Folliculitis is an inflammatory lesion of the hair follicle. It is of infectious origin.
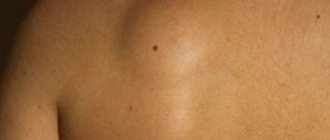
Bacterial folliculitis in humans is characterized by the formation of a papule. This is a cavityless element that rises above the surface of healthy skin and is usually red in color. Then a pustule appears in its place. This is a cavity element. It is filled with pus, and the top is exposed to the skin.
There is a hair in the center of the pustule. Then erosion appears in its place. When it dries, a crust forms. The pathology can spread to the entire follicle. This form is called sycosis.
Let's talk about what kind of disease this is. The causes of this disease may be different, but they are always infectious. However, the pathology is not contagious. It occurs more often in adults, less often in children.
Classification by etiological factor involves dividing pathology into the following forms:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- parasitic;
- fungal;
- syphilitic.
Bacterial folliculitis can be:
- staphylococcal;
- pseudomonas;
- Gram-negative.
In turn, staphylococcal is divided into superficial and deep.
Viral folliculitis is usually caused by the herpes simplex virus.
Fungal infections can be caused by dermatophytes or candida. In addition, it is caused by pityrospora (the culprit of seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff).
Parasitic folliculitis can develop against the background of demodicosis. The exact causes of the disease have not been established. However, risk factors are known. Among them:
- use of wax depilation;
- skin injuries while shaving on the face, legs or armpits;
- plucking hair with tweezers;
- use of pressure bandages;
- long-term use of the patch;
- hot climate;
- sedentary work (folliculitis on the butt may develop);
- the use of local glucocorticoids, because these drugs weaken the immune system;
- use of immunosuppressants (for example, after organ transplantation);
- diabetes;
- HIV or other diseases leading to immunodeficiency.
The disease often occurs in pregnant women. One of the reasons is ingrown hair. It penetrates the epidermis with its free end.
As a result, an inflammatory process occurs. This condition is caused by cosmetic procedures aimed at hair removal.
This problem usually does not occur after shaving. Because the razor only cuts off that part of the hair that is above skin level. However, it still penetrates the epidermis. If the hair is pulled out, then that part of it that is located deep in the skin is also removed. On the one hand, this allows you to resort to the services of a cosmetologist less often. Because hair takes longer to grow back. But, on the other hand, the epidermis can grow before the hair reaches the surface of the skin.
In fact, such hair will hit the “ceiling”, consisting of the upper layer of the skin. If he cannot “break through” this “ceiling”, then he will have to continue to grow sideways. As a result, the hair grows under the skin, which results in an inflammatory process. Often this condition is complicated by staphylococcal infection.
Features of the diagnosis of folliculitis and its symptoms
Folliculitis is an infectious skin disease that affects the hair follicle.
It is characterized by purulent inflammation first of the superficial area of the follicle, and with further development of the process - damage to the deeper layers. The infection penetrates the skin when it is scratched, through cracks, small wounds, and cuts. This disease manifests itself in the form of one or more purulent pimples, which, when opened, turn into ulcers. Most often they form in places where hair grows on almost any part of the body:
- in the armpits;
- in the groin area;
- on foot;
- on the skin of the face or scalp.
After healing, the ulcers leave virtually no traces; only in the case of deep skin damage, scars may remain.
The main symptoms of folliculitis:
- redness of the affected area;
- itching and pain;
- the presence of pimples on the skin - pustules with whitish purulent contents, often they appear in the place of hair growth;
- after opening the pustules, bleeding ulcers appear, which after a while become covered with a crust.
In regions with a hot climate, the prevalence of this disease is much higher than in cold countries.
Possible complications
If gram-negative folliculitis is treated incorrectly, complications associated with the spread of the inflammatory-purulent process may develop. The following complications may occur against the background of folliculitis.
Boils. With the development of this complication of folliculitis, the sebaceous gland and adjacent tissues are involved in the process. In this case, a painful knot is formed, with softening in the center. With the formation of multiple boils, a disturbance in general health may occur.
Carbuncles. This complication of folliculitis is characterized by necrotization of several nearby inflamed hair follicles. A common necrotic core is formed in the inflammatory focus. The formation is very painful; when carbuncles appear, the temperature often rises.
Abscesses. An abscess is formed with further spread of the inflammatory process, resulting in tissue melting with the formation of cavities limited by the capsule and filled with pus.
Phlegmon. The formation of phlegmon is a very serious complication of folliculitis. When phlegmon forms, the purulent process spreads beyond the capsule with inflammation of the fatty tissue. This complication of folliculitis requires urgent surgical treatment.
Causes of the disease
There are several reasons for this diagnosis:
- fungal infection - the causative agent can be dermatophytes, the genus Pityrosporum and Candida;
- viral infection - herpes or molluscum contagiosum;
- bacterial inflammation - staphylococcus bacteria, gonorrhea or syphilis pathogens are involved;
- The causative agent of the disease is parasites, for example, ticks.
Additional factors for the development of this disease may include:
- increased sweating;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- wearing clothes that are too tight;
- the presence of diseases associated with itching and constant scratching of the skin;
- diabetes mellitus, anemia and liver disease;
- malnutrition;
- decreased immunity and the presence of immunodeficiency states;
- prolonged skin contact with certain ointments or chemical liquids - industrial oils, kerosene.
To prevent any kind of skin diseases, including folliculitis, it is important to follow the rules of personal hygiene when shaving, depilation and other similar procedures, as well as when visiting public places - swimming pools, gyms, baths and saunas.
https://youtu.be/Dq7tJENVMfc
Clinical picture
As already noted, Hoffmann folliculitis affects men 20-35 years old; the favorite areas of localization are areas of the body with developed hair.
At the initial stages of the development of the disease, itching and burning appear. There are several affected areas, they become hyperemic. In rare cases, undermining folliculitis occupies most of the head, while healthy areas look like narrow stripes. As the disease progresses, the formation of oblong or hemispherical nodes is observed; they are surrounded by areas of hair loss.
If left untreated, the nodes turn into fistulas, the size of which reaches 1-2 centimeters; when they are palpated, pus is released, sometimes mixed with blood. In complicated cases, ulcers form at the site of nodes and fistulas, the surrounding skin becomes thinner, and alopecia (areas where hair is completely absent) spreads 1-2 centimeters around.
The general condition of the patient also changes, an increase in the size of regional lymph nodes and an increase in body temperature are observed.
In the absence of adequate therapy, abscess folliculitis may persist for several weeks, after which the ulcers heal, forming scars in their place. Alopecia persists and is accompanied by the formation of new nodes and abscesses. The disease is prone to relapse and may be present for several years.
Classifications of folliculitis
There are several classifications of such an unpleasant skin disease:
- For reasons of appearance - depending on the type of pathogen:
- viral;
- syphilitic;
- bacterial;
- fungal;
- parasitic.
- By degree of damage:
- superficial - it is characterized by redness of the skin, small pustules - up to 5 mm, absence or mild itching and soreness;
- deep - characterized by inflamed areas of the skin, painful dense red pustules up to 10 mm in size.
- According to the course of the disease:
- uncomplicated - goes away without complications - the pustules open, and ulcers form in their place, healing after a few days;
- complicated – damage to the deep layers of the skin and the spread of the inflammatory process.
There are a large number of varieties of folliculitis, sometimes similar in appearance to other skin diseases. Therefore, it is better not to self-medicate, but to entrust the doctor with making an accurate diagnosis and prescribing therapeutic measures.
Candidal folliculitis
This type of inflammation of the hair follicles is characterized by purulent rashes on the skin caused by a fungal infection - yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. Area of distribution: armpits, groin area, face and head.
The main symptoms are redness of the skin in the area of the hair follicle, in place of which a pustule forms, which subsequently opens, forming a wound or ulcer. In most cases, with timely treatment, the rash goes away in about 2 weeks.
Acne syphilide
This type of folliculitis is the result of a disease such as syphilis. A distinctive feature of this diagnosis is the presence of groups of damaged areas of the skin - inflamed follicular sacs, usually pale red in color.
Treatment of syphilide is possible only after getting rid of the main cause of its occurrence - the diagnosis of syphilis.
Staphylococcal folliculitis
The name staphylococcal folliculitis speaks for itself. Its causative agent is staphylococcus, the most dangerous of which is Staphylococcus aureus. The disease can affect adults and children, and the method of infection is usually airborne or contact.
Symptoms of this disease are the appearance of a purulent rash on the skin, which can be chronic. In childhood, an increase in body temperature, weakness and deterioration in general health are possible. As a treatment, in addition to medical intervention, personal hygiene and nutritional correction may be recommended.
Pathology caused by dermatophytes
This pathology usually develops on the scalp and may be accompanied by damage to the hair shafts. It is caused by infection with dermatophytes - molds.
The disease in question is quite unpleasant. It is characterized by inflammation of the epidermis in the area of the hair follicles with the formation of purulent pustules, which subsequently turn into ulcers - bleeding or with a crust formed.
Hot bath folliculitis
This type of folliculitis is associated with exposure to dirty, contaminated water - most often these are public places - swimming pools, beaches. The infection from the water gets onto the skin, and through minor damage, cracks, and wounds it enters the body, forming inflamed areas and purulent pustules, usually round in size and red in color. They cause an unpleasant itching sensation in a person.
In most cases, the rash disappears within 7-10 days. Additional treatment is prescribed by the doctor after taking the patient’s medical history.
Occupational folliculitis
This type of folliculitis is associated with professional activity and the specifics of certain professions - working with chemicals, gasoline, technical oils and lubricants. Prolonged contact of such substances with the skin causes irritation, redness and the formation of inflammatory foci.
Most often, the disease spreads to the back of the hands and the outer part of the forearms. One of the treatment options, in addition to therapy, may be to avoid working with specific chemicals.
Tick-borne folliculitis
A type of folliculitis that can occur after being bitten by insects such as ticks. Its symptoms in most cases are similar to the standard signs of such a diagnosis. Treatment for this disease will be prescribed after studying the specifics of the insect and getting rid of the consequences of the bite.
As a rule, tick-borne folliculitis takes much longer to cure than other types of similar diseases.
Gonorrheal folliculitis
Gonorrheal folliculitis is a consequence of an untreated or complex, long-term disease - gonorrhea. The causative agent in this case will be gonococci.
This rare disease, as a rule, affects the perineal area in women, and the foreskin in men and manifests itself in the form of rashes in these areas. Treatment of the disease in question will be fruitful after getting rid of gonorrhea.
Pathology caused by fungi
Folliculitis caused by a fungal infection does not have any special symptoms. It manifests itself in the form of a purulent red rash accompanied by the appearance of ulcers. To clarify the diagnosis and treatment methods, laboratory testing is required to identify the source of the disease.
Antifungal ointments and similar drugs are most often prescribed as therapeutic measures.
Gram-negative folliculitis
The cause of the development of such a disease is weakened human immunity. In most cases, an additional factor may be the use of antibiotics or hormonal drugs. A distinctive feature of the disease is its rapid development - the appearance of a purulent rash on the face and, in rare cases, on the chest and arms.
Depending on the severity of the disease, gram-negative folliculitis is divided into deep and superficial. Its treatment will depend on the severity of the disease and the general health of the patient.
Depilatory folliculitis
The disease in question usually affects men. The affected area is the lower limbs. The main symptoms are the formation of purulent inflammations on the skin of the legs, both single and group. Their distinctive feature is symmetry.
An additional factor provoking this diagnosis may be a hot climate and high air temperature.
Eosinophilic folliculitis
The causes of this disease are not fully understood. According to some data, the main one is the presence of immune system cells - eosinophils in the skin near the hair follicle. To identify such a disease, a biopsy and blood test are performed, based on the results of which treatment is prescribed.
Symptoms of eosinophilic folliculitis include redness of the skin in the area of inflammation, the presence of itching and purulent pustules of varying sizes on the face, scalp, back, and arms. The disease is observed in both adults and children.
Impetigo Bockhart
The peculiarity of this disease is the presence of hemispherical pustules of different sizes on the surface of the skin. As a rule, they are not solitary, but spread in groups.
The main reasons for the appearance of Impetigo Bockhart are maceration of the skin - a violation of its integrity, as well as excessive sweating. Often, an additional factor for the development of such a disease can be the use of warm compresses.
Read a detailed article about impetigo disease, its symptoms and treatment.
Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Most often, this disease occurs in middle-aged men and is accompanied by the formation of pustules, fistulas and nodules on the top of the head. The chronic course of the disease may be accompanied by the appearance of scars.
The causes of the disease may be acne, decreased immunity or its unusual reaction to external influences, or a bacterial infection. Antibacterial drugs or corticosteroids may be prescribed as treatment; in rare cases, surgery is indicated.
Decalvating (epilating) folliculitis
The causes of the disease in question have not been fully established; perhaps they are related to the characteristics of the patient’s body. This type of folliculitis is characterized by a chronic course, the appearance of papules and pustules, as well as the subsequent formation of scars at the site of inflammation.
Affected areas: scalp, groin area, armpits.
Treatment
For effective treatment of this disease, it is necessary to identify the pathogen that caused inflammation of the hair follicles. Therefore, smears are taken from the surface of the skin and examined in a bacteriological laboratory.
After identifying the pathogenic flora, the dermatologist decides how to treat this pathology and what medications to take.
- For bacterial forms of the disease, a course of antibiotics is prescribed; for mycoses, antifungal drugs are used; viral folliculitis is treated with special antiviral agents.
- In superficial forms of the disease, the pustules are opened and treated with antiseptic solutions and ointments.
Folliculitis of the scalp requires the use of powerful antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents and timely surgical procedures to open the abscesses. Treatment requires caution since the infection can quickly reach the meninges through the lymphatic vessels.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed taking into account the localization of folliculitis and after the acute stage of the disease has subsided. These methods help heal wounds and restore epidermal cells.
If therapy is started in a timely manner and there are no severe underlying diseases, the prognosis is favorable.
https://youtu.be/vb2I1bK__CY
Timely diagnosis of the disease
The patient can detect the first symptoms of folliculitis himself - the formation of pustules, ulcers, and itching of the skin. When visiting a doctor, the primary diagnostic method is an external examination of the patient - the symptoms of this disease are most often quite characteristic, which makes it possible to establish a diagnosis and select treatment methods.
In addition to the inspection, the following procedures are carried out:
- collection of anamnesis - medical history with a description of symptoms, complaints, dates of identification of signs of the disease;
- general blood test and determination of glucose levels;
- bacteriological culture and microscopic analysis of samples taken;
- biopsy;
- dermatoscopy;
- in some cases an immunogram may be required.
A similar series of procedures is necessary to establish the cause of folliculitis and differentiate it from other similar diseases - different types of lichen, acne, keratosis pilaris, prickly heat.
Preventive actions
It is much easier to prevent any disease than to treat it. To avoid skin problems, it is recommended:
- Carry out personal hygiene manipulations in areas with active hair growth with caution.
- Regularly undergo medical examination if you have a history of diabetes.
- Men should shave, and women should depilate only with the use of special products with disinfectant properties.
- Treat damaged or abraded skin with antiseptic solutions.
- Conduct timely treatment of diseases that can provoke the development of Hoffmann folliculitis.
- Carefully ensure that chemical solutions and compounds do not come into contact with your skin.
- If even minor pathological symptoms appear that resemble disruptive folliculitis, seek help from a doctor.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Enrich the body with vitamins A and E.
- Avoid excessively greasy hair.
To summarize, I would like to focus on the fact that Hoffmann’s folliculitis is a rather dangerous disease that requires timely treatment. Remember this, be attentive to your body, and it will thank you with good health.
What kind of disease is this?
Folliculitis is a skin pathology that occurs when the hair follicles become inflamed.
This disease is infectious in nature and can be caused by:
- staphylococci;
- gram-negative flora: pseudomanadas, legionella, speirochaetes, brucella, proteobacteria, borditellae, francisella, klebsiella;
- fungal pathogens: candida, malassezia, dermatophytes;
- herpetic virus.
Provoking factors that can contribute to the contamination of the dermis with pathogenic microbes and create favorable conditions for their reproduction are:
- constant microtraumatization of the skin (when shaving, squeezing out pimples, picking off scabs, scratching, etc.);
- scratches, abrasions, calluses;
- hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating) and active work of the sebaceous glands (oily skin);
- long-term and constant wearing of plaster, occlusive dressings, prostheses, compressive shoes, clothing made of dense synthetics;
- staying in a hot climate or living in apartments or houses with high humidity;
- long-term treatment with steroid drugs, immunosuppressants or antibiotic abuse;
- metabolic disorders, hormonal changes or endocrine pathologies.
Insect bites, as well as accompanying skin pathologies (eczema, erysipelas, dermatitis and dermatoses, allergic rashes, scabies, erythematous rashes, blisters) facilitate the penetration of the pathogen under the skin.
Folliculitis can develop after severe viral (influenza, ARVI) and venereal (syphilis, gonorrhea) infections against the background of a weakened immune system or with the uncontrolled use of aseptic skin care products that cause an imbalance in its pH environment.
Violation of the skin's protective barriers can also be caused by working with chemicals (household cleaners, bleach, gasoline, kerosene, technical oils).
Nutrition
Diet is not necessary when folliculitis occurs. But there are concomitant diseases for which dietary adjustments are necessary. Patients who are obese or have diabetes should follow a low-carbohydrate diet.
It is important to adhere to the following dietary rules:
- The consumption of animal fats should be limited.
- Eliminate flour products, spices, chocolate, sweets, alcohol, strong coffee and tea from your diet.
- Eat as many fresh vegetables as possible to provide your body with the required amount of fiber. You can also eat bran.
- You should include a sufficient amount of protein in your diet, including animal protein. Preference should be given to lean meats such as veal, chicken and turkey.
- It is worth eating more foods rich in vitamins. Carrots, beets, rose hips, and blueberries will be especially useful.
Barley
This is essentially the same folliculitis, but of a more specific localization. Ophthalmologists call it hordeolum. This is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelash. Accompanied by hyperemia of the skin of the eyelid and the formation of pustules with pus. A rather painful formation due to its location; often the eyes cannot even be opened due to swelling and pus.
The main cause of occurrence is the entry of Staphylococcus aureus into the hair follicle with reduced immunity.
It is necessary to contact an ophthalmologist urgently – and not to a dermatologist. If an autopsy is indicated, it will be performed exclusively in a hospital setting. How to treat inflammation of the hair follicle on the eye at home? In serious cases, such an idea is extremely unreasonable and can even lead to loss of vision.
ICD-10 code
In the modern medical classification of diseases, folliculitis belongs to the group of diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue L00-L99 . And in the subgroup “other specified diseases of the hair follicles” it was assigned the code L73.8.1 .
- chronic and constantly worsening inflammation of the hair follicles (sycosis) has the number - L73.8.0
- Hoffmann's folliculitis passes under the code - L73.9
- forms of the disease leading to baldness are numbered L66.3-L66.4
- cicatricial erythematous folliculitis is coded as L66.8.
Folliculitis is classified according to the duration of the disease (acute, chronic), pathogen, course, clinical signs:
- Superficial . Most often, such inflammation is caused by staphylococcus bacteria, which constantly live on human skin in small quantities, and when favorable conditions arise, they begin to actively multiply. Staphylococcal ostiofolliculitis is characterized by the formation of spherical or conical papules (pustules) filled with pus. Also, superficial forms of folliculitis can be caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The inflammatory process in this type of disease can affect single openings of hair follicles or affect large areas of the skin.
Superficial folliculitis: photo