oil into it. Drink the product twice a day, drinking 1 tbsp at a time. l.
- Boil 250 ml of milk and then reduce the heat to low. Add 10 g of propolis to it. Stirring until the mixture is homogeneous. When ready, strain the mixture twice and remove the resulting layer of wax from above. For inflammation, drink warm milk 3 times a day, 70 ml.
- Select a large black radish tuber and wash it. Cut out the core of the vegetable and fill the resulting space with chopped horseradish root. Add honey (50 ml) to this mixture. Simmer the vegetable in the oven for 20 minutes. at a temperature of 100 degrees. Take the medicine in the morning - 60 ml, in the evening - 30 m. The entire course is 10 days.
- Grind the cucumber seeds to a powder. Take 1 tsp in the morning with a glass of water. Continue therapy for 15 days.
- Pour 500 ml of vodka into 100 g of propolis. Place the mixture in the dark and close the lid tightly. After 20 days, clean the product twice to remove impurities. Drink the tincture daily, mixing 30 drops of the medicine with 50 ml of water half an hour before meals. The entire course is 3 weeks.
- Mix 15 g of crushed ferula rhizome with 400 ml of vodka. It should be infused in the dark at room temperature. Shake the container periodically for 1 month. At the end of the period, clean the tincture. Take 20 drops of the product, dissolving with water twice a day.
- Pour 200 g of willow leaves with a special mixture, which includes 200 ml of vinegar (9%) and 100 ml of water. After 15 min. drain the liquid, squeeze out the vegetable pulp and apply it as a compress to the painful area. Place film on top and secure with a warm scarf. After half an hour, remove the product. The entire course consists of 12 procedures.
- Pour 50 g of chaga with hot water (1 l), leave for 4 hours. When the component softens, chop it and re-fill with hot water, but not boiling water, in the same volume. Leave for 48 hours in the dark, clean. Take 200 ml of the drink 3 times throughout the day. The entire course is 20 days, can be repeated after 6 months.
Human spleen
This important organ is located between the 9th and 11th ribs. The spleen is in a vertical position on the left side of the peritoneum. Externally, the organ resembles an oval. By and large, the spleen is the largest lymph node, which performs a very important function - it cleanses the blood of harmful microorganisms. At the same time, blood clotting and other metabolic processes occur.
The spleen performs very important tasks:
- Detects foreign antigens and produces antibodies.
- Dissolves solid particles formed from burns and other injuries.
- Takes part in the formation of immunoglobulin.
Causes
The origin of splenomegaly can be different, but it is always secondary. The following are possible causes of an enlarged spleen.
- Infection:
- acute bacterial (expressed as typhoid-paratyphoid diseases, miliary tuberculosis, sepsis);
- chronic bacterial (abdominal tuberculosis, syphilis, brucellosis);
- viral (acute viral hepatitis, measles, rubella virus, infectious mononucleosis);
- protozoal (expressed as malaria, toxoplasmosis, leishmaniasis);
- fungal (mycosis in the form of histoplasmosis, blastomycosis);
- parasitic (helminthiasis – schistomiasis, echinococcosis).
- Focal lesion of the spleen:
- cyst;
- neoplasm;
- heart attack;
- abscess.
- Anemia:
- hemolytic;
- pernicious;
- thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura;
- idiopathic;
- cyclic agranulocytosis;
- hemoglobinopathy.
- Poor circulation:
- local (portal hypertension);
- general (Pick's cirrhosis).
- Systemic pathologies of the hematopoietic organs:
- leukemia – acute, chronic;
- malignant lymphoma;
- myelofibrosis.
- Autoimmune pathologies:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- nodular periarthritis.
- Disturbed material metabolism – hereditary or acquired:
- hemochromatosis;
- glycogenosis;
- essential dyslipidemia;
- Westphal-Wilson disease (Wilson-Konovalov).
Identifying the cause of splenomegaly is necessary to determine treatment tactics. Diagnosis of a pathological syndrome is aimed primarily at clarifying its origin.
Consequences of the disease
The danger of splenomegaly is that it is not an independent pathology. Therefore, it is important to get tested promptly and identify the root cause to prevent more serious health complications.
Possible consequences:
- organ rupture followed by internal hemorrhage;
- disruption of the hematopoietic process;
- regular infectious pathologies against the background of a low number of platelets, leukocytes and red blood cells;
- worsening blood clotting.
Selection of therapy
In order to get rid of the disease, it is very important to understand why exactly the change in the internal organ occurred. If cirrhosis has led to splenomegaly, then immediate measures must be taken to treat this pathology. Until the underlying disease is cured, it is impossible to talk about complete recovery.
Most often, treatment of the spleen is carried out with antibiotics or chemical therapy. However, in some situations this is not enough. In this case, you cannot do without surgery.
Gymnastics
Treatment of an enlarged spleen, regardless of the cause of the disease, is recommended with the help of special breathing exercises. In this case, gymnastics not only helps to reduce the size of the organ, but also strengthens the body as a whole.
Exercises:
- Lying on your back, inhale air and at the same time draw in your stomach. Then exhale gradually. When you inhale again, push your stomach out and then release the air. Do 6 to 10 repetitions of the exercise.
- While standing or lying down, place your hands on your stomach. Inhale air, sticking out your stomach. Repeat inhalation 2 more times and then release the air freely. Repeat 10 times, but gradually this figure should be increased to 40.
- Lie down, put your hands under your head, bend your legs. Inhale slowly, moving the abdominal wall, and then release the air. Repeat the exercises constantly, accelerating the pace. When you start to feel dizzy from too much oxygen, finish the task.
- Lie with your back down. Inhale the air deeply, and then begin to exhale intermittently, while repeating the syllable “cha”. During exhalation of air, the abdominal wall should create a sharp movement. For 1 inhalation, 3-4 exhalations should be carried out. Repeat 8 to 10 times.
- Take a standing position with your hands on your hips. Inhale and at the same time push your stomach forward. After this, raise one hand to your mouth, fold it into a tube and exhale the collected air into it. The next time you inhale, pull your stomach in as much as possible, and exhale according to the previous principle, but using the other hand. Repeat the exercise 8-12 times.
- Lie on your back. Inhale air and at the same time make a yawning movement, but keep your mouth closed. Hold your breath for 3 seconds and then release the air. Repeat 15 times.
Pathology of the spleen poses a danger to the entire body, since the natural process of filtration and hematopoiesis in the body is disrupted.
But it is worth understanding that the reason for the enlargement of the organ lies in the dysfunction of other organs. Therefore, the sooner it is identified and treated, the less negative the process will affect human health.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky