Hello, good health and easy walking!
Friends, summer is in full swing! Do you have the opportunity to walk barefoot on grass (lawn), sand or cool tiles? What a great feeling when your feet are free and your walk is easy! After all, most of the year we have to put our feet in shoes. Like it or not, it puts pressure on blood vessels, bones and muscles, imperceptibly deforming our gait.
The most delicate part of the foot, the toes, is especially often injured. That’s why we so often hear the complaint: “The joints of my toes hurt.” Doctors usually blame it on wearing unsuitable shoes. But the point, of course, is the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the limbs of each person.
Shoe fashion changes very quickly. Do you remember what pointed shoes and boots they wore 10 years ago? What kind of high heels are young women balancing on now? Or how many people trample their feet on plastic flip-flops, slippers, and flat sandals?
And the anatomy of the foot is individual for each person. Therefore, choosing the right and high-quality shoes is not easy. Happy are those who have the opportunity to buy good, suitable shoes. Many people have to limit themselves to what is affordable and necessary according to their living conditions.
Some people have to wear special shoes every day: rubber boots, side boots, heavy boots. In hot regions, many people constantly wear slates, and in the Arctic regions, where “there are 9 months of winter, and the rest is summer,” they wear fur and leather shoes.
The intensity of physical activity also plays a big role. Many athletes suffer from injuries and overloads on their lower extremities. Inactivity and excess weight also negatively affect the condition of the feet.
Mechanical reasons
Injury
The most obvious cause of long-term leg pain can be injury. Having hit his foot, a person will know exactly the cause of the discomfort.
The bruise has the following symptoms:
- the pain is sharp, severe and occurs at the time of injury;
- accompanied by swelling;
- functionality is impaired;
- it is possible to change the position of the finger (if it is dislocated or fractured).
If you injure your toe, you must definitely contact a traumatologist, since there may be a fracture that may heal incorrectly, which will lead to deformation of the foot, disruption of its physiological functions and aesthetics.
Ingrown nail
Another visually detectable cause may be an ingrown toenail. This trouble is possible as a result of a finger injury, too deep cutting of the nail plate, infection or fungus, and improperly selected shoes. This defect manifests itself as redness near the nail area, acute pain in the finger, and in some cases, the appearance of suppuration.
What to do if your finger is swollen and hurts
In case of injury, contact a traumatologist; in case of calluses and ingrown toenails, contact a dermatologist or podiatrist. Orthopedists treat flat feet, valgus and arthrosis. Arthritis and gout are managed by rheumatologists.
If the patient finds it difficult to choose a doctor, you can make an appointment with an orthopedist, who will issue a referral to the right specialist.
The survey includes the following activities:
- Survey. The doctor finds out when and under what circumstances the symptoms appeared and how the disease developed.
- Inspection. The doctor examines the foot at rest and during exercise, assesses skin color, the presence of edema and hyperemia, determines the range of movements, pulse in the arteries, localization of pain, condition of bones and soft tissues.
- Radiography. It is carried out for all diseases except dermatological ones. Allows you to identify arthrosis, flat feet, congenital deformities, and associated secondary disorders.
X-ray of feet for diagnosing diseases of the big toe.
According to indications, CT and MRI of the foot, plantoscopy and podography are performed. Rheumatological syndromes and diabetes mellitus are confirmed by special blood tests. If a fungus is suspected, a tissue sample is taken for microscopic examination. Vascular pathologies are diagnosed by ultrasound.
Internal reasons
Big toes also hurt as a result of severe inflammation in the body.
Circulatory disorders
Poor circulation in the leg is a consequence of diseases such as atherosclerosis of the arteries of the legs and obliterating endarteritis. If pain in the toes is caused by the presence of these diseases, they are accompanied by loss of sensation in the limbs and a burning sensation. The skin changes color to a paler color, nails become brittle, and feet are constantly cold. All this occurs as a result of insufficient oxygen access to tissues.
A patient with arthritis experiences pain periodically, most often at night.
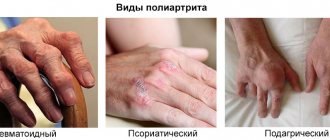
There are several types of this disease:
- psoriatic arthritis;
- reactive arthritis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- gout.
The different nature of arthritis manifests itself in pain in different fingers; the big toe hurts with psoriatic and reactive arthritis or gout.
Arthrosis
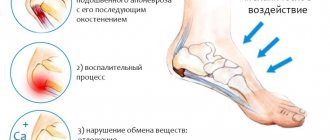
Arthrosis is a disease associated with joint deformation. This disease worries women more often, since they are the ones who are addicted to wearing uncomfortable, tight shoes with heels, which deform the foot and lead to the growth of a protruding bone.
Diabetes
When walking, the big toe may also hurt due to the development of diabetes. This disease is characterized by damage to many organs, including limbs.
There is even the concept of “diabetic foot,” which means the development of anatomical and functional changes leading to injury and infection of the tissues of the foot. Manifests itself in the form of necrotic processes, tissue rotting , ulcerative formations, changes in the shape of joints or bones.
Morton's neuroma
Women are five times more likely than men to develop diseases such as plantar fasciitis or Morton's neuroma. The development of this disease is associated with increased pressure on the nerve, physical overload, and flat feet.
Pathology occurs between the bones of the second and third fingers, but the pain also spreads to the thumb. A distinctive feature is that pain occurs in only one leg and only the base of the toe hurts.
Nerve lesions
Often women are guilty of loving high heels. These shoes are not comfortable for everyone, since the size and height of the foot play a major role in this. The front part of the foot gets used to taking the weight of the whole body. The load increases with fast walking and running. As a result of swelling of this part, the gaps through which small nerves pass are reduced.
With such pinched nerves, you can feel a burning sensation between the fingers. The pain sometimes becomes very sharp and cutting. It decreases when the feet are rested without shoes and immediately appears when wearing high-heeled shoes. When the head of the metatarsal bone is compressed in the area of the painful area, a sharp pain flares up and a nodule appears. The inflamed heads of the flux bones put pressure on the nerve endings. This is a neuroma.
With neuroma, the pain intensifies when a person walks on an uneven surface or steps on pebbles. Shoes with thin flat soles become unacceptable. At first, she is treated with anesthetic drugs with hydrocortisone. Therapeutic insoles and avoidance of high-heeled shoes help a lot. Many people go to the doctor when the illness becomes severe. In such cases, the pathology can only be eliminated through surgery.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have pain in your big toe for no apparent reason, you should definitely consult a doctor - the following specialists deal with such pathologies:
- surgeon;
- orthopedist;
- traumatologist;
- endocrinologist
A qualified medical professional will determine why your thumb hurts, conduct an examination, perform the necessary tests and prescribe effective treatment. Medical measures are primarily aimed at curing the disease caused by a similar symptom.
If the pain is associated with excessive skin growth on the finger and necrotic manifestations, cosmetic procedures and proper care are sufficient. Excess skin growths are cut off or removed using pumice; to remove dead cells or calluses, it is better to contact a cosmetologist or surgeon to avoid infection.
Discomfort in the thumb associated with the development of fungal diseases is eliminated by using special ointments and creams.
Anatomy of the toes
Knowledge of the anatomy of the toes is necessary in order to navigate the causes of pain in them.
Skeleton
The bones of the toes include the phalanges, which are small tubular bones consisting of a body and two epiphyses (
) – proximal (
) and distal (
). First (
) the toes of each foot consist of only two phalanges - proximal and distal, while all other toes consist of three phalanges - proximal, middle and distal.
The articular surface of the proximal epiphyses of the proximal and middle phalanges is concave. The articular surface of the distal epiphyses of the proximal and middle phalanges forms a block-shaped head. The distal epiphysis of the distal phalanges is represented by a tuberosity, on top of which the nail beds are located.
The joints of the toes are divided into metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal. The metatarsophalangeal joints are spherical in shape and allow flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and rotation around the axis of the bone. The interphalangeal joints are block-shaped, so only movements in one plane are possible in them - flexion and extension.
Joints
The joints of the toes are designed to ensure the displacement of the bones that form them relative to each other. Any joint consists of two articular surfaces and an articular membrane (
). Between the articular surfaces there is an articular space. The articular membrane consists of two layers - outer and inner. The outer layer consists of dense, shaped connective tissue and is highly resistant to mechanical stress. The inner layer is otherwise called synovial and consists of prismatic epithelium.
The nutrition of cartilage tissue is twofold. On the bone side, cartilage receives nutrients through a network of capillaries called the subchondral matrix. There are no blood vessels in the cartilage itself. In addition, cartilage receives nutrients from synovial fluid through diffusion (
The toes are able to bend thanks to two groups of joints - the metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints. The metatarsophalangeal joints consist of the articular surfaces of the heads of the metatarsal bones and the bases of the proximal phalanges. They are classified as spherical, however, despite this, they only perform flexion and extension. Only the big toes are capable of abduction, adduction and slight rotation (
Interphalangeal joints are formed between the articular surfaces of the heads and bases of the phalanges. These joints are classified as trochlear joints and allow movement only around one axis, that is, flexion and extension.
Ligaments
The main function of ligaments is to limit movement in the joints, as well as strengthen their membranes. In the toe area, there are only collateral ligaments located on the sides of the metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints. Thanks to this localization, they prevent lateral displacement of the phalanges of the fingers. These ligaments are partially woven into the fibrous membranes of the joints, increasing their strength.
The toes are moved by two groups of muscles - flexors and extensors. Each of the muscles of these groups has at least two tendons of its own, with the help of which it is attached to the bone. The extensor muscles are located on the back of the foot, and the flexor muscles are on the plantar surface.
In addition, the toes are not only driven by muscles that begin and end within the foot. In particular, we are talking about the long flexors and extensors, which are actually located in the lower leg area, but their long tendons pass between the bones, muscles and tendons of the foot, ultimately attaching to the phalanges of the fingers.
- extensor digitorum brevis;
- extensor digitorum longus;
- extensor hallucis brevis;
- extensor hallucis longus.
Toe flexor muscles
| Muscle name | Proximal (nearest) attachment site | Distal (far) attachment site | Muscle function |
| Extensor digitorum brevis | Superior and lateral surface of the calcaneus. | The base of the proximal, middle and distal phalanges of the 2nd to 5th toes. | Extension and slight abduction of 2–5 toes. |
| Extensor digitorum longus | The upper third of the tibia, the head of the fibula, the upper part of the interosseous membrane of the leg. | The base of the middle and distal phalanges of the 2nd to 5th toes. | Extension of the foot and 2 - 5 toes. Abduction of the foot and elevation of its lateral (outer) edge. |
| Extensor hallucis brevis | The anterior part of the upper surface of the calcaneus. | Proximal and distal phalanx of the big toe. | Extension of the big toe. |
| Extensor hallucis longus | The middle and lower third of the inner surface of the fibula and interosseous membrane. | The body of the proximal and the base of the distal phalanx of the big toe. | Extension of the big toe, extension and elevation of the inner side of the foot. |
- abductor hallucis muscle;
- adductor hallucis muscle;
- flexor hallucis brevis;
- flexor hallucis longus;
- flexor of the little toe brevis;
- muscle that abducts the little toe;
- muscle opposite the little toe;
- flexor digitorum brevis;
- flexor digitorum longus;
- quadratus plantae muscle.
| Muscle name | Proximal (nearest) attachment site | Distal (far) attachment site | Muscle function |
| Abductor hallux muscle | Lateral flexor retinaculum, medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity, plantar surface of the scaphoid. | Base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb and medial sesamoid bone. | Flexion and abduction of the big toe and arch support. |
| Adductor hallucis muscle | Consists of two heads - transverse and oblique. The transverse head tendon is attached to the capsules of the 3rd to 5th metatarsophalangeal joints, to the distal ends of the 2nd to 5th metatarsal bones, the plantar aponeurosis and to the deep transverse metatarsal ligaments. The tendon of the oblique head is attached to the plantar surface of the cuboid bone and lateral cuneiform bone, to the base of the 2nd - 5th metatarsal bones, and the long plantar ligament. Sometimes it is attached to the plantar synovial sheath of the peroneus longus muscle. | The base of the proximal phalanx of the big toe, as well as the lateral sesamoid bone. | Flexion and adduction of the big toe and arch support. |
| Flexor hallucis brevis | Medial cuneiform bone, plantar surface of the navicular bone, tibialis posterior tendon and long plantar ligament. | Both sesamoid bones and the base of the proximal phalanx of the big toe. | Flex your big toe and strengthen your arch. |
| Flexor hallucis longus | Lower 2/3 of the fibula, interosseous membrane and posterior intermuscular septum. | Base of the distal phalanx of the big toe. | Flexion of the big toe, as well as partially flexion of 2 - 4 toes. Participates in adduction and supination of the foot, and also strengthens the longitudinal arch of the foot. |
| Flexor of the little toe brevis | 5th metatarsal bone, long plantar ligament and plantar sheath of peroneus longus muscle. | Base of the proximal phalanx of the little toe. | Strengthening the lateral arch of the foot. Slight flexion of the little toe. |
| Abductor of the little toe muscle | Lateral and medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity, plantar aponeurosis. | Lateral side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the little finger. | Slightly abducts the little toe and also supports the lateral arch of the foot. |
| Muscle opponens the little toe | Long plantar ligament. | Distal end of the 5th metacarpal. | Slightly opposes the little toe. Participates in the formation of the arch of the foot. |
| Flexor toe brevis | Medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity and plantar aponeurosis. | The base of the middle phalanges of the 2nd to 5th toes. | Flex 2 - 5 toes and strengthen the arch of the foot. |
| Flexor toe longus | The middle third of the posterior part of the tibia and the deep layer of the fascia of the leg. | The base of the distal phalanges of the 2nd to 5th toes. | Slightly involved in the flexion of 2 - 5 toes. When walking, he presses his fingers against the support. Carries out flexion and supination of the foot, participates in strengthening its arch. |
| Quadratus plantaris muscle | Inferomedial surface of the calcaneus. | Outer edge of the flexor digitorum longus tendon. | Changes the direction of pull of the flexor digitorum longus to direct in relation to the muscles. |
On top of the joints and muscles of the toes there is a layer of subcutaneous fatty tissue and
. On the plantar side of the toes, that is, on their pads, this layer is more massive than on the back side.
The skin of the toes has some peculiarities. As in the rest of the body, it consists of stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium. On the dorsal and lateral surfaces of the fingers, this epithelium consists of four layers - basal, spinous, granular and horny. In addition, well-developed hair follicles with sebaceous and sweat glands are often located on the back of the skin. On the plantar side, the epidermis is denser due to the additional shiny layer.
The nail bed and nail deserve special attention. The nail bed consists of connective tissue and epithelial parts. The connective tissue part is located most deeply and is adjacent directly to the distal phalanges. It contains many elastic fibers. The epithelial part of the nail bed is located above the connective tissue part and represents the growth zone. The product of growth is a nail, consisting of keratin plates tightly adjacent to each other.
Treatment
The treatment method directly depends on the type of disease:
- For deforming osteoarthritis, it is recommended to limit physical activity, exercise therapy and anti-inflammatory drugs that promote the restoration of cartilage tissue.
- With arthrosis, the load on the damaged joints is limited, an orthopedic regimen, special procedures, pharmacotherapy, diet, spa treatment and physical therapy are prescribed.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chondroprotectors, glucocorticosteroids, and monoclonal antibodies. Additionally, calcium supplements and vitamin D3 are taken to strengthen bone tissue.
- Treatment of an injured limb varies depending on the severity of the injury: a dislocation is reduced, a fracture or crack is subject to fixation.
- Patients with gout must adhere to a special diet and undergo hospital treatment.
- Treatment of diabetes mellitus includes a special diet, when the patient’s diet is free of sugar, alcohol and sugar-containing products, with mandatory daily use of insulin and the use of medications that lower blood sugar levels.
What kind of treatment is required will be determined by a medical professional based on the results of the tests performed.
Treatment of pain and swelling on the big toe
Treatment of the joint and soft tissues of the big toe is prescribed by a doctor. Methods are determined by the type of disease:
- Injury. It is advised to temporarily reduce the load, apply cold first, then heat. Physiotherapy is carried out.
- Ingrown nail. Resection or complete removal of the nail is performed, if necessary, with plastic surgery of the nail bed.
- Corn. The formation is opened or removed, bandages are made.
- Transverse flatfoot, or planovalgus foot deformity. They recommend massage, exercise therapy, orthopedic insoles.
- Hallus Valgus. In the early stages, orthopedic devices, exercise therapy, massage, and physiotherapy are used. For large bones, surgery is indicated.
- Arthrosis. NSAIDs and chondroprotectors are prescribed in combination with physiotherapeutic procedures and orthopedic correction.
- Arthritis. Drug therapy includes NSAIDs, antibacterial drugs (for infectious forms), corticosteroids, immunosuppressants and cytostatics (for rheumatoid arthritis), chondroprotectors. Supplemented by exercise therapy and physiotherapy.
- Gout. Antigout drugs, immunosuppressants and corticosteroids are used. A special diet is required.
Prevention Tips
Care during the pedicure procedure will help avoid infection and the development of inflammatory processes. The nail plate should not be cut too deep or leave sharp corners that will injure the finger.
Comfortable shoes are the key to healthy feet; they should not be tight or cause discomfort or pain in the feet. High-quality material and the correct shape will avoid rubbing and curvature of the foot.
Excessive exercise is also not beneficial. When playing sports, it is important to correctly distribute the force and level of pressure on the legs.
Pain after injury
If discomfort appears after wearing open shoes, you need to check your feet for bites, minor scratches and other injuries, changes in the shape or color of the nails. Often, infections cause inflammation and swelling. Most often, the tips of the toes hurt. If the pain is mild, you can first consult a therapist. If the finger is very swollen, red or blue, or occupies an unnatural position, this may indicate a serious injury: a fracture, dislocation, or severe bruise. In this case, you need to contact a traumatologist.
External factors
External factors usually include traumatic injuries, calluses, ingrown toenails, and excessive exercise.
Toe injuries
Traumatic injuries occur due to severe bruising, dislocation or fracture. A simple injury - a blow or a heavy object falling on the leg - can lead to a violation of the integrity of the phalanx. A bruise, dislocation or fracture is most often the result of a domestic injury, but can also be obtained as a result of playing sports, and less often - at work. Both the thumb and little finger are affected.
When a bruise occurs, only soft tissues are damaged - muscles, skin and tendons. Sometimes bruises can be combined, that is, combined with a dislocation or fracture of the phalanx. If it hurts
- second finger, then it may well have a broken phalanx. Phalangeal injury has a variety of symptoms:
- with mild bruises, the subcutaneous tissue and the skin itself suffer, patients are bothered by acute pain and rapidly growing swelling. Externally, the integrity of the skin in the area of the fingers is not compromised;
- more severe injuries are characterized by hemorrhage into the soft tissue; if there is a hematoma, the phalanx becomes very swollen and cannot move. With such severe bruises, the nail plate suffers. If the hematoma spreads under the nail, then after a while it begins to turn blue, and then peels off and goes away, and a new nail grows in its place. With more serious injuries, hematomas do not appear immediately; they become visible only on the second or third day.
It will take a long time for a limb to recover from such an injury.
IMPORTANT! You can treat a bruise on your leg yourself only if there are no signs of dislocation and the finger remains in its normal position.
First of all, you need to apply ice or another cold object to the limb. This will help eliminate swelling in the feet and toes and stop the appearance of hematoma. It is recommended to apply cold compresses every hour for 15 minutes. If people suffer from diabetes, then applying cold compresses is not recommended, so as not to impair blood circulation.
You should not heat the bruised area - this can provoke internal bleeding, increase swelling and pain. If necessary, fix the nail if it is broken, this can be done using a regular adhesive plaster.
When treating a bruised leg, it is best to stay at home for a while and take care of the injured leg. Severe pain can be relieved with painkillers: Analgin, Solpadeine or Ketanov. If your finger continues to hurt, turns blue and is swollen, you should consult a doctor.
A phalanx fracture is a fairly common injury, since it can be sustained even at home. Damage can be open or closed, with or without displacement, complete or incomplete. In severe cases, patients can even break bones in several places at the same time. A toe fracture has a positive prognosis.
Symptoms of a fracture can be relative or absolute. Relative signs of damage include:
- intense pain that intensifies when trying to move;
- swelling at the site of injury;
- hematoma under the skin or under the nail;
- impaired functionality of the limbs.
Absolute symptoms include an unnatural position of the phalanx, a crunch at the site of injury, pathological mobility, i.e. instability of the finger.
INTERESTING! If you break the second to fifth toe, their functionality may not even be affected. Patients learn about a fracture only by the increasing pain that occurs against the background of the normal appearance of the fingers.
Wrong selection of shoes
Another reason for pain in the phalanges is wearing uncomfortable shoes. This factor usually leads to curvature of the fingers, but at the initial stage it is the pain syndrome that appears. Most often, pain is caused by narrow shoes, which compress the phalanges. Pain also appears with too high heels, if the load on the foot is distributed incorrectly - most of it falls on the front part. Calluses and lumps appear under the big toe because the support in the foot is incorrectly distributed.
Ingrown nail
Quite often, patients suffer from ingrown toenails. This occurs when the nail plate grows into the side edge of the roller. The thumb is most often affected because it is located on the edge, but the ring finger and even the little finger are also affected. The problem can occur in patients of any age.
An ingrown toenail must be removed by a doctor, since doing it yourself can only cause harm and cause infection.
The causes of ingrown toenails may be as follows:
Diseases of the feet
- incorrect pedicure technique;
- wearing tight shoes that squeeze your toes;
- nail plate injuries;
- flat feet;
- fungal infection;
- hallux valgus;
- excess soft tissue of the subungual pad (this is a congenital predisposition).
Symptoms of an ingrown toenail are typical. The nail fold becomes red and swollen, the patient suffers from constant pain caused by inflammation in the ingrowth area. The pain is felt both when walking and at rest. The foot twitches, and if a bacterial infection occurs, suppuration may begin. A purulent cavity forms in the area of the ingrown toenail - outwardly it looks like a yellow-green spot with pus contained there.
At the same time, the pain intensifies, “turnings” and pathological red granulations may appear on the skin. Diagnosing an ingrown toenail is quite easy. The patient is not recommended to provide help on his own, especially during suppurative processes, because this can provoke infection into the blood. During a visit to the clinic, the doctor will remove the ingrown nail or part of the plate, and will also correct the shape of the nail. If your middle finger hurts, the doctor will limit it from the neighboring ones with a special pad. The patient will receive recommendations on how to properly care for their nails to prevent relapse.
Physical exercise
Another common cause of pain is excessive physical activity. Typically, toe pain occurs in athletes or dancers who stand on their toes too often. At the same time, the tips of the fingers and the entire foot of the left and right leg hurt. As a result of this, each phalanx is loaded, the elements of the articulation begin to become inflamed and the person feels severe pain and burning.
When you consult a doctor, it turns out that excessive stress has caused complications such as arthrosis or arthritis. You can find out about this after magnetic resonance imaging, which perfectly visualizes even small joints. The decision on treatment is made depending on the complications that arise, but patients are definitely recommended to rest the limb and limit physical activity for some time.
Blisters
Blisters on the feet appear so often that many people don’t even pay attention to them. However, blisters can become a serious threat if they become infected. The fingertips, areas between the toes, the sides of the foot, and ankles suffer from blisters.
IMPORTANT! The cause of blisters is improperly fitted or new shoes that rub the seams on the toes. This is caused by open sandals with rough edges that fit right over the toes.
Blisters also occur when a foreign body enters. A painful huge blister can be caused by a small twig or sand in shoes that rubs when walking.
If a blister occurs, do not puncture it to avoid infection. Punctures can be made only for large blisters that interfere with walking. Using a syringe needle, previously disinfected in alcohol, the bubble is pierced and the liquid is released. The area can be dried with chlorhexidine or treated with any antiseptic solution.
What to do
If you have pain in the joints of your toes when walking, go to see a doctor who will diagnose the causes of the pain and he will prescribe the correct treatment. At the initial stage of diagnosis, the right decision would be to consult a therapist. After establishing a preliminary diagnosis, he will write out a referral to the right doctor:
- Neuropathologist;
- Surgeon;
- Rheumatologist.
The prescribed treatment depends on the established diagnosis. When treating arthritis, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed along with medications to relieve pain until recovery. Treatment is supplemented with antibiotics if the cause of arthritis is the presence of an inflammatory infection.
- Treatment of arthrosis is similar to the previous option. It is permissible to prescribe chondroprotectors, anti-inflammatory drugs, and a course of vitamins with a high calcium content is prescribed. Drug therapy is supplemented by massage, physical therapy, and some physical procedures at the discretion of the doctor. It is easier to treat the disease at the beginning.
- The basis of treatment for gout is following a diet and taking painkillers to relieve painful attacks. For treatment to produce results, you will need to give up bad habits - smoking, alcoholic beverages.
- Erythromelalgia, vasodilation, is treated using special therapeutic shoes and drugs aimed at narrowing blood vessels.
Vascular diseases
If pain in the legs occurs, you should consult a phlebologist, cardiologist, neurologist, or angiologist. After all, one of the reasons why pain appears in the foot under the toes when walking is problems with blood vessels.
Men often face a disease such as endarteritis. This is the name for inflammation of the arteries, which develops mainly in the legs. At the first steps the patient does not feel discomfort, but over time the pain begins to intensify, a feeling of heaviness and numbness appears. The condition improves after a short rest, but with the slightest load it worsens again.
Phlebitis and varicose veins are also causes of leg pain. But with these diseases they are not always concentrated in the forefoot, but can also affect other areas of the legs.
What to do during an attack of pain?
Only a specialist can provide qualified assistance in such situations. Before the doctor arrives, it is necessary, if possible, to immobilize the joint, free it from shoes, and remove socks and tights. You should take a body position in which there is no load on the joint. Painkillers available in home medicine cabinets will help reduce the severity of pain.
Upon arrival, the doctor will immediately examine the patient. Hospitalization may be required. In a clinical setting, through detailed laboratory and instrumental studies, it is possible to find out the true cause of pain and prescribe adequate treatment.
Diagnostics
What to do if your toes hurt? First of all, you should visit a doctor who will examine the diseased area and prescribe diagnostic measures to make a diagnosis. If you have a problem, you should visit a therapist, who, based on your medical history, will refer you to specialized specialists - a traumatologist, neurologist, rheumatologist or surgeon.
The main diagnostic methods used for pain in the lower extremities include:
- X-ray;
- computed tomography and MRI;
- Ultrasound;
- urine test to determine arthritis;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- determination of uric acid level.
Arthritis
This is an inflammation of the joints of the first finger, which can develop for several reasons:
- penetration of pathogenic microorganisms with the development of infectious arthritis (reactive, acute purulent, septic);
- allergic reactions (allergic arthritis);
- autoimmune processes (autoimmune arthritis).
All of these factors can cause both acute and chronic inflammation. Determining the cause of arthritis is very important, as treatment depends on it. Although the first toe rarely suffers from such ailments, its arthritis may be a sign of:
- psoriatic arthropathy,
- rheumatoid arthritis,
- systemic lupus erythematosus,
- systemic scleroderma and other autoimmune diseases.
The most typical involvement of the big toe in the pathological process is in reactive and psoriatic arthritis. Let's look at these diseases.
Psoriatic arthropathy
This is one of the manifestations of psoriasis (skin disease). Joint lesions occur in 7% of patients with this disease. Moreover, joint damage may precede the skin rash, occur simultaneously with it, or be present after the rash. The last option is most common. The causes of joint inflammation in psoriasis, as well as the disease itself, are unknown.
Psoriatic arthropathy
The joints of one or more fingers may become inflamed. They are asymmetrical in nature. A characteristic feature is axial damage, that is, all the joints of one finger are simultaneously retracted, as a result of which the latter becomes like a sausage. The finger swells, turns red, and pain develops.
If arthritis becomes chronic and the patient does not receive the necessary therapy, the foot begins to deform and the joints are destroyed. This may cause disability.
Reactive arthritis
This is inflammation of the joints of infectious etiology. The cause most often is urogenital infections, intestinal or respiratory. As a rule, joint inflammation begins 10-14 days after the initial infection. Several joints are affected simultaneously, including the first toe.
The pain varies in intensity. The joint becomes red, swollen, and the skin over it becomes hot to the touch. In some cases, limb function is impaired due to pain.
Arthritis responds well to treatment with antibacterial drugs and never leaves behind deformities. The prognosis is favorable, but sometimes it can become chronic with periodic exacerbations.
https://youtu.be/54p4r87u5Q0
Gout
Gout is a genetically determined disease with metabolic disorders. It is characterized by an enzymatic deficiency in the breakdown of purine compounds, due to which uric acid accumulates in the human body.
With this disease, the toes hurt due to the accumulation of salts of this acid in the joint capsules.
Most often the big toe is affected, but gradually the disease spreads or migrates to other parts of the body , affecting mainly the small joints of the phalanges. Gout develops in people with a congenital genetic defect, but it is provoked by the influence of predisposing factors. These include:
- consumption of large quantities of smoked products;
- the predominance of proteins in food (especially red meat);
- excess weight;
- inactive lifestyle;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- incorrect diet.
The disease is characterized by a chronic course with pronounced relapses. There is no clinical picture during the period of remission, and the disease can only be confirmed by laboratory tests. A bulge in the area of the finger joint can be visually detected. When your toe hurts, a gouty crisis begins. The pain syndrome is so intense that patients call it unbearable. The area around the joint becomes swollen and red with increased local temperature . Gradually, the pain goes away on its own and completely disappears until the next attack. A complete cure for gout is still elusive. However, quite effective methods have been developed to keep the pathology under control, reducing the number of relapses.
The basis of treatment is diet therapy with complete elimination of risk factors.
Groups of anti-inflammatory drugs are also used, but injections of the missing enzyme are considered the most effective. Thus, protein metabolism is quickly restored.
How to get rid of thumb bone pain
If a large lump hurts and inflammation of the bone tissue begins, redness appears near the joint, the woman’s gait will immediately change, it will be difficult for her to choose shoes, other pathologies will arise in the musculoskeletal system, including failure of the knee and hip joints due to improper load distribution, headaches and pain in the entire ankle will appear.
In case of pain in the bunion on the big toe, reconstructive surgery is necessary to strengthen the foot or fix the bone near the bunion with knitting needles in the correct position. After it, the woman should wear comfortable shoes with orthopedic insoles, inserts between the toes, and not forget about physical therapy.
If the lump hurts unbearably, shock wave and radiotherapy are used. Pain is relieved using phonophoresis and electrophoresis. A lump or toe bone and inflammation are treated with foot baths, compresses, and massages.
For a therapeutic bath you will need hot water (3 l), the temperature of which should not exceed 38-40˚C, soda (1 tablespoon) and iodine 8-10 drops. Take a foot bath for 10 minutes every 3 days. At night, the bones and skin around the joint should be lubricated with 5% iodine, and in the morning - with fatty cream or glycerin.
Several effective compress recipes:
- A paste of fresh onion or garlic is applied to the bones and left for 3-4 hours. If a burning sensation occurs, remove the compress immediately;
- Gum turpentine and ammonia will be needed for compresses on the bones for a month. They are applied alternately;
- Softened propolis is applied to the bone near the joint every day. A fresh piece will be needed after 3-4 times of using propolis.
Massages using lavender, cypress, pine, lemon and eucalyptus, rosemary and coriander oils relieve thumb bone pain, which is why people love this procedure so much. You can perform the massage yourself by adding 3 drops of the indicated oils to a vegetable oil base (50 ml). If there is not such a quantity of essential oils, add 20 drops of one of them. With the help of massage you can relieve inflammation near the bone.
For bursitis of the big toe, do the following:
- ankle immobilization;
- lubricated with non-steroidal external anti-inflammatory agents: Fastum gel or Diclak gel, ointment, for example, Ibuprofen;
- removal of exudate by puncture of the bursa and administration of steroid hormones to relieve inflammation (Kenalog, Hydrocortisone);
- antibiotics are injected into the joint cavity (bones) and intravenous infusions are given;
- physiotherapy: phonophoresis through therapeutic mud, using a magnet, UHF, paraffin wraps on the bones;
- bursectomy - the inflamed bursa is dissected.
For gout and gouty arthritis to relieve pain in the bone (bump) and inflammation:
- prescribe abundant alkaline drinking;
- apply compresses with Dimexide (50% solution);
- taking medications for inflammation: Naproxen, Indomethacin, Piroxicam;
- taking anti-pain medications: Colchicine and Nimesil.
To prevent pain in the big toe bone, patients take baths with the addition of sage infusion, chamomile flowers, calendula, and walnut leaves. It is recommended to adhere to a diet and remove uric acid with Allopurinol. Pain is relieved with a warm compress of St. John's wort, burdock root and yarrow in equal parts by weight. Herbs (1 tbsp) are steamed in a glass of boiling water and after 5 minutes they are applied to the pine cone. Many patients respond positively after using these procedures.
https://youtu.be/pdW5A9LsobI