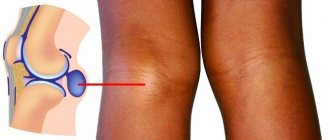
A brain cyst is a benign, volumetric neoplasm that resembles a bubble filled with fluid, which is located on a dead area of the brain or between the membranes of the brain.
Symptoms of a brain cyst are quite nonspecific. These may include frequent headaches, hearing and visual disturbances, sensations of pulsation and pressure in the head, and mental disorders. In some cases, the cyst may not manifest itself at all.
The cyst can be congenital or acquired (as a result of meningitis, encephalitis, stroke, insufficient blood supply to the brain, trauma, surgery).
Treatment of brain cysts can be medicinal or surgical.
What it is?
A cyst in the brain is a large benign formation inside the skull, which looks like a cavity filled with fluid. Often it has a latent subclinical course, not accompanied by a gradual increase in size. Basically, suspicion of the appearance of a cyst inside the head arises if a person suffers from epileptic paroxysms or intracranial hypertension. One of the features of this brain disease is that a significant proportion of patients exhibit symptoms corresponding to the site of cyst formation - this means that only CT and MRI are sufficient for diagnosis, as well as neurosonography for examining a newborn baby or an already grown child.
Many modern neurosurgeons argue that with the right approach to treatment, local accumulation of fluid in the intracerebral substance or membranes does not pose too great a danger for either an adult patient or a child.
Small-sized formations usually have a subclinical course and therefore are detected completely by chance through a neuroimaging examination of the head. If the cyst has sufficiently large volumes, then due to the limited intracranial space it can cause the development of intracranial hypertension, which subsequently causes severe compression of neighboring brain structures.
The clinically significant size of this benign formation varies significantly and depends on the location of its origin, as well as the compensatory capabilities of the cyst. For example, in a small child, the cranial bones are more pliable, due to which the latent course of the disease for a long time is not accompanied by severe liquor hypertension.
Education can be diagnosed at various periods of human life: from birth to old age. One of the specific features of the disease is that even a congenital cyst in the head of an adult patient is most often discovered after he reaches 30-50 years of age, and not in infancy.
Leading clinics in Israel
Assuta
Israel, Tel Aviv
Ikhilov
Israel, Tel Aviv
Hadassah
Israel, Jerusalem
The reason for the appearance of acquired types of cysts, more often in adults and adolescents:
- Bruises, falls from a height, and as a consequence, concussion, are often the cause of a head cyst;
- Consequences of a stroke, which is accompanied by hemorrhage, which can lead to the formation of a cystic cavity.
- There are frequent cases of cyst formation due to previous brain infections, such as meningitis and encephalitis.
- Cyst formation is possible due to sclerotic processes and autoimmune dysfunction.
- There are often cases when the cause of a cyst is parasites that have entered the bloodstream and settled in areas of the cerebral cortex.
The formation is most often not malignant. But this does not give reason to think that there is no need to be examined and treated, since cysts tend to grow. The rapid growth of the cyst can lead to compression of vital areas of the brain. And, as we know, the brain is a very delicate structure and the slightest intervention can lead to irreversible processes.
Classification
Cysts that form inside the membranes of the brain are divided into several types according to their location:
- Arachnoid sinuses are fluid-filled sinuses that arise between two adjacent meninges;
- Intracerebral - benign tumors, the location of which is the thickness of the tissue of the left or right hemisphere of the brain.
In addition, experts classify cysts by origin:
- Congenital – a consequence of a significant violation of intrauterine development of the fetus. Also, a common cause of the disease in this case may be the death of most of the brain tissue due to intrapartum asphyxia;
- Acquired - this type of cyst develops, as a rule, as a result of various head injuries, severe bleeding or inflammatory processes of a different nature.
Another classification is based on the characteristics of the tissues from which the detected cyst was formed:
- Arachnoid is a cyst that resembles a small spherical formation, inside of which there is cerebrospinal fluid. It should be noted that women suffer from it much less often than men. If the tumor does not increase over time, then doctors do not perform surgery on the patient: only regular monitoring is carried out in order to identify possible changes. Otherwise, the surgical method of removing the formation should not be neglected.
- A colloidal cyst is a benign formation, the development of which begins during the formation of the central nervous system (CNS). Usually the disease occurs without any symptoms until it reaches critical parameters. After this, the outflow of fluid that passes through the brain begins to block, and hydrocephalus often develops. In such conditions, urgent surgery is prescribed to remove the dangerous tumor.
- A dermoid cyst is also often called a dermoid - this is an anomaly in the development of the human brain, in which the germ cells intended to form the tissues of the frontal, temporal and other parts of the front of the face continue to remain between the spinal cord and the brain. Only surgery will help here.
- Epidermoid (epidermoid) is a type of cyst, the characteristic feature of which is the formation of germ cells required by a person for the development of skin, nails and hair. It is impossible to get rid of it with the help of medications; only a surgical method is needed to eliminate this plexus;
- A pineal cyst is a pineal-shaped body that can have different sizes. It is diagnosed in approximately 1-4% of patients. A characteristic symptom of the disease is the occurrence of a fairly severe headache when the eyes are raised upward, but for most people the cyst does not cause discomfort.
Diagnostic methods
Treatment of a brain cyst is prescribed only after a comprehensive examination of the patient’s body. Usually they resort to MRI or CT. Using these procedures, you can examine the contours of the tumor, determine its specific location, and also trace the dynamics of development.
Cysts should not be associated with cancer. It is extremely rare that they are malignant in nature. During a CT or MRI, a contrast agent is additionally injected into the cavity. With its help, the specialist determines the degree of malignancy of the cyst. Most often, this kind of pathology responds well to treatment if the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner.
To prevent the problem from growing rapidly, it is necessary to identify the root cause of its occurrence. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed the following diagnostic measures:
- Doppler study (allows you to evaluate the quality of blood flow in the brain).
- ECG.
- Blood test for clotting and cholesterol levels. These indicators most often cause blockage of blood vessels, as a result, the development of a brain cyst.
- Determination of blood pressure. Throughout the day, the computer records all the patient’s readings. In the case of sudden surges in pressure, we can talk about a high probability of a stroke.
- Blood test for autoimmune and infectious pathologies. This examination is necessary if multiple sclerosis is suspected.
Based on the results of the examination, studying the patient’s medical history and complaints, the doctor prescribes therapy. Also, at the appointment, he can tell you why a brain cyst is dangerous if you neglect its growth.
Causes
Factors that influence the appearance of a congenital brain cyst include almost all adverse effects on the fetus during the antenatal period of pregnancy. The most common causes of the disease are the following:
- Penetration of various intrauterine infections into the fetal blood;
- Fetoplacental insufficiency;
- If a woman, while pregnant, took medications that have a teratogenic effect;
- Rhesus conflict;
- Fetal hypoxia;
- Trauma during childbirth;
- If the child’s intrauterine development occurred under conditions of poisoning with narcotic drugs, nicotine or alcoholic beverages;
- If the expectant mother has been diagnosed with a chronic decompensated disease.
An acquired type cyst has other causes of development:
- Receiving a traumatic brain injury at any age;
- Applying a fairly strong blow to the occipital and parietal region;
- Transference of various diseases of inflammatory etiology, which include arachnoiditis, encephalitis, meningitis, as well as brain abscess;
- A number of acute disorders of intracerebral blood circulation that occur after an attack of hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, cerebral palsy, subarachnoid hemorrhage in the brain;
- Post-stroke complication;
- Lacunar stroke and cerebral infarction;
- Subepidermal ischemia;
- Posthemorrhagic complication.
Often an acquired tumor is of parasitic origin (paragominosis, echinococcosis, cerebral taeniasis).
Doctors distinguish a type of formation with iatrogenic origin. The factor causing it is called postoperative complications. In addition, degenerative or dystrophic processes can occur in the head, provoking the replacement of cerebral tissue by a cyst.
Additionally, doctors identify a number of factors that “force” a benign cystic formation to constantly grow, leading to serious complications:
- Various neuroinfections;
- All kinds of head injuries of varying severity;
- The occurrence of inflammatory processes inside the skull, regardless of their nature;
- Development of hydrocephalus;
- Vascular disorders, including stroke and deterioration of venous outflow from the cranial cavity.
Causes of cysts in the head
There are congenital and acquired forms of scalp cysts.
The reason for the appearance of congenital types of cysts:
- Asphyxia . Often, due to a number of reasons, a newborn suffers from oxygen starvation, which leads to the death of some brain cells, as a result of which a cyst is formed.
- Birth injuries are a common occurrence when a child, passing through the birth canal, due to some circumstances, receives bruises and injuries.
Symptoms of the disease
A brain cyst often has the following symptoms:
- Frequently recurring and prolonged attacks of headache;
- Regular dizziness;
- Inside the skull, a strong pulsation is felt in the left and right hemispheres, which almost always torments the patient;
- The feeling of pressure and bloating in the head prevents you from living fully;
- Noticeable deterioration in coordination of movements of all parts of the body;
- Hearing impairment and the appearance of extraneous noise in the ears;
- Deterioration of vision, which may be manifested by blurred objects and their double appearance;
- The occurrence of hallucinations;
- Significant reduction in the level of sensitivity of the skin surface;
- Paralysis;
- Paresis of the upper and lower extremities;
- Development of multiple sclerosis;
- Basal pneumosclerosis;
- Aneurysm of blood vessels;
- Quite frequent epileptic seizures;
- Severe tremor of the upper and lower extremities;
- Frequent loss of consciousness;
- Attacks of nausea, usually accompanied by vomiting;
- Lack of proper sleep.
Experts say that if the tumor has clinically insignificant parameters, then in most cases any of the multiple signs of the disease are completely absent. However, when the cavity reaches large volumes in a short period of time, a characteristic clinical picture appears, the features of which are determined by the location of the tumor, the force of compression of the surrounding tissues and the degree of deterioration in the outflow of cerebral cerebral fluid.
Types of violation
Treatment of a brain cyst is largely determined by its form. In total, there are several types of neoplasms, each of which has certain characteristics.
- Arachnoid cyst. The formation is localized mainly between the arachnoid membranes of the brain. Most often, the pathological process is detected in males, and in childhood and adolescence. It can be both congenital (occurs against the background of a disorder of embryonic development) and acquired (resulting from inflammatory diseases) in nature.
- A colloid cyst occurs at the stage of embryonic development of the fetus, when the central nervous system is formed. Most often, its presence in the body is not accompanied by a pronounced clinical picture. Sometimes a cyst leads to a disruption in the flow of cerebrospinal fluid. This, in turn, is dangerous due to hydrocephalus and death.
- Dermoid/epidermoid cyst. Pathology develops in the first days of fetal birth. Therefore, hair and fatty elements are often found in its composition. This form of the disease is characterized by rapid growth and is subject to surgical removal.
- Pineal cyst. If the disorder is not diagnosed in a timely manner, the likelihood of developing hydrocephalus, metabolic disorders, and vision problems increases.
Regardless of the type of pathological process, it cannot be neglected.
Diagnostic features
Today, the main methods of diagnosis and subsequent prognosis of this disease are MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and CT. The resulting tomogram shows the condition of all components of the brain (epiphysis, cerebellum, pituitary gland, nerve ganglia and other parts). With its help, you can see the location of the periventricular gliosis focus and atrophic scar traces inside the brain without opening the skull, and evaluate their shape, size and intrasellar growth.
In addition, these examination methods make it possible to make a differential diagnosis of an intermediate state between a benign cyst and a malignant tumor. After intravenous administration of a special contrast agent, its product accumulates in tumor tissues, but the cyst does not become contrasting.
Endoscopy and Doppler ultrasound scanning of blood vessels are also often performed to study their condition, blood supply to brain tissue, and identify the localization of ischemia, in which the formation of cysts is activated.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe the patient an ECG and Echo-CG, which are used to check for the presence of symptoms of heart failure, the presence of malfunctions in the heart, leading to a deterioration in the blood supply to all parts of the brain and the appearance of ischemic zones.
Constant measurement of blood pressure gives a specialist the opportunity to determine the severity of the risk of developing a stroke, which can not only cause the so-called “post-stroke cyst”, but also be fatal to human life.
It happens that patients are prescribed other tests:
- Carrying out blood tests to accurately determine the cause of the disease;
- Determination of inflammatory markers;
- Identification of various autoimmune processes that negatively affect the general condition of the body;
- Study of the degree of blood clotting;
- Determination of cholesterol concentration in the blood;
- The presence of infections in the patient's body.
Types of scalp cysts
Experts distinguish three types of cysts. Let's look at them:
- Subependymal . The cause is poor blood circulation. It is characterized by rapid progression, which requires timely diagnosis and adequate therapy. The organ of vision is most often affected.
- Arachnoid . Formed on the lining of the brain. Most often it compresses areas of the brain, as evidenced by frequent convulsions and neurological disorders of the patient. Vascular connection cyst. The safest type of brush, as it tends to dissolve without medical intervention. But this negates the fact that it is necessary to periodically undergo examination by a doctor.
Treatment
If a person is diagnosed with a brain cyst, it is necessary to select a treatment that will be as effective as possible and will completely cure this disease, stop the increase in the size of the cyst, and also prevent the occurrence of any complications.
The method of treating the disease depends on the location of the formation and its size. If the parameters of the cyst comply with established standards and do not pose a danger to human life, then, as a rule, traditional therapy is prescribed: homeopathy using individually selected drugs, to which the patient has no contraindications. Medicines containing iron are often prescribed. Such medications help strengthen blood vessels and improve blood supply.
If the cyst gradually increases in size, putting increased pressure on neighboring parts of the brain, then you should not wait until it resolves on its own. Such a case, as well as a noticeable deterioration in the patient’s well-being, is an indication for surgical intervention and laser surgery. This procedure allows you to completely get rid of the cavity filled with liquid.
Many people are engaged in treatment with folk remedies. According to the results of numerous studies, products prepared from elecampane and burdock have a positive effect on the treatment of the disease. They slow down the growth of the cyst, improve blood circulation, and normalize intracranial pressure. In addition, doctors often recommend that a person who has a cyst in his brain follow a balanced diet.
Brain cysts are considered one of the most common diseases. Even taking into account that this is a benign formation, it can lead to serious consequences. Therefore, even a small cyst requires constant monitoring. To recover and forget about this problem, the patient must strictly follow all the doctor’s prescriptions. Thus, you can avoid surgical intervention and use only medications and traditional medicine.
Pineal gland cyst, treatment
An epiphysis cyst is a serious deviation, the treatment of which cannot be successfully carried out without knowing the nature of its origin. The complexity is also aggravated by the lack of medications that resolve such cystic cavities.
The choice of treatment method depends on the nature of the epiphyseal cyst; treatment can be conservative or surgical.
The latter option poses a certain risk, therefore, in the presence of obvious symptoms and the absence of other reasons for invasive intervention, preference is given to drug or radiosurgical treatment, which allows minimizing manifestations that worsen the quality of life. In addition, contraindications to the operation include pregnancy, advanced age, and chemotherapy.
Pathological symptoms can be relieved by taking appropriate medications - analgesics, diuretics, antiemetics, hypnotics and antiepileptics.
An epiphysis cyst is such a serious pathology that the use of traditional methods of treatment for this diagnosis is useless and even dangerous, and can lead to loss of time and deterioration of the condition.
Immediately after a neoplasm is detected, provided that it does not affect adjacent brain tissues and structures, surgery is usually not performed, but MRI monitoring is prescribed to track the growth dynamics of the epiphyseal cyst.
Pineal cyst on MRI
Frequency of MRI examinations:
- first year – every 6 months;
- the next two years - once every 12 months.
If during this time there are no changes in the size of the cystic cavity, the amount of fluid in it has not increased, and the symptoms are amenable to conservative treatment, then surgical intervention is not performed at all.
Causes of brain cysts
The first thing a patient thinks about is how does a brain cyst develop? What causes it to appear? Experts identify several factors contributing to the occurrence of the disease:
- Concussions.
- Bruises of the head, neck, fractures, bone fragments entering the skull cavity.
- Brain damage by parasites.
- Infectious diseases accompanied by high fever.
- Ischemia, circulatory disorders, tissue necrosis.
- Meningitis.
- Atrophy of brain tissue, degenerative changes.
- Inflammation of the membranes of the brain.
- Encephalitis.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Asphyxia.
- Damage to cerebral vessels, hemorrhages.
Brain cysts are diagnosed even in infants. Causes:
- Congenital pathologies.
- Intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
- Oxygen starvation during childbirth.
Depending on the causes of the disease, the characteristics of fluid formations, symptoms and treatment vary.
Localization
The cyst can be located in all parts of the brain. This tumor is statistically often located in the reticular membrane covering the cerebral cortex, because its layers are a very delicate and susceptible to change structure. The cerebral cortex suffers most from inflammation and head injuries. Therefore, after receiving a severe brain injury, it is advisable to check for the presence of a mass or hematoma. This formation is called post-traumatic and such a cyst can resolve on its own, without surgery.
What are the sizes of a pineal cyst?
As soon as, as a result of the study, an epiphysis cyst was discovered in the patient, it must be measured. The size of a given pathology is not always decisive in determining the treatment method. There are two types of size - permissible and critical . These types are considered conditional, since they do not provide the opportunity to indicate the scope of meaning, since for each patient they are individual and depend on the structure of the brain.
Consequences
Some people, even if they have symptoms, do not consult a doctor or take any action. They can either self-treat or expect it to go away on its own. As a result, complications may arise that could have been prevented.
A brain cyst leads to impaired coordination and motor function. A person's hearing and vision may deteriorate. Hydrocephalus may begin, in which fluid accumulates excessively in the ventricular system of the brain due to difficulty moving to the area of absorption.
Encephalitis often occurs, in which inflammation of the brain begins. This disease can affect different areas of the organ, but in all situations it poses a danger to humans. A cyst can also lead to sudden death of the patient if left untreated.
To summarize, we note that if the cyst is small, it is not dangerous, but if it grows, it requires surgical intervention. If the disease is left to take its course and is not observed, then complications will appear - even death.
Arachnoid and cerebral cyst of the brain
A cyst (translated from Greek as a bubble) is the formation of a cavity with exudate in place of a dead area. This is how the body reacts to the lost amount of brain matter. To stop the process of brain death (atrophy) in the future, it is necessary to identify and eliminate the factor causing this pathology. A retrocerebellar cyst of the brain develops when cavities filled with fluid form in the medulla.
Arachnoid cyst
An arachnoid cyst is a pathology characterized by a thin-walled neoplasm containing cerebrospinal fluid. Occur between the arachnoid membrane and the surface of the brain. A benign course of the disease is noted.
It is possible that the cyst may progress in its growth, therefore, for the purpose of control, magnetic resonance imaging or CT is indicated.
Important! If the examination revealed the growth of a cyst, this means that the pathological process is influenced by negative factors, which means that the causes should be found and the necessary treatment should be directed to eliminate them.
The most typical causes of the progressive growth of an arachnoid cyst in the head are increased fluid pressure, inflammation of the meninges, and head injuries in the presence of cysts.
Retrocerebellar cyst
The size of a retrocerebellar cyst is affected by impaired blood circulation in the brain, which provokes new foci of microstrokes, as well as a condition characterized by an infectious process that affects the destruction of the brain matter (for example, multiple sclerosis).
The reasons that provoked this pathology are:
- cerebral circulatory insufficiency, which can be chronic or acute;
- various injuries or concussions;
- stroke ;
- infectious processes of the brain;
- surgical intervention;
- Marfan syndrome (also the main cause of subarachnoid cyst of the brain, which occurs predominantly in the male population).
In addition to the acquired pathology, a congenital retrocerebral cyst of the brain may occur; this condition is not pathological. Quite often, this condition is a variant of the brain tissue structure that does not cause symptomatic manifestations.
With the constant growth of cysts, characteristic clinical symptoms begin to appear:
- the person feels weak;
- frequent headaches;
- tinnitus;
- disruption of visual and auditory functions;
- nausea appears, turning into vomiting;
- the fingers of the lower and upper extremities become numb and lose mobility;
- convulsions appear;
- a feeling of pulsation occurs in the temples;
- coordination of motor functions is lost.
Treatment of pathology
Any formation in the cranial cavity can impair brain function and often threatens the patient’s life. Symptoms depend on the location and compression of the skull. Provided that the resulting neoplasm is not prone to growth and does not manifest itself with neurological symptoms, supportive drug treatment and constant monitoring are carried out.
If the neoplasm becomes larger in size and the patient begins to develop a clinical picture, the shape of the cyst is determined. In this case, arachnoid or cerebral, and only after that treatment for a brain cyst is prescribed.
If the cause of the pathology is infectious processes, antibiotics are used; antiviral drugs, that is, immunomodulators; if the cause of the neoplasm is a head injury, treatment is carried out for a bruise or concussion.
In the presence of brain cysts of various types, such as retrocerebellar and arachnoid, surges in blood pressure are observed, so treatment will be prescribed that normalizes blood pressure (enalapril, capoten).
To the treatment of cerebral cysts of the brain, agents are added that help improve blood clotting and reduce cholesterol. Next, treatment is carried out with anticoagulants, which affect the resorption of adhesions. Nootropics (cerebramin, nootropil and others) are used to restore brain function. Vitamin complexes and antioxidants are also prescribed.
Despite the fact that cysts are indirectly related to neuro-oncology, if an MRI study shows a significant growth of the cavity, which adversely affects the functioning of the brain and a person’s life in general, surgical treatment methods are used.
The type of operation is determined by an experienced specialist, which will be aimed at eliminating the contents and membrane of the cyst. Typically, excision, shunting, or puncture of the cyst walls is used. For operations, endoscopic techniques are used in most cases.
(Rate this article, be the first)
Signs of a cyst
If the size of the cyst in the pineal region is no more than 1 cm, it does not manifest itself in any way and is not detected. Their diagnosis is most often random during studies for other reasons related to brain pathology and MRI.
The greatest danger is posed by growing cysts of the pineal region, which can cause circulatory problems in the surrounding tissues and lead to hydrocephalus.
With a growing cyst, its manifestations may be as follows:
- causeless cephalgia that is not relieved by analgesics;
- diplopia;
- dizziness;
- decreased vision;
- fatigue and fatigue;
- apathy;
- insomnia at night and drowsiness during the day;
- disturbances of coordination and orientation.
Parasitic cysts may present with more severe symptoms and general intoxication:
- muscle weakness;
- convulsions;
- developmental delay in children with speech delay;
- decline in information perception;
- loss of vision and hearing;
- decreased tissue sensitivity;
- extrapyramidal disorders.
They are expressed in disturbances in motor activity due to impaired muscle tone. Either complete immobility or muscle twitching may occur.
The extrapyramidal system is responsible for human postures, the accuracy of his movements and the coordination of muscle actions. With extrapyramidal syndrome, all this is disrupted.
Signs and symptoms
The cyst can be of various sizes. With a small size, the disease is asymptomatic and is discovered inadvertently during other preventive examinations.
If the tumor grows and reaches large sizes, the following symptoms appear:
- Headache that does not go away after taking painkillers.
- Frequent dizziness.
- Feeling of heaviness in the head.
- Visual impairment.
- Hearing impairment.
- Feeling sick, accompanied by vomiting.
- Presence of pulsation in the head.
- Hallucinations.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Muscle cramps.
- Nervous breakdowns.
Symptoms depend on the size of the cyst and its location. Since any area of the brain performs its own functions. The manifestation of symptoms is also influenced by which part of the brain the tumor puts pressure on.
If the patient does not have these symptoms and signs of the disease, the existence of the cyst will not affect the person’s full life activity. A systematic medical examination will be sufficient. It is very important to monitor that the formation does not increase in size, otherwise the disease will begin to progress and the patient will need to begin treatment.
Previously, we examined in detail a similar issue about a cyst in the head of a newborn child.
The principle of formation of lacunar cysts
Cysts are divided according to the nature of their origin into: congenital, acquired.
The congenital variety is formed in the womb as a result of the influence of various processes, the natural development of which was disrupted by painful factors. Sometimes genes mutate, affecting pathologies suffered by a girl during pregnancy, the effects of alcohol and cigarettes, and other psychotropic drugs.
Secondary cysts refer to the results of a previous illness; several pathologies differ. The patient’s immunity takes part in the formation of lacunar cysts. Today, the formation of a lacunar cyst in the head is promoted by: diabetes, meningitis, hypertension, skull trauma, connective tissue disorder, etc.
Radical treatment methods
Shunting - a drainage is installed, with the help of which the cyst is emptied, after which its walls fall off and become overgrown. But surgery can often have negative consequences for the body due to the complexity of the brain structure.
Endoscopy – the cyst is removed through a puncture in the skull. This method does not cause complications, but there are contraindications in the form of visual impairment.
Craniotomy is an effective operation where a specific area of the skull is removed to gain access to the brain. Has a high risk of brain damage.
Types of brain cysts
Classification of brain cysts is made by specialists. Doctors divide liquid neoplasms:
- Depending on the location: intracerebral and arachnoid, located in the intercerebral membranes.
- By origin: congenital and acquired.
- According to the characteristics of the damaged tissues: with the content of cerebrospinal fluid - arachnoid, resulting from scarring - colloidal, from the germ cells of the face - dermoid, from cells intended for the formation of hair, nails - epidermoid, on the tissues of the pineal gland - peneal.
Each type has its own differences: in symptoms, location, nature of growth. Based on the type of pathology identified, the neurologist plans treatment or complete elimination of the tumor.
Arachnoid
A benign formation in the form of a bubble filled with fluid, located between the brain tissue and the arachnoid membrane, is called an arachnoid cyst.
Most often diagnosed in males, it may not manifest itself for a long time, not grow, or cause discomfort. A congenital arachnoid cyst consists of tissue from the arachnoid membrane of the brain. Formed as a result of an illness - from scar tissue.
Diagnosis is carried out using MRI. Surgery is used to treat dynamic formation. If it does not grow, does not pose a health threat, does not damage the membranes of the brain, the person is simply under medical supervision and takes medications that help improve cerebral circulation.
Retrocerebellar
When fluid accumulates in places where brain cells have died in the cerebellum area, a retrocerebellar cyst of the brain can form. There are several factors that provoke the development of education:
- Stroke, post-ischemic condition.
- Circulatory disorders.
- Trauma to the skull and brain.
- Encephalitis, meningitis.
Based on what caused the damage to the gray matter, treatment is selected. If the brain cyst grows, shunting or craniotomy is recommended. If the patient refuses surgical intervention, then such consequences as asthenic syndrome, seizures, epilepsy are possible.
Subarachnoid
Retrocerebellar cyst of the brain has a subtype - subarachnoid formation. It looks like a bubble with liquid and is located between the structures of the brain. To diagnose the disease, the patient undergoes an MRI. The usual treatment is taking medications that normalize vascular tone, vitamin therapy. Surgical intervention is performed only if the subarachnoid formation grows, puts pressure on the gray matter, hemorrhage is observed in it, and the functioning of the blood vessels is disrupted.
Pineal
The epiphysis cyst of the brain is located on the pineal (pineal) gland, which is responsible for endocrine function. A fluid-filled formation grows if the outflow of secretion synthesized by the pineal gland is disrupted. Typically, the cyst is not expressed symptomatically; it can be detected during an MRI examination.
Experts name several reasons for the development of the disease:
- The excretory channel becomes clogged due to viscous secretion. May occur due to genetic predisposition. The sac of liquid rarely reaches a large size and does not manifest itself symptomatically.
- The pineal gland is affected by echinococcus. Infection can occur due to human contact with farm animals and dogs. The tumor grows, puts pressure on the brain tissue, causes discomfort, headache, vomiting, and blurred vision.
A cyst that occurs due to a hereditary predisposition is usually not treated. A person simply undergoes an examination once a year. If the neoplasm provokes an infection with echinococcus, the cause of the disease is first eliminated. Small formations are treated with medications, large ones are removed surgically.
Liquor
The brain is protected from contact with the skull by cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). A cyst in the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid is called a cerebrospinal fluid cyst. It can be an arachnoid, penial, or retrocerebellar cyst - it depends on the location of the tumor.
Neurologists offer surgical removal of formations that cause significant discomfort to the patient. An asymptomatic cerebrospinal fluid lacunar cyst that is not growing is simply observed with periodic MRI scans of the brain.
Porencephalic
Porencephalic cyst of the brain is quite rare, most often in children. Intrauterine infections can cause the development of the disease:
- Cytomegalovirus.
- Herpes.
- Colds.
Or diseases that the newborn suffered after being born. Several formations may appear. The symptoms are severe, manifested in convulsive seizures, hydrocephalus, mental retardation, and loss of vision.
Treatment usually involves relieving symptoms. Surgeries are not performed due to low efficiency. Most often, children suffering from porencephalic pathology do not live to see one year of age.
Choroid plexus cyst
A choroid plexus cyst of the brain may be detected in a fetus at 6-7 months of intrauterine development. On an ultrasound, the doctor can see fluid-filled bubbles in the network of small blood vessels in the brain.
Such a neoplasm is not pathological and resolves without treatment by the birth of the child. Doctors pay attention to it, since the appearance of bubbles on the choroid plexuses may indicate the development of Down syndrome in a newborn.
Symptoms
As a rule, the signs of a pineal gland cyst, given its small size, are practically not expressed. The patient may not be bothered by headaches or visual disturbances, and he learns about the presence of pathology quite by accident. The situation will be different if the pineal cyst is caused by a parasitic infestation. In this case, the symptoms increase rapidly:
- The patient begins to suffer from constant headaches of unknown etiology, while the blood pressure level is normal. Often this condition is accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- It becomes difficult for the patient to rotate the eyeballs, especially if it is necessary to look up.
- Deterioration of vision, decreased acuity and double vision are noted.
- Constant drowsiness, consciousness becomes confused.
- Coordination problems may occur, and patients' gait becomes unsteady.
- Mental abnormalities and depressive states are observed, and the patient may periodically experience epileptic seizures.
- Women. Those who are trying to get pregnant report difficulties conceiving.
If at least several of the above symptoms occur, you should seek qualified help as soon as possible, since these conditions can lead to irreversible consequences.
Types of neoplasms
There are several types of lumps: pineoblastomas and pineocytomas. Doctors identify the main factor in the development of the problem - premature puberty.
A sign of pineocytoma on MRI is different intensity of signals from the tumor on the T2 image and clarity of the boundaries of the formation. The last sign indicates the benign nature of pineocytoma. The different signal intensities in the anterior and posterior sections of the formation are associated with the “sedimentation” of protein structures.
Pineoblastoma on MRI
An MRI reveals a large tumor. When examining the area with contrast, a homogeneous signal from pineoblastoma is noted. T1 and T2 images show damage to the posterior parts of the brain with a small area of hemorrhage.
The types of these tumors include teratoma, germinoma and mixed types of compactions. Damage to the pineal gland in this case is accompanied by the development of diabetes insipidus, impaired visual function and hypogonadism.
The MR sign of germinoma is a weak signal from the tumor compared to healthy areas of the pineal gland on the T2 image. On T1WI, germinoma is isointense with brain cells. There is deformation of the third ventricle and posterior displacement of the quadrigeminal plate.
Growing teratoma in a patient with intracranial germ cell tumor
MRI images visualize a heterogeneous structure of germinoma with many small cysts. There is slight swelling of the soft tissues around the tumor.
Germ cell tumors are classified as malignant. It metastasizes to other parts of the brain - the pituitary gland, the sella turcica.
MRI signs of mixed germ cell formation include:
- tumor foci in the pineal region;
- hemorrhages in the lateral ventricles;
- pronounced metastasis of the lateral ventricles during contrast-enhanced studies.
The group of neoplasms includes astrocytoma, glioblastoma, and epindymoma. They develop from the thalamus, midbrain, etc. As the disease develops, the abnormal cells spread to the pineal gland.
Astrocytoma, according to MRI images, is small in size with the manifestation of occlusive hydrocephalus. In terms of signal intensity, astrocytoma is practically no different from healthy areas of the brain. An increase in signal is detected when a contrast agent is administered intravenously. An MRI image of an astrocytoma is shown in the figure.
Anaplastic astrocytoma on MRI
We suggest you read: How to relieve swelling from gout
Glioblastoma is detected using contrast MRI. The images visualize a large compaction with necrotic contents. The main MR signs of pathology are compression of the posterior part of the third ventricle and the initial stages of hydrocephalus.
In addition to the listed types of tumors, MRI studies visualize mixed types of compactions and non-tumor formations in the epiphysis:
- lipoma;
- dermoid tumor;
- meningioma;
- cavernous;
- cysts.
How to treat retrocerebellar and arachnoid cysts
Treatment of brain cysts
When brain cysts are detected, regardless of their location, a comprehensive study is carried out to identify the cause of the formation.
Treatment is selected depending on the presence of complaints, the rate of growth of the cyst and the reasons that caused its formation. The cyst can cause headaches, sensations of pressure or fullness in the skull, hearing and vision impairment, and if there is pressure on the cerebellum, changes in handwriting and gait. Hallucinations, mental disorders, seizures, and fainting also occur. In these cases, immediate treatment of the disease that caused the development of the formation or removal of the cyst itself is required.
Treatment of epiphysis cyst
In most cases, treatment of pineal cysts does not require the use of drugs. The use of drugs is possible only for echinococcosis, at its earliest stage. Symptomatic treatment to eliminate the manifestations of the disease is prescribed only when they appear. And this happens when the blood vessels of the brain or its tissues are compressed by a growing cyst. Or surgical treatment is used - most often. Due to the complexity of access, operations are difficult and there is a high percentage of complications - 60-70%.
Indications for surgery:
- severe symptoms;
- parasitic nature of the cyst;
- cyst growth;
- hydrocephalus;
- influence on the cardiovascular system.
If pathology is identified, further treatment of a cyst in the pineal region of the brain is aimed at reducing the risk of its growth.
What about sports?
Fans of physical education are interested in whether it is possible to play sports with a brain cyst. It all depends on the cause of the brain cyst. So, if there were post-stroke cysts, a mandatory consultation with a neurologist about sports activities is required.
If no serious abnormalities are observed, the cyst does not grow in the head, doctors allow running, swimming, tennis and other sports where there is no high load, risk of falls and head concussions. Therefore, in order to prevent the appearance of a post-traumatic brain cyst, heavy lifting, horse riding, jumping, and extreme sports are excluded.
And obligatory: a control MRI of the brain to monitor the “behavior” of the cyst and examination by a neurologist (neurosurgeon) after 4 – 6 – 12 months.
The need for surgical intervention
When there is rapid growth and an increase in the size of the tumor, doctors usually suggest surgery to excise it. Removal of a brain cyst is possible in the following ways:
- Shunting. During surgery, a specialist installs a drainage. Using a special tube, excess fluid will subsequently be removed from the body of the cyst. Gradually, the walls of the formation begin to subside and become overgrown. It is worth noting that this method is not completely safe, as there is a risk of infection.
- Endoscopy. This method of intervention is most often used in adults. During the operation, the doctor makes several punctures through which he performs surgical procedures. The endoscopic method is considered the least traumatic, but has a number of contraindications. It is not recommended for patients with impaired vision to resort to its help.
- Trepanation of the skull. This operation is very effective. During this procedure, there is still a risk of additional brain injury.
The causes of brain cysts in children and adults are largely similar. That is why similar options for influencing the problem are used. However, surgical intervention is resorted to only in cases where the pathology really progresses and there is a danger for the development of the baby.
Thanks to timely and high-quality surgery, most negative consequences can be prevented. A brain cyst is often accompanied by mental disorders and developmental problems, and visual impairment. After the intervention, provided the patient has no complications, he is usually discharged after 4 days. Next, he must undergo preventive examinations in order to promptly recognize and eliminate a relapse.
Cyst in a pregnant woman
If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with a benign tumor, then the process of closely monitoring her begins. Pregnancy often aggravates and fuels a cyst; changes in a woman’s body cause it to grow in size. Despite this, surgical removal is carried out only if there is a risk of death of the mother and child. In other cases, they try to delay the operation until after birth. A pregnant woman must be observed by a doctor and strictly undergo all necessary examinations. If the cyst affects any functions of the body or severely impairs health, then surgery can be performed urgently.