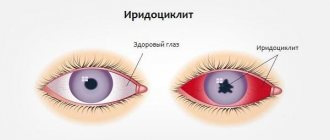
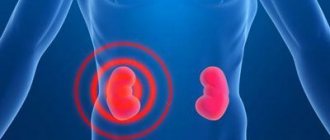
Nephritis in medicine refers to a whole group of various inflammatory kidney diseases. All of them have a different etiology, as well as a development mechanism, symptomatic and pathomorphological features. In this group, clinicians include local or widespread processes during which renal tissue grows, partially or completely destroys.
Online consultation on the disease “Nephritis”. Ask a question to the specialists for free: Urologist.
- Kinds
- Classification
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
The disease can occur in people from different age groups. Nephritis also develops in children and the elderly, but a little less frequently. This pathological condition can be either an independent disease or develop against the background of diseases already existing in the human body.
Kinds
Nephritis in medicine is divided into several types, which have their own etiology, symptoms and course characteristics. All types are dangerous to health and life, therefore, as soon as a person identifies the first symptoms of the disease, it is recommended to immediately contact a medical facility.
- glomerulonephritis. With this disease, the glomeruli of the kidneys are affected. In frequent cases, this type of nephritis develops as a result of a previously suffered sore throat and other ailments, the occurrence of which was provoked by hemolytic streptococcus. A characteristic sign of glomerulonephritis is hematuria. Swelling develops, lower back pain occurs, blood pressure rises;
- pyelonephritis (purulent nephritis). The inflammatory process affects the renal pelvis, calyces and renal parenchyma. The causative agents of the disease are staphylococci, E. coli and other bacteria. Pathogenic microflora enters the kidneys from other parts of the genitourinary system, but it can also be brought by the bloodstream from other foci of infection already present in the body. With pyelonephritis, the temperature rises, severe headache and lower back pain appear. Urination is frequent and painful;
- interstitial. The inflammatory process covers the tubules and interstitial tissue of the kidneys. This disease can be caused by taking certain groups of synthetic medications. Viral infections can also cause the development. The first symptoms: swelling, blood in the urine, weakness, increased blood pressure, polyuria, pain in the area where the kidneys are located;
- ray. The disease develops after prolonged exposure to ionizing radiation. As a rule, this leads to the inflammatory process affecting the renal tubules;
- shunt It is characterized by the combination of antibody complexes near the glomeruli of the kidneys;
- hereditary. Its appearance in the human body is directly related to existing congenital kidney pathologies.
Course of the disease
Acute interstitial nephritis, as well as other forms of the disease, occur in several stages:
- The initial stage with the appearance of edema, hypertension, azotemia.
- The latent period is associated with the appearance of protein in the urine and hematuria in small quantities.
- Degenerative period with a significant deterioration in the composition of urine and increased swelling (acute nephritic syndrome).
- The terminal stage with the appearance of symptoms of hypertension, renal failure, with an increase in the concentration of formed elements and protein in the urine.
Untimely therapy and continued exposure to negative factors lead to serious consequences and the disease becoming chronic.
Classification
In order to classify a disease as one type or another, in each clinical case it is necessary to first identify the nature and prevalence of the inflammatory process in the kidneys and the nature of the course of the disease. Clinicians use a certain classification of nephritis to make a more accurate diagnosis.
According to the localization and distribution of the pathological process, the disease is divided into:
- Focal. The inflammatory process “attacks” the renal interstitial tissue;
- Diffuse. The kidney glomeruli are affected.
According to the course of the disease, the following types are distinguished:
- Acute nephritis. In this case, acute renal dysfunction occurs. As a rule, this occurs due to the negative effects of pathogenic microflora. But this can also happen under the influence of toxic and immune causes;
- Chronic nephritis. With this form of the disease, two kidneys are affected at once. The process is chronic. Damage to kidney cells is associated with immune, metabolic, toxic and infectious factors.
- Subacute.
- Subchronic.
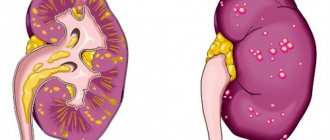
The structure of a healthy kidney
According to etiology, the disease is divided into:
- primary;
- secondary.
According to the absence or presence of kidney functions, nephritis is divided into:
- illness with preservation of kidney function;
- illness with insufficiency of renal function.
This classification is generally accepted and allows for a more accurate diagnosis and subsequently prescribing adequate treatment.
Forms of the disease
Depending on the area of kidney damage, there are several forms of the disease:
- Glomerulonephritis with lesions of the renal glomeruli (glomeruli);
- Pyelonephritis with damage to the renal pelvis and calyces;
- Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis (interstitial) with inflammation of the kidney tubules and interstitium (tissue around them).
Depending on the area of the affected tissue, nephritis is distinguished:
- Focal;
- Diffuse.
Based on the nature of the disease, the following are distinguished:
- Acute form;
- Chronic form.
In addition, it is possible to develop lupus nephritis with systemic lupus erythematosus, as well as the development of hereditary pathologies.
Causes
As mentioned above, the disease for reasons of development can be primary or secondary. In the first case, nephritis is formed as a result of primary renal diseases. The primary form accounts for about 80% of all clinical cases of morbidity.
The secondary form of nephritis develops against the background of existing pathological processes in the body.
Causative agents of nephritis:
- gonococcus;
- streptococcus;
- Pneumococcus;
- meningococcus
The main causes of nephritis:
- autoimmune diseases;
- nephropathy during pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- amyloid dystrophy;
- insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus;
- cancer;
- diseases of infectious nature;
- some diseases of the female reproductive system;
- thrombosis;
- urticarial rashes;
- long-term use of certain groups of synthetic medications;
- intoxication of the body with poisons or heavy metals.
Pyelonephritis
This is a purulent disease, the appearance of which is provoked by disturbances in the normal outflow of urine, arising for various functional and organic reasons.
Predisposing factors include immune disorders, diabetes mellitus, chronic inflammation and frequent hypothermia. In women, it often occurs after acute cystitis.
Often the disease is asymptomatic. Purulent nephritis is a kidney disease that must be treated at an early stage; in all subsequent stages, therapy will be ineffective, since the function of the organ will already be impaired.
The disease begins to manifest itself with a sharp increase in temperature to 40 °C. Then the following symptoms appear:
- Profuse sweating.
- Dull unilateral pain in the lumbar region.
- Cloudy or reddish urine.
- Loss of appetite.
- Severe weakness and headache.
- Sometimes nausea and vomiting.
Laboratory testing can reveal bacteriuria, proteinuria and microhematuria. Also, leukocytosis is observed in the patient’s blood, and in 30% of cases there is an increase in nitrogenous waste.
The untreated acute form of this disease is a common cause of chronic kidney nephritis in humans. What does it mean? That attention should be paid to the first symptoms that appear. Since pyelonephritis can develop on both sides, and a progressive disease of this form leads to the development of renal failure, arterial hypertension and a decrease in the specific gravity of urine.
Symptoms
Acute nephritis is a disease that often affects young people, as well as children. In most clinical situations, the process developed 10–12 days after a person suffered any infectious disease. The first signs of the development of acute nephritis are hyperthermia, weakness and weakness, aching pain occurs in the lumbar region.
Main symptoms:
- increased blood pressure;
- strong thirst;
- dry mouth;
- swelling appears. First they are localized on the face, mainly on the eyelids. As the disease progresses, swelling spreads to the entire body. Swelling can become significant in a short period of time. In severe cases, there is a possibility of developing ascites or accumulation of exudate in the pleural and cardiac cavities.
In acute nephritis, not only the kidneys are affected. The body’s cardiovascular system is also affected, in particular the vessels of the kidneys themselves.
The course of the acute form of this disease is favorable in most cases. Treatment can be long-term (up to three months), but, as a rule, it ends with the patient’s complete recovery. In some cases, a slight increase in pressure may be observed over the course of 6 months. This is not dangerous to health and there is no need to treat this condition.
The negative end of the disease is its transition to the chronic stage. This is possible if, within 9 months from the onset of the disease, its main symptoms do not disappear. This usually happens when a person has been misdiagnosed or given the wrong treatment. Chronic nephritis is characterized by alternating periods of exacerbation with periods of calm.
Chronic nephritis lasts a very long time. The patient himself feels constant weakness, weakness, and fatigue. He also develops headaches, his blood pressure rises slightly, and his appetite decreases. If you conduct a urine test, you will find small amounts of red blood cells, protein and casts in it.
The danger of chronic nephritis lies in the fact that with each exacerbation of it, more and more kidney glomeruli die. The kidneys themselves “shrink” and decrease in size. If nephritis is not adequately treated, a significant amount of kidney tissue will die and kidney failure will develop.
Consequences of jade
Other symptoms of nephritis:
- hyperthermia;
- fragility of hair and nail plates;
- dysuria;
- severe intoxication of the body;
- diarrhea;
- bloating;
- the patient's activity is significantly limited;
- vomiting and nausea;
- the skin is dry, icteric, and may peel;
- muscle pain;
- convulsions;
- paresthesia;
- the urine is cloudy and flakes may “float” in it.
Diagnosis of the disease
To make an accurate diagnosis, a nephrologist collects the patient’s medical history, conducts an examination, and identifies symptoms and the nature of pain. The list of necessary examinations includes:
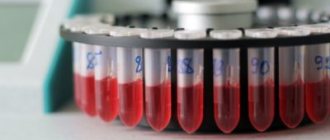
- General blood test and biochemical study to determine the content of leukocytes, ESR, anemia;
- General urine test to determine the amount of protein, leukocytes, red blood cells;
- Urine tests according to Zimnitsky to determine urine density and sodium content;
- Cystoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys (if indicated - X-ray or MRI) to determine the size of the damaged organ;
- Kidney biopsy using puncture;
- Urography.
Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis is accompanied by changes in the chemical content of the blood. In mild cases of the disease, the level of uric acid increases. Severe forms provoke an increase in certain indicators: residual nitrogen, urea, uric acid. Also, the concentration of organic acids in the blood increases and its alkalinity decreases. Functional blood tests reveal a tendency to slow fluid removal from the body. In some cases, uremic symptoms appear: dry mouth, thirst, drowsiness, loss of appetite, itchy skin. Nephritis is associated with metabolic acidosis and hepirkalemia with tubular dysfunction. Functional blood tests and histological examination of the damaged organ can reveal the cause of the disease and diagnose acute nephritic syndrome.
Treatment
Treatment of nephritis is carried out only in a hospital setting with strict adherence to bed rest. The doctor must prescribe a diet for nephritis. During the first two days, the patient should drink only 400 ml of water and eat 100 grams of sugar. The dose cannot be exceeded! This is the first stage of the diet for nephritis. Next, a diet with limited consumption of table salt is prescribed. It is allowed to eat no more than five grams of salt and drink up to 1500 ml of liquid. Animal proteins should also be limited in the diet. Fatty broths, spicy and salty foods are completely excluded. All this is replaced by low-fat varieties of fish, which are recommended to be consumed only in steamed form. The patient is also advised to eat fruits, vegetables and dairy products.
If you have nephritis, it is recommended to eat fruits and vegetables
Conservative therapy involves prescribing the following groups of synthetic medications:
- antibacterial;
- cardiac;
- antihypertensive;
- diuretic;
- antiallergic;
- immunosuppressants;
- calcium;
- routine;
- ascorbic acid.
In case of complex nephritis, treatment should only be comprehensive. Cytostatics and glucocorticosteroids are also added to the above medications. In emergency cases, hemosorption and plasmapheresis are indicated. Surgical treatment is also used, which will be aimed at removing the source of infection from the body.
If severe renal failure has developed, then the only correct method of treatment is kidney transplantation.
Drug therapy
Adequate treatment of kidney nephritis can only be prescribed by a doctor after an examination. What drugs will need to be treated depends on the type, form of the disease, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient.
But, as a rule, one of the following is prescribed:
- Antibacterial drugs: Cephalexin, Ampicillin, Erythromycin. They provoke the destruction of harmful bacteria in the kidneys, and therefore form the basis of therapy. After all, the most important thing in treatment is the direct impact on the cause.
- Antihypertensive drugs: “Zenusin”, “Gemiton”, “Isoptin”, “Adelfan”, “Triniton”. They normalize blood pressure. Contraindications are cardiovascular diseases, gastric and duodenal ulcers, as well as individual intolerance to the components.
- Heart medications: “Diroton”, “Enam”, “Captopril”. They normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system. These drugs should be used with caution. If a person has low blood pressure, hypersensitivity to ATP inhibitors, aortic or mitral stenosis, then it is better for him not to take them.
- Immunosuppressants: Cytoxan, Leukeran, Imuran. These drugs artificially suppress the immune system, which helps minimize kidney swelling. But if bone marrow functions are suppressed, they should be discontinued.
- Diuretics: Spironol, Hypothiazide, Aldopur, Furosemide. These drugs help increase the rate of urine formation and its exit from the body. They should not be taken in case of liver or kidney failure, or if a person has increased venous pressure, diabetes mellitus or anuria.
For kidney nephritis, the most effective drugs are Renel N, Canephron, Hepabel, Artibel, Urostin and Nephrox. The patient is also prescribed vitamins and calcium.
If the case is severe, the person may be referred to undergo a procedure to cleanse the blood of accumulated toxins (hemosorption and plasmapheresis).
Field
Jade is found on each of the four continents. The main deposits include:
- Ospinskoe;
- Ulan-Khodinskoe;
- Buromskoe;
- Khamarkhudinskoe.
Some of the places where jade is mined are the Urals and Kazakhstan. Foreign sources include countries such as China, New Zealand, Canada and the USA.
Prevention
The main measure to prevent interstitial nephritis is careful handling of medications. You can’t take medications without a doctor’s prescription, you can’t experiment with dietary supplements, you can’t increase the doses of medications prescribed by your doctor, you can’t take painkillers every time pain appears, you can’t drink herbal infusions of unknown origin (for example, weight loss teas), etc. If, due to a health condition (the presence of pain), you have to constantly take analgesics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, you must definitely consult a doctor, find the cause of the pain and eliminate it, and not “smooth out” the symptoms.
Zubkova Olga Sergeevna, medical observer, epidemiologist
16, total, today
( 161 votes, average: 4.57 out of 5)
Oxalate kidney stones
Phosphate kidney stones: treatment and diet
Related Posts
Application
Both in ancient times and now, quite a large number of people use jade to treat certain diseases and ailments. There are several tips that are best followed:
- Small beads can be used as exercises after a stroke. The ideal option is jade beads.
- Using a massage ball, roller and jade rod in combination will help get rid of problems with facial skin and fatigue.
- Green stone will help stabilize the heart and improve sleep. Beads are best suited for this.
- A slightly heated mineral can be applied to bruises.
Talismans
Jade is an excellent amulet that protects a person from misfortune and wrong decisions. White stone brings change and good fortune. It is often used by people who want to find their soulmate.
A small lock, which is carved from stone, is used as a talisman for children. You can put it on a chain and give it to a child. This way evil spirits will not be able to approach him.
Rings with a white stone are used as a talisman to preserve family happiness and success at work. Moreover, this mineral will help improve the effect of other amulets. The setting for the stone is mainly silver.
Jade is a symbol of intelligence and courage. If you wear such a talisman constantly, then a person can easily achieve his goal. It will give intelligence and courage to warriors, and will also protect them from injury and wounds.
It is best to use red stone for your home. It will protect you from natural disasters.
Stone care
Caring for jade is very easy because it is not picky. The original stone is not afraid of scratches and falls.
It is enough to store it in a separate soft bag, case or box. When cleaning, it is better to give preference to a soap solution without aggressive agents, and then rinse well under running water. You need to wipe the stone dry.
You can wipe jade jewelry with a damp soft cloth.
Interesting facts about jade
- Until the mid-19th century, jade and jade were considered one mineral and were called jade.
- Jade is the national symbol of China, the “stone of life.” It was valued even higher than gold and silver, as the Chinese believed in its powerful magical properties. There was even a saying that “gold has a price, but jade is priceless.” According to archaeological data, the Chinese began using jade about 7000-8000 years ago. Weapons and ritual things were created from it. Chinese philosophers said that jade has five virtues: soft shine - the personification of mercy, strength - moderation and justice, translucency - symbolized honesty, purity - wisdom, changeability - courage.
How are kidney inflammation cured?
Each type of jade has its own symptoms and treatment accordingly. For any type of kidney inflammation, hospitalization and bed rest are required. Each patient receives his own diet, the observance of which is mandatory. Physical activity should be minimal.
Drug treatment
A patient with nephritis is prescribed drug therapy only after determining the type of disease, its etiology and prevalence. To remove toxins, doctors advise using diuretics (Diacarb, Furosemide). Antihistamines (Suprastin) and glucocorticosteroids (Hydrocortisone) will help relieve inflammation. If kidney disease is caused by a cancerous tumor, the patient takes cytostatics (Azathioprine, Fluorouracil).
Blood pressure is normalized using diuretics (Furosemide) or beta-blockers (Atenopol). When deficiency begins to develop, it is necessary to take oxidants (riboflavin, cocarboxylase).
Antibiotics and antivirals are prescribed if kidney disease is caused by viruses or bacteria. For nephritis, the following complex of antibacterial drugs is used: penicillin + cephalosporins + fluoroquinoles/aminoglycosides.
Special nutrition for kidney inflammation
Treatment of nephritis with a diet includes a balanced diet and reducing salt intake to 2-4 grams per day. For the treatment of such diseases of the urinary system, Pevzner developed a special diet - table No. 7. During the first days, you can drink two glasses of sweet water, but you cannot eat anything. Total fluid per day is no more than one and a half liters. All further dishes must be steamed, or boiled, baked. Exclude pickles, smoked foods, fatty and salty products. Peas, all legumes, seaweed, and radishes are prohibited.
In case of severe swelling, use a dairy diet. But to avoid bloating, add a little baking soda to the liquid.
Surgical intervention
Such a radical method is carried out quite rarely. Surgery for nephritis is prescribed if traditional therapy does not help. If the kidney is dysfunctional due to its deformation, transplantation is performed. When the outflow of urine is disrupted, doctors perform catheterization of the ureter.
Pathogenesis: what happens with nephritis
Nephritis is a kidney disease with a complex development mechanism. Most experts associate the development of the disease with the formation of autoantibodies to organ tissues and the development of an allergic neurohumoral reaction.
If pyelonephritis is associated with ascending or hematogenous spread of an infectious agent and direct damage to the mucosa, then glomerular and tubulointerstitial nephritis develops somewhat more complexly. In these forms of the disease, the action of viruses and bacteria does not lead to direct infection of the kidney tissue - the pathogen is not detected there. As a rule, damage to the urinary system develops 2-3 weeks after the onset of symptoms of tonsillitis, scarlet fever or other infection, and is caused by the pathological activity of the body's own defenses.
Why in some people angina ends with complete recovery, while in others it provokes the development of acute nephritis is a question that has not been fully studied. There is probably a hereditary predisposition to autoaggression towards the body's own tissues.
Kidney damage always begins with a vascular reaction - the development of capillaritis. The blood supply to the kidneys is disrupted, and the inflammatory process in the organ causes not only disruption of the processes of formation and excretion of urine, but also general reactions:
Video on the topic
What forms does kidney nephritis have, symptoms and treatment of the disease - about this and much more in the video below:
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerular nephritis, or glomerulonephritis, is an immuno-allergic inflammatory pathology that affects the glomeruli of the kidneys.
Primary glomerulonephritis occurs due to a violation of the morphology of the kidneys. Secondary – due to infections, drug addiction or cancer.
The disease can be acute or chronic, with repeated exacerbations and periods of rest. A subacute (malignant) form is distinguished separately.
- Infectious diseases caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus most often lead to glomerulonephritis.
- Diseases caused by pneumococcus, staphylococcus, hepatitis C virus. Glomerulonephritis can appear 1-3 weeks after the flu or respiratory tract infections (sore throat, laryngitis).
- Allergies, insect bites, trauma, sun exposure, food or drug intolerance.
During an infection, the immune system produces antibodies to pathogenic microorganisms. Antibody complexes act on the vessels of the glomerulus, which becomes inflamed during nephritis.
Pyelonephritis
This is a kidney disease in which the destructive process affects the pyelocaliceal structure of the organ.
The cause of this nephritis in most people is E. coli. Other microorganisms that cause the disease include Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Proteus vulgaris. Less than 5% of cases are gram-positive staphylococci and enterococci.
- ascending route - from the lower urinary tract or genital organs;
- hematogenously - due to acute inflammation outside the genitourinary system (mastitis, tonsillitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, etc.).
Pyelonephritis in the acute stage can lead to renal failure.
Interstitial
Interstitial nephritis of the kidneys is characterized by a destructive-inflammatory process of connective tissue.
You can get sick due to taking antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Other factors include previous infections (sore throat, diphtheria), poisoning, burns, and injuries.
Medicines that can provoke the disease:
- antibiotics (Penicillin, Tetracycline, Ciprofloxacin);
- antiviral drugs (Acyclovir);
- most non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- diuretics (Furosemide, Triamterene);
- antihypertensives (Amlodipine, Captopril).
The risk of nephritis has been identified in people taking herbal medicines based on Chinese herbs. Plants containing aristolochic acid are unfavorable.
Characterized by polyuria, weakness, and a tendency to form kidney stones. Hypertension is expressed in 30-45% of patients.
Treatment involves discontinuation of the drug that caused the malaise, vitamin complexes, antihistamines and anti-sclerotic medications.
Purulent
Pyelonephritis can occur with severe and dangerous complications, in purulent forms. These include apostematous nephritis, carbuncle, and kidney abscess.
Complications with the occurrence of purulent processes can be a consequence of uncontrolled use of antibiotics. The immune system forms antibiotic-resistant strains of microorganisms. As a result, the classical treatment regimen for pyelonephritis becomes insufficiently effective. The inflammatory process gets out of control, flowing into suppuration of the kidneys.
Ray
Radiation nephritis is inflammation of the kidneys due to radiation. The disease occurs both after strong single radiation exposure and with prolonged exposure to small doses. The kidneys are most sensitive to the effects of radioactive radiation.
This type of nephritis can develop both during irradiation of the lumbar region directly and against the background of general radiation sickness. The renal glomeruli and tubular system are subject to dystrophic changes.
The clinical picture of the disease is changes in the composition of urine, hypertension, anemia, swelling. Treatment is similar to that of interstitial nephritis caused by other causes.
Toxic
This variety occurs under the influence of toxic chemicals. These include lead, mercury, nitrogen-containing compounds, cyanides, insecticides, etc. Toxic nephritis is typical for workers who directly deal with pesticides, polymers, and synthetic rubber.
The second factor is biological poisoning - poisonous mushrooms, snake and insect bites, poor quality food, as well as alcoholism.
Due to severe damage from toxic substances, kidney failure can be fatal.
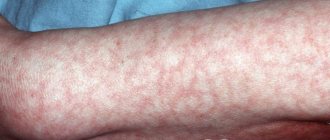
Lupus
This is the name for kidney damage in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). This is a disease of unknown etiology that provokes immune complex inflammation of the connective tissue of organs.
Suspected factors for lupus nephritis:
- genetic predisposition;
- increased estrogen levels;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- past infectious diseases.
The external manifestations of SLE are red rashes on the skin. But it is possible to reliably detect the presence of systemic lupus erythematosus only by the results of a blood test.
Treatment depends on the form of the disease and ranges from hormone therapy to kidney transplantation.
Congenital
Hereditary nephritis is classified as a genetically determined type of glomerulopathology. A child is diagnosed with a disorder in the morphology of the renal glomeruli. This disease is often accompanied by hearing loss and blindness.
The first symptoms of kidney damage become visible between the ages of 3 and 10 years. Hematuria (blood in the urine) may spontaneously appear and disappear in a child. To clarify the diagnosis, a biopsy of renal tissue is prescribed.
There are no effective treatments for hereditary nephritis. The child is prescribed a gentle regimen, limited physical activity, and a diet.
Primary and secondary
Types of kidney nephritis include primary and secondary. Primary nephritis has no previous disease. Secondary may be a consequence of autoimmune diseases, allergies, infections. The cause is diabetes, oncology or alcoholism.
Diffuse and focal
All types of nephritis can be divided into diffuse or focal. With the diffuse nature of the disease, the systemic immunoinflammatory process affects the entire tissue of the damaged organ. In focal cases, the lesion is localized in certain areas (foci) of the kidney.
Acute and chronic
An acute form of nephritis can occur in any of the types of this disease. This term refers to a rapidly developing inflammatory process. Characterized by high fever and severe pain.
A chronic disease accompanies a person for a long time, alternating stages of exacerbation and remission. Treatment is reduced to reducing the frequency of exacerbations and increasing periods of remission.
Physico-chemical characteristics of jade
Jade is a sodium and aluminum silicate. Its crystals are colored in shades of green, gray, yellow, white and black, and rarely blue and red. They are translucent or opaque, without shine and cleavage, with a monoclinic system, splintered at the fracture. They do not have pleochroism.
The hardness of jade on the Mohs scale is 5.5-6.5. Specific gravity 2.8-3.3 g/cm3. Refractive index 1.60-1.65.
An important optical property of jade is its ability to be translucent. The light is scattered within the stone, creating the illusion of a hazy glow. This phenomenon is especially pronounced in light green and blue samples.
The durability of jade crystals is also legendary. Thanks to its fibrous structure, the stone is practically not susceptible to mechanical stress; it is one of the few rocks that are both elastic and durable.
Diagnosis
To diagnose any type, the attending physician checks many factors that can provoke nephritis. He asks questions: “How did the disease begin to act?”, “What are the reasons?” (exposure to cold, high consumption of drugs, additional diseases, infection to which the body was exposed, etc.). Under the close supervision of medical personnel, research is carried out:
- various urine tests;
- general blood analysis;
- ultrasound examination of the kidneys;
- X-ray check;
- computed tomography;
- examination of organs using MRI;
- biopsy.
Please note: when you experience symptoms consistent with kidney disease, you should go to the hospital. If the body is not examined in a timely manner and the body is not treated, the condition will worsen, and consequently, kidney failure syndrome will appear.
There is a risk of long-term high pressure in the arteries (140 to 90 or more), as well as swelling. The results of a urine test reveal its decreased density and the disappearance of normal variability, which is explained by impaired fluid excretion by the kidneys.
At night, the volume of fluid that the patient secretes increases. This process is explained by the fact that the blood supply to the kidneys has improved.
If the current process is neglected, it will be much more difficult for medical professionals to detect circumstances indicating the presence of chronic nephritis. Its symptoms are not always clear and may indicate renal failure syndrome.
In the last stages of the disease, excessive deposition of toxins and wastes occurs in the blood, accompanying the development of certain symptoms:
- general malaise;
- renovascular hypertension;
- headache.
If the syndrome, in which there is a delay in metabolic products in the human body, increases, salts (usually contained in the urine) are released through the skin through various secretions, including gastric juice. The result of this is dry skin. Symptoms of many other diseases occur: pain in the lungs, heart, stomach, vomiting.
Impact on different zodiac signs
With the right color, jade suits absolutely any zodiac sign. But it must be used only with good intentions, because otherwise the power of the stone will turn against the owner. Jade has a power that is not typical for other minerals. For each zodiac sign it has a different meaning, and this is definitely worth taking into account.
Air element
Aquarius
People of this sign love freedom very much. Aquarius is the most powerful water sign. Jade will help you understand the energy of the universe. The best choice is a blue stone.
Jade will help good people protect themselves from enemies who want to cause harm and protect them from obstacles. It will protect you from danger, protect you from illness and indicate the wrong step.
Twins
This sign should pay special attention to the color of the stone, because it is this sign that can indicate that a person is doing something wrong. If the color of the jade has become darker, then you should stop.
People of this sign tend to get colds, so jade can protect against this. It is also necessary for problems with the genitourinary system.
Scales
It is better for this sign to choose round talismans. It is very difficult for Libra to make a choice, and the power of jade will help them.
This stone is able to give the necessary impetus for the right step. This amulet is especially recommended for a person with a large family or a large business. As well as firefighters and rescuers who save the lives of many people.
Girls and boys who want to find a soul mate should choose jewelry in the shape of paired animals. You should always carry it with you.
Earth Element
Taurus
The best choice is a stone that is milky white or green in color. The main problem of this sign is lack of self-confidence and tightness, which contributes to conflicts and failures. Such a talisman can help its owner become more confident and purposeful.
A red stone is necessary for creative people. It is he who can inspire new masterpieces.
Virgo
The mineral will give people of this sign integrity and health, as well as energy and the necessary vitality. It is worth choosing a stone according to eye color. It is this amulet that has the greatest power.
It is better to choose jewelry in the form of the Zodiac sign, because this is what will protect you from evil people.
The stone will give sexuality to virgin girls. For men, it is better to purchase a figurine made of this material so that they never encounter problems and diseases of the genital organs.
Capricorn
People of this sign will be able to find their love. It is best to choose a stone of dark shades. They are the ones who will show you the right path and help you gain trust and love.
In case of illness, any medications will have a better effect if you additionally wear a jade amulet.
Fire Release
Sagittarius
Jade will help Sagittarius people become calmer and more modest. For medicinal purposes, the stone is necessary for the nervous system. This way the person will become calmer, although Sagittarians often deny this problem.
The main thing is that a person believes in the power of the stone and trusts it.
Aries
The mineral will help this sign to achieve the desired heights and at the same time remain honest with themselves. All tasks will be much easier, and the result will not take long to arrive.
a lion
This sign can have several jade jewelry at once. They will be able to fill their owner with new creative ideas and revive forgotten ones. Leos are suitable for a stone of any shade and shape.
A person will want to travel more, explore, and will always be open to something new.
How to distinguish real jade from a fake
As an inexpensive stone, jade is rarely counterfeited, but imitations made from glass, clouded with pigments and fibrous structure additives, are still found.
They can be distinguished by the fact that glass is polished to a mirror shine, while jade always retains some dullness, and small defects are visible on its surface.
Detection of pathology
To create a complete picture and confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a full examination to the patient. In case of nephritis, the disease is diagnosed through biochemical and general blood tests, general urine analysis, and bacterial culture. They also do tests according to Nichiporenko, Amburge, Adis-Kakovsky, check the number of urinations and the daily volume of urine. An antibiogram and creatinine clearance are performed. At his discretion, the specialist refers the patient to additionally undergo a urine test for enzymes and determine its molarity, excretion of immunoglobulin in the urine. And tests according to Zimnitsky with ammonium will not interfere.
The devices are used to perform pelvic ultrasound, electronic urography, and measure blood pressure. Next, the diagnosis is based on the individual characteristics of the patient’s health status.
History of jade
People began using jade back in the Neolithic era. Then it was used in the manufacture of strong weapons and tools, and later it began to be used for jewelry. Jade was especially popular at all times in China. For example, there is a Buddha statue 6 meters high, carved from a single piece of milk jade.
Jade was also popular among other peoples due to its beauty and high strength. Tamerlane's tomb was covered with a black jade slab. The sarcophagus of Tsar Alexander III was also carved from jade.
Today jade is no less popular than in the old days as an ornamental and jewelry stone.
Jade colors
The color palette of jade is very diverse - from black to white due to the presence of various impurities. The most common jade is green and its shades: marsh, grassy, light green, emerald and yellow-green. Red and blue jade is very rare. The yellow-brown-green variety with a “cat’s eye” effect is also considered unique.