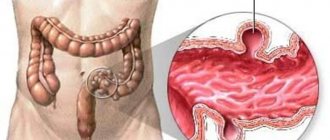
Gluten enteropathy (Celiac disease) is a type of autoimmune reaction to gluten. Gluten causes disruption of the digestive tract. The protein present in wheat, barley, and rye damages the small intestine, disrupting digestion.
The disease affects up to 1% of the population, and typical celiac disease is rare. Most people have extraintestinal manifestations: osteoporosis, dermatitis, infertility, iron deficiency anemia, autoimmune diabetes.
What is gluten and where is it found?
Gluten is a plant protein with a complex structure. It includes two main components - glutenin and gliadin. It is the second substance that poses the danger. Gluten is a component of wheat, barley and rye grains.
In the production of bread, it provides the product with elasticity and ductility. Without the substance, baked goods would not have such excellent taste. However, it is found not only in flour products.
It includes:
- barley;
- rye;
- oats;
- semolina porridge;
- bran;
- pasta;
- breading products;
- sausages;
- sausages;
- meatballs;
- cutlets;
- products containing soy;
- French fries;
- mayonnaise;
- chips;
- burgers;
- canned food with tomato sauce;
- undistilled vodka;
- ketchup;
- dried apricots;
- cottage cheese;
- juices;
- fruit drinks;
- compotes;
- lemonades;
- kvass;
- soft drinks containing sugar.
Gluten intolerance, the symptoms of which vary in adults, mainly manifests itself in true or false allergies.
The protein contains gliadin, which is toxic. An allergic reaction does not always appear in childhood. Medical studies have shown that the reaction can occur in any age category. If there is a disturbance in the enzyme system, gliadin is not broken down in the body or is not broken down completely. Toxins begin to poison the body, causing allergies.
If you made a mistake
Eating a gluten-free diet for celiac disease is a learning process not only for you, but also for your family and friends. You may make mistakes, especially in the early days after you are diagnosed.
If you have celiac disease and mistakenly eat a product containing gluten, you will typically begin to experience symptoms within a few hours of eating, which can last anywhere from a few hours to several days. However, the effects vary from person to person, depending primarily on how much gluten you eat, how sensitive your body is to it, and how long you've been on a gluten-free diet.
If you do have celiac disease, foods containing gluten will damage your intestines. If you make the occasional mistake and accidentally eat gluten, it is unlikely to cause much damage to your intestines.
Causes of Gluten Allergy
The reason for the lack of enzymes lies in the genetic factor.
There are several causes of an allergic reaction to gluten:
- Immunological. The body produces antibodies to gluten.
- Violation of the enzyme system of the gastrointestinal mucosa.
- Disorders of protein metabolism in the intestine, causing disruption of the absorption of gliadin.
- Increase in the number of antibodies to adenovirus. The body accepts them as antibodies to gluten.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions.
- Working with chemicals.
- Uncontrolled use of medications.
Gluten intolerance, which causes symptoms in adults due to genetic predisposition, is not caused by excessive consumption of foods containing the substance.
Symptoms
Textbooks distinguish three clinical forms of celiac disease. In fact, its manifestations are much more diverse: the symptoms of celiac disease are disguised as various diseases of the digestive system, hypovitaminosis, dermatological pathologies and many others. That is why the diagnosis of celiac disease is given to a limited number of patients, while the rest are endlessly treated for its manifestations.
On the other hand, there are many clinical cases when all the manifestations of one of the forms of celiac disease are present, even a blood test indicates this. But a biopsy of the small intestine does not confirm the doctors' assumptions.
In 1991, celiac disease was presented in the form of an iceberg: at the top there is a small number of confirmed variants that occur with clear clinical signs. Underwater there is a huge number of those same undiagnosed, “masked” cases. And at the base of the iceberg are people who have a genetic predisposition to celiac disease, but the disease develops only when exposed to provoking factors (stress, decreased immunity, eating a large amount of foods with gluten, and so on).
The earlier and in larger quantities gluten is introduced into food (for example, semolina porridge, beloved by all grandmothers), the faster celiac disease occurs and the more severe it is.
Symptoms in children
“Iceberg” of celiac disease: click to enlarge
The typical form has three prominent symptoms:
- frequent stool (up to 5 times a day or more): there is a lot of it, a mushy consistency, shiny due to the presence of fat, smells bad, can be foamy, of different colors, it is difficult to wash off
- bulging belly: the doctor will say that this is due to rickets in the child, the parents will think that the child is just eating well
- lag in height and weight: especially noticeable in the first two years (in weight), and in height - after 2 years. Insufficient weight gain is alarming precisely after the introduction of complementary foods, and until this moment the child gains weight well and grows and develops normally.
Other symptoms of celiac disease in children are associated with insufficiency of nutrients, vitamins and microelements, so they may be different for each child:
- fatigue, lethargy or, conversely, tearfulness, aggressive behavior, increased irritability
- poor skin and hair condition: dryness, weakness, flaking of the skin, atopic dermatitis in a child
- frequent fractures even with minor trauma - this despite the fact that fractures are actually rare in children, their bones are elastic
- incorrect posture
- hypotension - insufficient muscle tone
- manifestations in the oral cavity: bleeding gums, stomatitis in children, caries, crumbling enamel
- anemia (see iron supplements for anemia)
- the child looks unhappy
- a child with celiac disease is compared to a spider due to the presence of a large belly and thin arms and legs
Subsequently, the functioning of the reproductive system in children is disrupted: girls do not get their periods, boys experience sexual dysfunction.
Symptoms in adults
Symptoms of celiac disease in adults are characterized by atypical and latent forms. The atypical form appears only in the third or fourth decade of a person’s life. It represents one of three symptoms of a typical form and two or three accompanying ones. But in general, extraintestinal manifestations of celiac disease predominate:
- neurological: migraine, depression, etc.
- dermatological: herpetiform or atopic dermatitis
- dental: aphthous stomatitis, atrophic glossitis, enamel hypoplasia
- renal: nephropathy
- articular: arthritis, joint pain of unknown cause
- strange changes in biochemical blood tests: decreased cholesterol, increased alkaline phosphatase, transaminases, albumin
- reproductive: infertility
In clinical studies, 4-8% of women unsuccessfully treated for infertility were diagnosed with celiac disease. All of them managed to become happy mothers after being prescribed a gluten-free diet.
The latent form may not manifest itself at all, only occasionally causing concern with minor intestinal disorders or external manifestations (dermatitis and so on). Celiac disease is detected only during random examination.
Signs of gluten intolerance in adults
Gluten can cause significant harm to human health. Often the patient does not feel its negative effects. Below are the main symptoms that may bother a person with celiac disease.
Gastrointestinal problems
Symptoms of an allergic reaction to gluten are expressed in disruption of the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract.
The person begins to worry:
- disorder of the intestines;
- bloating;
- pain in the epigastric region;
- chronic diarrhea;
- foamy stools with an unpleasant odor.
Patients associate ailments with other pathologies. Irritable bowel syndrome is often diagnosed.
Unexplained weight changes
Allergies can cause both weight loss and weight gain. The basis of this symptom is a violation of metabolic processes.
Hormonal imbalance
There is a direct connection between gluten sensitivity and hormonal imbalances. In women, the menstrual cycle is disrupted and weight changes are observed. Often the patient is worried about premenstrual syndrome and insomnia.
Problems with the central nervous system
Adults may experience the following neurological symptoms:
- presence of seizures;
- epilepsy;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- schizophrenia;
- autism;
- Parkinson's disease;
- anxiety;
- dementia.
Gluten promotes the development of inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract and intestinal permeability.
As a result, a person may experience:
- loss of concentration;
- depression;
- feeling of anxiety;
- insomnia;
- asthenia;
- irritability.
Researchers say that people with gluten allergies are more likely to suffer from migraines than others. The patient may experience a headache every 30-60 minutes after eating.
Skin and nail problems
Keratosis pilaris and dermatitis herpetiformis are the main skin pathologies that are associated with the disease.
Often people are concerned about:
- itching;
- eczema;
- weakness and brittleness of the nail plates.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Gluten intolerance, in which symptoms in adults are triggered by a sensitivity to the protein, can cause hyperactivity or decreased attention. ADHD can develop in both children and adults. People suffering from pathology are unable to concentrate and solve problems.
Poor dental condition
Gluten can interfere with the absorption of essential minerals and elements in the intestines. A lack of calcium may cause dental problems. A person is concerned about the destruction of tooth enamel and ulcers on the oral mucosa.
Iron-deficiency anemia
Iron deficiency anemia is often a symptom of cealicia.
Its main symptoms include:
- asthenia;
- presence of shortness of breath;
- migraine;
- pale skin;
- development of arthritis.
Autoimmune diseases
Celiac disease is a pathology in which the immune system begins to attack intestinal cells when gluten enters the organ. The risk of developing autoimmune diseases increases.
Pathologies of this series include:
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis;
- autoimmune hepatitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- diabetes;
- vitiligo;
- arthritis;
- multiple sclerosis.
Complications of celiac disease
Complications arise with late treatment, when the symptoms of intestinal celiac disease are ignored for a long time, or with illiterate treatment.
Ulcers can develop on the walls of the intestines, hypovitaminosis, bone fractures, and the development of a tumor process, including cancer of any part of the digestive tract.
The patients suffer from infertility. In some cases, the patient complains: “I have been on a diet and undergoing treatment for a long time, but the disease does not go away,” then a suspicion arises of the development of a refractory form.
To avoid such severe complications, the only salvation is a diet with gluten-free foods; there are no other specific preventive measures.
Diagnosis of pathology
In some cases, the symptoms are subtle. To establish the pathology, a diagnosis must be made. To test at home, it is recommended to exclude gluten-containing foods from your diet for 2-4 weeks. If, after returning to a normal diet, you feel a deterioration in your health, then your body actually has an allergy to protein.
When making a diagnosis, the following are taken into account:
- assessment of clinical symptoms;
- immunological indicators;
- morphological analysis for celiac disease;
- lab tests.
Diagnosis of the disease involves a visual examination by a gastroenterologist. The doctor palpates the abdominal area to identify pain, measures the circumference of the abdomen, and also gives a referral to an allergist’s office. Single clinical indicators cannot confirm the development of the disease, but with a combination of manifestations, the disease can be suspected.
After assessing the medical history, a serological test is performed to detect antibodies and antigens. The study involves the analysis of seroimmunological parameters. Antibodies to tissue cells and reticulin of muscle connective tissue are detected.
For morphological diagnosis, fibrogastroduodenoscopy is performed.
The procedure involves:
- examination of the internal cavity of the stomach and intestines;
- examination of intestinal villi through biopsy sampling;
- assessment of the smoothness of intestinal folds;
- detection of atrophy and inflammatory process in the intestine.
Laboratory diagnostic methods include:
- Analysis for the level of hemoglobin, red blood cells, platelets and leukocytes. It allows you to determine the presence of inflammation.
- Blood test for immunoglobulin levels. It has a high degree of information content in the acute stage of the disease.
- Stool analysis. It allows you to determine the presence of hidden blood, as well as detect food fragments.
Diagnostics
Most often, celiac disease is detected when the whole body is diagnosed for one of the diseases listed above. Targeted diagnosis of celiac disease consists of three stages.
- Stage 1 – immunological blood tests. The level of antigliadin antibodies, the presence of autoimmune antibodies to reticulin, tissue transaglutaminase, and endomysium are determined.
- Stage 2 - if immunological tests are positive, a biopsy of the mucous membrane of the small intestine is performed, and the condition of its villi, the presence of inflammation and lymphocyte cells with altered receptors (discussed above) are determined. The second stage is the most important for making an accurate diagnosis.
- Stage 3 – prescribing a gluten-free diet and monitoring the patient for six months. If there is an improvement in the general condition and a reverse development of the symptoms of the disease, the diagnosis of celiac disease is made definitively.
The third stage of diagnosis is carried out with positive immunological tests and questionable and even negative biopsy results. If after six months the patient’s condition improves, a diagnosis of celiac disease is made. This form of celiac disease is called potential.
A year later, a repeat immunological examination is prescribed. It should reveal positive dynamics. And after one and a half to two years they do a second biopsy: the villi of the small intestine should be completely restored during this time.
Treatment of intolerance
The most effective treatment for celiac disease is following a strict diet that excludes gluten-containing foods. A balanced diet reduces symptoms and improves the patient’s general condition. Medications and folk remedies are also used.
Medicines
The following medications are used in drug therapy for celiac disease:
- Preparations containing protein in the form of plasma and albumin, as well as mixtures of amino acids.
- Steroid drugs Phenobolin and Retabolin. They synthesize protein.
- Emulsions containing fat. They are administered intravenously.
- Enterosgel. The drug normalizes the microbiological and immune status of the gastrointestinal tract. It is used for preventive purposes in the mornings and evenings.
- Panangin and calcium gluconate. They eliminate water and electrolyte imbalance.
- Vitamins of group A B C E K and nicotinic acid.
- Glucocotic steroid drugs. They suppress autoimmune mechanisms.
- Prednisolone and Methylprednisolone.
- Enterol. It normalizes intestinal flora.
- Probiotics Linex, Latium.
- Absorbents Smecta, Dermazol, Polyphepan.
- Loperamide and Imodium. The drugs suppress intestinal motility.
- Pentas. The drug stops the inflammatory process.
All medications and dosage are selected by a specialist. The general condition of the body and the degree of manifestation of symptoms are taken into account. In parallel, therapy for iron deficiency anemia is carried out.
In this case, the following technique is indicated:
- vitamin complexes and microelements;
- calcium;
- vitamin D.
If not treated in a timely manner, pathologies are provoked by:
- ulcer;
- hypovitaminosis;
- oncological tumors;
- infertility.
Folk remedies
Treatment of the disease is also carried out with folk remedies, which complement the basic therapy and diet. At the first signs of pathology, medicinal herbs such as honeydew, bedstraw, lungwort, swamp cudweed, meadowsweet, long-leaved speedwell, and bifolia will help alleviate the condition.
- To prepare the infusion, mix these herbs and brew them as tea. The mixture is infused for 30 minutes. Take 50 ml. 5 times a day.
- To eliminate inflammation in the intestines, an infusion based on chamomile, bileaf, meadowsweet, and lungwort is used. You should take 1 tbsp. l. collection and fill it with 250 ml. boiling water The medicinal infusion is taken 1 glass 3 times a day for 40 minutes. before meals.
- Sea buckthorn oil or honey can restore damaged intestinal mucosa. One of the remedies should be taken on an empty stomach or before bedtime, 1-2 tsp.
Gluten intolerance can be eliminated by using traditional medicine. Symptoms in adults are relieved with herbal infusions. This treatment complements the main course. It is advisable to consult a specialist.
Principles of nutrition, diet
The diet involves eating foods that contain gluten in small quantities.
Can be used:
- rice flour;
- soy;
- corn;
- fish;
- potato;
- fruits other than bananas and dates;
- legumes;
- fermented milk products except yoghurts;
- margarine;
- butter;
- vegetable oil;
- honey;
- berries;
- greenery;
- nuts;
- quail eggs;
- lean meats;
- home canned food.
Gluten intolerance, the symptoms of which may vary individually in adults, can be eliminated after just 3 weeks of following this diet. After a year, the intestinal mucosa is completely restored.
Celiac disease treatment
After establishing the final diagnosis, the most important point is timely and correct treatment of the disease.
Many experts believe that “celiac disease is not a disease, celiac disease is a way of life” and this is correct; the main thing in the treatment of celiac disease is the exclusion of foods containing gluten from the diet. And provided that a gluten-free diet is followed, a patient suffering from celiac disease is completely healthy, because the inflammatory reaction in his intestines completely stops without contact with gluten.
Complete disappearance of signs of the disease depends on the state of health of the person before treatment and takes from several months to several years. In children, normalization of intestinal functioning occurs on average within six months after starting the diet. In adult patients, this process is longer - up to 2 years.
Patients who find it difficult to limit themselves and completely give up bread and other products containing gluten need to remember the development of serious complications in the form of severe fractures, malignant neoplasms or other severe pathologies of internal organs that steadily progress without proper treatment.
Celiac disease treatment in adults
Therapy for this complex disease in adult patients has several stages aimed at reducing the inflammatory reaction and restoring normal intestinal functioning (enzyme therapy, taking probiotics, vitamin therapy), but first of all, a strict diet is prescribed that excludes all foods containing gluten from the diet.
Diet therapy in adult patients
An important factor in the treatment of this disease is the elimination of the pathological effects of specific immune complexes that are formed when products containing gluten enter the patient’s intestines - transfer to a constant strict diet and exclusion of all prohibited foods from the patient’s diet.
Therefore, patients need to know an approximate list of these products:
- bread and any products made from wheat, oats, barley and rye flour;
- all pasta and cereals made from these cereals;
— butter dough, cookies, cakes;
— canned food, sausages and semi-finished meat products;
- sauces;
— It is undesirable to eat whole milk, yogurt and ice cream due to the possible occurrence of cross-allergy to these products.
The diet can include products from buckwheat, corn, rice and soybeans, legumes, potatoes, all vegetables and fruits, fish and lean meat, vegetable oil and cottage cheese.
It is not advisable to eat hot or cold food; with this disease, it is better to steam dishes, excluding fatty and fried foods, smoked foods, dyes and preservatives.
Complete elimination of gluten from food allows you to eliminate its irritating effect on the walls of the small intestine and gradually restore the affected organs.
What foods are prohibited if you are allergic to gluten?
The diet involves giving up:
- processed meat;
- canned food;
- chocolate;
- coffee;
- cocoa;
- spicy dishes;
- salt;
- flour products;
- bouillon cubes;
- sausages;
- sausages;
- ham;
- cocoa;
- tea with aromatic additives;
- chips;
- crackers;
- sweets;
- marshmallows;
- halva;
- cakes;
- squash caviar;
- stew;
- meatballs;
- nuggets;
- wheat bran;
- pasta;
- corn flakes;
- carbonated drinks;
- condensed milk;
- hard cheese;
- pearl barley porridge;
- barley porridge;
- ice cream;
- alcoholic drinks.
What can you eat if you have celiac disease?
The diet for celiac disease in adults and children is based on the consumption of gluten-free foods, such as:
- Eggs and dairy products . Some dairy products may worsen your symptoms and signs of celiac disease. Read the ingredients on the package carefully. Some processed cheeses contain gluten.
- Flours and cereals made from amaranth, arrowroot, beans, buckwheat, corn, cornmeal, flax, millet, uncontaminated nuts and oat bran, potatoes, quinoa, rice, sorghum, soybeans, lentils, tapioca, or teff.
- Fresh, frozen and canned meat . If you buy canned food, read the label carefully as some ingredients may contain gluten.
- Fish , especially fatty fish (mackerel, herring, salmon, trout, sardines, sturgeon, anchovies, etc.), since these types of fish contain anti-inflammatory omega-3 fatty acids.
- Fresh, frozen, dried or canned fruits and vegetables , as long as they do not contain thickeners or other gluten-containing additives.
- Some alcoholic beverages including wine, liqueurs, whiskey, brandy, sherry and cider.
- Soft drinks , including fruit and vegetable juices, flavored waters and sodas.
Including anti-inflammatory foods in a gluten-free diet for celiac disease can help speed up recovery.
Sample menu for a week for gluten intolerance
| Day | Breakfast | Dinner | Dinner |
| First | Milk porridge on rice with berries. Coffee with gluten free bread. | Broccoli puree with grated cheese. Potatoes with chicken vegetable salad. | Wheat porridge with nuts and kefir. |
| Second | Fruit curd. Bread with honey. | Chicken soup. Pilaf and vegetable salad. | Potatoes with cream. |
| Third | Scrambled eggs with cheese and gluten free bread. | Fish soup. Chicken cutlets with rice garnish. Vegetable Salad. | Cottage cheese casserole. |
| Fourth | Carrot salad with cheese slices. | Vegetable soup. Stewed beans and chicken. | Draniki made from rice flour, fish, orange. |
| Fifth | Pancakes with honey on gluten-free flour. | Chicken cutlets with rice. | Fish baked in foil with stewed mushrooms. |
| Sixth | Corn flakes with milk. Two hard-boiled eggs. | Meat borscht. Meatballs with mashed potatoes. | Buckwheat porridge with boiled chicken. |
| Seventh | Cheesecakes with dried fruits. | Cheese and herb soup. Fish with buckwheat porridge. | Baked chicken fillet with vegetable salad. |
Recommended Products
If you suspect celiac disease, you should seek help from a gastroenterologist. The specialist will prescribe tests and a diet. The doctor will give you a list of foods, what you can eat if you have celiac disease, and how best to prepare your meals.
Authorized products:
- light vegetable soups with lean turkey and chicken;
- corn pasta;
- Buckwheat and millet groats do not contain gluten;
- berries, vegetables and fruits contain complex carbohydrates that are beneficial for celiac disease;
- weakly brewed tea, jelly;
- olive, corn, sunflower oil;
- butter;
- boiled chicken eggs or steam omelet;
- bakery products made from buckwheat, corn, rice, soy flour;
- boiled fish;
- honey.
Fermented milk products are useful for various gastrointestinal disorders. They help restore intestinal microflora and improve the functioning of internal organs.
The disease is dangerous due to lack of nutrients. Therefore, along with the diet, the doctor will prescribe vitamins.
Forms of celiac disease and their features
Gastroenterologists divide the disease into 4 forms:
- Typical. It is characterized by many symptoms that are associated with the functioning of the digestive system. The first signs of typical gluten intolerance appear in childhood.
- Atypical. Often the first symptoms appear closer to 35 years of age. They are associated not only with disruption of the digestive system, but also with malfunctions of the bones, brain, and reproductive organs.
- Latent. It is the most dangerous because it is asymptomatic. The disease manifests itself when dangerous complications arise, such as diabetes, cancer and others.
- Refractory. The first symptoms appear in adulthood and old age. The disease is accompanied by complete atrophy of the intestinal villi.
Interesting Facts
To have a clearer understanding of the disease, it is useful to familiarize yourself with some interesting facts:
- The beginning of the existence of the disease was marked by human consumption of cereal products in the form of rye and wheat, enriched with gluten, as a result of which the age of the disease goes back several thousand years.
- The female population was more susceptible to celiac disease. The ethnic factor also played an important role. Thus, Africans, Chinese and Japanese rarely suffered from this disease, which was largely due to dietary habits and the genetic component.
- In a number of Russian regions, the disease in question is not recognized as an illness. However, medical specialists are prohibited from making such a diagnosis.
- Some doctors tend to attribute excess gluten to a precancerous condition, which increases the risk of developing cancer of the digestive tract.
- If the parents have such a disease, the risk of the child becoming ill is 1:10.
Forecast
Clinical improvement is noted after just a few days of following a special gluten-free diet, with persistent improvement after 3-6 months. With good adherence to the diet, the prognosis is relatively favorable; observation by a gastroenterologist is required 1-2 times a year.
The prognosis worsens with a late start of treatment, the development of refractory celiac disease, the formation of complications, dynamic observation of a therapist and gastroenterologist, and consultations with other specialists (surgeon, endocrinologist, obstetrician-gynecologist, urologist, rheumatologist, dermatologist) are required. Mortality rates in patients not following a gluten-free diet are around 10-30%. Against the background of a diet, this figure becomes less than 1%.
It should be remembered that gluten intolerance lasts throughout life. Diet and treatment will only help remove disturbing symptoms. In the process of mastering a new lifestyle, societies of people suffering from the same disease and Internet sites specializing in the supply of gluten-free products can help you.
What needs to be excluded?
The list of permitted products is quite extensive. As well as prohibited ones. Every patient should be familiar with the latter, because violating the diet for celiac disease can lead to unpleasant and even serious consequences.
Here the following stands out:
- Bread. All bakery products are made from wheat and rye flour.
- Soups. With meatballs, quenelles, to which gluten flour is added.
- Meat and poultry. Minced meat containing gluten flour. Instead, when chopping, you need to add either already boiled meat or rice. Processed sausages, wieners, frankfurters, pates and other canned meats are prohibited.
- Fish. Salted, smoked, and canned fish in tomato sauce.
- Vegetables. Beets, white cabbage, radishes, turnips, radishes, rutabaga, cucumbers, sorrel, spinach, mushrooms, squash or eggplant caviar, tomato paste, prepared in industrial conditions.
- Cereals. Barley, pearl barley, Poltava, semolina, Artek. Barley, oat, corn, wheat, rice flakes with malt extract - the so-called “quick breakfasts”.
- Eggs. Fried, hard-boiled, raw - at the acute stage.
- Fruits, berries and treats. Sour varieties of both fruits and berries. Plums, apricots, grapes - at the stage of exacerbation of the disease. Caramel and chocolate candies with filling, lollipops, ice cream, oriental sweets, jam not homemade, but industrially produced.
- Milk products. Both sharp and salty cheeses, glazed cheeses, yoghurts.
- Sauces and seasonings. Products containing gluten flour. Multi-component seasonings, which may contain gluten elements, as well as bouillon cubes and ketchup. Pepper, mayonnaise, mustard, horseradish.
- Beverages. Instant coffee, cocoa drinks, surrogate coffee products. Carbonated drinks like Coke and Pepsi. Powdered jelly. Juices: plum, grape, apricot. Kvass, fruit drink - during periods of exacerbation. Alcohol products, especially beer and vodka.
- Fats. All types except butter.
Forms of the disease
The disease comes in several forms. Each variety has its own set of symptoms and requires an individual approach to treatment. There are 5 forms of the disease in total:
- The typical form is characterized by many symptoms of gastrointestinal dysfunction. A person suffering from this form of the disease is worried about loose stools, bloating, and a sharp decrease in body weight. There is also chronic intolerance to dairy products, which, when consumed, cause poor health, intestinal upset, and nausea.
- Atypical form - characterized by minimal symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract. With an atypical form, the patient experiences a whole range of problems, each of which affects different systems of the body. A person experiences chronic fatigue, and tests reveal a low level of hemoglobin. Physical activity decreases, which entails the appearance of dizziness, apathy, and pale skin. A common occurrence of this form is constipation and constant pain in the bones.
- The hidden form never actually reveals itself. In most cases, a person does not suspect that he has a disease, leaning towards the version that he has a slight intestinal disorder and rare bloating.
- Latent form - is asymptomatic, the disease is indicated only by positive tests.
- Refractory form - with this type of disease, a whole range of disappointing symptoms are observed, including intestinal upset, bloating, and abdominal pain. Treatment with a special gluten-free diet does not produce results. Analyzes in this form remain unchanged.
Only a qualified doctor can diagnose the correct form of the disease. A diagnosis can be made and treatment can begin only after collecting all the necessary information and tests.
Causes
Based on observations, scientists have found that women are more likely to suffer from celiac disease. In most cases, the disease develops in childhood. It can be triggered by various factors: mental trauma, neurological damage, changes in diet, pregnancy, childbirth, food poisoning.
The body's inability to digest gluten is a consequence of a congenital deficiency in the intestinal mucosa of enzymes intended for this process. There is reason to believe that celiac disease is highly likely to be inherited. Evidence of this is the cases of illness in the patient’s relatives and the similarity of the tests.
Causes
The main cause of celiac disease in adults is genetic predisposition. Thus, genetic disorders in patients’ bodies create favorable conditions for damage to the intestinal mucosa. It is most often observed when consuming foods containing protein. In medicine, the following risk groups are distinguished:
- close relatives;
- Irritable bowel disease is a serious intestinal disorder characterized by severe abdominal pain. The pain becomes less pronounced after defecation;
- presence of Down syndrome;
- autoimmune form of thyroid disease;
- diabetes;
- lymphocytic form of colitis - an inflammatory process in the colon, where an increased number of lymphocytes accumulates;
- chronic form of hepatitis.
Complicating factors that the patient has no control over can also lead to the disease. This may include:
- excessive consumption of protein and grain products containing large amounts of gluten;
- infectious form of the disease;
- severe stress and prolonged depression;
- intestinal infections;
- unsuccessful surgical treatment.
It should be noted that patients suffering from this pathology have specific HLA genotypes. This can also trigger illness. But this factor is not sufficient to cause pathological manifestations in one hundred percent. About 30 percent of the world's population have this genotype, but remain completely healthy.
Possible complications
If you do not adhere to treatment and healthy eating rules for gluten intolerance, you may encounter unpleasant and sometimes dangerous complications. Since absorption in the intestines is impaired in celiac disease, the body lacks the beneficial components necessary for its full functioning. Therefore, the first complications are dermatitis, vitamin deficiency, and inflammatory processes occurring in the stomach and intestines.
With diarrhea, which is one of the symptoms of the disease, dehydration occurs. The body becomes exhausted and mental disorders develop.
Possible complications of gluten intolerance are:
- cancer of the digestive system;
- pericarditis;
- diabetes mellitus type 2;
- malfunction of the thyroid gland;
- autoimmune type hepatitis;
- rheumatoid arthritis.
If complications occur in adults, more serious drug treatment will be required, so proper nutrition for celiac disease should be taken with full responsibility.
Diagnosis of celiac disease: symptoms and harmful gene
The symptoms of celiac disease resemble other diseases, so doctors use special diagnostic methods.
- 1 Genetic analysis: allows you to detect special genes in human DNA - HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8, which are responsible for the development of gluten intolerance. If the genes are found, this indicates a very high degree of predisposition to celiac disease.
- 2 Immunological analysis: allows you to detect antibodies characteristic of celiac disease in the blood. Two types of proteins can indicate the presence of the disease: antibodies against tissue transglutaminase and antibodies (or immunoglobulins: IgA, IgG) against endomysium.
- 3 Histological analysis: allows for a definitive diagnosis. To do this, fibrogastroduodenoscopy is performed, during which a biopsy of the small intestine is taken. The presence of characteristic signs of inflammation confirms the diagnosis of celiac disease.
Skin tests for allergies are, unfortunately, not suitable for diagnosing celiac disease. Gluten intolerance can be detected using immunological and genetic tests (blood tests). A biopsy of the small intestine, which is taken during fibrogastroduodenoscopy, will help make a final diagnosis.
Symptoms of celiac disease
Manifestations of celiac disease from the gastrointestinal tract are quite common. However, they may be vague, unclear, or even absent. Individuals with gastrointestinal symptoms often report the following:
- Diarrhea,
- strong-smelling stool
- abdominal discomfort
- increased gas formation,
- bloating.
- Drops of mucus or fat in the stool (indicates incomplete digestion of food).
Celiac disease is also accompanied by symptoms not related to the gastrointestinal tract, and often these may be the only symptoms that patients have. These are vague symptoms such as:
- Fatigue,
- sudden weight loss,
- joint pain.
- Neurological symptoms: headaches, peripheral neuropathy (tingling/numbness in the hands or feet).
- Psychiatric symptoms: depression, anxiety,
- an itchy rash (called “dermatitis herpetiformis”).
Dietary recommendations for children
If gluten intolerance is detected in young children, you need to follow simple rules:
- If possible, try to feed your baby breast milk for longer;
- the first complementary foods should be introduced without the presence of milk, cereals should consist of one element;
- monitor the baby’s condition when the mother gives new foods;
- When purchasing baby food, carefully study the composition.
It is important to stick to the diet, be attentive when the child is sick, and not give medications containing gluten.
The disease cannot be cured with medication. Treatment for celiac disease is aimed at eliminating symptoms. Patients have to adhere to a diet that is highly effective all their lives. The gluten-free menu allows you to eat nutritiously without lacking healthy ingredients. Normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is established within six months from the time of complete restriction of hazardous foods for celiac disease.
We recommend: How to identify and treat childhood peritonitis
Diet content
Now let’s determine the chemical composition and energy value (per day) for the diet for celiac disease in children and adults:
- Proteins: within 100-120 g.
- Fats: within 100-110 g.
- Carbohydrates: within 400-450 g.
- Calorie content: from 2950 to 3250 Kcal.
- Table salt content: no more than 5-7 g.
- Free liquid intake: at least 1.5 liters.
Signs of anemia with intolerance to natural gluten
Celiac disease is diagnosed with low hemoglobin levels . Iron deficiency anemia develops. The patient develops shortness of breath with little physical exertion and fatigue. A person constantly feels weakness in the muscles.
Immunity sharply decreases: there is a predisposition to viral and infectious diseases. The process of rehabilitation after illness increases. Intellectual abilities decrease.
A person cannot concentrate, memory and the ability to analyze and perceive information deteriorate. Ulcers appear on the mucous membranes, and the tongue darkens.
Celiac disease in adults - symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
In recent years, a disease such as celiac disease has become a real problem for many, many people.
What is celiac disease?
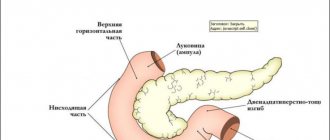
Celiac disease, or gluten enteropathy, is a rather serious disease of the intestines (namely, the small intestine), which is chronic and hereditary in nature and is characterized by impaired digestion of cereal products.
This is, as a rule, wheat, barley, oats, rye.
The reason is that these grains contain gliadin (a component of the cereal protein gluten), and when such food enters the small intestine, the size of the villi of the small intestinal mucosa decreases. The result is a disruption of the digestive process.
Why is this happening:
- Research shows that gluten gliadin, when grains enter the small intestine, acts like a fairly strong toxin on the mucous membrane.
- And as a result, an “incorrect”, abnormal immune reaction occurs on the intestinal mucosa, which leads to disruption of the functioning of the villi and their further atrophy.