Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic disease of the endocrine system, which in the last few years has acquired epidemic proportions and ranks third after pathologies of the cardiovascular system and cancer. According to the International Diabetes Federation, diabetes mellitus affects 10% of the population, and the disease is more common in men than in women. The reason for such indicators is early hormonal changes in the male body, as well as a careless attitude towards one’s health and the reluctance to seek help from medical specialists at the first ailments. Before considering the symptoms of diabetes in men, you need to understand what kind of disease it is, where it comes from and what the risk factors are.
Causes of diabetes in men
Predisposing factors for the development of diabetes mellitus
- Hereditary predisposition (if there were people with diabetes in the family).
- Diseases of the pancreas (for example, chronic pancreatitis).
- Viral infections.
- Stressful situations.
- Overweight.
- Autoimmune disorders.
Diabetes mellitus type 1. Causes
A genetic defect in the immune system that causes T lymphocytes and autoantibodies to cause the death of B cells in the pancreatic islets, which in turn produce insulin. (Most often, a genetic defect occurs after a viral infection).
In 10% of patients, B cells die without any reason.
Lack of insulin >> glucose levels increase, but insulin does not deliver it to organs and tissues >> the body evaluates this as a lack of glucose and triggers mechanisms for breaking down proteins and fats and converting them into glucose >> glucose becomes more and more, but there is no insulin in the body >> a vicious circle leads to “hunger of the body against the background of an excess of glucose.”
Diabetes mellitus type 2
The sensitivity of receptors in organs and tissues to insulin decreases (insulin is produced, there is a lot of it, it can bind to glucose, but tissues lose sensitivity to it).
The sensitivity of B cells to glucose decreases. (Normally, when blood glucose increases >5.6 mmol/l, a glucose molecule enters the B cell and stimulates the release of insulin. When sensitivity decreases, insulin secretion does not occur >> the mechanism of converting glycogen into glucose is triggered >> blood glucose levels increase ).
By the way, we recommend reading the article Signs of diabetes in women after 50
How does the disease manifest itself?
The most common are type 1 diabetes, the frequency of diagnosis of the total number of patients is 10-15%, and type 2 diabetes. With each of the pathologies, high sugar levels are noted, but the symptoms and manifestations of the diseases have significant differences.
Rapid weight loss not associated with any reasons (diet, illness, etc.) most often occurs with type 1 disease, but with type 2 diabetes, weight loss is also possible, but only if sugar is elevated for a sufficiently long period, those. with decompensation. In this case, to supply the cells with the energy they need, the body begins to burn fat.
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by damage to nerve cells and blood vessels. Patients note tingling, numbness in the arms and legs, a feeling of “goosebumps” on the skin, and a burning sensation. Skin lesions on the body take a very long time to heal, can fester and develop into deep wounds. Weakening of the immune system leads to the activation of pathogenic pathogens (fungi, bacteria).
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes in men
How to identify pathology? In addition to examining your medical history, the specialist will prescribe blood and urine tests. In type 1 diabetes, the presence of acetone is noted in the urine, and the sugar level can reach 20 mmol/l.
Why there may be acetone in a child’s urine is described in the article.
The disease is diagnosed at a young age, then after 40-50 years. It develops very quickly, suddenly. No genetic predisposition has been identified.
Due to the lack of insulin, the body's cells do not receive sufficient “recharge”; it cannot be obtained from glucose, so proteins and fats are used. A person’s body weight decreases, and the smell of pickled apples (acetone) is clearly audible when breathing.
Because Insulin directs glucose into cells, and when its level is low, glucose accumulates in the blood. The plasma becomes thick, the person suffers from thirst, and constantly wants to drink. The body tries to remove excess sugar, this happens through the kidneys, therefore, with type 1 diabetes, frequent urination is observed, especially at night.
In representatives of the stronger sex, the disease develops at a very rapid pace with age. At the same time, problems arise in the genitourinary area: potency and libido decrease, testosterone levels drop.
Type 2 diabetes
This type of diabetes occurs at the age of 35-40 years. The development of the disease is gradual and is detected by chance during testing. High probability of genetic predisposition. In approximately 80% of cases, patients are overweight.
In this case, there is insulin in the body, but the main problem is that the cells are insensitive to the hormone.
Characteristic signs of type 2 diabetes:
- Feeling thirsty. The sign is not constant and is not very pronounced.
- Frequent urination. Due to the fact that in type 2 diabetes the sugar level is increased, the body tries to remove the excess in the urine. It turns out that the higher the glucose level, the more often the desire to visit the toilet arises.
- Dehydration causes dry and itchy skin and eyes. The functionality of taste buds decreases, a person ceases to feel the taste of foods.
- Excessive fluid intake. Polydipsia is a natural reaction of the body to ongoing dehydration.
- Feeling weak, tired. Constant thirst and visits to the restroom do not provide the opportunity to fully rest.
Signs of type 2 diabetes characteristic of men include: decreased libido, disturbances in the genetic material (for example, changes in the quality and composition of sperm); hair loss, even baldness.
Signs of diabetes mellitus in men: non-insulin dependent form
There may be several symptomatic manifestations, maybe one or two, but the most important thing is to pay attention to all the “signs” that the body gives.
In the non-insulin-dependent form of diabetes in men, the following are observed:
- night urge to urinate;
- increased thirst, dry mucous membranes in the mouth;
- insomnia, fatigue;
- urge to vomit, gastrointestinal disorders;
- prolonged healing of wounds, cuts (especially on the legs);
- impaired ability to concentrate, decreased performance and memory;
- changes in blood pressure values;
- itchy skin, especially in the groin area;
- smell of acetone from the mouth.
Most of the symptoms described are non-specific and can occur in other diseases, but in any case they must be taken into account.
Men should pay attention to the following factors that provoke diabetes:
- high body mass index (BMI);
- physical inactivity, lack of physical activity;
- incorrect approach to nutrition, eating fast carbohydrates, sweets, baked goods, fast food;
- regular stress, nervous disorders;
- there is a family history of diabetes.
To calculate BMI, you need to divide your body weight (in kg) by the square of the person’s height (in cm).
The result obtained can be assessed using the table
According to scientific research, diabetes is often genetic in nature. For example, type 2 diabetes can be diagnosed in identical twins.
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes develops acutely and symptoms increase.
- Polyuria (a lot of urine) is the first sign of diabetes. Appears when blood glucose exceeds 9.5–10 mmol/l.
- Frequent urination , especially at night. The amount of urine at night begins to exceed the amount of urine during the day.
- Thirst (caused by loss of fluid) and dry mouth .
- Loss of body weight (can lose up to 10 kg of body weight within 2 weeks).
- Increased appetite (“attacks of wild hunger”).
In the absence of treatment with INSULIN, symptoms increase, weakness appears, appetite decreases >> hyperglycemic coma develops (diabetic ketoacidosis). Type 1 diabetes is often first discovered when a patient is admitted with diabetic ketoacidosis.
Diagnostic methods
Many people for a long time do not suspect that they have already developed diabetes mellitus. This disease is detected during the treatment of concomitant pathologies or at the time of testing. If an increased glycemic value is detected, the patient should consult an endocrinologist. The doctor will prescribe additional examinations, the results of which can confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Tests to diagnose diabetes:
- Blood test (from a finger). Testing is carried out on an empty stomach. An indicator value exceeding 6.1 mmol/l is a sign of diabetes.
- Glucose tolerance test. The method is based on the study of blood taken on an empty stomach and after the patient has drunk a glucose solution. If 2 hours after taking the sweet syrup the sugar level exceeds 7.8 mmol/l, the presence of the disease is confirmed.
- Blood determination of the level of glycosylated hemoglobin. The study allows us to determine the severity of the disease.
- Analysis of urine. This study is carried out to determine the level of acetone and sugar, which should not be present in a healthy person.
Sugar curve during glucose tolerance test
The results of the studies allow us to determine the degree of development of the disease:
- Prediabetes. This degree is characterized by the absence of a person’s feeling of any abnormalities or disturbances in the functioning of the body.
- Hidden form. In this state there are no obvious manifestations of pathology. The disease can only be detected using a glucose tolerance test.
- Overt diabetes. This degree of disease is characterized by the presence of obvious symptoms of the disease. An increase in glycemia is determined based on urine and blood tests.
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes
The same symptoms (polyuria, frequent urge, dry mouth) are less pronounced than with type 1 diabetes and patients do not pay attention to them.
50% of type 2 diabetes is asymptomatic for 5 years. A person may not even be aware that he or she has diabetes, and the disease slowly leads to irreversible consequences.
The first signs of type 2 diabetes
The first signs of type 2 diabetes often include complications caused by the disease.
- Erectile dysfunction (decreased potency, decreased libido).
- Pain in the limbs.
- Deterioration of vision.
- Loss of sensation (there may be numbness in the arms and legs).
- Long-lasting wounds.
- Unsteady gait.
- Itchy skin, itching in the groin and anus.
- Inflammation of the foreskin.
- The first symptoms persist (dry mouth, thirst, nocturnal enuresis, weakness).
In patients with type 2 diabetes, weight loss does not occur! On the contrary, weight gain may increase.
Secondary signs
Hypertension will lower your blood pressure to normal levels without chemicals or side effects! More details
If the first symptoms were not noticed and treatment was not carried out, a drop in testosterone may begin, leading to disturbances in the blood supply to the pelvic organs. Insufficient supply of nutrients to the genitals can lead to progressive impotence. Men's health is impaired, which is manifested in the clinical signs of diabetes in the form of:
- decreased potency;
- decreased libido;
- premature ejaculation;
- defects in reproductive function (decreased quantity and quality of sperm).
How do other problems besides male ones manifest themselves? The patient suffers from unpleasant conditions:
- microcracks in mucous membranes;
- peeling of the skin;
- the occurrence of fungal diseases and viral infections due to poor wound healing;
- incessant itching.
In addition to external signs of diabetes mellitus, an experienced patient may experience damage to DNA, the carrier of hereditary information. Over time, if diabetes is not treated, it can cause a number of associated diseases: gangrene, polyneuropathy, vision problems and others.
Our readers write
Topic: Conquered diabetes
From: Galina S. ( [email protected] )
To: Administration aboutdiabetes.ru
At the age of 47, I was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. In a few weeks I gained almost 15 kg. Constant fatigue, drowsiness, feeling of weakness, vision began to fade.
And here is my story
When I turned 55, I was already steadily injecting myself with insulin, everything was very bad... The disease continued to develop, periodic attacks began, the ambulance literally brought me back from the other world. I always thought that this time would be the last...
Everything changed when my daughter gave me an article to read on the Internet. You can’t imagine how grateful I am to her for this. This article helped me completely get rid of diabetes, a supposedly incurable disease. Over the last 2 years I have started to move more; in the spring and summer I go to the dacha every day, grow tomatoes and sell them at the market. My aunts are surprised how I manage to do everything, where so much strength and energy comes from, they still can’t believe that I’m 66 years old.
Who wants to live a long, energetic life and forget about this terrible disease forever, take 5 minutes and read this article.
Go to article>>>
Treatment of diabetes
Diabetes mellitus type 1
- Diet.
- Insulin therapy (continuously, daily).
- Physical activity
All three components are required!
NEED TO KNOW!
If you have been diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, especially type 1, do not try to treat it with folk remedies! This can lead to dire consequences. Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs are suitable only for prevention, but not for the treatment of diabetes.
Diabetes mellitus type 2, types of treatment
- Sometimes only diet (with moderate hyperglycemia).
- Diet + glucose-lowering drugs in tablets (1 or a combination of drugs).
- Diet + glucose-lowering drugs in tablets + insulin therapy.
- Diet + insulin therapy.
Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with insulin can be temporary:
- during surgery;
- severe acute diseases;
- during the period of myocardial infarction and for a year after.
By the way, we recommend reading the article What are the main differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Goal of diabetes treatment
- Achieving and maintaining normal blood glucose levels.
- Normalization of body weight.
- Normalization of blood lipid levels (increasing HDL levels, decreasing LDL and triglycerides).
- Normalization of blood pressure if there is arterial hypertension.
- Prevention of vascular complications.
KEEP YOUR CALORITY EATERS
- BMI = 20–25 (normal limits) – 1600–2500 kcal/day, depending on physical activity.
- BMI = 25–29 (overweight) – 1300–1500 kcal/day.
- BMI >= 30 (obesity) – 1000–1200 kcal/day.
- BMI < 20 (low body weight) often in patients with type 1 diabetes – 3000–3500 kcal/day.
BMI (Body Mass Index) = weight (kg) / height (m2)
Medical indications
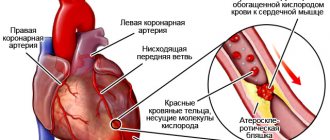
Diabetes is accompanied by damage to small and large vessels, nerve trunks and endings. The kidneys, eyes, heart, and legs are most often affected. Symptoms of macroangiopathy are similar to signs of atherosclerosis. In men, the blood supply to some organ is disrupted. The most typical symptom of the disease is sexual infertility caused by atherosclerosis.
According to statistics, deep vascular and cardiac changes are diagnosed in 30% of cases. A full life is ensured with timely examination, proper nutrition and adequate treatment. Diabetes impairs physical activity. The patient cannot lift the big toe 50 degrees from the floor. In case of serious violations, the fingers are always bent.
The disease can lead to stroke, heart attack, renal sclerosis, and ischemia. Other complications include impaired functioning of the reproductive system, ejaculation dysfunction, and absence of the body. Similar consequences are associated with a decrease in the formation of testosterone in the body and cessation of blood flow to the genitals. It is not recommended to take drugs that stimulate potency. To prevent complications, it is recommended to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
The clinical picture depends on the type of diabetes. In the first stage, insulin is not produced because the beta cells of the pancreas are damaged. The disease is provoked by a viral infection. In type 2 diabetes, insulin production is observed. But it is incorrectly perceived by the cells of the body. Obesity develops. Type 2 diabetes is considered a disease of adulthood. The risk group includes people over 45 years of age.
Type 1 diabetes develops quickly. The disease manifests itself with a clear clinical picture. The patient, despite a good appetite, is rapidly losing weight. He complains of fatigue, thirst and drowsiness. Due to the frequent urge to urinate, sleep is disturbed. The more common type of diabetes is the second. The disease progresses slowly, but is difficult to diagnose.
Signs of type 2:
- thirst;
- weight loss;
- excessive urination;
- fatigue;
- drowsiness;
- weakness;
- vomiting with nausea.
Diabetes of any type can provoke hypoglycemia, ketoacidosis, and lactic acid coma. In the absence of timely treatment, death occurs. Diabetes leads to blindness and skin dysfunction. Latent or hidden diabetes mellitus occurs without symptoms. Men do not suffer from a negative clinical picture.
To make a diagnosis, glucose tolerance testing is ordered. If the indicator exceeds 120 mg on an empty stomach or 200 mg after a meal, then the diagnosis is confirmed. Diabetes is often diagnosed after a stroke or heart attack.
The first external signs of the disease include problems with the nervous system. Risk factors include potassium deficiency in the blood, obesity, and hypertension.
Doctors include infectious processes that cannot be treated as indirect symptoms of developing diabetes. Doctors make a similar diagnosis with prolonged healing of wounds, low body temperature and cramps of the calf muscles. Symptoms are pronounced due to the special structure of the hormonal system.
Urgent help from an endocrinologist is necessary in the following cases:
- rapid weight loss;
- thirst without swelling in the morning;
- loss of appetite;
- pigmentation of the limbs;
- itching;
- brittle nails and hair;
- smell of acetone from the mouth;
- dizziness;
- weakness.
Since symptoms also appear in other pathologies, it is recommended to take a blood sugar test. If glucose increases slightly, tolerance may be impaired. This condition precedes diabetes. It is considered reversible.
A reliable diagnosis can be made after laboratory tests are used to assess the level of glucose in the blood. The critical value of the indicator is 7 mmol/l. Normally, glucose levels should not exceed 5.5 mmol/l.
Glucose tolerance testing is performed to confirm the diagnosis. The World Health Organization recommends diagnosing the disease by examining glycated hemoglobin. The method shows the average blood glucose level over the past 3 months. The result and clinical signs of the disease are not affected by the following factors:
- eating;
- time of analysis.
The normal value of the indicator is 6.5% HbA1C. This corresponds to 7.8 mmol/l, which is considered a clear sign of diabetes. If the rate is 6%, then the risk of developing the disease is increased. To prevent complications, the patient is advised to change his lifestyle. With modern treatment in combination with a special diet, the patient’s life can be made comfortable and fulfilling.
Diabetes causes cuts, bruises, and contusions to heal slowly. The skin is more susceptible to fungal infections. In the first type, skin pigmentation is disrupted. The disease of the 2nd degree is accompanied by darkening of the skin folds. But this symptom rarely appears.
Sometimes the skin on the back of the back and neck thickens. Atherosclerosis leads to problematic blood flow to the epidermis. Oxygen starvation develops, which provokes hair loss. Sometimes there is coldness in the legs and arms. The clinical picture is complemented by numbness of the legs, gangrene and amputation.
Dependence of diabetes mellitus in men on age
Type 1 diabetes mellitus affects mainly young men. It is often diagnosed in childhood. And type 2 diabetes is considered a disease of older age after 40–50 years. In most cases, the symptoms of diabetes in men 30 years of age will correspond to the symptoms of type 1 diabetes (described above). Many people by this age have not yet developed complications of diabetes. The most common signs of diabetes in men after 40–50 years of age are: decreased potency, blurred vision and pain in the lower extremities, frequent urge to urinate, especially at night.
Causes of diabetes in old age
Typically, men, unlike women, devote much less time to their health and are in no hurry to visit a doctor when unpleasant symptoms appear.
In addition, they are more likely to abuse nicotine and alcohol, do not watch their extra pounds and diet, and experience stressful situations more heavily and longer. All this is the reason that diabetes has become far from uncommon in older men.
Speaking in more detail about the nature of diabetes, we can highlight the following reasons for its occurrence:
- unbalanced diet . A large load on the pancreas occurs with frequent consumption of harmful fast carbohydrates, fast foods, a lot of fatty, sweet, salty, fried foods. As a result, the endocrine system suffers;
- sedentary lifestyle . If you consume a lot of calories without spending them at the same time, you become overweight. It is the cause of the development of diabetes mellitus;
- obesity . Most often, this is facilitated by the abuse of beer, which causes a “beer belly.” The organs become covered with a huge layer of fat, especially in the abdomen and waist. These excess fat deposits make it difficult for glucose to be absorbed;
- stressful situations and constant overwork . Regular stress increases blood sugar levels. Moreover, due to the psychological characteristics of adult men, they experience stress quite hard, thereby aggravating the situation;
- heredity . Having close relatives with diabetes increases the risk of developing the disease;
- chronic diseases . Because of them, the cells that produce insulin die. Pancreatitis is especially dangerous in this case;
- taking medications for a long time . If you take beta blockers, diuretics, antidepressants for a long time, then the likelihood of the disease occurring is very high;
- viral infections . Diabetes can develop as a result of mumps, rubella, chickenpox, hepatitis, and measles.
It is very important to monitor blood sugar levels for those men who have relatives with this disease, since they also have this predisposition.
Why is diabetes dangerous?
Diabetes mellitus is a complex and insidious disease. The disease affects blood vessels (first small, and then large) and nerve endings. As everyone knows, blood vessels and nerves are present in all vital organs and tissues, so diabetes gradually affects the entire body.
Consequences of diabetes
- Diabetic retinopathy (eg, retinal damage).
- Diabetic cardiopathy (various diseases of the cardiovascular system, such as left ventricular hypertrophy or heart rhythm disturbances).
- Diabetic nephropathy (kidney damage, mainly glomerular filtration is impaired, which leads to renal failure).
- Diabetic dermopathy (skin lesions: brown spots, trophic ulcers, poor wound healing). This can lead to the development of gangrene and amputation of the foot.
- Diabetic neuropathy (numbness in the limbs, pain, itching, unsteady gait, decreased sensitivity to external influences).
- Potency is impaired, libido decreases, and infertility may develop.
As you know, it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. Take care of your health, listen to your body, do not ignore symptoms, even such as thirst. Get your blood sugar tested and your blood pressure checked annually. Lead a healthy and active lifestyle, eat right, keep your weight normal! And your body will thank you.
Diagnosis by a doctor
If you suspect that a man has diabetes, you should immediately contact an endocrinologist. He will take a medical history, review any symptoms, and conduct laboratory tests.
The goal of laboratory research is to detect dysfunction of insulin-producing cells. Biochemically, this is confirmed by increased blood sugar, detection of glucose in the urine, and a decrease in the level of a special substance C-peptide in the blood and urine.
For research, samples of venous blood are taken and the glucose concentration in its plasma is determined using automatic analyzers. Recently, test strips and glucometers have become widespread.
Definition of illness
This disease is a chronic pathology caused by disruption of the pancreas and insufficient synthesis of insulin, a hormone necessary for normal carbohydrate metabolism. As a result, sugar accumulates in the blood, which leads to increased fragility of small vessels and capillaries and, as a result, malfunction of internal organs.
Young people are more susceptible to developing this disease than women. This is explained both by physiological characteristics and by a more careless attitude towards one’s own health, as well as by ignoring minor changes in well-being, which are often the first signs of illness.
Complications and consequences of diabetes
Acute complications are unpredictable. The destruction in the body can be serious. The effects of diabetes worsen gradually over several years. The person's condition is getting worse all the time.
Acute complications include:
- hypoglycemic coma,
- hyperglycemic state.
Late complications include:
- damage to the circulatory system in different places,
- disruption of nerve endings.
Retinopathy is a common complication of diabetes in male patients over 50. Blood vessels in the eyes become damaged due to increased blood sugar levels. The problem can develop to retinal detachment, cataracts, and clouding of the lens. By the age of 60, there is a risk of vision loss.
Diabetes causes complications on the kidneys, nephropathy develops. The pathology has several stages, the first is diagnosed only through laboratory tests. Nephropathy can develop asymptomatically for several years.
Kidney failure occurs in patients if they neglect treatment. Encephalopathy can occur if vascular disease worsens and reaches the central nervous system. The patient often has a headache, coordination of movements improves, and fatigue increases.
Diabetic foot is a condition in which the nerve tissue is affected and the legs become numb. As a result, the patient does not feel the slightest damage, infection and gangrene may develop.
The likelihood of gangrene requires special attention. In this case, the affected limb must be amputated. For elderly patients, this increases the likelihood of death to 40%.
You need to monitor the amount of glucose in the body, blood pressure levels, and stop drinking alcohol or tobacco products.
Regeneration of the skin is difficult to achieve, but it is possible to restrain the destructive process in tissues and blood vessels.
Problems with potency
Diabetes negatively affects the male reproductive system. The disease causes a decrease in testosterone levels. Increased glucose levels affect the functioning of the blood vessels and nerves of the penis. Men over 50 experience problems achieving and maintaining an erection. Due to metabolic disorders, sperm production decreases and early ejaculation occurs.
Erectile dysfunction leads to nervous breakdowns. Alarming signs of impotence require treatment.
Diet
To prevent the development of complications such as gangrene, nephropathy, and vision problems, you need to follow dietary recommendations. Adjusting your diet helps you monitor your own weight and blood sugar levels. This method of combating the disease helps in the first stages and in mild forms.
Doctors advise excluding fatty, smoked, salty or spicy foods that contain a lot of carbohydrates from the diet. For type 1 diabetes, the diet is less restrictive, since insulin is the main means of lowering blood sugar. When using other medications, you need to take your condition more seriously.
The effectiveness of glucose-lowering drugs decreases with age; if there is no effect of use, the therapeutic method must be adjusted. In such a situation, the diet will be more strict.
Complications of the disease
Diabetes mellitus is fraught with the fact that several years after the onset of primary symptoms, a number of complications develop from all possible organs and systems.
Nephropathy
Kidney damage, which is accompanied by a violation of their filtration function. A significant amount of protein appears in the urine. Structural changes begin 2-3 years from the onset of the underlying disease. Severe pathology develops after 10-15 years. The final result is complete sclerosis of the renal vessels, which leads to the death of the patient.
Neuropathy
Damage to the peripheral nervous system, which occurs due to a violation of adequate blood supply, including through the epineural vessels.
Complaints include:
- pain in the legs or vice versa, decreased pain sensitivity;
- numbness;
- feeling of tingling and crawling;
- changes in tactile, temperature, vibration sensitivity.
Retinopathy
Damage to the ocular analyzer, characterized by changes in the state of the retina. It manifests itself as impaired visual acuity, the appearance of aneurysms, hemorrhages on the retina, and the appearance of a veil before the eyes.
Most patients find out that they have diabetes only after being examined by an ophthalmologist.
Important! At the initial stages, the symptoms are less pronounced; changes are more often determined during the next examination by an ophthalmologist.
Diabetes and men's health
Diabetes mellitus in men has a negative impact on sexual function. Initially, patients experience decreased sexual desire. This is due to the accumulation of ketone bodies as a result of impaired protein metabolism. They suppress the production of the male sex hormone - testosterone. Then the erection is gradually impaired, ejaculation dysfunction is observed, and orgasm is absent.
When metabolic disorders occur, the DNA structure is damaged and the amount of sperm is reduced, resulting in infertility. Poor blood circulation contributes to a decrease in potency in diabetes. Blood cannot flow to the genitals in sufficient quantities due to vascular angiopathy (impaired vascular tone) characteristic of diabetes.
Therapy aimed at lowering sugar levels does not by itself improve sexual function in men. For a positive result, it is recommended to normalize weight, increase physical activity and additionally take medications that improve blood circulation. Medicines that increase potency - Viagra, Superviga, Cialis - are contraindicated for patients with diabetes mellitus, as they can worsen the condition.