Lichen planus in humans (Wilson's lichen) is a very common skin disease. It is classified as a chronic dermatoses that mainly affects the skin, nail plates and mucous membranes. This disease is distinguished by its long course and a wide variety of manifestations.
Lichen ruber most often affects older people, but it can also occur in younger people. This form is not contagious, which means it is not transmitted from person to person either through touch or in any other way.
Reasons for development
The true causes of lichen planus in humans are not clear, as are all the links in the complex pathogenesis of this disease. There are a number of theories, but none of them have become generally accepted:
- Viral concept. It was assumed that the cause of the disease was the penetration of a virus into the skin, weakening the patient’s immunity and causing characteristic symptoms. But there is no objective data confirming this theory.
- Neurogenic concept. In patients with lichen planus, increased excitability of the autonomic nervous system, changes in the electroencephalogram indicating excitation in the brain, and an increase in the concentration of adrenaline and dopamine, stress hormones, were detected. In addition, the appearance of rashes is often preceded by severe emotional trauma or mental illness.
- Hereditary concept. There is no data indicating a direct influence of genetic information on the disease. Only in 11% of cases did the patients' relatives suffer from some kind of dermatosis. But in the presence of a relationship, the symptoms of the disease appear earlier, and the frequency and duration of relapses are higher than in patients without a hereditary nature of the process.
- Liver and gastrointestinal dysfunction. In diseases of these organs, special substances are produced that attack skin cells. This can lead to symptoms of shingles.
- Diabetes. In patients with diabetes mellitus, the likelihood of developing any skin diseases increases due to microcirculatory disorders.
- Immunological concept. Immune complexes have been identified in the skin of patients that increase the activity of lymphocytes and force them to attack the body’s own cells. This indicates the role of immune system disorders in the pathogenesis of the disease.
Causes
Despite the fact that this disease has existed for quite a long time, and a lot of time has been devoted to its research, neither the causes of the pathology nor the methods of its spread have yet been clarified.
The majority of specialists in this field of medicine are inclined to the autoimmune nature of lichen planus, while others identify a number of possible causes:
- neurogenic pain (they are supported by the fact that Wilson’s lichen most often develops against the background of any stress or shock to the nervous system).
- allergic reaction.
- hereditary transmission from generation to generation;
- due to the introduction of the virus into the human body.
Lichen planus is more common on the forearms and lower legs on the inside; the elbow and knee bends are also affected; it can also appear on the torso and scalp. Nails and oral mucosa are susceptible to disease.
Very rarely, this pathology occurs in children, however, the older the patient becomes, the higher the likelihood of developing the disease.
The relationship between the form of lichen and the age of the patient has also been established. For example,
- the skin is more likely to be affected when the patient is about 40-45 years old;
- Older patients, namely those over 55 years of age, are susceptible to mucosal damage.
Although the root causes are not known, factors that can trigger the onset of symptoms and cause the rapid progression of the onset of the disease are known:
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- various hormonal disorders in the body. Such as: diabetes, thyroid problems and others.
- hypertonic disease.
- constant stressful situations at home and at work. Nervous state of the patient.
- allergies and predisposition to them.
- uncontrolled use of medications such as analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs. It has been proven that “gold” injections prescribed for rheumatoid arthritis and anti-malarial tablets can also catalyze the onset of the disease.
- acquired infections of bacterial or viral origin (hepatitis, tuberculosis).
- if one of the patient’s relatives suffered from lichen ruber, then the likelihood of the disease manifesting itself is very high.
- The risk of developing pathology increases with a person’s age.
- various injuries of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
Also, observations of patients suffering from this disease revealed that the initial appearance of symptoms of lichen, as well as the probable return of the disease, often occur against the background of severe nervous exhaustion, lack of sleep, or simply severe chronic fatigue.
The appearance of lichen ruber in the oral cavity can be caused by rubbing the mucous membrane with low-quality dentures, or due to microtrauma caused by sharp edges of the teeth.
Is lichen ruber contagious?
There is no definite answer to this question, since all theories about the occurrence of this dermatosis are currently unproven. However, there are known cases of lichen planus occurring in members of the same family, including both spouses. In addition, an episode of infection of a doctor who took tissue from a patient’s lesion (biopsy) for further research is described. A month after the manipulation, his first single lesion appeared, and three weeks later, new numerous rashes, identical to those that his patient had.
Therefore, we should not forget that infection is probably still possible, but most likely through close contact. And if you live with a sick person, then make it a rule: do not share scissors, a razor, a toothbrush cup, underwear, a towel, clothes or shoes with him.
Lichen ruber: causes of pathology
The autoimmune nature of the disease (the body, with the help of the immune system, fights against its own cells) does not allow us to clearly say what exactly triggers the pathological process; one can only assume:
- Lichen planus is inherited (there are observations of relatives in three generations who suffered from lichen planus).
- The disease is neurogenic in nature, that is, the impetus for the development of the disease is psycho-emotional stress and frequent nervous stress.
- The disease is associated with endocrine disorders, for example, the disease develops against the background of early menopause; According to statistics, approximately 65% of patients experience such disorders.
- Ringworm is caused by a filter virus located in skin cells and activated under the influence of any negative factors such as stress, injury or exhaustion. This theory is quite widespread, but the virus itself has not yet been isolated.
- The pathology is a reaction to toxic-allergic aggression and develops when certain foods and chemicals, including drugs, enter the body. The cause of the development of lichen planus can be antibiotics, vitamins, diuretics, antiarrhythmics and many other drugs.
- The disease is associated with metabolic disorders (metabolism) - scientists have identified common mechanisms for the development of atypical forms of lichen planus and diabetes mellitus.
In addition, among the suspected causes of the development of lichen ruber are infectious diseases such as hepatitis (especially C and B), cirrhosis of the liver, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and xanthomatosis (deposition of cholesterol in the skin, tendons and other tissues of the body).
Attention! Currently, most experts are inclined to believe that lichen planus develops as a result of inferior immune regulation of the body, that is, they are adherents of the immune-allergic hypothesis of the occurrence of the disease. According to it, the skin and mucous membranes are the most important part of the immune system and take an active part in protecting a person from external and internal factors that lead to disruption of self-regulation (homeostasis) of the body.
Symptoms of red lichen
In humans, the symptoms of lichen planus (see photo) are varied, however, they all boil down to the formation of a monomorphic rash, which consists of small flat papules with a diameter of up to 0.5 cm.
- The nodules can be red-violet or crimson-red. The center of the papules is retracted, their surface is shiny. The nodules are especially visible in side lighting.
- Peeling, as a rule, is not too pronounced. The scales can be separated with difficulty. Sometimes the peeling resembles the picture of psoriasis. In this case, we are talking about the psoriasiform variety of the disease.
- The scalp, palms, soles and face are not attractive places for inflammation caused by lichen planus to develop. However, in approximately 10% of people, the pathology affects the head with its scalp and face. In this case, the lichen looks like a dark red lump that is very itchy. As the pathology progresses, hair begins to fall out of the head.
- In 25% of people whose lichen has formed on the mucous membranes, papules do not appear on the dermis. They affect the oral cavity, the head of the penis, and the entrance to the vagina. They can be grouped into rings, circles, or a grid. On the mucous membranes, the nodules have a grayish tint. If the tongue is involved in the pathological process, then flat plaques with jagged edges form on it. If the lips are affected by the disease, then purple plaques with mild peeling at the top are visible on them.
- Multiple rashes predominate when the nodules are located in groups. They can be combined into garlands, stripes, circles, or merge to form plaques. Elements of the rash form again around these fusions. After the nodules resolve, an area with persistent red pigmentation remains on the affected area.
- All rashes cause anxiety to the patient in the form of severe itching. This often leads to problems with night rest, ultimately provoking neurotic disorders. The ones that itch the most are the ones that are localized on the fingers. Therefore, many people mistake lichen for scabies. (
How to treat lichen ruber in humans
The doctor chooses treatment methods based on the severity of the disease. In the initial stages, treatment for lichen ruber is local. Hydrocortisone, flucinar and ointments with dexamethasone and diprospan are prescribed. Dimexide is added to the products for better penetration through the skin. Applications with these drugs are applied to inflamed mucous membranes.
The erosive-ulcerative form of lichen often occurs in children. The child cannot eat normally because... the tongue and oral cavity are covered with small wounds. In such cases, it is recommended to apply a solution of kudesan and actovegin to areas inflamed by lichen. Open wounds on the body are sprinkled with honsurid powder. Ulcers are pre-treated with antiseptics so as not to create a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogens of infectious diseases.
Antihistamines for lichen
Medicines can reduce itching in LLP and reduce the activity of allergens. In some patients, epithelization of lesions is observed after their use. The doctor prescribes an antihistamine for lichen planus when the cause of the disease is a reaction to contact with an allergen. If the occurrence of the disease is associated with abnormalities in the functioning of internal organs, then such drugs are not used. For lichen erythematosus, patients are prescribed:
- diphenhydramine;
- claritin;
- erius;
- tavegil;
- suprastin.
In case of severe allergic manifestations, the medication should be taken in courses of 7-10 days. If after this time the disease cannot be cured, patients are prescribed hormonal therapy. It is undesirable to use antihistamines and immunomodulatory drugs together. This can aggravate the allergenic reaction and cause the Wickham's grid symptom. In reviews of antihistamines, patients often mention their sedative effect, so it is better to take them before bed.
- Remedy for lichen in humans - types of disease, medications and traditional medicine recipes
- Lichen versicolor - treatment with ointments, tablets, diet and folk remedies
- How to treat lichen in humans
Sedatives
Neurological disorders in 40% of cases cause rashes and ulcers on the skin. Doctors prescribe sedatives for acute and subacute forms of lichen for people who are in a state of nervous tension. Phenazepam or medazepam is taken orally for 14 days. The dosage of the drugs is determined by the severity of the disease, but cannot exceed 10 mg in the case of mezapam.
Vitamins for lichen planus
Patients are prescribed injections of nicotinic acid, vitamin B, retinol, and tocopherol. It is possible to take vitamins for moderate lichen in the form of tablets. Patients are prescribed neovir and other immune-restoring drugs. Vitamins C and D are indicated for complex treatment of skin with lichen. They reduce vascular permeability, have a depigmenting effect, and improve protein synthesis in tissues.
Antibiotics
Tetracycline, doxycycline, metacycline are prescribed to patients suffering from a severe stage of the disease. Antibiotics for lichen planus are taken in tablets. If there is a progressive infection in the body, then ceftriaxone solution is injected intramuscularly and 3-3.5 grams of amoxicillin are drunk. Taking erythromycin, sumamed, and azithromycin will help reduce swelling and relieve inflammation from tissues. After completing a course of antibiotic treatment, the patient must take antifungal and immunomodulatory drugs.
Corticosteroids for lichen
A course of injections of novocaine with flosterone inhibits the spread of the disease. Prednisolone for lichen ruber is taken every other day, 25 mg. Synthetic acids, such as delagil, plaquenil and presocial, have immunosuppressive anti-inflammatory effects. They are taken in tablets. The drugs Advantan and Elokom are intended to reduce the inflammatory process. They are available in the form of powder for solutions and cream.
Complications
Lichen planus is especially unpleasant in the genital area, in the vagina. The disease leads to pain and disrupts sex life. Scars may remain in place of the elements. Sexual dysfunction may subsequently persist for a long time.
There is evidence that lichen planus, although to a small extent, may increase the risk of squamous cell carcinoma. Your dermatologist may recommend that you be screened for cancer cells in the lesions.
Skin pigmentation in places where nodules and plaques were located persists for a long time.
Photo of pink lichen: what it looks like
Scaly round or oval spots, bordered by a bright pink color, are concentrated on the shoulders, back, and hips.
The flaky central zone of the mother spot is sunken and pale in color. At the edges, the plaque rises slightly above the skin and has a bright pink color. When the scales of the plaque peel off, a brownish stain will remain in their place.
Diagnostics
In most cases, a doctor can easily make a diagnosis during an examination. Difficulties may arise if the skin is not affected, and the elements are only on the mucous membrane.
Tests for lichen planus that a dermatologist may prescribe:
- Biopsy. The doctor obtains a piece of tissue in the area of the nodules and plaques and sends it to the laboratory for analysis. Most often this is done using scrapings. When microscopying samples, you can see cells characteristic of lichen planus.
- Blood test for hepatitis C. This viral disease often provokes the occurrence of lichen planus. If during the conversation the doctor decides that you had a risk of contracting hepatitis, he will order this test.
- Allergy tests. Allergies can also trigger the occurrence of lichen planus. Your dermatologist may refer you to an allergist who can perform an allergy test. Solutions containing different potential allergens will be applied to your skin. A positive reaction will be indicated by the appearance of redness and a blister in the place where the “culprit” allergen was applied.
Not everyone needs these studies. They are prescribed if there is a suspicion of a particular disease in cases where the diagnosis is difficult to establish.
Diagnosis of lichen
Before looking for ways to quickly and easily get rid of lichen ruber, it is necessary to clarify the methods for identifying the disease.
In some cases, the disease is diagnosed after a visual examination, but in atrophic, erosive-ulcerative and pigmented lichen, a histological examination of the collected skin biopsy is required.
If ulcers form in the oral cavity, a cytological type analysis will be required. According to a blood test, the presence of a problem can be suspected by an increase in ESR values, an increase in the content of leukocytes and eosinophils.
Photo
What lichen planus looks like, see the photo for more details:
Classification of forms and symptoms of manifestation
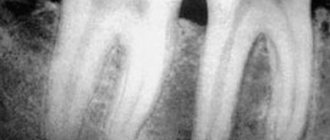
The main sign of lichen planus in the oral cavity is a characteristic rash on the mucous membrane. The pathology consists of small flat nodules with a diameter of no more than 2 millimeters. The papules have a light gray tint and together form a specific openwork pattern.
According to clinical manifestations, there are several forms of lesions of lichen planus of the oral mucosa.
Typical
This form of rash is observed in most cases. The pathology is easy to diagnose due to typical manifestations:
- the formation of white papules with a pearlescent coating, which can form patterns on the mucous membrane in the form of stripes, lace or rings;
- There is a slight dryness and burning sensation in the mouth.
Typical form of lichen planus
In most cases, lichen planus of the typical form does not have pronounced symptoms. Sometimes it is only noticed during an examination at the dentist.
Exudative-hyperemic
This type of pathology is not common. It is characterized by the presence of plaques and ulcers with a fibrous coating. The mucous membrane becomes inflamed and swollen. The disease is accompanied by pain and burning. At the same time, it is difficult for the patient to talk and eat.
During the development of the disease, the pattern of papules characteristic of the pathology practically disappears. It can only be seen during treatment after swelling of the mucous membrane has been removed.
Hyperkeratotic
This form is observed in rare cases. Its peculiarity is the different outlines of the grayish plaques. Hyperkeratotic nodules rise significantly above the surface of the mucous membrane and have pronounced boundaries.
Lesions are mainly observed on the tongue and inner cheeks.
Erosive-ulcerative
This type of lichen planus is the most dangerous. The disease is characterized by a strong inflammatory process. A lesion of this type occurs against the background of complications of the exudative-hyperemic and typical form due to trauma to the oral cavity.
In addition to plaques, ulcers and erosions form on the mucous membrane. The affected area becomes inflamed and there is severe swelling. Erosive rashes are covered with a characteristic fibrinous coating, when removed, bleeding begins.
Such rashes may not epithelialize for quite a long time. And even after the erosions heal, sometimes the disease relapses. The danger of the erosive-ulcerative type of lichen planus lies in cases of lesions turning into a malignant form.
Bullous
The disease occurs in only four percent of cases. In addition to light pearlescent papules, blisters with a diameter of up to 6 millimeters are observed. Such formations on the oral mucosa may contain bloody contents. After two days, they burst, forming erosive areas that are quickly filled with epithelium.
Such rapid healing of erosions on the mucous membrane separates bullous and erosive-ulcerative forms.
A feature of the disease is the possibility of transition from one form of damage to another. At the same time, a simple typical type of pathology can, over time, become a more complex type of lichen planus. Such transformation is caused by the presence of dental diseases or other local factors.
How to treat lichen planus
The basis of this dermatosis is immune inflammation (tissue response to damage by the immune system), which destroys cells of the skin and mucous membranes.
Therefore, when treating lichen planus in humans, the following are used:
- drugs that reduce the activity of the immune system - drugs of choice (prescribed first) in severe cases of the disease
- products that improve tissue nutrition and accelerate their recovery
- medications that reduce itching, improve sleep, normalize the functioning of the nervous system
- local ointments
In addition, provoking factors are eliminated:
- stress
- Prosthetics and treatment of diseases of the oral cavity, as well as foci of chronic infection, are carried out
- medications and occupational hazards are excluded
- We recommend a diet that does not irritate the oral mucosa
- and others
Medicines are prescribed to patients in cases where there is a violation of their general health. The selection of the necessary funds depends on each clinical case. The following oral medications can be used to treat lichen planus:
- immunosuppressants: Cyclosporine A, Chloroquine, Hydroxychloroquine;
- antihistamines: Tavegil, Zyrtec, Diazolin, Clemastine, Promethazine, Loratadine, Fenkarol, etc.;
- corticosteroids: Metipred, Prednisolone;
- systemic retinoids: Neotigazon, Acitretin, Tigazon, Isotretion, Etretinate;
- synthetic interferons: Ridostin, Neovir, Interferon-alpha 2B;
- antibiotics: Tetracycline, Metacycline, Doxycycline, Azithromycin, Sumamed, Roxithromycin;
- sleeping pills and sedatives: Phenazepam, Medazepam;
- vascular drugs to improve tissue trophism: Xanthinol, Trental, etc.;
- vitamin preparations: Ascorbic acid, B vitamins, vitamin D.
In addition, the drug therapy plan may include drugs for the treatment of concomitant diseases: diabetes mellitus, neurosis, arterial hypertension, chronic inflammatory processes (for example, glossitis, stomatitis, etc.).
For local therapy of lichen planus, the following agents are used:
- ointments based on corticosteroids: Cloveit, Flumethasone, Hydrocortisone, Betameson, Triamcinolone;
- non-hormonal antiallergic ointments: Gistan, Fenistil;
- non-hormonal anti-inflammatory ointments: Pimecrolimus, Tacrolimus;
- exfoliating ointments: Belosalik, Diprosalik;
- ointments to accelerate tissue regeneration: Solcoseryl.
Local remedies for the treatment of this dermatosis can be used either independently or in combination with each other. They can only be prescribed by a doctor who takes into account the form, severity and stage of the disease.
Causes and mechanism of development
There are various theories explaining the causes of lichen planus:
- hereditary, based on cases of the disease in twins, as well as in relatives in the second and third generations;
- neurogenic, or neuroendocrine, which considers the main cause to be emotional stress, long-term neuropsychiatric disorders, sleep disorders and the function of the autonomic nervous system in various diseases (diencephalic syndrome, hypertension, early menopause, hypothyroidism, hypoestrogenism, etc.); the theory is based on the fact that in 65% of patients there is a clear connection between these disorders and disorders with the onset or relapse of the disease;
- viral, which explains the development of the disease by the presence of a filterable virus, which is found in a person’s skin cells and is activated when the body’s defenses decrease under the influence of mental or physical and chemical injuries, prolonged exhaustion, etc.; however, to date the pathogen itself has not been identified and, therefore, there is no incubation period;
- toxic-allergic, which is based on an allergic reaction to certain components of food products or chemicals, vitamin preparations, tetracycline antibiotics and streptomycin, sulfonamides, preparations containing gold, mercury, arsenic, para-aminosalicylic acid and its analogues, diuretics (Furosemide) and antiarrhythmic drugs, and others;
- theory of endocrine and metabolic disorders; it is based on the common mechanisms of development of diabetes mellitus and lichen planus, which often occur together, especially its atypical forms and lesions of the oral mucosa.
All these theories do not so much explain the cause of the development of lichen planus as the presence of various provoking and predisposing factors and their participation in the pathogenesis of the disease (development mechanism).
Contributing factors also include:
- infectious diseases, in particular hepatitis B and, especially, hepatitis C;
- metabolic disorders in the form of dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome, carbohydrate metabolism disorders in diabetes mellitus, etc.;
- primary biliary cirrhosis of the liver;
- xanthomatosis;
- chronic diseases and dysfunction of the digestive system.
Immune-allergic hypothesis for the development of lichen planus
To date, there is no single assumption about what causes lichen planus and no single idea about its development mechanisms. The most acceptable hypothesis is the immuno-allergic one, which considers the disease as multifactorial, which is based on the inferiority of immune regulation.
The skin and mucous membranes in humans, in accordance with modern concepts, are considered an essential part of the immune system. They play a particularly significant role as protectors against the background of the growing influence of external and internal antigenic (allergenic) factors, leading to significant structural and functional disturbances in the constancy (homeostasis) of the internal environment of the body.
In accordance with the immune theory, lichen planus is considered an acquired systemic inflammatory autoimmune disease that develops as a result of the body's inadequate regulation of metabolic and immune processes. This explains the inadequate pathological reaction, disturbances of enzymatic systems with a decrease in individual enzymes, etc. in response to the effects of injury, viruses, drugs, chemicals and other factors.
Particular importance as triggers is given to the influence of persistent viruses and other infectious pathogens present in the body in an inactive state, as well as vaccines, serums and other antiviral and antimicrobial drugs that activate an inadequate response of cellular and humoral immunity.
The body's protective reaction in response to exposure to an irritating factor is initially expressed by adaptive processes that develop both at the level of the central and peripheral parts, which are represented by the skin and/or mucous membranes. Pathogenic factors lead to a sharp activation of humoral (blood, tissue fluid, lymph, saliva, gastrointestinal juices) and tissue mediators, as well as inflammatory modulators. This reaction is aimed at removing or neutralizing the causative factor. If, as a result of the resulting inflammatory reaction, the damaging agent is not completely eliminated or neutralized, maladaptation of the protective mechanisms occurs, and the inflammation becomes chronic.
Subsequently, the presence of pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic microorganisms that have the quality of antigens sensitizes (increases sensitivity) tissues, which leads to further damage and the formation of autoantigens (antigens that become their own tissues), as well as complexes consisting of a combination of microorganisms with damaged cells fabrics.
A normal protective response of the immune system develops to this process, which does not disrupt homeostasis in the body as long as the functional state of specific lymphocytes is maintained. As the suppressive function of the latter is depleted due to constant long-term antigenic exposure, disintegration of the main protective function of tissues occurs, an uncontrolled immune response to antigens by the body with damage to its own healthy tissues under any provoking factors.
These immunoallergic disorders can be provoked by almost any disorder of the function of neurovegetative regulation, vascular and metabolic disorders, various intoxications, hereditary factors, infectious bacterial and viral pathogens. At the same time, the dysfunction of all body systems itself occurs as a result of immune disorders, forming a vicious circle.
The formation of erosive and ulcerative processes not only on the skin and in the oral cavity, but also in the esophagus, stomach, intestines, rectum, on the mucous membrane of the vestibule of the vagina, urethra and bladder, on the head penis.
Is lichen planus contagious or not?
Taking into account these concepts of the causes and mechanisms of disease development, the answer to this question easily becomes clear. Despite the fact that the disease is not dangerous in terms of infection, unlike, for example, ringworm, it must be remembered that it is often combined with chronic viral hepatitis “C”, the causative agent of which, under certain conditions, is transmitted from person to person.
Physiotherapy
PUVA therapy. This is one of the most effective physiotherapeutic procedures for lichen planus. The treatment process combines the use of photosensitizers taken orally and ultraviolet radiation. It is this technique that gives good results after the first 3-4 procedures. The course of treatment consists of 15-20 procedures.
However, this method of physiotherapy also has side effects. Nausea, dizziness, skin burns. In the future, the likelihood of developing skin cancer, the occurrence of tumors, etc. increases.
Lichen planus can be successfully treated with laser therapy and magnetic therapy. These procedures affect the activity of healthy skin cells and inhibit the development of affected skin areas. When these methods are combined with drug treatment, good results are achieved.
Complications and consequences
One of the complications of pityriasis rosea is its transition to an atypical form - Vidal's ring-shaped lichen. It is characterized by huge spots and tends to become protracted. Such lichen can recur for several years.
The result of pityriasis rosea and its treatment can also be:
- Adverse skin reactions, for example, drug hypersensitivity syndrome.
- Transition of pathology into eczema, folliculitis or streptococcal impetigo.
- Accompanying the disease with serious diseases, for example, purulent skin lesions.
With inadequate treatment, it is also possible that an allergic component may join the main course of the disease. This also applies to improper skin care.
The disease occurs secondarily extremely rarely. If infection does occur, the main location of the plaques will be in thin areas of the skin or areas of concentration of sweat glands.
Folk remedies
Many examples are given that promise an unprecedented result and tell how to quickly treat lichen ruber in humans. Unfortunately, none of these methods are scientifically proven and often people can only observe a cure as a placebo effect.
“Dummy” and the power of human persuasion sometimes really work psychosomatically and the mechanism of healing by persuasion has not yet been studied. Nevertheless, in medical practice, even if only a little, similar examples still occur.
Try to avoid aggressive treatments such as applying hot objects or products containing acids and other similar substances. This will only make the situation worse, causing injury to the affected areas of the skin.
Popular folk remedies include:
- sea buckthorn oil – has a wound-healing effect;
- birch tar is a remedy actively used in the treatment of psoriasis and other dermatitis;
- laundry soap - its natural composition does not damage the skin.
When using this or that technique, you need to focus on your own feelings. Allergic reactions and individual intolerance can appear at any time.
Treatment of pityriasis rosea
During treatment for pityriasis rosea, patients are advised not to wear tight clothing that causes friction and pressure - this can lead to the appearance of new spots and make existing ones itchy.
Skin care and following a hypoallergenic diet are also indicated. If there is itching, along with the main therapy, antihistamines are prescribed, and if accompanied by fever, antipyretics are prescribed. Antibacterial therapy is also indicated in case of infection. It will take a week for all the spots to disappear from the skin. After this, pale pigment spots will remain on the skin for some time. It will take more than a month for the skin to return to its original appearance.
Ointments and suspensions
Antibiotic or antiallergic ointments are prescribed in case of constant exacerbation of the disease or its severe course.
It is recommended to lubricate the affected areas of the skin with the following corticosteroids or antibiotic ointments:
- Lorinden A - reduces flaking, relieves itching and swelling - an excellent remedy for fighting inflammation and allergies.
- Sinalar - in addition to relieving inflammatory symptoms, softens and brightens the skin.
- Flucinar is a hormonal drug that helps get rid of scale spots and relieve itching.
You should not abuse corticosteroids: although they quickly relieve discomfort, they at the same time negatively affect the skin, causing its atrophic changes.
There is also an excellent remedy: Lassara salicylic-zinc ointment. This paste has an antimicrobial effect: it will relieve swelling, eliminate redness and make the lesions almost invisible, which is important for atypical lichen that appears on the face.
In addition to ointments, you can wipe your skin with Tsindol suspension a couple of times a day. The zinc contained in it perfectly dries the skin, reducing itching and preventing the spread of germs. Resorcinol solution also has an antiseptic effect.
If lichen is accompanied by the appearance of blisters, it is necessary to use antiviral ointments such as Zovirax or Acyclovir. They will speed up their drying and prevent the appearance of new papules.
Pills
Tablets for the treatment of Zhiber's disease are divided into antihistamines and antivirals. The first (Zyrtec, Claritin) will relieve itching, the second (Acyclovir, Erythromycin) will stop the action of viruses. Taking multivitamin complexes is also indicated: since the onset of the disease is associated with weakened immunity, it is necessary to compensate for the lack of vitamins in the body. Often, for roseola, characterized by profuse peeling, regular activated carbon is prescribed. It removes toxic components and allergens from the body.
Diet
Complex treatment of pityriasis rosea should include adherence to a hypoallergenic diet. It is necessary to completely eliminate allergens from the diet for 2-3 weeks, which include all types of citrus fruits, sweets, nuts, eggs, milk and baked goods. During this period, it is better to replace tea and coffee with compote or clean water. Spices and flavorings should also be avoided when cooking.
During illness, it is recommended to eat vegetables and herbs, porridge, preferably oatmeal or rice.
ethnoscience
Folk remedies will also help relieve the symptoms of the pathology:
- Calendula. 10 grams of flowers must be ground to a powder and mixed with 50 grams of Vaseline ointment. The resulting mixture can be applied to the affected areas up to three times a day.
- Ashes of a white sheet of paper. It is necessary to give the paper a conical shape and set it on fire. The resulting ash can be used to lubricate the affected areas.
- Cabbage tandem with sour cream. Spread the cabbage leaf with sour cream and apply it to the fireplace. Keep it on until the compress is completely dry.
- Kitchen to the rescue. In addition to cabbage and sour cream, you can use other food products for treatment: you can coat the spots with butter or sea buckthorn oil;
- A decoction of beets with a few tablespoons of honey is also not bad for wiping the affected areas.
Folk remedies should be used with caution and with the permission of a doctor. Otherwise, the disease may not be cured, but rather worsened. If skin irritation or the appearance of new spots is noticed after wiping, treatment should be stopped.
Recommendations
For patients suffering from pityriasis rosea, the following indications and restrictions are recommended to alleviate the condition:
- you should not take baths, it is better to replace them with a warm daily shower - sweat can irritate the skin and aggravate the course of the disease;
- You need to wash with a soft washcloth and the same detergents - otherwise the skin may dry out;
- try to avoid direct rays of the sun;
- give up woolen clothes and synthetics - only items made from natural fabrics should be present in your wardrobe;
- worries and excessive physical activity should be reduced to nothing.
In addition, the patient must systematically change bed and underwear and use a personal towel.
A combination of four factors plays a huge role in speeding up recovery: hardening, walking, proper nutrition and emotional stability.
Diet
There is no special diet for the treatment of lichen planus. However, nutrition plays an important role, because it is impossible to cure lichen planus by abusing foods harmful to the body. In addition, taking some drinks can reduce the effectiveness of drugs, and a number of products can cause allergic reactions and provoke a sharp increase in blood sugar levels.
During the treatment period, you should avoid drinking alcohol and confectionery. Products that it is advisable to limit your consumption include:
- citrus;
- products containing cocoa;
- products containing purine: meat and dishes prepared on its basis (broth, meat sauce, jelly); fatty fish, fish soup, fried and salted fish, canned fish; meat by-products; mushrooms;
- legumes: peas, beans, soybeans, lentils;
- eggs;
- strong brewed tea or coffee;
- products with a high content of preservatives, dyes, flavoring additives: sausages, canned food, carbonated drinks.
The following products will benefit the body:
- dairy;
- green vegetables;
- healing mineral water;
- iron-containing products;
- honey.
A diet for lichen planus is necessary if the disease often recurs and is difficult to treat.
It is better to introduce each new product into the diet gradually. If the condition worsens, the diet should be extended.
How to cure
Treatment depends on the severity of the process, the cause of its occurrence and concomitant diseases.
How to get rid of the disease for adults
Severe itching:
- antihistamines (Clemastine, Tavegil);
- sleeping pills (Medazepam);
- sedatives (Chloropyramine, Cetirizine).
Foci of chronic infection - antibiotics: Penicillin, Erythromycin, Doxycycline (medium doses).
For extensive lesions - drugs of the aminoquinolone group: Plaquenil, Delagil. Course 3 weeks, 1 tablet 2 times a day.
In the acute phase - systemic corticosteroid therapy. Prednisolone tablets. Diprospan IM 1-2 ml once a week. Course 2-3 weeks.
Immunomodulators: Ridostin, Neovir.
Peripheral vasodilators: Nicotinic acid.
Vitamin complexes containing vitamin A.
Physiotherapy:
- PUVA therapy.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Laser therapy.
Some doctors recommend: electrosleep, acupuncture, sanitary-epidemiological treatment.
Treatment with ointments:
- Corticosteroids: Advantan, Elokom, Celestoderm.
- Inducing agents in the composition with salicylic acid, tar, naphthalan, ichthyol.
- Antiallergic: Gistan, Fenistil.
Any complex of treatment should be selected only by the attending physician, taking into account an individual approach.
How to cure a child
Children are rarely diagnosed with LP.
This is usually a bullous form (atypical). It is complicated and difficult to treat. In many cases, symptomatic treatment is used, as in adults. The treatment methods used make it possible to suppress the symptoms of the disease and increase the period of remission.
It is impossible to completely cure LP in children. Such patients are registered at a dispensary at their place of residence.
Prevention
As you know, it is better to prevent any disease than to treat it. A number of simple recommendations will greatly reduce the risk of developing the disease.
- To prevent the risk of developing the disease, you should carefully monitor the health of your body and consult a doctor in a timely manner. Carefully monitor and exclude from circulation items that constantly injure the skin and mucous membranes.
- Proper nutrition, adherence to a routine and maintaining personal hygiene can significantly reduce the likelihood of acquiring pathology.
- It is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, play sports and give up bad habits.
- Hardening will help to avoid many diseases, including lichen red.
Ringworm is a fairly serious disease that can lead to dangerous complications. But with proper and timely treatment, the prognosis is very favorable and a complete recovery of the patient is possible.
During pregnancy
In the early stages of pregnancy, pityriasis rosea is very dangerous. It can cause spontaneous abortion and have a negative effect on the fetus.
A woman may feel:
- increased fatigue;
- pain in the head area;
- lack of sleep;
- decreased appetite.
This symptomatology is typical for the normal state of pregnancy, but if it is accompanied by the appearance of any kind of spots, you should urgently consult a specialist.
Complications can also arise if the disease manifests itself in the second and third trimesters. In the first case, this is fraught with hypotension and slowness of the baby’s movements. And in the second - premature birth.
The reason for the development of roseola exfoliating in pregnant women is the same reduced immunity coupled with hormonal changes.
Visually, lichen in pregnant women looks the same as everyone else’s, and treatment should be selected taking into account the patient’s position.
Forecast
In many cases, lichen planus regresses without treatment due to the cessation of exposure to the triggering factor. Some forms of the disease can be chronic, occurring after years of remission. Sometimes lichen ruber becomes refractory to therapy, which reduces the patient’s quality of life. The patient develops pigment spots in the focal lesion area and scars form. Rashes in the oral cavity may persist throughout life.
Pityriasis versicolor Herpes zoster Pink lichen of Zhibera Solar lichen Feline lichen in humans Cervical erosion
Varieties and atypical forms
A typical pityriasis rosea is characterized by the formation of a maternal plaque, characterized by a bright pink color, a scaly membrane and up to 4-5 centimeters in diameter. If there is no plaque, we are talking about an atypical configuration of the pathology, which is quite rare and manifests itself in the form of papules, blisters or vesicles.
Very rarely, symptoms of pityriasis rosea can be found on the face; the presence of severe itching is also not a characteristic feature of Gibert's disease. Sometimes pityriasis can manifest itself in the form of a blistering rash, when pinpoint rashes merge with each other and form an element with a diameter of up to eight centimeters.
The atypical form of the disease is characterized by three stages:
- Itching of the skin in places where lesions subsequently appear.
- The formation of shapeless papules that are rough and fine-grained to the touch.
- The appearance of clearly protruding foci of thickened dermis over healthy skin.
Treatment
Since the real causes of lichen planus have not yet been identified, there is no single treatment regimen that will get rid of the disease. After the patient consults a doctor, chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, metabolic disorders and immune system disorders are detected.
If the rash is located on the mucous membranes, it is necessary to treat the oral cavity. You should also adjust your diet and exclude from your diet foods that irritate the mucous membrane (spices, spicy foods, alcoholic drinks).
In the complex treatment of lichen planus, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Corticosteroids. Preparations in the form of tablets or injections are used if an erosive process affecting the mucous membranes interferes with food intake, or the disease affects large areas of the skin and, despite the treatment started, progresses.
- Antihistamines. They are prescribed if lichen planus appears after exposure to allergens, or when the disease is accompanied by severe itching
- Retinoids. Vitamin A derivatives reduce inflammation and accelerate skin regeneration. Drugs in this group are effective against damage to the red border of the lips and oral mucosa.
- Carotenoids. They are used for damage to the mucous membranes of the genital organs or the oral cavity, especially in the erosive-ulcerative form of the disease.
- Adaptogens. Drugs in this group help improve the functioning of the immune system and allow the body to more actively fight the disease.
- Antidepressants and sedatives. Used if the disease causes neurotic disorders or sleep disorders.
Externally, corticosteroids, tar-naphthalan or antihistamines are used to treat lichen planus. For the warty form of the disease, they are applied under a bandage. Corticosteroids are also effective if the disease affects the scalp. They are applied along the edge of the plaque, and not in the center.
When lichen planus appears in the oral cavity, products with triamcinol or fluocinol in combination with antiseptics are used, this helps get rid of the rash and prevents the development of candidiasis.
A symptom of lichen planus is a rash consisting of flat, bandless blisters measuring 2–3 mm and located on different parts of the body.
Physiotherapeutic methods play a special role in the treatment of lichen planus:
- Reflexology.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Electrophoresis.
- Phonophoresis.
- Laser therapy.
Is the disease contagious?
The existence of a large number of theories about the causes of this disease does not make it possible to give a direct answer to this question. All of them are still unproven and do not have 100% confirmation.
There are known cases of the development of lichen planus in husband and wife or several family members. An episode of infection of a dermatologist who performed a tissue biopsy of a patient is described. After 30 days, the first skin lesions appeared, and after 21 days, the same skin lesions appeared as in the patient.
That is why experts do not yet recommend completely rejecting the possibility of infection with lichen planus (especially with close contact) and adhering to a number of rules. When communicating with a patient, you should avoid shaking hands and other physical contacts, and do not share dishes, clothes, shoes, scissors and other personal hygiene items.
What it is?
Lichen planus in humans is a chronic multifactorial dermatosis that affects the skin, nails, and mucous membranes. It is distinguished by a long course and a variety of clinical manifestations, and most often affects elderly people.
Unlike other forms of lichen, lichen planus is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person. A number of scientific studies have been devoted to the study of this dermatosis, but the exact cause of the disease has not yet been established.
Which doctor should I contact?
If skin rashes appear, you should consult a dermatologist. Self-diagnosis and self-medication can be dangerous to health.
Lichen planus is accompanied by damage to various organs and systems, so many specialists are involved in its treatment: an endocrinologist (for diabetes), a psychiatrist (for neuroses), a dentist (for damage to the oral cavity), a cardiologist (for hypertension). It is useful to consult an immunologist who will help determine the impaired components of the immune system.
Health-saving channel, a specialist talks about lichen planus:
Rating: (votes - 1 , average: 5.00 out of 5)
Causes
Ringworm occurs due to a malfunction of the immune system. As a result, the cells become defenseless against any negative influence.
Lichen planus has the following causes:
- pathologies caused by infections and viruses;
- autoimmune diseases;
- neurogenic disorders;
- metabolic problems;
- genetic predisposition;
- intoxication of the body;
- allergy;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- vascular and heart diseases.
For effective therapy, it is recommended to get rid of the cause of red lichen and use local remedies for treatment.
Kinds
Lichen ruber occurs in a variety of forms, which may differ in nature. If lesions appear on the skin, you should carefully consider their appearance, location and color. Based on these important characteristics, the appropriate treatment is selected.
On the Internet you can find many photos with signs of lichen planus that will help determine the correct shape. It is important to conduct a full examination with the required tests.
The typical form is usually found, its prevalence is 45%. During it, nodules with a pearlescent color are formed. In appearance they look like a healed wound or scar.
Over time, a white coating appears on the affected areas, which cannot be removed by scraping. The rashes are accompanied by the following unpleasant conditions:
- Feeling of intense itching;
- Constant fatigue;
- Prostration;
- Discomfort;
- Nervousness, irritability.
Atypical forms
There are more than 15 types, but it is worth highlighting the main ones:
- Atrophic. The prevalence rate is from 2 to 10%. The rash appears as spots. Their shape can be round or oval, and their color is purple. In the center there are inclusions of a dark color, and on the surface there are lines with a pearlescent and waxy color;
- Verrucous. It is called verrucous and has a prevalence of 15%. Papules or plaques with a light red color appear on the surface, sometimes they can have a bluish color. The lesions may be round, oval or uneven. They are resistant to medical therapy. Accompanied by an intense feeling of itching;
- Bullous. This is the bladder variety. It can affect the mucous membrane. During it, small and large bubbles are observed. The diameter is 2-3 mm, inside they have transparent serous contents;
- Follicular. During it, small papules with sharp ends are formed; they appear in the areas of the mouths of the hair follicles. They are blue or red in color;
- Erosive-ulcerative. It has a long course and is resistant to medical therapy. Erosions and small ulcerative formations with a painful structure appear. They have uneven shapes.
Types of disease
The pathology of the epidermis that occurs against the background of diseases of the internal organs is what lichen planus is. The disease affects young and middle-aged men and women. The pathology is rare in children and the elderly.
Forms of lichen planus:
- Typical. This form is characterized by polygonal formations of a pink tone with a lilac tint;
- Erosive-ulcerative. One of the most severe forms of the disease, which is difficult to treat. Characterized by rashes on the mucous membranes. Most often, formations occur in the oral cavity, less often on the head in men or in the vagina in women. First, lesions appear, which quickly become ulcers, accompanied by pain;
- Hypertrophic. Another name is warty. They are plaques on which warts are located. The shade of the rash is brown, purple, pink. The rashes appear in groups and tend to grow together. Location: shins. Less commonly, formations are found in other parts of the body. This form of pathology is the most difficult to treat;
- Sclerotic. Another name is atrophic. This form of LP pathology occurs due to atrophic and sclerotic changes in the epidermis at the site of formation. It is characterized by the appearance of flat gray spots on the skin, which are surrounded by a pink rim. If the rash occurs on the head, pubis or armpits, then alopecia will occur in this place;
- Erythematous. The disease is characterized by rapid development. The epidermis quickly turns red, soft tissues swell, and itching appears at the sites of injury. Later, nodules form on the skin;
- Bullous or cystic. This form of lichen occurs rarely in humans and is severe. Lichen ruber in this form is characterized by the appearance of vesicles on the epidermis and their rapid spread throughout the entire skin. The rash is surrounded by papules and plaques. The risk group for the disease includes women over 50 years of age. Inside the formation there is a bloody-serous fluid. The blisters do not open for a long time, and after the abscess ruptures, ulcers remain in its place. Rashes with this form appear not only on the epidermis, but also in the oral cavity;
- Ring-shaped. Occurs due to expansion of the lesion with fading of the center. As a result, the formations become ring-like. Hence the name of this form of the disease. Men are susceptible to pathology. Rashes usually appear on the penis, on the epidermis of the lower extremities and mucous membranes;
- Pointed. Along with characteristic rashes, pointed plaques appear;
- Atypical. With this form, ulcers with a whitish coating appear on the inside of the lower lip. The soft tissue of the gums swells and begins to bleed. Painful sensations occur while eating food.
Lichen planus can develop into a malignant oncological pathology. For this reason, the problem cannot be ignored and at the first symptoms you should contact a specialist.
Broadcast
Vidal's ring-shaped lichen has been studied quite little by scientists, so it is quite difficult to accurately determine the cause of its occurrence. Please note that this disease can be inherited. So, if someone from your family has encountered this disease, then you need to pay special attention to hygiene and monitor the condition of your skin. As we noted above, this lichen does not pose a particular danger to humans, but nevertheless it causes unnecessary stress due to very unpleasant symptoms. It is expressed in the fact that warts begin to appear on the body. The most unpleasant thing is that the disease is recurrent, so you will have to deal with it throughout your life.
Unfortunately, it is not contagious.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the form, but there are general signs of lichen planus in humans:
- rash of a red, brown or purple hue;
- foci of the rash form in the bends of the limbs, in the groin, armpits, and on the head;
- the nodules have a shiny surface and clearly defined contours;
- papules can be pinpoint or collect in small plaques and rings;
- the rashes are accompanied by severe itching, the ulcers are painful.
More than half of patients have a rash on the oral mucosa. 10–15% of people with this dermatosis have affected nails.
The disease is characterized by a relapsing chronic course. Symptoms bother the patient for a month, then the symptoms subside. However, relapses of lichen red in humans can occur for years until the provoking factor is eliminated.
Localization
Lichen planus differs significantly from other forms of this disease. As a rule, the inflammatory process manifests itself in the following places:
- joints and forearms in the flexion area;
- neck area;
- shin;
- external genitalia in men.
As for the mucous membrane, the infection manifests itself in the following places:
- mucous membrane of the genital organs;
- oral mucosa.
Pathology most often manifests itself in the mouth. At the initial stage of development, lichen planus symptoms resemble ordinary stomatitis. However, medications to treat stomatitis do not provide any relief.
Pityriasis rosea and pregnancy
Despite the fact that pityriasis rosea is a self-limiting disease and resolves on its own within 6-8 weeks with virtually no complications, many experts are concerned about its impact on pregnant women.
When studying 38 cases of Zhiber's disease in pregnant women, it was found that 5 expectant mothers had miscarriages. For those women who fell ill in the first trimester of pregnancy, the rate of spontaneous abortion was 62%. In babies born to women who had pityriasis in the second trimester of pregnancy, doctors discovered hypotension and general slowness of movements. And only 33% of women in labor gave birth to completely healthy children. True, nine of them gave birth prematurely, but, nevertheless, the babies turned out to be healthy.
It should be noted that in women with an exceptionally severe form of Gibert's disease, pregnancy ended in miscarriage. In addition to extensive skin rashes, they had symptoms that were completely atypical for this pathology. Patients complained of severe headaches, insomnia, increased fatigue and lack of appetite. During a detailed examination of one of the patients who suffered a miscarriage, specialists found out that both she and the fetus were diagnosed with type VI herpesvirus, which was in the active phase.
These studies suggest that pityriasis rosea in the early stages of pregnancy is fraught with spontaneous abortion, as well as problems with the health of the unborn child. Unfortunately, today doctors do not know how and with what help they can fight this disease and its complications.
According to statistics, pityriasis rosea occurs in pregnant women much more often than in the general population. I would like to emphasize that the study involved a small group of subjects, and therefore the results obtained require re-checking, but at the same time, this information should be taken into account.
Location
As for the location of the spots, they are most often diagnosed on the back of the head, in the lumbar region, on the back of the thighs, on the inside of the cheeks, in the upper back, in the hollows under the elbows and knees, as well as in the female genital area.
The disease begins when a slight itch appears on the skin. It is at this stage that you should consult a doctor, since at this time you can still somehow influence the disease. After the first papules appear, the skin becomes very dry and gradually peels off. After this, warts appear on the skin, which have a pinkish tint. After a while they become covered with scales.