In everyday life, cuts are quite common. There is not a single person who does not cut his hand. A cut is a break in the skin that leads to bleeding. Sometimes the bleeding is so severe that it can only be stopped with special means and special methods.
When a cut occurs, the integrity of the blood vessels is damaged, which is why blood flows. After some time, the blood will begin to clot and a wound will form in place. However, we need to speed up this process before the person loses a lot of blood. In addition, we need to protect the open wound from infection.
Most often, cuts occur on the fingers, where there is a collection of blood vessels. This is why a cut on your finger bleeds so much. If you cut yourself, you need to quickly determine the approximate depth of the wound. After all, the principles of stopping bleeding in deep and superficial cuts are slightly different.
How to stop bleeding from a superficial cut
- For a small cut, rinse the wound with a stream of cold water. This will not only cleanse the cut of contaminants (relevant when cutting with a dirty knife or broken glass), but will also slightly narrow the blood vessels.
- If blood continues to flow after cold water, you need to apply pressure to the wound with a clean cotton swab or bandage. Applying pressure for a few minutes will help stop the bleeding.
- Then treat the edges of the wound with a bactericidal agent and apply a plaster or bandage to the wound.
Capillary
The easiest type of bleeding is capillary. It occurs with superficial damage: abrasions, small cuts, insect bites. In this case, the entire surface of the wound bleeds - slowly and drop by drop. The main measures required at the initial stage will be treating the wound with an antiseptic, applying an aseptic dressing and raising the limb. This is becoming enough. Light bleeding may stop on its own.
You can stop capillary bleeding at home using other means that are at hand. It happens that there is no first aid kit with hydrogen peroxide at home. Then some substances with astringent, antiseptic and hemostatic effects will come to the rescue. These include the following:
- Petrolatum.
- White vinegar.
- Witch hazel.
- Corn starch.
- Sugar.
- Web.
- Antiperspirant.
- Listerine.
- Alum.
- Paprika.
Many of them seem completely unexpected, but in the absence of other options and in extreme situations, you should not neglect the beneficial properties of known remedies. If the bleeding does not stop, you should definitely consult a doctor. You may also have to stitch up the wound.
How to stop bleeding from a deep cut
- If there is a deep cut, you must act quickly because the person may lose a lot of blood. To provide first aid, you need a bandage, a piece of clean cloth, an antiseptic, and water.
It is forbidden! If there are shards of glass left in the cut, you should not widen the wound or try to remove the foreign object. You need to apply a tourniquet to your arm or leg 10 cm above the wound to stop the bleeding, cover the wound with a clean cloth and go to the hospital immediately.
Main causes of bleeding
Capillaries are the smallest vessels, damage to which is considered not life-threatening. In most cases, capillary hemorrhage does not harm health and stops spontaneously.
Capillary bleeding is quite easy to identify, with bright red blood oozing from the damaged area. Blood flows out of the wound slowly, there is no pulsation, since the blood pressure in these vessels is low.
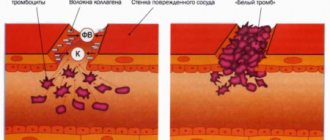
The coagulation system instantly reacts to capillary damage. The blood vessel contracts, blood flow slows down, and blood loss decreases. Platelets and fibrin fibers form a blood clot that closes the damaged area. This process takes from 3 to 5 minutes.
Capillary bleeding occurs for the following reasons:
- Burns;
- Cuts, abrasions;
- Thrombocytopenic purpura - increased bleeding due to a low concentration of platelets in the blood;
- Hemophilia – decreased blood clotting;
- Pseudogemophilia – spontaneous bleeding due to increased vascular permeability;
- Oncological formations;
- Purulent inflammation of the skin, which damages blood vessels;
- Atherosclerotic damage to capillaries;
- Tissue necrosis due to various diseases;
- Hormonal imbalance.
We suggest you read: How alcohol affects blood sugar
The above-described pathologies provoke damage to the walls of blood vessels and hemorrhage.
A sign of external capillary bleeding is that the blood flows outward, and with internal bleeding, it is released from the vessels of the internal organs (stomach, intestines, uterus) into the body cavity.
With capillary hemorrhage, blood flows out evenly over the entire surface of the wound or in a thin stream.
With significant blood loss, the victim complains of weakness, drowsiness, his skin turns pale, and the oral mucosa dries out. In addition, the pulse quickens and blood pressure decreases. In some cases, dizziness, nausea, shortness of breath occur, vision becomes dark, and a person may lose consciousness.
Next, you will learn how to stop capillary bleeding, what needs to be done to provide first aid, how to apply a tourniquet correctly, and what mistakes happen during first aid.
Among the possible causes of capillary bleeding, experts distinguish coagulopathic, traumatic, pathological:
- various blood clotting diseases. These include von Willebrand disease, thrombocytopenic purpura, hemophilia;
- vascular diseases, which are accompanied by damage to the epidermis and tissues. Among them are purulent lesions of the epithelium involving blood vessels, tumors;
- traumatic lesions. These include burns, abrasions, and cuts. Traumatic injuries are divided into thermal (formed under the influence of high temperatures), mechanical (their occurrence is influenced by various extreme situations);
- the presence of common diseases, which include necrosis, tumor processes, atherosclerosis. With such diseases, damage to the vascular walls of the entire body is noted. In such cases, plasma and blood cells leak out, forming extensive bleeding;
- presence of disturbances in hormonal function.
What can cause bleeding? It is appropriate to note here that two fundamentally different types are also distinguished, based on the factor of whether the normal vessel is damaged or the pathological condition arose against the background of destruction of the altered vascular wall. In the first case, bleeding is called mechanical, in the second - pathological.
The following main causes of bleeding can be identified:
- Traumatic injuries. They can be thermal (from exposure to critical temperatures), mechanical (from a bone fracture, wound, bruise). The latter occur in various extreme situations: road accidents, train and plane crashes, falls from a height, fights involving piercing objects, gunshot wounds. There are also industrial and domestic injuries.
- Vascular diseases, including tumors (purulent tissue lesions involving blood vessels, atherosclerosis, hemangiosarcoma).
- Diseases of the blood coagulation system and liver (hemophilia, von Willebrand disease, fibrinogen deficiency, hypovitaminosis K, hepatitis, cirrhosis).
- General diseases. For example, diabetes mellitus, infections (viral, sepsis), lack of vitamins, and poisoning cause damage to the vascular walls throughout the body, as a result of which plasma and blood cells leak through them and bleeding occurs.
- Diseases affecting various organs. Bleeding from the lungs can cause tuberculosis, cancer; from the rectum - tumors, hemorrhoids, fissures; from the digestive tract - stomach and intestinal ulcers, polyps, diverticula, tumors; from the uterus - endometriosis, polyps, inflammation, neoplasms.
Among the possible causes of capillary bleeding, experts highlight the following factors:
- all kinds of diseases that prevent normal blood clotting. Among them are von Willebrand disease, hemophilia, thrombocytopenic purpura;
- vascular diseases, in which there is damage to tissues and skin. These include purulent skin lesions, as well as various tumors;
- various injuries. These include abrasions, burns, and cuts. Injuries can be thermal in nature, caused by exposure to high temperatures, as well as mechanical, resulting from various extreme situations;
- the patient has all kinds of general diseases, such as spreading tumors, necrosis, and atherosclerosis. In such cases, damage occurs to the walls of blood vessels throughout the body. At the same time, the blood plasma and its cells begin to spread, with the formation of extensive bleeding;
- all kinds of hormonal disorders.
Antiseptics for disinfecting cuts
Before bandaging a wound, you need to disinfect its edges. Because getting germs, bacteria and infections inside can lead to serious problems. You can disinfect a wound with several bactericidal agents that are found in every home.
- Hydrogen peroxide. This is a universal remedy that should be in every home. Hydrogen peroxide, in addition to being a powerful antibacterial agent, does not sting or cause pain when treating a wound.
- Iodine and its derivatives - Iodoform, Iodonate, Betadine, Iodonol, Yox.
- Zelenka (brilliant green solution). Now in the pharmacy you can buy brilliant green not only in its traditional form, but in the form of powder and pencil, which makes treating the wound much easier.
- Potassium permanganate. A strong solution of potassium permanganate is used to wash cuts, burns, and abrasions.
- Furacilin. These yellow tablets are found in every home, and when a cut occurs, their solution can disinfect the wound no worse than peroxide.
- Alcohol or vodka. When traveling, when there are no medications at hand, you can disinfect a cut with alcohol or vodka. However, be prepared to sting.
- Vishnevsky ointment. It is used to treat purulent formations and cuts, and has a pronounced antiseptic property.
Be careful! If you treated the wound yourself and stopped the bleeding, you should observe the cut for several days. If after a few days the edges of the wound become red, swollen and painful, it means that infection has occurred. Stronger antiseptics should be used, and it is better to consult a doctor. The same should be done if, after a cut, you notice a disturbance in the movements of your fingers. You could damage the tendons, which led to such consequences.
How to recognize and help with internal bleeding
Internal bleeding from small vessels does not have pronounced symptoms, so their onset often goes unnoticed. Prolonged bleeding can lead to the development of anemia.
Common signs and symptoms of internal bleeding:
- Weakness and drowsiness even after proper rest;
- Constant thirst;
- Frequent dizziness;
- Stable low blood pressure with rapid pulse;
- A blood test reveals signs of anemia.
Symptoms of internal bleeding in an adult, characteristic of different organs:
- Vomiting brown clots indicates the presence of blood in the stomach cavity;
- Tarry stools indicate bleeding in the initial parts of the intestine;
- Drops of unchanged blood in the stool are observed with bleeding hemorrhoids or intestinal bleeding;
- Coloring of urine occurs when bleeding into the lumen of the urinary tract.
Parenchymal bleeding, what is it? This presence of extensive bleeding surface of parenchymal organs (spleen, kidneys, liver) is characterized by the effusion of blood into the abdominal cavity and the frequent development of blood sepsis.
Hemarthrosis occurs when small vessels are damaged and blood accumulates in the joint capsule due to injury or dysfunction of blood clotting.
We suggest you read: Is thrombophlebitis dangerous?
Help with internal capillary bleeding:
- it is necessary to place the victim on a flat surface and apply cold to the suspected site of damage to the vessel; if a joint is injured, raise it above the level of the heart, apply a tight bandage and also use cold.
Methods of providing assistance
If a person is seriously cut by a knife or blade, it is necessary to take timely measures and provide him with assistance . This will help stop the bleeding if you cut your finger or other part of the body.
First, you should clean the damaged surface from dirt, remove any splinters or traces of rust, if any. For minor scratches, you can use clean running water and soap or a cotton-gauze swab moistened with hydrogen peroxide. Deep and serious damage requires more thorough treatment with antibacterial agents.
First aid
The first actions should be to quickly stop the bleeding. To do this, rinse the cut area with plenty of running water as quickly as possible. If the scratch is small, then with the help of only this procedure it will be possible to stop the bleeding.
If there are any foreign bodies in the wound, for example, sand, splinters, splinters, etc., you should first remove them. To do this, you need to use tweezers or a bandage, which must be sterile. If these first aid items are not available, you can use a handkerchief. The scratch must be cleaned carefully without causing pain. The main thing in this procedure is to prevent the foreign object from going deep into the muscle tissue.
First aid involves applying a tampon from a sterile bandage. It is used for shallow cuts. If hydrogen peroxide is available, then the wound should be pre-treated with this solution. It has a hemostatic effect. It is recommended to lubricate the edges of the scratch with brilliant green or brilliant green.
First aid for a wound or deep cut should be accompanied by the application of a tourniquet, which should be placed above the injured part. It should be remembered that the tourniquet is applied for a certain period of time, so you should put a note under it indicating the time at which it was applied. In the cold season, it can be kept for no longer than 60 minutes; for children the time limit is 30 minutes.
Important information: How to treat dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB) and its symptoms
The goal of first aid is to prevent infection from entering the wound. The faster the bleeding is stopped, the less likely it is that germs will enter the wound.
Superficial cut
First aid for minor wounds and bleeding should be limited to washing the damaged area and removing contamination. Cold water will have a constricting effect on the blood vessels, which will slow down bleeding.
However, if it continues, you need to press a cotton swab or bandage onto the cut area. If there is bleeding, you should hold it for several minutes. This should stop the flow of blood. After this, the edges of the scratch must be treated with any antiseptic. It is then covered with a plaster or bandaged.
Correctly provided first aid for cuts often saves you from complications.
Deep cut
If the victim’s cut is deep and the wound is bleeding heavily, then the affected area should be treated as quickly as possible. If this is not done, blood loss can lead to fainting and a number of dangerous consequences.
You will need a bandage or tape of clean cotton material, water and an antiseptic solution. The injured arm is raised so that it is above the level of the heart. This will reduce bleeding. Then, using a cloth previously moistened with water, the incised area is washed. If you put your wounded hand under a stream of water, the blood will begin to flow even more intensely, so this is not recommended.
It is imperative to remove small objects that were at the site of the injury, and only then try to stop the bleeding from the cut: if this cannot be done, there is a risk that the foreign parts will go deeper. The wound should be bandaged and the victim sent to a medical center.
Important information: Methods to stop parenchymal bleeding and first aid
However, they first try to clean the wound as much as possible, using hydrogen peroxide or another antiseptic. These actions will help reduce the risk of infection as much as possible. You can pour the peroxide solution over the wound or apply a piece of cloth soaked in the product to it.
In case of severe damage of a cutting or puncture nature, you should immediately consult a doctor after providing first aid.
Providing first aid for wounds and bleeding should not be accompanied by attempts to expand the wound in order to remove a foreign object, such as glass. You need to leave it in the same place, and apply a tourniquet or bandage above the injured area. Then immediately go to the hospital.
Medicines that stop bleeding
Your home first aid kit must contain medications that will help you quickly provide first aid for these types of injuries. I would like to draw your attention to medical glue BF-6. It is applied in a thin layer to the cut, previously treated with an antiseptic (for example, hydrogen peroxide or Miramistin). After drying, the glue forms a film that reliably protects the wound from infection (dust, dirt) and promotes rapid healing. The edges of the film should be made as thin as possible so that the glue lasts longer. If it is damaged, a second coat can be applied.
There are products that can be applied under a bandage for the purpose of healing, disinfection and relief of inflammation . These include:
- Levomekol (a good regenerating agent, dries the wound and kills germs).
- Tetracycline ointment (heals and reduces inflammation).
- Vishnevsky ointment (a well-known remedy in the fight against suppuration).
- Streptocide (disinfects).
- Chlorhexidine and Miramistin (both are good antiseptics; they are used to treat the wound, after which healing preparations can be applied to it).
- Baneocin.
- Bepanten.
- Panthenol.
If the wound is accompanied by severe pain, then you can take painkillers, for example, Nise or Nurofen. If necessary, you should purchase an antibiotic with a doctor's prescription to treat and prevent inflammatory processes.
Capillary bleeding
Capillary is the unusual name for the smallest vessel in the body. Bleeding from these vessels was observed by anyone who fell unsuccessfully to their knees in childhood. The blood does not flow out in a stream, but seeps onto the surface of the abrasion in small droplets . Similar bleeding occurs when cut with a blade.
It is not life-threatening, but it is useful to know what to do if you cut yourself after shaving:
- The abrasion is washed with cold, clean water . This eliminates contamination of the wound. In the case of a minor abrasion, the bleeding will stop at this stage.
- You will definitely need any antiseptic from the first aid kit . Regular iodine will also come in handy. But we will talk about the best and most convenient hemostatic drugs below.
- If the antiseptic stings , you can only treat the edges of the cut.
- Apply a clean bandage. It should not be tight, because the purpose of applying it to an abrasion is not to stop the bleeding, but to protect it from contamination.
- You cannot use cotton wool or cotton pads for abrasions - their fibers will remain in the wound and begin to become inflamed. It is best to use a sterile bandage or clean cotton cloth.
Minor abrasions and cuts heal quickly, and after a couple of days the bandage is removed. At this point, bleeding from the dried crust may resume. Therefore, it is better not to pull off the bandage. It is pre-moistened with hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine.
Folk remedies
If the affected person is a follower of traditional medicine, then you can use old, proven recipes designed to stop bleeding from an arm or leg at home . These include:
- Aloe juice has a good healing effect. You need to apply a leaf of the plant, having previously cut it, or treat the wound with juice. Aloe will soften the wound and disinfect it, as it is considered a natural antiseptic.
- Since childhood, everyone has known the ability of plantain to stop bleeding, when bruised dirty knees were treated with this miraculous remedy. But you should still wash the plant first and knead it a little. You can secure the plantain with a bandage or simply press it against the wound for a short time (10-15 minutes) until the bleeding stops.
- Another well-known folk remedy is calendula flowers. It is used as a disinfectant, after brewing 1 tsp. in a glass of boiling water. The wound is washed with this infusion.
- A decoction of yarrow will also help stop bleeding.
These remedies will help relieve pain and stop bleeding. But as soon as the opportunity arises, the wound must be treated with medication.
Therapy after stopping bleeding in the hospital
The use of blood coagulation improving drugs, blood replacement drugs, whole blood/plasma/platelet suspension is mandatory. Intravenous fluid therapy is also necessary to restore ion balance. Since bleeding is usually not the only problem after serious traumatic incidents, in parallel with the work to stop it, doctors carry out emergency diagnosis and treatment of associated disorders.
The main thing is not to lose your head if something bad happens to someone around you and the person is bleeding. In order to cope with it, you can use materials from your car first aid kit, items from your own bag, items of clothing or household items.
The task and duty of every normal person is to provide first aid to the victim, which consists in temporarily stopping the loss of blood. And then you should immediately take the patient to a medical facility under your own power or urgently call an ambulance.
What and how to stop bleeding without inconvenience
In principle, after all the above steps, the bleeding from the cut should stop. However, it can be quite difficult to carry out all the above actions in order to stop the bleeding on your own. Most of us do not have special skills in applying bandages, and doing it yourself is even more difficult than helping someone else. Therefore, if you are reading this article, not when someone is gushing blood from a finger in the kitchen, but in preparation for the need to stop the bleeding at home in a calm environment, then here are some tips on what you can put in your first aid kit, what would significantly make it easier for yourself and your family to stop bleeding in cases of force majeure of this kind.
The most common remedy used in everyday life to stop bleeding is hydrogen peroxide in the form of a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide in water. Contrary to popular belief, hydrogen peroxide does not promote wound healing itself, however, when it penetrates the wound, a fairly large amount of foam is formed, which stops the bleeding and is subsequently quite easily washed off with an antiseptic solution. Therefore, if the cut has not cut through any significant artery, treatment with hydrogen peroxide is quite enough to stop the bleeding so that it is comfortable to apply a bandage to the wound.
Personally, as the most preferred method of combating bleeding at home, I use the so-called hemostatic sponge.
How to stop bleeding? Of course, with the help of a hemostatic sponge!
With its help, the blood is often stopped by emergency doctors, who simply may not have time to tinker with bandages for a long time and evaluate their effectiveness as the car moves. Such a sponge is simply applied to the wound and glued with an adhesive plaster or wrapped with a small amount of bandage. The sponge swells quite a bit and then reliably stops the bleeding. In addition, it contains disinfectants and topical antibiotics, so you don’t have to worry about the need to disinfect a household wound and don’t have to change the bandage for the first few days.
I suggest you watch a short video by the author, which can slightly supplement the information from this article.
What types of bleeding are there and why do they occur?
There are many classifications of this pathological condition and specialists teach them all.
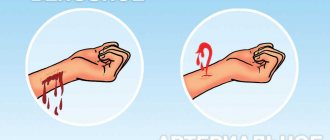
However, we are interested in dividing bleeding into types, first of all, from a practical point of view. The following classification is important for successful first aid. It shows the types of bleeding depending on the nature of the damaged vessel. It comes from the arteries containing oxygenated blood flowing from the lungs to all organs and tissues. This is a serious problem, since these vessels are usually located deep in the tissue, close to the bones, and situations where they are injured are the result of very strong impacts. Sometimes this type of bleeding stops on its own, since the arteries have a pronounced muscular layer. When such a vessel is injured, the latter goes into spasm.
Its source is venous vessels. Through them, blood containing metabolic products and carbon dioxide flows from cells and tissues to the heart and further to the lungs. Veins are located more superficially than arteries, so they are damaged more often. These vessels do not contract during injury, but they can stick together because their walls are thinner and their diameter is larger than that of arteries.
Blood bleeds from small vessels, most often the skin and mucous membranes; usually such bleeding is insignificant. Although it can be frighteningly abundant with a wide wound, since the number of capillaries in the tissues of the body is very large.
Separately, so-called parenchymal bleeding is also distinguished. The organs of the body are hollow, essentially “bags” with multi-layered walls, and parenchymal, which consist of tissue. The latter include the liver, spleen, kidneys, lungs, and pancreas. Typically, this type of bleeding can only be seen by a surgeon during an operation, since all parenchymal organs are “hidden” deep in the body.
Depending on whether the blood remains in the cavity of the body or organ or pours out of the body, bleeding is distinguished:
- Internal. Blood does not come out, staying inside: in the abdominal, thoracic, pelvic cavities, joints, and ventricles of the brain. A dangerous type of blood loss that is difficult to diagnose and treat because there are no outward signs of bleeding. There are only general manifestations of its loss and symptoms of significant dysfunction of the organ(s).
- External bleeding. Blood is poured into the external environment, most often the causes of this condition are injuries and various ailments that affect individual organs and systems. These bleedings can be pulmonary, uterine, from the skin and mucous membranes, gastric and intestinal, from the urinary system. In this case, visible outpourings of blood are called obvious, and those that occur in a hollow organ communicating with the external environment are called hidden. The latter may not be detected immediately after bleeding begins, because it takes time for blood to come out, for example, from a long digestive tube.
Typically, bleeding with clots is external, hidden or internal, when the blood is retained inside the organ and partially coagulates.
- Spicy. In this case, a large amount of blood is lost in a short period of time, usually occurring suddenly as a result of injury. As a result, a person develops a state of acute anemia (anemia).
- Chronic. Long-term loss of small volumes of this biological fluid is usually caused by chronic diseases of organs with ulceration of the vessels of their walls. Causes a state of chronic anemia.
Which doctor should I contact if I have bleeding?
The choice of specialist depends on the location of the vessel integrity violation.
Who will help the victim:
- nosebleeds - otolaryngologist;
- uterine – gynecologist;
- others – surgeon;
- stroke – neurosurgeon, neurologist;
- eyes - an ophthalmologist in a hospital.
After the condition has normalized, the doctor may recommend consultations with specialists in various medical specialties.
Bleeding is a life-threatening condition. There is no need to wait and hope that everything will work itself out. Even if you can’t cope with an ordinary cut, seek specialized help.
Chumachenko Olga, doctor, medical observer
7, total, today
( 184 votes, average: 4.72 out of 5)
What is an “acute abdomen”: symptoms and first aid
Chest injuries, fractures of the sternum and ribs: symptoms and first aid
Related Posts
Wound care
Even an ordinary scratch or abrasion, if treated carelessly, can turn into a real problem, requiring additional costs and treatment. Proper care of a cut will speed up healing and, if it is not a laceration, will leave virtually no marks on the skin. Of the folk methods for treating cuts of varying depths, the most popular is a remedy that is made from a mixture of fish oil (1 tsp) and honey (3 tsp). This substance is used as an ointment. Among the purchased medications, Spasatel, Pentanol, and Levomikol are good for treating cuts.
To quickly resolve swelling, local ointments are prescribed, such as Heparin ointment, Menovasin or Lyoton; these same drugs act as antiseptics and anti-inflammatory substances.
What not to do
You can't panic. If the pain is severe, try to call for help, especially if you have an injury to your hands. Bandaging with one hand will be awkward.
Never try to remove fragments or foreign objects yourself. If you cut yourself with broken glass, the fragments will be small, you simply will not find them.
Or, conversely, the fragment will be too large and you will need to expand the edges of the wound to remove it. It is dangerous to perform such actions on your own, without medical education and practice.
There is no need to sprinkle any traditional medicine on the wound. Do not use sugar or starch for these purposes. This will only make things worse.
If the injury is serious, simply apply a tourniquet a couple of centimeters higher, cover the open area with a sterile bandage and immediately go to the doctor.
Treatment
Therapeutic methods are used to stop blood loss. These drugs are: sodium etamsilate, Vikasol, Calcium chloride. The dosage is determined by the doctor.
We recommend reading:What are the types of bleeding?
If the patient’s condition is serious and there are symptoms of peritonitis, the cause of anemia will be sought only on the operating table. The operation is called "laparotomy". It involves examining the entire abdominal cavity and pelvic organs after a large incision.
Sometimes a big surprise for surgeons is the discovery of a disintegrating tumor or a huge cyst. To stop the flow of blood into the cavity, the vessels are ligated, and, if possible, the tumor is removed within healthy tissue. Inspection of the condition of neighboring organs allows you to ensure that bleeding has stopped.
To remove blood from the pleural cavity, a puncture is performed with careful suction. The X-ray picture is used to monitor the expansion of the lung.
Blood is also removed from the joint using a puncture. At the same time, antibiotics are administered to prevent inflammation.
When bleeding from dilated veins of the esophagus in patients with cirrhosis of the liver, palliative surgery is performed by inserting a balloon into the esophagus and inflating it with air. This achieves compression of the veins and subsequent thrombosis.
Bleeding hemorrhoids are ligated, removed, or sclerosing agents are injected into them.
If the patient’s condition allows, he is offered endoscopic methods of surgical treatment. The goal of any treatment for bleeding is to preserve and restore the damaged organ as much as possible.
Symptoms of uterine bleeding
Signs of blood loss are:
- cardiopalmus;
- weak pulse filling;
- hypotension;
- decreased ability to work, weakness;
- pale skin;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- confusion, fainting.
How to distinguish from menstruation
- Clots appear in the discharge.
- Discharge increases at night.
- More than 5 pads are used per day.
- Menstruation lengthens.
- Blood appears after sexual intercourse.
- There is pain in the lower abdomen, an unpleasant odor, and an increase in body temperature.
Specialized care: stopping bleeding
Immediately after hospitalization, diagnostic measures are carried out. Based on their results, the doctor makes a conclusion about the severity of the pathological process.
If the blood loss is minor, in most cases the body can cope with it. To help the defense mechanisms, doctors administer medications to the victim.
Prescribed drugs for internal bleeding:
- Fibrinolysis inhibitors. Examples of agents: “Aminocaproic acid”, “Aprotinin”, “Thrombin”.
- "Etamzilat." Necessary for improving microcirculation.
- Synthetic analogues of vitamin K.
These are the main ways to stop internal bleeding as part of specialized care. But only if a small amount of liquid connective tissue is lost.
Nosebleeds - how to stop?
The nasal mucosa is rich in tiny capillaries, so any injury can cause bleeding. They are distinguished by duration and intensity. Often, bleeding from the nose begins to bleed for no apparent reason, but usually such bleeding is caused by a blow, prolonged use of vasoconstrictor drops in the nose, fragility and weakness of blood vessels, sun or heatstroke, hypertension or anatomical defects of the nasal cavity.
Providing first aid for capillary nosebleeds is very simple, it is only important to do everything correctly:
The patient should be in an upright position, preferably sitting, with the head slightly tilted forward. This ensures unimpeded flow of blood from the nostrils. You can’t throw your head back, because blood flowing into the nasopharynx can cause vomiting or coughing, and this will only increase bleeding;
Apply ice to the nose area;
Press the wings of the nose against the septum for five minutes. This promotes the formation of a blood clot;
Place a swab soaked in a solution of 3% hydrogen peroxide into the nasal passage.
It is advisable to perform all procedures with rubber gloves, or at least pre-disinfect your hands. If you have frequent nosebleeds, you need to take regular preventive measures, strengthen blood vessels, take ascorutin or ascorbic acid.
Danger of nosebleeds
A condition in which blood is released from the nasal cavity can be life-threatening if the cause is a serious illness or injury. It is necessary and very important to temporarily stop bleeding before arriving at the hospital. If the nose bleeds for more than half an hour and is not stopped by the methods described above, and the volume of blood loss is more than 200 ml, you need to call an ambulance, regardless of the suspected causes of the bleeding.
Author of the article: Alekseeva Maria Yurievna | General practitioner
About the doctor: From 2010 to 2019. practicing physician at the therapeutic hospital of the central medical unit No. 21, the city of Elektrostal. Since 2019 he has been working at diagnostic center No. 3.
10 Proven Reasons to Eat Chia Seeds Every Day!
15 substances that speed up brain function and improve memory
Arterial bleeding is one of the most dangerous bleedings, posing a direct threat to human life. This is primarily due to the fact that blood loss is high and intense. Therefore, it is important to know its main signs and first aid rules.
Despite the fact that there are no minor reasons that could provoke such a phenomenon, situations can still be different. Sometimes you can wait a few hours before the start of a new working day and go to see a doctor as usual, but sometimes the situation is urgent: you should call a doctor.
Gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB) is the leakage of blood from blood vessels damaged by disease into the cavities of the gastrointestinal tract. Gastrointestinal bleeding is a common and serious complication of a wide range of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, posing a threat to health and even.
Uterine bleeding is the discharge of blood from the uterus. Most often it is a serious symptom of diseases of the female body. Any uterine bleeding should be diagnosed in time, and the woman should receive medical assistance. Ignoring such a symptom leads to serious consequences, even death.
Bleeding from the nose (scientifically called epistaxis) is a very common human pathology. With it, there is a discharge of blood from the nasal cavity, which occurs due to rupture of blood vessels. In some cases, it leads to large blood loss and threatens human life. In 20% of such bleeding, immediate medical attention is required.
Bleeding gums is the release of a certain amount of blood, accompanied by inflammation. The stronger the inflammatory process, the greater the amount of blood will be released from the gums. In some cases, it appears even when the gums are at rest, for example, at night. This problem is quite.
| Bleeding | |
| Capillary bleeding from a finger | |
| ICD-10 | R58 |
| ICD-9 | 456.20 456.20 |
| MedlinePlus | 000045 |
| MeSH | D006470 |
Bleeding
- release of blood beyond the vascular bed or heart into the environment (open bleeding), into the body cavity or the lumen of a hollow organ (internal bleeding).
Examples of external bleeding are metrorrhagia (uterine), melena (intestinal), internal - hemopericardium, hemothorax, hemoperitoneum, hemarthrosis (respectively into the cavity of the heart sac, into the pleural cavity, into the abdominal and articular cavities).
Providing first aid to a person with suspected internal bleeding
Everyone needs to know the algorithm of actions for internal bleeding. Adequate tactics for providing emergency first aid for this pathology can save a person’s life and minimize blood loss.
If internal bleeding is suspected, first of all, you should call an ambulance - or, if possible, transport the patient to the hospital in a personal car.
Until this point, you need to do the following:
- In case of severe trauma to the chest, the victim is placed in a semi-sitting position, and a small cushion is placed under his feet.
- If blood flows into the peritoneum, the patient is placed on a flat, hard surface without any elevations. If there is vomiting, it should be turned on its side.
- It would be a good idea to apply cold to the suspected site of bleeding. This can stop the pathological process and reduce pain.
- It is necessary to ensure a flow of fresh air into the room where the patient is located. The victim's neck and chest must be freed from constrictive clothing.
It is very important not to allow the patient to move or talk: this will only increase blood loss and worsen the general condition. It is necessary to remember the list of activities that should not be carried out during internal bleeding:
- Do cleansing enemas, give medications that have a laxative effect.
- Apply a warm heating pad to the damaged area.
- Massage the sore area.
- Administer medications that affect heart function.
- Give food, drink. In cases where the victim is tormented by severe thirst, he is allowed to rinse his mouth with cold water.
Causes
The most common causes of internal hemorrhages are injuries to the chest and abdominal cavity with fractures of the ribs, sternum, pelvic bones, and limbs. In this case, direct damage to the organ occurs with rupture or indirectly through bone fragments. Rupture of the liver, spleen, vessels of the intestinal mesentery, kidneys, and rupture of the ureter are diagnosed.
Acute and chronic diseases:
- gynecological diseases lead to hemorrhage into the cavity of the ovarian cyst, rupture of the cyst or tube during ectopic pregnancy;
- pulmonary tuberculosis causes pulmonary hemorrhage;
- peptic ulcer disease contributes to vascular damage, perforation of the ulcer and release of blood into the peritoneum, intestines, and duodenum;
- cirrhosis of the liver causes bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus;
- malignant tumors of the intestines and stomach, when disintegrating, can cause severe bleeding;
- Aortic aneurysm dissection is a common cause of bleeding in older people.
Physical activity and poor diet can provoke bleeding.
Internal bleeding poses a particular danger in hereditary diseases associated with insufficiency of blood factors (hemophilia). They can occur for no apparent reason and are severe. Most often the joints are affected. Such hemorrhages can be stopped only by transfusion of plasma with the necessary factors.
The only first aid for a patient with hemophilia is ice on the joint.
Causes of pathology
Most often, patients seek help in this condition, after receiving injuries to the chest, abdominal cavity, when there is a fracture of the limbs, ribs and pelvic bones. This also leads to damage to some organs, for example, the spleen and liver. So, after a fall from a hill or an accident, damage to the intestines and mesentery is diagnosed, and the result of a traumatic brain injury can be bleeding in the cranial cavity. In the latter case, even a small amount of blood fluid puts pressure on the brain and poses a threat. It is necessary to clarify that this condition may not occur immediately, but after a couple of hours or even days, sometimes this happens even when the patient is feeling well. This problem can be caused by the following diseases that occur in acute or chronic form:
- Tuberculosis. Leads to pulmonary hemorrhages.
- Ulcers. They can damage blood vessels, resulting in blood in the intestines, peritoneum, and duodenum.
- Cirrhosis. Promotes hemorrhage from varicose veins located in the esophagus.
- Malignant tumors formed in the intestines and stomach. Their breakdown sometimes causes blood loss.
- Aortic aneurysm dissection. This is not a rare cause of such ailment in elderly patients.
- Gynecological pathologies.
- Mallory-Weiss syndrome. There are cracks in the esophagus, which have caused frequent drinking or overeating.
The list continues with physical activity and poor diet.