Euthyroidism is a condition bordering on serious pathology of the thyroid gland.
Thyroid diseases are a common pathology that affects the functioning of the body as a whole. However, an analysis of the hormones T3, TSH and T4 cannot always detect the disease. A pathological condition in which hormonal levels remain normal is euthyroidism.
Against the background of euthyroidism, a person may develop more severe pathologies, leading to irreversible changes in the thyroid gland. What is euthyroidism of the thyroid gland, is it dangerous and how to treat it - every person who cares about their health should know this.
Why does the disease develop?
As observations show, several factors become the culprits of the disease. These include the negative impact of the environment, unfavorable ecology.
Euthyroidism may have genetic causes: the pathology is inherited.
Euthyroidism can be caused by diseases of the thyroid gland, which develop during inflammatory processes.
Doctors recommend paying attention to the condition of your thyroid gland if you are a resident of a region that is iodine deficient. And this is almost the entire territory of Russia.
A lack of iodine in the diet can lead to the fact that the organ begins to compensate for the deficiency by growing, and colloid cysts may appear.
Euthyroidism can develop after pregnancy. During pregnancy, the entire female body experiences serious stress, and the thyroid gland is no exception. It sometimes increases in size. Usually the discomfort this causes disappears after the baby is born.
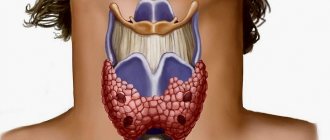
Euthyroidism of the thyroid gland
Euthyroidism of the thyroid gland is a borderline state of functioning of the organ.
That is, when a diagnosis is made, the patient exhibits a pathological deviation from a healthy state, which in the future can lead to the development of an endocrine disease. During hormonal testing, all thyroid and thyroid-stimulating components are normal. Euthyroidism of the thyroid gland does not have a pronounced manifestation.
Only an ultrasound examination can detect some changes in the endocrine system.
Development mechanism and reasons
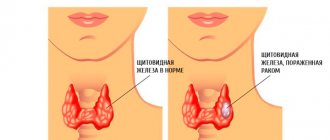
Euthyroidism of the thyroid gland refers to pathological changes in the structure of the gland that are reversible. The tissues of the organ grow rapidly, which leads to its diffuse growth or enlargement of nodes.
At the same time, the level of thyroid-stimulating and thyroid hormones remains unchanged, although the likelihood of a hormonal surge is very high. The formation of several nodes means the development of a multinodular goiter.
Against the background of a short-term euthyroid state, pathological processes develop that accompany hyper- or hypofunctionality of the thyroid gland. Given this fact, if euthyroidism is detected, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment.
The endocrine system has increased sensitivity to exogenous and endogenous factors. The thyroid gland is most vulnerable in this regard.
The occurrence of thyroid gland euthyroidism is caused by the following reasons:
- stress;
- ecology;
- iodine deficiency;
- thyroid pathology of an inflammatory nature;
- aggravated heredity;
- hyperthyroidism in pregnancy;
- chronic autoimmune thyroiditis (AIT).
Euthyroidism during pregnancy occurs due to the fact that a woman's hormonal levels undergo significant changes. As a rule, the disease disappears with the normalization of hormonal levels.
If necessary, drug therapy should be resorted to to ensure the preservation of the fetus.
Women suffering from increased thyroid function should be observed by an endocrinologist before and during pregnancy.
In addition to the main causes, the development of the disease can be triggered by the following factors:
- the use of drugs that suppress the functioning of the thyroid gland (drug euthyroidism);
- excessive stress of a psychological or physical nature;
- poisoning with active components (arsenic, strontium).
Clinical euthyroidism of the thyroid gland can last for several years without deterioration, being a stage of autoimmune type thyroiditis.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of the disease called euthyroidism of the thyroid gland is a list of the following symptoms:
- enlargement of the thyroid gland;
- disruption of circadian rhythms (human internal clock);
- difficulty swallowing;
- insomnia;
- the formation of a nodular goiter (a goiter with one node, with multiple nodes - both autonomously located and combined with each other) and diffuse tissue proliferation;
- pain in the larynx, aching and pressing type;
- chronic fatigue, apathy;
- emotional exhaustion.
Patients also complain to the doctor about the presence of a false foreign body in the throat and a lack of air when inhaling. This indicates that the organs of the endocrine system are not working properly. Euthyroidism, the symptoms of which include the presence of nodular goiter, is accompanied by weight loss, extrasystole and other disturbances in the functioning of the heart muscle.
Classification
According to clinical data, the disease is divided into 4 forms:
- nodular goiter of the 1st degree with one enlarged node;
- nodular goiter of the 2nd degree with many enlarged nodes;
- multiple nodes are combined with each other;
- goiter, which is caused by a lack of iodine in the body.
Generally accepted classification of the degree of manifestation of the disease:
- when palpating the iron, it is practically not felt and any deviations are not externally noticeable;
- upon external examination, the goiter is not visible, but is noticeable upon palpation;
- The goiter is clearly visible upon examination and can be easily palpated.
If a patient develops a nodular non-toxic goiter, the following symptoms may appear:
- feeling of fullness in the chest, presence of a foreign body;
- sudden weight loss;
- heart rhythm disturbances, tachycardia.
If you notice such symptoms, you must go to the clinic and undergo an examination.
Complications
If you do not pay attention to the symptoms of pathology in time, they can result in serious consequences. An increase in euthyroid goiter leads to compression of the vessels and arteries located in the neck. Such people have difficulty breathing, pain occurs when swallowing, their voice becomes hoarse, and over time it disappears altogether.
Improper functioning of the thyroid gland affects the human nervous system, as a result of which irritability develops into permanent depressive states. Such people experience deterioration in memory and attention, as well as a decrease in reaction.
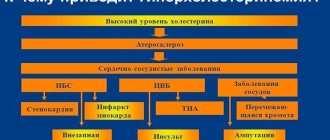
A lack of iodine-containing hormones leads to an increase in cholesterol levels in the blood, causing atherosclerotic heart and vascular disease. The reproductive system also undergoes changes. In women, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, and in men, erection deteriorates. In the future, infertility may develop.
The most dangerous consequence of nodular goiter is the degeneration of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one.
Diagnostics
Diffuse euthyroid goiter can be easily detected during a routine examination or by palpation. To clarify the exact volume and structure of the thyroid gland (to classify the type of damage), ultrasound diagnostics is performed.
If during the examination the presence of nodular changes in the gland tissue was proven, then scintigraphy and fine-needle biopsy are prescribed.
Research in the laboratory includes:
- Analysis of an immunogram that determines the presence of lymphocytes, antibodies for thyroglobulin and thyroid cells.
- Determination of the level of TSH, T3, T4, as well as the presence of thyroglobulin in the blood.
During a severe form of euthyroidism (severe compression of the neck, active growth of goiter), the patient is sent for a contrast X-ray.
Treatment of euthyroidism
The euthyroid state does not always require drug treatment. Thus, with minor diffuse changes in the thyroid gland and 1-2 nodes with a diameter of up to 0.8 cm (for example, with autoimmune euthyroidism), endocrinologists recommend only active observation: once every 6 months. You should undergo an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland.
For a patient who wants to maintain his health, such tactics will not cause difficulties: ultrasound examination is affordable in terms of cost.
If quite serious structural changes in the thyroid tissue are detected in a patient against the background of severe symptoms, a course of drug treatment is prescribed.
- To normalize the patient's condition and, at a minimum, stop tissue proliferation, iodine preparations (Microiodine, Camphodal, Antistrumin and others) or L-Thyroxine (Levothyroxine) are prescribed.
Initial manifestations of pathology
Symptoms of euthyroidism, although too obvious, begin to appear quite quickly. Against the background of normal hormone levels, unpleasant sensations arise.
- The person becomes nervous and feels constant tension.
- He feels as if there is a lump in his throat.
- A person often feels sleepy and gets tired quickly.
- During an external examination, the doctor may notice an increase in the size of the thyroid gland.
- A person feels some discomfort in the neck area.
- If we are talking about euthyroidism with an unchanged thyroid gland, then any symptoms will be absent, but in the case when we are talking about euthyroid diffuse or nodular goiter, then the manifestations, although quite scanty, do occur.
Thyroid pathologies are more common in women than in men. The reason for visiting a doctor for representatives of the fair half is often dissatisfaction with their appearance.
When the gland increases in size and it becomes noticeable from the outside, some ladies go to see a doctor.
This usually occurs when diffuse changes reach the second and third degrees. In addition to a cosmetic defect, discomfort in the throat is often disturbing. It becomes more difficult to breathe, swallow food, and the throat often feels sore. The timbre of the voice may change.
Symptoms
Symptoms of euthyroidism are directly related to the manifestations of the underlying disease. The very first symptom that occurs in a person is nervousness. Next comes increased fatigue. Later the following symptoms appear:
- discomfort in the neck area;
- a characteristic symptom of thyroid pathologies is a feeling of a lump in the throat;
- feeling overwhelmed;
- possible headache;
- drowsiness;
- an increase in the size of the thyroid gland. This symptom may indicate not only non-euthyroidism, but also more serious pathologies of the gland;
- a person gains weight very quickly, while continuing to follow his usual diet;
- voice change. This symptom appears against the background of an increase in the size of the thyroid gland. In the future, a dry cough may appear.
Nodular goiter
Separately, it is worth highlighting the most common form of euthyroidism – nodular goiter. This condition is characterized by the appearance of pathological growths on the gland. Clinicians distinguish 5 types of nodular goiter:
- endemic goiter, which progresses due to insufficient iodine concentration in the body;
- nodular goiter, which is characterized by the binding of nodular formations;
- goiter with a single node;
- goiter with numerous nodules.
Degrees:
- 1st degree. At this stage of development, the thyroid gland is not enlarged and there is no way to palpate it;
- 2nd degree. The gland can be palpated;
- 3rd degree. The outline of the gland can be seen when swallowing;
- 4th degree. The goiter is localized over a large area of the neck;
- 5th degree. The gland is so enlarged that it begins to put pressure on the surrounding tissues and organs.
In case of progression of nodular goiter, the general clinical picture is supplemented by the following symptoms:
- discomfort in the sternum;
- tachycardia;
- arrhythmia.
Methods for treating euthyroidism
Treatment may not be needed. The need for therapy is determined by the result of the laboratory analysis. If the patient feels normal and does not express any special complaints, and no enlargement of the gland is observed, the hormonal data also fits into the standards, then the doctor can simply observe the patient.
If you feel unwell or have hormonal imbalances, a therapy method is selected. The first step is the use of medications.
Products containing iodine and levothyroxine are used. They help relieve symptoms of the disease and stabilize hormonal levels. With medication, the thyroid gland returns to its normal size.
Nodular goiter with euthyroidism
Euthyroidism provoked by iodine deficiency is accompanied by nodular goiter: diffuse proliferation of the thyroid gland and the formation of single or multiple nodes. Depending on the nature of the structural changes, several forms of nodular goiter with euthyroidism are considered:
- diffuse increase without nodular inclusions;
- identified single node;
- multiple nodes detected;
- multiple nodes merging with each other.
Features of the disease
Since the condition of a patient with euthyroidism can change at any time, and yesterday’s normal state of health can today be replaced by a serious illness, doctors recommend not letting the process take its course. To monitor the progress of the disease, it is worth visiting a doctor periodically.
It is recommended to undergo an ultrasound examination every six months and take a blood test. This is necessary to make sure the condition of the organ: whether the size has changed, whether nodular formations are developing. It also monitors the level of thyroid hormones.
The same recommendations are given to patients who have undergone treatment with thyreostatics.
Causes
The amount of pituitary hormones and specific thyroid substances is individual for each person. If there are no physiological changes in the organ itself and in normal human life, then the concentration of produced hormonal units is purely a matter of numbers. This indicator acquires a diagnostic criterion only against the background of symptoms of euthyroidism of the thyroid gland.
There can be many reasons for the development of the condition. First of all, these are genetically determined characteristics, which are also often associated with the following factors:
- Features of the ecological situation and place of human residence. For the normal functioning of the thyroid gland, iodine is necessary, which is absent in certain regions - often mountainous, remote from the sea. In people living in such regions, euthyroidism is detected in almost 100% of cases, although the disease does not always develop.
- Poisoning with toxic substances that inhibit the functions of the thyroid gland. First of all, these are salts of heavy metals, but harmful compounds can also be found in medicines.
- Constant stress disrupts the normal functioning of the thyroid gland.
- The development of serious pathologies - for example, diffuse goiter, thyroid cancer. In this case, the disorders will progress very quickly, the clinical picture will develop from “doubtful” to bright in an extremely short time.
- In women, hormonal status changes during pregnancy. During this period, serious endocrine disorders may develop, especially against the background of even minor deviations from the norm.
Any inflammatory or other abnormal processes in the thyroid gland can provoke a sharp deterioration in the condition. The status of euthyroidism indicates that this organ is a “weak point”, usually due to genetically determined factors, so throughout a person’s life they will need to be examined from time to time by a specialized specialist. It is advisable to conduct examinations with all tests, visual and hardware examinations in order to prevent the development of serious diseases in time.
Degrees
The disease has its own stages of development, and the duration of each stage of the disease varies in terms of time strictly individually.
Basically, the following classification of pathology stages is used in diagnosis:
- The first degree is not determined visually or by palpation. The presence of nodes, which may be less than 10 mm, can be determined at this stage only by ultrasound examination.
- The second degree is characterized by the presence of changes in the gland, which are determined by palpation and ultrasound.
- The third degree can be diagnosed visually. A fairly visible swelling of the neck forms, sometimes more enlarged on the right side. A person experiences significant discomfort due to the formation of nodes.
The third stage can be complicated by the first signs of hypo- or hyperthyroidism, since it is significant changes in the tissues of the gland that can lead to a change in its functionality.
Complications
If symptoms of the disease appear, it is necessary to undergo examination. Late diagnosis and lack of treatment lead to progression of euthyroidism. Large goiters provoke complications. The patient has:
- compression of arteries and vessels in the neck, causing circulatory problems;
- dizziness;
- risks of developing myocardial infarction, stroke;
- depression;
- change in voice up to complete loss;
- decreased response;
- deterioration of attention, memory;
- panic attacks;
- depression;
- nervous exhaustion.
Iodine deficiency leads to hormonal imbalances that negatively affect the functioning of the body. If corrective treatment is not carried out during the development of euthyroidism, you may encounter the following problems:
- labored breathing;
- pain when swallowing, especially solid foods;
- heart failure;
- increased blood pressure;
- thyroid fibrosis;
- atherosclerosis as a result of increased cholesterol in the blood;
- heart rhythm disturbances – bradycardia, tachycardia.
The euthyroid state is dangerous due to the degeneration of a benign formation into a malignant cancer form. The pathology causes serious damage to the reproductive system. Thyroid dysfunction affects the body of men and women. Euthyroidism in the absence of treatment causes:
- erectile dysfunction;
- impotence;
- menstrual irregularities;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- infertility.
Prevention
The first level is sanitary educational work, which increases the level of knowledge of the population regarding such a disease as euthyroid goiter, as well as methods of its prevention. Popular scientific publications and television programs that explain the essence of diseases in simple language play an important role. For example, Dr. V.V. Fadeev gives numerous interviews and appears on medical programs, thereby helping to educate people.
In addition, the bill on iodization of all table salt will allow for mass prevention of iodine deficiency diseases, which will significantly reduce morbidity rates, especially in areas where iodine deficiency is endemic.
The second level of prevention is to detect and register for dynamic observation of persons who have undergone thyroid surgery, pregnant women, and those living in endemic areas. Persons at increased risk are given individual recommendations on therapeutic nutrition, as well as the use of iodine preparations as a preventive measure.
Prevention of the disease consists of the following actions:
- proper nutrition;
- use of increased amounts of iodine-containing products;
- restoration of sleep patterns, when the process of falling asleep is transferred to an earlier time - 22 hours;
- active recreation: in winter - skiing in the forest, in summer - at sea;
- prevention of neck osteochondrosis.
Exercises for the entire spine, especially the neck, are beneficial. 15 minutes of therapeutic exercises a day can relieve a person from the unpleasant consequences of multinodular non-toxic goiter of the thyroid gland.
To reduce the likelihood of non-toxic multinodular goiter, people living in areas with iodine deficiency should periodically take iodine supplements. In some cases, the disease is hereditary. Therefore, if a goiter occurs in one person, all family members are recommended to undergo a preventive examination by an endocrinologist.
As the brilliant surgeon and scientist N.I. Pirogov argued: “It is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it.”
During preventive examinations, doctors primarily pay attention to patients who have a hereditary predisposition to thyroid diseases. Such people should try to avoid prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation, including sunbathing and visiting a solarium. Stress can provoke illness, so you need to try to smooth out any conflict situations.
Pregnant women who are predisposed to thyroid diseases should adjust their diet in favor of foods containing iodine. The same recommendation also applies to children who have been diagnosed with thyroid dysfunction. If you have euthyroidism, you should undergo regular medical examinations, including an endocrinologist.
Take the test to find out your risk of developing diabetes
Take the test to find out how strong your immune system is
materials about all hormones,
information about diseases,
drugs and tests
All information on the site is provided for informational purposes. Before using any recommendations, be sure to consult your doctor. Self-medication can be dangerous to your health.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease may be absent until the condition of the gland is changed. Then the symptomatic picture of euthyroidism will consist of signs of the underlying disease.
Regardless of the level of hormones in the blood, a patient with progressive euthyroidism may experience the following symptoms:
- nervous disorders, exposure to stress factors;
- enlargement of the gland up to a visually noticeable tumor in the neck;
- signs of pressure on the neck (difficulty breathing, hoarse voice);
- sensation of a lump in the larynx;
- increased fatigue and drowsiness.
On the external side, with euthyroidism, the outline of the neck changes - the thyroid gland steadily grows in volume. These changes are more clearly noticeable among women.
The first stage of the disease is characterized by minor, almost imperceptible changes, which cannot be said about the second and third stages, which are usually accompanied by diffuse changes that provoke the formation of nodular goiter.
Symptoms of this pathology include pronounced changes in voice timbre, problems with breathing and eating.
Advanced euthyroidism negatively affects the hormonal state of the body.
Improper production of hormones by the gland negatively affects a person’s well-being, causing weight fluctuations, problems with the heart and blood vessels, disorders of the nervous system, etc.
Such conditions require drug therapy, but after the hormone balance is restored, euthyroidism develops again.