Vitamin complexes are becoming increasingly popular. It has become fashionable to buy them at the pharmacy and take them for any illness, without following the recommended dosages and without waiting for doctor’s orders. Such uncontrolled consumption causes an excess of vitamins, or hypervitaminosis, a dangerous condition for humans. As a result of a single overdose of the drug, an acute condition occurs that resembles poisoning in symptoms. But most often, latent hypervitaminosis develops, when every day the body receives more vitamins and microelements than it needs. Let's consider which elements in excess are most dangerous to health, when hypervitaminosis occurs and what its symptoms are in adults and children.
Symptoms
Symptoms of hypervitaminosis depend on the type of vitamin and have characteristic features in each specific case.
Currently, about 10 groups (or families) of fat- and water-soluble vitamins are known.
Hypervitaminosis A
Signs of acute hypervitaminosis A:
- psychomotor agitation or, on the contrary, depression of consciousness;
- headache;
- lack of appetite, dyspeptic symptoms (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea);
- increased body temperature;
- photophobia (photophobia);
- development of convulsions, paralysis.
Hypervitaminosis A is manifested by skin rashes, itching and peeling
In chronic hypervitaminosis A, similar symptoms are observed, less pronounced than in the acute form. In addition, there are:
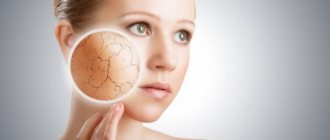
- skin manifestations - dryness, itching and flaking of the skin, rashes of various shapes and localizations, seizures in the corners of the mouth, as well as dry mucous membranes, hair loss, brittle nails;
- visual impairment – so-called night blindness (deterioration of twilight vision), decreased visual acuity;
- deterioration in general health;
- specific damage to connective tissue - inhibition of the processes of osteo- and chondrogenesis, destruction of bone and cartilage tissue, osteoporosis (discharge of bone beams);
- formation of foci of calcification in internal organs.
Hypervitaminosis D
In acute hypervitaminosis D the following are noted:
- a sharp decrease in appetite up to complete absence;
- drowsiness, lethargy, thirst;
- dry skin and mucous membranes;
- arterial hypertension;
- bradycardia (decreased heart rate);
- dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, unstable stool);
- increased urination;
- the appearance of neurological symptoms (convulsions, loss of consciousness).
With hypervitaminosis D, sleep patterns are disrupted. I want to sleep during the day, but not at night.
Chronic hypervitaminosis D is characterized by the following symptoms:
- disorders of the neuropsychic status of a cyclical nature (increased fatigue, weight loss, decreased tolerance to habitual physical activity are replaced by episodes of increased activity, speech and motor agitation);
- disturbances in the sleep-wake pattern (drowsiness during the day, insomnia at night);
- damage to parenchymal organs (kidneys, liver, spleen);
- neuromuscular symptoms (convulsions, muscle twitching);
- development of heart failure.
Hypervitaminosis of B vitamins
Acute and chronic forms of hypervitaminosis of B vitamins have similar symptoms; the main difference is the speed of development of the pathological reaction.
Hypervitaminosis B1 is manifested by cholinergic urticaria (rash on the forearms and upper body, accompanied by itching, fever, dyspeptic disorders), liver and kidney damage (up to acute failure), photosensitivity (increased sensitivity to sunlight).
Tonic cramps in the calf muscles signal hypervitaminosis B6
Hypervitaminosis B6 is expressed in progressive ataxia, loss of deep sensitivity of the lower extremities; however, pain, temperature and tactile sensitivity are preserved.
Hypervitaminosis B9 is characterized by tonic cramps (usually in the calf muscles) regardless of the time of day, as well as allergic reactions.
Other hypervitaminosis
Symptoms of other hypervitaminosis:
- with the erroneous administration of large doses of vitamin E, necrotizing enterocolitis and sepsis may develop;
- hypervitaminosis K is characterized by the development of hemolytic syndrome exclusively in newborns;
- Excessive intake of nicotinic acid (vitamin PP) is accompanied by facial hyperemia with a feeling of heat and allergic reactions.
Reasons for development
A pathological excess of vitamins in humans most often occurs due to uncontrolled intake of artificial supplements and complex drugs. More often than not, we all prescribe multivitamins ourselves, considering them useful in any case. Many, without hesitation, exceed the dosage indicated in the instructions, professing the principle “you can’t spoil porridge with oil.” In other cases, the doctor prescribes drugs without conducting a thorough diagnosis, prescribing them “for show.” Symptoms of hypervitaminosis appear more quickly in children and adults suffering from chronic diseases. Adherents of all kinds of weight loss diets fall into this same group.
In rare cases, but still possible, the cause of this pathological condition is prolonged consumption of large quantities of foods containing one or another vitamin.
The most dangerous from the point of view of the development of hypervitaminosis are fat-soluble vitamins - retinol (A), calciferol (D), tocopherol (E) and menaquinone (K). They are able to accumulate in the liver, unlike water-soluble ones, which are mostly excreted in the urine.
Treatment
Treatment of hypervitaminosis consists of immediately discontinuing vitamin preparations [and (or) changing the diet] in order to prevent further intake of the vitamin into the body.
As a rule, after stopping the intake of vitamin-containing products, the condition returns to normal.
The first action for hypervitaminosis is discontinuation of the drug that caused the overdose.
In severe or moderate conditions, symptomatic treatment is recommended in accordance with the clinical picture.
Diagnosis of hypervitaminosis
There are no specific diagnostic methods for vitamin A overdose. When making a diagnosis, the doctor is guided by the results of the anamnesis (data collection) and clinical symptoms:
- slowing or stopping growth in children;
- anorexia in adults;
- low resistance to infectious diseases;
- ulcerative lesions of the mucous membranes;
- signs of inflammation of the meninges.
Carefully examine the skin for pigmentation, rashes, and peeling.
Laboratory research methods include blood and urine tests for vitamin A levels. Additionally, a biochemical blood test may be prescribed to determine cholesterol levels.
An abdominal ultrasound is performed to assess the condition of internal organs..
For whom can this substance be dangerous?
Despite all the beneficial properties of vitamin C, there are diseases and situations in which it must be used with extreme caution. These are the following states:
- Presence of stones in the genitourinary system.
- Diabetes.
- Pregnancy and lactation period.
If these conditions exist, you should use the product only after consultation with a specialist.
Many parents who are concerned about the health of their child and strengthening his immunity give him ascorbic acid. However, its independent use can lead to an overdose of vitamin C. And it, in turn, is dangerous for the development of diabetes in childhood. During pregnancy, hypervitaminosis can lead to spontaneous abortion. Sometimes women who abuse vitamin C give birth to children with developmental defects.
Description
Vitamin B12 belongs to the water-soluble vitamin group.
Vitamin B12 includes:
- adenosylcobalamin;
- Hydroxycobalamin;
- methylcobalamin;
- cyanocobalamin.
However, the most important element for the human body is cyanocobalamin, which enters the body with food. The described substance accumulates in such internal organs as the lungs, kidneys, liver and spleen.
Vitamin B12 is presented in the form of a dark red, odorless powder with highly dispersed particles. The element has this particular color because its molecules contain cobalt, which makes cyanocobalamin the only substance that contains this metal.
Scientists learned about cyanocobalamin through studying pernicious anemia, which was caused by a lack of vitamin B12. And in 1948, Smith and Folkers isolated oxycobalamin and cyanocobalamin separately from each other. The structure of the described element was studied for eight years by three scientists - Todd, Hodgin and Smith. In 1972, the complete synthesis of vitamin B12 was carried out by Eschenmoser and Woodward.
What does an increase in vitamin B12 in the blood mean?
If your blood level exceeds B12, you must undergo additional medical examination. An excess of the vitamin warns of the presence of prerequisites for the development of cancer. If measures are not taken in time, cancer will occur. Elevated levels of cyanocobalamin are characteristic of diabetes mellitus, blood leukemia, and liver diseases. If you are diagnosed with liver cancer, hepatitis, or cirrhosis, you need to monitor its content. Although an increased level of B12 provokes the development of chronic diseases, the presence of its excess in the body does not always mean that a person is seriously ill.
Elevated B12 rarely occurs naturally. Hypovitaminosis b12 is much more common. Vegetarians, vegans and people over 50 are at risk. Hypovitaminosis occurs with liver disease or diabetes. When B12 deficiency occurs, they try to increase it artificially by taking a synthetic vitamin.
Products containing vitamin C
Ascorbic acid should be consumed as an additional source of a substance important for the body. However, the bulk of vitamin C must be obtained from food. So what foods contain this substance? These are the following products:
- Cabbage.
- Berries: cranberries, currants, rose hips.
- Citrus fruits (grapefruits, lemons, tangerines, oranges).
- Parsley.
- Tomatoes.
- Bell pepper.
- Kiwi.
When consuming these foods, you must be careful to avoid such a phenomenon as an overdose of vitamin C.
Doctors recommend eating these fruits and vegetables in the following quantities:
- One orange.
- 1 bell pepper.
- 2 medium sized tomatoes.
- Black currants (twenty pieces).
- One hundred to two hundred grams of cabbage.
- Kiwi (1 piece).
This is a daily norm that is important to strictly adhere to. It should be remembered that during freezing and heat treatment, a significant proportion of the vitamin is still preserved.
Prevention
To avoid an excess of vitamins, you should not abuse vitamin supplements and complexes. It is enough to consume them only in autumn and winter, and during the rest of the year it is better to diversify your diet in order to get the necessary substances from foods.
To prevent hypervitaminosis, you should take a break of a month after taking each vitamin complex. Also, unfamiliar alcohol solutions and products are used with increased caution. When taking vitamins, strictly follow your doctor's recommendations. Without consulting a doctor, it is prohibited to give your child any medications or biologically active substances containing large amounts of vitamins. The vitamins themselves should be kept out of the reach of children.
Remember that you can get enough vitamins if you eat a balanced diet. If this is not possible for some reason, you should start taking vitamins. In most cases, domestically produced vitamins are prescribed, since they are created taking into account the population that lives in the region. These additives are strictly controlled and tested.
Moreover, there are special treatment complexes in which the daily norm can be significantly exceeded, even tens of times. If you start taking these medications without consulting a doctor and without medical supervision, you will definitely have hypervitaminosis. So before starting any drug, be sure to consult your doctor. Only in this case will you be able to avoid dangerous conditions. If the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor immediately.
The main causes of vitamin A overdose
Why can there be an excess of this vitamin in the body? Acute hypervitaminosis develops due to a one-time excess of the permissible dosage, which provokes a bright, acute clinical picture. Sometimes a chronic form of poisoning occurs, when retinol accumulates in the body due to systematic, prolonged use. Chronic overdose has less pronounced manifestations, but causes no less harm and damage, and its consequences can be very serious.
Provoking factors:
- simultaneous intake of vitamin A and food that is rich in retinol;
- excessive consumption of eggs, liver and other offal;
- independent and uncontrolled increase in the dosage of a multivitamin complex purchased at a pharmacy;
- taking suspicious dietary supplements;
- high sensitivity to retinol, which causes an allergic reaction;
- individual intolerance to the component, which is accompanied by metabolic disorders.
It is important to avoid self-medication and take any medications only as prescribed by your doctor.
Vitamin A in capsules
Where is vitamin B12 found?
The main sources of vitamin B12 are animal products:
- beef, pork or chicken liver - 60, 30 and 17 mcg, respectively ;
- octopus meat - 20 mcg ;
- fish (mackerel, sardine, perch) - 12, 11 and 2.5 mg, respectively ;
- rabbit meat - 4.5 mcg ;
- beef - 2.6 mcg ;
- pork or lamb meat - 2 mcg ;
- Dutch cheese - 1.5 mcg ;
- crab - 1 mcg ;
- chicken egg - 0.5 mcg ;
- sour cream - 0.5 mcg .
Cyanocobalamin is also found in small amounts in plant sources, namely soy products, hops and yeast. But there is a lot of debate today regarding the latest product. It has been proven that nutritional or brewer's yeast itself does not supply cyanocobalamin to the body. This is only possible if the supplement is additionally enriched with B12.
So, with regard to nutritional and brewer’s yeast (from the standpoint of B12 supply), you shouldn’t count on much. The reasons are as follows:
- Brewer's yeast is often sold by weight. The seller or owner of the outlet may order a type of product that does not contain vitamin B12. The product name is often identical, but the composition differs.
- Cyanocobalamin is sensitive to sunlight. So, if the yeast was stored in transparent containers, then the beneficial vitamin may not remain in the composition.
If brewer's yeast is used to obtain B12, it is recommended to check the source of the vitamin for quality and composition. In addition, the purchased product should be stored in the freezer and away from sunlight.
Numerous drugs also act as suppliers of cyanocobalamin, including:
- Aqueous solution of B12 with sodium chloride (Cyanocobalamin). This product is available in ampoules of 200 and 500 mcg. The solution is administered intramuscularly, intralumbarally, intravenously or subcutaneously. The dosage varies depending on the disease. The administration option is determined by the doctor. Thus, for sclerosis or myelosis, cyanocobalamin is injected intralumbarally (into the spinal canal).
- Neurobion is vitamin B12, which is available in ampoules. Manufacturer: German company Merck. Contraindications for use: lactation, pregnancy, age under 12 years, allergic reactions.
- Vitagram - cyanocobalamin in ampoules. The drug is produced in Russia. The composition contains lidocaine, which reduces pain in the event of an injection. Use is not recommended during pregnancy, in the presence of bleeding and for children.
- Beplex is a multivitamin complex that is sold in ampoule form. Contains a group of vitamins B and PP. Prescribed for vitamin deficiency, gastrointestinal disorders, dermatitis, encephalopathy.
- Neurobion is a complex that contains a whole group of B vitamins: B1, B6, B12. A serving of cyanocobalamin exceeds the body's daily requirement by 20 percent. The composition is prescribed to normalize the functioning of the central nervous system and improve metabolic processes in the spinal cord and brain.
- Neurovitan is a vitamin complex made in Italy. Each tablet contains 0.24 mg of cyanocobalamin, which more than covers the daily requirement (taking into account the peculiarities of absorption of the vitamin in the case of oral administration). The drug is prescribed to normalize the functioning of the central nervous system, for skin diseases, neuritis, and deterioration of hair and skin condition.
- Compligram B is a Russian drug that is sold in ampoules and contains B1, B6 and B12. The drug also contains lidocaine, which acts as an anesthetic.
The human body needs vitamin B12. The sources of this element are discussed above - these are food of animal and plant origin, as well as vitamin complexes. The main thing in the intake process is to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and maintain the dosage.
Harm from large doses of fat-soluble vitamins
Some vitamins are fat-soluble; they are also called fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K, H). Excess amounts of these vitamins may not cause immediate harm, because their excess in the body is stored in fatty tissue. The problem is that if a person decides to lose weight, he will definitely start using these reserves of vitamins and then negative consequences are possible.
Hypervitaminosis A
Hypervitaminosis A (when the daily norm is exceeded 20 times) can cause:
- joint pain,
- hair loss,
- cracked lips,
- dry skin,
- headache.
Overdoses of this vitamin are especially dangerous for pregnant women due to the fact that they endanger their fetus.
Hypervitaminosis D and E
Large doses of vitamins D and E are also not recommended.
If you take large amounts of vitamin D (3 to 4 times the daily requirement), damage to the inner lining of the arteries is possible. These disorders contribute to the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques
.
Features of the disease
Understanding what hypervitaminosis is, it is worth noting that these are disturbances in the functioning of our body, caused precisely by an excess amount of useful substances.
At its core, it can be of two types - acute and chronic. Acute appears when taking a large dose of one or several vitamins at once. Its symptoms are very similar to poisoning. At the same time, chronic hypervitaminosis develops regularly when a person systematically consumes more vitamins than he needs. In this case, the symptoms may not be as obvious.
What products does it contain?
Vitamin B12 is the only vitamin formed exclusively during the life of microorganisms. The process of cyanocobalamin synthesis occurs in the intestines of small and large ruminants, fish, birds and in the human intestines. The most important source of the described vitamin is the animal’s liver.
However, there are products with vitamin B12 that are artificially enriched with it. These food sources include:
- energy bars;
- breakfast cereals;
- fortified corn flakes;
- chocolate.
What other foods contain vitamin B12? Experts list the following food sources rich in cyanocobalamin:
- chicken eggs;
- seafood (shrimp, mussels, octopus);
- meat products (lamb, beef, chicken, rabbit, poultry);
- dairy products (sour cream, kefir, cheese, condensed milk, cottage cheese);
- fish products (halibut, perch, Atlantic herring, scallops, cod and salmon);
- offal (veal liver, kidneys, lungs, heart).
Products high in vitamin B12 (the amount of cyanocobalamin is indicated in mcg per hundred grams of product):
- beef liver – 60;
- pork liver, chicken hearts – 26;
- octopus – 20;
- herring – 18.7;
- mussels, mackerel – 12.
A small amount of vitamin B12 is found in sour cream, chicken eggs and kefir.
Food sources of plant origin practically do not contain cyanocobalamin. But it can still be found in tops, sea cabbage, soybeans, green salad and hops, but in very small quantities. Those who adhere to a vegan diet should make sure that cyanocobalamin enters the body in normal quantities. In this regard, for vegetarians, vitamin B12 is usually prescribed as an additional medicine that helps fill the body with the necessary amount of the substance.
During cooking, cyanocobalamin still retains its high concentration. Over the course of forty-five minutes of stewing, the veal will lose only a quarter of the substance. The milk will lose only a third of its cyanocobalamin after boiling for five minutes. With prolonged heat treatment and sterilization, the effect of the described vitamin is destroyed.
Interaction with other substances
When consuming or administering intramuscular preparations with cyanocobalamin, you need to know how vitamin B12 interacts with other elements inside the human body. Scientists focus on the following important points:
- You should not combine cyanocobalamin and other B vitamins (thiamine, pyridoxine and riboflavin) in one injection, since vitamin B12 contains cobalt ion, which has a bad effect on other beneficial elements, destroying their effect.
- When vitamin B12 is combined with retinol and iron, the former helps speed up the action of the latter two.
- The combined use of cyanocobalamin with folic and ascorbic acid, as well as vitamin B5, has a positive effect on the body, ensuring normal metabolism, protection from stressful situations and the effects of depression.
- Cyanocobalamin interacts poorly with potassium, leading to poor absorption of the metal by the body.
- In order for vitamin B12 to be better absorbed by the intestines, you need to eat calcium-containing food sources (milk, cottage cheese).
It should also be said that cyanocobalamin cannot be combined with medicinal compounds that increase blood clotting.
Symptoms of hypervitaminosis D in infants
Symptoms common to all ages are indigestion, difficulty breathing, increased blood pressure, headaches, joint and muscle pain and cramps. It is difficult to identify most of these signs in a small child who cannot say what hurts. Symptoms hinting at excess vitamin D in children:
- taking a long time to fall asleep, restless sleep, crying at night;
- frequent regurgitation or even vomiting;
- loss of appetite, sudden weight loss;
- slower hair growth;
- severe thirst, increased urine output;
- constipation or diarrhea.
When the first signs appear, be sure to consult a doctor and tell them what medications and vitamins your baby is receiving.
First aid
Ascorbic acid is highly soluble in aqueous media and is therefore quickly excreted by the renal system.
- At the first suspicion of an overdose, you should ensure that you drink plenty of fluids and stop taking further vitamins.
- When using excessively high doses of the drug one-time, it is necessary to quickly remove it from the body, for which you need to induce vomiting and rinse the stomach.
- Then you need to take an adsorbent drug like activated carbon or Smecta.
- If you drink plenty of water, water-soluble ascorbic acid will be absorbed by the body in the quantities it needs, and the rest will be excreted by the kidneys in urine. But you need to drink a lot of water.
- And the adsorbent taken in time will absorb excess vitamins from the gastrointestinal system, neutralize them and quickly remove them from the body.
Further tactics for treating overdose are chosen by a specialist. If the overdose is minor, then the patient is allowed to stay at home for treatment, but in case of serious intoxication, hospitalization may be required.
When is it recommended to use ascorbic acid?
This product is an artificial source of vitamin C. It is important to use this substance correctly, because its excess can cause harm rather than benefit. Before you start taking vitamin C (dragées), the instructions for use should be carefully studied.
First of all, you need to decide to whom this remedy is recommended.
So, you need to take ascorbic acid in the following cases:
- Presence of alcohol or nicotine addiction.
- Physical overexertion.
- Living in an area with an unfavorable climate.
- Puberty.
- Infections.
- Rehabilitation after serious illnesses.
- Period of use of hormonal contraceptives.
- Intoxication.
In the presence of the above conditions, vitamin C (dragees) is used in a dose of 500 milligrams. However, you should not self-medicate, because the remedy is not as harmless as it seems. To avoid taking too much vitamin C, you should consult your doctor before starting to take it.
Why does the norm exist?
Alas, the concept of “more is better” does not work for living beings; for them it is more important to stick to the middle. Moreover, this applies to everything: the amount of food necessary for life, the amount of water, hours of sleep. Man is no exception. His body itself knows its own norm very well and tries to adhere to it, removing unnecessary things. After all, people rarely think about moderation when they eat delicious foods or drink their favorite drinks. They want more. The concept of “norm” or “measure” also applies to vitamins.
All of them are active enzymes that have a significant impact on the overall functioning and condition of the body, so their maintenance is extremely important. If there is little, it’s bad, if there’s too much, it’s also bad. The body can easily process some vitamins, passing them through liquid if it senses an excess, while others remain. For example, an excess of vitamin B12 occurs due to the body's inability to absorb it.
Vitamin B12 itself is considered an important representative of its group; its structure was determined back in the 60s of the last twentieth century. Natural sources of this vitamin:
- Yeast;
- Beneficial bacteria;
- Seaweed;
- Some types of mold;
- Pharmacological source - drugs.
Moreover, B12 has several forms, of which a person needs only one – cyanocobalamin. The movement of the vitamin is influenced by the Castle factor when it travels from the gastrointestinal tract to other cells. The factor helps it reach the places where cells need B12 most.
Why is too much B12 dangerous?
Excessive intake of cyanocobalamin is possible if the dosage of special drugs (in the form of injections or tablets) is exceeded. The vitamin norm is 0.4-2.4 mcg per day, depending on age. Thus, children under three years of age are recommended to take 0.4-.0.9 mcg per day, people aged 4-13 years - 1.2-1.8 mcg per day, and adults - 2.4 mcg . During pregnancy and lactation, the dosage increases to 2.6-2.8 mcg .
An excess of vitamin B12 leads to the following problems:
- allergy;
- increased excitability;
- violation of the blood clotting process;
- the appearance of acne.
If an overdose is caused by an increase in the permissible volume of injections, then the consequences can be more serious:
- thrombosis;
- heart failure;
- pulmonary edema;
- hives;
- anaphylactic shock.
When taking B12 supplements, it is important to pay attention to the interaction of cyanocobalamin with other elements . Thus, when taken together with ascorbic acid, the body’s ability to absorb the vitamin from food deteriorates. To avoid a lack of cyanocobalamin during co-administration, it is recommended to check the vitamin content in the blood.
Knowing the consequences of excess vitamin B12, symptoms and possible disorders, it is easier to normalize the diet and eliminate risks. One of the most unpleasant and common is the appearance of acne. Scientists have conducted a number of studies regarding the connection between acne and vitamin B12. It has previously been proven that taking supplements with cyanocobalamin leads to deterioration of the skin, but the essence of the mechanism was only recently discovered.
The entry of B12 into the blood serum leads to a decrease in the production of cyanocobalamin by skin bacteria and the synthesis of elements that contribute to the occurrence of inflammatory processes. The main culprits of acne are the bacteria Propionibacterium acnes. During the experiment, scientists found out why these microbes cause acne in one category of people, but not in others. It turns out that the activity of bacterial genes in healthy and sick people differs, and the process itself is directly related to the biosynthesis of cyanocobalamin. It was also found that decreased production of the vitamin by bacteria increases the risk of developing inflammatory processes.
The danger of excess and its treatment.
The danger of vitamin A, or rather its overdose, lies not only in the formation of several negative factors. Long-term use of large doses of the substance has a toxic effect on the body, leading to various types of disorders such as blurred vision, an increase in the size of the spleen, changes in the structure of the liver, and others.
An excess of this element during pregnancy is especially dangerous, since it has a negative effect on the formation and development of the fetus.
In case of acute vitamin A poisoning, emergency measures must be taken: induce vomiting, rinse the stomach and immediately call an ambulance. The patient will then be treated in a hospital, which usually lasts 3 to 5 days.
As for the chronic condition, the situation here is much more complicated, since long-term exposure to increased doses does not go away without leaving a trace. To normalize the functioning of the body, it will take time, during which you should completely review your diet, eliminating from it all foods containing vitamin A. Your doctor or nutritionist will help you figure out the menu and foods that can be taken and which cannot.